1501:
1262:
and comparing it to their normal side is a method to assess the degree of paralysis. A common brachial plexus injury is from a hard landing where the shoulder widely separates from the neck (such as in the case of motorcycle accidents or falling from a tree). These stretches can cause ruptures to the superior portions of the brachial plexus or avulse the roots from the spinal cord. Upper brachial plexus injuries are frequent in newborns when excessive stretching of the neck occurs during delivery. Studies have shown a relationship between a newborn's weight and brachial plexus injuries; however, the number of cesarean deliveries necessary to prevent a single injury is high at most birth weights.
1232:
1489:
1465:
440:
1358:
brachial plexus over other imaging modalities due to its multiplanar capability and the tissue contrast difference between brachial plexus and adjacent vessels. The plexuses are best imaged in coronal and sagittal planes, but axial images give an idea about the nerve roots. Generally, T1 WI and T2 WI images are used in various planes for the imaging; but new sequences like MR Myelolography, Fiesta 3D and T2 cube are also used in addition to the basic sequences to gather more information to evaluate the anatomy more.
1513:
1429:
1441:
1477:
1309:. Shoulder dystocia can cause obstetric brachial plexus palsy (OBPP), which is the actual injury to the brachial plexus. The incidence of OBPP in the United States is 1.5 per 1000 births, while it is lower in the United Kingdom and the Republic of Ireland (0.42 per 1000 births). While there are no known risk factors for OBPP, if a newborn does have shoulder dystocia it increases their risk for OBPP 100-fold. Nerve damage has been connected to
41:
1413:
1247:
1453:
29:
264:. There are five "terminal" branches and numerous other "pre-terminal" or "collateral" branches, such as the subscapular nerve, the thoracodorsal nerve, and the long thoracic nerve, that leave the plexus at various points along its length. A common structure used to identify part of the brachial plexus in cadaver dissections is the M or W shape made by the
1269:
To differentiate between preganglionic and postganglionic injury, clinical examination requires that the physician keep the following points in mind. Preganglionic injuries cause loss of sensation above the level of the clavicle, pain in an otherwise insensate hand, ipsilateral Horner's syndrome, and
1261:
Injuries can be caused by stretching, diseases, and wounds to the lateral cervical region (posterior triangle) of the neck or the axilla. Depending on the location of the injury, the signs and symptoms can range from complete paralysis to anesthesia. Testing the patient's ability to perform movements
1235:
This shows a simulated example of motorcyclist colliding with the floor at an angle, which may damage the brachial plexus nerves. The photo shows how head and shoulder are extremely separated, which may stretch or even tear the nerves in the between area. Protective gear can help prevent nerve damage
1304:
Brachial plexus injuries can occur during the delivery of newborns when after the delivery of the head, the anterior shoulder of the infant cannot pass below the pubic symphysis without manipulation. This manipulation can cause the baby's shoulder to stretch, which can damage the brachial plexus to
1282:
One sports injury that is becoming prevalent in contact sports, particularly in the sport of
American football, is called a "stinger." An athlete can incur this injury in a collision that can cause cervical axial compression, flexion, or extension of nerve roots or terminal branches of the brachial
1273:
Acute brachial plexus neuritis is a neurological disorder that is characterized by the onset of severe pain in the shoulder region. Additionally, the compression of cords can cause pain radiating down the arm, numbness, paresthesia, erythema, and weakness of the hands. This kind of injury is common
1257:
may affect sensation or movement of different parts of the arm. Injury can be caused by the shoulder being pushed down and the head being pulled up, which stretches or tears the nerves. Injuries associated with malpositioning commonly affect the brachial plexus nerves, rather than other peripheral
300:. The brachial plexus emerges at five different levels: C5, C6, C7, C8, and T1. C5 and C6 merge to establish the upper trunk, C7 continuously forms the middle trunk, and C8 and T1 merge to establish the lower trunk. Prefixed or postfixed formations in some cases involve C4 or T2, respectively. The
1357:
Imaging of the
Brachial Plexus can be done effectively by using a higher magnetic strength MRI Scanner like 1.5 T or more. It is impossible to evaluate the brachial plexuses with plain Xray, CT and ultrasound scanning can manage to view the plexuses to an extent; hence MRI is preferred in imaging
1295:
Most penetration wounds require immediate treatment and are not as easy to repair. For example, a deep knife wound to the brachial plexus could damage and/or sever the nerve. According to where the cut was made, it could inhibit action potentials needed to innervate that nerve's specific muscle or
1265:
For the upper brachial plexus injuries, paralysis occurs in those muscles supplied by C5 and C6 like the deltoid, biceps, brachialis, and brachioradialis. A loss of sensation in the lateral aspect of the upper limb is also common with such injuries. An inferior brachial plexus injury is far less
1283:
plexus. In a study conducted on football players at United States
Military Academy, researchers found that the most common mechanism of injury is, "the compression of the fixed brachial plexus between the shoulder pad and the superior medial scapula when the pad is pushed into the area of
936:
skin of the posterior arm and posterior forearm as the posterior cutaneous nerve of the arm and the posterior cutaneous nerve of the forearm, respectively. Also superficial branch of radial nerve supplies back of the hand, including the web of skin between the thumb and index finger.
1287:, where the brachial plexus is most superficial.". The result of this is a "burning" or "stinging" pain that radiates from the region of the neck to the fingertips. Although this injury causes only a temporary sensation, in some cases it can cause chronic symptoms.
453:
1258:
nerve groups. Due to the brachial plexus nerves being very sensitive to position, there are very limited ways of preventing such injuries. The most common victims of brachial plexus injuries consist of victims of motor vehicle accidents and newborns.
449:
1500:
1266:
common but can occur when a person grasps something to break a fall or a baby's upper limb is pulled excessively during delivery. In this case, the short muscles of the hand would be affected and cause the inability to form a full fist position.
447:
454:
450:
482:
are listed below. Most branches arise from the cords, but few branches arise (indicated in italics) directly from earlier structures. The five on the left are considered "terminal branches". These terminal branches are the
1703:
456:
457:
1270:
loss of function of muscles supplied by branches arising directly from roots—i.e., long thoracic nerve palsy leading to winging of scapula and elevation of ipsilateral diaphragm due to phrenic nerve palsy.
443:
444:
458:
1488:
446:
1136:
The terminal branches of the brachial plexus (musculocutaneous n., axillary n., radial n., median n., and ulnar n.) all have specific sensory, motor and proprioceptive functions.
451:
455:
1711:
466:
Anatomical illustration of the brachial plexus with areas of roots, trunks, divisions and cords marked. Clicking on names of branches will link to their
Knowledge entry.
1725:
Cooper, DE; Jenkins, RS; Bready, L; Rockwood Jr, CA (1988). "The prevention of injuries of the brachial plexus secondary to malposition of the patient during surgery".
452:
448:
445:
1760:
Jeyaseelan, L.; Singh, V. K.; Ghosh, S.; Sinisi, M.; Fox, M. (2013). "Iatropathic brachial plexus injury: A complication of delayed fixation of clavicle fractures".
1440:
132:
1830:
Ecker, Jeffrey L.; Greenberg, James A.; Norwitz, Errol R.; Nadel, Allan S.; Repke, John T. (1997). "Birth Weight as a
Predictor of Brachial Plexus Injury".
1428:
1506:
The brachial plexus, including all branches of the C5-T1 ventral primary rami. Includes mnemonics for learning the plexus's connections and branches.
463:
462:
461:
460:
2025:
459:
1110:
the skin of the medial side of the hand and medial one and a half fingers on the palmar side and medial two and a half fingers on the dorsal side
312:, a muscle that involves lifting the first ribs during respiration. The long thoracic nerve arises from C5, C6, and C7. This nerve innervates the
108:
1476:
2734:
2730:
2810:
2806:
2610:
1464:
2054:
Doumouchtsis, Stergios K.; Arulkumaran, Sabaratnam (2009-09-01). "Are all brachial plexus injuries caused by shoulder dystocia?".
2893:
2868:
2464:
2173:
1346:
892:
760:
2907:
2880:
2395:
2266:
1654:
1058:
2897:
2796:
2725:
1133:). The brachial plexus communicates through the sympathetic trunk via gray rami communicantes that join the plexus roots.
2575:
2533:
2136:
2903:
2699:
519:
further connecting them. There have been several variations reported in the branching pattern but these are very rare.
308:
which retract and downwardly rotate the scapula. The subclavian nerve originates in both C5 and C6 and innervates the
2964:
2802:
2766:
2720:
1939:"Recurrent burner syndrome due to presumed cervical spine osteoblastoma in a collision sport athlete - a case report"
1882:
1687:
1580:
1412:
1398:
1036:
385:
when observing the body in the anatomical position, the anterior divisions are superficial to the posterior divisions
2889:
2782:
139:
2260:
2241:
1548:
1494:
Diagram of the brachial plexus using colour to illustrate the contributions of each nerve root to the branches.
289:
1512:
2771:
2619:
2603:
127:
2026:"Brachial Plexus Injuries Information Page: National Institute of Neurological Disorders and Stroke (NINDS)"
2917:
2792:
2787:
2711:
1990:"A retrospective study looking at the incidence of 'stinger' injuries in professional rugby union players"
2913:
2827:
2715:
2166:
2142:
2033:
1274:
for people who have prolonged hyperabduction of the arm when they are performing tasks above their head.
1121:
The brachial plexus provides nerve supply to the skin and muscles of the arms, with two exceptions: the
316:, which draws the scapula laterally and is the prime mover in all forward-reaching and pushing actions.
2816:
1284:
1089:
988:
2141:
Learn the
Brachial Plexus in Five Minutes or Less by Daniel S. Romm, M.D. and Dennis A. Chu Chu, M.D.
1231:
2596:
2378:
2373:
2356:
2351:
2346:
1679:
1130:
313:
91:
1598:"Multiple unilateral variations in medial and lateral cords of brachial plexus and their branches"
2851:
2847:
2657:
2469:
2341:
2336:
2331:
2326:
2321:
2316:
2311:
2306:
2301:
2276:
2233:
2228:
2223:
2218:
2213:
2208:
2203:
2198:
923:
845:
797:
649:
607:
602:
569:
563:
359:
355:
348:
341:
337:
193:
189:
185:
181:
177:
1874:
1867:
1236:
by providing extra support on the opposite side of the head to prevent over-stretching the neck.
1215:
Hypothenar eminence, some forearm flexors, thumb adductor, lumbricals 3-4, interosseous muscles
2695:
2683:
2159:
1254:
1241:
1155:
1126:
1101:
994:
980:
738:
704:
512:
504:
484:
265:
115:
103:
1189:
Triceps brachii, brachioradialis, anconeus, extensor muscles of the posterior arm and forearm
2959:
2753:
2637:
2538:
2509:
2504:
2499:
2494:
2489:
2435:
2430:
2425:
2420:
2415:
2281:
1795:
Midha, Rajiv (1997). "Epidemiology of
Brachial Plexus Injuries in a Multitrauma Population".
1446:
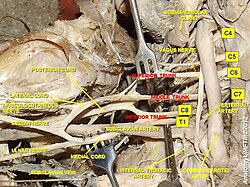
The outermost (distal) part of the brachial plexus shown from a dissected cadaveric specimen.
1367:
945:
724:
557:
547:
301:
201:
2110:
1671:
2146:
1321:
but it also has to do with the delivery methods. Although very hard to prevent during live
1085:
984:
213:
209:
173:
169:
8:
2857:
2653:
2641:
1672:
1434:
Nerves in the infraclavicular portion of the right brachial plexus in the axillary fossa.
819:
676:
592:
2368:
2271:
1965:
1938:
1622:
1597:
636:
1843:
2452:
2079:
2071:
1970:
1919:
1878:
1847:
1812:
1808:
1777:
1742:
1738:
1683:
1650:
1627:
1576:
1544:
1306:
663:
612:
309:
2005:
2563:
2063:
2001:
1989:
1960:
1950:
1911:
1839:
1804:
1769:
1734:
1617:
1609:
1452:
1005:
portions of hand not served by ulnar or radial, i.e skin of the palmar side of the
957:
953:
832:
746:
720:
716:
579:
305:
2137:
Brachial Plexus Injury/Illustration, Cincinnati
Children's Hospital Medical Center
398:
or large fiber bundles. The cords are named by their position with respect to the
2550:
2383:
2293:
2247:
2190:
2067:
1773:
1419:
998:
931:
575:
399:
96:
2588:
529:
indicate spinal roots that frequently, but not always, contribute to the nerve.
65:
2864:
2838:
1899:
1168:
1097:
1093:
1022:
879:
867:
754:
488:
408:
1915:
1649:(3rd ed.). Baltimore: Lippincott Williams & Wilkins. pp. 430–1.
2953:
2521:
2481:
2447:
2407:
2075:
1923:
1613:
1388:
1329:
with precise and gentle movements to decrease chances of injuring the child.
1014:
805:
691:
687:
626:
430:
is simply a continuation of the anterior division of the lower trunk (C8, T1)
165:
120:
421:
is formed from the anterior divisions of the upper and middle trunks (C5-C7)
2876:
2823:
2707:
2675:
2182:
2083:
1974:
1955:
1781:
1631:
1393:
1383:
1342:
1310:
1194:
1181:
1105:
1010:
971:
903:
772:
516:
508:
496:
492:
417:
293:
269:
161:
1851:
1816:
1746:
2778:
2745:
2648:
1207:
1077:
1018:
885:
854:
500:
426:
333:
296:, after they have given off their segmental supply to the muscles of the
273:
197:
33:
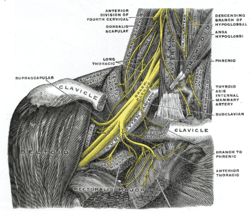
The right brachial plexus with its short branches, viewed from in front.
1596:
Goel, Shivi; Rustagi, SM; Kumar, A; Mehta, V; Suri, RK (Mar 13, 2014).
1482:
Spinal cord. Brachial plexus. Cerebrum. Inferior view. Deep dissection.
1338:
750:
412:
is formed from the three posterior divisions of the trunks (C5-C8, T1)
145:
1250:
Brachial Plexus relation with the clavicle and the subclavian artery.
1122:
915:
895:
Innervates the skin of the lateral shoulder and arm: shoulder joint.
1710:. New York School of Regional Anesthesia. 2013-09-20. Archived from
40:
1314:
919:
221:
1246:
1326:
1186:
Posterior aspect of the lateral forearm and wrist; posterior arm
927:
911:
229:
46:
2151:
1378:
1318:
1026:
763:
Innervates the skin of the anterolateral forearm; elbow joint.
205:
45:
The roots, trunks and cords of the plexus shown in a dissected
1724:
1082:
C7, C8, T1(C7 because it supplies to the Flexor carpi ulnaris)
1322:
1202:
Forearm flexors, thenar eminence, lumbricals of the hand 1-2
1006:
217:
79:
1873:. Philadelphia: Lippincott Williams & Wilkins. pp.
297:
233:
1829:
1759:
382:
posterior divisions of the upper, middle, and lower trunks
28:
1199:
Skin of lateral 2/3rd of hand and the tips of digits 1-4
1048:
379:
anterior divisions of the upper, middle, and lower trunks
225:
1566:
1564:
1562:
1560:
2053:
1575:(7 ed.). New York: McGraw Hill. pp. 489–491.
1534:
1532:
1305:
varying degrees. This type of injury is referred to as
1129:) and an area of skin near the axilla (supplied by the
1943:
Journal of
Brachial Plexus and Peripheral Nerve Injury
1900:"Management of Common Neurologic Conditions in Sports"
1674:
Anatomy and
Physiology: The Unity of Form and Function
1173:
Skin of lateral portion of the shoulder and upper arm
1595:
1557:
1529:
1212:
Skin of palm and medial side of hand and digits 3-5
2104:(7th ed.). McGraw-Hill Education. p. 491.
1866:
525:indicates primary spinal root component of nerve.
2618:
2147:Video of the dissected axilla and brachial plexus
1337:Tumors that may occur in the brachial plexus are
503:. Due to both emerging from the lateral cord the
304:comes from the superior trunk and innervates the
2951:
394:These six divisions regroup to become the three
1898:Dimberg, Elliot L.; Burns, Ted M. (July 2005).
1543:. Singapore: World Scientific. pp. 6, 20.
442:
204:in the neck, over the first rib, and into the
2604:
2167:
1538:
1163:Brachialis, biceps brachii, coracobrachialis
1897:
1470:Mind map showing branches of brachial plexus
515:has even been shown to send a branch to the
256:(three anterior and three posterior), three
2674:
1823:
371:Each trunk then splits in two, to form six
2611:
2597:
2174:
2160:
1727:Clinical Orthopaedics and Related Research
1638:
39:
27:
1964:
1954:
1644:
1621:
244:The brachial plexus is divided into five
1718:
1347:malignant peripheral nerve sheath tumors
1299:
1245:
1230:
1221:
438:
2465:Posterior branches of the lumbar nerves
2099:
1987:
1669:
1570:
893:superior lateral cutaneous nerve of arm
2952:
2056:Obstetrical & Gynecological Survey
1678:. New York, NY: McGraw-Hill. pp.
761:lateral cutaneous nerve of the forearm
2592:
2396:Posterior branches of thoracic nerves
2267:Posterior branches of cervical nerves
2155:
1936:
1864:
1794:
1290:
1059:medial cutaneous nerve of the forearm
991:that supplies the 2nd and 3rd digits
1404:
1325:, doctors must be able to deliver a
2576:Posterior branch of coccygeal nerve
2534:Posterior branches of sacral nerves
2108:
13:
1994:British Journal of Sports Medicine
1418:The brachial plexus surrounds the
1361:
1277:
1160:Skin of the anterolateral forearm
882:and a small area of overlying skin
14:
2976:
2869:superior lateral cutaneous of arm
2379:Thoraco-abdominal nerves – T7–T11
2181:
2130:
1037:medial cutaneous nerve of the arm
69:) of nerves that supply the arms.
1809:10.1097/00006123-199706000-00014
1803:(6): 1182–8, discussion 1188–9.
1739:10.1097/00003086-198803000-00005
1704:"Axillary Brachial Plexus Block"
1645:Moore, K.L.; Agur, A.M. (2007).
1511:
1499:
1487:
1475:
1463:
1451:
1439:
1427:
1411:
853:subscapularis (lower part ) and
196:). This plexus extends from the
140:Anatomical terms of neuroanatomy
2093:
2047:
2018:
2006:10.1136/bjsports-2011-090606.60
1981:
1930:
1891:
1858:
1788:
1753:
1696:
1663:
1589:
1539:Kawai, H; Kawabata, H (2000).
1518:Mixed fibres of a spinal nerve
1317:being more susceptible to the
1:
2620:Nerve supply of the human arm
1844:10.1016/S0029-7844(97)00007-0
1523:
1255:Injury to the brachial plexus
1047:front and medial skin of the
1001:by a recurrent thenar branch
324:These roots merge to form the
2700:lateral cutaneous of forearm
2068:10.1097/OGX.0b013e3181b27a3a
1774:10.1302/0301-620X.95B1.29625
1762:The Bone & Joint Journal
1088:, the medial two bellies of
366:
239:
7:
2767:medial cutaneous of forearm
1869:Clinically Oriented Anatomy
1832:Obstetrics & Gynecology
1372:
1116:
1069:medial skin of the forearm
783:fibres to the median nerve
723:(by communicating with the
473:
10:
2981:
1904:Clinics in Sports Medicine
1647:Essential Clinical Anatomy
1602:Anatomy & Cell Biology
1365:
1352:
1239:
1090:flexor digitorum profundus
989:flexor digitorum profundus
822:(middle subscapular nerve)
434:
2931:
2837:
2744:
2667:
2626:
2549:
2480:
2406:
2292:
2189:
2111:"Brachial Plexus Anatomy"
2100:Saladin, Kenneth (2014).
1916:10.1016/j.csm.2005.04.002
1670:Saladin, Kenneth (2007).
1571:Saladin, Kenneth (2015).
1399:List of anatomy mnemonics
1332:
1226:
891:posterior branch becomes
319:
138:
126:
114:
102:
90:
78:
73:
59:
54:
38:
26:
21:
2965:Nerves of the upper limb
1614:10.5115/acb.2014.47.1.77
1176:Deltoid and teres minor
1131:intercostobrachial nerve
1125:muscle (supplied by the
1104:which are served by the
997:muscles. muscles of the
511:are well connected. The
389:
279:
160:is a network of nerves (
2894:inferior lateral of arm
2772:medial cutaneous of arm
2374:Intercostobrachial – T2
846:lower subscapular nerve
798:upper subscapular nerve
650:nerve to the subclavius
354:"inferior" or "lower" (
2918:posterior interosseous
2470:Superior cluneal L1–L3
2277:Greater occipital – C2
2102:Anatomy and Physiology
1956:10.1186/1749-7221-2-13
1573:Anatomy and Physiology
1251:
1242:Brachial plexus injury
1237:
1156:musculocutaneous nerve
1127:spinal accessory nerve
1102:lumbricals of the hand
1094:intrinsic hand muscles
981:flexors in the forearm
739:musculocutaneous nerve
705:lateral pectoral nerve
513:musculocutaneous nerve
505:musculocutaneous nerve
485:musculocutaneous nerve
467:
266:musculocutaneous nerve
64:
2908:dorsal digital nerves
2811:proper palmar digital
2807:common palmar digital
2797:dorsal digital nerves
2735:proper palmar digital
2731:common palmar digital
2716:anterior interosseous
2539:Medial cluneal nerves
1865:Moore, Keith (2006).
1541:Brachial Plexus Palsy
1368:Brachial plexus block
1300:Injuries during birth
1249:
1234:
1222:Clinical significance
1150:Muscular Innervation
946:medial pectoral nerve
725:medial pectoral nerve
558:dorsal scapular nerve
465:
302:dorsal scapular nerve
290:anterior primary rami
214:efferent nerve fibers
202:cervicoaxillary canal
2898:posterior of forearm
2282:Third occipital – C3
1937:Elias, Ilan (2014).
1147:Sensory Innervation
1100:and the two lateral
1086:flexor carpi ulnaris
985:flexor carpi ulnaris
771:lateral root of the
1988:Cunnane, M (2011).
970:medial root of the
888:and deltoid muscles
820:thoracodorsal nerve
677:suprascapular nerve
593:long thoracic nerve
272:, medial cord, and
2109:Kishner, Stephen.
1291:Penetrating wounds
1252:
1238:
908:C5, C6, C7, C8, T1
884:posterior branch:
468:
168:of the lower four
2947:
2946:
2927:
2926:
2658:to the subclavius
2586:
2585:
2453:Lumbosacral trunk
2272:Suboccipital – C1
2030:www.ninds.nih.gov
2000:(15): A19.1–A19.
1656:978-0-7817-6274-8
1405:Additional images
1307:shoulder dystocia
1219:
1218:
1114:
1113:
987:and that part of
878:anterior branch:
664:subclavius muscle
613:serratus anterior
314:serratus anterior
154:
153:
149:
85:plexus brachialis
16:Network of nerves
2972:
2890:posterior of arm
2696:musculocutaneous
2684:lateral pectoral
2672:
2671:
2613:
2606:
2599:
2590:
2589:
2564:Coccygeal plexus
2176:
2169:
2162:
2153:
2152:
2126:
2124:
2122:
2105:
2088:
2087:
2051:
2045:
2044:
2042:
2041:
2032:. Archived from
2022:
2016:
2015:
2013:
2012:
1985:
1979:
1978:
1968:
1958:
1934:
1928:
1927:
1895:
1889:
1888:
1872:
1862:
1856:
1855:
1827:
1821:
1820:
1792:
1786:
1785:
1757:
1751:
1750:
1722:
1716:
1715:
1700:
1694:
1693:
1677:
1667:
1661:
1660:
1642:
1636:
1635:
1625:
1593:
1587:
1586:
1568:
1555:
1554:
1536:
1515:
1503:
1491:
1479:
1467:
1455:
1443:
1431:
1415:
1139:
1138:
958:pectoralis minor
954:pectoralis major
833:latissimus dorsi
747:coracobrachialis
721:pectoralis minor
717:pectoralis major
580:levator scapulae
576:rhomboid muscles
532:
531:
441:
306:rhomboid muscles
268:, lateral cord,
164:) formed by the
146:edit on Wikidata
143:
43:
31:
19:
18:
2980:
2979:
2975:
2974:
2973:
2971:
2970:
2969:
2950:
2949:
2948:
2943:
2939:Brachial plexus
2923:
2833:
2758:ansa pectoralis
2754:medial pectoral
2740:
2688:ansa pectoralis
2668:Infraclavicular
2663:
2638:dorsal scapular
2627:Supraclavicular
2622:
2617:
2587:
2582:
2545:
2476:
2402:
2384:Subcostal – T12
2288:
2253:Brachial plexus
2248:Cervical plexus
2185:
2180:
2133:
2120:
2118:
2096:
2091:
2052:
2048:
2039:
2037:
2024:
2023:
2019:
2010:
2008:
1986:
1982:
1935:
1931:
1896:
1892:
1885:
1863:
1859:
1828:
1824:
1793:
1789:
1758:
1754:
1723:
1719:
1702:
1701:
1697:
1690:
1668:
1664:
1657:
1643:
1639:
1594:
1590:
1583:
1569:
1558:
1551:
1537:
1530:
1526:
1519:
1516:
1507:
1504:
1495:
1492:
1483:
1480:
1471:
1468:
1459:
1458:Brachial plexus
1456:
1447:
1444:
1435:
1432:
1423:
1420:brachial artery
1416:
1407:
1375:
1370:
1364:
1362:In anaesthetics
1355:
1335:
1302:
1293:
1280:
1278:Sports injuries
1244:
1229:
1224:
1143:Terminal Branch
1119:
999:thenar eminence
932:brachioradialis
926:muscles of the
883:
476:
470:
464:
439:
437:
400:axillary artery
392:
369:
322:
282:
242:
170:cervical nerves
158:brachial plexus
150:
63:Network (nerve
50:
34:
22:Brachial plexus
17:
12:
11:
5:
2978:
2968:
2967:
2962:
2945:
2944:
2942:
2941:
2935:
2933:
2929:
2928:
2925:
2924:
2922:
2921:
2911:
2901:
2883:
2873:
2872:
2861:
2860:
2855:
2843:
2841:
2839:posterior cord
2835:
2834:
2832:
2831:
2820:
2819:
2814:
2800:
2790:
2785:
2775:
2774:
2769:
2762:
2761:
2760:
2759:
2750:
2748:
2742:
2741:
2739:
2738:
2728:
2723:
2718:
2704:
2703:
2692:
2691:
2690:
2689:
2680:
2678:
2669:
2665:
2664:
2662:
2661:
2645:
2630:
2628:
2624:
2623:
2616:
2615:
2608:
2601:
2593:
2584:
2583:
2581:
2580:
2579:
2578:
2568:
2567:
2566:
2555:
2553:
2547:
2546:
2544:
2543:
2542:
2541:
2536:
2526:
2525:
2524:
2513:
2512:
2507:
2502:
2497:
2492:
2486:
2484:
2478:
2477:
2475:
2474:
2473:
2472:
2467:
2457:
2456:
2455:
2450:
2439:
2438:
2433:
2428:
2423:
2418:
2412:
2410:
2404:
2403:
2401:
2400:
2399:
2398:
2388:
2387:
2386:
2381:
2376:
2371:
2360:
2359:
2354:
2349:
2344:
2339:
2334:
2329:
2324:
2319:
2314:
2309:
2304:
2298:
2296:
2290:
2289:
2287:
2286:
2285:
2284:
2279:
2274:
2269:
2257:
2256:
2255:
2250:
2237:
2236:
2231:
2226:
2221:
2216:
2211:
2206:
2201:
2195:
2193:
2187:
2186:
2179:
2178:
2171:
2164:
2156:
2150:
2149:
2144:
2139:
2132:
2131:External links
2129:
2128:
2127:
2106:
2095:
2092:
2090:
2089:
2062:(9): 615–623.
2046:
2017:
1980:
1929:
1910:(3): 637–662.
1890:
1883:
1857:
1822:
1787:
1752:
1733:(228): 33–41.
1717:
1714:on 2017-07-12.
1708:www.nysora.com
1695:
1688:
1662:
1655:
1637:
1588:
1581:
1556:
1549:
1527:
1525:
1522:
1521:
1520:
1517:
1510:
1508:
1505:
1498:
1496:
1493:
1486:
1484:
1481:
1474:
1472:
1469:
1462:
1460:
1457:
1450:
1448:
1445:
1438:
1436:
1433:
1426:
1424:
1417:
1410:
1406:
1403:
1402:
1401:
1396:
1391:
1386:
1381:
1374:
1371:
1366:Main article:
1363:
1360:
1354:
1351:
1334:
1331:
1301:
1298:
1292:
1289:
1279:
1276:
1240:Main article:
1228:
1225:
1223:
1220:
1217:
1216:
1213:
1210:
1204:
1203:
1200:
1197:
1191:
1190:
1187:
1184:
1178:
1177:
1174:
1171:
1169:axillary nerve
1165:
1164:
1161:
1158:
1152:
1151:
1148:
1145:
1118:
1115:
1112:
1111:
1108:
1098:thenar muscles
1083:
1080:
1075:
1071:
1070:
1067:
1064:
1061:
1056:
1052:
1051:
1045:
1042:
1039:
1034:
1030:
1029:
1003:
977:
974:
968:
964:
963:
960:
951:
948:
943:
939:
938:
934:
909:
906:
901:
900:posterior cord
897:
896:
889:
876:
870:
868:axillary nerve
865:
864:posterior cord
861:
860:
857:
851:
848:
843:
842:posterior cord
839:
838:
835:
830:
823:
817:
816:posterior cord
813:
812:
809:
803:
800:
795:
794:posterior cord
791:
790:
787:
781:
775:
769:
765:
764:
757:
755:biceps brachii
744:
741:
736:
732:
731:
728:
714:
707:
702:
698:
697:
694:
685:
679:
674:
670:
669:
666:
661:
652:
647:
643:
642:
639:
634:
629:
623:
619:
618:
615:
610:
595:
590:
586:
585:
582:
573:
560:
555:
551:
550:
545:
542:
539:
536:
489:axillary nerve
475:
472:
436:
433:
432:
431:
422:
413:
409:posterior cord
391:
388:
387:
386:
383:
380:
368:
365:
364:
363:
352:
345:
336:" or "upper" (
321:
318:
281:
278:
241:
238:
208:, it supplies
200:, through the
174:thoracic nerve
152:
151:
142:
136:
135:
130:
124:
123:
118:
112:
111:
106:
100:
99:
94:
88:
87:
82:
76:
75:
71:
70:
61:
57:
56:
52:
51:
44:
36:
35:
32:
24:
23:
15:
9:
6:
4:
3:
2:
2977:
2966:
2963:
2961:
2958:
2957:
2955:
2940:
2937:
2936:
2934:
2930:
2919:
2915:
2912:
2909:
2905:
2902:
2899:
2895:
2891:
2887:
2884:
2882:
2878:
2875:
2874:
2870:
2866:
2863:
2862:
2859:
2858:thoracodorsal
2856:
2853:
2849:
2846:subscapular (
2845:
2844:
2842:
2840:
2836:
2829:
2825:
2822:
2821:
2818:
2815:
2812:
2808:
2804:
2801:
2798:
2794:
2791:
2789:
2786:
2784:
2780:
2777:
2776:
2773:
2770:
2768:
2764:
2763:
2757:
2756:
2755:
2752:
2751:
2749:
2747:
2743:
2736:
2732:
2729:
2727:
2724:
2722:
2719:
2717:
2713:
2709:
2706:
2705:
2701:
2697:
2694:
2693:
2687:
2686:
2685:
2682:
2681:
2679:
2677:
2673:
2670:
2666:
2659:
2655:
2654:suprascapular
2651:
2650:
2646:
2643:
2642:long thoracic
2639:
2635:
2632:
2631:
2629:
2625:
2621:
2614:
2609:
2607:
2602:
2600:
2595:
2594:
2591:
2577:
2574:
2573:
2572:
2569:
2565:
2562:
2561:
2560:
2557:
2556:
2554:
2552:
2548:
2540:
2537:
2535:
2532:
2531:
2530:
2527:
2523:
2522:Sacral plexus
2520:
2519:
2518:
2515:
2514:
2511:
2508:
2506:
2503:
2501:
2498:
2496:
2493:
2491:
2488:
2487:
2485:
2483:
2479:
2471:
2468:
2466:
2463:
2462:
2461:
2458:
2454:
2451:
2449:
2448:Lumbar plexus
2446:
2445:
2444:
2441:
2440:
2437:
2434:
2432:
2429:
2427:
2424:
2422:
2419:
2417:
2414:
2413:
2411:
2409:
2405:
2397:
2394:
2393:
2392:
2389:
2385:
2382:
2380:
2377:
2375:
2372:
2370:
2367:
2366:
2365:
2362:
2361:
2358:
2355:
2353:
2350:
2348:
2345:
2343:
2340:
2338:
2335:
2333:
2330:
2328:
2325:
2323:
2320:
2318:
2315:
2313:
2310:
2308:
2305:
2303:
2300:
2299:
2297:
2295:
2291:
2283:
2280:
2278:
2275:
2273:
2270:
2268:
2265:
2264:
2263:
2262:
2258:
2254:
2251:
2249:
2246:
2245:
2244:
2243:
2239:
2238:
2235:
2232:
2230:
2227:
2225:
2222:
2220:
2217:
2215:
2212:
2210:
2207:
2205:
2202:
2200:
2197:
2196:
2194:
2192:
2188:
2184:
2183:Spinal nerves
2177:
2172:
2170:
2165:
2163:
2158:
2157:
2154:
2148:
2145:
2143:
2140:
2138:
2135:
2134:
2116:
2112:
2107:
2103:
2098:
2097:
2085:
2081:
2077:
2073:
2069:
2065:
2061:
2057:
2050:
2036:on 2016-12-02
2035:
2031:
2027:
2021:
2007:
2003:
1999:
1995:
1991:
1984:
1976:
1972:
1967:
1962:
1957:
1952:
1948:
1944:
1940:
1933:
1925:
1921:
1917:
1913:
1909:
1905:
1901:
1894:
1886:
1884:0-7817-3639-0
1880:
1876:
1871:
1870:
1861:
1853:
1849:
1845:
1841:
1838:(5): 643–47.
1837:
1833:
1826:
1818:
1814:
1810:
1806:
1802:
1798:
1791:
1783:
1779:
1775:
1771:
1768:(1): 106–10.
1767:
1763:
1756:
1748:
1744:
1740:
1736:
1732:
1728:
1721:
1713:
1709:
1705:
1699:
1691:
1689:9789814646437
1685:
1681:
1676:
1675:
1666:
1658:
1652:
1648:
1641:
1633:
1629:
1624:
1619:
1615:
1611:
1607:
1603:
1599:
1592:
1584:
1582:9789814646437
1578:
1574:
1567:
1565:
1563:
1561:
1552:
1546:
1542:
1535:
1533:
1528:
1514:
1509:
1502:
1497:
1490:
1485:
1478:
1473:
1466:
1461:
1454:
1449:
1442:
1437:
1430:
1425:
1421:
1414:
1409:
1408:
1400:
1397:
1395:
1392:
1390:
1389:Cranial nerve
1387:
1385:
1382:
1380:
1377:
1376:
1369:
1359:
1350:
1348:
1344:
1343:neurofibromas
1340:
1330:
1328:
1324:
1320:
1316:
1312:
1308:
1297:
1288:
1286:
1275:
1271:
1267:
1263:
1259:
1256:
1248:
1243:
1233:
1214:
1211:
1209:
1206:
1205:
1201:
1198:
1196:
1193:
1192:
1188:
1185:
1183:
1180:
1179:
1175:
1172:
1170:
1167:
1166:
1162:
1159:
1157:
1154:
1153:
1149:
1146:
1144:
1141:
1140:
1137:
1134:
1132:
1128:
1124:
1109:
1107:
1103:
1099:
1096:, except the
1095:
1091:
1087:
1084:
1081:
1079:
1076:
1073:
1072:
1068:
1065:
1062:
1060:
1057:
1054:
1053:
1050:
1046:
1043:
1040:
1038:
1035:
1032:
1031:
1028:
1024:
1020:
1016:
1015:middle finger
1012:
1008:
1004:
1002:
1000:
996:
990:
986:
982:
978:
975:
973:
969:
966:
965:
961:
959:
955:
952:
949:
947:
944:
941:
940:
935:
933:
929:
925:
921:
917:
913:
910:
907:
905:
902:
899:
898:
894:
890:
887:
881:
877:
874:
871:
869:
866:
863:
862:
858:
856:
852:
849:
847:
844:
841:
840:
836:
834:
831:
828:
824:
821:
818:
815:
814:
810:
807:
806:subscapularis
804:
801:
799:
796:
793:
792:
788:
786:
785:(see below)
782:
779:
776:
774:
770:
767:
766:
762:
758:
756:
752:
748:
745:
742:
740:
737:
734:
733:
729:
726:
722:
718:
715:
712:
708:
706:
703:
700:
699:
695:
693:
692:infraspinatus
689:
688:supraspinatus
686:
683:
680:
678:
675:
672:
671:
667:
665:
662:
660:
656:
653:
651:
648:
645:
644:
640:
638:
635:
633:
630:
628:
627:phrenic nerve
624:
621:
620:
616:
614:
611:
609:
605:
604:
599:
596:
594:
591:
588:
587:
583:
581:
577:
574:
572:
571:
566:
565:
561:
559:
556:
553:
552:
549:
546:
543:
540:
537:
534:
533:
530:
528:
524:
520:
518:
514:
510:
506:
502:
498:
494:
490:
486:
481:
471:
429:
428:
423:
420:
419:
414:
411:
410:
405:
404:
403:
401:
397:
384:
381:
378:
377:
376:
374:
361:
357:
353:
350:
346:
343:
339:
335:
331:
330:
329:
327:
317:
315:
311:
307:
303:
299:
295:
294:spinal nerves
291:
288:are the five
287:
277:
275:
271:
267:
263:
259:
255:
251:
247:
237:
235:
231:
227:
223:
219:
215:
211:
207:
203:
199:
195:
191:
187:
183:
179:
175:
171:
167:
166:anterior rami
163:
159:
147:
141:
137:
134:
131:
129:
125:
122:
119:
117:
113:
110:
107:
105:
101:
98:
95:
93:
89:
86:
83:
81:
77:
72:
68:
67:
62:
58:
53:
48:
42:
37:
30:
25:
20:
2960:Nerve plexus
2938:
2885:
2712:lateral root
2676:lateral cord
2647:
2633:
2570:
2558:
2528:
2516:
2459:
2442:
2390:
2363:
2259:
2252:
2240:
2119:. Retrieved
2114:
2101:
2094:Bibliography
2059:
2055:
2049:
2038:. Retrieved
2034:the original
2029:
2020:
2009:. Retrieved
1997:
1993:
1983:
1946:
1942:
1932:
1907:
1903:
1893:
1868:
1860:
1835:
1831:
1825:
1800:
1797:Neurosurgery
1796:
1790:
1765:
1761:
1755:
1730:
1726:
1720:
1712:the original
1707:
1698:
1673:
1665:
1646:
1640:
1608:(1): 77–80.
1605:
1601:
1591:
1572:
1540:
1394:Spinal nerve
1384:Nerve plexus
1356:
1336:
1313:with larger
1311:birth weight
1303:
1294:
1281:
1272:
1268:
1264:
1260:
1253:
1195:median nerve
1182:radial nerve
1142:
1135:
1120:
1106:median nerve
993:1st and 2nd
992:
972:median nerve
904:radial nerve
872:
826:
808:(upper part)
784:
777:
773:median nerve
768:lateral cord
759:Becomes the
735:lateral cord
710:
701:lateral cord
681:
658:
654:
631:
601:
597:
568:
562:
526:
522:
521:
517:median nerve
509:median nerve
497:median nerve
493:radial nerve
479:
477:
469:
425:
418:lateral cord
416:
407:
395:
393:
372:
370:
325:
323:
285:
283:
270:median nerve
261:
257:
253:
249:
245:
243:
162:nerve plexus
157:
155:
109:A14.2.03.001
84:
2904:superficial
2830:: see above
2828:medial root
2803:superficial
2765:cutaneous:
2746:medial cord
2649:upper trunk
2369:Intercostal
1949:: e61–e65.
1339:schwannomas
1285:Erb's point
1208:ulnar nerve
1078:ulnar nerve
1074:medial cord
1055:medial cord
1033:medial cord
1019:ring finger
1017:, half the
979:all of the
967:medial cord
942:medial cord
886:teres minor
855:teres major
673:upper trunk
646:upper trunk
501:ulnar nerve
427:medial cord
274:ulnar nerve
260:, and five
198:spinal cord
74:Identifiers
2954:Categories
2040:2016-11-28
2011:2015-02-12
1550:9810231393
1524:References
1021:, and the
751:brachialis
743:C5, C6, C7
625:branch to
499:, and the
347:"middle" (
310:subclavius
172:and first
2886:cutaneous
2726:recurrent
2571:posterior
2551:Coccygeal
2529:posterior
2460:posterior
2391:posterior
2261:posterior
2076:1533-9866
1924:0278-5919
1296:muscles.
1123:trapezius
1025:of these
995:lumbrical
916:supinator
914:brachii,
637:Diaphragm
632:C3, C4,C5
548:Cutaneous
373:divisions
367:Divisions
284:The five
254:divisions
240:Structure
49:specimen.
47:cadavaric
2881:muscular
2865:axillary
2783:muscular
2559:anterior
2517:anterior
2443:anterior
2364:anterior
2294:Thoracic
2242:anterior
2191:Cervical
2115:Medscape
2084:19691859
1975:17553154
1782:23307682
1632:24693486
1373:See also
1315:newborns
1117:Function
1023:nail bed
924:extensor
920:anconeus
507:and the
480:branches
474:Branches
334:superior
262:branches
248:, three
222:shoulder
210:afferent
60:Function
2117:. WebMD
1966:1904218
1852:9166293
1817:9179891
1747:3342585
1623:3968270
1353:Imaging
1327:newborn
1027:fingers
983:except
928:forearm
912:triceps
880:deltoid
544:Muscles
527:Italics
435:Diagram
292:of the
230:forearm
216:to the
97:D001917
55:Details
2877:radial
2824:median
2793:dorsal
2788:palmar
2721:palmar
2708:median
2482:Sacral
2408:Lumbar
2121:29 Nov
2082:
2074:
1973:
1963:
1922:
1881:
1875:778–81
1850:
1815:
1780:
1745:
1686:
1653:
1630:
1620:
1579:
1547:
1379:Plexus
1333:Tumors
1319:injury
1227:Injury
1092:, the
1063:C8, T1
1041:C8, T1
1009:, the
976:C8, T1
950:C8, T1
930:, and
922:, the
850:C5, C6
802:C5, C6
780:,C6,C7
495:, the
491:, the
487:, the
326:trunks
320:Trunks
252:, six
250:trunks
232:, and
206:armpit
192:, and
66:plexus
2932:Other
2852:lower
2848:upper
2779:ulnar
1323:birth
1011:index
1007:thumb
622:roots
589:roots
554:roots
541:Roots
538:Nerve
396:cords
390:Cords
286:roots
280:Roots
258:cords
246:roots
218:chest
144:[
80:Latin
2914:deep
2817:deep
2634:root
2123:2015
2080:PMID
2072:ISSN
1971:PMID
1920:ISSN
1879:ISBN
1848:PMID
1813:PMID
1778:PMID
1766:95-B
1743:PMID
1684:ISBN
1651:ISBN
1628:PMID
1577:ISBN
1545:ISBN
1345:and
1013:and
956:and
875:, C6
829:, C8
825:C6,
753:and
719:and
713:, C7
709:C5,
690:and
684:, C6
578:and
535:From
523:Bold
478:The
424:The
415:The
406:The
298:neck
234:hand
212:and
156:The
133:5906
121:6395
104:TA98
92:MeSH
2357:T12
2352:T11
2347:T10
2064:doi
2002:doi
1961:PMC
1951:doi
1912:doi
1840:doi
1805:doi
1770:doi
1735:doi
1731:228
1680:491
1618:PMC
1610:doi
1049:arm
226:arm
128:FMA
116:TA2
2956::
2896:,
2892:,
2879::
2850:,
2809:,
2781::
2714::
2656:,
2640:,
2510:S5
2505:S4
2500:S3
2495:S2
2490:S1
2436:L5
2431:L4
2426:L3
2421:L2
2416:L1
2342:T9
2337:T8
2332:T7
2327:T6
2322:T5
2317:T4
2312:T3
2307:T2
2302:T1
2234:C8
2229:C7
2224:C6
2219:C5
2214:C4
2209:C3
2204:C2
2199:C1
2113:.
2078:.
2070:.
2060:64
2058:.
2028:.
1998:45
1996:.
1992:.
1969:.
1959:.
1947:02
1945:.
1941:.
1918:.
1908:24
1906:.
1902:.
1877:.
1846:.
1836:89
1834:.
1811:.
1801:40
1799:.
1776:.
1764:.
1741:.
1729:.
1706:.
1682:.
1626:.
1616:.
1606:47
1604:.
1600:.
1559:^
1531:^
1349:.
1341:,
962:-
918:,
873:C5
859:-
837:-
827:C7
811:-
789:-
778:C5
749:,
730:-
711:C6
696:-
682:C5
668:-
659:C6
657:,
655:C5
641:-
617:-
608:C7
606:,
603:C6
600:,
598:C5
584:-
570:C5
567:,
564:C4
402:.
375::
360:T1
356:C8
349:C7
342:C6
338:C5
328::
276:.
236:.
228:,
224:,
220:,
194:T1
190:C8
188:,
186:C7
184:,
182:C6
180:,
178:C5
2920:)
2916:(
2910:)
2906:(
2900:)
2888:(
2871:)
2867:(
2854:)
2826:/
2813:)
2805:(
2799:)
2795:(
2737:)
2733:(
2710:/
2702:)
2698:(
2660:)
2652:(
2644:)
2636:(
2612:e
2605:t
2598:v
2175:e
2168:t
2161:v
2125:.
2086:.
2066::
2043:.
2014:.
2004::
1977:.
1953::
1926:.
1914::
1887:.
1854:.
1842::
1819:.
1807::
1784:.
1772::
1749:.
1737::
1692:.
1659:.
1634:.
1612::
1585:.
1553:.
1422:.
1066:-
1044:-
727:)
362:)
358:-
351:)
344:)
340:-
332:"
176:(
148:]
Text is available under the Creative Commons Attribution-ShareAlike License. Additional terms may apply.