1557:
212:
632:, the key being searched for does not exist in the tree. Otherwise, if the key equals that of the root, the search is successful and the node is returned. If the key is less than that of the root, the search proceeds by examining the left subtree. Similarly, if the key is greater than that of the root, the search proceeds by examining the right subtree. This process is repeated until the key is found or the remaining subtree is
3882:
280:
The performance of a binary search tree is dependent on the order of insertion of the nodes into the tree since arbitrary insertions may lead to degeneracy; several variations of the binary search tree can be built with guaranteed worst-case performance. The basic operations include: search,
2618:
is a key to the usefulness of the binary search tree. This can be achieved by "self-balancing" mechanisms during the updation operations to the tree designed to maintain the tree height to the binary logarithmic complexity.
1243:
Operations such as finding a node in a BST whose key is the maximum or minimum are critical in certain operations, such as determining the successor and predecessor of nodes. Following is the pseudocode for the operations.
1298:
Operations such as insertion and deletion cause the BST representation to change dynamically. The data structure must be modified in such a way that the properties of BST continue to hold. New nodes are inserted as
575:. However, the search complexity of a BST depends upon the order in which the nodes are inserted and deleted; since in worst case, successive operations in the binary search tree may lead to degeneracy and form a
264:
for fast lookup, addition, and removal of data items. Since the nodes in a BST are laid out so that each comparison skips about half of the remaining tree, the lookup performance is proportional to that of
3886:
2861:, using the node's key as priorities. Adding new elements to the queue follows the regular BST insertion operation but the removal operation depends on the type of priority queue:
2294:
3789:
2269:
2635:. The heights of all the nodes on the path from the root to the modified leaf node have to be observed and possibly corrected on every insert and delete operation to the tree.
2449:: Nodes from the left subtree get visited first, followed by the root node and right subtree. Such a traversal visits all the nodes in the order of non-decreasing key sequence.
3785:
2404:
2360:
1742:
1698:
1628:
1524:
1458:
784:
762:
674:
652:
2382:
2338:
2316:
2150:
2128:
2106:
2084:
2062:
2037:
2015:
1993:
1971:
1949:
1924:
1902:
1880:
1858:
1833:
1811:
1789:
1767:
1720:
1676:
1654:
1606:
1580:
1556:
1546:
1502:
1480:
1436:
1410:
1388:
1154:
1132:
1110:
1088:
1066:
1044:
1022:
2742:
2627:
A tree is height-balanced if the heights of the left sub-tree and right sub-tree are guaranteed to be related by a constant factor. This property was introduced by the
2616:
992:
499:
329:
3173:
2782:
2762:
2687:
933:
880:
378:
2649:
In a weight-balanced tree, the criterion of a balanced tree is the number of leaves of the subtrees. The weights of the left and right subtrees differ at most by
2583:
is number of items in a tree), so that the lookup performance is deteriorated to that of a linear search. Keeping the search tree balanced and height bounded by
2707:
2667:
2581:
2561:
953:
900:
349:
249:
with the key of each internal node being greater than all the keys in the respective node's left subtree and less than the ones in its right subtree. The
3513:
3088:
Paul E. Black, "red-black tree", in
Dictionary of Algorithms and Data Structures , Paul E. Black, ed. 12 November 2019. (accessed May 19 2022) from:
3072:
462:
The time complexities of a binary search tree increases boundlessly with the tree height if the nodes are inserted in an arbitrary order, therefore
3820:
3855:
3110:
3358:
2271:
procedure deals with the 3 special cases mentioned above. Lines 2-3 deal with case 1; lines 4-5 deal with case 2 and lines 6-16 for case 3. The
3419:
4940:
3897:
3567:
2868:
If it is a descending order priority queue, removal of an element with the highest priority is done through rightward traversal of the BST.
3134:
2865:
If it is an ascending order priority queue, removal of an element with the lowest priority is done through leftward traversal of the BST.
2764:-weight-balanced trees gives an entire family of balance conditions, where each left and right subtrees have each at least a fraction of
3781:
281:
traversal, insert and delete. BSTs with guaranteed worst-case complexities perform better than an unsorted array, which would require
4616:
3851:
3451:
4004:
3591:
4040:
4910:
4341:
3638:
3162:
4548:
955:
is the total number of nodes in the BST, because an unbalanced BST may degenerate to a linked list. However, if the BST is
3951:
528:
in 1962 for the efficient organization of information. It was the first self-balancing binary search tree to be invented.
17:
2193:
9 Shift-Nodes(BST, E, E.right) 10 E.right := D.right 11 E.right.parent := E 12
4092:
3816:
3066:
448:
274:
2839:, where all the elements are inserted at once and the tree is traversed at an in-order fashion. BSTs are also used in
4849:
3993:
3940:
3710:
3585:
3543:
3473:
3293:
3218:
2543:
Without rebalancing, insertions or deletions in a binary search tree may lead to degeneration, resulting in a height
2538:
463:
381:
3415:
3354:
4639:
4208:
3984:
2894:
289:
3203:
4644:
3490:
431:
The binary search tree algorithm was discovered independently by several researchers, including P.F. Windley,
4609:
4718:
537:
269:. BSTs were devised in the 1960s for the problem of efficient storage of labeled data and are attributed to
3049:
689:
612:
293:
2277:
4723:
4706:
3388:
2252:
903:
545:
3926:
3812:
3279:
3102:
591:
4922:
4689:
4684:
4173:
3843:
3624:
3457:
3347:
2889:
2884:
2197:
13 Shift-Nodes(BST, D, E) 14 E.left := D.left 15 E.left.parent := E 16
2461:: Nodes from the left subtree get visited first, followed by the right subtree, and finally, the root.
384:
variants of BSTs are introduced to bound the worst lookup complexity to that of the binary logarithm.
4679:
4558:
3132:
Adelson-Velsky, Georgy; Landis, Evgenii (1962). "An algorithm for the organization of information".
2924:
4713:
4672:
4602:
4114:
3630:
3411:
587:
404:
2925:"Explaining the Behaviour of Binary Search Trees Under Prolonged Updates: A Model and Simulations"
2387:
2343:
1725:
1681:
1611:
1507:
1441:
767:
745:
657:
635:
4953:
4930:
3324:
3210:
261:
40:
2365:
2321:
2299:
2133:
2111:
2089:
2067:
2045:
2020:
1998:
1976:
1954:
1932:
1907:
1885:
1863:
1841:
1816:
1794:
1772:
1750:
1703:
1659:
1637:
1589:
1563:
1529:
1485:
1463:
1419:
1393:
1371:
1137:
1115:
1093:
1071:
1049:
1027:
1005:
380:. To address the boundless increase of the tree height with arbitrary insertions and deletions,
4935:
4735:
4085:
3959:
2977:
2712:
2586:
962:
469:
299:
4979:
4974:
4861:
4816:
4778:
4252:
4101:
3169:
2767:
2747:
2672:
521:
389:
254:
3737:
4801:
4242:
4197:
4009:
3914:
3612:
3315:
3267:
3013:
2929:
2644:
2439:
2421:
956:
799:
3892:
3310:
909:
856:
459:
in 1960. One of the earliest and popular binary search tree algorithm is that of
Hibbard.
354:
8:
4356:
4036:
3988:. Vol. 3: "Sorting and Searching" (3rd ed.). Addison-Wesley. pp. 426–458.
3717:
The 2–3 trees defined at the close of
Section 6.2.3 are equivalent to B-Trees of order 3.
2973:
2959:
2899:
2435:
432:
62:
3008:
4844:
4694:
4654:
4523:
4482:
4308:
4298:
4212:
4132:
3847:
3762:
3745:
3684:
3532:
3144:
3106:
2989:
2692:
2652:
2632:
2566:
2546:
938:
885:
576:
514:
444:
400:
334:
270:
3560:
2960:"Analysis of the standard deletion algorithms in exact fit domain binary search trees"
4763:
4662:
4417:
4118:
4078:
4028:
3989:
3936:
3706:
3676:
3634:
3581:
3539:
3509:
3469:
3289:
3214:
3062:
2431:
595:
568:
440:
416:
70:
2158:
The following pseudocode implements the deletion operation in a binary search tree.
579:(or "unbalanced tree") like structure, thus has the same worst-case complexity as a
4786:
4508:
3918:
3910:
3766:
3754:
3666:
3616:
3608:
3573:
3505:
3461:
3384:
3328:
3271:
3263:
3022:
2981:
2938:
572:
266:
220:
176:
3688:
2993:
586:
Binary search trees are also a fundamental data structure used in construction of
4806:
4748:
4452:
4202:
2272:
1303:
in the BST. Following is an iterative implementation of the insertion operation.
1046:
is crucial. Assuming all the keys of a BST are distinct, the successor of a node
412:
250:
81:
4898:
4876:
4701:
4625:
4405:
4400:
4283:
4217:
4016:
Data
Structures and Algorithms Visualization-A PowerPoint Slides Based Approach
3963:
3922:
3729:
3620:
3538:. Twelfth International Conference on Very Large Databases (VLDB 1986). Kyoto.
3275:
3089:
3058:
2858:
2852:
2801:
2427:
2415:
1134:'s key. The following pseudocode finds the successor and predecessor of a node
616:
525:
393:
246:
85:
4055:
3332:
4968:
4871:
4768:
4753:
4553:
4533:
4376:
4265:
4192:
3733:
3680:
3654:
3465:
2943:
561:
456:
3577:
3027:
2296:
is used within the deletion algorithm for the purpose of replacing the node
536:
A binary search tree is a rooted binary tree in which nodes are arranged in
4513:
4477:
4293:
4288:
4270:
4182:
4127:
4019:
3979:
3045:
2964:
2809:
627:
452:
436:
408:
66:
3671:
3491:"On the Average Number of Rebalancing Operations in Weight-Balanced Trees"
1310:
1 BST-Insert(T, z) 2 y := NIL 3 x := T.root 4
4866:
4791:
4563:
4528:
4518:
4432:
4366:
4361:
4351:
4260:
4109:
2879:
580:
282:
243:
240:
2455:: The root node gets visited first, followed by left and right subtrees.
505:
binary search trees were introduced to confine the tree height, such as
351:
nodes. In the worst case, they degrade to that of a singly linked list:
4854:
4758:
4573:
4543:
4503:
4346:
4275:
4222:
4142:
4070:
3534:
A Study of Index
Structures for Main Memory Database Management Systems
2985:
2813:
1300:
795:
685:
611:
Searching in a binary search tree for a specific key can be programmed
388:
were the first self-balancing binary search trees, invented in 1962 by
215:
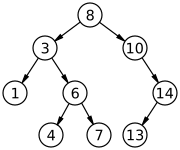
Fig. 1: A binary search tree of size 9 and depth 3, with 8 at the root.
3925:(2001). "12: Binary search trees, 15.5: Optimal binary search trees".
3758:
4796:
4743:
4578:
4538:
4385:
4313:
4303:
3932:
3285:
2840:
2836:
2830:
850:
623:
420:
385:
211:
4893:
4839:
4667:
4583:
4467:
4457:
4437:
4410:
4395:
4157:
4147:
3572:, Washington, D.C.: IEEE Computer Society Press, pp. 540–545,
2628:
2519:
Postorder-Tree-Walk(x.left) Postorder-Tree-Walk(x.right)
506:
4594:
2130:
first gets replaced by its own right child, and then it displaces
4888:
4834:
4568:
4472:
4447:
4390:
4237:
4167:
4162:
4137:
3844:"CS 2112 Lecture and Recitation Notes: Priority Queues and Heaps"
4883:
4824:
4487:
4462:
4442:
4427:
4336:
4227:
4152:
2805:
2793:
2792:
There are several self-balanced binary search trees, including
2503:
Preorder-Tree-Walk(x.left) Preorder-Tree-Walk(x.right)
3786:
Princeton
University School of Engineering and Applied Science
798:. On most machines, the iterative version is found to be more
540:
in which the nodes with keys greater than any particular node
4331:
4232:
4187:
2797:
794:
The recursive version of the search can be "unrolled" into a
676:
subtree is reached, then the key is not present in the tree.
510:
2362:. This procedure handles the deletion (and substitution) of
1416:
loop along lines 4-11 causes the pointers to be updated. If
4905:
4323:
3902:
3201:
Thareja, Reema (13 October 2018). "Hashing and
Collision".
2835:
Binary search trees are used in sorting algorithms such as
2465:
Following is a recursive implementation of the tree walks.
4067:(JavaScript animation of various BT-based data structures)
4064:
3909:
3607:
3262:
2744:
rebalancing work during insert and delete operations. The
4057:
3530:
Lehman, Tobin J.; Carey, Michael J. (25–28 August 1986).
3308:
1548:
on the lines 15-19 and the node is inserted accordingly.
3813:"A Connection Between Binary Search Trees and Quicksort"
3569:
30th Annual
Symposium on Foundations of Computer Science
1068:
in a BST is the node with the smallest key greater than
1482:
is inserted as the root node of the binary search tree
1112:
in a BST is the node with the largest key smaller than
3819:, The Department of Mathematics and Computer Science.
1526:, insertion proceeds by comparing the keys to that of
2770:
2750:
2715:
2695:
2675:
2655:
2589:
2569:
2549:
2390:
2368:
2346:
2324:
2302:
2280:
2255:
2136:
2114:
2092:
2070:
2048:
2023:
2001:
1979:
1957:
1935:
1910:
1888:
1866:
1844:
1819:
1797:
1775:
1753:
1728:
1706:
1684:
1662:
1640:
1614:
1592:
1566:
1532:
1510:
1488:
1466:
1444:
1422:
1396:
1374:
1140:
1118:
1096:
1090:'s key. On the other hand, the predecessor of a node
1074:
1052:
1030:
1008:
965:
941:
912:
888:
859:
770:
748:
660:
638:
472:
357:
337:
302:
3131:
2918:
2916:
2689:
of the weights, since a strong balance condition of
1860:has both left and right children, the successor of
466:were introduced to bound the height of the tree to
3531:
3202:
2776:
2756:
2736:
2701:
2681:
2661:
2610:
2575:
2555:
2398:
2376:
2354:
2332:
2310:
2288:
2263:
2144:
2122:
2100:
2078:
2056:
2031:
2009:
1987:
1965:
1943:
1918:
1896:
1874:
1852:
1827:
1805:
1783:
1761:
1736:
1714:
1692:
1670:
1648:
1622:
1600:
1574:
1540:
1518:
1496:
1474:
1452:
1430:
1404:
1382:
1148:
1126:
1104:
1082:
1060:
1038:
1016:
986:
947:
927:
894:
874:
778:
756:
668:
646:
493:
372:
343:
323:
2913:
1835:'s position in the tree, as shown in (b) and (c).
4966:
1813:to point to the child node, consequently taking
3309:R. A. Frost; M. M. Peterson (1 February 1982).
3258:
3256:
3254:
3252:
3250:
2532:
853:, the running time complexity of BST search is
3248:
3246:
3244:
3242:
3240:
3238:
3236:
3234:
3232:
3230:
2957:
2923:Culberson, J.; Munro, J. I. (1 January 1989).
2922:
2669:. However, the difference is bound by a ratio
1791:gets elevated by modifying the parent node of
552:and the nodes with keys equal to or less than
4610:
4086:
3728:
3172:, Department of Computer Science. p. 6.
3006:
2857:Binary search trees are used in implementing
2185:7 E := BST-Successor(D) 8
2173:3 Shift-Nodes(BST, D, D.right) 4
1368:The procedure maintains a "trailing pointer"
1229:x := y y := y.parent
1190:x := y y := y.parent
399:Binary search trees can be used to implement
3898:Dictionary of Algorithms and Data Structures
3705:. Vol. 3 (2 ed.). Addison Wesley.
3559:Aragon, Cecilia R.; Seidel, Raimund (1989),
3558:
3488:
3090:https://www.nist.gov/dads/HTML/redblack.html
2958:Culberson, J.; Munro, J. I. (28 July 1986).
2846:
2181:5 Shift-Nodes(BST, D, D.left) 6
997:
906:. However, the worst case for BST search is
688:implements the BST search procedure through
567:Binary search trees are also efficacious in
3529:
3227:
3135:Proceedings of the USSR Academy of Sciences
2819:
654:. If the searched key is not found after a
253:of operations on the binary search tree is
4617:
4603:
4093:
4079:
3601:
3445:
3443:
3441:
3439:
3437:
2239:9 v.parent := u.parent 10
1024:, finding the successor or predecessor of
742:The recursive procedure continues until a
3956:Interactive Data Structure Visualizations
3890:
3779:
3670:
3345:
3196:
3194:
3048:(1998). "Section 6.2.3: Balanced Trees".
3040:
3038:
3026:
2942:
2227:6 u.parent.right := v 7
4100:
4026:
3982:(1997). "6.2.2: Binary Tree Searching".
3409:
3000:
2638:
2622:
2223:5 u.parent.left := v 5
732:Recursive-Tree-Search(x.right, key)
257:with respect to the height of the tree.
210:
3629:(second ed.). MIT Press. pp.
3434:
3200:
3160:
849:Since the search may proceed till some
725:Recursive-Tree-Search(x.left, key)
14:
4967:
3657:(June 1979), "The Ubiquitous B-Tree",
3489:Blum, Norbert; Mehlhorn, Kurt (1978).
3191:
3035:
1769:has only one child, the child node of
1412:. After initialization on line 2, the
1330:9 x := x.right 10
296:, the insert, delete and search takes
4598:
4074:
3978:
3823:from the original on 26 February 2021
3700:
3653:
3449:
3311:"A Short Note on Binary Search Trees"
3179:from the original on 14 February 2019
3044:
1326:7 x := x.left 8
1002:For certain operations, given a node
3949:
3858:from the original on 21 October 2021
3738:"Self-Adjusting Binary Search Trees"
2784:of the total weight of the subtree.
2289:{\displaystyle {\text{Shift-Nodes}}}
786:being searched for are encountered.
556:are stored on the left sub-trees to
4624:
3348:"Design and Analysis of Algorithms"
2264:{\displaystyle {\text{BST-Delete}}}
2215:3 BST.root := v 4
2207:1 Shift-Nodes(BST, u, v) 2
1656:is a leaf node, the parent node of
789:
679:
24:
3950:Jarc, Duane J. (3 December 2005).
3874:
3817:Oxford College of Emory University
3792:from the original on 22 March 2021
3364:from the original on 13 April 2021
3113:from the original on 27 April 2021
3109:, Department of Computer Science.
1555:
1358:18 y.right := z 19
809:Iterative-Tree-Search(x, key)
699:Recursive-Tree-Search(x, key)
622:Searching begins by examining the
464:self-balancing binary search trees
25:
4991:
4048:
3841:
3810:
3701:Knuth, Donald M (1998). "6.2.4".
3623:(2001). "Red–Black Trees".
3163:"CSC263: Balanced BSTs, AVL tree"
3100:
2539:Self-balancing binary search tree
2108:'s right child, as shown in (e),
1973:'s right child, as shown in (d),
1354:16 y.left := z 17
1346:14 T.root := z 15
1338:12 z.parent := y 13
443:. The algorithm is attributed to
29:Rooted binary tree data structure
4043:from the original on 2022-01-30.
4002:
3885: This article incorporates
3880:
3519:from the original on 2022-10-09.
3422:from the original on 4 July 2021
3416:University of California, Irvine
3391:, Department of Computer Science
3355:University of Texas at Arlington
3078:from the original on 2022-10-09.
3009:"Trees, Forests and Rearranging"
3007:P. F. Windley (1 January 1960).
2430:through three basic algorithms:
2039:'s right child remain unchanged.
3985:The Art of Computer Programming
3835:
3804:
3773:
3722:
3703:The Art of Computer Programming
3694:
3647:
3597:from the original on 2022-10-09
3552:
3523:
3482:
3403:
3382:
3376:
3339:
3302:
3051:The Art of Computer Programming
2895:Geometry of binary search trees
2480:Inorder-Tree-Walk(x.left)
2165:1 BST-Delete(BST, D) 2
3852:Department of Computer Science
3154:
3125:
3094:
3082:
2951:
2731:
2719:
2605:
2593:
2484:Inorder-Tree-Walk(x.right)
1608:, from the binary search tree
1318:5 y := x 6
981:
969:
922:
916:
869:
863:
488:
476:
367:
361:
318:
306:
13:
1:
3935:. pp. 253–272, 356–363.
3800:– via cs.princeton.edu.
3782:"COS226: Binary search trees"
3450:Brass, Peter (January 2011).
3412:"ICS 46: Binary Search Trees"
2906:
601:
520:The AVL tree was invented by
3510:10.1016/0304-3975(80)90018-3
3498:Theoretical Computer Science
3149:Soviet Mathematics - Doklady
3057:. Vol. 3 (2 ed.).
2533:Balanced binary search trees
2409:
2399:{\displaystyle {\text{BST}}}
2355:{\displaystyle {\text{BST}}}
2086:'s right subtree but is not
1926:by following the two cases:
1737:{\displaystyle {\text{BST}}}
1693:{\displaystyle {\text{NIL}}}
1623:{\displaystyle {\text{BST}}}
1586:The deletion of a node, say
1582:to be deleted has 2 children
1519:{\displaystyle {\text{nil}}}
1453:{\displaystyle {\text{nil}}}
1293:
779:{\displaystyle {\text{key}}}
757:{\displaystyle {\text{nil}}}
669:{\displaystyle {\text{nil}}}
647:{\displaystyle {\text{nil}}}
606:
7:
4941:Directed acyclic word graph
4707:Double-ended priority queue
3389:Loyola Marymount University
3103:"CS 312 Lecture: AVL Trees"
2872:
1551:
531:
10:
4996:
3928:Introduction to Algorithms
3780:Narayanan, Arvind (2019).
3626:Introduction to Algorithms
3458:Cambridge University Press
3281:Introduction to Algorithms
2890:Optimal binary search tree
2885:Join-based tree algorithms
2850:
2828:
2709:cannot be maintained with
2642:
2536:
2511:Postorder-Tree-Walk(x)
2419:
2413:
2377:{\displaystyle {\text{u}}}
2340:in the binary search tree
2333:{\displaystyle {\text{v}}}
2311:{\displaystyle {\text{u}}}
2145:{\displaystyle {\text{Z}}}
2123:{\displaystyle {\text{Y}}}
2101:{\displaystyle {\text{Z}}}
2079:{\displaystyle {\text{Z}}}
2057:{\displaystyle {\text{Y}}}
2032:{\displaystyle {\text{Y}}}
2010:{\displaystyle {\text{Z}}}
1988:{\displaystyle {\text{Y}}}
1966:{\displaystyle {\text{Z}}}
1944:{\displaystyle {\text{Y}}}
1919:{\displaystyle {\text{Z}}}
1897:{\displaystyle {\text{Y}}}
1875:{\displaystyle {\text{Z}}}
1853:{\displaystyle {\text{Z}}}
1828:{\displaystyle {\text{Z}}}
1806:{\displaystyle {\text{Z}}}
1784:{\displaystyle {\text{Z}}}
1762:{\displaystyle {\text{Z}}}
1715:{\displaystyle {\text{Z}}}
1671:{\displaystyle {\text{Z}}}
1649:{\displaystyle {\text{Z}}}
1601:{\displaystyle {\text{Z}}}
1575:{\displaystyle {\text{D}}}
1541:{\displaystyle {\text{y}}}
1497:{\displaystyle {\text{T}}}
1475:{\displaystyle {\text{z}}}
1431:{\displaystyle {\text{y}}}
1405:{\displaystyle {\text{x}}}
1383:{\displaystyle {\text{y}}}
1174:BST-Minimum(x.right)
1149:{\displaystyle {\text{x}}}
1127:{\displaystyle {\text{x}}}
1105:{\displaystyle {\text{x}}}
1083:{\displaystyle {\text{x}}}
1061:{\displaystyle {\text{x}}}
1039:{\displaystyle {\text{x}}}
1017:{\displaystyle {\text{x}}}
832:x := x.right
451:, who used it for storing
426:
260:Binary search trees allow
4949:
4921:
4815:
4777:
4734:
4653:
4632:
4496:
4375:
4322:
4251:
4108:
4061:(PDF; 1675 kB) 2004.
3561:"Randomized Search Trees"
3161:Pitassi, Toniann (2015).
2847:Priority queue operations
2737:{\displaystyle O(\log n)}
2611:{\displaystyle O(\log n)}
2492:Preorder-Tree-Walk(x)
1460:, the BST is empty, thus
1213:BST-Maximum(x.left)
998:Successor and predecessor
987:{\displaystyle O(\log n)}
828:x := x.left
494:{\displaystyle O(\log n)}
324:{\displaystyle O(\log n)}
182:
175:
152:
129:
106:
91:
80:
76:
57:
49:
39:
34:
4673:Retrieval Data Structure
4549:Left-child right-sibling
3952:"Binary Tree Traversals"
3466:10.1017/CBO9780511800191
2820:Examples of applications
2787:
2472:Inorder-Tree-Walk(x)
2152:'s position in the tree.
1217:y := x.parent
1202:BST-Predecessor(x)
1178:y := x.parent
588:abstract data structures
4954:List of data structures
4931:Binary decision diagram
4379:data partitioning trees
4337:C-trie (compressed ADT)
4027:Parlante, Nick (2001).
3578:10.1109/SFCS.1989.63531
3453:Advanced Data Structure
3410:Thornton, Alex (2021).
3333:10.1093/comjnl/25.1.158
3325:Oxford University Press
3211:Oxford University Press
3205:Data Structures Using C
2824:
2777:{\displaystyle \alpha }
2757:{\displaystyle \alpha }
2682:{\displaystyle \alpha }
1259:x := x.right
544:is stored on the right
4936:Directed acyclic graph
4065:Binary Tree Visualizer
3960:University of Maryland
3887:public domain material
2978:University of Waterloo
2944:10.1093/comjnl/32.1.68
2778:
2758:
2738:
2703:
2683:
2663:
2612:
2577:
2557:
2400:
2378:
2356:
2334:
2312:
2290:
2265:
2146:
2124:
2102:
2080:
2058:
2033:
2011:
1989:
1967:
1945:
1920:
1898:
1876:
1854:
1829:
1807:
1785:
1763:
1738:
1716:
1694:
1672:
1650:
1624:
1602:
1583:
1576:
1542:
1520:
1498:
1476:
1454:
1432:
1406:
1384:
1279:x := x.left
1163:BST-Successor(x)
1150:
1128:
1106:
1084:
1062:
1040:
1018:
988:
949:
929:
896:
876:
780:
758:
670:
648:
495:
374:
345:
325:
216:
3915:Leiserson, Charles E.
3672:10.1145/356770.356776
3613:Leiserson, Charles E.
3268:Leiserson, Charles E.
3170:University of Toronto
3147:by Myron J. Ricci in
3028:10.1093/comjnl/3.2.84
2779:
2759:
2739:
2704:
2684:
2664:
2639:Weight-balanced trees
2631:and continued by the
2623:Height-balanced trees
2613:
2578:
2558:
2401:
2379:
2357:
2335:
2313:
2291:
2266:
2147:
2125:
2103:
2081:
2059:
2034:
2012:
1990:
1968:
1946:
1921:
1899:
1877:
1855:
1830:
1808:
1786:
1764:
1739:
1717:
1695:
1673:
1651:
1625:
1603:
1577:
1559:
1543:
1521:
1499:
1477:
1455:
1433:
1407:
1385:
1151:
1129:
1107:
1085:
1063:
1041:
1019:
989:
950:
930:
897:
877:
781:
759:
671:
649:
522:Georgy Adelson-Velsky
496:
390:Georgy Adelson-Velsky
375:
346:
326:
214:
4802:Unrolled linked list
4559:Log-structured merge
4102:Tree data structures
4033:CS Education Library
4005:"Binary Search Tree"
3893:"Binary Search Tree"
3385:"Binary Search Tree"
3316:The Computer Journal
3151:, 3:1259–1263, 1962.
3061:. pp. 458–481.
3014:The Computer Journal
2930:The Computer Journal
2768:
2748:
2713:
2693:
2673:
2653:
2645:Weight-balanced tree
2587:
2567:
2547:
2422:Threaded binary tree
2388:
2366:
2344:
2322:
2300:
2278:
2253:
2134:
2112:
2090:
2068:
2046:
2021:
1999:
1977:
1955:
1933:
1908:
1886:
1864:
1842:
1817:
1795:
1773:
1751:
1726:
1722:is removed from the
1704:
1682:
1660:
1638:
1612:
1590:
1564:
1530:
1508:
1486:
1464:
1442:
1420:
1394:
1372:
1271:BST-Minimum(x)
1255:x.right ≠ NIL
1251:BST-Maximum(x)
1167:x.right ≠ NIL
1138:
1116:
1094:
1072:
1050:
1028:
1006:
963:
939:
928:{\displaystyle O(n)}
910:
886:
875:{\displaystyle O(h)}
857:
768:
746:
658:
636:
470:
373:{\displaystyle O(n)}
355:
335:
300:
4850:Self-balancing tree
4037:Stanford University
3966:on 27 February 2014
3145:English translation
2974:Springer Publishing
2900:Ternary search tree
2563:of the tree (where
2459:Postorder tree walk
2189:E.parent ≠ D
1275:x.left ≠ NIL
1206:x.left ≠ NIL
433:Andrew Donald Booth
401:abstract data types
292:of BST shows that,
290:complexity analysis
18:Binary search trees
4830:Binary search tree
4695:Double-ended queue
4524:Fractal tree index
4119:associative arrays
3848:Cornell University
3746:Journal of the ACM
3730:Sleator, Daniel D.
3107:Cornell University
2986:10.1007/BF01840390
2774:
2754:
2734:
2699:
2679:
2659:
2608:
2573:
2553:
2453:Preorder tree walk
2396:
2374:
2352:
2330:
2308:
2286:
2261:
2219:u = u.parent.left
2142:
2120:
2098:
2076:
2054:
2029:
2007:
1985:
1963:
1941:
1916:
1894:
1872:
1850:
1825:
1803:
1781:
1759:
1744:, as shown in (a).
1734:
1712:
1690:
1668:
1646:
1620:
1598:
1584:
1572:
1538:
1516:
1494:
1472:
1450:
1428:
1402:
1380:
1146:
1124:
1102:
1080:
1058:
1036:
1014:
984:
945:
925:
904:height of the tree
892:
872:
817:key ≠ x.key
776:
754:
666:
644:
596:associative arrays
577:singly linked list
538:strict total order
491:
445:Conway Berners-Lee
417:sorting algorithms
370:
341:
321:
283:linear search time
271:Conway Berners-Lee
237:sorted binary tree
231:), also called an
225:binary search tree
217:
35:Binary search tree
4962:
4961:
4764:Hashed array tree
4663:Associative array
4592:
4591:
3919:Rivest, Ronald L.
3911:Cormen, Thomas H.
3759:10.1145/3828.3835
3734:Tarjan, Robert E.
3659:Computing Surveys
3640:978-0-262-03293-3
3617:Rivest, Ronald L.
3609:Cormen, Thomas H.
3272:Rivest, Ronald L.
3264:Cormen, Thomas H.
2702:{\displaystyle 1}
2662:{\displaystyle 1}
2576:{\displaystyle n}
2556:{\displaystyle n}
2530:
2529:
2447:Inorder tree walk
2394:
2372:
2350:
2328:
2306:
2284:
2259:
2247:
2246:
2140:
2118:
2096:
2074:
2052:
2027:
2005:
1983:
1961:
1939:
1914:
1892:
1870:
1848:
1823:
1801:
1779:
1757:
1732:
1710:
1700:and consequently
1688:
1678:gets replaced by
1666:
1644:
1630:has three cases:
1618:
1596:
1570:
1536:
1514:
1492:
1470:
1448:
1426:
1400:
1378:
1366:
1365:
1350:z.key < y.key
1322:z.key < x.key
1291:
1290:
1241:
1240:
1144:
1122:
1100:
1078:
1056:
1034:
1012:
948:{\displaystyle n}
895:{\displaystyle h}
847:
846:
774:
752:
740:
739:
664:
642:
626:. If the tree is
573:search algorithms
441:Thomas N. Hibbard
344:{\displaystyle n}
209:
208:
205:
204:
16:(Redirected from
4987:
4787:Association list
4619:
4612:
4605:
4596:
4595:
4095:
4088:
4081:
4072:
4071:
4044:
4023:
4013:
3999:
3975:
3973:
3971:
3962:. Archived from
3946:
3931:(2nd ed.).
3906:
3884:
3883:
3868:
3867:
3865:
3863:
3839:
3833:
3832:
3830:
3828:
3808:
3802:
3801:
3799:
3797:
3777:
3771:
3770:
3742:
3726:
3720:
3719:
3698:
3692:
3691:
3674:
3651:
3645:
3644:
3605:
3599:
3598:
3596:
3565:
3556:
3550:
3549:
3537:
3527:
3521:
3520:
3518:
3495:
3486:
3480:
3479:
3447:
3432:
3431:
3429:
3427:
3407:
3401:
3400:
3398:
3396:
3380:
3374:
3373:
3371:
3369:
3363:
3352:
3343:
3337:
3336:
3306:
3300:
3299:
3284:(2nd ed.).
3260:
3225:
3224:
3208:
3198:
3189:
3188:
3186:
3184:
3178:
3167:
3158:
3152:
3143:
3129:
3123:
3122:
3120:
3118:
3098:
3092:
3086:
3080:
3079:
3077:
3056:
3042:
3033:
3032:
3030:
3004:
2998:
2997:
2955:
2949:
2948:
2946:
2920:
2783:
2781:
2780:
2775:
2763:
2761:
2760:
2755:
2743:
2741:
2740:
2735:
2708:
2706:
2705:
2700:
2688:
2686:
2685:
2680:
2668:
2666:
2665:
2660:
2617:
2615:
2614:
2609:
2582:
2580:
2579:
2574:
2562:
2560:
2559:
2554:
2468:
2467:
2405:
2403:
2402:
2397:
2395:
2392:
2383:
2381:
2380:
2375:
2373:
2370:
2361:
2359:
2358:
2353:
2351:
2348:
2339:
2337:
2336:
2331:
2329:
2326:
2317:
2315:
2314:
2309:
2307:
2304:
2295:
2293:
2292:
2287:
2285:
2282:
2270:
2268:
2267:
2262:
2260:
2257:
2161:
2160:
2151:
2149:
2148:
2143:
2141:
2138:
2129:
2127:
2126:
2121:
2119:
2116:
2107:
2105:
2104:
2099:
2097:
2094:
2085:
2083:
2082:
2077:
2075:
2072:
2063:
2061:
2060:
2055:
2053:
2050:
2038:
2036:
2035:
2030:
2028:
2025:
2016:
2014:
2013:
2008:
2006:
2003:
1994:
1992:
1991:
1986:
1984:
1981:
1972:
1970:
1969:
1964:
1962:
1959:
1950:
1948:
1947:
1942:
1940:
1937:
1925:
1923:
1922:
1917:
1915:
1912:
1903:
1901:
1900:
1895:
1893:
1890:
1881:
1879:
1878:
1873:
1871:
1868:
1859:
1857:
1856:
1851:
1849:
1846:
1834:
1832:
1831:
1826:
1824:
1821:
1812:
1810:
1809:
1804:
1802:
1799:
1790:
1788:
1787:
1782:
1780:
1777:
1768:
1766:
1765:
1760:
1758:
1755:
1743:
1741:
1740:
1735:
1733:
1730:
1721:
1719:
1718:
1713:
1711:
1708:
1699:
1697:
1696:
1691:
1689:
1686:
1677:
1675:
1674:
1669:
1667:
1664:
1655:
1653:
1652:
1647:
1645:
1642:
1629:
1627:
1626:
1621:
1619:
1616:
1607:
1605:
1604:
1599:
1597:
1594:
1581:
1579:
1578:
1573:
1571:
1568:
1547:
1545:
1544:
1539:
1537:
1534:
1525:
1523:
1522:
1517:
1515:
1512:
1503:
1501:
1500:
1495:
1493:
1490:
1481:
1479:
1478:
1473:
1471:
1468:
1459:
1457:
1456:
1451:
1449:
1446:
1437:
1435:
1434:
1429:
1427:
1424:
1411:
1409:
1408:
1403:
1401:
1398:
1389:
1387:
1386:
1381:
1379:
1376:
1306:
1305:
1247:
1246:
1159:
1158:
1155:
1153:
1152:
1147:
1145:
1142:
1133:
1131:
1130:
1125:
1123:
1120:
1111:
1109:
1108:
1103:
1101:
1098:
1089:
1087:
1086:
1081:
1079:
1076:
1067:
1065:
1064:
1059:
1057:
1054:
1045:
1043:
1042:
1037:
1035:
1032:
1023:
1021:
1020:
1015:
1013:
1010:
993:
991:
990:
985:
954:
952:
951:
946:
934:
932:
931:
926:
901:
899:
898:
893:
881:
879:
878:
873:
805:
804:
790:Iterative search
785:
783:
782:
777:
775:
772:
763:
761:
760:
755:
753:
750:
695:
694:
680:Recursive search
675:
673:
672:
667:
665:
662:
653:
651:
650:
645:
643:
640:
630:
500:
498:
497:
492:
379:
377:
376:
371:
350:
348:
347:
342:
330:
328:
327:
322:
267:binary logarithm
221:computer science
201:
192:
177:Space complexity
171:
162:
148:
139:
125:
116:
78:
77:
32:
31:
21:
4995:
4994:
4990:
4989:
4988:
4986:
4985:
4984:
4965:
4964:
4963:
4958:
4945:
4917:
4811:
4807:XOR linked list
4773:
4749:Circular buffer
4730:
4649:
4628:
4626:Data structures
4623:
4593:
4588:
4492:
4371:
4318:
4247:
4243:Weight-balanced
4198:Order statistic
4112:
4104:
4099:
4051:
4007:
3996:
3969:
3967:
3943:
3923:Stein, Clifford
3891:Paul E. Black.
3881:
3877:
3875:Further reading
3872:
3871:
3861:
3859:
3842:Myers, Andrew.
3840:
3836:
3826:
3824:
3809:
3805:
3795:
3793:
3778:
3774:
3740:
3727:
3723:
3713:
3699:
3695:
3652:
3648:
3641:
3621:Stein, Clifford
3606:
3602:
3594:
3588:
3563:
3557:
3553:
3546:
3528:
3524:
3516:
3493:
3487:
3483:
3476:
3448:
3435:
3425:
3423:
3408:
3404:
3394:
3392:
3381:
3377:
3367:
3365:
3361:
3350:
3346:Junzhou Huang.
3344:
3340:
3307:
3303:
3296:
3276:Stein, Clifford
3261:
3228:
3221:
3199:
3192:
3182:
3180:
3176:
3165:
3159:
3155:
3130:
3126:
3116:
3114:
3101:Myers, Andrew.
3099:
3095:
3087:
3083:
3075:
3069:
3054:
3043:
3036:
3005:
3001:
2956:
2952:
2921:
2914:
2909:
2904:
2875:
2859:priority queues
2855:
2849:
2833:
2827:
2822:
2790:
2769:
2766:
2765:
2749:
2746:
2745:
2714:
2711:
2710:
2694:
2691:
2690:
2674:
2671:
2670:
2654:
2651:
2650:
2647:
2641:
2625:
2588:
2585:
2584:
2568:
2565:
2564:
2548:
2545:
2544:
2541:
2535:
2526:
2507:
2488:
2424:
2418:
2412:
2391:
2389:
2386:
2385:
2369:
2367:
2364:
2363:
2347:
2345:
2342:
2341:
2325:
2323:
2320:
2319:
2303:
2301:
2298:
2297:
2281:
2279:
2276:
2275:
2273:helper function
2256:
2254:
2251:
2250:
2243:
2211:u.parent = NIL
2201:
2137:
2135:
2132:
2131:
2115:
2113:
2110:
2109:
2093:
2091:
2088:
2087:
2071:
2069:
2066:
2065:
2049:
2047:
2044:
2043:
2024:
2022:
2019:
2018:
2002:
2000:
1997:
1996:
1980:
1978:
1975:
1974:
1958:
1956:
1953:
1952:
1936:
1934:
1931:
1930:
1911:
1909:
1906:
1905:
1889:
1887:
1884:
1883:
1867:
1865:
1862:
1861:
1845:
1843:
1840:
1839:
1820:
1818:
1815:
1814:
1798:
1796:
1793:
1792:
1776:
1774:
1771:
1770:
1754:
1752:
1749:
1748:
1729:
1727:
1724:
1723:
1707:
1705:
1702:
1701:
1685:
1683:
1680:
1679:
1663:
1661:
1658:
1657:
1641:
1639:
1636:
1635:
1615:
1613:
1610:
1609:
1593:
1591:
1588:
1587:
1567:
1565:
1562:
1561:
1554:
1533:
1531:
1528:
1527:
1511:
1509:
1506:
1505:
1504:, if it is not
1489:
1487:
1484:
1483:
1467:
1465:
1462:
1461:
1445:
1443:
1440:
1439:
1423:
1421:
1418:
1417:
1397:
1395:
1392:
1391:
1390:as a parent of
1375:
1373:
1370:
1369:
1362:
1296:
1287:
1267:
1237:
1198:
1141:
1139:
1136:
1135:
1119:
1117:
1114:
1113:
1097:
1095:
1092:
1091:
1075:
1073:
1070:
1069:
1053:
1051:
1048:
1047:
1031:
1029:
1026:
1025:
1009:
1007:
1004:
1003:
1000:
964:
961:
960:
957:height-balanced
940:
937:
936:
911:
908:
907:
887:
884:
883:
858:
855:
854:
843:
824:key < x.key
792:
771:
769:
766:
765:
749:
747:
744:
743:
736:
718:key < x.key
682:
661:
659:
656:
655:
639:
637:
634:
633:
628:
609:
604:
560:satisfying the
534:
515:red–black trees
503:height-balanced
471:
468:
467:
429:
413:priority queues
356:
353:
352:
336:
333:
332:
301:
298:
297:
251:time complexity
195:
186:
165:
156:
142:
133:
119:
110:
82:Time complexity
30:
23:
22:
15:
12:
11:
5:
4993:
4983:
4982:
4977:
4960:
4959:
4957:
4956:
4950:
4947:
4946:
4944:
4943:
4938:
4933:
4927:
4925:
4919:
4918:
4916:
4915:
4914:
4913:
4903:
4902:
4901:
4899:Hilbert R-tree
4896:
4891:
4881:
4880:
4879:
4877:Fibonacci heap
4874:
4869:
4859:
4858:
4857:
4852:
4847:
4845:Red–black tree
4842:
4837:
4827:
4821:
4819:
4813:
4812:
4810:
4809:
4804:
4799:
4794:
4789:
4783:
4781:
4775:
4774:
4772:
4771:
4766:
4761:
4756:
4751:
4746:
4740:
4738:
4732:
4731:
4729:
4728:
4727:
4726:
4721:
4711:
4710:
4709:
4702:Priority queue
4699:
4698:
4697:
4687:
4682:
4677:
4676:
4675:
4670:
4659:
4657:
4651:
4650:
4648:
4647:
4642:
4636:
4634:
4630:
4629:
4622:
4621:
4614:
4607:
4599:
4590:
4589:
4587:
4586:
4581:
4576:
4571:
4566:
4561:
4556:
4551:
4546:
4541:
4536:
4531:
4526:
4521:
4516:
4511:
4506:
4500:
4498:
4494:
4493:
4491:
4490:
4485:
4480:
4475:
4470:
4465:
4460:
4455:
4450:
4445:
4440:
4435:
4430:
4425:
4408:
4403:
4398:
4393:
4388:
4382:
4380:
4373:
4372:
4370:
4369:
4364:
4359:
4357:Ternary search
4354:
4349:
4344:
4339:
4334:
4328:
4326:
4320:
4319:
4317:
4316:
4311:
4306:
4301:
4296:
4291:
4286:
4281:
4273:
4268:
4263:
4257:
4255:
4249:
4248:
4246:
4245:
4240:
4235:
4230:
4225:
4220:
4215:
4205:
4200:
4195:
4190:
4185:
4180:
4170:
4165:
4160:
4155:
4150:
4145:
4140:
4135:
4130:
4124:
4122:
4106:
4105:
4098:
4097:
4090:
4083:
4075:
4069:
4068:
4062:
4050:
4049:External links
4047:
4046:
4045:
4029:"Binary Trees"
4024:
4000:
3994:
3976:
3947:
3941:
3907:
3876:
3873:
3870:
3869:
3834:
3803:
3772:
3753:(3): 652–686.
3721:
3711:
3693:
3665:(2): 123–137,
3655:Comer, Douglas
3646:
3639:
3600:
3586:
3551:
3544:
3522:
3504:(3): 303–320.
3481:
3474:
3433:
3402:
3375:
3357:. p. 12.
3338:
3301:
3294:
3226:
3219:
3209:(2 ed.).
3190:
3153:
3138:(in Russian).
3124:
3093:
3081:
3068:978-0201896855
3067:
3059:Addison-Wesley
3034:
2999:
2950:
2911:
2910:
2908:
2905:
2903:
2902:
2897:
2892:
2887:
2882:
2876:
2874:
2871:
2870:
2869:
2866:
2853:Priority queue
2851:Main article:
2848:
2845:
2829:Main article:
2826:
2823:
2821:
2818:
2802:red-black tree
2789:
2786:
2773:
2753:
2733:
2730:
2727:
2724:
2721:
2718:
2698:
2678:
2658:
2643:Main article:
2640:
2637:
2633:red–black tree
2624:
2621:
2607:
2604:
2601:
2598:
2595:
2592:
2572:
2552:
2537:Main article:
2534:
2531:
2528:
2527:
2515:x ≠ NIL
2510:
2508:
2496:x ≠ NIL
2491:
2489:
2476:x ≠ NIL
2471:
2463:
2462:
2456:
2450:
2416:Tree traversal
2414:Main article:
2411:
2408:
2245:
2244:
2235:v ≠ NIL
2206:
2203:
2202:
2177:D.right = NIL
2164:
2156:
2155:
2154:
2153:
2040:
1836:
1745:
1553:
1550:
1364:
1363:
1314:x ≠ NIL
1309:
1295:
1292:
1289:
1288:
1270:
1268:
1250:
1239:
1238:
1221:y ≠ NIL
1201:
1199:
1182:y ≠ NIL
1162:
999:
996:
983:
980:
977:
974:
971:
968:
959:the height is
944:
924:
921:
918:
915:
891:
871:
868:
865:
862:
845:
844:
813:x ≠ NIL
808:
791:
788:
738:
737:
698:
684:The following
681:
678:
608:
605:
603:
600:
590:such as sets,
533:
530:
526:Evgenii Landis
490:
487:
484:
481:
478:
475:
457:magnetic tapes
428:
425:
415:, and used in
394:Evgenii Landis
382:self-balancing
369:
366:
363:
360:
340:
320:
317:
314:
311:
308:
305:
247:data structure
207:
206:
203:
202:
193:
184:
180:
179:
173:
172:
163:
154:
150:
149:
140:
131:
127:
126:
117:
108:
104:
103:
98:
93:
89:
88:
86:big O notation
74:
73:
61:P.F. Windley,
59:
55:
54:
51:
47:
46:
43:
37:
36:
28:
9:
6:
4:
3:
2:
4992:
4981:
4978:
4976:
4973:
4972:
4970:
4955:
4952:
4951:
4948:
4942:
4939:
4937:
4934:
4932:
4929:
4928:
4926:
4924:
4920:
4912:
4909:
4908:
4907:
4904:
4900:
4897:
4895:
4892:
4890:
4887:
4886:
4885:
4882:
4878:
4875:
4873:
4872:Binomial heap
4870:
4868:
4865:
4864:
4863:
4860:
4856:
4853:
4851:
4848:
4846:
4843:
4841:
4838:
4836:
4833:
4832:
4831:
4828:
4826:
4823:
4822:
4820:
4818:
4814:
4808:
4805:
4803:
4800:
4798:
4795:
4793:
4790:
4788:
4785:
4784:
4782:
4780:
4776:
4770:
4769:Sparse matrix
4767:
4765:
4762:
4760:
4757:
4755:
4754:Dynamic array
4752:
4750:
4747:
4745:
4742:
4741:
4739:
4737:
4733:
4725:
4722:
4720:
4717:
4716:
4715:
4712:
4708:
4705:
4704:
4703:
4700:
4696:
4693:
4692:
4691:
4688:
4686:
4683:
4681:
4678:
4674:
4671:
4669:
4666:
4665:
4664:
4661:
4660:
4658:
4656:
4652:
4646:
4643:
4641:
4638:
4637:
4635:
4631:
4627:
4620:
4615:
4613:
4608:
4606:
4601:
4600:
4597:
4585:
4582:
4580:
4577:
4575:
4572:
4570:
4567:
4565:
4562:
4560:
4557:
4555:
4552:
4550:
4547:
4545:
4542:
4540:
4537:
4535:
4534:Hash calendar
4532:
4530:
4527:
4525:
4522:
4520:
4517:
4515:
4512:
4510:
4507:
4505:
4502:
4501:
4499:
4495:
4489:
4486:
4484:
4481:
4479:
4476:
4474:
4471:
4469:
4466:
4464:
4461:
4459:
4456:
4454:
4451:
4449:
4446:
4444:
4441:
4439:
4436:
4434:
4431:
4429:
4426:
4423:
4421:
4415:
4413:
4409:
4407:
4404:
4402:
4399:
4397:
4394:
4392:
4389:
4387:
4384:
4383:
4381:
4378:
4374:
4368:
4365:
4363:
4360:
4358:
4355:
4353:
4350:
4348:
4345:
4343:
4340:
4338:
4335:
4333:
4330:
4329:
4327:
4325:
4321:
4315:
4312:
4310:
4309:van Emde Boas
4307:
4305:
4302:
4300:
4299:Skew binomial
4297:
4295:
4292:
4290:
4287:
4285:
4282:
4280:
4278:
4274:
4272:
4269:
4267:
4264:
4262:
4259:
4258:
4256:
4254:
4250:
4244:
4241:
4239:
4236:
4234:
4231:
4229:
4226:
4224:
4221:
4219:
4216:
4214:
4210:
4206:
4204:
4201:
4199:
4196:
4194:
4191:
4189:
4186:
4184:
4181:
4179:
4178:Binary search
4175:
4171:
4169:
4166:
4164:
4161:
4159:
4156:
4154:
4151:
4149:
4146:
4144:
4141:
4139:
4136:
4134:
4131:
4129:
4126:
4125:
4123:
4120:
4116:
4111:
4107:
4103:
4096:
4091:
4089:
4084:
4082:
4077:
4076:
4073:
4066:
4063:
4060:
4058:
4053:
4052:
4042:
4038:
4034:
4030:
4025:
4021:
4017:
4011:
4006:
4001:
3997:
3995:0-201-89685-0
3991:
3987:
3986:
3981:
3980:Knuth, Donald
3977:
3965:
3961:
3957:
3953:
3948:
3944:
3942:0-262-03293-7
3938:
3934:
3930:
3929:
3924:
3920:
3916:
3912:
3908:
3904:
3900:
3899:
3894:
3888:
3879:
3878:
3857:
3853:
3849:
3845:
3838:
3822:
3818:
3814:
3807:
3791:
3787:
3783:
3776:
3768:
3764:
3760:
3756:
3752:
3748:
3747:
3739:
3735:
3731:
3725:
3718:
3714:
3712:9780201896855
3708:
3704:
3697:
3690:
3686:
3682:
3678:
3673:
3668:
3664:
3660:
3656:
3650:
3642:
3636:
3632:
3628:
3627:
3622:
3618:
3614:
3610:
3604:
3593:
3589:
3587:0-8186-1982-1
3583:
3579:
3575:
3571:
3570:
3562:
3555:
3547:
3545:0-934613-18-4
3541:
3536:
3535:
3526:
3515:
3511:
3507:
3503:
3499:
3492:
3485:
3477:
3475:9780511800191
3471:
3467:
3463:
3459:
3455:
3454:
3446:
3444:
3442:
3440:
3438:
3421:
3417:
3413:
3406:
3390:
3386:
3379:
3360:
3356:
3349:
3342:
3334:
3330:
3326:
3322:
3318:
3317:
3312:
3305:
3297:
3295:0-262-03293-7
3291:
3287:
3283:
3282:
3277:
3273:
3269:
3265:
3259:
3257:
3255:
3253:
3251:
3249:
3247:
3245:
3243:
3241:
3239:
3237:
3235:
3233:
3231:
3222:
3220:9780198099307
3216:
3212:
3207:
3206:
3197:
3195:
3175:
3171:
3164:
3157:
3150:
3146:
3141:
3137:
3136:
3128:
3112:
3108:
3104:
3097:
3091:
3085:
3074:
3070:
3064:
3060:
3053:
3052:
3047:
3046:Knuth, Donald
3041:
3039:
3029:
3024:
3020:
3016:
3015:
3010:
3003:
2995:
2991:
2987:
2983:
2979:
2975:
2971:
2967:
2966:
2961:
2954:
2945:
2940:
2936:
2932:
2931:
2926:
2919:
2917:
2912:
2901:
2898:
2896:
2893:
2891:
2888:
2886:
2883:
2881:
2878:
2877:
2867:
2864:
2863:
2862:
2860:
2854:
2844:
2842:
2838:
2832:
2817:
2815:
2811:
2807:
2803:
2799:
2795:
2785:
2771:
2751:
2728:
2725:
2722:
2716:
2696:
2676:
2656:
2646:
2636:
2634:
2630:
2620:
2602:
2599:
2596:
2590:
2570:
2550:
2540:
2525:
2522:
2518:
2514:
2509:
2506:
2502:
2499:
2495:
2490:
2487:
2483:
2479:
2475:
2470:
2469:
2466:
2460:
2457:
2454:
2451:
2448:
2445:
2444:
2443:
2441:
2437:
2433:
2429:
2426:A BST can be
2423:
2417:
2407:
2274:
2242:
2238:
2234:
2230:
2226:
2222:
2218:
2214:
2210:
2205:
2204:
2200:
2196:
2192:
2188:
2184:
2180:
2176:
2172:
2169:D.left = NIL
2168:
2163:
2162:
2159:
2041:
1928:
1927:
1837:
1746:
1633:
1632:
1631:
1558:
1549:
1415:
1361:
1357:
1353:
1349:
1345:
1341:
1337:
1333:
1329:
1325:
1321:
1317:
1313:
1308:
1307:
1304:
1302:
1285:
1282:
1278:
1274:
1269:
1265:
1262:
1258:
1254:
1249:
1248:
1245:
1235:
1232:
1228:
1224:
1220:
1216:
1212:
1209:
1205:
1200:
1196:
1193:
1189:
1185:
1181:
1177:
1173:
1170:
1166:
1161:
1160:
1157:
995:
978:
975:
972:
966:
958:
942:
919:
913:
905:
889:
866:
860:
852:
841:
838:
835:
831:
827:
823:
820:
816:
812:
807:
806:
803:
801:
797:
787:
735:
731:
728:
724:
721:
717:
713:
710:
706:
702:
697:
696:
693:
691:
687:
677:
631:
625:
620:
618:
614:
599:
597:
593:
589:
584:
582:
578:
574:
570:
565:
563:
562:binary search
559:
555:
551:
548:to that node
547:
543:
539:
529:
527:
523:
518:
516:
512:
508:
504:
485:
482:
479:
473:
465:
460:
458:
454:
450:
449:David Wheeler
446:
442:
438:
434:
424:
422:
418:
414:
410:
409:lookup tables
406:
402:
397:
395:
391:
387:
383:
364:
358:
338:
315:
312:
309:
303:
295:
291:
286:
284:
278:
276:
275:David Wheeler
272:
268:
263:
262:binary search
258:
256:
252:
248:
245:
242:
238:
234:
230:
226:
222:
213:
199:
194:
190:
185:
181:
178:
174:
169:
164:
160:
155:
151:
146:
141:
137:
132:
128:
123:
118:
114:
109:
105:
102:
99:
97:
94:
90:
87:
83:
79:
75:
72:
68:
64:
60:
56:
52:
48:
44:
42:
38:
33:
27:
19:
4980:Search trees
4975:Binary trees
4829:
4724:Disjoint-set
4419:
4411:
4276:
4209:Left-leaning
4177:
4115:dynamic sets
4110:Search trees
4056:
4032:
4020:SUNY Oneonta
4015:
4003:Long, Sean.
3983:
3968:. Retrieved
3964:the original
3955:
3927:
3896:
3860:. Retrieved
3837:
3825:. Retrieved
3806:
3794:. Retrieved
3775:
3750:
3744:
3724:
3716:
3702:
3696:
3662:
3658:
3649:
3625:
3603:
3568:
3554:
3533:
3525:
3501:
3497:
3484:
3452:
3424:. Retrieved
3405:
3393:. Retrieved
3378:
3366:. Retrieved
3341:
3320:
3314:
3304:
3280:
3204:
3181:. Retrieved
3156:
3148:
3139:
3133:
3127:
3115:. Retrieved
3096:
3084:
3050:
3018:
3012:
3002:
2969:
2965:Algorithmica
2963:
2953:
2937:(1): 68–69.
2934:
2928:
2856:
2834:
2791:
2648:
2626:
2542:
2523:
2520:
2516:
2512:
2504:
2500:
2497:
2493:
2485:
2481:
2477:
2473:
2464:
2458:
2452:
2446:
2442:tree walks.
2425:
2248:
2240:
2236:
2232:
2228:
2224:
2220:
2216:
2212:
2208:
2198:
2194:
2190:
2186:
2182:
2178:
2174:
2170:
2166:
2157:
2064:lies within
1904:, displaces
1585:
1413:
1367:
1359:
1355:
1351:
1347:
1343:
1339:
1335:
1331:
1327:
1323:
1319:
1315:
1311:
1297:
1283:
1280:
1276:
1272:
1263:
1260:
1256:
1252:
1242:
1233:
1230:
1226:
1222:
1218:
1214:
1210:
1207:
1203:
1194:
1191:
1187:
1186:x = y.right
1183:
1179:
1175:
1171:
1168:
1164:
1001:
848:
839:
836:
833:
829:
825:
821:
818:
814:
810:
793:
741:
733:
729:
726:
722:
719:
715:
711:
708:
707:key = x.key
704:
700:
683:
621:
610:
585:
566:
557:
553:
549:
541:
535:
519:
502:
461:
453:labeled data
437:Andrew Colin
430:
405:dynamic sets
398:
287:
279:
259:
236:
232:
228:
224:
218:
197:
188:
167:
158:
144:
135:
121:
112:
100:
95:
71:T.N. Hibbard
67:A.J.T. Colin
26:
4867:Binary heap
4792:Linked list
4509:Exponential
4497:Other trees
4054:Ben Pfaff:
3811:Xiong, Li.
2880:Search tree
2283:Shift-Nodes
1225:x = y.left
617:iteratively
613:recursively
581:linked list
244:binary tree
58:Invented by
4969:Categories
4855:Splay tree
4759:Hash table
4640:Collection
4453:Priority R
4203:Palindrome
3862:21 October
3796:21 October
3426:21 October
3383:Ray, Ray.
3142:: 263–266.
2907:References
2814:Splay tree
2521:visit node
2501:visit node
2482:visit node
2420:See also:
2258:BST-Delete
1995:displaces
1301:leaf nodes
1156:in a BST.
796:while loop
686:pseudocode
602:Operations
564:property.
501:. Various
294:on average
101:Worst case
63:A.D. Booth
4911:Hash tree
4797:Skip list
4744:Bit array
4645:Container
4539:iDistance
4418:implicit
4406:Hilbert R
4401:Cartesian
4284:Fibonacci
4218:Scapegoat
4213:Red–black
3933:MIT Press
3681:0360-0300
3286:MIT Press
3021:(2): 84.
2841:quicksort
2837:tree sort
2831:Tree sort
2772:α
2752:α
2726:
2677:α
2600:
2440:postorder
2428:traversed
2410:Traversal
1560:The node
1294:Insertion
976:
851:leaf node
800:efficient
690:recursion
624:root node
607:Searching
592:multisets
546:sub-trees
507:AVL trees
483:
421:tree sort
386:AVL trees
313:
92:Operation
4840:AVL tree
4719:Multiset
4668:Multimap
4655:Abstract
4554:Link/cut
4266:Binomial
4193:Interval
4041:Archived
3970:30 April
3856:Archived
3821:Archived
3790:Archived
3736:(1985).
3592:archived
3514:Archived
3420:Archived
3359:Archived
3278:(2001).
3174:Archived
3111:Archived
3073:Archived
2873:See also
2810:2–3 tree
2629:AVL tree
2436:preorder
1552:Deletion
1342:y = NIL
703:x = NIL
569:sortings
532:Overview
419:such as
403:such as
50:Invented
4894:R+ tree
4889:R* tree
4835:AA tree
4514:Fenwick
4478:Segment
4377:Spatial
4294:Pairing
4289:Leftist
4211:)
4183:Dancing
4176:)
4174:Optimal
3767:1165848
3327:: 158.
2980:: 297.
2972:(1–4).
2432:inorder
2231:8
2217:else if
2175:else if
1348:else if
1334:11
902:is the
764:or the
427:History
239:, is a
233:ordered
96:Average
4923:Graphs
4884:R-tree
4825:B-tree
4779:Linked
4736:Arrays
4564:Merkle
4529:Fusion
4519:Finger
4443:Octree
4433:Metric
4367:Y-fast
4362:X-fast
4352:Suffix
4271:Brodal
4261:Binary
3992:
3939:
3827:4 June
3765:
3709:
3689:101673
3687:
3679:
3637:
3633:–301.
3584:
3542:
3472:
3395:17 May
3368:17 May
3292:
3217:
3183:19 May
3117:19 May
3065:
2994:971813
2992:
2812:, and
2806:B-tree
2794:T-tree
2524:end if
2505:end if
2486:end if
2438:, and
2241:end if
2229:end if
2199:end if
2195:end if
1882:, say
1360:end if
1336:repeat
1332:end if
1284:return
1281:repeat
1264:return
1261:repeat
1234:return
1231:repeat
1215:end if
1211:return
1195:return
1192:repeat
1176:end if
1172:return
935:where
882:where
840:return
837:repeat
834:end if
734:end if
730:return
723:return
714:x
712:return
594:, and
513:, and
511:Treaps
255:linear
241:rooted
157:O(log
153:Delete
134:O(log
130:Insert
111:O(log
107:Search
69:, and
4817:Trees
4690:Queue
4685:Stack
4633:Types
4574:Range
4544:K-ary
4504:Cover
4347:Radix
4332:Ctrie
4324:Tries
4253:Heaps
4233:Treap
4223:Splay
4188:HTree
4143:(a,b)
4133:2–3–4
3889:from
3763:S2CID
3741:(PDF)
3685:S2CID
3595:(PDF)
3564:(PDF)
3517:(PDF)
3494:(PDF)
3362:(PDF)
3351:(PDF)
3323:(1).
3177:(PDF)
3166:(PDF)
3076:(PDF)
3055:(PDF)
2990:S2CID
2798:treap
2788:Types
2384:from
2318:with
1414:while
1312:while
1273:while
1253:while
1219:while
1180:while
811:while
183:Space
4906:Trie
4862:Heap
4680:List
4579:SPQR
4458:Quad
4386:Ball
4342:Hash
4314:Weak
4304:Skew
4279:-ary
3990:ISBN
3972:2006
3937:ISBN
3903:NIST
3864:2021
3829:2022
3798:2021
3707:ISBN
3677:ISSN
3635:ISBN
3582:ISBN
3540:ISBN
3470:ISBN
3428:2021
3397:2022
3370:2021
3290:ISBN
3215:ISBN
3185:2022
3119:2022
3063:ISBN
2825:Sort
2517:then
2498:then
2478:then
2249:The
2237:then
2225:else
2221:then
2213:then
2191:then
2183:else
2179:then
2171:then
2017:and
1356:else
1352:then
1344:then
1328:else
1324:then
1208:then
1169:then
830:else
826:then
727:else
720:then
709:then
571:and
524:and
447:and
411:and
392:and
331:for
288:The
273:and
223:, a
53:1960
45:tree
41:Type
4714:Set
4584:Top
4438:MVP
4396:BSP
4148:AVL
4128:2–3
4010:PPT
3755:doi
3667:doi
3631:273
3574:doi
3506:doi
3462:doi
3329:doi
3140:146
3023:doi
2982:doi
2939:doi
2723:log
2597:log
2393:BST
2349:BST
2042:If
1951:is
1929:If
1838:If
1747:If
1731:BST
1687:NIL
1634:If
1617:BST
1513:nil
1447:nil
1438:is
1223:and
1184:and
973:log
815:and
773:key
751:nil
663:nil
641:nil
629:nil
615:or
583:.
517:.
480:log
455:in
310:log
235:or
229:BST
219:In
84:in
4971::
4569:PQ
4483:VP
4473:R*
4468:R+
4448:PH
4422:-d
4414:-d
4391:BK
4238:UB
4163:B*
4158:B+
4138:AA
4039:.
4035:.
4031:.
4018:.
4014:.
3958:.
3954:.
3921:;
3917:;
3913:;
3901:.
3895:.
3854:.
3850:,
3846:.
3815:.
3788:.
3784:.
3761:.
3751:32
3749:.
3743:.
3732:;
3715:.
3683:,
3675:,
3663:11
3661:,
3619:;
3615:;
3611:;
3590:,
3580:,
3566:,
3512:.
3502:11
3500:.
3496:.
3468:.
3460:.
3456:.
3436:^
3418:.
3414:.
3387:.
3353:.
3321:25
3319:.
3313:.
3288:.
3274:;
3270:;
3266:;
3229:^
3213:.
3193:^
3168:.
3105:.
3071:.
3037:^
3017:.
3011:.
2988:.
2976:,
2968:.
2962:.
2935:32
2933:.
2927:.
2915:^
2843:.
2816:.
2808:,
2804:,
2800:,
2796:,
2513:if
2494:if
2474:if
2434:,
2406:.
2233:if
2209:if
2187:if
2167:if
1340:if
1320:if
1316:do
1286:x
1277:do
1266:x
1257:do
1236:y
1227:do
1204:if
1197:y
1188:do
1165:if
994:.
842:x
822:if
819:do
802:.
716:if
705:or
701:if
692:.
619:.
598:.
558:A,
509:,
439:,
435:,
423:.
407:,
396:.
285:.
277:.
196:O(
187:O(
166:O(
143:O(
120:O(
65:,
4618:e
4611:t
4604:v
4488:X
4463:R
4428:M
4424:)
4420:k
4416:(
4412:k
4277:d
4228:T
4207:(
4172:(
4168:B
4153:B
4121:)
4117:/
4113:(
4094:e
4087:t
4080:v
4059:.
4022:.
4012:)
4008:(
3998:.
3974:.
3945:.
3905:.
3866:.
3831:.
3769:.
3757::
3669::
3643:.
3576::
3548:.
3508::
3478:.
3464::
3430:.
3399:.
3372:.
3335:.
3331::
3298:.
3223:.
3187:.
3121:.
3031:.
3025::
3019:3
2996:.
2984::
2970:5
2947:.
2941::
2732:)
2729:n
2720:(
2717:O
2697:1
2657:1
2606:)
2603:n
2594:(
2591:O
2571:n
2551:n
2371:u
2327:v
2305:u
2139:Z
2117:Y
2095:Z
2073:Z
2051:Y
2026:Y
2004:Z
1982:Y
1960:Z
1938:Y
1913:Z
1891:Y
1869:Z
1847:Z
1822:Z
1800:Z
1778:Z
1756:Z
1709:Z
1665:Z
1643:Z
1595:Z
1569:D
1535:y
1491:T
1469:z
1425:y
1399:x
1377:y
1143:x
1121:x
1099:x
1077:x
1055:x
1033:x
1011:x
982:)
979:n
970:(
967:O
943:n
923:)
920:n
917:(
914:O
890:h
870:)
867:h
864:(
861:O
554:A
550:A
542:A
489:)
486:n
477:(
474:O
368:)
365:n
362:(
359:O
339:n
319:)
316:n
307:(
304:O
227:(
200:)
198:n
191:)
189:n
170:)
168:n
161:)
159:n
147:)
145:n
138:)
136:n
124:)
122:n
115:)
113:n
20:)
Text is available under the Creative Commons Attribution-ShareAlike License. Additional terms may apply.