60:
529:
209:
517:
505:
40:
261:. The superior pubic ligament connects together the two pubic bones superiorly, extending laterally as far as the pubic tubercles. The inferior ligament in the pubic arch is also known as the arcuate pubic ligament or subpubic ligament; it is a thick, triangular arch of ligamentous fibers, connecting together the two pubic bones below, and forming the upper boundary of the
373:
The pubic symphysis widens slightly when the legs are stretched far apart. In sports where these movements are often performed, the risk of a pubic symphysis blockage is high, in which case, after completion of the movement, the bones at the symphysis do not realign correctly and can get jammed in a
427:
remodel this ligamentous capsule allowing the pelvic bones to be more flexible for delivery. The gap of the symphysis pubis, normally is 4–5 mm but during pregnancy there will be an increase of at least 2–3 mm, therefore, it is considered that a total width of up to 9 mm between the
356:
Analysis of the pelvis shows the skinny regions function as arches, transferring the weight of the upright trunk from the sacrum to the hips. The symphysis pubis connects these two weight-bearing arches, and the ligaments that surround this pelvic region maintain the mechanical integrity.
339:
In the newborn, the symphysis pubis is 9–10 mm in width, with thick cartilaginous end-plates. By mid-adolescence the adult size is achieved. During adulthood the end-plates decrease in width to a thinner layer. Degeneration of the symphysis pubis accompanies aging and
849:
Obstetrics and
Gynaecology in The Tropics and Developing Countries. J. B. Lawson, Professor of Obstetrics and Gynaecology, University of Ibadan, Nigeria; D. B. Stewart, Professor of Obstetrics and Gynaecology, University of The West Indies,
403:, the most common inflammatory disease in this area, is treated with anti-inflammatory medication and rest. Degenerative joint disease of the symphysis, which can cause groin pain, results from instability or from abnormal pelvic mechanics.
475:
This practice was carried out in Europe before the introduction of the
Caesarean section. Historically, during obstructed labor, the skull of the fetus was also, at least occasionally, crushed in order to further facilitate the delivery.
493:, as they can be used to estimate the age of adult skeletons. Throughout life, the surfaces are worn at a fairly predictable rate. By examining the wear of the pubic symphysis, it is possible to estimate the age of the person at death.
378:
position. The resulting pain can be severe, especially when further strain is put upon the affected joint. In most cases, the joint can only be successfully reduced into its normal position by a trained medical professional.
463:
is a surgical procedure in which the cartilage of the pubic symphysis is divided to widen the pelvis allowing childbirth when there is a mechanical problem. It allows the safe delivery of the fetus where
331:
is the white, shiny gristle at the end of long bones. This cartilage has poor healing potential, and efforts to induce it to repair itself frequently end up with a similar, but poorer fibrocartilage.
234:
attached to the fibrocartilage. The fibrocartilaginous disk is reinforced by a series of ligaments. These ligaments cling to the fibrocartilaginous disk to the point that fibers intermix with it.
360:
The main motions of the symphysis pubis are superior/inferior glide and separation/compression. The functions of the joint are to absorb shock during walking and allow delivery of a baby.
230:, possibly due to the nature of the compressive forces passing through this joint, which may lead to harmful vascular disease. The ends of both pubic bones are covered by a thin layer of
320:. Perichondrium surrounds the cartilage of developing bone; it has a layer of dense, irregular connective tissue and functions in the growth and repair of cartilage.
245:, which provide the most stability; the anterior and posterior ligaments are weaker. The strong and thicker superior ligament is reinforced by the tendons of the
344:. Women have a greater thickness of this pubic disc which allows more mobility of the pelvic bones, hence providing a greater diameter of pelvic cavity during
133:
955:
528:
109:
1133:
222:
joint. The width of the pubic symphysis at the front is 3–5 mm greater than its width at the back. This joint is connected by
193:. In most adults, it can be moved roughly 2 mm and with 1 degree rotation. This increases for women at the time of childbirth.
948:
1261:
304:. The collagenous fibers are usually placed in an orderly arrangement parallel to tension on the tissue. It has a low content of
766:
Scicluna, J.K.; et al. (January 2004). "Epidural analgesia for acute symphysis pubis dysfunction in the second trimester".
1079:
17:
265:. Above, it is blended with the interpubic fibrocartilaginous lamina; laterally, it is attached to the inferior rami of the
1306:
941:
873:
Franklin, D (January 2010). "Forensic age estimation in human skeletal remains: current concepts and future directions".
190:
1212:
250:
1443:
1207:
186:
1256:
1153:
1012:
1311:
1148:
1007:
910:
1438:
918:
at the SUNY Downstate
Medical Center – "Major Joints of the Lower Extremity – hip and sacrum (anterior view)"
274:
128:
662:
Gamble, J.G.; Simmons, S.C. (February 1986). "The
Symphysis Pubis: Anatomic and Pathologic Considerations".
516:
1433:
1117:
927:
504:
1326:
1248:
1113:
697:
Lebel, D.E.; et al. (2010). "Symphysiolysis as an independent risk factor for cesarean delivery".
433:
1279:
1199:
1053:
921:
915:
803:"Pregnancy-related pelvic girdle pain (PPP), I: Terminology, clinical presentation, and prevalence"
411:
is separation or slipping of the symphysis. It has been estimated to occur in 0.2% of pregnancies.
92:
1415:
1410:
1128:
452:(PGP). Overall, about 45% of all pregnant women and 25% of all women postpartum suffer from PGP.
246:
1452:
1316:
545:
396:
140:
116:
104:
428:
two bones is normal for a pregnant woman. The symphysis pubis separates to some degree during
1457:
1271:
1239:
1048:
1036:
490:
437:
1284:
388:
270:
174:
45:
8:
1379:
1344:
1298:
1189:
1104:
1075:
170:
924:
at the SUNY Downstate
Medical Center – "The Male Pelvis: Hemisection of the Male Pelvis"
1387:
827:
802:
722:
639:
614:
590:
565:
449:
305:
258:
468:
is not an option. Symphysiotomy is suggested for woman in isolated areas experiencing
1181:
890:
832:
783:
714:
679:
675:
644:
630:
595:
581:
465:
375:
328:
297:
231:
726:
300:
bundles have cartilage cells between them; these cells to a certain extent resemble
189:
attaches to the pubic symphysis. In females, the pubic symphysis is attached to the
1425:
1084:
999:
980:
886:
882:
822:
814:
775:
706:
671:
634:
626:
585:
577:
469:
1487:
1482:
1392:
1041:
1031:
309:
254:
182:
97:
933:
1095:
1023:
779:
534:
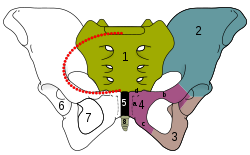
Anterior view of the body pelvis from a dissection. Pubic symphysis anteriorly.
407:
400:
289:
223:
219:
818:
710:
395:
results in calcific deposits in the symphysis. Inflammatory diseases, such as
1476:
1123:
460:
317:
292:
is composed of small, chained bundles of thick, clearly defined, type I
121:
1366:
894:
836:
787:
718:
648:
599:
313:
227:
178:
49:
683:
1375:
1163:
989:
301:
266:
146:
59:
429:
392:
345:
262:
208:
1067:
420:
341:
27:
Cartilaginous joint between the front of the left and right hip bones
968:
445:
293:
216:
752:"Pubic Symphysial Diastasis During Normal Vaginal Delivery of a",
441:
424:
44:
The pubic symphysis sits between and joins of the left and right
756:
Vol. 55 No. 4 July/August 2005 pp:365-366 S. A. Panditrao et al.
1230:
278:
972:
964:
269:; below, it is free, and is separated from the fascia of the
80:
930:—Plastination Laboratory at the Medical University of Vienna
743:(2002), 13: 141-155 Kelly Owens, Anne Pearson, Gerald Mason.
448:
condition. A diastasis of the symphysis pubis is a cause of
308:(2% of dry weight). Glycosaminoglycans are long, unbranched
312:(relatively complex carbohydrates) consisting of repeating
39:
566:"The adult human pubic symphysis: a systematic review"
563:
226:
and may contain a fluid-filled cavity; the center is
564:Becker, I.; Woodley, S.J.; Stringer, M.D. (2010).
316:units. Fibrocartilage does not have a surrounding
963:
768:International Journal of Obstetric Anesthesiology
472:where other medical intervention is unavailable.
1474:
489:Pubic symphyses have importance in the field of
699:Journal of Maternal-Fetal and Neonatal Medicine
612:
484:
949:
661:
432:. In some women this separation can become a
1449:ligaments connecting the sacrum and ischium
615:"Nutrition pathways to the symphysis pubis"
440:could be the result of a rapid birth, or a
988:
956:
942:
664:Clinical Orthopaedics and Related Research
399:, result in bony fusion of the symphysis.
58:
38:
1134:Tectorial membrane of atlanto-axial joint
928:Cross section image: pelvis/pelvis-e12-15
911:Pelvic Instability Network Support (PINS)
826:
638:
589:
872:
765:
613:da Rocha, RC; Chopard, RP (March 2004).
522:Median sagittal section of female pelvis
363:
207:
14:
1475:
510:Median sagittal section of male pelvis
479:
937:
696:
1307:intraarticular sternocostal ligament
496:
323:
196:The name comes from the Greek word
191:suspensory ligament of the clitoris
162:
24:
800:
741:Fetal and Maternal Medicine Review
181:. It is in front of and below the
25:
1499:
1213:posterior sacrococcygeal ligament
904:
284:
251:abdominal external oblique muscle
86:symphysis pubica, symphysis pubis
1444:interosseous sacroiliac ligament
1208:anterior sacrococcygeal ligament
676:10.1097/00003086-198602000-00033
631:10.1111/j.0021-8782.2004.00271.x
582:10.1111/j.1469-7580.2010.01300.x
527:
515:
503:
455:
434:diastasis of the symphysis pubis
273:by an opening through which the
187:suspensory ligament of the penis
1154:posterior atlantoaxial ligament
1013:posterior longitudinal ligament
866:
853:
423:in the human, hormones such as
1312:radiate sternocostal ligaments
1149:anterior atlantoaxial ligament
1008:anterior longitudinal ligament
887:10.1016/j.legalmed.2009.09.001
861:New York Times Review of Books
843:
801:Wu, W.H.; et al. (2004).
794:
759:
746:
739:"Pubic symphysis separation".
733:
690:
655:
606:
557:
334:
200:, meaning 'growing together'.
13:
1:
1439:posterior sacroiliac ligament
875:Legal Medicine (Tokyo, Japan)
551:
275:deep dorsal vein of the penis
1434:anterior sacroiliac ligament
1118:Transverse ligament of atlas
485:Use in forensic anthropology
414:
387:Metabolic diseases, such as
203:
7:
539:
351:
237:Two such ligaments are the
173:between the left and right
10:
1504:
1114:Cruciate ligament of atlas
780:10.1016/j.ijoa.2003.08.006
543:
391:, produce widening, while
382:
1424:
1401:
1374:
1365:
1343:
1325:
1297:
1270:
1247:
1238:
1229:
1198:
1180:
1162:
1103:
1094:
1066:
1021:
997:
979:
819:10.1007/s00586-003-0615-y
711:10.3109/14767050903420291
368:
215:The pubic symphysis is a
139:
127:
115:
103:
91:
79:
74:
69:
57:
37:
32:
1280:Costotransverse ligament
1262:Intra-articular ligament
1054:intertransverse ligament
922:Anatomy photo:44:03-0104
916:Anatomy photo:17:st-0206
1416:inferior pubic ligament
1411:superior pubic ligament
1129:Apical ligament of dens
247:rectus abdominis muscle
243:inferior pubic ligament
239:superior pubic ligament
1453:sacrotuberous ligament
1317:costoxiphoid ligaments
807:European Spine Journal
754:Journal of Obste India
546:anatomical terminology
444:delivery, or may be a
397:ankylosing spondylitis
212:
141:Anatomical terminology
64:#5 is pubic symphysis.
18:Arcuate pubic ligament
1458:sacrospinous ligament
1049:interspinous ligament
1037:supraspinous ligament
491:forensic anthropology
364:Clinical significance
296:fibers. This fibrous
211:
1285:Lumbocostal ligament
389:renal osteodystrophy
271:urogenital diaphragm
177:of the pubis of the
1190:iliolumbar ligament
1076:intervertebral disc
480:Society and culture
171:cartilaginous joint
1388:Obturator membrane
619:Journal of Anatomy
570:Journal of Anatomy
544:This article uses
450:pelvic girdle pain
306:glycosaminoglycans
259:muscles of the hip
213:
1470:
1469:
1466:
1465:
1361:
1360:
1293:
1292:
1225:
1224:
1221:
1220:
1062:
1061:
863:, 22 October 2006
859:Hope Langer, MD;
497:Additional images
466:caesarean section
329:Hyaline cartilage
324:Hyaline cartilage
298:connective tissue
232:hyaline cartilage
169:) is a secondary
155:
154:
150:
16:(Redirected from
1495:
1372:
1371:
1257:Radiate ligament
1245:
1244:
1236:
1235:
1101:
1100:
1085:nucleus pulposus
1024:vertebral arches
1000:vertebral bodies
995:
994:
986:
985:
958:
951:
944:
935:
934:
899:
898:
870:
864:
857:
851:
847:
841:
840:
830:
798:
792:
791:
763:
757:
750:
744:
737:
731:
730:
694:
688:
687:
670:(203): 261–272.
659:
653:
652:
642:
610:
604:
603:
593:
561:
531:
519:
507:
470:obstructed labor
277:passes into the
185:. In males, the
164:
147:edit on Wikidata
144:
62:
42:
30:
29:
21:
1503:
1502:
1498:
1497:
1496:
1494:
1493:
1492:
1473:
1472:
1471:
1462:
1420:
1403:Pubic symphysis
1397:
1393:Obturator canal
1357:
1339:
1321:
1289:
1272:Costotransverse
1266:
1217:
1194:
1176:
1158:
1090:
1080:anulus fibrosus
1058:
1042:nuchal ligament
1032:ligamenta flava
1017:
975:
962:
907:
902:
871:
867:
858:
854:
848:
844:
799:
795:
764:
760:
751:
747:
738:
734:
695:
691:
660:
656:
611:
607:
562:
558:
554:
549:
542:
535:
532:
523:
520:
511:
508:
499:
487:
482:
458:
417:
385:
371:
366:
354:
337:
326:
310:polysaccharides
287:
255:gracilis muscle
220:amphiarthrodial
206:
183:urinary bladder
159:pubic symphysis
151:
65:
53:
33:Pubic symphysis
28:
23:
22:
15:
12:
11:
5:
1501:
1491:
1490:
1485:
1468:
1467:
1464:
1463:
1461:
1460:
1455:
1446:
1441:
1436:
1430:
1428:
1422:
1421:
1419:
1418:
1413:
1407:
1405:
1399:
1398:
1396:
1395:
1390:
1384:
1382:
1369:
1363:
1362:
1359:
1358:
1356:
1355:
1349:
1347:
1341:
1340:
1338:
1337:
1331:
1329:
1323:
1322:
1320:
1319:
1314:
1309:
1303:
1301:
1295:
1294:
1291:
1290:
1288:
1287:
1282:
1276:
1274:
1268:
1267:
1265:
1264:
1259:
1253:
1251:
1242:
1240:Costovertebral
1233:
1227:
1226:
1223:
1222:
1219:
1218:
1216:
1215:
1210:
1204:
1202:
1200:Sacrococcygeal
1196:
1195:
1193:
1192:
1186:
1184:
1178:
1177:
1175:
1174:
1168:
1166:
1160:
1159:
1157:
1156:
1151:
1145:
1144:
1137:
1136:
1131:
1126:
1121:
1109:
1107:
1098:
1096:Synovial joint
1092:
1091:
1089:
1088:
1082:
1072:
1070:
1064:
1063:
1060:
1059:
1057:
1056:
1051:
1046:
1045:
1044:
1034:
1028:
1026:
1019:
1018:
1016:
1015:
1010:
1004:
1002:
992:
983:
977:
976:
961:
960:
953:
946:
938:
932:
931:
925:
919:
913:
906:
905:External links
903:
901:
900:
865:
852:
842:
813:(7): 575–589.
793:
758:
745:
732:
705:(5): 417–420.
689:
654:
625:(3): 209–215.
605:
555:
553:
550:
541:
538:
537:
536:
533:
526:
524:
521:
514:
512:
509:
502:
498:
495:
486:
483:
481:
478:
457:
454:
416:
413:
408:Symphysiolysis
401:Osteitis pubis
384:
381:
370:
367:
365:
362:
353:
350:
336:
333:
325:
322:
290:Fibrocartilage
286:
285:Fibrocartilage
283:
224:fibrocartilage
205:
202:
153:
152:
143:
137:
136:
131:
125:
124:
119:
113:
112:
107:
101:
100:
95:
89:
88:
83:
77:
76:
72:
71:
67:
66:
63:
55:
54:
43:
35:
34:
26:
9:
6:
4:
3:
2:
1500:
1489:
1486:
1484:
1481:
1480:
1478:
1459:
1456:
1454:
1450:
1447:
1445:
1442:
1440:
1437:
1435:
1432:
1431:
1429:
1427:
1423:
1417:
1414:
1412:
1409:
1408:
1406:
1404:
1400:
1394:
1391:
1389:
1386:
1385:
1383:
1381:
1380:pelvic girdle
1377:
1373:
1370:
1368:
1364:
1354:
1351:
1350:
1348:
1346:
1345:Costochondral
1342:
1336:
1333:
1332:
1330:
1328:
1327:Interchondral
1324:
1318:
1315:
1313:
1310:
1308:
1305:
1304:
1302:
1300:
1296:
1286:
1283:
1281:
1278:
1277:
1275:
1273:
1269:
1263:
1260:
1258:
1255:
1254:
1252:
1250:
1246:
1243:
1241:
1237:
1234:
1232:
1228:
1214:
1211:
1209:
1206:
1205:
1203:
1201:
1197:
1191:
1188:
1187:
1185:
1183:
1179:
1173:
1170:
1169:
1167:
1165:
1164:Zygapophysial
1161:
1155:
1152:
1150:
1147:
1146:
1143:
1139:
1138:
1135:
1132:
1130:
1127:
1125:
1124:Alar ligament
1122:
1119:
1115:
1111:
1110:
1108:
1106:
1105:Atlanto-axial
1102:
1099:
1097:
1093:
1086:
1083:
1081:
1077:
1074:
1073:
1071:
1069:
1065:
1055:
1052:
1050:
1047:
1043:
1040:
1039:
1038:
1035:
1033:
1030:
1029:
1027:
1025:
1020:
1014:
1011:
1009:
1006:
1005:
1003:
1001:
996:
993:
991:
987:
984:
982:
978:
974:
970:
966:
959:
954:
952:
947:
945:
940:
939:
936:
929:
926:
923:
920:
917:
914:
912:
909:
908:
896:
892:
888:
884:
880:
876:
869:
862:
856:
846:
838:
834:
829:
824:
820:
816:
812:
808:
804:
797:
789:
785:
781:
777:
773:
769:
762:
755:
749:
742:
736:
728:
724:
720:
716:
712:
708:
704:
700:
693:
685:
681:
677:
673:
669:
665:
658:
650:
646:
641:
636:
632:
628:
624:
620:
616:
609:
601:
597:
592:
587:
583:
579:
576:(5): 475–87.
575:
571:
567:
560:
556:
547:
530:
525:
518:
513:
506:
501:
500:
494:
492:
477:
473:
471:
467:
462:
461:Symphysiotomy
456:Symphysiotomy
453:
451:
447:
443:
439:
435:
431:
426:
422:
412:
410:
409:
404:
402:
398:
394:
390:
380:
377:
361:
358:
349:
347:
343:
332:
330:
321:
319:
318:perichondrium
315:
311:
307:
303:
299:
295:
291:
282:
280:
276:
272:
268:
264:
260:
256:
252:
248:
244:
240:
235:
233:
229:
225:
221:
218:
210:
201:
199:
194:
192:
188:
184:
180:
176:
175:superior rami
172:
168:
160:
148:
142:
138:
135:
132:
130:
126:
123:
120:
118:
114:
111:
108:
106:
102:
99:
96:
94:
90:
87:
84:
82:
78:
73:
68:
61:
56:
51:
47:
46:superior rami
41:
36:
31:
19:
1448:
1402:
1353:no ligaments
1352:
1335:no ligaments
1334:
1299:Sternocostal
1172:no ligaments
1171:
1142:no ligaments
1141:
878:
874:
868:
860:
855:
845:
810:
806:
796:
774:(1): 50–52.
771:
767:
761:
753:
748:
740:
735:
702:
698:
692:
667:
663:
657:
622:
618:
608:
573:
569:
559:
488:
474:
459:
418:
406:
405:
386:
372:
359:
355:
338:
327:
314:disaccharide
302:tendon cells
288:
242:
238:
236:
214:
197:
195:
166:
158:
156:
110:A03.6.02.001
85:
1376:Syndesmoses
1249:Head of rib
1182:Lumbosacral
990:Syndesmosis
335:Development
267:pubic bones
217:nonsynovial
75:Identifiers
50:pubic bones
1477:Categories
1426:Sacroiliac
881:(1): 1–7.
552:References
430:childbirth
393:ochronosis
376:dislocated
346:childbirth
342:postpartum
263:pubic arch
1140:Lateral:
1068:Symphysis
981:Vertebral
969:ligaments
438:diastasis
421:pregnancy
415:Pregnancy
257:, and by
228:avascular
204:Structure
198:symphysis
179:hip bones
167:symphyses
1112:Medial:
895:19853490
837:15338362
788:15321442
727:42116716
719:20199196
649:15032910
600:20840351
540:See also
446:prenatal
352:Function
294:collagen
241:and the
850:Jamaica
828:3476662
684:3955988
640:1571274
591:3035856
442:forceps
425:relaxin
419:During
383:Disease
98:D011631
70:Details
48:of the
1488:Joints
1483:Pelvis
1367:Pelvis
1231:Thorax
965:Joints
893:
835:
825:
786:
725:
717:
682:
647:
637:
598:
588:
436:. The
369:Injury
279:pelvis
253:, the
249:, the
973:torso
723:S2CID
145:[
134:16950
81:Latin
967:and
891:PMID
833:PMID
784:PMID
715:PMID
680:PMID
645:PMID
596:PMID
157:The
122:1855
105:TA98
93:MeSH
1378:of
1022:Of
998:Of
971:of
883:doi
823:PMC
815:doi
776:doi
707:doi
672:doi
668:203
635:PMC
627:doi
623:204
586:PMC
578:doi
574:217
163:pl.
129:FMA
117:TA2
1479::
1451::
889:.
879:12
877:.
831:.
821:.
811:13
809:.
805:.
782:.
772:13
770:.
721:.
713:.
703:23
701:.
678:.
666:.
643:.
633:.
621:.
617:.
594:.
584:.
572:.
568:.
348:.
281:.
165::
1120:)
1116:(
1087:)
1078:(
957:e
950:t
943:v
897:.
885::
839:.
817::
790:.
778::
729:.
709::
686:.
674::
651:.
629::
602:.
580::
548:.
161:(
149:]
52:.
20:)
Text is available under the Creative Commons Attribution-ShareAlike License. Additional terms may apply.