17:
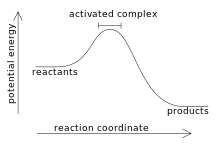
48:. The region represents not one defined state, but a range of unstable configurations that a collection of atoms pass through between the reactants and products of a reaction. Activated complexes have partial reactant and product character, which can significantly impact their behaviour in chemical reactions.
122:, which states that for a reaction to occur, reacting molecules must collide with a minimum energy and correct orientation. The reactants are first transformed into the activated complex before breaking into the products. From the properties of the activated complex and reactants, the reaction rate constant is
88:
is the minimum amount of energy to initiate a chemical reaction and form the activated complex. The energy serves as a threshold that reactant molecules must surpass to overcome the energy barrier and transition into the activated complex. Endothermic reactions absorb energy from the surroundings,
356:
89:
while exothermic reactions release energy. Some reactions occur spontaneously, while others necessitate an external energy input. The reaction can be visualized using a reaction coordinate diagram to show the activation energy and potential energy throughout the reaction.
55:
are often used interchangeably, but they represent different concepts. Transition states only represent the highest potential energy configuration of the atoms during the reaction, while activated complex refers to a range of configurations near the transition state. In a
117:
Transition state theory explains the reaction dynamics of reactions. The theory is based on the idea that there is an equilibrium between the activated complex and reactant molecules. The theory incorporates concepts from
228:
396:, and their properties are similar to activated complexes. However, activated complexed have an extra degree of translation associated with their approach to the energy barrier, crossing it, and then dissociating.
81:. The transition state, represented by the double dagger symbol represents the exact configuration of atoms that has an equal probability of forming either the reactants or products of the given reaction.
225:
into the rotational partition functions for the reactants and activated complexes. To reduce errors, symmetry numbers can by omitted by multiplying the rate expression by a statistical factor:
168:
392:
The activated complex is a collection of molecules that forms and then explodes along a particular internal normal coordinate. Ordinary molecules have three translational
383:
213:. Transition state theory is based on classical mechanics, as it assumes that as the reaction proceeds, the molecules will never return to the transition state.
199:
545:
516:
428:
60:, the transition state is the configuration at the maximum of the diagram while the activated complex can refer to any point near the maximum.
789:
92:
Activated complexes were first discussed in transition state theory (also called activated complex theory), which was first developed by
393:
386:
351:{\displaystyle k=l^{\ddagger }{\frac {k_{B}T}{h}}{\frac {Q_{\ddagger }}{Q_{A}Q_{B}}}e^{\left(-{\frac {\epsilon }{k_{B}T}}\right)}}
613:
596:
502:
125:
1001:
878:
695:
221:
An activated complex with high symmetry can decrease the accuracy of rate expressions. Error can arise from introducing
835:
1142:
782:
469:
1050:
1045:
855:
1215:
1210:
1241:
775:
40:
are breaking and forming. The activated complex is an arrangement of atoms in an arbitrary region near the
1236:
1180:
870:
734:
20:
Reaction coordinate diagram showing the activated complex in the region with highest potential energy.
907:
807:
206:
1137:
45:
1185:
986:
482:
63:
940:
361:
93:
1170:
1102:
960:
950:
410:
97:
1165:
893:
405:
171:
8:
1175:
1107:
1092:
1035:
57:
708:
1200:
970:
799:
202:
177:
385:
is the number of equivalent activated complexes that can be formed, and the Q are the
1190:
1152:
1097:
1016:
996:
932:
754:
712:
675:
633:
592:
578:
498:
465:
85:
71:
67:
33:
555:
526:
438:
1127:
1076:
1030:
746:
704:
667:
655:
625:
584:
559:
550:
530:
521:
490:
442:
433:
119:
52:
1205:
1117:
1066:
222:
210:
101:
494:
912:
901:
588:
1230:
1160:
1132:
1040:
991:
965:
758:
716:
679:
637:
554:, 2nd ed. (the "Gold Book") (1997). Online corrected version: (2006–) "
525:, 2nd ed. (the "Gold Book") (1997). Online corrected version: (2006–) "
437:, 2nd ed. (the "Gold Book") (1997). Online corrected version: (2006–) "
37:
767:
563:
534:
446:
1112:
918:
825:
815:
457:
41:
1071:
1006:
750:
671:
629:
1122:
25:
656:"The Activated Complex and the Absolute Rate of Chemical Reactions"
70:
of reactions that pass through a defined intermediate state with
1025:
845:
16:
32:
represents a collection of intermediate structures in a
364:
180:
231:
128:
66:(also known as activated complex theory) studies the
389:from the symmetry numbers that have been omitted.
377:
350:
193:
162:
1228:
693:Pechukas, P (1981). "Transition State Theory".
732:
797:
783:
614:"The Activated Complex in Chemical Reactions"
480:
483:"The transition state and cognate concepts"
790:
776:
489:, vol. 53, Elsevier, pp. 29–68,
112:
583:. Dordrecht: Springer Netherlands. 2006.
692:
15:
733:Murrell, J. N.; Laidler, K. J. (1968).
580:Chemical Kinetics and Reaction Dynamics
481:Tuñón, Iñaki; Williams, Ian H. (2019),
1229:
816:Unimolecular nucleophilic substitution
653:
611:
487:Advances in Physical Organic Chemistry
163:{\displaystyle k=K{\frac {k_{B}T}{h}}}
826:Bimolecular nucleophilic substitution
771:
728:
726:
649:
647:
573:
571:
464:(8th ed., W.H. Freeman 2006), p.809
879:Electrophilic aromatic substitution
739:Transactions of the Faraday Society
735:"Symmetries of activated complexes"
709:10.1146/annurev.pc.32.100181.001111
696:Annual Review of Physical Chemistry
72:standard Gibbs energy of activation
13:
846:Nucleophilic internal substitution
836:Nucleophilic aromatic substitution
723:
551:Compendium of Chemical Terminology
522:Compendium of Chemical Terminology
434:Compendium of Chemical Terminology
14:
1253:
644:
568:
107:
51:The terms activated complex and
1002:Lindemann–Hinshelwood mechanism
618:The Journal of Chemical Physics
1051:Outer sphere electron transfer
1046:Inner sphere electron transfer
856:Nucleophilic acyl substitution
686:
605:
539:
510:
474:
451:
422:
1:
1216:Diffusion-controlled reaction
416:
358:where the statistical factor
7:
871:Electrophilic substitutions
495:10.1016/bs.apoc.2019.09.001
399:
216:
10:
1258:
1181:Energy profile (chemistry)
1143:More O'Ferrall–Jencks plot
808:Nucleophilic substitutions
378:{\textstyle l^{\ddagger }}
1211:Michaelis–Menten kinetics
1151:
1085:
1059:
1015:
979:
931:
892:
869:
806:
589:10.1007/978-1-4020-4547-9
207:thermodynamic temperature
1138:Potential energy surface
1017:Electron/Proton transfer
902:Unimolecular elimination
46:potential energy surface
1186:Transition state theory
987:Intramolecular reaction
913:Bimolecular elimination
654:Eyring, Henry. (1935).
564:10.1351/goldbook.T06468
535:10.1351/goldbook.T06470
527:Transition State Theory
447:10.1351/goldbook.A00092
113:Transition State Theory
64:Transition state theory
980:Unimolecular reactions
941:Electrophilic addition
612:Eyring, Henry (1935).
379:
352:
195:
164:
21:
1171:Rate-determining step
1103:Reactive intermediate
961:Free-radical addition
951:Nucleophilic addition
894:Elimination reactions
411:Reaction intermediate
380:
353:
196:
165:
19:
1166:Equilibrium constant
751:10.1039/TF9686400371
460:and Julio de Paula,
406:Coordination complex
362:
229:
178:
172:equilibrium constant
126:
1242:Reaction mechanisms
1176:Reaction coordinate
1108:Radical (chemistry)
1093:Elementary reaction
1036:Grotthuss mechanism
800:reaction mechanisms
672:10.1021/cr60056a006
387:partition functions
58:reaction coordinate
1201:Arrhenius equation
971:Oxidative addition
933:Addition reactions
462:Physical Chemistry
394:degrees of freedom
375:
348:
203:Boltzmann constant
194:{\textstyle k_{B}}
191:
160:
22:
1237:Chemical kinetics
1224:
1223:
1196:Activated complex
1191:Activation energy
1153:Chemical kinetics
1098:Reaction dynamics
997:Photodissociation
630:10.1063/1.1749604
598:978-1-4020-4546-2
504:978-0-08-102900-8
439:Activated complex
339:
304:
268:
211:Planck's constant
158:
86:activation energy
34:chemical reaction
30:activated complex
1249:
1128:Collision theory
1077:Matrix isolation
1031:Harpoon reaction
908:E1cB-elimination
792:
785:
778:
769:
768:
763:
762:
730:
721:
720:
690:
684:
683:
660:Chemical Reviews
651:
642:
641:
609:
603:
602:
575:
566:
556:Transition State
543:
537:
514:
508:
507:
478:
472:
455:
449:
426:
384:
382:
381:
376:
374:
373:
357:
355:
354:
349:
347:
346:
345:
341:
340:
338:
334:
333:
320:
305:
303:
302:
301:
292:
291:
281:
280:
271:
269:
264:
260:
259:
249:
247:
246:
223:symmetry numbers
200:
198:
197:
192:
190:
189:
169:
167:
166:
161:
159:
154:
150:
149:
139:
120:collision theory
80:
53:transition state
1257:
1256:
1252:
1251:
1250:
1248:
1247:
1246:
1227:
1226:
1225:
1220:
1206:Eyring equation
1147:
1118:Stereochemistry
1081:
1067:Solvent effects
1055:
1011:
975:
956:
946:
927:
922:
888:
884:
865:
861:
851:
841:
831:
821:
802:
796:
766:
731:
724:
691:
687:
652:
645:
610:
606:
599:
577:
576:
569:
544:
540:
515:
511:
505:
479:
475:
456:
452:
427:
423:
419:
402:
369:
365:
363:
360:
359:
329:
325:
324:
319:
315:
311:
310:
306:
297:
293:
287:
283:
282:
276:
272:
270:
255:
251:
250:
248:
242:
238:
230:
227:
226:
219:
185:
181:
179:
176:
175:
170:where K is the
145:
141:
140:
138:
127:
124:
123:
115:
110:
74:
12:
11:
5:
1255:
1245:
1244:
1239:
1222:
1221:
1219:
1218:
1213:
1208:
1203:
1198:
1193:
1188:
1183:
1178:
1173:
1168:
1163:
1157:
1155:
1149:
1148:
1146:
1145:
1140:
1135:
1130:
1125:
1120:
1115:
1110:
1105:
1100:
1095:
1089:
1087:
1086:Related topics
1083:
1082:
1080:
1079:
1074:
1069:
1063:
1061:
1060:Medium effects
1057:
1056:
1054:
1053:
1048:
1043:
1038:
1033:
1028:
1022:
1020:
1013:
1012:
1010:
1009:
1004:
999:
994:
989:
983:
981:
977:
976:
974:
973:
968:
963:
958:
954:
948:
944:
937:
935:
929:
928:
926:
925:
920:
916:
910:
905:
898:
896:
890:
889:
887:
886:
882:
875:
873:
867:
866:
864:
863:
859:
853:
849:
843:
839:
833:
829:
823:
819:
812:
810:
804:
803:
795:
794:
787:
780:
772:
765:
764:
745:(0): 371–377.
722:
703:(1): 159–177.
685:
643:
624:(2): 107–115.
604:
597:
567:
538:
509:
503:
473:
450:
420:
418:
415:
414:
413:
408:
401:
398:
372:
368:
344:
337:
332:
328:
323:
318:
314:
309:
300:
296:
290:
286:
279:
275:
267:
263:
258:
254:
245:
241:
237:
234:
218:
215:
188:
184:
157:
153:
148:
144:
137:
134:
131:
114:
111:
109:
106:
9:
6:
4:
3:
2:
1254:
1243:
1240:
1238:
1235:
1234:
1232:
1217:
1214:
1212:
1209:
1207:
1204:
1202:
1199:
1197:
1194:
1192:
1189:
1187:
1184:
1182:
1179:
1177:
1174:
1172:
1169:
1167:
1164:
1162:
1161:Rate equation
1159:
1158:
1156:
1154:
1150:
1144:
1141:
1139:
1136:
1134:
1133:Arrow pushing
1131:
1129:
1126:
1124:
1121:
1119:
1116:
1114:
1111:
1109:
1106:
1104:
1101:
1099:
1096:
1094:
1091:
1090:
1088:
1084:
1078:
1075:
1073:
1070:
1068:
1065:
1064:
1062:
1058:
1052:
1049:
1047:
1044:
1042:
1041:Marcus theory
1039:
1037:
1034:
1032:
1029:
1027:
1024:
1023:
1021:
1018:
1014:
1008:
1005:
1003:
1000:
998:
995:
993:
992:Isomerization
990:
988:
985:
984:
982:
978:
972:
969:
967:
966:Cycloaddition
964:
962:
959:
952:
949:
942:
939:
938:
936:
934:
930:
924:
917:
914:
911:
909:
906:
903:
900:
899:
897:
895:
891:
880:
877:
876:
874:
872:
868:
857:
854:
847:
844:
837:
834:
827:
824:
817:
814:
813:
811:
809:
805:
801:
793:
788:
786:
781:
779:
774:
773:
770:
760:
756:
752:
748:
744:
740:
736:
729:
727:
718:
714:
710:
706:
702:
698:
697:
689:
681:
677:
673:
669:
665:
661:
657:
650:
648:
639:
635:
631:
627:
623:
619:
615:
608:
600:
594:
590:
586:
582:
581:
574:
572:
565:
561:
557:
553:
552:
547:
542:
536:
532:
528:
524:
523:
518:
513:
506:
500:
496:
492:
488:
484:
477:
471:
470:0-7167-8759-8
467:
463:
459:
454:
448:
444:
440:
436:
435:
430:
425:
421:
412:
409:
407:
404:
403:
397:
395:
390:
388:
370:
366:
342:
335:
330:
326:
321:
316:
312:
307:
298:
294:
288:
284:
277:
273:
265:
261:
256:
252:
243:
239:
235:
232:
224:
214:
212:
208:
204:
186:
182:
173:
155:
151:
146:
142:
135:
132:
129:
121:
108:Reaction Rate
105:
103:
99:
95:
90:
87:
82:
78:
73:
69:
65:
61:
59:
54:
49:
47:
43:
39:
35:
31:
27:
18:
1195:
1113:Molecularity
742:
738:
700:
694:
688:
666:(1): 65–77.
663:
659:
621:
617:
607:
579:
549:
541:
520:
512:
486:
476:
461:
458:Peter Atkins
453:
432:
424:
391:
220:
116:
91:
83:
76:
62:
50:
42:saddle point
29:
23:
1072:Cage effect
1007:RRKM theory
923:elimination
209:, and h is
205:, T is the
1231:Categories
417:References
104:in 1935.
1123:Catalysis
1019:reactions
759:0014-7672
717:0066-426X
680:0009-2665
638:0021-9606
371:‡
322:ϵ
317:−
278:‡
244:‡
26:chemistry
400:See also
217:Symmetry
68:kinetics
201:is the
102:Polanyi
798:Basic
757:
715:
678:
636:
595:
501:
468:
100:, and
94:Eyring
1026:Redox
862:Acyl)
546:IUPAC
517:IUPAC
429:IUPAC
98:Evans
44:of a
38:bonds
36:when
28:, an
915:(E2)
904:(E1)
755:ISSN
713:ISSN
676:ISSN
634:ISSN
593:ISBN
499:ISBN
466:ISBN
84:The
885:Ar)
842:Ar)
747:doi
705:doi
668:doi
626:doi
585:doi
560:doi
558:".
531:doi
529:".
491:doi
443:doi
441:".
24:In
1233::
953:(A
943:(A
881:(S
858:(S
852:i)
848:(S
838:(S
832:2)
828:(S
822:1)
818:(S
753:.
743:64
741:.
737:.
725:^
711:.
701:32
699:.
674:.
664:17
662:.
658:.
646:^
632:.
620:.
616:.
591:.
570:^
548:,
519:,
497:,
485:,
431:,
174:,
96:,
957:)
955:N
947:)
945:E
921:i
919:E
883:E
860:N
850:N
840:N
830:N
820:N
791:e
784:t
777:v
761:.
749::
719:.
707::
682:.
670::
640:.
628::
622:3
601:.
587::
562::
533::
493::
445::
367:l
343:)
336:T
331:B
327:k
313:(
308:e
299:B
295:Q
289:A
285:Q
274:Q
266:h
262:T
257:B
253:k
240:l
236:=
233:k
187:B
183:k
156:h
152:T
147:B
143:k
136:K
133:=
130:k
79:°
77:G
75:Δ
Text is available under the Creative Commons Attribution-ShareAlike License. Additional terms may apply.