20:
204:, each carbon atom uses only 3 of its 4 outer energy level electrons in covalently bonding to three other carbon atoms in a plane. Each carbon atom contributes one electron to a delocalized system of electrons that is also a part of the chemical bonding. The delocalized electrons are free to move throughout the plane. For this reason, graphite conducts electricity along the planes of carbon atoms, but does not conduct in a direction at
245:
In the methane molecule, ab initio calculations show bonding character in four molecular orbitals, sharing the electrons uniformly among all five atoms. There are two orbital levels, a bonding molecular orbital formed from the 2s orbital on carbon and triply degenerate bonding molecular orbitals from
154:
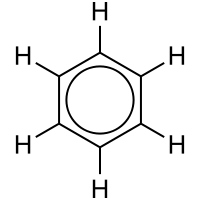
ring is often graphically indicated by a circle. The fact that the six C-C bonds are equidistant is one indication that the electrons are delocalized; if the structure were to have isolated double bonds alternating with discrete single bonds, the bond would likewise have alternating longer and
200:
atom are 'localized' between the atoms in covalent bonding. The movement of electrons is restricted and diamond does not conduct an electric current. In
185:) in a "sea" of delocalized electrons. This means that the electrons are free to move throughout the structure, and gives rise to properties such as
105:
223:
177:
Delocalized electrons also exist in the structure of solid metals. Metallic structure consists of aligned positive
231:
246:
each of the 2p orbitals on carbon. The localized sp orbitals corresponding to each individual bond in
309:
314:
186:
239:
259:
160:
129:
82:
135:
8:
247:
156:
101:
97:
230:
that, in general, extend over an entire molecule and have the symmetry of the molecule.
235:
90:
269:
227:
217:
116:
112:
86:
78:
172:
303:
63:
250:
can be obtained from a linear combination of the four molecular orbitals.
205:
73:
is general and can have slightly different meanings in different fields:
19:
289:
264:
35:
16:
Electrons that are not associated with a single atom or covalent bond
201:
47:
43:
27:
193:
147:
139:
23:
197:
182:
55:
59:
178:
119:
electrons that have extended over several adjacent atoms.
51:
238:
of the delocalized orbitals, given by an appropriate
301:
159:, delocalization in benzene is represented by
166:
18:
302:
58:that are not associated with a single
211:
224:ab initio quantum chemistry methods
13:
14:
326:
196:all four outer electrons of each
26:, with the delocalization of the
282:
1:
275:
123:
7:
253:
10:
331:
215:
170:
127:
30:indicated by the circle
240:unitary transformation
31:
260:Aromatic ring current
234:may then be found as
167:Electrical conduction
130:Resonance (chemistry)
106:electrical conduction
40:delocalized electrons
22:
228:delocalized orbitals
161:resonance structures
155:shorter lengths. In
136:simple aromatic ring
248:valence bond theory
236:linear combinations
157:valence bond theory
98:solid-state physics
232:Localized orbitals
212:Molecular orbitals
208:to the plane.
91:aromatic compounds
87:conjugated systems
32:
270:Solvated electron
218:Molecular orbital
117:molecular orbital
113:quantum chemistry
79:organic chemistry
322:
310:Chemical bonding
294:
288:IUPAC Gold Book
286:
173:Metallic bonding
104:that facilitate
330:
329:
325:
324:
323:
321:
320:
319:
315:Electron states
300:
299:
298:
297:
287:
283:
278:
256:
220:
214:
175:
169:
153:
132:
126:
115:, it refers to
100:, it refers to
81:, it refers to
17:
12:
11:
5:
328:
318:
317:
312:
296:
295:
291:delocalization
280:
279:
277:
274:
273:
272:
267:
262:
255:
252:
216:Main article:
213:
210:
171:Main article:
168:
165:
151:
144:delocalization
128:Main article:
125:
122:
121:
120:
109:
102:free electrons
94:
71:delocalization
15:
9:
6:
4:
3:
2:
327:
316:
313:
311:
308:
307:
305:
293:
292:
285:
281:
271:
268:
266:
263:
261:
258:
257:
251:
249:
243:
241:
237:
233:
229:
225:
219:
209:
207:
203:
199:
195:
190:
188:
184:
180:
174:
164:
162:
158:
149:
145:
141:
137:
131:
118:
114:
110:
107:
103:
99:
95:
92:
88:
84:
80:
76:
75:
74:
72:
67:
65:
64:covalent bond
61:
57:
53:
49:
45:
41:
37:
29:
25:
21:
290:
284:
244:
221:
206:right angles
191:
187:conductivity
176:
143:
133:
70:
68:
39:
33:
148:π electrons
304:Categories
276:References
150:over the C
265:Electride
222:Standard
124:Resonance
83:resonance
69:The term
54:or solid
44:electrons
36:chemistry
28:electrons
254:See also
226:lead to
202:graphite
48:molecule
194:diamond
183:cations
146:of six
140:benzene
134:In the
24:Benzene
198:carbon
142:, the
62:or a
56:metal
46:in a
179:ions
89:and
60:atom
42:are
192:In
138:of
111:In
96:In
85:in
77:In
52:ion
34:In
306::
242:.
189:.
163:.
66:.
50:,
38:,
181:(
152:6
108:.
93:.
Text is available under the Creative Commons Attribution-ShareAlike License. Additional terms may apply.