477:
the
Flavian age, there was a radical change in the layout and functions of the villa. In the main nucleus, some floors were replaced; the viridarium with pergola was replaced by a complex series of service rooms (kitchens, storerooms, tubs). A grandiose peristyle with Tuscan travertine columns and a series of small rooms on the three sides of the peristyle was built alongside the western side with the main nucleus. These small rooms - about thirty in all - are generally similar in size with floors of bare rock, except for the central room on the west side which was larger and paved with black and white mosaic and contained an altar, and a marble seat, while a masonry counter in the NW corner of the room bore the long and important eulogy for
47:
24:
391:
40:
399:
222:
375:) and this seems to have continued, with a corresponding deterioration of the quality of the residential part, up to the end of the 4th century AD. The villa was restored between the 3rd and 4th centuries AD. Traces of devastation (including the violent shattering of the statues) and of fires have been revealed by excavations but the villa was frequented until the 5th century AD, when a small cemetery was set up in the residential part.
496:
Behind the ergastulum peristyle there is an open corner at the end of a road, evidently used as a point of arrival and parking for wagons from the surrounding countryside. Room 34 at the NW corner of the peristyle is a latrine and along the south side of the same complex are 50 closets intended for
476:
in the western part of the "noble" nucleus. In this phase a series of entrances to the portico were opened and the new wing was given black and white mosaic floors. Among these the floors of tablinum 13 and room 8 stand out for their finesse and complexity. During the first century AD, probably in
468:
with ashlar columns supporting pergolas, while a portico ran externally along the western side, perhaps to connect the villa with the adjacent fields. The eastern side of the villa had very fine geometric mosaics, among which the one decorating room 18 has a polychrome imitation of
Hellenistic
481:(consul of 3 AD) and Q. Volusius Saturninus (consul of 56). In this room (and all around the peristyle) were fragmented portrait statues and marble busts of L. Volusius Saturninus, his wife Cornelia, Q. Volusius Saturninus and perhaps
445:. Overall, around sixty rooms have been identified built in the republican and imperial eras. Some rooms retain polychrome mosaics with beautiful geometric decorations often finished with flowers, birds and various symbols.
344:
villas, in vogue in the
Augustan age, equipping it with residential and spa facilities, enriching it with new mosaic decorations and expanding the residential part with the construction of a gigantic peristyle and with a
777:
Arnoldus
Huyzendveld, Antonia; Palombini, Augusto; Pietroni, Eva; Sanna, Valentina; Zanni, Sara; Remondino, Fabio (2013). "Una metodologia condivisa per l'analisi del paesaggio antico: il Progetto 'Valle del Tevere'".
382:, a religious building was first built and then a small fortified centre with towers and, finally, a rustic farmhouse reported in the maps of the area of the 16th century.
285:
The excavation of the complex, cut in two by the highway's access ramp, was done from 1962 to 1971. Renovation continued until the 1990s with the restoration of the
273:
and related structures in the area were known, and it was very close to the known Lucus
Feroniae sanctuary: in 1962 it was found during the construction of the
469:
carpets. The exceptional opus sectile floor in room 23, one of the oldest known examples of such flooring, seems to date back to this period too.
845:
813:
980:
93:
489:
of the slaves with a complex set of furnishings, sculptures and inscriptions in the great peristyle is remarkable and was related to the
337:
363:
Around this date the villa changed radically from a suburban luxury villa into a large agricultural production centre typical of a
862:
Boenzi, Giuliana; Ciccarese, Antonella; Di
Giammatteo, Paola; Fei, Francesca; Gazzetti, Gianfranco; Stanco, Enrico Angelo (1997).
478:
312:
The villa that can be seen today was largely built around the middle of the 1st century BC by the senatorial family of the
527:
The Villa dei
Volusii, as well as Lucus Feroniae, was included in the project of the Virtual Museum of the Tiber Valley.
39:
975:
309:
by senatorial families not far from Rome in a fertile area, being not only a country residence but also a large farm.
482:
76:
871:
Sgubini
Moretti, Anna Maria (1998). "La ristrutturazione in età augustea". In Sgubini Moretti, Anna Maria (ed.).
910:
La Villa dei
Volusii Saturnini a Lucus Feroniae: ambienti virtuali per la ricerca archeologica (Doctoral Thesis)
965:
357:
456:
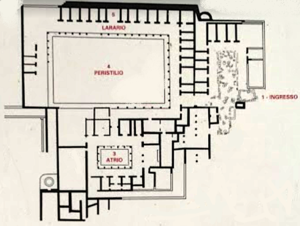
flanked by side rooms, a series of rooms of various sizes on the long sides of the atrium which include
329:
960:
269:
The discovery of the scale and importance of the site was completely accidental even though a Roman
938:
213:
349:
with statues of the family's ancestors. The family also owned the more commercial villa-estate at
252:
This villa is a unique example of an almost entirely excavated large senatorial villa in Italy.
970:
422:
8:
880:
Sforzini, Clementina (1998). "Le fasi successive". In
Sgubini Moretti, Anna Maria (ed.).
406:
The villa was located about 400 metres (1,300 ft) from Lucus Feroniae alongside the
274:
839:
807:
314:
257:
825:(in Italian). Vol. 3. Cassia, Clodia, Flaminia, Tiberina, Labicana, Prenestina.
255:
It was a luxurious villa owned by the politically powerful senatorial family of the
917:
473:
28:
View of the archaeological site of Villa dei Volusii with the adjacent A1 highway
908:
448:
The original phase from about 50 BC consisted of: a large hexastyle atrium with
418:
340:, cousin of Tiberius, who enlarged the building. He adapted it in the style of
306:
270:
242:
161:
497:
washing and bathing, all part of the slave economy of the imperial-age villa.
390:
954:
350:
302:
128:
108:
95:
944:
398:
411:
407:
320:
246:
238:
174:
164:
66:
776:
519:, a building used to keep dangerous slaves in chains or to punish slaves.
410:
and was built on an embankment that offered a panoramic view of the lower
23:
379:
365:
360:
who was consul in 56 AD, the villa was probably acquired by the emperor.
341:
290:
221:
515:
465:
461:
449:
427:
371:
502:
438:
486:
457:
453:
442:
433:
346:
325:
753:
M. Torelli, LUCUS FERONIAE, Enciclopedia dell' Arte Antica (1973)
945:
Villa dei Volusii on Lazio cultural heritage department web site
328:
who had their assets seized after their death. From the senator
214:
http://sabap-rm-met.beniculturali.it/it/300/la-villa-dei-volusii
333:
286:
80:
900:
Roman villas in central Italy: a social and economic history
864:
Terra di Fiano : ricerche di storia, arte, archeologia
882:
Fastosa rusticatio: la villa dei Volusii a Lucus Feroniae
873:
Fastosa rusticatio: la villa dei Volusii a Lucus Feroniae
417:
It was built on two levels, the upper one supported by a
318:, probably on an existing villa that had belonged to the
237:
is an archaeological site located in the municipality of
472:
A second phase from the Augustan period is indicated by
289:
floors, walls and structures, the setting up of a small
574:
Autostrade, rivista tecnica e di informazioni stradali
830:
Sgubini Moretti, Anna Maria; Moretti, Mario (1977).
485:known from an epigraph from the Hadrianic age. The
241:, next to the ancient Roman town and sanctuary of
493:or slave quarters (for no less than 500 slaves).
952:
829:
730:Catasto Alessandrino, table 433/30, May 10, 1660
823:La campagna romana: antica, medievale e moderna
800:Supplemento all'Enciclopedia dell'Arte Antica
893:(in Italian). Rome: L'Erma di Bretschneider.
513:, or farm which included an oil mill and an
305:fits into the group of villas built in the
844:: CS1 maint: location missing publisher (
812:: CS1 maint: location missing publisher (
421:which housed the residential part with an
293:and the installation of protective roofs.
22:
338:Lucius Volusius Saturninus (consul 12 BC)
46:
397:
389:
220:
571:
261:, and one of the largest Roman villas.
953:
884:(in Italian). L'Erma di Bretschneider.
875:(in Italian). L'Erma di Bretschneider.
522:
369:, complete with large slave quarters (
832:La villa dei Volusii a Lucus Feroniae
782:(in Italian). All'insegna del Giglio.
572:VV. AA. (1968). "Villa dei Volusii".
888:
870:
981:Houses completed in the 1st century
855:La villa dei Volusii a Fiano Romano
509:The lower part of the site was the
13:
861:
452:columns surrounded by a beautiful
394:Mosaic floors at Villa dei Volusii
14:
992:
932:
77:Metropolitan City of Rome Capital
889:De Franceschini, Marina (2005).
500:The site included a cistern and
45:
38:
820:
790:
770:
756:
747:
733:
724:
710:
696:
682:
668:
277:at the Fiano Romano tollbooth.
654:
640:
626:
612:
598:
584:
565:
551:
537:
464:and living rooms; below was a
385:
336:, the villa passed to his son
1:
879:
853:Gazzetti, Gianfranco (1997).
852:
821:Tomassetti, Giuseppe (1980).
530:
280:
245:, along the route of ancient
897:
797:
264:
7:
857:(in Italian). Rome: Quasar.
741:Sgubini Moretti and Moretti
648:Sgubini Moretti and Moretti
358:Quintus Volusius Saturninus
235:Villa dei Volusii-Saturnini
10:
997:
906:
898:Marzano, Annalisa (2007).
479:Lucius Volusius Saturninus
296:
976:National museums of Italy
780:Archeologia e Calcolatori
209:
201:
197:Società Autostrade S.p.A.
193:
185:
180:
170:
157:
147:
139:
134:
124:
87:
72:
62:
33:
21:
378:Starting from the early
143:Volusii-Saturnini Family
109:42.1328000°N 12.600611°E
798:Torelli, Mario (1973).
891:Ville dell'agro romano
403:
395:
226:
225:Villa dei Volusii plan
966:Roman villas in Italy
916:(in Italian). Milan:
866:(in Italian). Quasar.
401:
393:
324:family, opponents of
224:
186:Excavation dates
153:(2073–2074 years ago)
114:42.1328000; 12.600611
907:Zanni, Sara (2013).
307:Roman republican age
834:(in Italian). Rome.
802:(in Italian). Rome.
523:Archaeological site
105: /
18:
547:, pp. 725–726
404:
396:
229:The ancient Roman
227:
202:Public access
54:Shown within Lazio
16:
315:Volusii Saturnini
258:Volusii Saturnini
231:Villa dei Volusii
219:
218:
17:Villa dei Volusii
988:
961:Museums in Lazio
939:Official website
927:
925:
924:
918:Milan University
915:
903:
902:. Boston: Brill.
894:
885:
876:
867:
858:
849:
843:
835:
826:
817:
811:
803:
784:
783:
774:
768:
767:
760:
754:
751:
745:
744:
743:, pp. 10–18
737:
731:
728:
722:
721:
714:
708:
707:
700:
694:
693:
686:
680:
679:
678:, pp. 24–27
672:
666:
665:
664:, pp. 69–73
658:
652:
651:
650:, pp. 46–47
644:
638:
637:
630:
624:
623:
622:, pp. 83–84
616:
610:
609:
602:
596:
595:
588:
582:
581:
569:
563:
562:
555:
549:
548:
541:
483:Volusia Torquata
474:opus reticulatum
402:Mosaic in detail
356:On the death of
330:Quintus Volusius
120:
119:
117:
116:
115:
110:
106:
103:
102:
101:
98:
49:
48:
42:
26:
19:
15:
996:
995:
991:
990:
989:
987:
986:
985:
951:
950:
935:
930:
922:
920:
913:
837:
836:
805:
804:
793:
788:
787:
775:
771:
762:
761:
757:
752:
748:
739:
738:
734:
729:
725:
716:
715:
711:
702:
701:
697:
688:
687:
683:
676:Sgubini Moretti
674:
673:
669:
662:De Franceschini
660:
659:
655:
646:
645:
641:
632:
631:
627:
618:
617:
613:
604:
603:
599:
590:
589:
585:
570:
566:
557:
556:
552:
543:
542:
538:
533:
525:
388:
299:
283:
267:
152:
113:
111:
107:
104:
99:
96:
94:
92:
91:
58:
57:
56:
55:
52:
51:
50:
29:
12:
11:
5:
994:
984:
983:
978:
973:
968:
963:
949:
948:
942:
934:
933:External links
931:
929:
928:
904:
895:
886:
877:
868:
859:
850:
827:
818:
794:
792:
789:
786:
785:
769:
755:
746:
732:
723:
709:
695:
681:
667:
653:
639:
625:
611:
597:
583:
576:(in Italian).
564:
550:
535:
534:
532:
529:
524:
521:
419:cryptoporticus
387:
384:
298:
295:
282:
279:
271:cryptoporticus
266:
263:
243:Lucus Feroniae
217:
216:
211:
207:
206:
203:
199:
198:
195:
191:
190:
187:
183:
182:
178:
177:
172:
168:
167:
162:Roman Republic
159:
155:
154:
149:
145:
144:
141:
137:
136:
132:
131:
126:
122:
121:
89:
85:
84:
74:
70:
69:
64:
60:
59:
53:
44:
43:
37:
36:
35:
34:
31:
30:
27:
9:
6:
4:
3:
2:
993:
982:
979:
977:
974:
972:
969:
967:
964:
962:
959:
958:
956:
946:
943:
940:
937:
936:
919:
912:
911:
905:
901:
896:
892:
887:
883:
878:
874:
869:
865:
860:
856:
851:
847:
841:
833:
828:
824:
819:
815:
809:
801:
796:
795:
781:
773:
765:
759:
750:
742:
736:
727:
719:
713:
705:
699:
691:
690:Boenzi et al.
685:
677:
671:
663:
657:
649:
643:
635:
634:Boenzi et al.
629:
621:
615:
607:
601:
593:
587:
579:
575:
568:
561:, p. 278
560:
554:
546:
540:
536:
528:
520:
518:
517:
512:
507:
505:
504:
498:
494:
492:
488:
484:
480:
475:
470:
467:
463:
459:
455:
451:
446:
444:
441:, garden and
440:
437:, with large
436:
435:
430:
429:
424:
420:
415:
413:
409:
400:
392:
383:
381:
376:
374:
373:
368:
367:
361:
359:
354:
352:
351:Settefinestre
348:
343:
339:
335:
331:
327:
323:
322:
317:
316:
310:
308:
304:
303:villa rustica
294:
292:
288:
278:
276:
272:
262:
260:
259:
253:
250:
248:
244:
240:
236:
232:
223:
215:
212:
208:
204:
200:
196:
192:
188:
184:
179:
176:
173:
169:
166:
163:
160:
156:
151:around 50 BC;
150:
146:
142:
138:
133:
130:
129:Villa rustica
127:
123:
118:
97:42°07′58.08″N
90:
86:
82:
78:
75:
71:
68:
65:
61:
41:
32:
25:
20:
971:Fiano Romano
947:(in Italian)
941:(in Italian)
921:. Retrieved
909:
899:
890:
881:
872:
863:
854:
831:
822:
799:
791:Bibliography
779:
772:
766:, p. 31
763:
758:
749:
740:
735:
726:
720:, p. 31
717:
712:
706:, p. 30
703:
698:
692:, p. 59
689:
684:
675:
670:
661:
656:
647:
642:
636:, p. 30
633:
628:
619:
614:
608:, p. 35
605:
600:
594:, p. 23
591:
586:
577:
573:
567:
558:
553:
544:
539:
526:
514:
511:pars rustica
510:
508:
501:
499:
495:
490:
471:
447:
432:
426:
416:
412:Tiber Valley
408:Via Tiberina
405:
377:
370:
364:
362:
355:
319:
313:
311:
300:
284:
268:
256:
254:
251:
247:Via Tiberina
239:Fiano Romano
234:
230:
228:
175:Ancient Rome
165:Roman Empire
67:Fiano Romano
386:Description
380:Middle Ages
366:latifundium
342:Hellenistic
332:, known to
291:antiquarium
112: /
100:12°36′2.2″E
88:Coordinates
955:Categories
923:2022-04-27
531:References
516:ergastulum
503:nymphaeums
491:ergastulum
466:viridarium
462:triclinium
450:travertine
428:triclinium
372:ergastulum
281:Excavation
275:A1 highway
194:Management
181:Site notes
840:cite book
808:cite book
559:Tomasetti
439:peristyle
265:Discovery
189:1962-1972
764:Gazzetti
718:Sforzini
704:Sforzini
580:: 13–15.
487:lararium
458:cubicula
454:tablinum
443:lararium
434:tablinum
347:lararium
326:Augustus
171:Cultures
63:Location
620:Marzano
545:Torelli
321:Egnatii
297:History
210:Website
158:Periods
148:Founded
140:Builder
135:History
83:, Italy
423:atrium
334:Cicero
287:mosaic
73:Region
914:(PDF)
606:Zanni
592:Zanni
301:This
81:Lazio
846:link
814:link
460:, a
125:Type
233:or
205:yes
957::
842:}}
838:{{
810:}}
806:{{
506:.
431:,
425:,
414:.
353:.
249:.
79:,
926:.
848:)
816:)
578:8
Text is available under the Creative Commons Attribution-ShareAlike License. Additional terms may apply.