397:
25:
122:
443:
Even where temporal hours continued to be used (especially in monasteries), the mechanical clock was used. This required two different settings for the day and for the night, or one clock each for the day and the night. For the latter, the speed of the
282:
Due to the continuous change of the duration of daylight over the course of the year, the duration of the day division, i.e. the temporal day hours and the temporal night hours, also changes over the year.
366:. This division of time allowed the work of the day -such as eating, praying, or working -to always be performed at the same (temporal) hour, regardless of season (
519:
126:
471:
419:
141:
440:
created during the transition to the equal-duration equinoctial hours display temporal hours in addition to the new equal-duration hours.
210:
periods of time because days are longer and nights shorter in summer than in winter. Their use in everyday life was replaced in the late
433:, which varied throughout the year, served as a parameter on which the varying duration of the temporal hours during the year depended.
89:
61:
448:(Waag) was changed, for example, in 26 steps (i.e., half the numerical value of 52 weeks). In the weeks of the
309:
Temporal hours were common in many cultures. A division of day and night into twelve hours each was first recorded in
108:
68:
617:
75:
46:
42:
331:
410:
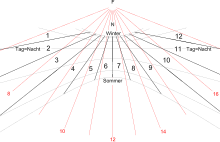
shows the temporal hours on curved golden lines: respective end of the hour indicated with a black number.
57:
524:
551:
Hieratische Papyri aus
Tebtunis I (Carsten Niebuhr Institute of Ancient Eastern Studies Copenhagen)
35:
322:
612:
504:
424:
367:
146:
131:
82:
8:
607:
476:
314:
466:
437:
499:
494:
137:
445:
225:. For example, if daylight and night are each divided into twelve temporal hours,
578:
Temporaluhren: Die Suche nach mechanischen Uhren, die mit
Temporalstunden liefen.
540:
Temporaluhren: Die Suche nach mechanischen Uhren, die mit
Temporalstunden liefen.
484:
363:
345:
276:
452:, both clocks could be operated with the middle weight position on the balance.
396:
349:
318:
197:
601:
514:
378:
310:
286:
The temporal hours of day and night are equal only at the spring and autumn
294:
356:
301:) every day in summer and rises every day in winter. Day does not occur.
211:
592:
509:
489:
359:
era. They had particular relevance in the fixed daily schedule of the
402:
360:
272:
24:
461:
430:
264:
230:
449:
415:
374:
298:
287:
260:
254:
218:
163:
152:
151:). The equinoctial hours are equal to the temporal hours at the
553:. Museum Tusculanum Press, Copenhagen 1998, ISBN 8-7728-9280-3.
353:
268:
222:
171:
385:
167:
16:
A system where hour lengths are unequal or not all 60 minutes
313:. A similar division of day and night was later made in the
407:
336:
226:
558:
544:
121:
414:
For the display of temporal hours almost exclusively the
560:. Westdeutscher Vlg, Wiesbaden 1980, ISBN 3-531-11515-4.
236:
A clock that displays the temporal hours is called a
136:
for the simultaneous display of temporal (black) and
49:. Unsourced material may be challenged and removed.
279:in summer and 8 equinoctial hours in winter.
373:This chronology is used by Jewish religious law (
599:
140:(red) daylight hours with a dot-shaped shadow (
388:encouraged the adoption of equinoctial hours.
217:The first temporal hour of daylight begins at
155:; the lines of both types of hours intersect.
233:are each the beginning of the seventh hour.
263:, the duration of daylight depends on the
214:by the now common ones of equal duration.
109:Learn how and when to remove this message
395:
271:. At 49° north/south latitude (e.g., in
120:
600:
293:From 66.5° north/south latitude (
243:
252:corresponds the astronomical concept
170:into 12 sections each, whatever the
47:adding citations to reliable sources
18:
13:
14:
629:
586:
321:into twelve temporal hours each (
391:
23:
532:
34:needs additional citations for
570:
400:The astronomical clock of the
297:) the sun no longer sets (the
1:
564:
275:), it varies between 16
337:
259:. With the exception of the
7:
455:
429:as hand was once used. The
348:they were adopted from the
10:
634:
546:Band 51, 2012, S. 143–160.
379:Halachic division of hours
326:
304:
319:Classical Greek Antiquity
352:and were adopted in the
221:, the first of night at
162:are the division of the
174:. They are also called
618:History of timekeeping
411:
201:
156:
399:
124:
520:Ancient Egyptian day
377:), hence the Jewish
127:wall-mounted sundial
43:improve this article
593:Die Temporalstunden
438:astronomical clocks
431:position of the Sun
368:Prayer of the Hours
315:Mediterranean basin
244:Astronomical basics
576:Karlheinz Deußer:
538:Karlheinz Deußer:
467:Terminator (solar)
412:
248:To the concept of
157:
556:Rudolf Wendorff:
495:equinoctial hours
335:
119:
118:
111:
93:
625:
581:
574:
528:
480:
446:verge escapement
428:
340:
330:
328:
277:equinoctal hours
208:unequal duration
203:horae temporales
150:
135:
114:
107:
103:
100:
94:
92:
51:
27:
19:
633:
632:
628:
627:
626:
624:
623:
622:
598:
597:
589:
584:
575:
571:
567:
535:
522:
485:Time perception
474:
472:Diurnal climate
458:
422:
394:
346:Western culture
307:
246:
179:seasonal hours,
176:temporal hours,
144:
129:
115:
104:
98:
95:
58:"Unequal hours"
52:
50:
40:
28:
17:
12:
11:
5:
631:
621:
620:
615:
610:
596:
595:
588:
587:External links
585:
583:
582:
568:
566:
563:
562:
561:
554:
549:Jürgen Osing:
547:
534:
531:
530:
529:
517:
512:
507:
502:
497:
492:
487:
482:
469:
464:
457:
454:
393:
390:
350:Roman calendar
338:horai kairikai
306:
303:
245:
242:
238:temporal clock
117:
116:
31:
29:
22:
15:
9:
6:
4:
3:
2:
630:
619:
616:
614:
611:
609:
606:
605:
603:
594:
591:
590:
579:
573:
569:
559:
555:
552:
548:
545:
541:
537:
536:
526:
521:
518:
516:
515:Chronobiology
513:
511:
508:
506:
503:
501:
498:
496:
493:
491:
488:
486:
483:
478:
473:
470:
468:
465:
463:
460:
459:
453:
451:
447:
441:
439:
434:
432:
426:
421:
417:
409:
405:
404:
398:
392:Temporal time
389:
387:
382:
380:
376:
371:
369:
365:
362:
358:
355:
351:
347:
342:
339:
333:
327:ὥραι καιρικαί
324:
323:Ancient Greek
320:
316:
312:
311:Ancient Egypt
302:
300:
296:
295:polar circles
291:
289:
284:
280:
278:
274:
270:
266:
262:
258:
256:
251:
241:
239:
234:
232:
228:
224:
220:
215:
213:
209:
205:
204:
199:
195:
191:
188:, as well as
187:
183:
180:
177:
173:
169:
165:
161:
160:Unequal hours
154:
148:
143:
139:
133:
128:
123:
113:
110:
102:
91:
88:
84:
81:
77:
74:
70:
67:
63:
60: –
59:
55:
54:Find sources:
48:
44:
38:
37:
32:This article
30:
26:
21:
20:
577:
572:
557:
550:
543:
539:
533:Bibliography
442:
435:
413:
401:
383:
372:
343:
308:
292:
285:
281:
253:
249:
247:
237:
235:
216:
207:
206:). They are
202:
193:
189:
186:Jewish hours
185:
181:
178:
175:
159:
158:
105:
99:January 2023
96:
86:
79:
72:
65:
53:
41:Please help
36:verification
33:
613:Timekeeping
523: [
500:equal hours
481:(in German)
475: [
423: [
384:Mechanical
317:from about
212:Middle Ages
194:Roman hours
145: [
138:equinoctial
130: [
608:Jewish law
602:Categories
565:References
510:Julian day
490:Civil time
257:of the Sun
125:Dial of a
69:newspapers
403:Zytglogge
332:romanized
288:equinoxes
273:Karlsruhe
250:light day
168:nighttime
153:equinoxes
462:Twilight
456:See also
361:monastic
357:Medieval
354:European
267:and the
265:latitude
231:midnight
182:biblical
166:and the
450:equinox
416:sundial
375:Halacha
334::
305:History
299:horizon
261:equator
255:Day arc
219:sunrise
190:ancient
164:daytime
83:scholar
386:clocks
364:orders
269:season
227:midday
223:sunset
172:season
85:
78:
71:
64:
56:
580:2012.
527:]
505:Danna
479:]
436:Many
427:]
420:Nodus
418:with
198:Latin
149:]
142:Nodus
134:]
90:JSTOR
76:books
542:In:
408:Bern
229:and
62:news
406:in
370:).
344:In
341:).
192:or
184:or
45:by
604::
525:de
477:de
425:de
381:.
329:,
325::
290:.
240:.
200::
147:de
132:de
196:(
112:)
106:(
101:)
97:(
87:·
80:·
73:·
66:·
39:.
Text is available under the Creative Commons Attribution-ShareAlike License. Additional terms may apply.