242:
466:
161:
122:
291:
241:
32:
263:
1445:
509:, most of whom live in sub-Saharan Africa. A 2008 review of malnutrition found that about 55 million children are wasted, including 19 million who have severe wasting or severe acute malnutrition. In 2020, a research paper that mapped stunting, wasting, and underweight among children across 105 low- and middle-income countries found that only five countries were expected to meet global nutrition targets in all
382:
extreme physical and intellectual disability. This affects the children's ability to achieve their full potential. In 2011 UNICEF reported that 30 percent of households in the developing world were not consuming iodized salt, which accounted for 41 million infants and newborns in whom iodine deficiency could still be prevented. Maternal body size is strongly associated with the size of newborn children.
144:
under 5. Malnutrition during the early stages of development can have negative and severe effects on growth and intellectual development. This effect on a child's intellectual quotient makes it harder for them later in life to achieve their true potential abilities. Breaking the cycle of malnutrition during early childhood development can break the cycle of intergenerational poverty among poor communities.
438:; this resulted in a 10 percent reduction in the prevalence of stunting in children 12–36 months old. Milk fortified with zinc and iron reduced the incidence of diarrhea by 18 percent in a study in India. In Nigeria, the use of imported Ready to Use Therapeutic Food (RUTF) has been used to combat malnutrition in the North. However, research has shown that
143:
is especially dangerous for women and children. Malnourished women will usually have malnourished fetuses while they are pregnant, which can lead to physically and mentally stunted children, creating a cycle of malnutrition and underdevelopment. One of the most severe at risk populations are children
318:
In almost all countries, the poorest quintile of children has the highest rate of malnutrition. However, inequalities in malnutrition between children of poor and rich families vary from country to country, with studies finding large gaps in Peru and very small gaps in Egypt. In 2000, rates of child
232:
Prenatal malnutrition and early life growth patterns can alter metabolism and physiological patterns and have lifelong effects on the risk of cardiovascular disease. Children who are undernourished are more likely to be short in adulthood, have lower educational achievement and economic status, and
194:
In terms of more immediate risk factors for malnutrition and the many growth impairments that accompany it, a child’s gender, age, and size at birth are all decent indicators of their likelihood of presenting as stunted or wasted. These measures of malnutrition are interrelated, but studies for the
147:
There are a variety of ways in which malnutrition can affect the body. Globally, 162 million children show symptoms of malnutrition such as stunting, which is an indicator of malnourishment. The WHO reported that two out of five children that are stunted live in
Southern Asia, however Africa is the
456:
Breastfeeding can reduce rates of malnutrition and dehydration caused by diarrhea, but mothers are sometimes wrongly advised not to breastfeed their children. Breastfeeding has been shown to reduce mortality in infants and young children. Since only 38 percent of children worldwide under 6 months
501:
The World Health
Organization estimates that malnutrition accounts for 54 percent of child mortality worldwide, about 1 million children. Another estimate also by WHO states that childhood underweight is the cause for about 35% of all deaths of children under the age of five years worldwide.
381:
Infants born to young mothers who are not fully developed are found to have low birth weights. The level of maternal nutrition during pregnancy can affect a newborn baby's body size and composition. Iodine deficiency in mothers usually causes brain damage in their offspring, and some cases cause
228:
Malnutrition often results in many diseases and health concerns that require immediate medical attention. Of these side effects, there is an emphasis on addressing the increased risk of hypoglycemia, hypothermia, cardiac failure, and the likelihood of missing the presence of an infection. All of
151:
Protein-Energy
Malnutrition (PEM) is another form of malnutrition that affects children. PEM can appear as conditions called marasmus, kwashiorkor, and an intermediate state of marasmus-kwashiorkor. Although malnutrition can have severe and lasting health effects on women and children, they are
397:
A study in
Bangladesh in 2008 reported that rates of malnutrition were higher in female children than male children. Other studies show that, at the national level, differences between undernutrition prevalence rates between young boys and girls are generally small. Girls often have a lower
209:
Undernutrition in children causes direct structural damage to the brain and impairs infant motor development and exploratory behavior. Children who are undernourished before age two and gain weight quickly later in childhood and in adolescence are at high risk of chronic diseases related to
489:. This confirms the recommendation, "In addition to the provision of RUTF , children need to receive a short course of basic oral medication to treat infections." contained in "Community-based management of severe acute malnutrition, A Joint Statement by the World Health Organization, the
1079:
Bhutta, Z. A.; Ahmed, T.; Black, R. E.; Cousens, S.; Dewey, K.; Giugliani, E.; Haider, B. A.; Kirkwood, B.; Morris, S. S.; Sachdev, H. P. S.; Shekar, M.; Maternal Child
Undernutrition Study Group (2008). "What works? Interventions for maternal and child undernutrition and survival".
148:
only region where there is an increasing number of stunted children. Common micronutrient deficiencies are iron, zinc, iodine, and vitamin A. Micronutrient deficiencies can cause an increase of illness due to a compromised immune systems or abnormal physiology and development.
233:
give birth to smaller infants. Children often face malnutrition during the age of rapid development, which can have long-lasting impacts on health. Hospitals can and should diagnose, manage and prioritize treatments for malnutrition in order to alleviate long-lasting impacts.
365:
Children with chronic diseases like HIV have a higher risk of malnutrition, since their bodies cannot absorb nutrients as well. Diseases such as measles are a major cause of malnutrition in children; thus, immunizations present a way to relieve the burden.
1202:
Ngure, Francis M.; Reid, Brianna M.; Humphrey, Jean H.; Mbuya, Mduduzi N.; Pelto, Gretel; Stoltzfus, Rebecca J. (January 2014). "Water, sanitation, and hygiene (WASH), environmental enteropathy, nutrition, and early child development: making the links".
406:
Measurements of a child's growth provide the key information for the presence of malnutrition. However, weight and height measurements alone can lead to failure to recognize kwashiorkor and an underestimation of the severity of malnutrition in children.
410:
Since undernourished children are also more likely to die from preventable infections, there is some research into developing a rapid diagnostic tool to detect malnourishment and common infections from a drop of blood. This research was spearheaded by
93:
accounts for 54 percent of child mortality worldwide, which is about 1 million children. Another estimate, also by WHO, states that childhood underweight is the cause for about 35% of all deaths of children under the age of five worldwide.
213:
Studies have found a strong association between undernutrition and child mortality. Once malnutrition is treated, adequate growth is an indication of health and recovery. Even after recovering from severe malnutrition, children often remain
442:, a locally sourced and prepared blend consisting of peanut, millet, and soya beans, contains the components of the Ready to Use Therapeutic Food (RUTF) and this has been used massively to reduce malnutrition in the north.
245:
The prevalence of child stunting generally increases as cities become smaller and moving away from urban centres while child wasting and overweight are lower and exhibit less evident trends across the rural-urbann
427:. Iodine supplement trials in pregnant women have been shown to reduce offspring deaths during infancy and early childhood by 29 percent. However, universal salt iodization has largely replaced this intervention.
337:
and other infections can cause malnutrition through decreased nutrient absorption, decreased intake of food, increased metabolic requirements, and direct nutrient loss. Parasite infections, in particular
1013:
Victora, Cesar G; Adair, Linda; Fall, Caroline; Hallal, Pedro C; Martorell, Reynaldo; Richter, Linda; Sachdev, Harshpal Singh; et al. (Maternal and Child
Undernutrition Study Group) (2008-01-26).
173:
Children under the age of five are most likely to experience malnutrition and often face a variety of diseases and growth inhibitors as a result. There are three commonly used measures for detecting
1459:
322:
Studies in
Bangladesh in 2009 found that the mother's illiteracy, low household income, higher number of siblings, less access to mass media, less supplementation of diets, unhygienic water and
457:
are exclusively breastfed, education programs could have large impacts on children's malnutrition rates. However, breastfeeding cannot fully prevent PEM if not enough nutrients are consumed.
905:
Adebisi, Yusuff
Adebayo; Ibrahim, Kirinya; Lucero-Prisno, Don Eliseo; Ekpenyong, Aniekan; Micheal, Alumuku Iordepuun; Chinemelum, Iwendi Godsgift; Sina-Odunsi, Ayomide Busayo (January 2019).
1496:
1724:
Kinyoki, Damaris K.; Osgood-Zimmerman, Aaron E.; Pickering, Brandon V.; Schaeffer, Lauren E.; et al. (Local Burden of
Disease Child Growth Failure Collaborators) (January 8, 2020).
1694:
77:
to maintain good health. It is common globally and may result in both short and long term irreversible adverse health outcomes. Undernutrition is sometimes used synonymously with
423:
Measures have been taken to reduce child malnutrition. Studies for the World Bank found that, from 1970 to 2000, the number of malnourished children decreased by 20 percent in
643:
The addition of antibiotics to therapeutic regimens for uncomplicated severe acute malnutrition was associated with a significant improvement in recovery and mortality rates.
198:
Children with severe acute malnutrition are very thin, but they often also have swollen hands and feet, making the internal problems more evident to health workers.
1257:
Khan, MM; Kraemer, A (August 2009). "Factors associated with being underweight, overweight and obese among ever-married non-pregnant urban women in
Bangladesh".
1439:
The epidemiology of coeliac disease (CD) is changing. Presentation of CD with malabsorptive symptoms or malnutrition is now the exception rather than the rule.
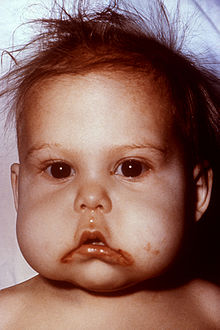
266:
A child with Kwashiorkor caused by inadequate dietary protein intake, show signs of thinning hair or "Flag Sign", edema, inadequate growth, and weight loss.
1470:
319:
malnutrition were much higher in low- income countries (36 percent) compared to middle-income countries (12 percent) and the United States (1 percent).
310:
as a result of inadequate sanitation. However, the relative contribution of diarrhea to undernutrition and, in turn, stunting remains controversial.
398:
nutritional status in South and Southeastern Asia compared to boys. In other developing regions, the nutritional status of girls is slightly higher.
865:
Black, R. (2003) Micronutrient Deficiency – An Underlying Cause of Morbidity and Mortality. Bulletin of the World Health Organization. 81(2). 79.
773:
843:"Levels and trends in child malnutrition: UNICEF/WHO/The World Bank Group joint child malnutrition estimates: key findings of the 2019 edition"
595:
Trehan, Indi; Goldbach, Hayley S.; LaGrone, Lacey N.; Meuli, Guthrie J.; Wang, Richard J.; Maleta, Kenneth M.; Manary, Mark J. (2013-01-31).
524:
effects of malnutrition. The combination of direct and indirect deaths from malnutrition caused by unsafe water, sanitation, and hygiene (
1698:; The World Food Programme, the United Nations System Standing Committee on Nutrition and the United Nations Children's Fund (May 2007).
302:
estimated in 2008 that globally, half of all cases of undernutrition in children under five were caused by unsafe water, inadequate
465:
1186:
740:
1127:
374:
The nutrition of children 5 years and younger depends strongly on the nutrition level of their mothers during pregnancy and
569:
Adam Wagstaff; Naoke Watanabe (November 1999). "Socioeconomic Inequalities in Child Malnutrition in the Developing World".
1654:
342:(helminthiasis), can also lead to malnutrition. A leading cause of diarrhea and intestinal worm infections in children in
164:
A child's upper arm is measured to detect malnutrition in the village of Baggad, in Madhya Pradesh's Dhar district (India)
485:
improves the response and survival rate of severely malnourished children to an outpatient treatment plan which provided
1801:
294:
Poor sanitary conditions in the environment that can contribute to malnutrition and disease in children (Kibera, Kenya)
1699:
354:. Other diseases that cause chronic intestinal inflammation may lead to malnutrition, such as some cases of untreated
692:
666:
486:
386:
279:
793:"Water-Food-Nutrition-Health Nexus: Linking Water to Improving Food, Nutrition and Health in Sub-Saharan Africa"
250:
Inadequate food intake, infections, psychosocial deprivation, the environment (lack of sanitation and hygiene),
40:
774:
Safer water, better health – Costs, benefits and sustainability of interventions to protect and promote health
520:
disease burden of malnutrition is estimated to be an order of magnitude higher than the disease burden of the
1639:
160:
537:
1342:
359:
1695:
973:
842:
493:, the United Nations System Standing Committee on Nutrition and the United Nations Children's Fund."
431:
299:
121:
86:
1571:
Nubé, M.; Van Den Boom, G. J. M. (2003). "Gender and adult undernutrition in developing countries".
1338:
528:) practices is estimated to lead to 860,000 deaths per year in children under five years of age.
510:
389:(IUGR). However, environmental factors can weaken the effect of IUGR on cognitive performance.
1614:
682:
1820:
656:
574:
195:
World Bank found that only 9 percent of children exhibit stunting, underweight, and wasting.
225:
mortality and malaria. This risk is greatly increased in more severe cases of malnutrition.
1737:
1212:
490:
424:
343:
1356:
Altomare R, Damiano G, Abruzzo A, Palumbo VD, Tomasello G, Buscemi S, et al. (2015).
878:
8:
1825:
1741:
1216:
1176:
866:
1766:
1725:
1596:
1519:
1384:
1357:
1315:
1288:
1236:
1105:
1047:
1014:
939:
906:
819:
792:
629:
596:
48:
1444:
1289:"The Paradox of Nutrition-Related Diseases in the Arab Countries: The Need for Action"
1093:
1030:
1797:
1771:
1753:
1588:
1430:
1389:
1320:
1266:
1228:
1182:
1157:
1149:
1144:
1097:
1052:
1034:
944:
926:
824:
746:
736:
688:
662:
634:
616:
570:
251:
82:
1600:
1544:
1523:
1240:
1109:
1015:"Maternal and child undernutrition: consequences for adult health and human capital"
385:
Short stature of the mother and poor maternal nutrition stores increase the risk of
290:
1761:
1745:
1640:"Africa's Next Einstein Forum builds expertise in science, tech, engineering, math"
1580:
1515:
1511:
1420:
1379:
1369:
1310:
1300:
1220:
1139:
1089:
1042:
1026:
934:
918:
814:
804:
624:
608:
516:
As underweight children are more vulnerable to almost all infectious diseases, the
505:
According to a 2008 review, an estimated 178 million children under age 5 are
221:
Even mild degrees of malnutrition double the risk of mortality for respiratory and
435:
110:
81:, however, malnutrition could mean both undernutrition or overnutrition (causing
1584:
907:"Prevalence and Socio-economic Impacts of Malnutrition Among Children in Uganda"
891:
1358:"Enteral nutrition support to treat malnutrition in inflammatory bowel disease"
506:
355:
215:
181:
74:
53:
1749:
1814:
1757:
1153:
1038:
930:
922:
750:
620:
474:
451:
375:
339:
307:
1287:
Musaiger, Abdulrahman O.; Hassan, Abdelmonem S.; Obeid, Omar (August 2011).
1178:
Environmental health and child survival epidemiology, economics, experiences
31:
1794:
The First 1,000 Days: A Crucial Time for Mothers and Children—And the World
1775:
1592:
1434:
1393:
1324:
1270:
1232:
1161:
1101:
1056:
948:
828:
809:
638:
412:
306:, or insufficient hygiene. This link is often due to repeated diarrhea and
174:
140:
90:
1305:
730:
612:
1723:
1457:
478:
271:
1409:"Coeliac disease in the 21st century: paradigm shifts in the modern age"
1224:
347:
323:
303:
102:
1726:"Mapping child growth failure across low- and middle-income countries"
1425:
1408:
1374:
201:
Children with severe malnutrition are very susceptible to infection.
904:
791:
Mabhaudhi, Tafadzwanashe; Chibarabada, Tendai; Modi, Albert (2016).
597:"Antibiotics as part of the management of severe acute malnutrition"
1673:
482:
334:
275:
262:
222:
73:, occurs when children do not consume enough calories, protein, or
735:(4th ed.). Hamilton, Ontario: B.C. Decker. pp. 127–141.
1293:
International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health
797:
International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health
351:
326:
are associated with chronic and severe malnutrition in children.
106:
98:
43:
infections in school-age children in Guimaras Island, Philippines
729:
Duggan, Christopher; Watkins, John B.; Walker, W. Allan (2008).
1655:"Severe Malnutrition, A Disturbance in Nigerian Health Sector"
270:
Inadequate food intake such as a lack of proteins can lead to
1355:
732:
Nutrition in pediatrics: basic science, clinical applications
1181:. Washington, DC: Environment Department of the World Bank.
568:
525:
254:
and perhaps genetics contribute to childhood malnutrition.
877:
Atassi, H. (2019). Protein-Energy Malnutrition. MedScape.
724:
594:
109:, factors related to society, diseases, maternal factors,
1700:"Community-based management of severe acute malnutrition"
722:
720:
718:
716:
714:
712:
710:
708:
706:
704:
229:
these complications can result in severe health effects.
1252:
1250:
892:"Malnutrition Among Children Under Five Years in Uganda"
790:
772:
Prüss-Üstün, A., Bos, R., Gore, F., Bartram, J. (2008).
1078:
879:
https://emedicine.medscape.com/article/1104623-overview
434:
with nutritional education and micronutrient-fortified
1201:
1012:
776:. World Health Organization (WHO), Geneva, Switzerland
701:
687:. Jones & Bartlett Publishers. 2011. p. 194.
469:
Getting support to children with malnutrition in Kenya
1247:
867:
https://www.scielosp.org/pdf/bwho/2003.v81n2/79-79/en
97:
The main causes of malnutrition are often related to
1458:
Sue Horton; Harold Alderman, Juan A. Rivera (2008).
1349:
1286:
1132:
Journal of Pediatric Gastroenterology and Nutrition
728:
1705:(in English and French). World Health Organization
152:still susceptible to other water-related dangers.
968:
966:
964:
962:
960:
958:
1812:
1570:
1008:
1006:
1004:
1002:
1000:
998:
996:
994:
564:
562:
560:
558:
556:
554:
552:
187:underweight (extremely low weight for age), and
1451:
1256:
1074:
1072:
1070:
1068:
1066:
955:
1545:"Micronutrients – Iodine, Iron and Vitamin A"
661:. Abingdon, Oxon: Routledge. pp. 36–38.
1791:
1566:
1564:
1562:
991:
590:
588:
586:
584:
549:
1400:
1063:
1688:
1488:
1460:"The Challenge of Hunger and Malnutrition"
1282:
1280:
1205:Annals of the New York Academy of Sciences
1174:
190:wasting (extremely low weight for height).
30:
1765:
1559:
1424:
1383:
1373:
1314:
1304:
1143:
1046:
938:
818:
808:
628:
581:
257:
1125:
675:
648:
464:
430:The Progresa program in Mexico combined
289:
261:
204:
159:
120:
1652:
1646:
1406:
1331:
1277:
786:
784:
782:
1813:
1665:
1407:Newnham, E. D. (2017). Newnham (ed.).
1121:
1119:
1494:
889:
654:
155:
1615:"Quartz Africa Innovators 2016 list"
1467:Copenhagen Consensus Challenge Paper
779:
768:
766:
764:
762:
760:
313:
16:Medical condition affecting children
1653:Chinedu, Obasi (October 12, 2018).
1642:. The Associated Press. 2016-03-11.
1337:
1116:
601:The New England Journal of Medicine
369:
13:
1785:
1671:
1343:"Complications of coeliac disease"
1128:"Treatment of Severe Malnutrition"
684:Essentials of International Health
511:second administrative subdivisions
240:
14:
1837:
757:
113:issues as well as other factors.
1443:
1145:10.1097/00005176-200105000-00003
911:Nutrition and Metabolic Insights
445:
1717:
1632:
1607:
1537:
1195:
1168:
898:
890:Ratib, Mawa (January 1, 1970).
883:
871:
496:
387:intrauterine growth retardation
184:(extremely low height for age),
1516:10.1080/09737189.2008.11885247
859:
835:
1:
1094:10.1016/S0140-6736(07)61693-6
1031:10.1016/S0140-6736(07)61692-4
543:
418:
285:
218:for the rest of their lives.
116:
538:Child nutrition in Australia
460:
401:
7:
1674:"Introduction to Nutrition"
1585:10.1080/0301446031000119601
531:
329:
280:Protein–energy malnutrition
168:
101:: unsafe water, inadequate
10:
1842:
1547:. UNICEF. 14 December 2011
1126:Ashworth, Ann (May 2001).
449:
432:conditional cash transfers
360:inflammatory bowel disease
340:intestinal worm infections
308:intestinal worm infections
71:Undernutrition in children
1750:10.1038/s41586-019-1878-8
1696:World Health Organization
1259:Singapore Medical Journal
847:World Health Organization
392:
300:World Health Organization
236:
87:World Health Organization
60:
47:
41:soil transmitted helminth
38:
29:
24:
923:10.1177/1178638819887398
125:Starved child in Somalia
25:Malnutrition in children
1573:Annals of Human Biology
1497:"Malnutrition in Women"
1413:J Gastroenterol Hepatol
810:10.3390/ijerph13010107
470:
295:
267:
258:Inadequate food intake
247:
165:
126:
56:, underweight, wasting
1792:Roger Thurow (2016).
1659:Public Health Nigeria
1495:Dewan, Manju (2008).
1306:10.3390/ijerph8093637
613:10.1056/NEJMoa1202851
468:
293:
265:
244:
205:Effects later in life
163:
139:of all child deaths,
124:
89:(WHO) estimates that
1504:Stud. Home Comm. Sci
1476:on November 15, 2012
658:Food and development
655:Young, E.M. (2012).
491:World Food Programme
425:developing countries
344:developing countries
39:Malnutrition due to
1742:2020Natur.577..231L
1341:(4 December 2016).
1217:2014NYASA1308..118N
1175:World Bank (2008).
917:: 117863881988739.
278:and other forms of
1419:(Suppl 1): 82–85.
1225:10.1111/nyas.12330
471:
296:
268:
248:
166:
156:Signs and symptoms
127:
1796:. PublicAffairs.
1736:(7789): 231–234.
1426:10.1111/jgh.13704
1375:10.3390/nu7042125
1188:978-0-8213-7237-1
1088:(9610): 417–440.
1025:(9609): 340–357.
742:978-1-55009-361-2
314:Social inequality
252:social inequality
223:diarrheal disease
83:childhood obesity
68:
67:
19:Medical condition
1833:
1807:
1780:
1779:
1769:
1721:
1715:
1714:
1712:
1710:
1704:
1692:
1686:
1685:
1683:
1681:
1669:
1663:
1662:
1650:
1644:
1643:
1636:
1630:
1629:
1627:
1626:
1611:
1605:
1604:
1568:
1557:
1556:
1554:
1552:
1541:
1535:
1534:
1532:
1530:
1501:
1492:
1486:
1485:
1483:
1481:
1475:
1469:. Archived from
1464:
1455:
1449:
1448:
1447:
1441:
1428:
1404:
1398:
1397:
1387:
1377:
1353:
1347:
1346:
1335:
1329:
1328:
1318:
1308:
1299:(9): 3637–3671.
1284:
1275:
1274:
1254:
1245:
1244:
1199:
1193:
1192:
1172:
1166:
1165:
1147:
1123:
1114:
1113:
1076:
1061:
1060:
1050:
1010:
989:
988:
986:
984:
978:
974:"Facts for Life"
970:
953:
952:
942:
902:
896:
895:
887:
881:
875:
869:
863:
857:
856:
854:
853:
839:
833:
832:
822:
812:
788:
777:
770:
755:
754:
726:
699:
698:
679:
673:
672:
652:
646:
645:
632:
592:
579:
578:
566:
487:therapeutic food
436:food supplements
370:Maternal factors
138:
137:
133:
105:or insufficient
64:1 million a year
34:
22:
21:
1841:
1840:
1836:
1835:
1834:
1832:
1831:
1830:
1811:
1810:
1804:
1788:
1786:Further reading
1783:
1722:
1718:
1708:
1706:
1702:
1693:
1689:
1679:
1677:
1670:
1666:
1651:
1647:
1638:
1637:
1633:
1624:
1622:
1613:
1612:
1608:
1569:
1560:
1550:
1548:
1543:
1542:
1538:
1528:
1526:
1499:
1493:
1489:
1479:
1477:
1473:
1462:
1456:
1452:
1442:
1405:
1401:
1354:
1350:
1336:
1332:
1285:
1278:
1255:
1248:
1200:
1196:
1189:
1173:
1169:
1124:
1117:
1077:
1064:
1011:
992:
982:
980:
976:
972:
971:
956:
903:
899:
888:
884:
876:
872:
864:
860:
851:
849:
841:
840:
836:
789:
780:
771:
758:
743:
727:
702:
695:
681:
680:
676:
669:
653:
649:
593:
582:
567:
550:
546:
534:
499:
473:Treatment with
463:
454:
448:
421:
404:
395:
372:
332:
316:
288:
260:
239:
207:
171:
158:
135:
131:
130:
119:
20:
17:
12:
11:
5:
1839:
1829:
1828:
1823:
1809:
1808:
1803:978-1610395854
1802:
1787:
1784:
1782:
1781:
1716:
1687:
1664:
1645:
1631:
1606:
1579:(5): 520–537.
1558:
1536:
1487:
1450:
1399:
1368:(4): 2125–33.
1348:
1330:
1276:
1246:
1211:(1): 118–128.
1194:
1187:
1167:
1138:(5): 516–518.
1115:
1062:
990:
954:
897:
882:
870:
858:
834:
778:
756:
741:
700:
693:
674:
667:
647:
607:(5): 425–435.
580:
547:
545:
542:
541:
540:
533:
530:
498:
495:
462:
459:
450:Main article:
447:
444:
420:
417:
403:
400:
394:
391:
371:
368:
356:celiac disease
331:
328:
315:
312:
287:
284:
259:
256:
238:
235:
206:
203:
192:
191:
188:
185:
170:
167:
157:
154:
118:
115:
75:micronutrients
66:
65:
62:
58:
57:
54:Stunted growth
51:
45:
44:
36:
35:
27:
26:
18:
15:
9:
6:
4:
3:
2:
1838:
1827:
1824:
1822:
1819:
1818:
1816:
1805:
1799:
1795:
1790:
1789:
1777:
1773:
1768:
1763:
1759:
1755:
1751:
1747:
1743:
1739:
1735:
1731:
1727:
1720:
1701:
1697:
1691:
1675:
1668:
1660:
1656:
1649:
1641:
1635:
1621:. 7 July 2016
1620:
1619:Quartz Africa
1616:
1610:
1602:
1598:
1594:
1590:
1586:
1582:
1578:
1574:
1567:
1565:
1563:
1546:
1540:
1525:
1521:
1517:
1513:
1509:
1505:
1498:
1491:
1472:
1468:
1461:
1454:
1446:
1440:
1436:
1432:
1427:
1422:
1418:
1414:
1410:
1403:
1395:
1391:
1386:
1381:
1376:
1371:
1367:
1363:
1359:
1352:
1344:
1340:
1334:
1326:
1322:
1317:
1312:
1307:
1302:
1298:
1294:
1290:
1283:
1281:
1272:
1268:
1265:(8): 804–13.
1264:
1260:
1253:
1251:
1242:
1238:
1234:
1230:
1226:
1222:
1218:
1214:
1210:
1206:
1198:
1190:
1184:
1180:
1179:
1171:
1163:
1159:
1155:
1151:
1146:
1141:
1137:
1133:
1129:
1122:
1120:
1111:
1107:
1103:
1099:
1095:
1091:
1087:
1083:
1075:
1073:
1071:
1069:
1067:
1058:
1054:
1049:
1044:
1040:
1036:
1032:
1028:
1024:
1020:
1016:
1009:
1007:
1005:
1003:
1001:
999:
997:
995:
975:
969:
967:
965:
963:
961:
959:
950:
946:
941:
936:
932:
928:
924:
920:
916:
912:
908:
901:
893:
886:
880:
874:
868:
862:
848:
844:
838:
830:
826:
821:
816:
811:
806:
802:
798:
794:
787:
785:
783:
775:
769:
767:
765:
763:
761:
752:
748:
744:
738:
734:
733:
725:
723:
721:
719:
717:
715:
713:
711:
709:
707:
705:
696:
694:9781449667719
690:
686:
685:
678:
670:
668:9781135999414
664:
660:
659:
651:
644:
640:
636:
631:
626:
622:
618:
614:
610:
606:
602:
598:
591:
589:
587:
585:
576:
572:
565:
563:
561:
559:
557:
555:
553:
548:
539:
536:
535:
529:
527:
523:
519:
514:
512:
508:
503:
494:
492:
488:
484:
480:
476:
467:
458:
453:
452:Breastfeeding
446:Breastfeeding
443:
441:
437:
433:
428:
426:
416:
414:
408:
399:
390:
388:
383:
379:
377:
376:breastfeeding
367:
363:
361:
357:
353:
349:
346:is a lack of
345:
341:
336:
327:
325:
320:
311:
309:
305:
301:
292:
283:
281:
277:
273:
264:
255:
253:
243:
234:
230:
226:
224:
219:
217:
211:
202:
199:
196:
189:
186:
183:
180:
179:
178:
177:in children:
176:
162:
153:
149:
145:
142:
123:
114:
112:
108:
104:
100:
95:
92:
88:
84:
80:
76:
72:
63:
59:
55:
52:
50:
46:
42:
37:
33:
28:
23:
1821:Malnutrition
1793:
1733:
1729:
1719:
1707:. Retrieved
1690:
1678:. Retrieved
1667:
1658:
1648:
1634:
1623:. Retrieved
1618:
1609:
1576:
1572:
1549:. Retrieved
1539:
1527:. Retrieved
1507:
1503:
1490:
1478:. Retrieved
1471:the original
1466:
1453:
1438:
1416:
1412:
1402:
1365:
1361:
1351:
1333:
1296:
1292:
1262:
1258:
1208:
1204:
1197:
1177:
1170:
1135:
1131:
1085:
1081:
1022:
1018:
981:. Retrieved
914:
910:
900:
885:
873:
861:
850:. Retrieved
846:
837:
800:
796:
731:
683:
677:
657:
650:
642:
604:
600:
521:
517:
515:
504:
500:
497:Epidemiology
472:
455:
439:
429:
422:
413:Evelyn Gitau
409:
405:
396:
384:
380:
373:
364:
333:
321:
317:
297:
269:
249:
231:
227:
220:
212:
208:
200:
197:
193:
175:malnutrition
172:
150:
146:
141:malnutrition
128:
96:
91:malnutrition
79:malnutrition
78:
70:
69:
1709:January 31,
1510:(1): 7–10.
479:amoxicillin
475:antibiotics
272:Kwashiorkor
210:nutrition.
1826:Pediatrics
1815:Categories
1625:2020-08-17
1415:(Review).
1364:(Review).
1082:The Lancet
852:2022-12-09
803:(1): 107.
544:References
419:Prevention
348:sanitation
324:sanitation
304:sanitation
286:Sanitation
246:continuum.
129:Linked to
117:Background
103:sanitation
1758:0028-0836
1362:Nutrients
1154:0277-2116
1039:0140-6736
931:1178-6388
751:492175371
621:1533-4406
461:Treatment
402:Diagnosis
1776:31915393
1680:March 3,
1676:. UNICEF
1672:UNICEF.
1601:25229403
1593:12959894
1551:March 3,
1529:March 3,
1524:39557892
1480:March 3,
1435:28244672
1394:25816159
1325:22016708
1271:19710981
1241:21280033
1233:24571214
1162:11429507
1110:18345055
1102:18206226
1057:18206223
983:March 3,
979:. UNICEF
949:31802887
829:26751464
639:23363496
532:See also
518:indirect
483:cefdinir
477:such as
440:Soy Kunu
335:Diarrhea
330:Diseases
276:Marasmus
182:stunting
169:Measures
49:Symptoms
1767:7015855
1738:Bibcode
1385:4425135
1316:3194109
1213:Bibcode
1048:2258311
940:6878600
820:4730498
630:3654668
507:stunted
352:hygiene
216:stunted
134:⁄
107:hygiene
99:poverty
85:). The
1800:
1774:
1764:
1756:
1730:Nature
1599:
1591:
1522:
1433:
1392:
1382:
1323:
1313:
1269:
1239:
1231:
1185:
1160:
1152:
1108:
1100:
1055:
1045:
1037:
1019:Lancet
947:
937:
929:
827:
817:
749:
739:
691:
665:
637:
627:
619:
575:632505
573:
522:direct
393:Gender
237:Causes
111:gender
61:Deaths
1703:(PDF)
1597:S2CID
1520:S2CID
1500:(PDF)
1474:(PDF)
1463:(PDF)
1237:S2CID
1106:S2CID
977:(PDF)
1798:ISBN
1772:PMID
1754:ISSN
1711:2013
1682:2014
1589:PMID
1553:2014
1531:2014
1482:2014
1431:PMID
1390:PMID
1321:PMID
1267:PMID
1229:PMID
1209:1308
1183:ISBN
1158:PMID
1150:ISSN
1098:PMID
1053:PMID
1035:ISSN
985:2014
945:PMID
927:ISSN
825:PMID
747:OCLC
737:ISBN
689:ISBN
663:ISBN
635:PMID
617:ISSN
571:SSRN
526:WASH
358:and
350:and
298:The
1762:PMC
1746:doi
1734:577
1581:doi
1512:doi
1421:doi
1380:PMC
1370:doi
1339:NHS
1311:PMC
1301:doi
1221:doi
1140:doi
1090:doi
1086:371
1043:PMC
1027:doi
1023:371
935:PMC
919:doi
815:PMC
805:doi
625:PMC
609:doi
605:368
481:or
1817::
1770:.
1760:.
1752:.
1744:.
1732:.
1728:.
1657:.
1617:.
1595:.
1587:.
1577:30
1575:.
1561:^
1518:.
1506:.
1502:.
1465:.
1437:.
1429:.
1417:32
1411:.
1388:.
1378:.
1360:.
1319:.
1309:.
1295:.
1291:.
1279:^
1263:50
1261:.
1249:^
1235:.
1227:.
1219:.
1207:.
1156:.
1148:.
1136:32
1134:.
1130:.
1118:^
1104:.
1096:.
1084:.
1065:^
1051:.
1041:.
1033:.
1021:.
1017:.
993:^
957:^
943:.
933:.
925:.
915:12
913:.
909:.
845:.
823:.
813:.
801:13
799:.
795:.
781:^
759:^
745:.
703:^
641:.
633:.
623:.
615:.
603:.
599:.
583:^
551:^
513:.
415:.
378:.
362:.
282:.
274:,
1806:.
1778:.
1748::
1740::
1713:.
1684:.
1661:.
1628:.
1603:.
1583::
1555:.
1533:.
1514::
1508:2
1484:.
1423::
1396:.
1372::
1366:7
1345:.
1327:.
1303::
1297:8
1273:.
1243:.
1223::
1215::
1191:.
1164:.
1142::
1112:.
1092::
1059:.
1029::
987:.
951:.
921::
894:.
855:.
831:.
807::
753:.
697:.
671:.
611::
577:.
136:3
132:1
Text is available under the Creative Commons Attribution-ShareAlike License. Additional terms may apply.