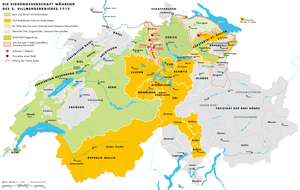
801:, and occupied Bremgarten. United with the Zürcher troops, the Bernese marched towards Baden, which was forced to surrender on 1 June. The fortress of the Catholic city, the Stein, which had been built after the First War of Villmergen despite protests from the Reformed cantons, was immediately destroyed to symbolise the Protestant victory. Bern and Zürich had now successfully prevented the five cantons from splitting them in Aargau. The five cantons moved towards peace negotiations on 3 June, and on 18 July 1712, Zürich, Bern, Lucerne and Uri signed a treaty in
982:. Zürich and Bern occupied the Princely Lands and governed it together. Many of the monastic movable goods that were left behind in St. Gallen, including parts of the archive and the library, were taken away by them. Because of what he considered to be outrageous damage to the rights of the Imperial Abbey, as well as the danger posed to the Catholic religion in Toggenburg, Bürgisser obtained the Peace of Rohrschach, which was finally approved on 28 March 1714 after a series of negotiations with Zürich and Bern. After the death of Bürgisser, a new treaty, the
25:
101:
758:
220:
557:
319:
279:
240:
309:
289:
569:
260:
250:
230:
349:
329:
299:
339:
630:). In 1711, several Catholic municipalities once again subjected themselves to the abbot. The "Pines" then militarily occupied the municipalities, the abbatial goods and the monasteries of Magdenau and Neu St. Johann with the tacit approval of Bern and Zürich. That incident definitively forced the prince-abbot to take military counteractions and spread the crisis throughout Confederacy.
540:
1451) and to enter into the
Austrian sphere of influence (the Swiss had fought for centuries to uphold their independence from the Habsburgers). Especially both Appenzells but also Zürich could not accept such a turn of affairs. Also, the Princely Lands housed the fourth greatest population within the Confederacy, and they had essential economic importance in eastern Switzerland.
998:
start of the war. Further objects from the
Bernese spoils of war were returned to St Gallen in 1721. However, several valuable pieces of the monastic library of St. Gallen remained in Zürich, including manuscripts, paintings, astronomy tools and the globe of St. Gallen. The conflict on the cultural goods (
522:. The refusal of the Wattwilers to collaborate in building the road, which they regarded as a threat to their religious freedom and as leading to their financial suppression, caused a serious conflict with the prince-abbot, who eventually resorted to incarcerating the highest Toggenburg magistrate, the
595:
character. The
Confederacy chose sides along its fault lines of faith for either the prince-abbot of St Gall or the Reformed Toggenburgers. Attempts at mediation by both Imperial and French envoys to the Confederacy failed, and the Reformed cantons urged for settling the conflict before the end of the
547:
in 1703 and 1704. Moreover, the
Protestant outposts of Zürich and Bern were becoming more and more supportive of the Toggenburg cause. In 1707, they presented the prince-abbot with a mediation proposal in which Toggenburg would be granted far-reaching autonomy, but Bürgisser did not respond. A series
966:
as well as in the governance of the
Vogteien, and all conflicts in which both religions were concerned now had parity. In the Landvogteien Thurgau, Baden, Sargans and Rheintal, the Reformed municipalities kept the guarantee of their religious exercise under Zürcher sovereignty, and the rights of the
594:
democracy. All abbatial magistrates and the governor were extradited and freedom of religion was promulgated, which obviously threatened the
Catholic cantons' interests. The Catholic protector canton of Schwyz defected to the camp of the prince-abbot, and the conflict now assumed a clearly religious
539:
in 1706. Those events threatened to raise the conflict to a
European level. Moreover, that constituted a grave breach of the structure and sovereignty of the Confederacy since the Imperial Abbey of St Gall seemed to escape all of the influence of the Confederacy (despite St Gall being a member since
997:
soon denounced the peace in a letter no longer had any effect on the settlement of the conflict. Abbot von
Rudolphi returned to the monastery of St Gall on 7 September 1718 after a six-year exile. On 23 March 1719, he managed to retrieve a large part of the library that was removed to Zürich at the
890:
of 11 August 1712, the Fourth
Landfrieden in the history of the Confederacy, Bern and Zürich secured their rule over the Gemeine Herrschaften. The political hegemony of the Catholic cantons in the Gemeine Herrschaften since 1531 thus came to an end. That simultaneously meant the restoration of a
967:
Catholics were secured. Instead of mere tolerance, the
Protestants now received equal treatment before the law to the traditionally-favoured Catholic religion. A "Landfriedliche Kommission", composed of representatives from Zürich, Bern, Lucerne and Uri, began to oversee matters of religion.
820:, Giacomo Caracciolo, had rejected the Treaty of Aarau. In Lucerne and Uri, the people also demanded from the government to take up arms once more against the Protestant cantons. On 20 July, the first strike of the forces of the five cantons on the Bernese armed bands occurred at
451:, about two thirds of the Toggenburg population were Protestants, but they were not the majority in every municipality. After the transaction of sovereignty to the Imperial Abbey, the Reformed inhabitants of Toggenburg were promised by their Swiss allies of the Cantons of
852:, Niklaus von Diesbach and Jean de Sacconay fought against 12,000 men from Central Switzerland under command of Franz Konrad von Sonnenberg and Ludwig Christian Pfyffer. The long-undecided battle was finally determined by the intervention of a fresh corps from
464:. In all municipalities, including those that were almost completely Reformed, the position of Catholics was strengthened, and new Catholic churches were built in several towns, which made the common usage of parish churches no longer required.
961:
Juridically, the Fourth Landfrieden made the Second Landfrieden of Kappel of 1531, confirmed at the Third Landfrieden in 1656, cease to function. Therefore, Protestantism was formally treated equally before the law in the
526:
Josef Germann, in order to break the opposition. Because Germann was a Catholic, the Toggenburgers' complaints were heard by the protector cantons, which began acting on behalf of the Toggenburgers. In that situation,
1005:
The animosity between the Imperial Abbey and Toggenburg increased further until the abolishment of the monastic state in 1798, after two abbatial magistrates had been murdered in 1735 and after a 1739 conference in
487:
was Braun's punishment reduced to banishment. Four years later, through the intervention of their protector cantons, the Toggenburgers succeeded in having abbot Gallus Alt (r. 1654–1687) remove Schorno from office.
589:
at Wattwil, which installed an autonomous governance for Toggenburg and maintained the sovereignty of the Imperial Abbey of St Gall over it. The Toggenburgers thus acted upon the example given by Appenzell as a
459:
and by the prince-abbot that the principle of equal treatment in religious matters would be respected. However, the abbots of St Gall undertook attempts to return Toggenburg to Catholicism in the frame of the
1064:) was still an associate of the Confederacy, not a Swiss canton, and so there were only five cantons on the Catholic side. It was only in 1815 that Valais became a full member of the new Swiss Confederacy.
721:
and the assault on the abbatial lands. In mid-May, about 3000 Zürichers, 2000 Bernese, 2000 Toggenburgers and 1800 Protestant Thurgauers marched into the Princely Lands. They hit upon the abbatial city of
511:. That would be strategically and economically important for the Catholic cantons by enabling a rapid movement of Catholic troops to Toggenburg and the Princely Lands in case of war.
475:
practice of the day. That resulted in conflicts by the infringement of the Protestant clergy by the abbatial authorities. In 1663, for example, the abbatial governor of Toggenburg in
633:
On 13 April 1712, Bern and Zürich published a manifesto against the prince-abbot of St Gall and so revealed their support for the Toggenburgers. The five Catholic inner cantons of
491:
In 1695, in the framework of the Counter-Reformation, the seven Catholic cantons of the Confederacy and the prince-abbot of St Gall formed an alliance for the salvation of
413:, a war for hegemony in the Confederacy and an uprising of subjects. The war ended in a Protestant victory and upset the balance of political power within the Confederacy.
990:(r. 1717–1740) on 16 June 1718. The Imperial Abbey of St Gall was restored, including its rule over Toggenburg, and its autonomy and freedom of religion were confirmed.
583:
The first step towards escalation was made by the Toggenburgers, with the approval of Bern and of Zürich, by adopting a design for a constitution on 23 March 1707 at a
709:
As Bern and Zürich had long been preparing for war, they seized the offensive. Bern opened the first war phase on 26 April, when its first troops crossed the river
798:
471:, began to organise the abbatial sovereign territories more strictly and to subject them to an at least tentatively modern governance in the frame of the
789:
and thereby threatened to drive a wedge between Zürich and Bern. The Bernese immediately launched a counteroffensive under the command of General-Major
1423:
790:
880:
829:
697:
without regard to Bern and France, the Reformed city of St Gallen was surrounded by the abbatial territory and Glarus was internally divided. The
602:
The struggle reached such a peak that the Toggenburgers armed themselves with the support of Zürich, and they occupied the abbatial fortresses at
701:
mobilised in favour of the Protestant cause because of their alliance with Zürich from 1707, but they did not participate in any combat actions.
531:
Fidel von Thurn moved Bürgisser to seek diplomatic ties within the Holy Roman Empire, and a treaty of protection was concluded with Emperor
914:. That secured the military connection between Zürich and the Bernese land of Aargau and blocked the Catholic cantons' access to the north.
518:
in 1697, Bürgisser ordered the municipality of Wattwil to start constructing the road over the Ricken Pass on the Toggenburg side through
1448:
942:
In the Gemeine Herrschaften and Toggenburg, subjects kept their right to exercise both the Catholic and the Protestant religions.
543:
The Toggenburgers sought and found allies, mainly in their protector cantons, Schwyz and Glarus, with which they renewed their
797:
near Mellingen. The battle went in favour of the Bernese, who then took the city. On 26 May, they were also victorious at the
1341:
1333:
754:, the abbey and its goods were put an under a military governance, and its chattel and riches were sent to Bern and Zürich.
1386:
1147:
817:
1092:
19 (1993), pp. 11–33; Nattrass, "Further sources for the Swiss civil war of 1712 in the British Library's collections",
1428:
1076:
Encarta-encyclopedie Winkler Prins (1993–2002) s.v. "Zwitserland. §5.2 Reformatie". Microsoft Corporation/Het Spectrum.
1418:
1366:
1313:
1207:
1185:
614:
in 1710. Religious strife was now splitting the Toggenburgers themselves along religious boundaries in the moderate "
68:
46:
871:
to Unterwalden and via Rapperswil to the Linthebene. That made the resistance of the five cantons finally collapse.
499:, Schwyz proposed to Prince-Abbot Leodegar Bürgisser (r. 1696–1717) in 1699 the construction of a new road over the
39:
536:
484:
1288:
1438:
670:
342:
596:
532:
479:, Wolfgang Friedrich Schorno, sentenced a vicar, Jeremias Braun, to death because he had allegedly committed
1433:
645:
published a countermanifesto, and armed themselves for war. Bern and Zürich found support with the city of
848:
once again became the site of the decisive battle. The 8000-strong Bernese companies under the command of
495:
against the "un-Catholic religion". To strengthen the connections between the Imperial Abbey and Catholic
864:
576:
654:
92:
894:
The territorial conditions for peace were somewhat sharpened from those of the first peace treaty:
867:, the Bernese and the Zürichers advanced into the Lucernese territory, the land of Zug, across the
607:
33:
1031:
1002:) between Zürich and St. Gallen flared up in the 1990s but was finally settled amicably in 2006.
766:
1404:
Online Museum of Hütten: "Villmergerkriege 1656 und 1712 – Befestigte Grenze Kanton Zürich Süd"
983:
50:
841:
650:
263:
849:
572:
382:
170:
1230:
Administration des historisch-biographischen Lexikons der Schweiz (Neuchâtel 1934), p. 259f.
422:
1025:
806:
443:
426:
406:
243:
1247:(Neuchâtel 1921), p. 8. Administration des historisch-biographischen Lexikons der Schweiz.
1178:
Schriftenreihe der Schweizerischen Gesellschaft für Militärhistorische Studienreisen (GMS)
860:
as well as the superior Bernese artillery. During the battle 2,000 Catholics were killed.
832:). On 22 July, the Schwyzer and Zuger troops launched a failed attack against the Zürcher
8:
1443:
1019:
987:
971:
731:
694:
496:
461:
390:
282:
1355:
Unruhige Untertanen. Die Rebellion der Luzerner Bauern im zweiten Villmergerkrieg (1712)
1291:). Leemann, Zürich-Selnau 1912 (Zugleich: Zürich, Universität, Dissertation, 1911/1912).
975:
739:
452:
402:
223:
885:
782:
774:
690:
1086:
1362:
1337:
1329:
1309:
1203:
1181:
936:
634:
472:
348:
292:
100:
955:
947:
773:
became the most important scene of combat. The five cantons occupied the cities of
770:
438:
434:
430:
312:
1202:. Jefferson, North Carolina and London: McFarland & Company, Inc. p. 16.
927:
Bern now had coruled in all Gemeine Herrschaften in which it had not had a share:
994:
932:
899:
794:
786:
735:
386:
1380:
1140:
1134:
1128:
1037:
743:
456:
398:
233:
903:
868:
726:, which fell on 22 May after a short siege. The allies then pushed forward to
685:
352:
1412:
1326:
1712. Zeitgenössische Quellen zum Zweiten Villmerger- oder Toggenburgerkrieg.
907:
698:
666:
638:
585:
410:
394:
332:
302:
757:
750:, but initially left the abbot without any support. According to the time's
825:
821:
476:
958:) and the Vogtei Gaster were not supported by Bern and the other cantons.
603:
556:
219:
898:
Zürich and Bern, together with Glarus, maintained their ownership of the
837:
751:
658:
642:
500:
492:
467:
In the 17th century the prince-abbots and their worldly magistrates, the
448:
375:
322:
318:
746:
that the abbey had acquired in 1699. The five Catholic cantons occupied
1007:
963:
921:
911:
845:
747:
727:
515:
278:
239:
483:
during a Reformed sermon. Only through interference by the Protestant
421:
The war was caused by a conflict between the prince-abbot of St Gall,
778:
611:
480:
378:
308:
288:
993:
Zürich and Bern ratified the Peace on 11 August 1718. The fact that
974:, Leodegar Bürgisser, went into exile with his convent on 29 May to
568:
433:
since 1460 but was simultaneously connected to the Swiss Cantons of
917:
The lordship of Rapperswil was acquired by Zürich, Bern and Glarus.
874:
857:
812:
The second and much bloodier phase of the war was triggered by the
259:
249:
229:
1403:
1323:
Hans Luginbühl, Anne Barth-Gasser, Fritz Baumann, Dominique Piller
816:
of Schwyz, Zug and Unterwalden who, after being influenced by the
328:
298:
928:
853:
833:
805:. It decided that the five cantons would lose their share in the
718:
662:
508:
338:
951:
689:. The remaining cantons stayed neutral, the Catholic cantons of
979:
714:
680:
646:
519:
504:
253:
548:
of events then began, which would eventually escalate to war.
802:
615:
1141:
675:
623:
1135:
1129:
514:
After the settlement of the "Cross War" with the Reformed
824:, which then retreated to join the main guard of Bern at
723:
710:
561:
891:
compromised religious peace within the Old Confederacy.
809:
of the County of Baden and (partially) the Freie Ämter.
978:, the residence of a new lordship of St Gall north of
1010:
between the parties had failed to yield any results.
1369:(Zugleich: Zürich, Universität, Dissertation, 1995).
1308:
Band 2. (Zürich 1977) p. 673–784. Berichthaus.
535:
in 1702. Bürgisser even received the investiture as
1087:
The Swiss civil war of 1712 in contemporary sources
1176:, "Blätter aus der Schweizer Militärgeschichte",
924:) became a Gemeine Herrschaft of Zürich and Bern.
1410:
599:to reduce the chance of a foreign intervention.
564:on 21 May 1712 by Zürcher and Bernese artillery.
1281:Zürichs Anteil am Zweiten Villmergerkrieg, 1712
1241:Historisch-Biographisches Lexikon der Schweiz.
1224:Historisch-Biographisches Lexikon der Schweiz.
1285:Schweizer Studien zur Geschichtswissenschaft,
1180:Volume 15 (Frauenfeld 1995) p. 158. Huber.
793:. On 22 May, the forces had clashed in the
1197:
1424:18th century in the Old Swiss Confederacy
717:to support Zürich with the occupation of
69:Learn how and when to remove this message
1359:Luzerner historische Veröffentlichungen.
1056:
1054:
756:
567:
555:
32:This article includes a list of general
761:Plan of the second battle of Villmergen
575:, general of the Bernese troops at the
551:
1411:
1328:Merker im Effingerhof (Lenzburg 2011)
875:Peace of Aarau or "Fourth Landfrieden"
669:. The five cantons found support with
1120:
1118:
1051:
425:, and his Protestant subjects in the
385:from 12 April to 11 August 1712. The
1387:Historical Dictionary of Switzerland
1361:Band 29). Rex-Verlag, (Luzern 1995)
1148:Historical Dictionary of Switzerland
986:, was concluded with his successor,
405:as well as the abbatial subjects of
18:
13:
1449:18th-century Reformed Christianity
1306:Handbuch der Schweizer Geschichte.
1115:
1060:At the time, Valais (known as the
429:. It had belonged to the Imperial
38:it lacks sufficient corresponding
14:
1460:
1394:
704:
485:Canton of Appenzell Ausserrhoden
347:
337:
327:
317:
307:
297:
287:
277:
258:
248:
238:
228:
218:
99:
23:
1250:
1233:
946:Zürich's further claims to the
186:Peace of Aarau (11 August 1712)
1216:
1191:
1167:
1154:
1099:
1079:
1067:
1062:Republic of the Seven Tithings
1:
1267:
1044:
653:as well as its allies in the
597:War of the Spanish Succession
416:
192:Sack of the Abbey of St. Gall
189:Peace of Baden (16 June 1718)
1198:Clodfelter, Micheal (1992).
906:, limited by a line between
391:Imperial Abbey of Saint Gall
195:End of the Catholic hegemony
7:
1336:(2nd print, Lenzburg 2012,
1200:Warfare and Armed Conflicts
1094:The British Library Journal
1090:The British Library Journal
1013:
865:Second Battle of Villmergen
863:After their victory in the
577:Second Battle of Villmergen
516:Imperial City of St. Gallen
16:Swiss religious war in 1712
10:
1465:
939:and the upper Freie Ämter.
117:Bern and Zürich and allies
1429:Civil wars in Switzerland
655:Prince-Bishopric of Basel
651:Principality of Neuchâtel
264:Principality of Neuchâtel
205:
161:12 April – 11 August 1712
153:
98:
93:European wars of religion
90:
83:
1419:1712 in military history
1381:Villmergerkrieg, Zweiter
1351:Martin Merki-Vollenwyder
1222:"Villmergerkriege", in:
1125:Second War of Villmergen
920:The Schwyzer Hurden (in
389:"inner cantons" and the
368:Second War of Villmergen
86:Second War of Villmergen
1032:First War of Villmergen
767:First War of Villmergen
372:Swiss Civil War of 1712
53:more precise citations.
1439:18th-century conflicts
1239:"Aarauer Friede." In:
1096:25 (1999), pp. 164–79.
762:
742:, a lordship north of
580:
565:
447:since 1436. After the
1174:Walter Schaufelberger
785:with their strategic
760:
571:
559:
533:Leopold I of Habsburg
409:. The conflict was a
383:Old Swiss Confederacy
323:Canton of Unterwalden
171:Old Swiss Confederacy
129:Five Catholic cantons
1277:Gottfried Guggenbühl
1026:Second War of Kappel
976:Neuravensburg Castle
970:The prince-abbot of
807:Gemeine Herrschaften
738:. The abbot fled to
552:Escalation of crisis
427:County of Toggenburg
366:, also known as the
1434:Religion-based wars
1020:First War of Kappel
988:Joseph von Rudolphi
799:Battle of Fischbach
732:Abbey of Saint Gall
622:) and the radical "
573:Samuel Frisching II
560:The bombardment of
497:Central Switzerland
462:Counter-Reformation
283:Abbey of Saint Gall
182:Protestant victory
763:
683:as well as in the
581:
566:
423:Leodegar Bürgisser
115:Protestant cantons
1342:978-3-8564-8141-4
1334:978-3-8564-8139-1
1085:Graham Nattrass,
1000:Kulturgüterstreit
937:County of Sargans
765:Just like in the
730:and occupied the
360:
359:
293:Canton of Lucerne
244:Toggenburg rebels
201:
200:
149:
148:
79:
78:
71:
1456:
1402:
1377:
1374:
1352:
1349:
1324:
1321:
1299:
1296:
1278:
1275:
1261:
1254:
1248:
1237:
1231:
1228:Tinguely – Zyro.
1220:
1214:
1213:
1195:
1189:
1175:
1171:
1165:
1158:
1152:
1143:
1137:
1131:
1122:
1113:
1107:
1103:
1097:
1083:
1077:
1075:
1071:
1065:
1058:
948:County of Uznach
889:
850:Samuel Frisching
791:Jean de Sacconay
771:Canton of Aargau
529:Landeshofmeister
469:Landeshofmeister
431:Abbey of St Gall
351:
341:
331:
321:
313:Canton of Schwyz
311:
301:
291:
281:
262:
252:
242:
232:
224:Canton of Zürich
222:
155:
154:
140:
126:
112:
106:
105:
103:
81:
80:
74:
67:
63:
60:
54:
49:this article by
40:inline citations
27:
26:
19:
1464:
1463:
1459:
1458:
1457:
1455:
1454:
1453:
1409:
1408:
1400:
1397:
1375:
1372:
1350:
1347:
1322:
1319:
1297:
1294:
1289:ZDB-ID 503936-8
1287:Band 4, Nr. 1,
1276:
1273:
1270:
1265:
1264:
1255:
1251:
1238:
1234:
1221:
1217:
1210:
1196:
1192:
1173:
1172:
1168:
1159:
1155:
1123:
1116:
1105:
1104:
1100:
1084:
1080:
1073:
1072:
1068:
1059:
1052:
1047:
1016:
995:Pope Clement XI
933:Vogtei Rheintal
900:County of Baden
883:
877:
795:County of Baden
736:Vogtei Rheintal
707:
554:
537:Imperial Prince
419:
173:
145:
143:Neutral parties
138:
132:
124:
118:
110:
104:
85:
75:
64:
58:
55:
45:Please help to
44:
28:
24:
17:
12:
11:
5:
1462:
1452:
1451:
1446:
1441:
1436:
1431:
1426:
1421:
1407:
1406:
1396:
1395:External links
1393:
1392:
1391:
1370:
1345:
1317:
1302:Ancien Régime.
1292:
1269:
1266:
1263:
1262:
1260:(1977) p. 699.
1258:Ancien Régime.
1249:
1232:
1215:
1208:
1190:
1166:
1164:(1977) p. 695.
1162:Ancien Régime.
1153:
1145:in the online
1114:
1110:Ancien Régime.
1098:
1078:
1066:
1049:
1048:
1046:
1043:
1042:
1041:
1038:Sonderbund War
1035:
1029:
1023:
1015:
1012:
984:Peace of Baden
956:Old Zürich War
944:
943:
940:
925:
918:
915:
902:and the lower
881:Peace of Aarau
876:
873:
844:. On 25 July,
830:Battle of Sins
814:Landsgemeinden
744:Lake Constance
706:
703:
553:
550:
418:
415:
364:Toggenburg War
358:
357:
356:
355:
345:
335:
325:
315:
305:
295:
285:
268:
267:
266:
256:
254:City of Geneva
246:
236:
234:Canton of Bern
226:
208:
207:
203:
202:
199:
198:
197:
196:
193:
190:
187:
179:
175:
174:
169:
167:
163:
162:
159:
151:
150:
147:
146:
137:
134:
133:
123:
120:
119:
109:
96:
95:
88:
87:
84:Toggenburg War
77:
76:
31:
29:
22:
15:
9:
6:
4:
3:
2:
1461:
1450:
1447:
1445:
1442:
1440:
1437:
1435:
1432:
1430:
1427:
1425:
1422:
1420:
1417:
1416:
1414:
1405:
1399:
1398:
1389:
1388:
1383:
1382:
1371:
1368:
1367:3-7252-0614-7
1364:
1360:
1356:
1346:
1343:
1339:
1335:
1331:
1327:
1318:
1315:
1314:3-8557-2021-5
1311:
1307:
1303:
1298:Ulrich Im Hof
1293:
1290:
1286:
1282:
1272:
1271:
1259:
1253:
1246:
1242:
1236:
1229:
1225:
1219:
1211:
1209:0-89950-814-6
1205:
1201:
1194:
1187:
1186:3-7193-1111-2
1183:
1179:
1170:
1163:
1157:
1150:
1149:
1144:
1138:
1132:
1126:
1121:
1119:
1112:1977, p. 694.
1111:
1102:
1095:
1091:
1088:
1082:
1070:
1063:
1057:
1055:
1050:
1039:
1036:
1033:
1030:
1027:
1024:
1021:
1018:
1017:
1011:
1009:
1003:
1001:
996:
991:
989:
985:
981:
977:
973:
968:
965:
959:
957:
954:(lost in the
953:
949:
941:
938:
934:
930:
926:
923:
919:
916:
913:
909:
908:Oberlunkhofen
905:
901:
897:
896:
895:
892:
887:
882:
872:
870:
866:
861:
859:
855:
851:
847:
843:
839:
835:
831:
827:
823:
819:
815:
810:
808:
804:
800:
796:
792:
788:
784:
780:
776:
772:
768:
759:
755:
753:
749:
745:
741:
740:Neuravensburg
737:
733:
729:
725:
720:
716:
712:
705:Course of war
702:
700:
699:Three Leagues
696:
692:
688:
687:
682:
678:
677:
673:and in their
672:
668:
667:La Neuveville
664:
660:
656:
652:
648:
644:
640:
636:
631:
629:
625:
621:
617:
613:
612:Schwarzenbach
609:
605:
600:
598:
593:
592:Landsgemeinde
588:
587:
586:Landsgemeinde
578:
574:
570:
563:
558:
549:
546:
541:
538:
534:
530:
525:
521:
517:
512:
510:
506:
502:
498:
494:
489:
486:
482:
478:
474:
470:
465:
463:
458:
454:
450:
446:
445:
440:
436:
432:
428:
424:
414:
412:
411:religious war
408:
404:
400:
396:
392:
388:
384:
380:
377:
373:
369:
365:
354:
350:
346:
344:
340:
336:
334:
333:Canton of Zug
330:
326:
324:
320:
316:
314:
310:
306:
304:
303:Canton of Uri
300:
296:
294:
290:
286:
284:
280:
276:
275:
274:
273:
269:
265:
261:
257:
255:
251:
247:
245:
241:
237:
235:
231:
227:
225:
221:
217:
216:
215:
214:
210:
209:
204:
194:
191:
188:
185:
184:
183:
180:
177:
176:
172:
168:
165:
164:
160:
157:
156:
152:
144:
136:
135:
130:
122:
121:
116:
108:
107:
102:
97:
94:
89:
82:
73:
70:
62:
52:
48:
42:
41:
35:
30:
21:
20:
1385:
1379:
1358:
1354:
1325:
1305:
1301:
1284:
1280:
1257:
1252:
1244:
1240:
1235:
1227:
1223:
1218:
1199:
1193:
1177:
1169:
1161:
1156:
1146:
1124:
1109:
1101:
1093:
1089:
1081:
1069:
1061:
1004:
999:
992:
969:
960:
945:
893:
878:
862:
818:papal nuncio
813:
811:
764:
708:
684:
674:
632:
627:
619:
601:
591:
584:
582:
544:
542:
528:
523:
513:
490:
477:Lichtensteig
468:
466:
442:
420:
371:
367:
363:
361:
271:
270:
212:
211:
206:Belligerents
181:
142:
128:
114:
65:
56:
37:
1401:(in German)
1373:(in German)
1348:(in German)
1320:(in German)
1295:(in German)
1274:(in German)
1106:(in German)
904:Freie Ämter
884: [
869:Brünig Pass
838:Richterswil
752:laws of war
686:Freie Ämter
643:Unterwalden
501:Ricken Pass
493:Catholicism
449:Reformation
397:cantons of
393:fought the
381:during the
353:Freie Ämter
213:Protestants
59:August 2016
51:introducing
1444:Toggenburg
1413:Categories
1376:Thomas Lau
1268:Literature
1245:A – Basel.
1074:(in Dutch)
1045:References
1008:Frauenfeld
972:Saint Gall
964:Tagsatzung
922:Freienbach
912:Fahrwangen
846:Villmergen
783:Bremgarten
748:Rapperswil
728:St. Gallen
641:, Zug and
637:, Schwyz,
524:Landweibel
473:absolutist
417:Background
407:Toggenburg
395:Protestant
131:and allies
34:references
779:Mellingen
695:Solothurn
616:Lime Tree
604:Lütisburg
545:Landrecht
481:blasphemy
444:Landrecht
379:civil war
272:Catholics
1384:(2013).
1256:Im Hof:
1243:Band 1:
1226:Band 7:
1160:Im Hof:
1108:Im Hof:
1014:See also
858:Lenzburg
834:redoubts
734:and the
691:Fribourg
676:Vogteien
649:and the
503:between
441:through
387:Catholic
374:, was a
166:Location
91:Part of
1142:Italian
929:Thurgau
879:At the
854:Seengen
719:Thurgau
663:Moutier
635:Lucerne
509:Wattwil
370:or the
47:improve
1365:
1340:
1332:
1312:
1206:
1184:
1136:French
1130:German
1040:(1847)
1034:(1656)
1028:(1531)
1022:(1529)
980:Lindau
935:, the
931:, the
842:Hütten
769:, the
715:Stilli
681:Ticino
671:Valais
647:Geneva
520:socage
505:Uznach
453:Zürich
439:Schwyz
435:Glarus
403:Zürich
343:Valais
178:Result
141:
139:
127:
125:
113:
111:
36:, but
888:]
803:Aarau
787:fords
775:Baden
628:Harte
620:Linde
608:Iberg
376:Swiss
1363:ISBN
1338:ISBN
1330:ISBN
1310:ISBN
1304:In:
1204:ISBN
1182:ISBN
1139:and
1127:in
952:Höfe
910:and
856:and
840:and
826:Muri
822:Sins
781:and
693:and
665:and
659:Biel
624:Pine
610:and
507:and
457:Bern
455:and
437:and
401:and
399:Bern
362:The
158:Date
1357:(=
1283:(=
836:at
724:Wil
713:at
711:Aar
679:in
639:Uri
626:" (
618:" (
562:Wil
1415::
1378:,
1353:,
1344:).
1300:,
1279:,
1133:,
1117:^
1053:^
950:,
886:fr
777:,
661:,
657::
606:,
1390:.
1316:.
1212:.
1188:.
1151:.
828:(
579:.
72:)
66:(
61:)
57:(
43:.
Text is available under the Creative Commons Attribution-ShareAlike License. Additional terms may apply.