430:), so that slow worms crawl much more stiffly and clumsily than snakes. The scaling of the head is similar to that of snakes. The ear openings are mostly completely hidden under the scales. The relatively small eyes have movable, closable eyelids (these are fused in snakes) and round pupils. The rather short tongue is broad, bilobed and does not end in fine tips. To lick, i.e. to absorb odorous substances, slow worms have to open their mouths slightly, as they lack the gap in the upper lip that snakes possess. The pointed, sometimes loosely fixed teeth are curved backwards; there are 7 to 9 teeth in the premaxilla, 10 to 12 in the maxilla and 14 to 16 in the lower jaw.
463:
206:
679:
655:
434:
410:
82:
57:
667:
321:
447:
691:
1628:
282:, and can be encouraged to enter and help remove pest insects by placing black plastic or providing places to shelter such as piles of logs, corrugated iron sheets or under tiles. On warm days, one or more slow worms can often be found underneath these heat collectors. One of the biggest causes of mortality in slow worms in suburban areas is the domestic cat, against which it has no defence.
38:
475:; at birth, the 7 to 10 cm long young animals are in a very thin, transparent egg shell, which they pierce immediately afterwards. They initially weigh less than a gram and still have a remnant of the yolk. Juvenile slow worms have a contrasting color scheme and pattern. The top of the body is silvery-white to golden yellow, while the sides and underside are black.
719:
700:
425:
The skin surface consists of smooth, round-to-hexagonal scales which overlap like roof tiles and are roughly the same shape on the dorsal and ventral surfaces of the body. There are several longitudinal rows running along the underside. In total, the trunk has 125 to 150 transverse scale rows and the
454:
In
Central Europe, the mating season of the species is usually between late April and June. The males often wrestle violently around the females, although in most populations they are in the majority. The opponents try to push each other to the ground, bite each other and wrap themselves tightly
417:
Slow worms have an elongated body with a circular cross-section without limbs and reach a maximum length of up to 57.5 cm. Most adult animals are between 40 and 45 cm long, with up to 22 cm on the head and trunk section and the rest on the tail. There is no visible neck. The tail,
483:
Adult slow worms grow to be about 50 cm (20") long, and are known for their exceptionally long lives; the slow worm may be the longest-living lizard, living about 30 years in the wild and up to at least 54 years in captivity (this record is held by a male slow worm that lived at the
470:
Sometimes females mate with other males later. The gestation period of the females lasts 11 to 14 weeks, and subsequently, between mid-July and the end of August, and sometimes even later, they usually give birth to between eight and twelve young (extreme values: 2 to 28). Slow worms are
722:
721:
726:
725:
720:
422:, the severing of the tail when it is pulled by predators. When regrown, the tail grows back only to a short stub, probably because loss of the tail does not sufficiently affect the species' locomotion, foraging and defence abilities to necessitate full and rapid regeneration.
727:
488:
from 1892 until 1946, the age when first obtained is unknown). The female often has a stripe along the spine and dark sides, while the male may have blue spots dorsally. Juveniles of both sexes are gold with dark brown bellies and sides with a dark stripe along the spine.
706:
704:
701:
705:
724:
545:
These reptiles are largely nocturnal and do not bask in the sun like other reptiles, but choose to warm themselves indirectly underneath objects, such as rocks, which have been warmed by the sun. They can often be found in long
703:
723:
598:
The slow worm is assumed to be non-native in
Ireland, possibly arriving in the 1900s. Due to their secretive habits they are difficult to observe and have been sighted only in parts of
278:, meaning that they have the ability to shed their tails to escape predators. While the tail regrows, it does not reach its original length. In the UK, they are common in gardens and
702:
1888:
1027:
1463:
1162:
274:, spending much of their time hiding underneath objects. The skin of slow worms is smooth with scales that do not overlap one another. Like many other lizards, they
904:
1195:
1097:
Barr JI, Boisvert CA, Bateman PW. 2021. At what cost? Trade-offs and influences on energetic investment in tail regeneration in lizards following autotomy.
1014:
1792:
1844:
1911:
1344:"A method of obtaining dietary data for slow worms (Anguis fragilis) by means of non‐harmful cooling and results from a Danish population"
1494:
1389:
1766:
1805:
678:
1810:
1148:
1064:
806:
1936:
1470:
1166:
1931:
920:
1123:
587:
1745:
967:
1849:
550:
and other damp environments In a 2009 study of a Danish population, the diet of the slow-worm was found to include
455:
around each other. When mating, the female is bitten in the head or neck region, while the male introduces his two
1758:
1291:
970:"Slow worm, Anguis fragilis (Reptilia: Anguidae) as a species complex: Geneticstructure reveals deep divergences"
196:
1831:
1584:"Fossil lizards and worm lizards (Reptilia, Squamata) from the Neogene and Quaternary of Europe: an overview"
1219:
1243:
1267:
537:. Slow worms detect the presence of predators with their tongues by flicking them in and out to 'smell'.
418:
which ends in a horny tip, is continuous with the trunk and is often slightly longer. Slow worms exhibit
846:
654:
1926:
1509:
874:
712:
A slow worm moving through grass. This individual is a juvenile, as evinced by its golden colouration.
1682:
784:
1921:
81:
944:
1632:
1180:
583:
462:
1043:
205:
1797:
1644:
296:
the word "slow". In Middle
English it was written "slowurm", from Old English "slāwyrm", where
1823:
1393:
1008:
968:
Václav Gvozˇ dík, David
Jandzik, Petros Lymberakis, Daniel Jablonski, Jirˇ í Moravec (2010).
621:
279:
176:
1875:
666:
1714:
899:
395:
8:
579:
46:
1564:
1371:
433:
76:
765:
1870:
1701:
1605:
1568:
1556:
1536:
1488:
1363:
1144:
1119:
1060:
1039:
989:
763:
385:
1375:
305:
1883:
1706:
1595:
1548:
1355:
981:
779:
821:
1916:
1857:
636:
530:
506:
419:
409:
356:
286:
1836:
985:
1753:
1740:
567:
485:
293:
233:
1600:
1583:
1552:
1414:
1359:
1905:
1818:
1667:
1609:
1560:
1437:
1367:
1316:
770:
590:, to intentionally kill, injure, sell, or advertise to sell them is illegal.
472:
375:
309:
192:
66:
61:
1343:
1342:
Pedersen, Iben
Lindegaard; Jensen, Jan Kjærgaard; Toft, Søren (2009-04-01).
361:(found in eastern and northern Europe, eastern Balkans and in western Asia).
993:
744:
599:
534:
510:
502:
19:"Slow-worm", "Slowworm", and "blindworm" redirect here. For the genus, see
426:
tail has another 130 to 160 rows. Under the scales there are bony plates (
1779:
1676:
1537:"Amphibians and squamates in the Eocene of Europe: what do they tell us?"
563:
259:
The "blind" in blindworm refers to the lizard's small eyes, similar to a
1862:
1771:
1693:
603:
260:
1784:
945:"Živa – Přehlížená rozmanitost slepýšů (Jiří Moravec, Václav Gvoždík)"
620:, to which the slow worm belongs, first appeared in Europe during the
320:
1727:
559:
456:
427:
267:
93:
1638:
446:
1732:
1661:
1032:
A record-sized specimen of the western slow worm (Anguis fragilis).
969:
625:
526:
275:
143:
133:
113:
690:
624:
14, between 43.5 and 41.2 million years ago, corresponding to the
351:(found in western Europe, northern Europe and western Balkans) and
640:
522:
237:
123:
1076:
Bryant SV, Bellairs ADA. 1967. Tail regeneration in the lizards
1719:
1627:
807:"Feeding state and selected body temperatures in the slow worm"
629:
616:
514:
271:
153:
103:
20:
586:. The slow worm population has been decreasing, and under the
459:
into the female's cloaca. Copulation can take several hours.
555:
547:
1057:
Die
Amphibien und Reptilien Europas. Alle Arten im Porträt.
551:
37:
518:
304:
means "serpent, reptile". It is related to the
Norwegian
905:
The
American Heritage Dictionary of the English Language
764:
Agasyan, A.; Avci, A.; Tuniyev, B.; et al. (2021).
1129:
578:
In the United
Kingdom, the slow worm has been granted
1104:
1390:"BBC - Science & Nature - Wildfacts - Slow worm"
339:), but they are now classified as separate species:
1341:
1582:Villa, Andrea; Delfino, Massimo (November 2019).
450:Juvenile slow worm, paperclip for size comparison
365:Three more species were later distinguished from
1903:
1112:Blindschleiche – Anguis fragilis Linnaeus, 1758.
289:, consisting of 5 distinct but similar species.
1141:Die Amphibien und Reptilien Baden-Württembergs.
1139:In: Hubert Laufer, Klemens Fritz, Peter Sowig:
1137:Blindschleiche, Anguis fragilis Linnaeus, 1758.
785:10.2305/IUCN.UK.2021-2.RLTS.T47113126A744263.en
331:was traditionally divided into two subspecies (
263:(although the slowworm's eyes are functional).
1435:
1314:
466:Evening mating of slow worms (Anguis fragilis)
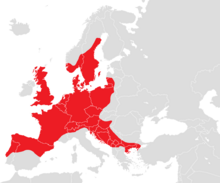
324:Distribution of species of European slow worms
1194:Ornithology, British Trust for (2010-11-24).
1059:Quelle & Meyer Verlag, Wiebelsheim 2015,
573:
1581:
1292:"Slow worms: Britain's most unusual lizards"
1013:: CS1 maint: multiple names: authors list (
1507:
1193:
1049:
869:
867:
204:
55:
36:
1599:
1541:Palaeobiodiversity and Palaeoenvironments
1116:Die Amphibien und Reptilien Deutschlands.
1086:Zoological Journal of the Linnean Society
783:
461:
445:
432:
408:
319:
864:
609:
1904:
1493:: CS1 maint: archived copy as title (
844:
1643:
1642:
1163:"The British Amphibians and Reptiles"
1160:
974:Molecular Phylogenetics and Evolution
478:
400:(native to the Peloponnese Peninsula)
1759:68effafe-82b2-4725-af2e-5193dfff081c
1534:
1268:"Smooth snake | The Wildlife Trusts"
300:means 'earthworm' or 'slowworm' and
1912:IUCN Red List least concern species
1535:Rage, Jean-Claude (December 2012).
1415:"Wildlife and Countryside Act 1981"
1200:BTO - British Trust for Ornithology
847:"How can I help garden slow worms?"
771:IUCN Red List of Threatened Species
757:
437:Close-up of the head of a slow worm
285:Slow worms have been shown to be a
13:
1135:Heribert Wolfbeck, Klemens Fritz:
908:. Houghton Mifflin Harcourt. 2017.
404:
390:(found on the Apennine Peninsula).
14:
1948:
1620:
1118:Gustav Fischer, Jena u. a. 1996,
1036:Zeitschrift für Feldherpetologie.
937:
875:"Slow worm | The Wildlife Trusts"
588:Wildlife and Countryside Act 1981
1626:
1436:Grace Bettayeb (16 March 2022).
1315:Grace Bettayeb (16 March 2022).
1110:Rainer Günther, Wolfgang Völkl:
1099:Journal of Developmental Biology
717:
698:
689:
677:
665:
653:
80:
1575:
1528:
1501:
1456:
1429:
1407:
1382:
1335:
1308:
1284:
1260:
1236:
1212:
1187:
1173:
1154:
1091:
1070:
441:
380:(found in southern Balkans) and
1588:Swiss Journal of Palaeontology
1510:"Slow worm makes its entrance"
1021:
961:
913:
892:
838:
799:
1:
1508:Dick Warner (18 March 2013).
1438:"Species in Focus: Slow Worm"
1317:"Species in Focus: Slow Worm"
845:Vernon, Jean (24 July 2019).
820:: 59–62. 2008. Archived from
750:
733:A slow worm seeks protection.
582:, alongside all other native
1114:In: Rainer Günther (Hrsg.):
684:Slow worm in turquoise color
492:
292:The name "slowworm" is only
7:
1937:Taxa named by Carl Linnaeus
986:10.1016/j.ympev.2010.01.007
738:
315:
10:
1953:
1932:Reptiles described in 1758
1348:Journal of Natural History
646:
632:. Remains assigned to the
593:
574:Protected status in the UK
540:
18:
1651:
1601:10.1007/s13358-018-0172-y
1553:10.1007/s12549-012-0087-3
1360:10.1080/00222930802702464
212:
203:
182:
175:
77:Scientific classification
75:
53:
44:
35:
30:
16:Species of legless lizard
639:are known from the late
1161:Smith, Malcolm (1951).
1143:Ulmer, Stuttgart 2007,
584:British reptile species
1444:. Irish Wildlife Trust
1323:. Irish Wildlife Trust
1272:www.wildlifetrusts.org
879:www.wildlifetrusts.org
851:Richard Jackson Garden
814:Herpetological Journal
778:: e.T47113126A744263.
467:
451:
438:
414:
325:
240:. It is also called a
1392:. BBC. Archived from
1038:Bd. 19, Nr. 1, 2012,
622:Mammal Paleogene zone
614:Members of the genus
465:
449:
436:
412:
323:
1754:Fauna Europaea (new)
1635:at Wikimedia Commons
1417:. Legislation.gov.uk
1354:(15–16): 1011–1025.
925:The Reptile Database
610:Evolutionary history
413:Slow worm in Germany
312:, of same meaning.
251:, or regionally, a
47:Conservation status
1088:46 (310): 297-305.
479:Size and longevity
468:
452:
439:
415:
396:Anguis cephalonica
326:
236:native to western
1927:Lizards of Europe
1899:
1898:
1871:Open Tree of Life
1645:Taxon identifiers
1631:Media related to
1514:irishexaminer.com
1224:surrey-arg.org.uk
1149:978-3-8001-4385-6
1065:978-3-494-01581-1
921:"Anguis fragilis"
766:"Anguis fragilis"
728:
707:
672:A slow worm close
386:Anguis veronensis
220:
219:
70:
1944:
1892:
1891:
1879:
1878:
1866:
1865:
1853:
1852:
1840:
1839:
1837:NBNSYS0000005072
1827:
1826:
1814:
1813:
1801:
1800:
1788:
1787:
1775:
1774:
1762:
1761:
1749:
1748:
1736:
1735:
1723:
1722:
1710:
1709:
1697:
1696:
1687:
1686:
1685:
1672:
1671:
1670:
1640:
1639:
1630:
1614:
1613:
1603:
1579:
1573:
1572:
1532:
1526:
1525:
1523:
1521:
1516:. Irish Examiner
1505:
1499:
1498:
1492:
1484:
1482:
1481:
1475:
1469:. Archived from
1468:
1460:
1454:
1453:
1451:
1449:
1433:
1427:
1426:
1424:
1422:
1411:
1405:
1404:
1402:
1401:
1386:
1380:
1379:
1339:
1333:
1332:
1330:
1328:
1312:
1306:
1305:
1303:
1302:
1288:
1282:
1281:
1279:
1278:
1264:
1258:
1257:
1255:
1254:
1248:www.froglife.org
1240:
1234:
1233:
1231:
1230:
1216:
1210:
1209:
1207:
1206:
1191:
1185:
1184:
1177:
1171:
1170:
1165:. Archived from
1158:
1152:
1133:
1127:
1108:
1102:
1095:
1089:
1074:
1068:
1053:
1047:
1025:
1019:
1018:
1012:
1004:
1002:
1000:
965:
959:
958:
956:
955:
941:
935:
934:
932:
931:
917:
911:
909:
896:
890:
889:
887:
885:
871:
862:
861:
859:
857:
842:
836:
835:
833:
832:
826:
811:
803:
797:
796:
794:
792:
787:
761:
730:
729:
709:
708:
693:
681:
669:
657:
580:protected status
208:
188:
168:A. fragilis
85:
84:
64:
59:
58:
40:
28:
27:
1952:
1951:
1947:
1946:
1945:
1943:
1942:
1941:
1922:Lizards of Asia
1902:
1901:
1900:
1895:
1887:
1882:
1874:
1869:
1861:
1858:Observation.org
1856:
1848:
1843:
1835:
1830:
1822:
1817:
1809:
1804:
1796:
1791:
1783:
1778:
1770:
1765:
1757:
1752:
1744:
1739:
1731:
1726:
1718:
1713:
1705:
1700:
1692:
1690:
1683:Anguis fragilis
1681:
1680:
1675:
1666:
1665:
1660:
1653:Anguis fragilis
1647:
1633:Anguis fragilis
1623:
1618:
1617:
1580:
1576:
1533:
1529:
1519:
1517:
1506:
1502:
1486:
1485:
1479:
1477:
1473:
1466:
1464:"Archived copy"
1462:
1461:
1457:
1447:
1445:
1434:
1430:
1420:
1418:
1413:
1412:
1408:
1399:
1397:
1388:
1387:
1383:
1340:
1336:
1326:
1324:
1313:
1309:
1300:
1298:
1290:
1289:
1285:
1276:
1274:
1266:
1265:
1261:
1252:
1250:
1242:
1241:
1237:
1228:
1226:
1218:
1217:
1213:
1204:
1202:
1192:
1188:
1179:
1178:
1174:
1159:
1155:
1134:
1130:
1109:
1105:
1096:
1092:
1082:Lacerta dugesii
1078:Anguis fragilis
1075:
1071:
1055:Dieter Glandt:
1054:
1050:
1026:
1022:
1006:
1005:
998:
996:
966:
962:
953:
951:
943:
942:
938:
929:
927:
919:
918:
914:
898:
897:
893:
883:
881:
873:
872:
865:
855:
853:
843:
839:
830:
828:
827:on 17 June 2009
824:
809:
805:
804:
800:
790:
788:
762:
758:
753:
741:
734:
731:
718:
713:
710:
699:
694:
685:
682:
673:
670:
661:
658:
649:
637:species complex
634:Anguis fragilis
612:
596:
576:
568:pill millipedes
543:
495:
481:
444:
420:caudal autotomy
407:
405:Physical traits
357:Anguis colchica
345:Anguis fragilis
329:Anguis fragilis
318:
294:contaminated by
287:species complex
266:Slow worms are
229:Anguis fragilis
199:
190:
186:Anguis fragilis
184:
171:
79:
71:
60:
56:
49:
24:
17:
12:
11:
5:
1950:
1940:
1939:
1934:
1929:
1924:
1919:
1914:
1897:
1896:
1894:
1893:
1880:
1867:
1854:
1841:
1828:
1815:
1802:
1789:
1776:
1763:
1750:
1741:Fauna Europaea
1737:
1724:
1711:
1698:
1688:
1673:
1657:
1655:
1649:
1648:
1637:
1636:
1622:
1621:External links
1619:
1616:
1615:
1594:(2): 177–211.
1574:
1547:(4): 445–457.
1527:
1500:
1455:
1428:
1406:
1381:
1334:
1307:
1283:
1259:
1235:
1211:
1186:
1172:
1169:on 2017-09-16.
1153:
1128:
1103:
1090:
1069:
1048:
1028:Wolfgang Böhme
1020:
980:(2): 460–472.
960:
936:
912:
891:
863:
837:
798:
755:
754:
752:
749:
748:
747:
740:
737:
736:
735:
732:
716:
714:
711:
697:
695:
688:
686:
683:
676:
674:
671:
664:
662:
659:
652:
648:
645:
611:
608:
595:
592:
575:
572:
542:
539:
494:
491:
486:Copenhagen Zoo
480:
477:
443:
440:
406:
403:
402:
401:
391:
381:
363:
362:
352:
337:A. f. colchica
333:A. f. fragilis
317:
314:
234:legless lizard
218:
217:
210:
209:
201:
200:
191:
180:
179:
173:
172:
165:
163:
159:
158:
151:
147:
146:
141:
137:
136:
131:
127:
126:
121:
117:
116:
111:
107:
106:
101:
97:
96:
91:
87:
86:
73:
72:
54:
51:
50:
45:
42:
41:
33:
32:
15:
9:
6:
4:
3:
2:
1949:
1938:
1935:
1933:
1930:
1928:
1925:
1923:
1920:
1918:
1915:
1913:
1910:
1909:
1907:
1890:
1885:
1881:
1877:
1872:
1868:
1864:
1859:
1855:
1851:
1846:
1842:
1838:
1833:
1829:
1825:
1820:
1816:
1812:
1807:
1803:
1799:
1794:
1790:
1786:
1781:
1777:
1773:
1768:
1764:
1760:
1755:
1751:
1747:
1742:
1738:
1734:
1729:
1725:
1721:
1716:
1712:
1708:
1703:
1699:
1695:
1689:
1684:
1678:
1674:
1669:
1663:
1659:
1658:
1656:
1654:
1650:
1646:
1641:
1634:
1629:
1625:
1624:
1611:
1607:
1602:
1597:
1593:
1589:
1585:
1578:
1570:
1566:
1562:
1558:
1554:
1550:
1546:
1542:
1538:
1531:
1515:
1511:
1504:
1496:
1490:
1476:on 2014-02-03
1472:
1465:
1459:
1443:
1439:
1432:
1416:
1410:
1396:on 4 May 2007
1395:
1391:
1385:
1377:
1373:
1369:
1365:
1361:
1357:
1353:
1349:
1345:
1338:
1322:
1318:
1311:
1297:
1296:www.nhm.ac.uk
1293:
1287:
1273:
1269:
1263:
1249:
1245:
1239:
1225:
1221:
1215:
1201:
1197:
1190:
1182:
1176:
1168:
1164:
1157:
1151:, S. 619–632.
1150:
1146:
1142:
1138:
1132:
1126:, S. 617–631.
1125:
1124:3-437-35016-1
1121:
1117:
1113:
1107:
1100:
1094:
1087:
1083:
1079:
1073:
1067:, S. 322–327.
1066:
1062:
1058:
1052:
1046:, S. 117–118.
1045:
1041:
1037:
1033:
1029:
1024:
1016:
1010:
995:
991:
987:
983:
979:
975:
971:
964:
950:
946:
940:
926:
922:
916:
907:
906:
901:
895:
880:
876:
870:
868:
852:
848:
841:
823:
819:
815:
808:
802:
786:
781:
777:
773:
772:
767:
760:
756:
746:
743:
742:
715:
696:
692:
687:
680:
675:
668:
663:
656:
651:
650:
644:
642:
638:
635:
631:
628:stage of the
627:
623:
619:
618:
607:
605:
601:
591:
589:
585:
581:
571:
569:
565:
561:
557:
553:
549:
538:
536:
535:smooth snakes
532:
528:
524:
520:
519:domestic cats
516:
512:
511:birds of prey
508:
504:
500:
497:Predators of
490:
487:
476:
474:
473:ovoviviparous
464:
460:
458:
448:
435:
431:
429:
423:
421:
411:
399:
398:
397:
392:
389:
388:
387:
382:
379:
378:
377:
376:Anguis graeca
372:
371:
370:
368:
360:
359:
358:
353:
350:
349:
348:sensu stricto
346:
342:
341:
340:
338:
334:
330:
322:
313:
311:
307:
303:
299:
295:
290:
288:
283:
281:
277:
273:
269:
268:semifossorial
264:
262:
258:
254:
250:
246:
243:
239:
235:
231:
230:
225:
216:
211:
207:
202:
198:
194:
189:
187:
181:
178:
177:Binomial name
174:
170:
169:
164:
161:
160:
157:
156:
152:
149:
148:
145:
142:
139:
138:
135:
132:
129:
128:
125:
122:
119:
118:
115:
112:
109:
108:
105:
102:
99:
98:
95:
92:
89:
88:
83:
78:
74:
68:
63:
62:Least Concern
52:
48:
43:
39:
34:
29:
26:
22:
1652:
1591:
1587:
1577:
1544:
1540:
1530:
1518:. Retrieved
1513:
1503:
1478:. Retrieved
1471:the original
1458:
1446:. Retrieved
1441:
1431:
1421:20 September
1419:. Retrieved
1409:
1398:. Retrieved
1394:the original
1384:
1351:
1347:
1337:
1325:. Retrieved
1320:
1310:
1299:. Retrieved
1295:
1286:
1275:. Retrieved
1271:
1262:
1251:. Retrieved
1247:
1238:
1227:. Retrieved
1223:
1214:
1203:. Retrieved
1199:
1189:
1175:
1167:the original
1156:
1140:
1136:
1131:
1115:
1111:
1106:
1098:
1093:
1085:
1081:
1077:
1072:
1056:
1051:
1035:
1031:
1023:
1009:cite journal
997:. Retrieved
977:
973:
963:
952:. Retrieved
949:ziva.avcr.cz
948:
939:
928:. Retrieved
924:
915:
903:
894:
882:. Retrieved
878:
854:. Retrieved
850:
840:
829:. Retrieved
822:the original
817:
813:
801:
789:. Retrieved
775:
769:
759:
633:
615:
613:
602:, mainly in
600:County Clare
597:
577:
564:caterpillars
544:
498:
496:
482:
469:
453:
442:Reproduction
424:
416:
394:
393:
384:
383:
374:
373:
366:
364:
355:
354:
347:
344:
343:
336:
332:
328:
327:
301:
297:
291:
284:
270:(burrowing)
265:
256:
253:long-cripple
252:
248:
244:
241:
228:
227:
223:
221:
214:
185:
183:
167:
166:
154:
25:
1780:iNaturalist
1677:Wikispecies
1244:"Slow-Worm"
1220:"Slow Worm"
1196:"Slow-worm"
1181:"Slow Worm"
745:Glass snake
660:A slow worm
499:A. fragilis
367:A. fragilis
308:or Swedish
242:deaf adder,
215:A. fragilis
1906:Categories
1480:2014-01-25
1400:2007-05-16
1301:2024-03-19
1277:2022-09-10
1253:2022-09-10
1229:2022-09-10
1205:2022-09-10
954:2021-03-24
930:2021-04-07
900:"Slowworm"
831:2009-06-03
751:References
604:the Burren
560:earthworms
428:osteoderms
280:allotments
276:autotomize
261:blindsnake
257:hazelworm.
31:Slow worm
1610:1664-2384
1569:128651937
1561:1867-1594
1368:0022-2933
1101:9(4): 53.
1044:0946-7998
643:onwards.
531:pheasants
527:hedgehogs
493:Predators
457:hemipenes
249:blindworm
245:slow worm
213:Range of
162:Species:
100:Kingdom:
94:Eukaryota
1889:fragilis
1824:47113126
1798:11238828
1691:BioLib:
1662:Wikidata
1520:31 March
1489:cite web
1376:84703263
994:20079858
739:See also
626:Lutetian
606:region.
501:include
316:Taxonomy
224:slowworm
193:Linnaeus
144:Anguidae
140:Family:
134:Squamata
124:Reptilia
114:Chordata
110:Phylum:
104:Animalia
90:Domain:
67:IUCN 3.1
1811:1146449
1772:2468095
1668:Q183660
1448:1 April
1327:1 April
999:1 April
884:26 July
856:26 July
647:Gallery
641:Miocene
594:Ireland
541:Ecology
507:badgers
272:lizards
238:Eurasia
232:) is a
150:Genus:
130:Order:
120:Class:
65: (
1917:Anguis
1876:449663
1850:102178
1785:343021
1746:214587
1733:ANGSFR
1720:453239
1608:
1567:
1559:
1442:iwt.ie
1374:
1366:
1321:iwt.ie
1147:
1122:
1063:
1042:
992:
791:9 June
630:Eocene
617:Anguis
556:snails
503:adders
310:ormslå
155:Anguis
21:Anguis
1793:IRMNG
1707:672H4
1565:S2CID
1474:(PDF)
1467:(PDF)
1372:S2CID
825:(PDF)
810:(PDF)
552:slugs
548:grass
523:foxes
515:crows
1845:NCBI
1819:IUCN
1806:ITIS
1767:GBIF
1728:EPPO
1606:ISSN
1557:ISSN
1522:2022
1495:link
1450:2022
1423:2015
1364:ISSN
1329:2022
1145:ISBN
1120:ISBN
1080:and
1061:ISBN
1040:ISSN
1034:In:
1015:link
1001:2022
990:PMID
886:2022
858:2022
793:2022
776:2021
566:and
533:and
335:and
302:wyrm
298:slā-
255:and
222:The
197:1758
1863:445
1832:NBN
1715:EoL
1702:CoL
1694:364
1596:doi
1592:138
1549:doi
1356:doi
982:doi
780:doi
306:slo
1908::
1886::
1884:RD
1873::
1860::
1847::
1834::
1821::
1808::
1795::
1782::
1769::
1756::
1743::
1730::
1717::
1704::
1679::
1664::
1604:.
1590:.
1586:.
1563:.
1555:.
1545:92
1543:.
1539:.
1512:.
1491:}}
1487:{{
1440:.
1370:.
1362:.
1352:43
1350:.
1346:.
1319:.
1294:.
1270:.
1246:.
1222:.
1198:.
1084:.
1030::
1011:}}
1007:{{
988:.
978:55
976:.
972:.
947:.
923:.
902:.
877:.
866:^
849:.
818:18
816:.
812:.
774:.
768:.
570:.
562:,
558:,
554:,
529:,
525:,
521:,
517:,
513:,
509:,
505:,
369::
247:,
195:,
1612:.
1598::
1571:.
1551::
1524:.
1497:)
1483:.
1452:.
1425:.
1403:.
1378:.
1358::
1331:.
1304:.
1280:.
1256:.
1232:.
1208:.
1183:.
1017:)
1003:.
984::
957:.
933:.
910:)
888:.
860:.
834:.
795:.
782::
226:(
69:)
23:.
Text is available under the Creative Commons Attribution-ShareAlike License. Additional terms may apply.