2826:(HDMR) (the term is due to H. Rabitz) is essentially an emulator approach, which involves decomposing the function output into a linear combination of input terms and interactions of increasing dimensionality. The HDMR approach exploits the fact that the model can usually be well-approximated by neglecting higher-order interactions (second or third-order and above). The terms in the truncated series can then each be approximated by e.g. polynomials or splines (REFS) and the response expressed as the sum of the main effects and interactions up to the truncation order. From this perspective, HDMRs can be seen as emulators which neglect high-order interactions; the advantage is that they are able to emulate models with higher dimensionality than full-order emulators.
1009:. This appears a logical approach as any change observed in the output will unambiguously be due to the single variable changed. Furthermore, by changing one variable at a time, one can keep all other variables fixed to their central or baseline values. This increases the comparability of the results (all 'effects' are computed with reference to the same central point in space) and minimizes the chances of computer program crashes, more likely when several input factors are changed simultaneously. OAT is frequently preferred by modelers because of practical reasons. In case of model failure under OAT analysis the modeler immediately knows which is the input factor responsible for the failure.
2869:
motivations of its author may become a matter of great importance, and a pure sensitivity analysis – with its emphasis on parametric uncertainty – may be seen as insufficient. The emphasis on the framing may derive inter-alia from the relevance of the policy study to different constituencies that are characterized by different norms and values, and hence by a different story about 'what the problem is' and foremost about 'who is telling the story'. Most often the framing includes more or less implicit assumptions, which could be political (e.g. which group needs to be protected) all the way to technical (e.g. which variable can be treated as a constant).
792:
2873:
quantitative information with the generation of `Pedigrees' of numbers. Sensitivity auditing has been especially designed for an adversarial context, where not only the nature of the evidence, but also the degree of certainty and uncertainty associated to the evidence, will be the subject of partisan interests. Sensitivity auditing is recommended in the
European Commission guidelines for impact assessment, as well as in the report Science Advice for Policy by European Academies.
183:
2905:" I have proposed a form of organized sensitivity analysis that I call 'global sensitivity analysis' in which a neighborhood of alternative assumptions is selected and the corresponding interval of inferences is identified. Conclusions are judged to be sturdy only if the neighborhood of assumptions is wide enough to be credible and the corresponding interval of inferences is narrow enough to be useful."
2854:. In a design of experiments, one studies the effect of some process or intervention (the 'treatment') on some objects (the 'experimental units'). In sensitivity analysis one looks at the effect of varying the inputs of a mathematical model on the output of the model itself. In both disciplines one strives to obtain information from the system with a minimum of physical or numerical experiments.
2433:
thus overcomes the scale issue of traditional sensitivity analysis methods. More importantly, VARS is able to provide relatively stable and statistically robust estimates of parameter sensitivity with much lower computational cost than other strategies (about two orders of magnitude more efficient). Noteworthy, it has been shown that there is a theoretical link between the VARS framework and the
22:
1064:. With 5 inputs, the explored space already drops to less than 1% of the total parameter space. And even this is an overestimate, since the off-axis volume is not actually being sampled at all. Compare this to random sampling of the space, where the convex hull approaches the entire volume as more points are added. While the sparsity of OAT is theoretically not a concern for
2509:, that approximates the input/output behavior of the model itself. In other words, it is the concept of "modeling a model" (hence the name "metamodel"). The idea is that, although computer models may be a very complex series of equations that can take a long time to solve, they can always be regarded as a function of their inputs
2736:, although random designs can also be used, at the loss of some efficiency. The selection of the metamodel type and the training are intrinsically linked since the training method will be dependent on the class of metamodel. Some types of metamodels that have been used successfully for sensitivity analysis include:
571:-function) multiple times. Depending on the complexity of the model there are many challenges that may be encountered during model evaluation. Therefore, the choice of method of sensitivity analysis is typically dictated by a number of problem constraints, settings or challenges. Some of the most common are:
2910:
Note Leamer's emphasis is on the need for 'credibility' in the selection of assumptions. The easiest way to invalidate a model is to demonstrate that it is fragile with respect to the uncertainty in the assumptions or to show that its assumptions have not been taken 'wide enough'. The same concept is
1226:
function. Similar to OAT, local methods do not attempt to fully explore the input space, since they examine small perturbations, typically one variable at a time. It is possible to select similar samples from derivative-based sensitivity through Neural
Networks and perform uncertainty quantification.
1225:
indicates that the derivative is taken at some fixed point in the space of the input (hence the 'local' in the name of the class). Adjoint modelling and
Automated Differentiation are methods which allow to compute all partial derivatives at a cost at most 4-6 times of that for evaluating the original
782:
The various types of "core methods" (discussed below) are distinguished by the various sensitivity measures which are calculated. These categories can somehow overlap. Alternative ways of obtaining these measures, under the constraints of the problem, can be given. In addition, an engineering view of
2932:
Different statistical tests and measures are applied to the problem and different factors rankings are obtained. The test should instead be tailored to the purpose of the analysis, e.g. one uses Monte Carlo filtering if one is interested in which factors are most responsible for generating high/low
2872:
In order to take these concerns into due consideration the instruments of SA have been extended to provide an assessment of the entire knowledge and model generating process. This approach has been called 'sensitivity auditing'. It takes inspiration from NUSAP, a method used to qualify the worth of
2432:
for a given perturbation scale can be considered as a comprehensive illustration of sensitivity information, through linking variogram analysis to both direction and perturbation scale concepts. As a result, the VARS framework accounts for the fact that sensitivity is a scale-dependent concept, and
704:
Sometimes it is not possible to evaluate the code at all desired points, either because the code is confidential or because the experiment is not reproducible. The code output is only available for a given set of points, and it can be difficult to perform a sensitivity analysis on a limited set of
186:
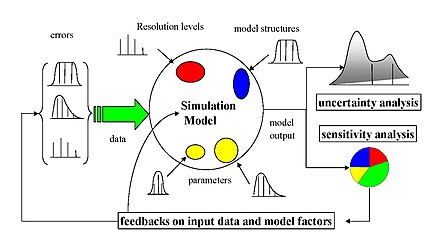
Figure 1. Schematic representation of uncertainty analysis and sensitivity analysis. In mathematical modeling, uncertainty arises from a variety of sources - errors in input data, parameter estimation and approximation procedure, underlying hypothesis, choice of model, alternative model structures
2868:
It may happen that a sensitivity analysis of a model-based study is meant to underpin an inference, and to certify its robustness, in a context where the inference feeds into a policy or decision-making process. In these cases the framing of the analysis itself, its institutional context, and the
1249:
as direct measures of sensitivity. The regression is required to be linear with respect to the data (i.e. a hyperplane, hence with no quadratic terms, etc., as regressors) because otherwise it is difficult to interpret the standardised coefficients. This method is therefore most suitable when the
1020:
The proportion of input space which remains unexplored with an OAT approach grows superexponentially with the number of inputs. For example, a 3-variable parameter space which is explored one-at-a-time is equivalent to taking points along the x, y, and z axes of a cube centered at the origin. The
695:
A code is said to be stochastic when, for several evaluations of the code with the same inputs, different outputs are obtained (as opposed to a deterministic code when, for several evaluations of the code with the same inputs, the same output is always obtained). In this case, it is necessary to
2635:
to within an acceptable margin of error. Then, sensitivity measures can be calculated from the metamodel (either with Monte Carlo or analytically), which will have a negligible additional computational cost. Importantly, the number of model runs required to fit the metamodel can be orders of
550:
Taking into account uncertainty arising from different sources, whether in the context of uncertainty analysis or sensitivity analysis (for calculating sensitivity indices), requires multiple samples of the uncertain parameters and, consequently, running the model (evaluating the
121:, errors in input data, parameter estimation and approximation procedure, absence of information and poor or partial understanding of the driving forces and mechanisms, choice of underlying hypothesis of model, and so on. This uncertainty limits our confidence in the
745:
There are a large number of approaches to performing a sensitivity analysis, many of which have been developed to address one or more of the constraints discussed above. They are also distinguished by the type of sensitivity measure, be it based on (for example)
688:
is a vector or function. When outputs are correlated, it does not preclude the possibility of performing different sensitivity analyses for each output of interest. However, for models in which the outputs are correlated, the sensitivity measures can be hard to
84:
or system (numerical or otherwise) can be divided and allocated to different sources of uncertainty in its inputs. This involves estimating sensitivity indices that quantify the influence of an input or group of inputs on the output. A related practice is
1229:
One advantage of the local methods is that it is possible to make a matrix to represent all the sensitivities in a system, thus providing an overview that cannot be achieved with global methods if there is a large number of input and output variables.
1276:, and decompose the output variance into parts attributable to input variables and combinations of variables. The sensitivity of the output to an input variable is therefore measured by the amount of variance in the output caused by that input.
1884:
Variance-based methods allow full exploration of the input space, accounting for interactions, and nonlinear responses. For these reasons they are widely used when it is feasible to calculate them. Typically this calculation involves the use of
2954:
The importance of understanding and managing uncertainty in model results has inspired many scientists from different research centers all over the world to take a close interest in this subject. National and international agencies involved in
2468:
and represent the average marginal contribution of a given factors across all possible combinations of factors. These value are related to Sobol’s indices as their value falls between the first order Sobol’ effect and the total order effect.
109:(for example in biology, climate change, economics, renewable energy, agronomy...) can be highly complex, and as a result, its relationships between inputs and outputs may be faultily understood. In such cases, the model can be viewed as a
1012:
Despite its simplicity however, this approach does not fully explore the input space, since it does not take into account the simultaneous variation of input variables. This means that the OAT approach cannot detect the presence of
132:
In models involving many input variables, sensitivity analysis is an essential ingredient of model building and quality assurance and can be useful to determine the impact of a uncertain variable for a range of purposes, including:
2455:
to represent a multivariate function (the model) in the frequency domain, using a single frequency variable. Therefore, the integrals required to calculate sensitivity indices become univariate, resulting in computational savings.
1216:
1082:
Named after statistician Max D. Morris this method is suitable for screening systems with many parameters. This is also known as method of elementary effects because it combines repeated steps along the various parametric axes.
2834:
Sensitivity analysis via Monte Carlo filtering is also a sampling-based approach, whose objective is to identify regions in the space of the input factors corresponding to particular values (e.g., high or low) of the output.
2427:
Basically, the higher the variability the more heterogeneous is the response surface along a particular direction/parameter, at a specific perturbation scale. Accordingly, in the VARS framework, the values of directional
2489:). Generally, these methods focus on efficiently (by creating a metamodel of the costly function to be evaluated and/or by “ wisely ” sampling the factor space) calculating variance-based measures of sensitivity.
5002:
Van der Sluijs, JP; Craye, M; Funtowicz, S; Kloprogge, P; Ravetz, J; Risbey, J (2005). "Combining quantitative and qualitative measures of uncertainty in model based environmental assessment: the NUSAP system".
4001:
Kabir HD, Khosravi A, Nahavandi D, Nahavandi S. Uncertainty
Quantification Neural Network from Similarity and Sensitivity. In2020 International Joint Conference on Neural Networks (IJCNN) 2020 Jul 19 (pp. 1-8).
4844:
Li, G.; Hu, J.; Wang, S.-W.; Georgopoulos, P.; Schoendorf, J.; Rabitz, H. (2006). "Random
Sampling-High Dimensional Model Representation (RS-HDMR) and orthogonality of its different order component functions".
1852:
921:
using scatter plots, and observe the behavior of these pairs. The diagrams give an initial idea of the correlation and which input has an impact on the output. Figure 2 shows an example where two inputs,
1728:
585:
Time-consuming models are very often encountered when complex models are involved. A single run of the model takes a significant amount of time (minutes, hours or longer). The use of statistical model (
4524:
Storlie, C.B.; Swiler, L.P.; Helton, J.C.; Sallaberry, C.J. (2009). "Implementation and evaluation of nonparametric regression procedures for sensitivity analysis of computationally demanding models".
3651:
2945:
This is when one performs sensitivity analysis on one sub-model at a time. This approach is non conservative as it might overlook interactions among factors in different sub-models (Type II error).
2477:
The principle is to project the function of interest onto a basis of orthogonal polynomials. The Sobol indices are then expressed analytically in terms of the coefficients of this decomposition.
1458:
2422:
762:
Quantify the uncertainty in each input (e.g. ranges, probability distributions). Note that this can be difficult and many methods exist to elicit uncertainty distributions from subjective data.
147:
Uncertainty reduction, through the identification of model input that cause significant uncertainty in the output and should therefore be the focus of attention in order to increase robustness.
3006:
779:
In some cases this procedure will be repeated, for example in high-dimensional problems where the user has to screen out unimportant variables before performing a full sensitivity analysis.
2485:
A number of methods have been developed to overcome some of the constraints discussed above, which would otherwise make the estimation of sensitivity measures infeasible (most often due to
2926:, although even then it may be hard to build distributions with great confidence. The subjectivity of the probability distributions or ranges will strongly affect the sensitivity analysis.
2285:(CDFs) to characterize the maximum distance between the unconditional output distribution and conditional output distribution (obtained by varying all input parameters and by setting the
2716:"Training" the metamodel using the sample data from the model – this generally involves adjusting the metamodel parameters until the metamodel mimics the true model as well as possible.
5101:
2633:
2798:, in conjunction with canonical models such as noisy models. Noisy models exploit information on the conditional independence between variables to significantly reduce dimensionality.
2321:
One of the major shortcomings of the previous sensitivity analysis methods is that none of them considers the spatially ordered structure of the response surface/output of the model
4397:
Haghnegahdar, Amin; Razavi, Saman (September 2017). "Insights into sensitivity analysis of Earth and environmental systems models: On the impact of parameter perturbation scale".
433:
317:
737:
To address the various constraints and challenges, a number of methods for sensitivity analysis have been proposed in the literature, which we will examine in the next section.
2991:
2117:
2675:
2580:
2360:
and covariograms, variogram analysis of response surfaces (VARS) addresses this weakness through recognizing a spatially continuous correlation structure to the values of
1518:
2278:-importance measure, the new correlation coefficient of Chatterjee, the Wasserstein correlation of Wiesel and the kernel-based sensitivity measures of Barr and Rabitz.
2190:
2082:
2249:
1487:
990:
One of the simplest and most common approaches is that of changing one-factor-at-a-time (OAT), to see what effect this produces on the output. OAT customarily involves
5368:
1996:
2276:
380:
3011:
2542:
2354:
2148:
1969:
1879:
1628:
1575:
1548:
1370:
1308:
1140:
974:
947:
899:
520:
2704:
1062:
1889:
methods, but since this can involve many thousands of model runs, other methods (such as metamodels) can be used to reduce computational expense when necessary.
2378:
2303:
2214:
1939:
1915:
1601:
1328:
1113:
919:
731:
686:
615:
569:
540:
477:
453:
340:
249:
217:
3114:
Saltelli, A.; Ratto, M.; Andreas, T.; Campolongo, F.; Gariboni, J.; Gatelli, D.; Saisana, M.; Tarantola, S. (2008). "Global sensitivity analysis: the primer".
187:
and so on. They propagate through the model and have an impact on the output. The uncertainty on the output is described via uncertainty analysis (represented
125:
of the model's response or output. Further, models may have to cope with the natural intrinsic variability of the system (aleatory), such as the occurrence of
624:, which grows exponentially in size with the number of inputs. Therefore, screening methods can be useful for dimension reduction. Another way to tackle the
2255:, the moment-independent global sensitivity measure satisfies zero-independence. This is a relevant statistical property also known as Renyi's postulate D.
1148:
3001:
1897:
Moment-independent methods extend variance-based techniques by considering the probability density or cumulative distribution function of the model output
4044:
Borgonovo, E., Tarantola, S., Plischke, E., Morris, M. D. (2014). "Transformations and invariance in the sensitivity analysis of computer experiments".
4666:"Categorical Inputs, Sensitivity Analysis, Optimization and Importance Tempering with tgp Version 2, an R Package for Treed Gaussian Process Models"
4433:
2996:
640:
between model inputs, but sometimes inputs can be strongly correlated. Correlations between inputs must then be taken into account in the analysis.
156:
Enhancing communication from modelers to decision makers (e.g. by making recommendations more credible, understandable, compelling or persuasive).
5112:
Science Advice for Policy by
European Academies, Making sense of science for policy under conditions of complexity and uncertainty, Berlin, 2019.
1633:
173:
To identify important connections between observations, model inputs, and predictions or forecasts, leading to the development of better models.
1283:: they represent the proportion of variance explained by an input or group of inputs. This expression essentially measures the contribution of
153:
Model simplification – fixing model input that has no effect on the output, or identifying and removing redundant parts of the model structure.
765:
Identify the model output to be analysed (the target of interest should ideally have a direct relation to the problem tackled by the model).
3147:
Saltelli, A.; Tarantola, S.; Campolongo, F.; Ratto, M. (2004). "Sensitivity analysis in practice: a guide to assessing scientific models".
2847:
in the conclusions of the study, sensitivity analysis tries to identify what source of uncertainty weighs more on the study's conclusions.
1377:
159:
Finding regions in the space of input factors for which the model output is either maximum or minimum or meets some optimum criterion (see
2305:-th input, consequentially). The difference between the unconditional and conditional output distribution is usually calculated using the
799:(vertical axis) is a function of four factors. The points in the four scatterplots are always the same though sorted differently, i.e. by
4801:
Cardenas, IC (2019). "On the use of
Bayesian networks as a meta-modeling approach to analyse uncertainties in slope stability analysis".
3553:
2939:
This may be acceptable for the quality assurance of sub-models but should be avoided when presenting the results of the overall analysis.
5224:
1733:
4551:
Wang, Shangying; Fan, Kai; Luo, Nan; Cao, Yangxiaolu; Wu, Feilun; Zhang, Carolyn; Heller, Katherine A.; You, Lingchong (2019-09-25).
3742:
Bailis, R.; Ezzati, M.; Kammen, D. (2005). "Mortality and
Greenhouse Gas Impacts of Biomass and Petroleum Energy Futures in Africa".
2972:
5193:
2281:
Another measure for global sensitivity analysis, in the category of moment-independent approaches, is the PAWN index. It relies on
1029:
which has a volume only 1/6th of the total parameter space. More generally, the convex hull of the axes of a hyperrectangle forms a
2888:
In uncertainty and sensitivity analysis there is a crucial trade off between how scrupulous an analyst is in exploring the input
1998:, can be defined through an equation similar to variance-based indices replacing the conditional expectation with a distance, as
3224:
Bahremand, A.; De Smedt, F. (2008). "Distributed
Hydrological Modeling and Sensitivity Analysis in Torysa Watershed, Slovakia".
113:, i.e. the output is an "opaque" function of its inputs. Quite often, some or all of the model inputs are subject to sources of
3795:
Murphy, J.; et al. (2004). "Quantification of modelling uncertainties in a large ensemble of climate change simulations".
4766:
Ratto, M.; Pagano, A. (2010). "Using recursive algorithms for the efficient identification of smoothing spline ANOVA models".
5064:
Lo Piano, S; Robinson, M (2019). "Nutrition and public health economic evaluations under the lenses of post normal science".
3669:
3131:
3039:
2823:
2788:
2446:
2309:(KS). The PAWN index for a given input parameter is then obtained by calculating the summary statistics over all KS values.
5358:
2383:
3084:
2434:
1263:
874:
The first intuitive approach (especially useful in less complex cases) is to analyze the relationship between each input
747:
655:
542:(by calculating the corresponding sensitivity indices). Figure 1 provides a schematic representation of this statement.
2976:
2748:
4445:
3601:
3034:
2544:. By running the model at a number of points in the input space, it may be possible to fit a much simpler metamodels
2282:
637:
57:
1268:
Variance-based methods are a class of probabilistic approaches which quantify the input and output uncertainties as
3461:
3410:
492:
2968:
578:
Sensitivity analysis is almost always performed by running the model a (possibly large) number of times, i.e. a
5363:
2585:
783:
the methods that takes into account the four important sensitivity analysis parameters has also been proposed.
2636:
magnitude less than the number of runs required to directly estimate the sensitivity measures from the model.
5348:
4619:
Oakley, J.; O'Hagan, A. (2004). "Probabilistic sensitivity analysis of complex models: a
Bayesian approach".
3892:
2811:
620:
The model has a large number of uncertain inputs. Sensitivity analysis is essentially the exploration of the
347:
3364:"Quasi-Monte Carlo technique in global sensitivity analysis of wind resource assessment with a study on UAE"
696:
separate the variability of the output due to the variability of the inputs from that due to stochasticity.
3318:
Effective Groundwater Model Calibration, with Analysis of Data, Sensitivities, Predictions, and Uncertainty
1251:
488:
195:
showing the proportion that each source of uncertainty contributes to the total uncertainty of the output).
188:
4553:"Massive computational acceleration by using neural networks to emulate mechanism-based biological models"
4268:"A simple and efficient method for global sensitivity analysis based on cumulative distribution functions"
1630:
and its interactions with any of the other input variables. The total effect index is given as following:
3406:"Generalized Hoeffding-Sobol decomposition for dependent variables - application to sensitivity analysis"
3064:
2306:
997:
returning the variable to its nominal value, then repeating for each of the other inputs in the same way.
985:
387:
258:
2843:
Sensitivity analysis is closely related with uncertainty analysis; while the latter studies the overall
1254:
is large. The advantages of regression analysis are that it is simple and has a low computational cost.
150:
Searching for errors in the model (by encountering unexpected relationships between inputs and outputs).
3079:
2771:, where a succession of simple regressions are used to weight data points to sequentially reduce error.
114:
94:
90:
4974:
Hornberger, G.; Spear, R. (1981). "An approach to the preliminary analysis of environmental systems".
4350:"A new framework for comprehensive, robust, and efficient global sensitivity analysis: 2. Application"
2087:
4489:
4239:
Barr, J., Rabitz, H. (31 March 2022). "A Generalized Kernel Method for Global Sensitivity Analysis".
3548:
3029:
2959:
studies have included sections devoted to sensitivity analysis in their guidelines. Examples are the
2721:
2710:
Sampling (running) the model at a number of points in its input space. This requires a sample design.
755:
144:
Increased understanding of the relationships between input and output variables in a system or model.
32:
191:
on the output) and their relative importance is quantified via sensitivity analysis (represented by
170:
For calibration of models with large number of parameters, by focusing on the sensitive parameters.
5153:
5124:
3512:
3195:"Sensitivity Analysis of Normative Economic Models: Theoretical Framework and Practical Strategies"
3044:
2733:
2642:
2547:
1273:
1246:
1014:
122:
5250:
Pianosi, F.; Beven, K.; Freer, J.; Hall, J.W.; Rougier, J.; Stephenson, D.B.; Wagener, T. (2016).
4633:
1492:
4665:
4301:"A new framework for comprehensive, robust, and efficient global sensitivity analysis: 1. Theory"
2193:
2153:
1886:
625:
118:
4992:
Box GEP, Hunter WG, Hunter, J. Stuart. Statistics for experimenters . New York: Wiley & Sons
2001:
4628:
2778:
2222:
1463:
3507:
1974:
39:
3054:
2851:
2486:
2261:
791:
769:
579:
5245:
3921:
Morris, M. D. (1991). "Factorial Sampling Plans for Preliminary Computational Experiments".
2512:
2324:
5263:
5252:"Sensitivity analysis of environmental models: A systematic review with practical workflow"
5012:
4932:
4897:
4854:
4810:
4713:
4564:
4406:
4361:
4312:
3806:
3753:
3700:
3332:
3267:
Hill, M.; Kavetski, D.; Clark, M.; Ye, M.; Arabi, M.; Lu, D.; Foglia, L.; Mehl, S. (2015).
3233:
3059:
2863:
2850:
The problem setting in sensitivity analysis also has strong similarities with the field of
2252:
2126:
2120:
1947:
1918:
1857:
1606:
1553:
1526:
1348:
1286:
1118:
952:
925:
877:
498:
456:
86:
2680:
1036:
8:
5353:
5200:
3089:
2960:
1238:
1002:
751:
5267:
5016:
4936:
4901:
4858:
4814:
4717:
4568:
4410:
4365:
4316:
4000:
3810:
3757:
3704:
3237:
2505:
approaches that involve building a relatively simple mathematical function, known as an
5244:
International Series in Management Science and Operations Research, Springer New York.
5162:
5133:
5081:
5046:
4956:
4826:
4783:
4646:
4593:
4552:
4203:
4158:
3938:
3868:
3830:
3777:
3724:
3562:
3470:
3419:
3386:
3249:
3210:
2987:
The following pages discuss sensitivity analyses in relation to specific applications:
2923:
2752:
2740:
2363:
2288:
2199:
1924:
1900:
1586:
1313:
1098:
1092:
904:
716:
671:
600:
554:
525:
462:
438:
325:
234:
202:
164:
106:
81:
4194:
Wiesel, J. C. W. (November 2022). "Measuring association with Wasserstein distances".
3549:"An efficient methodology for modeling complex computer codes with Gaussian processes"
2810:. In all cases, it is useful to check the accuracy of the emulator, for example using
1211:{\displaystyle \left|{\frac {\partial Y}{\partial X_{i}}}\right|_{{\textbf {x}}^{0}},}
5218:
5085:
5038:
5024:
4948:
4870:
4830:
4642:
4598:
4580:
4441:
4379:
4330:
4221:
4176:
4131:
4096:
4061:
3822:
3769:
3744:
3728:
3716:
3691:
3665:
3597:
3529:
3488:
3437:
3390:
3298:
3290:
3194:
3127:
3094:
2964:
2956:
2795:
2768:
2258:
The class of moment-independent sensitivity measures includes indicators such as the
1242:
1006:
710:
647:
590:
5050:
4960:
4739:
Sudret, B. (2008). "Global sensitivity analysis using polynomial chaos expansions".
3781:
3166:
Der Kiureghian, A.; Ditlevsen, O. (2009). "Aleatory or epistemic? Does it matter?".
1250:
model response is in fact linear; linearity can be confirmed, for instance, if the
5333:
5281:
5271:
5073:
5028:
5020:
4940:
4905:
4862:
4818:
4787:
4775:
4748:
4721:
4680:
4650:
4638:
4588:
4572:
4533:
4501:
4470:
4414:
4369:
4320:
4279:
4248:
4213:
4168:
4123:
4088:
4053:
4043:
3930:
3901:
3860:
3848:
3814:
3797:
3761:
3708:
3657:
3630:
3572:
3521:
3480:
3429:
3378:
3363:
3344:
3280:
3253:
3241:
3206:
3179:
3175:
3119:
2897:
2803:
2784:
2774:
2502:
2480:
994:
moving one input variable, keeping others at their baseline (nominal) values, then,
651:
5276:
5251:
5077:
4822:
4418:
4284:
4267:
4172:
3834:
3687:"Photosynthetic Control of Atmospheric Carbonyl Sulfide During the Growing Season"
3456:
3405:
775:
Using the resulting model outputs, calculate the sensitivity measures of interest.
713:) from the available data (that we use for training) to approximate the code (the
495:,...), sensitivity analysis aims to measure and quantify the impact of each input
5316:. Mathematics in Science and Engineering, 177. Academic Press, Inc., Orlando, FL.
4944:
3591:
3508:"Global sensitivity analysis of stochastic computer models with joint metamodels"
3069:
1269:
1030:
138:
4888:
Li, G. (2002). "Practical approaches to construct RS-HDMR component functions".
4803:
Georisk: Assessment and Management of Risk for Engineered Systems and Geohazards
4725:
3988:
Evaluating Derivatives, Principles and Techniques of Algorithmic Differentiation
3888:"Threshold for the volume spanned by random points with independent coordinates"
2889:
2497:
Metamodels (also known as emulators, surrogate models or response surfaces) are
5321:
Ecosystem Modeling in Theory and Practice: An Introduction with Case Histories.
4752:
4576:
4537:
4505:
4202:(4). Bernoulli Society for Mathematical Statistics and Probability: 2816–2832.
4127:
3686:
3576:
3348:
2762:
2725:
2452:
484:
4779:
3906:
3887:
3525:
3245:
1001:
Sensitivity may then be measured by monitoring changes in the output, e.g. by
827:
in turn. Note that the abscissa is different for each plot: (−5, +5) for
5342:
4584:
4383:
4334:
4225:
4180:
4135:
4100:
4065:
4025:
Sobol', I (1993). "Sensitivity analysis for non-linear mathematical models".
4013:
Sobol', I (1990). "Sensitivity estimates for nonlinear mathematical models".
3533:
3492:
3441:
2913:
uncertainties in inputs must be suppressed lest outputs become indeterminate.
2758:
2729:
2498:
2465:
1077:
4046:
Journal of the Royal Statistical Society. Series B (Statistical Methodology)
3765:
3712:
3661:
3635:
3618:
2747:), where any combination of output points is assumed to be distributed as a
5309:
5042:
4952:
4874:
4602:
3826:
3773:
3720:
3333:"Survey of sampling based methods for uncertainty and sensitivity analysis"
3302:
3049:
1065:
160:
5296:
Useless Arithmetic. Why Environmental Scientists Can't Predict the Future.
4685:
3123:
4374:
4349:
4325:
4300:
3973:
Sensitivity and Uncertainty Analysis: Applications to Large-Scale Systems
3649:
2920:
Not enough information to build probability distributions for the inputs:
2844:
1022:
97:; ideally, uncertainty and sensitivity analysis should be run in tandem.
77:
3818:
3331:
Helton, J. C.; Johnson, J. D.; Salaberry, C. J.; Storlie, C. B. (2006).
758:. In general, however, most procedures adhere to the following outline:
5286:
5166:
5137:
5033:
4252:
4217:
4092:
4057:
3942:
3872:
3285:
3268:
2806:
problem, which can be difficult if the response of the model is highly
1026:
665:
480:
126:
4909:
4866:
4474:
3484:
3433:
3382:
3294:
5001:
4149:
Chatterjee, S. (2 October 2021). "A New Coefficient of Correlation".
3074:
3024:
2893:
2807:
2429:
2357:
621:
228:
192:
182:
110:
5122:
Leamer, Edward E. (1983). "Let's Take the Con Out of Econometrics".
5102:
European Commission. 2021. “Better Regulation Toolbox.” November 25.
3934:
3864:
2677:(metamodel) that is a sufficiently close approximation to the model
70:
Study of uncertainty in the output of a mathematical model or system
5242:
Sensitivity Analysis: An Introduction for the Management Scientist.
4701:
4208:
4163:
4114:
Borgonovo, E. (June 2007). "A new uncertainty importance measure".
2751:. Recently, "treed" Gaussian processes have been used to deal with
1330:(averaged over variations in other variables), and is known as the
141:
of the results of a model or system in the presence of uncertainty.
4461:
Owen, A. B. (1 January 2014). "Sobol' Indices and Shapley Value".
3567:
3475:
3457:"Sensitivity analysis for multidimensional and functional outputs"
3424:
650:, can inaccurately measure sensitivity when the model response is
594:
2744:
2356:
in the parameter space. By utilizing the concepts of directional
2312:
3269:"Practical use of computationally frugal model analysis methods"
3146:
2982:
2817:
2481:
Complementary research approaches for time-consuming simulations
1847:{\displaystyle X_{\sim i}=(X_{1},...,X_{i-1},X_{i+1},...,X_{p})}
1017:
between input variables and is unsuitable for nonlinear models.
4702:"Bayesian sensitivity analysis of bifurcating nonlinear models"
4490:"Global sensitivity analysis using polynomial chaos expansions"
3971:
Cacuci, Dan G.; Ionescu-Bujor, Mihaela; Navon, Michael (2005).
1520:
denote the variance and expected value operators respectively.
795:
Figure 2. Sampling-based sensitivity analysis by scatterplots.
5334:
Web site with material from SAMO conference series (1995-2025)
4469:(1). Society for Industrial and Applied Mathematics: 245–251.
3617:
Sacks, J.; Welch, W. J.; Mitchell, T. J.; Wynn, H. P. (1989).
3499:
3113:
5151:
Leamer, Edward E. (1985). "Sensitivity Analyses Would Help".
4523:
3448:
3330:
2911:
expressed by Jerome R. Ravetz, for whom bad modeling is when
1241:, in the context of sensitivity analysis, involves fitting a
772:, dictated by the method of choice and the input uncertainty.
646:
Some sensitivity analysis approaches, such as those based on
5323:
John Wiley & Sons, New York, NY. isbn=978-0-471-34165-9.
4247:(1). Society for Industrial and Applied Mathematics: 27–54.
3851:(1999). "One-Factor-at-a-Time Versus Designed Experiments".
2896:
may be. The point is well illustrated by the econometrician
2713:
Selecting a type of emulator (mathematical function) to use.
2440:
4079:
Rényi, A. (1 September 1959). "On measures of dependence".
3546:
1723:{\displaystyle S_{i}^{T}=1-{\frac {V(\mathbb {E} )}{V(Y)}}}
199:
The object of study for sensitivity analysis is a function
3547:
Marrel, A.; Iooss, B.; Van Dorpe, F.; Volkova, E. (2008).
3505:
2881:
Some common difficulties in sensitivity analysis include:
1577:
has with other variables. A further measure, known as the
545:
177:
3506:
Marrel, A.; Iooss, B.; Da Veiga, S.; Ribatet, M. (2012).
2639:
Clearly, the crux of an metamodel approach is to find an
668:, sensitivity analysis extends to cases where the output
582:-based approach. This can be a significant problem when:
4923:
Rabitz, H (1989). "System analysis at molecular scale".
3970:
3650:
Da Veiga, S., Gamboa, F., Iooss, B., Prieur, C. (2021).
1550:
does not measure the uncertainty caused by interactions
4436:. In Petropoulos, George; Srivastava, Prashant (eds.).
4434:"Challenges and Future Outlook of Sensitivity Analysis"
3454:
3165:
2451:
The Fourier amplitude sensitivity test (FAST) uses the
628:
is to use sampling based on low discrepancy sequences.
617:-function is one way of reducing the computation costs.
4265:
3616:
3593:
Uncertain Judgements: Eliciting Experts' Probabilities
3455:
Gamboa, F.; Janon, A.; Klein, T.; Lagnoux, A. (2014).
522:
or a group of inputs on the variability of the output
5249:
3885:
3403:
3309:
2683:
2645:
2588:
2550:
2515:
2386:
2366:
2327:
2291:
2264:
2225:
2202:
2156:
2129:
2090:
2004:
1977:
1950:
1927:
1903:
1860:
1736:
1636:
1609:
1589:
1556:
1529:
1495:
1466:
1453:{\displaystyle S_{i}={\frac {V(\mathbb {E} )}{V(Y)}}}
1380:
1351:
1316:
1289:
1151:
1121:
1101:
1039:
955:
928:
907:
880:
719:
674:
603:
557:
528:
501:
465:
441:
390:
350:
328:
261:
237:
205:
4843:
4027:
Mathematical Modeling & Computational Experiment
2417:{\displaystyle {\frac {\partial Y}{\partial x_{i}}}}
5301:Santner, T. J.; Williams, B. J.; Notz, W.I. (2003)
4438:
Sensitivity Analysis in Earth Observation Modelling
3266:
4699:
4396:
4238:
3741:
2922:Probability distributions can be constructed from
2698:
2669:
2627:
2574:
2536:
2416:
2372:
2348:
2297:
2270:
2243:
2208:
2184:
2142:
2111:
2076:
1990:
1963:
1933:
1909:
1873:
1846:
1722:
1622:
1595:
1569:
1542:
1512:
1481:
1452:
1364:
1322:
1302:
1210:
1134:
1107:
1091:Local derivative-based methods involve taking the
1056:
968:
941:
913:
893:
725:
680:
609:
563:
534:
514:
471:
447:
427:
374:
334:
311:
243:
211:
5369:Mathematical and quantitative methods (economics)
5314:Design sensitivity analysis of structural systems
4618:
3223:
1086:
5340:
5063:
4348:Razavi, Saman; Gupta, Hoshin V. (January 2016).
4299:Razavi, Saman; Gupta, Hoshin V. (January 2016).
4193:
4081:Acta Mathematica Academiae Scientiarum Hungarica
636:Most common sensitivity analysis methods assume
459:aims to describe the distribution of the output
4973:
4151:Journal of the American Statistical Association
3361:
1944:The moment-independent sensitivity measures of
1279:This amount is quantified and calculated using
740:
4463:SIAM/ASA Journal on Uncertainty Quantification
4241:SIAM/ASA Journal on Uncertainty Quantification
4148:
3540:
3404:Chastaing, G.; Gamboa, F.; Prieur, C. (2012).
2949:
1854:denotes the set of all input variables except
1523:Importantly, first-order sensitivity index of
4550:
4113:
4107:
4037:
3920:
3619:"Design and Analysis of Computer Experiments"
3260:
2983:Specific applications of sensitivity analysis
2818:High-dimensional model representations (HDMR)
1892:
4663:
4440:(1st ed.). Elsevier. pp. 397–415.
3958:Sensitivity and Uncertainty Analysis: Theory
3554:Computational Statistics & Data Analysis
3315:
2876:
1917:. Thus, they do not refer to any particular
1681:
1414:
5303:Design and Analysis of Computer Experiments
5294:Pilkey, O. H. and L. Pilkey-Jarvis (2007),
5097:
5095:
4765:
4741:Reliability Engineering & System Safety
4700:Becker, W.; Worden, K.; Rowson, J. (2013).
4526:Reliability Engineering & System Safety
4460:
4431:
4347:
4298:
4116:Reliability Engineering & System Safety
3589:
3371:Journal of Renewable and Sustainable Energy
768:Run the model a number of times using some
654:with respect to its inputs. In such cases,
4481:
4142:
4024:
4012:
3107:
2720:Sampling the model can often be done with
5285:
5275:
5057:
5032:
4986:
4684:
4632:
4592:
4519:
4517:
4515:
4373:
4324:
4283:
4207:
4162:
4078:
3905:
3653:Basics and Trends in Sensitivity Analysis
3634:
3566:
3474:
3423:
3337:Reliability Engineering and System Safety
3284:
2973:Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change
2628:{\displaystyle {\hat {f}}(X)\approx f(X)}
2441:Fourier amplitude sensitivity test (FAST)
2313:Variogram analysis of response surfaces (
1671:
1497:
1404:
1257:
705:data. We then build a statistical model (
58:Learn how and when to remove this message
5183:, New Internationalist Publications Ltd.
5092:
4800:
4706:Mechanical Systems and Signal Processing
4157:(536). Taylor & Francis: 2009–2022.
3994:
3985:
3684:
3362:Tsvetkova, O.; Ouarda, T.B.M.J. (2019).
3217:
2829:
976:are highly correlated with the output.
790:
181:
4272:Environmental Modelling \& Software
3847:
3192:
3186:
2857:
1372:, Sobol index is defined as following:
1310:alone to the uncertainty (variance) in
546:Challenges, settings and related issues
178:Mathematical formulation and vocabulary
5341:
5319:Hall, C. A. S. and Day, J. W. (1977).
5256:Environmental Modelling & Software
5223:: CS1 maint: archived copy as title (
5150:
5121:
4922:
4738:
4614:
4612:
4512:
4487:
4399:Environmental Modelling & Software
4187:
3886:Gatzouras, D; Giannopoulos, A (2009).
3794:
3397:
2937:Too many model outputs are considered:
1233:
979:
4995:
4768:AStA Advances in Statistical Analysis
4664:Gramacy, R. B.; Taddy, M. A. (2010).
4072:
3140:
3040:Fourier amplitude sensitivity testing
2824:high-dimensional model representation
2789:high-dimensional model representation
2765:are trained, and the result averaged.
2706:. This requires the following steps,
2447:Fourier amplitude sensitivity testing
5298:New York: Columbia University Press.
4259:
4232:
3929:(2). Taylor & Francis: 161–174.
2802:The use of an emulator introduces a
2787:, normally used in conjunction with
2781:to approximate the response surface.
2472:
1247:standardized regression coefficients
1068:, true linearity is rare in nature.
384:The variability in input parameters
15:
4976:Journal of Environmental Management
4609:
4494:Bayesian Networks in Dependability]
3975:. Vol. II. Chapman & Hall.
3085:Variance-based sensitivity analysis
2838:
1264:Variance-based sensitivity analysis
1192:
428:{\displaystyle X_{i},i=1,\ldots ,p}
312:{\displaystyle X=(X_{1},...,X_{p})}
13:
5234:
4887:
3960:. Vol. I. Chapman & Hall.
3955:
3685:Campbell, J.; et al. (2008).
3211:10.1111/j.1574-0862.1997.tb00449.x
2977:US Environmental Protection Agency
2749:multivariate Gaussian distribution
2459:
2398:
2390:
2380:, and hence also to the values of
1168:
1160:
786:
14:
5380:
5327:
5308:Haug, Edward J.; Choi, Kyung K.;
4266:Pianosi, F., Wagener, T. (2015).
3590:O'Hagan, A.; et al. (2006).
3035:Experimental uncertainty analysis
2437:and derivative-based approaches.
2283:Cumulative Distribution Functions
862:is most important in influencing
5025:10.1111/j.1539-6924.2005.00604.x
4643:10.1111/j.1467-9868.2004.05304.x
3462:Electronic Journal of Statistics
3411:Electronic Journal of Statistics
2930:Unclear purpose of the analysis:
2112:{\displaystyle d(\cdot ,\cdot )}
1245:to the model response and using
1115:with respect to an input factor
1025:bounding all these points is an
20:
5186:
5173:
5144:
5115:
5106:
4967:
4916:
4881:
4847:Journal of Physical Chemistry A
4837:
4794:
4759:
4732:
4693:
4673:Journal of Statistical Software
4657:
4544:
4454:
4425:
4390:
4341:
4292:
4006:
3979:
3964:
3949:
3914:
3879:
3841:
3788:
3735:
3678:
3643:
3610:
3583:
3316:Hill, M.; Tiedeman, C. (2007).
2969:Office of Management and Budget
2791:(HDMR) truncations (see below).
1033:which has a volume fraction of
706:
662:Multiple or functional outputs:
586:
89:, which has a greater focus on
3355:
3324:
3180:10.1016/j.strusafe.2008.06.020
3159:
3007:Multi-criteria decision making
2693:
2687:
2664:
2658:
2652:
2622:
2616:
2607:
2601:
2595:
2569:
2563:
2557:
2531:
2525:
2343:
2337:
2232:
2229:
2166:
2123:between probability measures,
2106:
2094:
2071:
2068:
2052:
2027:
2021:
1841:
1753:
1714:
1708:
1700:
1697:
1675:
1667:
1583:, gives the total variance in
1507:
1501:
1476:
1470:
1444:
1438:
1430:
1427:
1408:
1400:
1087:Derivative-based local methods
866:as it imparts more 'shape' on
366:
360:
306:
268:
29:This article needs editing to
1:
5277:10.1016/j.envsoft.2016.02.008
5078:10.1016/j.futures.2019.06.008
4890:Journal of Physical Chemistry
4823:10.1080/17499518.2018.1498524
4419:10.1016/j.envsoft.2017.03.031
4285:10.1016/j.envsoft.2015.01.004
4173:10.1080/01621459.2020.1758115
4015:Matematicheskoe Modelirovanie
3893:Israel Journal of Mathematics
3101:
2963:(see e.g. the guidelines for
2761:, in which a large number of
2670:{\displaystyle {\hat {f}}(X)}
2575:{\displaystyle {\hat {f}}(X)}
2492:
1333:first-order sensitivity index
435:have an impact on the output
100:
5181:No-Nonsense Guide to Science
4945:10.1126/science.246.4927.221
4432:Gupta, H; Razavi, S (2016).
2755:and discontinuous responses.
1513:{\displaystyle \mathbb {E} }
1252:coefficient of determination
741:Sensitivity analysis methods
622:multidimensional input space
7:
5359:Business intelligence terms
4726:10.1016/j.ymssp.2012.05.010
4023:; translated in English in
3065:Probability bounds analysis
3017:
2950:SA in international context
2892:and how wide the resulting
2886:Assumptions vs. inferences:
2775:Polynomial chaos expansions
2185:{\displaystyle P_{Y|X_{i}}}
986:One-factor-at-a-time method
10:
5385:
4753:10.1016/j.ress.2007.04.002
4577:10.1038/s41467-019-12342-y
4538:10.1016/j.ress.2009.05.007
4506:10.1016/j.ress.2007.04.002
4128:10.1016/J.RESS.2006.04.015
3577:10.1016/j.csda.2008.03.026
3349:10.1016/j.ress.2005.11.017
3226:Water Resources Management
3080:Uncertainty quantification
2861:
2444:
2077:{\displaystyle \xi _{i}=E}
1893:Moment-independent methods
1261:
1075:
983:
342:, presented as following:
95:propagation of uncertainty
91:uncertainty quantification
4780:10.1007/s10182-010-0148-8
3907:10.1007/s11856-009-0007-z
3526:10.1007/s11222-011-9274-8
3246:10.1007/s11269-007-9168-x
3030:Elementary effects method
2877:Pitfalls and difficulties
2722:low-discrepancy sequences
2244:{\displaystyle d()\geq 0}
1482:{\displaystyle V(\cdot )}
1274:probability distributions
1071:
664:Generally introduced for
5154:American Economic Review
5125:American Economic Review
4354:Water Resources Research
4305:Water Resources Research
4122:(6). Elsevier: 771–784.
3513:Statistics and Computing
3320:. John Wiley & Sons.
3045:Info-gap decision theory
2979:'s modeling guidelines.
2734:Latin hypercube sampling
2464:Shapley effects rely on
1991:{\displaystyle \xi _{i}}
1272:, represented via their
76:is the study of how the
31:comply with Knowledge's
3766:10.1126/science.1106881
3713:10.1126/science.1164015
3662:10.1137/1.9781611976694
3193:Pannell, D. J. (1997).
2728:– due to mathematician
2307:Kolmogorov–Smirnov test
2271:{\displaystyle \delta }
2194:conditional probability
748:variance decompositions
656:variance-based measures
626:curse of dimensionality
375:{\displaystyle Y=f(X).}
5240:Borgonovo, E. (2017).
3199:Agricultural Economics
3116:John Wiley \& Sons
2992:Environmental sciences
2943:Piecewise sensitivity:
2907:
2779:orthogonal polynomials
2700:
2671:
2629:
2576:
2538:
2537:{\displaystyle Y=f(X)}
2418:
2374:
2350:
2349:{\displaystyle Y=f(X)}
2299:
2272:
2245:
2210:
2186:
2144:
2113:
2078:
1992:
1965:
1935:
1911:
1875:
1848:
1724:
1624:
1597:
1571:
1544:
1514:
1483:
1454:
1366:
1324:
1304:
1258:Variance-based methods
1212:
1136:
1109:
1058:
970:
943:
915:
895:
871:
841:, (−10, +10) for
727:
682:
611:
576:Computational expense:
565:
536:
516:
473:
449:
429:
376:
336:
313:
245:
213:
196:
5364:Mathematical modeling
4686:10.18637/jss.v033.i06
4557:Nature Communications
3986:Griewank, A. (2000).
3853:American Statistician
3636:10.1214/ss/1177012413
3596:. Chichester: Wiley.
3124:10.1002/9780470725184
3055:Perturbation analysis
2933:values of the output.
2903:
2852:design of experiments
2830:Monte Carlo filtering
2701:
2672:
2630:
2577:
2539:
2487:computational expense
2419:
2375:
2351:
2300:
2273:
2246:
2211:
2192:are the marginal and
2187:
2145:
2143:{\displaystyle P_{Y}}
2114:
2079:
1993:
1966:
1964:{\displaystyle X_{i}}
1936:
1912:
1876:
1874:{\displaystyle X_{i}}
1849:
1725:
1625:
1623:{\displaystyle X_{i}}
1598:
1572:
1570:{\displaystyle X_{i}}
1545:
1543:{\displaystyle X_{i}}
1515:
1484:
1455:
1367:
1365:{\displaystyle X_{i}}
1325:
1305:
1303:{\displaystyle X_{i}}
1213:
1137:
1135:{\displaystyle X_{i}}
1110:
1059:
971:
969:{\displaystyle Z_{4}}
944:
942:{\displaystyle Z_{3}}
916:
896:
894:{\displaystyle Z_{i}}
794:
770:design of experiments
728:
702:Data-driven approach:
683:
658:are more appropriate.
612:
566:
537:
517:
515:{\displaystyle X_{i}}
474:
450:
430:
377:
337:
314:
246:
214:
185:
165:Monte Carlo filtering
119:errors of measurement
5349:Sensitivity analysis
5179:Ravetz, J.R., 2007,
4375:10.1002/2015WR017559
4326:10.1002/2015WR017558
3343:(10–11): 1175–1209.
3149:Wiley Online Library
3060:Probabilistic design
2864:Sensitivity auditing
2858:Sensitivity auditing
2699:{\displaystyle f(X)}
2681:
2643:
2586:
2548:
2513:
2384:
2364:
2325:
2289:
2262:
2223:
2200:
2154:
2127:
2121:statistical distance
2088:
2002:
1975:
1948:
1925:
1901:
1858:
1734:
1634:
1607:
1587:
1554:
1527:
1493:
1464:
1378:
1349:
1314:
1287:
1221:where the subscript
1149:
1119:
1099:
1057:{\displaystyle 1/n!}
1037:
953:
926:
905:
878:
834:, (−8, +8) for
717:
672:
601:
555:
526:
499:
463:
457:uncertainty analysis
439:
388:
348:
326:
259:
235:
203:
87:uncertainty analysis
74:Sensitivity analysis
5268:2016EnvMS..79..214P
5017:2005RiskA..25..481V
4937:1989Sci...246..221R
4902:2002JPCA..106.8721L
4859:2006JPCA..110.2474L
4815:2019GAMRE..13...53C
4718:2013MSSP...34...57B
4569:2019NatCo..10.4354W
4488:Sudret, B. (2008).
4411:2017EnvMS..95..115H
4366:2016WRR....52..440R
4317:2016WRR....52..423R
3819:10.1038/nature02771
3811:2004Natur.430..768M
3758:2005Sci...308...98B
3705:2008Sci...322.1085C
3699:(5904): 1085–1088.
3623:Statistical Science
3238:2008WatRM..22..393B
3090:Multiverse analysis
2967:), the White House
2961:European Commission
1941:, whence the name.
1651:
1239:Regression analysis
1234:Regression analysis
1003:partial derivatives
980:One-at-a-time (OAT)
752:partial derivatives
666:single-output codes
597:to approximate the
80:in the output of a
40:improve the content
5305:; Springer-Verlag.
4621:J. R. Stat. Soc. B
4278:. Elsevier: 1–11.
4253:10.1137/20M1354829
4218:10.3150/21-BEJ1438
4093:10.1007/BF02024507
4058:10.1111/rssb.12052
3286:10.1111/gwat.12330
2924:expert elicitation
2741:Gaussian processes
2696:
2667:
2625:
2572:
2534:
2414:
2370:
2346:
2295:
2268:
2241:
2206:
2182:
2140:
2109:
2074:
1988:
1971:, here denoted by
1961:
1931:
1907:
1871:
1844:
1720:
1637:
1620:
1593:
1580:total effect index
1567:
1540:
1510:
1479:
1450:
1362:
1320:
1300:
1208:
1132:
1105:
1093:partial derivative
1054:
966:
939:
911:
891:
872:
756:elementary effects
723:
678:
634:Correlated inputs:
607:
561:
532:
512:
469:
445:
425:
372:
332:
309:
241:
221:mathematical model
209:
197:
107:mathematical model
82:mathematical model
4931:(4927): 221–226.
4910:10.1021/jp014567t
4896:(37): 8721–8733.
4867:10.1021/jp054148m
4532:(11): 1735–1763.
4475:10.1137/130936233
3849:Czitrom, Veronica
3805:(7001): 768–772.
3671:978-1-61197-668-7
3561:(10): 4731–4744.
3485:10.1214/14-EJS895
3434:10.1214/12-EJS749
3383:10.1063/1.5120035
3168:Structural Safety
3133:978-0-470-05997-5
3095:Feature selection
3012:Model calibration
2965:impact assessment
2957:impact assessment
2796:Bayesian networks
2785:Smoothing splines
2769:Gradient boosting
2655:
2598:
2560:
2473:Chaos polynomials
2412:
2373:{\displaystyle Y}
2298:{\displaystyle i}
2209:{\displaystyle Y}
1934:{\displaystyle Y}
1910:{\displaystyle Y}
1718:
1596:{\displaystyle Y}
1448:
1339:main effect index
1323:{\displaystyle Y}
1243:linear regression
1194:
1182:
1108:{\displaystyle Y}
1007:linear regression
914:{\displaystyle Y}
726:{\displaystyle f}
711:data-driven model
681:{\displaystyle Y}
648:linear regression
610:{\displaystyle f}
591:data-driven model
564:{\displaystyle f}
535:{\displaystyle Y}
472:{\displaystyle Y}
448:{\displaystyle Y}
335:{\displaystyle Y}
244:{\displaystyle p}
212:{\displaystyle f}
68:
67:
60:
5376:
5291:
5289:
5279:
5229:
5228:
5222:
5214:
5212:
5211:
5205:
5199:. Archived from
5198:
5190:
5184:
5177:
5171:
5170:
5148:
5142:
5141:
5119:
5113:
5110:
5104:
5099:
5090:
5089:
5061:
5055:
5054:
5036:
4999:
4993:
4990:
4984:
4983:
4971:
4965:
4964:
4920:
4914:
4913:
4885:
4879:
4878:
4853:(7): 2474–2485.
4841:
4835:
4834:
4798:
4792:
4791:
4763:
4757:
4756:
4736:
4730:
4729:
4697:
4691:
4690:
4688:
4670:
4661:
4655:
4654:
4636:
4616:
4607:
4606:
4596:
4548:
4542:
4541:
4521:
4510:
4509:
4485:
4479:
4478:
4458:
4452:
4451:
4429:
4423:
4422:
4394:
4388:
4387:
4377:
4345:
4339:
4338:
4328:
4296:
4290:
4289:
4287:
4263:
4257:
4256:
4236:
4230:
4229:
4211:
4191:
4185:
4184:
4166:
4146:
4140:
4139:
4111:
4105:
4104:
4076:
4070:
4069:
4052:(5). : 925–947.
4041:
4035:
4034:
4022:
4010:
4004:
3998:
3992:
3991:
3983:
3977:
3976:
3968:
3962:
3961:
3953:
3947:
3946:
3918:
3912:
3911:
3909:
3883:
3877:
3876:
3845:
3839:
3838:
3792:
3786:
3785:
3752:(5718): 98–103.
3739:
3733:
3732:
3682:
3676:
3675:
3647:
3641:
3640:
3638:
3614:
3608:
3607:
3587:
3581:
3580:
3570:
3544:
3538:
3537:
3503:
3497:
3496:
3478:
3452:
3446:
3445:
3427:
3401:
3395:
3394:
3368:
3359:
3353:
3352:
3328:
3322:
3321:
3313:
3307:
3306:
3288:
3264:
3258:
3257:
3221:
3215:
3214:
3190:
3184:
3183:
3163:
3157:
3156:
3144:
3138:
3137:
3111:
2898:Edward E. Leamer
2839:Related concepts
2812:cross-validation
2804:machine learning
2705:
2703:
2702:
2697:
2676:
2674:
2673:
2668:
2657:
2656:
2648:
2634:
2632:
2631:
2626:
2600:
2599:
2591:
2581:
2579:
2578:
2573:
2562:
2561:
2553:
2543:
2541:
2540:
2535:
2503:machine learning
2423:
2421:
2420:
2415:
2413:
2411:
2410:
2409:
2396:
2388:
2379:
2377:
2376:
2371:
2355:
2353:
2352:
2347:
2304:
2302:
2301:
2296:
2277:
2275:
2274:
2269:
2250:
2248:
2247:
2242:
2215:
2213:
2212:
2207:
2191:
2189:
2188:
2183:
2181:
2180:
2179:
2178:
2169:
2149:
2147:
2146:
2141:
2139:
2138:
2118:
2116:
2115:
2110:
2083:
2081:
2080:
2075:
2067:
2066:
2065:
2064:
2055:
2039:
2038:
2014:
2013:
1997:
1995:
1994:
1989:
1987:
1986:
1970:
1968:
1967:
1962:
1960:
1959:
1940:
1938:
1937:
1932:
1916:
1914:
1913:
1908:
1880:
1878:
1877:
1872:
1870:
1869:
1853:
1851:
1850:
1845:
1840:
1839:
1815:
1814:
1796:
1795:
1765:
1764:
1749:
1748:
1729:
1727:
1726:
1721:
1719:
1717:
1703:
1696:
1695:
1674:
1662:
1650:
1645:
1629:
1627:
1626:
1621:
1619:
1618:
1602:
1600:
1599:
1594:
1576:
1574:
1573:
1568:
1566:
1565:
1549:
1547:
1546:
1541:
1539:
1538:
1519:
1517:
1516:
1511:
1500:
1488:
1486:
1485:
1480:
1459:
1457:
1456:
1451:
1449:
1447:
1433:
1426:
1425:
1407:
1395:
1390:
1389:
1371:
1369:
1368:
1363:
1361:
1360:
1329:
1327:
1326:
1321:
1309:
1307:
1306:
1301:
1299:
1298:
1270:random variables
1217:
1215:
1214:
1209:
1204:
1203:
1202:
1201:
1196:
1195:
1187:
1183:
1181:
1180:
1179:
1166:
1158:
1141:
1139:
1138:
1133:
1131:
1130:
1114:
1112:
1111:
1106:
1063:
1061:
1060:
1055:
1047:
975:
973:
972:
967:
965:
964:
948:
946:
945:
940:
938:
937:
920:
918:
917:
912:
900:
898:
897:
892:
890:
889:
732:
730:
729:
724:
693:Stochastic code:
687:
685:
684:
679:
616:
614:
613:
608:
570:
568:
567:
562:
541:
539:
538:
533:
521:
519:
518:
513:
511:
510:
478:
476:
475:
470:
454:
452:
451:
446:
434:
432:
431:
426:
400:
399:
381:
379:
378:
373:
341:
339:
338:
333:
318:
316:
315:
310:
305:
304:
280:
279:
250:
248:
247:
242:
227:"), viewed as a
225:programming code
218:
216:
215:
210:
63:
56:
52:
49:
43:
24:
23:
16:
5384:
5383:
5379:
5378:
5377:
5375:
5374:
5373:
5339:
5338:
5330:
5237:
5235:Further reading
5232:
5216:
5215:
5209:
5207:
5203:
5196:
5194:"Archived copy"
5192:
5191:
5187:
5178:
5174:
5149:
5145:
5120:
5116:
5111:
5107:
5100:
5093:
5062:
5058:
5000:
4996:
4991:
4987:
4972:
4968:
4921:
4917:
4886:
4882:
4842:
4838:
4799:
4795:
4764:
4760:
4737:
4733:
4698:
4694:
4668:
4662:
4658:
4617:
4610:
4549:
4545:
4522:
4513:
4486:
4482:
4459:
4455:
4448:
4430:
4426:
4395:
4391:
4346:
4342:
4297:
4293:
4264:
4260:
4237:
4233:
4192:
4188:
4147:
4143:
4112:
4108:
4077:
4073:
4042:
4038:
4011:
4007:
3999:
3995:
3984:
3980:
3969:
3965:
3956:Cacuci, Dan G.
3954:
3950:
3935:10.2307/1269043
3919:
3915:
3884:
3880:
3865:10.2307/2685731
3846:
3842:
3793:
3789:
3740:
3736:
3683:
3679:
3672:
3648:
3644:
3615:
3611:
3604:
3588:
3584:
3545:
3541:
3504:
3500:
3453:
3449:
3402:
3398:
3366:
3360:
3356:
3329:
3325:
3314:
3310:
3265:
3261:
3222:
3218:
3191:
3187:
3164:
3160:
3145:
3141:
3134:
3112:
3108:
3104:
3099:
3070:Robustification
3020:
2985:
2952:
2879:
2866:
2860:
2841:
2832:
2820:
2753:heteroscedastic
2743:(also known as
2682:
2679:
2678:
2647:
2646:
2644:
2641:
2640:
2590:
2589:
2587:
2584:
2583:
2552:
2551:
2549:
2546:
2545:
2514:
2511:
2510:
2495:
2483:
2475:
2462:
2460:Shapley effects
2449:
2443:
2405:
2401:
2397:
2389:
2387:
2385:
2382:
2381:
2365:
2362:
2361:
2326:
2323:
2322:
2319:
2290:
2287:
2286:
2263:
2260:
2259:
2224:
2221:
2220:
2201:
2198:
2197:
2174:
2170:
2165:
2161:
2157:
2155:
2152:
2151:
2134:
2130:
2128:
2125:
2124:
2089:
2086:
2085:
2060:
2056:
2051:
2047:
2043:
2034:
2030:
2009:
2005:
2003:
2000:
1999:
1982:
1978:
1976:
1973:
1972:
1955:
1951:
1949:
1946:
1945:
1926:
1923:
1922:
1902:
1899:
1898:
1895:
1865:
1861:
1859:
1856:
1855:
1835:
1831:
1804:
1800:
1785:
1781:
1760:
1756:
1741:
1737:
1735:
1732:
1731:
1704:
1688:
1684:
1670:
1663:
1661:
1646:
1641:
1635:
1632:
1631:
1614:
1610:
1608:
1605:
1604:
1588:
1585:
1584:
1561:
1557:
1555:
1552:
1551:
1534:
1530:
1528:
1525:
1524:
1496:
1494:
1491:
1490:
1465:
1462:
1461:
1434:
1421:
1417:
1403:
1396:
1394:
1385:
1381:
1379:
1376:
1375:
1356:
1352:
1350:
1347:
1346:
1315:
1312:
1311:
1294:
1290:
1288:
1285:
1284:
1266:
1260:
1236:
1197:
1191:
1190:
1189:
1188:
1175:
1171:
1167:
1159:
1157:
1153:
1152:
1150:
1147:
1146:
1126:
1122:
1120:
1117:
1116:
1100:
1097:
1096:
1095:of the output
1089:
1080:
1074:
1043:
1038:
1035:
1034:
1031:hyperoctahedron
988:
982:
960:
956:
954:
951:
950:
933:
929:
927:
924:
923:
906:
903:
902:
901:and the output
885:
881:
879:
876:
875:
861:
854:
847:
840:
833:
826:
819:
812:
805:
789:
787:Visual analysis
743:
718:
715:
714:
673:
670:
669:
602:
599:
598:
556:
553:
552:
548:
527:
524:
523:
506:
502:
500:
497:
496:
479:(providing its
464:
461:
460:
440:
437:
436:
395:
391:
389:
386:
385:
349:
346:
345:
327:
324:
323:
300:
296:
275:
271:
260:
257:
256:
236:
233:
232:
204:
201:
200:
180:
103:
71:
64:
53:
47:
44:
37:
33:Manual of Style
25:
21:
12:
11:
5:
5382:
5372:
5371:
5366:
5361:
5356:
5351:
5337:
5336:
5329:
5328:External links
5326:
5325:
5324:
5317:
5306:
5299:
5292:
5247:
5236:
5233:
5231:
5230:
5185:
5172:
5161:(3): 308–313.
5143:
5114:
5105:
5091:
5056:
5011:(2): 481–492.
4994:
4985:
4966:
4915:
4880:
4836:
4793:
4774:(4): 367–388.
4758:
4747:(7): 964–979.
4731:
4712:(1–2): 57–75.
4692:
4656:
4627:(3): 751–769.
4608:
4543:
4511:
4500:(7): 964–979.
4480:
4453:
4446:
4424:
4389:
4360:(1): 440–455.
4340:
4311:(1): 423–439.
4291:
4258:
4231:
4186:
4141:
4106:
4087:(3): 441–451.
4071:
4036:
4017:(in Russian).
4005:
3993:
3978:
3963:
3948:
3913:
3900:(1): 125–153.
3878:
3859:(2): 126–131.
3840:
3787:
3734:
3677:
3670:
3642:
3629:(4): 409–435.
3609:
3602:
3582:
3539:
3520:(3): 833–847.
3498:
3447:
3396:
3354:
3323:
3308:
3279:(2): 159–170.
3259:
3232:(3): 293–408.
3216:
3205:(2): 139–152.
3185:
3174:(2): 105–112.
3158:
3139:
3132:
3105:
3103:
3100:
3098:
3097:
3092:
3087:
3082:
3077:
3072:
3067:
3062:
3057:
3052:
3047:
3042:
3037:
3032:
3027:
3021:
3019:
3016:
3015:
3014:
3009:
3004:
2999:
2994:
2984:
2981:
2951:
2948:
2947:
2946:
2940:
2934:
2927:
2916:
2915:
2902:
2901:
2878:
2875:
2862:Main article:
2859:
2856:
2840:
2837:
2831:
2828:
2819:
2816:
2800:
2799:
2792:
2782:
2772:
2766:
2763:decision trees
2759:Random forests
2756:
2726:Sobol sequence
2724:, such as the
2718:
2717:
2714:
2711:
2695:
2692:
2689:
2686:
2666:
2663:
2660:
2654:
2651:
2624:
2621:
2618:
2615:
2612:
2609:
2606:
2603:
2597:
2594:
2571:
2568:
2565:
2559:
2556:
2533:
2530:
2527:
2524:
2521:
2518:
2494:
2491:
2482:
2479:
2474:
2471:
2466:Shapley values
2461:
2458:
2453:Fourier series
2445:Main article:
2442:
2439:
2435:variance-based
2408:
2404:
2400:
2395:
2392:
2369:
2345:
2342:
2339:
2336:
2333:
2330:
2318:
2311:
2294:
2267:
2240:
2237:
2234:
2231:
2228:
2205:
2177:
2173:
2168:
2164:
2160:
2137:
2133:
2108:
2105:
2102:
2099:
2096:
2093:
2073:
2070:
2063:
2059:
2054:
2050:
2046:
2042:
2037:
2033:
2029:
2026:
2023:
2020:
2017:
2012:
2008:
1985:
1981:
1958:
1954:
1930:
1906:
1894:
1891:
1868:
1864:
1843:
1838:
1834:
1830:
1827:
1824:
1821:
1818:
1813:
1810:
1807:
1803:
1799:
1794:
1791:
1788:
1784:
1780:
1777:
1774:
1771:
1768:
1763:
1759:
1755:
1752:
1747:
1744:
1740:
1716:
1713:
1710:
1707:
1702:
1699:
1694:
1691:
1687:
1683:
1680:
1677:
1673:
1669:
1666:
1660:
1657:
1654:
1649:
1644:
1640:
1617:
1613:
1592:
1564:
1560:
1537:
1533:
1509:
1506:
1503:
1499:
1478:
1475:
1472:
1469:
1446:
1443:
1440:
1437:
1432:
1429:
1424:
1420:
1416:
1413:
1410:
1406:
1402:
1399:
1393:
1388:
1384:
1359:
1355:
1319:
1297:
1293:
1262:Main article:
1259:
1256:
1235:
1232:
1219:
1218:
1207:
1200:
1186:
1178:
1174:
1170:
1165:
1162:
1156:
1129:
1125:
1104:
1088:
1085:
1076:Main article:
1073:
1070:
1053:
1050:
1046:
1042:
999:
998:
995:
984:Main article:
981:
978:
963:
959:
936:
932:
910:
888:
884:
859:
852:
845:
838:
831:
824:
817:
810:
803:
788:
785:
777:
776:
773:
766:
763:
742:
739:
735:
734:
722:
698:
697:
690:
677:
659:
641:
631:
630:
629:
618:
606:
560:
547:
544:
531:
509:
505:
468:
444:
424:
421:
418:
415:
412:
409:
406:
403:
398:
394:
371:
368:
365:
362:
359:
356:
353:
331:
308:
303:
299:
295:
292:
289:
286:
283:
278:
274:
270:
267:
264:
240:
208:
179:
176:
175:
174:
171:
168:
157:
154:
151:
148:
145:
142:
102:
99:
69:
66:
65:
48:September 2024
28:
26:
19:
9:
6:
4:
3:
2:
5381:
5370:
5367:
5365:
5362:
5360:
5357:
5355:
5352:
5350:
5347:
5346:
5344:
5335:
5332:
5331:
5322:
5318:
5315:
5311:
5310:Komkov, Vadim
5307:
5304:
5300:
5297:
5293:
5288:
5283:
5278:
5273:
5269:
5265:
5261:
5257:
5253:
5248:
5246:
5243:
5239:
5238:
5226:
5220:
5206:on 2011-04-26
5202:
5195:
5189:
5182:
5176:
5168:
5164:
5160:
5156:
5155:
5147:
5139:
5135:
5131:
5127:
5126:
5118:
5109:
5103:
5098:
5096:
5087:
5083:
5079:
5075:
5071:
5067:
5060:
5052:
5048:
5044:
5040:
5035:
5030:
5026:
5022:
5018:
5014:
5010:
5006:
5005:Risk Analysis
4998:
4989:
4981:
4977:
4970:
4962:
4958:
4954:
4950:
4946:
4942:
4938:
4934:
4930:
4926:
4919:
4911:
4907:
4903:
4899:
4895:
4891:
4884:
4876:
4872:
4868:
4864:
4860:
4856:
4852:
4848:
4840:
4832:
4828:
4824:
4820:
4816:
4812:
4808:
4804:
4797:
4789:
4785:
4781:
4777:
4773:
4769:
4762:
4754:
4750:
4746:
4742:
4735:
4727:
4723:
4719:
4715:
4711:
4707:
4703:
4696:
4687:
4682:
4678:
4674:
4667:
4660:
4652:
4648:
4644:
4640:
4635:
4634:10.1.1.6.9720
4630:
4626:
4622:
4615:
4613:
4604:
4600:
4595:
4590:
4586:
4582:
4578:
4574:
4570:
4566:
4562:
4558:
4554:
4547:
4539:
4535:
4531:
4527:
4520:
4518:
4516:
4507:
4503:
4499:
4495:
4491:
4484:
4476:
4472:
4468:
4464:
4457:
4449:
4447:9780128030318
4443:
4439:
4435:
4428:
4420:
4416:
4412:
4408:
4404:
4400:
4393:
4385:
4381:
4376:
4371:
4367:
4363:
4359:
4355:
4351:
4344:
4336:
4332:
4327:
4322:
4318:
4314:
4310:
4306:
4302:
4295:
4286:
4281:
4277:
4273:
4269:
4262:
4254:
4250:
4246:
4242:
4235:
4227:
4223:
4219:
4215:
4210:
4205:
4201:
4197:
4190:
4182:
4178:
4174:
4170:
4165:
4160:
4156:
4152:
4145:
4137:
4133:
4129:
4125:
4121:
4117:
4110:
4102:
4098:
4094:
4090:
4086:
4082:
4075:
4067:
4063:
4059:
4055:
4051:
4047:
4040:
4032:
4028:
4020:
4016:
4009:
4003:
3997:
3989:
3982:
3974:
3967:
3959:
3952:
3944:
3940:
3936:
3932:
3928:
3924:
3923:Technometrics
3917:
3908:
3903:
3899:
3895:
3894:
3889:
3882:
3874:
3870:
3866:
3862:
3858:
3854:
3850:
3844:
3836:
3832:
3828:
3824:
3820:
3816:
3812:
3808:
3804:
3800:
3799:
3791:
3783:
3779:
3775:
3771:
3767:
3763:
3759:
3755:
3751:
3747:
3746:
3738:
3730:
3726:
3722:
3718:
3714:
3710:
3706:
3702:
3698:
3694:
3693:
3688:
3681:
3673:
3667:
3663:
3659:
3655:
3654:
3646:
3637:
3632:
3628:
3624:
3620:
3613:
3605:
3603:9780470033302
3599:
3595:
3594:
3586:
3578:
3574:
3569:
3564:
3560:
3556:
3555:
3550:
3543:
3535:
3531:
3527:
3523:
3519:
3515:
3514:
3509:
3502:
3494:
3490:
3486:
3482:
3477:
3472:
3468:
3464:
3463:
3458:
3451:
3443:
3439:
3435:
3431:
3426:
3421:
3418:: 2420–2448.
3417:
3413:
3412:
3407:
3400:
3392:
3388:
3384:
3380:
3377:(5): 053303.
3376:
3372:
3365:
3358:
3350:
3346:
3342:
3338:
3334:
3327:
3319:
3312:
3304:
3300:
3296:
3292:
3287:
3282:
3278:
3274:
3270:
3263:
3255:
3251:
3247:
3243:
3239:
3235:
3231:
3227:
3220:
3212:
3208:
3204:
3200:
3196:
3189:
3181:
3177:
3173:
3169:
3162:
3154:
3150:
3143:
3135:
3129:
3125:
3121:
3117:
3110:
3106:
3096:
3093:
3091:
3088:
3086:
3083:
3081:
3078:
3076:
3073:
3071:
3068:
3066:
3063:
3061:
3058:
3056:
3053:
3051:
3048:
3046:
3043:
3041:
3038:
3036:
3033:
3031:
3028:
3026:
3023:
3022:
3013:
3010:
3008:
3005:
3003:
3000:
2998:
2995:
2993:
2990:
2989:
2988:
2980:
2978:
2974:
2970:
2966:
2962:
2958:
2944:
2941:
2938:
2935:
2931:
2928:
2925:
2921:
2918:
2917:
2914:
2909:
2908:
2906:
2899:
2895:
2891:
2887:
2884:
2883:
2882:
2874:
2870:
2865:
2855:
2853:
2848:
2846:
2836:
2827:
2825:
2815:
2813:
2809:
2805:
2797:
2793:
2790:
2786:
2783:
2780:
2776:
2773:
2770:
2767:
2764:
2760:
2757:
2754:
2750:
2746:
2742:
2739:
2738:
2737:
2735:
2731:
2730:Ilya M. Sobol
2727:
2723:
2715:
2712:
2709:
2708:
2707:
2690:
2684:
2661:
2649:
2637:
2619:
2613:
2610:
2604:
2592:
2566:
2554:
2528:
2522:
2519:
2516:
2508:
2504:
2500:
2499:data-modeling
2490:
2488:
2478:
2470:
2467:
2457:
2454:
2448:
2438:
2436:
2431:
2425:
2406:
2402:
2393:
2367:
2359:
2340:
2334:
2331:
2328:
2316:
2310:
2308:
2292:
2284:
2279:
2265:
2256:
2254:
2238:
2235:
2226:
2217:
2203:
2195:
2175:
2171:
2162:
2158:
2135:
2131:
2122:
2103:
2100:
2097:
2091:
2061:
2057:
2048:
2044:
2040:
2035:
2031:
2024:
2018:
2015:
2010:
2006:
1983:
1979:
1956:
1952:
1942:
1928:
1920:
1904:
1890:
1888:
1882:
1866:
1862:
1836:
1832:
1828:
1825:
1822:
1819:
1816:
1811:
1808:
1805:
1801:
1797:
1792:
1789:
1786:
1782:
1778:
1775:
1772:
1769:
1766:
1761:
1757:
1750:
1745:
1742:
1738:
1711:
1705:
1692:
1689:
1685:
1678:
1664:
1658:
1655:
1652:
1647:
1642:
1638:
1615:
1611:
1590:
1582:
1581:
1562:
1558:
1535:
1531:
1521:
1504:
1473:
1467:
1441:
1435:
1422:
1418:
1411:
1397:
1391:
1386:
1382:
1373:
1357:
1353:
1345:For an input
1343:
1341:
1340:
1335:
1334:
1317:
1295:
1291:
1282:
1281:Sobol indices
1277:
1275:
1271:
1265:
1255:
1253:
1248:
1244:
1240:
1231:
1227:
1224:
1205:
1198:
1184:
1176:
1172:
1163:
1154:
1145:
1144:
1143:
1127:
1123:
1102:
1094:
1084:
1079:
1078:Morris_method
1069:
1067:
1066:linear models
1051:
1048:
1044:
1040:
1032:
1028:
1024:
1018:
1016:
1010:
1008:
1004:
996:
993:
992:
991:
987:
977:
961:
957:
934:
930:
908:
886:
882:
869:
865:
858:
851:
844:
837:
830:
823:
816:
809:
802:
798:
793:
784:
780:
774:
771:
767:
764:
761:
760:
759:
757:
753:
749:
738:
720:
712:
708:
703:
700:
699:
694:
691:
675:
667:
663:
660:
657:
653:
649:
645:
644:Nonlinearity:
642:
639:
635:
632:
627:
623:
619:
604:
596:
592:
588:
584:
583:
581:
577:
574:
573:
572:
558:
543:
529:
507:
503:
494:
490:
486:
482:
466:
458:
442:
422:
419:
416:
413:
410:
407:
404:
401:
396:
392:
382:
369:
363:
357:
354:
351:
343:
329:
322:
301:
297:
293:
290:
287:
284:
281:
276:
272:
265:
262:
254:
251:-dimensional
238:
230:
226:
222:
206:
194:
190:
184:
172:
169:
166:
162:
158:
155:
152:
149:
146:
143:
140:
136:
135:
134:
130:
128:
124:
120:
116:
112:
108:
98:
96:
92:
88:
83:
79:
75:
62:
59:
51:
41:
36:
34:
27:
18:
17:
5320:
5313:
5302:
5295:
5259:
5255:
5241:
5208:. Retrieved
5201:the original
5188:
5180:
5175:
5158:
5152:
5146:
5132:(1): 31–43.
5129:
5123:
5117:
5108:
5069:
5065:
5059:
5008:
5004:
4997:
4988:
4979:
4975:
4969:
4928:
4924:
4918:
4893:
4889:
4883:
4850:
4846:
4839:
4809:(1): 53–65.
4806:
4802:
4796:
4771:
4767:
4761:
4744:
4740:
4734:
4709:
4705:
4695:
4676:
4672:
4659:
4624:
4620:
4560:
4556:
4546:
4529:
4525:
4497:
4493:
4483:
4466:
4462:
4456:
4437:
4427:
4402:
4398:
4392:
4357:
4353:
4343:
4308:
4304:
4294:
4275:
4271:
4261:
4244:
4240:
4234:
4199:
4195:
4189:
4154:
4150:
4144:
4119:
4115:
4109:
4084:
4080:
4074:
4049:
4045:
4039:
4030:
4026:
4018:
4014:
4008:
3996:
3987:
3981:
3972:
3966:
3957:
3951:
3926:
3922:
3916:
3897:
3891:
3881:
3856:
3852:
3843:
3802:
3796:
3790:
3749:
3743:
3737:
3696:
3690:
3680:
3652:
3645:
3626:
3622:
3612:
3592:
3585:
3558:
3552:
3542:
3517:
3511:
3501:
3466:
3460:
3450:
3415:
3409:
3399:
3374:
3370:
3357:
3340:
3336:
3326:
3317:
3311:
3276:
3272:
3262:
3229:
3225:
3219:
3202:
3198:
3188:
3171:
3167:
3161:
3152:
3148:
3142:
3115:
3109:
3050:Interval FEM
3002:Epidemiology
2986:
2953:
2942:
2936:
2929:
2919:
2912:
2904:
2885:
2880:
2871:
2867:
2849:
2842:
2833:
2821:
2801:
2777:, which use
2719:
2638:
2582:, such that
2506:
2496:
2484:
2476:
2463:
2450:
2426:
2320:
2314:
2280:
2257:
2218:
2196:measures of
1943:
1896:
1883:
1579:
1578:
1522:
1374:
1344:
1338:
1337:
1332:
1331:
1280:
1278:
1267:
1237:
1228:
1222:
1220:
1090:
1081:
1019:
1015:interactions
1011:
1000:
989:
873:
867:
863:
856:
849:
842:
835:
828:
821:
814:
807:
800:
796:
781:
778:
744:
736:
701:
692:
661:
643:
638:independence
633:
593:) including
575:
549:
383:
344:
320:
252:
224:
220:
198:
161:optimization
137:Testing the
131:
117:, including
104:
73:
72:
54:
45:
38:Please help
30:
5287:10871/21086
5262:: 214–232.
5034:1874/386039
4563:(1): 4354.
4405:: 115–131.
3469:: 575–603.
3273:Groundwater
2890:assumptions
2845:uncertainty
1887:Monte Carlo
1023:convex hull
733:-function).
231:, with the
219:, (called "
123:reliability
115:uncertainty
78:uncertainty
5354:Simulation
5343:Categories
5210:2009-10-16
5072:: 102436.
4209:2102.00356
4164:1909.10140
4033:: 407–414.
4021:: 112–118.
3102:References
2507:metamodels
2493:Metamodels
2430:variograms
2358:variograms
1603:caused by
1027:octahedron
707:meta-model
689:interpret.
587:meta-model
481:statistics
193:pie charts
139:robustness
127:stochastic
101:Motivation
5086:198636712
4831:216590427
4629:CiteSeerX
4585:2041-1723
4384:1944-7973
4335:1944-7973
4226:1350-7265
4196:Bernoulli
4181:0162-1459
4136:0951-8320
4101:1588-2632
4066:1369-7412
3729:206515456
3568:0802.1099
3534:0960-3174
3493:1935-7524
3476:1311.1797
3442:1935-7524
3425:1112.1788
3391:208835771
3075:ROC curve
3025:Causality
2894:inference
2808:nonlinear
2794:Discrete
2653:^
2611:≈
2596:^
2558:^
2399:∂
2391:∂
2266:δ
2236:≥
2104:⋅
2098:⋅
2007:ξ
1980:ξ
1790:−
1743:∼
1690:∼
1659:−
1505:⋅
1474:⋅
1169:∂
1161:∂
652:nonlinear
417:…
229:black box
111:black box
5219:cite web
5051:15988654
5043:15876219
4961:23088466
4953:17839016
4875:16480307
4603:31554788
3827:15306806
3782:14404609
3774:15802601
3721:19008442
3656:. SIAM.
3303:25810333
3018:See also
2997:Business
2253:distance
2084:, where
580:sampling
455:. While
319:and the
129:events.
5312:(1986)
5264:Bibcode
5167:1814801
5138:1803924
5066:Futures
5013:Bibcode
4982:: 7–18.
4933:Bibcode
4925:Science
4898:Bibcode
4855:Bibcode
4811:Bibcode
4788:7678955
4714:Bibcode
4651:6130150
4594:6761138
4565:Bibcode
4407:Bibcode
4362:Bibcode
4313:Bibcode
3990:. SIAM.
3943:1269043
3873:2685731
3807:Bibcode
3754:Bibcode
3745:Science
3701:Bibcode
3692:Science
3295:1286771
3254:9710579
3234:Bibcode
2745:kriging
485:moments
255:vector
5165:
5136:
5084:
5049:
5041:
4959:
4951:
4873:
4829:
4786:
4649:
4631:
4601:
4591:
4583:
4444:
4382:
4333:
4224:
4179:
4134:
4099:
4064:
3941:
3871:
3835:980153
3833:
3825:
3798:Nature
3780:
3772:
3727:
3719:
3668:
3600:
3532:
3491:
3440:
3389:
3301:
3293:
3252:
3130:
2971:, the
1919:moment
1730:where
1460:where
1072:Morris
321:output
223:" ou "
5204:(PDF)
5197:(PDF)
5163:JSTOR
5134:JSTOR
5082:S2CID
5047:S2CID
4957:S2CID
4827:S2CID
4784:S2CID
4679:(6).
4669:(PDF)
4647:S2CID
4204:arXiv
4159:arXiv
4002:IEEE.
3939:JSTOR
3869:JSTOR
3831:S2CID
3778:S2CID
3725:S2CID
3563:arXiv
3471:arXiv
3420:arXiv
3387:S2CID
3367:(PDF)
3250:S2CID
2251:is a
2119:is a
253:input
5225:link
5039:PMID
4949:PMID
4871:PMID
4599:PMID
4581:ISSN
4442:ISBN
4380:ISSN
4331:ISSN
4222:ISSN
4177:ISSN
4132:ISSN
4097:ISSN
4062:ISSN
3823:PMID
3770:PMID
3717:PMID
3666:ISBN
3598:ISBN
3530:ISSN
3489:ISSN
3438:ISSN
3299:PMID
3291:OSTI
3128:ISBN
2975:and
2315:VARS
2150:and
1921:of
1881:.
1489:and
949:and
848:and
595:HDMR
163:and
93:and
5282:hdl
5272:doi
5074:doi
5070:112
5029:hdl
5021:doi
4941:doi
4929:246
4906:doi
4894:106
4863:doi
4851:110
4819:doi
4776:doi
4749:doi
4722:doi
4681:doi
4639:doi
4589:PMC
4573:doi
4534:doi
4502:doi
4471:doi
4415:doi
4370:doi
4321:doi
4280:doi
4249:doi
4214:doi
4169:doi
4155:116
4124:doi
4089:doi
4054:doi
3931:doi
3902:doi
3898:169
3861:doi
3815:doi
3803:430
3762:doi
3750:308
3709:doi
3697:322
3658:doi
3631:doi
3573:doi
3522:doi
3481:doi
3430:doi
3379:doi
3345:doi
3281:doi
3242:doi
3207:doi
3176:doi
3120:doi
2732:or
2219:If
1336:or
1005:or
754:or
493:cdf
489:pdf
189:pdf
5345::
5280:.
5270:.
5260:79
5258:.
5254:.
5221:}}
5217:{{
5159:75
5157:.
5130:73
5128:.
5094:^
5080:.
5068:.
5045:.
5037:.
5027:.
5019:.
5009:25
5007:.
4978:.
4955:.
4947:.
4939:.
4927:.
4904:.
4892:.
4869:.
4861:.
4849:.
4825:.
4817:.
4807:13
4805:.
4782:.
4772:94
4770:.
4745:93
4743:.
4720:.
4710:34
4708:.
4704:.
4677:33
4675:.
4671:.
4645:.
4637:.
4625:66
4623:.
4611:^
4597:.
4587:.
4579:.
4571:.
4561:10
4559:.
4555:.
4530:94
4528:.
4514:^
4498:93
4496:.
4492:.
4465:.
4413:.
4403:95
4401:.
4378:.
4368:.
4358:52
4356:.
4352:.
4329:.
4319:.
4309:52
4307:.
4303:.
4276:67
4274:.
4270:.
4245:10
4243:.
4220:.
4212:.
4200:28
4198:.
4175:.
4167:.
4153:.
4130:.
4120:92
4118:.
4095:.
4085:10
4083:.
4060:.
4050:76
4048:.
4029:.
3937:.
3927:33
3925:.
3896:.
3890:.
3867:.
3857:53
3855:.
3829:.
3821:.
3813:.
3801:.
3776:.
3768:.
3760:.
3748:.
3723:.
3715:.
3707:.
3695:.
3689:.
3664:.
3625:.
3621:.
3571:.
3559:52
3557:.
3551:.
3528:.
3518:22
3516:.
3510:.
3487:.
3479:.
3465:.
3459:.
3436:.
3428:.
3414:.
3408:.
3385:.
3375:11
3373:.
3369:.
3341:91
3339:.
3335:.
3297:.
3289:.
3277:54
3275:.
3271:.
3248:.
3240:.
3230:22
3228:.
3203:16
3201:.
3197:.
3172:31
3170:.
3151:.
3126:.
3118:.
2822:A
2814:.
2424:.
2216:.
1342:.
1142::
855:.
820:,
813:,
806:,
750:,
709:,
589:,
491:,
487:,
483:,
167:).
105:A
5290:.
5284::
5274::
5266::
5227:)
5213:.
5169:.
5140:.
5088:.
5076::
5053:.
5031::
5023::
5015::
4980:7
4963:.
4943::
4935::
4912:.
4908::
4900::
4877:.
4865::
4857::
4833:.
4821::
4813::
4790:.
4778::
4755:.
4751::
4728:.
4724::
4716::
4689:.
4683::
4653:.
4641::
4605:.
4575::
4567::
4540:.
4536::
4508:.
4504::
4477:.
4473::
4467:2
4450:.
4421:.
4417::
4409::
4386:.
4372::
4364::
4337:.
4323::
4315::
4288:.
4282::
4255:.
4251::
4228:.
4216::
4206::
4183:.
4171::
4161::
4138:.
4126::
4103:.
4091::
4068:.
4056::
4031:1
4019:2
3945:.
3933::
3910:.
3904::
3875:.
3863::
3837:.
3817::
3809::
3784:.
3764::
3756::
3731:.
3711::
3703::
3674:.
3660::
3639:.
3633::
3627:4
3606:.
3579:.
3575::
3565::
3536:.
3524::
3495:.
3483::
3473::
3467:8
3444:.
3432::
3422::
3416:6
3393:.
3381::
3351:.
3347::
3305:.
3283::
3256:.
3244::
3236::
3213:.
3209::
3182:.
3178::
3155:.
3153:1
3136:.
3122::
2900::
2694:)
2691:X
2688:(
2685:f
2665:)
2662:X
2659:(
2650:f
2623:)
2620:X
2617:(
2614:f
2608:)
2605:X
2602:(
2593:f
2570:)
2567:X
2564:(
2555:f
2532:)
2529:X
2526:(
2523:f
2520:=
2517:Y
2501:/
2407:i
2403:x
2394:Y
2368:Y
2344:)
2341:X
2338:(
2335:f
2332:=
2329:Y
2317:)
2293:i
2239:0
2233:)
2230:(
2227:d
2204:Y
2176:i
2172:X
2167:|
2163:Y
2159:P
2136:Y
2132:P
2107:)
2101:,
2095:(
2092:d
2072:]
2069:)
2062:i
2058:X
2053:|
2049:Y
2045:P
2041:,
2036:Y
2032:P
2028:(
2025:d
2022:[
2019:E
2016:=
2011:i
1984:i
1957:i
1953:X
1929:Y
1905:Y
1867:i
1863:X
1842:)
1837:p
1833:X
1829:,
1826:.
1823:.
1820:.
1817:,
1812:1
1809:+
1806:i
1802:X
1798:,
1793:1
1787:i
1783:X
1779:,
1776:.
1773:.
1770:.
1767:,
1762:1
1758:X
1754:(
1751:=
1746:i
1739:X
1715:)
1712:Y
1709:(
1706:V
1701:)
1698:]
1693:i
1686:X
1682:|
1679:Y
1676:[
1672:E
1668:(
1665:V
1656:1
1653:=
1648:T
1643:i
1639:S
1616:i
1612:X
1591:Y
1563:i
1559:X
1536:i
1532:X
1508:]
1502:[
1498:E
1477:)
1471:(
1468:V
1445:)
1442:Y
1439:(
1436:V
1431:)
1428:]
1423:i
1419:X
1415:|
1412:Y
1409:[
1405:E
1401:(
1398:V
1392:=
1387:i
1383:S
1358:i
1354:X
1318:Y
1296:i
1292:X
1223:x
1206:,
1199:0
1193:x
1185:|
1177:i
1173:X
1164:Y
1155:|
1128:i
1124:X
1103:Y
1052:!
1049:n
1045:/
1041:1
962:4
958:Z
935:3
931:Z
909:Y
887:i
883:Z
870:.
868:Y
864:Y
860:4
857:Z
853:4
850:Z
846:3
843:Z
839:2
836:Z
832:1
829:Z
825:4
822:Z
818:3
815:Z
811:2
808:Z
804:1
801:Z
797:Y
721:f
676:Y
605:f
559:f
530:Y
508:i
504:X
467:Y
443:Y
423:p
420:,
414:,
411:1
408:=
405:i
402:,
397:i
393:X
370:.
367:)
364:X
361:(
358:f
355:=
352:Y
330:Y
307:)
302:p
298:X
294:,
291:.
288:.
285:.
282:,
277:1
273:X
269:(
266:=
263:X
239:p
207:f
61:)
55:(
50:)
46:(
42:.
35:.
Text is available under the Creative Commons Attribution-ShareAlike License. Additional terms may apply.