32:
20:
183:
created by the malicious client bind resources on the server and may eventually exceed the resources available on the server. At that point, the server cannot connect to any clients, whether legitimate or otherwise. This effectively denies service to legitimate clients. Some systems may also
39:, green) sends several packets but does not send the "ACK" back to the server. The connections are hence half-opened and consuming server resources. Legitimate user Alice (purple) tries to connect, but the server refuses to open a connection, a denial of service.
55:
in which an attacker rapidly initiates a connection to a server without finalizing the connection. The server has to spend resources waiting for half-opened connections, which can consume enough resources to make the system unresponsive to legitimate traffic.
132:
173:
The server will wait for the acknowledgement for some time, as simple network congestion could also be the cause of the missing
287:
276:
369:
237:
60:
86:
70:
364:
48:
321:
308:
184:
malfunction or crash when other operating system functions are starved of resources in this way.
179:
8:
242:
147:
74:
94:
90:
52:
257:
349:
135:, and is the foundation for every connection established using the TCP protocol.
232:
192:
There are a number of well-known countermeasures listed in RFC 4987 including:
358:
206:
36:
24:
252:
138:
A SYN flood attack works by not responding to the server with the expected
214:
247:
151:
65:
277:"CERT Advisory CA-1996-21 TCP SYN Flooding and IP Spoofing Attacks"
142:
code. The malicious client can either simply not send the expected
31:
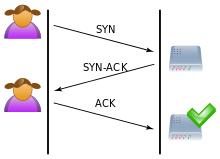
27:) and a server. The three-way handshake is correctly performed.
97:
exchange a series of messages which normally runs like this:
19:
284:
Carnegie Mellon
University Software Engineering Institute
309:
New York's Panix
Service Is Crippled by Hacker Attack
162:to a falsified IP address – which will not send an
356:
101:The client requests a connection by sending a
166:because it "knows" that it never sent a
30:
18:
357:
350:Official CERT advisory on SYN Attacks
311:, New York Times, September 14, 1996
127:, and the connection is established.
80:
23:A normal connection between a user (
13:
187:
85:When a client attempts to start a
14:
381:
343:
238:Internet Control Message Protocol
77:used to establish a connection.
290:from the original on 2000-12-14
158:, cause the server to send the
63:that the attacker sends is the
314:
302:
269:
1:
263:
177:. However, in an attack, the
123:The client responds with an
89:connection to a server, the
7:
226:
202:Reducing SYN-RECEIVED timer
10:
386:
370:Denial-of-service attacks
35:SYN Flood. The attacker (
322:"What is a DDoS Attack?"
116:this request by sending
109:) message to the server.
49:denial-of-service attack
16:Denial-of-service attack
133:TCP three-way handshake
40:
28:
222:Firewalls and proxies
205:Recycling the oldest
180:half-open connections
34:
22:
365:Attacks against TCP
243:IP address spoofing
131:This is called the
120:back to the client.
75:three-way handshake
53:data communications
199:Increasing backlog
69:packet, a part of
41:
29:
219:Hybrid approaches
81:Technical details
377:
338:
337:
335:
333:
318:
312:
306:
300:
299:
297:
295:
281:
273:
258:UDP flood attack
176:
169:
165:
161:
157:
145:
141:
126:
119:
104:
68:
385:
384:
380:
379:
378:
376:
375:
374:
355:
354:
346:
341:
331:
329:
320:
319:
315:
307:
303:
293:
291:
279:
275:
274:
270:
266:
229:
190:
188:Countermeasures
174:
167:
163:
159:
155:
143:
139:
124:
117:
102:
83:
64:
17:
12:
11:
5:
383:
373:
372:
367:
353:
352:
345:
344:External links
342:
340:
339:
326:Cloudflare.com
313:
301:
267:
265:
262:
261:
260:
255:
250:
245:
240:
235:
233:Fraggle attack
228:
225:
224:
223:
220:
217:
212:
209:
203:
200:
197:
189:
186:
129:
128:
121:
110:
82:
79:
15:
9:
6:
4:
3:
2:
382:
371:
368:
366:
363:
362:
360:
351:
348:
347:
327:
323:
317:
310:
305:
289:
285:
278:
272:
268:
259:
256:
254:
251:
249:
246:
244:
241:
239:
236:
234:
231:
230:
221:
218:
216:
213:
210:
208:
207:half-open TCP
204:
201:
198:
195:
194:
193:
185:
182:
181:
171:
153:
149:
136:
134:
122:
115:
111:
108:
100:
99:
98:
96:
92:
88:
78:
76:
72:
67:
62:
57:
54:
50:
47:is a form of
46:
38:
33:
26:
21:
330:. Retrieved
328:. Cloudflare
325:
316:
304:
294:18 September
292:. Retrieved
283:
271:
253:Smurf attack
191:
178:
172:
137:
130:
114:acknowledges
113:
106:
84:
58:
44:
42:
215:SYN cookies
150:the source
112:The server
107:synchronize
359:Categories
264:References
248:Ping flood
152:IP address
211:SYN cache
196:Filtering
45:SYN flood
288:Archived
227:See also
148:spoofing
146:, or by
160:SYN-ACK
154:in the
118:SYN-ACK
37:Mallory
95:server
91:client
61:packet
332:4 May
280:(PDF)
25:Alice
334:2020
296:2019
93:and
59:The
175:ACK
168:SYN
164:ACK
156:SYN
144:ACK
140:ACK
125:ACK
103:SYN
87:TCP
73:'s
71:TCP
66:SYN
51:on
361::
324:.
286:.
282:.
170:.
43:A
336:.
298:.
105:(
Text is available under the Creative Commons Attribution-ShareAlike License. Additional terms may apply.