17:
1862:
1539:
1874:
76:
traits) are inherited characteristics – meaning the trait values are usually alike within closely related species, while trait values of distantly related biological species do not resemble each other to a such great degree. It is often said that traits that are more similar in closely related taxa
202:). With a help of the mentioned methods one is able to quantify the value of phylogenetic autocorrelation for a studied trait throughout the phylogeny. Another method commonly used in studying phylogenetic signal is so-called Brownian diffusion model of trait evolution that is based on the
100:). Similarly high value of phylogenetic signal results in an existence of similar traits between closely related biological species, while increasing evolutionary distance between related species leads to decrease in similarity. With a help of phylogenetic signal we can
63:
Phylogenetic signal is usually described as the tendency of related biological species to resemble each other more than any other species that is randomly picked from the same phylogenetic tree. In other words, phylogenetic signal can be defined as the
123:, evolutionary heterogeneity etc.) relations between evolutionary rate, evolutionary process and phylogenetic signal are more complex, and can not be easily generalized using mentioned perception of the relation between two
206:(BM) principle. Using Brownian diffusion model, one can not only study values but also compare those measures between various phylogenies. Phylogenetic signal in continuous traits can be quantified and measured using
187:
in an aspect of evolutionary relatedness. With a help of measuring phylogenetic signal one can determine exactly how studied traits are correlated with phylogenetic relationship between species.
107:
On the other hand, some authors advise against such interpretations (the ones based on estimates of phylogenetic signal) of evolutionary rate and process. While studying simple models for
1001:"Phylogenetic niche conservatism, phylogenetic signal and the relationship between phylogenetic relatedness and ecological similarity among species | Request PDF"
267:
96:
leads to low phylogenetic signal and vice versa (hence, high phylogenetic signal is usually a consequence of either low rate of evolution either
429:
Münkemüller, Tamara; Lavergne, Sébastien; Bzeznik, Bruno; Dray, Stéphane; Jombart, Thibaut; Schiffers, Katja; Thuiller, Wilfried (2012-04-10).
781:"Simultaneously estimating evolutionary history and repeated traits phylogenetic signal: applications to viral and host phenotypic evolution"
779:
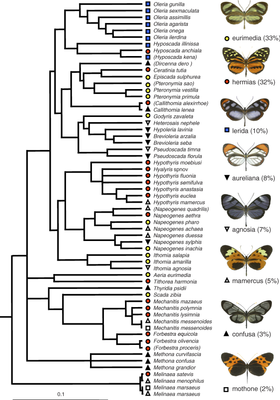
Vrancken, Bram; Lemey, Philippe; Rambaut, Andrew; Bedford, Trevor; Longdon, Ben; Günthard, Huldrych F.; Suchard, Marc A. (2014-11-13).
115:, it appears to be no relation between phylogenetic signal and rate of evolution. Within other models (e.g. functional constraint,
1477:
210:. Within this technique values from zero to infinity are used and higher value also means greater level of phylogenetic signal.
131:
and for each trait. It is also not clear if all of the possible traits do exhibit phylogenetic signal and if it is measurable.
1024:
Thuiller, Wilfried; Lavergne, Sébastien; Roquet, Cristina; Boulangeat, Isabelle; Lafourcade, Bruno; Araujo, Miguel B. (2011).
1144:
Li, Danfeng; Du, Yanjun; Xu, Wubing; Peng, Danxiao; Primack, Richard; Chen, Guoke; Mao, Ling Feng; Ma, Keping (2021-06-01).
1672:
1281:"Selectivity in Mammalian Extinction Risk and Threat Types: a New Measure of Phylogenetic Signal Strength in Binary Traits"
190:
Some of the earliest ways of quantifying phylogenetic signal were based on the use of various statistical methods (such as
1146:"Phylogenetic conservatism of fruit development time in Chinese angiosperms and the phylogenetic and climatic correlates"
1632:
1712:
399:
77:
than in distant relatives exhibit greater phylogenetic signal. On the other hand, some traits are a consequence of
1717:
1650:
394:
168:
120:
81:
and appear more similar in distantly related taxa than in relatives. Such traits show lower phylogenetic signal.
1878:
1727:
1657:
1239:
Abouheif, E. (1999). "A method for testing the assumption of phylogenetic independence in comparative data".
353:
1190:"Conservatism and diversification of plant functional traits: Evolutionary rates versus phylogenetic signal"
147:
Among many questions that can be answered using a concept of phylogenetic signal, the most common ones are:
213:
The table below shows the most common indices and associated tests used for analyzing phylogenetic signal.
191:
1637:
1544:
1500:
1470:
719:"Phylogenetic signal in the community structure of host-specific microbiomes of tropical marine sponges"
68:
among species' trait values that is a consequence of their phylogenetic relationships. The traits (e.g.
32:. This display confirms closely related species share color patterns more often than expected at random.
1827:
1753:
1087:
Diniz-Filho, José Alexandre F.; Santos, Thiago; Rangel, Thiago
Fernando; Bini, Luis Mauricio (2012).
896:
Borges, Rui; Machado, João Paulo; Gomes, Cidália; Rocha, Ana Paula; Antunes, Agostinho (2019-06-01).
1265:
180:
101:
1089:"A comparison of metrics for estimating phylogenetic signal under alternative evolutionary models"
1707:
1505:
670:"Testing for Phylogenetic Signal in Biological Traits: The Ubiquity of Cross-Product Statistics"
1905:
1866:
1590:
1463:
183:
phylogenetic signal can be done using a range of various methods that are used for researching
144:
Phylogenetic signal is a concept widely used in different ecological and evolutionary studies.
65:
1900:
1842:
1520:
1252:
962:
116:
97:
1679:
1585:
1410:
1037:
199:
85:
78:
69:
8:
1604:
51:
to resemble each other more than any other species that is randomly picked from the same
1414:
1041:
477:"Testing for Phylogenetic Signal in Comparative Data: Behavioral Traits Are More Labile"
1645:
1599:
1515:
1442:
1371:
1324:
1308:
1240:
1216:
1189:
1121:
1088:
1069:
982:
974:
873:
865:
813:
753:
718:
645:
612:
584:
520:
504:
492:
108:
48:
1573:
1446:
1434:
1426:
1379:
1363:
1316:
1300:
1296:
1221:
1167:
1126:
1108:
1061:
1053:
966:
927:
919:
857:
818:
800:
758:
740:
699:
691:
686:
669:
650:
632:
576:
568:
524:
512:
496:
452:
447:
430:
93:
52:
21:
1328:
1244:
1104:
1000:
945:
Webb, Campbell O.; Ackerly, David D.; McPeek, Mark A.; Donoghue, Michael J. (2002).
914:
897:
1662:
1616:
1418:
1355:
1292:
1211:
1201:
1157:
1116:
1100:
1073:
1045:
958:
909:
877:
849:
808:
792:
748:
730:
681:
640:
624:
588:
558:
488:
442:
986:
16:
1763:
203:
1162:
1145:
1737:
546:
1025:
563:
1894:
1732:
1702:
1609:
1486:
1430:
1367:
1304:
1171:
1112:
1057:
970:
923:
861:
804:
780:
744:
735:
695:
636:
572:
500:
456:
242:
112:
1206:
796:
1837:
1783:
1778:
1773:
1758:
1566:
1561:
1438:
1383:
1320:
1225:
1130:
1065:
931:
822:
762:
703:
654:
628:
580:
516:
315:
184:
127:. Some authors argue that phylogenetic signal is not always strong in each
40:
898:"Measuring phylogenetic signal between categorical traits and phylogenies"
1832:
1525:
281:
270:
207:
195:
1312:
1280:
1049:
1510:
1375:
978:
946:
869:
837:
508:
476:
339:
124:
44:
617:
Philosophical
Transactions of the Royal Society B: Biological Sciences
1847:
1811:
1806:
1801:
1696:
1578:
1343:
158:
104:
to what degree closely related biological taxa share similar traits.
29:
1359:
613:"Phylogenetic signal in primate behaviour, ecology and life history"
1398:
853:
73:
1422:
545:
Revell, Liam J.; Harmon, Luke J.; Collar, David C. (2008-08-01).
25:
1455:
1023:
475:
Blomberg, Simon P.; Garland, Theodore; Ives, Anthony R. (2003).
1538:
1026:"Consequences of climate change on the tree of life in Europe"
428:
1667:
1595:
128:
47:
term, that describes the tendency or the pattern of related
1399:"Inferring the historical patterns of biological evolution"
1086:
778:
89:
84:
Phylogenetic signal is a measure, closely related with an
944:
895:
151:
To what degree are investigated traits in correlation?
547:"Phylogenetic Signal, Evolutionary Process, and Rate"
1534:
474:
24:above shows significant phylogenetic signal in the
544:
611:Kamilar, Jason M.; Cooper, Natalie (2013-05-19).
1892:
668:Pavoine, Sandrine; Ricotta, Carlo (2012-11-06).
1194:Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences
667:
1471:
716:
610:
431:"How to measure and test phylogenetic signal"
717:Easson, Cole G.; Thacker, Robert W. (2014).
1278:
835:
154:How, when and why do certain traits evolve?
1478:
1464:
1344:"Notes on Continuous Stochastic Phenomena"
1143:
164:Do niches get conserved along phylogenies?
1215:
1205:
1161:
1120:
913:
812:
752:
734:
685:
644:
562:
446:
157:Which processes are the driving force of
1279:FRITZ, SUSANNE A.; PURVIS, ANDY (2010).
1238:
963:10.1146/annurev.ecolsys.33.010802.150448
951:Annual Review of Ecology and Systematics
838:"Phylogenies and the Comparative Method"
111:evolution, such as the homogeneous rate
15:
1187:
1893:
134:
1459:
1396:
1341:
1183:
1181:
1873:
891:
889:
887:
774:
772:
606:
604:
602:
600:
598:
540:
538:
536:
534:
470:
468:
466:
424:
422:
420:
418:
416:
414:
947:"Phylogenies and Community Ecology"
231:Statistical framework/applied test
13:
1178:
1137:
1080:
493:10.1111/j.0014-3820.2003.tb00285.x
58:
14:
1917:
1485:
884:
769:
595:
531:
463:
411:
1872:
1861:
1860:
1713:Phylogenetic comparative methods
1537:
1297:10.1111/j.1523-1739.2010.01455.x
785:Methods in Ecology and Evolution
687:10.1111/j.1558-5646.2012.01823.x
448:10.1111/j.2041-210x.2012.00196.x
435:Methods in Ecology and Evolution
400:Phylogenetic comparative methods
1718:Phylogenetic niche conservatism
1390:
1335:
1272:
1232:
1150:Global Ecology and Conservation
1105:10.1590/S1415-47572012005000053
1017:
993:
938:
395:Phylogenetic niche conservatism
169:vulnerability to climate change
121:phylogenetic niche conservatism
1093:Genetics and Molecular Biology
829:
710:
661:
217:Analyzing phylogenetic signal
167:Is there any relation between
72:, ecological, life-history or
1:
1200:(Supplement 2): 19699–19706.
1188:Ackerly, David (2009-11-17).
915:10.1093/bioinformatics/bty800
405:
175:
98:stabilizing type of selection
836:Felsenstein, Joseph (1985).
192:phylogenetic autocorrelation
7:
1638:Phylogenetic reconciliation
1545:Evolutionary biology portal
1501:Computational phylogenetics
1163:10.1016/j.gecco.2021.e01543
388:
194:coefficients, phylogenetic
10:
1922:
92:. It is thought that high
1856:
1828:Phylogenetic nomenclature
1820:
1794:
1746:
1688:
1625:
1554:
1532:
1493:
723:Frontiers in Microbiology
564:10.1080/10635150802302427
1342:Moran, P. A. P. (1950).
736:10.3389/fmicb.2014.00532
1708:Molecular phylogenetics
1658:Distance-matrix methods
1506:Molecular phylogenetics
1207:10.1073/pnas.0901635106
842:The American Naturalist
797:10.1111/2041-210x.12293
139:
1728:Phylogenetics software
1642:Probabilistic methods
1591:Long branch attraction
1260:Cite journal requires
629:10.1098/rstb.2012.0341
66:statistical dependence
33:
1521:Evolutionary taxonomy
200:autoregressive models
117:fluctuating selection
19:
1680:Three-taxon analysis
1586:Phylogenetic network
1397:Pagel, Mark (1999).
1285:Conservation Biology
228:Based on the model?
86:evolutionary process
79:convergent evolution
1723:Phylogenetic signal
1415:1999Natur.401..877P
1050:10.1038/nature09705
1042:2011Natur.470..531T
222:Type of statistics
218:
171:and taxa phylogeny?
135:Aim and methodology
88:and development of
37:Phylogenetic signal
1651:Bayesian inference
1646:Maximum likelihood
551:Systematic Biology
354:Maximum likelihood
216:
109:quantitative trait
49:biological species
34:
1888:
1887:
1633:Maximum parsimony
1626:Inference methods
1574:Phylogenetic tree
1409:(6756): 877–884.
1036:(7335): 531–534.
908:(11): 1862–1869.
386:
385:
94:rate of evolution
53:phylogenetic tree
28:structure of the
22:phylogenetic tree
1913:
1876:
1875:
1864:
1863:
1663:Neighbor-joining
1617:Ghost population
1547:
1542:
1541:
1480:
1473:
1466:
1457:
1456:
1451:
1450:
1394:
1388:
1387:
1339:
1333:
1332:
1291:(4): 1042–1051.
1276:
1270:
1269:
1263:
1258:
1256:
1248:
1236:
1230:
1229:
1219:
1209:
1185:
1176:
1175:
1165:
1141:
1135:
1134:
1124:
1084:
1078:
1077:
1021:
1015:
1014:
1012:
1011:
997:
991:
990:
942:
936:
935:
917:
893:
882:
881:
833:
827:
826:
816:
776:
767:
766:
756:
738:
714:
708:
707:
689:
665:
659:
658:
648:
608:
593:
592:
566:
542:
529:
528:
472:
461:
460:
450:
426:
323:Autocorrelation
251:Autocorrelation
219:
215:
1921:
1920:
1916:
1915:
1914:
1912:
1911:
1910:
1891:
1890:
1889:
1884:
1852:
1816:
1790:
1764:Symplesiomorphy
1742:
1684:
1621:
1550:
1543:
1536:
1530:
1494:Relevant fields
1489:
1484:
1454:
1395:
1391:
1360:10.2307/2332142
1340:
1336:
1277:
1273:
1261:
1259:
1250:
1249:
1237:
1233:
1186:
1179:
1142:
1138:
1085:
1081:
1022:
1018:
1009:
1007:
999:
998:
994:
943:
939:
894:
885:
834:
830:
777:
770:
715:
711:
666:
662:
609:
596:
543:
532:
473:
464:
427:
412:
408:
391:
204:Brownian motion
178:
142:
137:
61:
59:Characteristics
12:
11:
5:
1919:
1909:
1908:
1903:
1886:
1885:
1883:
1882:
1870:
1857:
1854:
1853:
1851:
1850:
1845:
1840:
1835:
1830:
1824:
1822:
1818:
1817:
1815:
1814:
1809:
1804:
1798:
1796:
1792:
1791:
1789:
1788:
1787:
1786:
1781:
1776:
1768:
1767:
1766:
1761:
1750:
1748:
1744:
1743:
1741:
1740:
1738:Phylogeography
1735:
1730:
1725:
1720:
1715:
1710:
1705:
1700:
1692:
1690:
1689:Current topics
1686:
1685:
1683:
1682:
1677:
1676:
1675:
1670:
1665:
1655:
1654:
1653:
1648:
1640:
1635:
1629:
1627:
1623:
1622:
1620:
1619:
1614:
1613:
1612:
1602:
1593:
1588:
1583:
1582:
1581:
1571:
1570:
1569:
1558:
1556:
1555:Basic concepts
1552:
1551:
1549:
1548:
1533:
1531:
1529:
1528:
1523:
1518:
1513:
1508:
1503:
1497:
1495:
1491:
1490:
1483:
1482:
1475:
1468:
1460:
1453:
1452:
1389:
1354:(1/2): 17–23.
1334:
1271:
1262:|journal=
1231:
1177:
1136:
1099:(3): 673–679.
1079:
1016:
992:
937:
902:Bioinformatics
883:
854:10.1086/284325
828:
768:
709:
680:(3): 828–840.
660:
594:
557:(4): 591–601.
530:
487:(4): 717–745.
462:
441:(4): 743–756.
409:
407:
404:
403:
402:
397:
390:
387:
384:
383:
381:
378:
375:
372:
369:
362:
361:
359:
356:
351:
348:
345:
336:
335:
333:
330:
327:
324:
321:
312:
311:
309:
306:
303:
300:
297:
290:
289:
287:
284:
279:
276:
273:
264:
263:
261:
258:
255:
252:
249:
239:
238:
235:
232:
229:
226:
223:
177:
174:
173:
172:
165:
162:
155:
152:
141:
138:
136:
133:
60:
57:
9:
6:
4:
3:
2:
1918:
1907:
1906:Phylogenetics
1904:
1902:
1899:
1898:
1896:
1881:
1880:
1871:
1869:
1868:
1859:
1858:
1855:
1849:
1846:
1844:
1841:
1839:
1836:
1834:
1831:
1829:
1826:
1825:
1823:
1819:
1813:
1810:
1808:
1805:
1803:
1800:
1799:
1797:
1793:
1785:
1782:
1780:
1777:
1775:
1772:
1771:
1769:
1765:
1762:
1760:
1757:
1756:
1755:
1752:
1751:
1749:
1745:
1739:
1736:
1734:
1733:Phylogenomics
1731:
1729:
1726:
1724:
1721:
1719:
1716:
1714:
1711:
1709:
1706:
1704:
1703:DNA barcoding
1701:
1699:
1698:
1694:
1693:
1691:
1687:
1681:
1678:
1674:
1673:Least squares
1671:
1669:
1666:
1664:
1661:
1660:
1659:
1656:
1652:
1649:
1647:
1644:
1643:
1641:
1639:
1636:
1634:
1631:
1630:
1628:
1624:
1618:
1615:
1611:
1610:Ghost lineage
1608:
1607:
1606:
1603:
1601:
1597:
1594:
1592:
1589:
1587:
1584:
1580:
1577:
1576:
1575:
1572:
1568:
1565:
1564:
1563:
1560:
1559:
1557:
1553:
1546:
1540:
1535:
1527:
1524:
1522:
1519:
1517:
1514:
1512:
1509:
1507:
1504:
1502:
1499:
1498:
1496:
1492:
1488:
1487:Phylogenetics
1481:
1476:
1474:
1469:
1467:
1462:
1461:
1458:
1448:
1444:
1440:
1436:
1432:
1428:
1424:
1423:10.1038/44766
1420:
1416:
1412:
1408:
1404:
1400:
1393:
1385:
1381:
1377:
1373:
1369:
1365:
1361:
1357:
1353:
1349:
1345:
1338:
1330:
1326:
1322:
1318:
1314:
1310:
1306:
1302:
1298:
1294:
1290:
1286:
1282:
1275:
1267:
1254:
1246:
1242:
1235:
1227:
1223:
1218:
1213:
1208:
1203:
1199:
1195:
1191:
1184:
1182:
1173:
1169:
1164:
1159:
1155:
1151:
1147:
1140:
1132:
1128:
1123:
1118:
1114:
1110:
1106:
1102:
1098:
1094:
1090:
1083:
1075:
1071:
1067:
1063:
1059:
1055:
1051:
1047:
1043:
1039:
1035:
1031:
1027:
1020:
1006:
1002:
996:
988:
984:
980:
976:
972:
968:
964:
960:
956:
952:
948:
941:
933:
929:
925:
921:
916:
911:
907:
903:
899:
892:
890:
888:
879:
875:
871:
867:
863:
859:
855:
851:
847:
843:
839:
832:
824:
820:
815:
810:
806:
802:
798:
794:
790:
786:
782:
775:
773:
764:
760:
755:
750:
746:
742:
737:
732:
728:
724:
720:
713:
705:
701:
697:
693:
688:
683:
679:
675:
671:
664:
656:
652:
647:
642:
638:
634:
630:
626:
622:
618:
614:
607:
605:
603:
601:
599:
590:
586:
582:
578:
574:
570:
565:
560:
556:
552:
548:
541:
539:
537:
535:
526:
522:
518:
514:
510:
506:
502:
498:
494:
490:
486:
482:
478:
471:
469:
467:
458:
454:
449:
444:
440:
436:
432:
425:
423:
421:
419:
417:
415:
410:
401:
398:
396:
393:
392:
382:
379:
376:
373:
371:Evolutionary
370:
367:
364:
363:
360:
357:
355:
352:
349:
347:Evolutionary
346:
344:
341:
338:
337:
334:
331:
328:
325:
322:
320:
319:
314:
313:
310:
307:
304:
301:
299:Evolutionary
298:
295:
292:
291:
288:
285:
283:
280:
277:
275:Evolutionary
274:
272:
269:
266:
265:
262:
259:
256:
253:
250:
247:
244:
241:
240:
236:
233:
230:
227:
224:
221:
220:
214:
211:
209:
205:
201:
198:, as well as
197:
193:
188:
186:
182:
170:
166:
163:
160:
156:
153:
150:
149:
148:
145:
132:
130:
126:
122:
118:
114:
113:genetic drift
110:
105:
103:
99:
95:
91:
87:
82:
80:
75:
71:
70:morphological
67:
56:
54:
50:
46:
42:
38:
31:
27:
23:
18:
1901:Biodiversity
1877:
1865:
1838:Sister group
1821:Nomenclature
1784:Autapomorphy
1779:Synapomorphy
1759:Plesiomorphy
1747:Group traits
1722:
1695:
1567:Cladogenesis
1562:Phylogenesis
1406:
1402:
1392:
1351:
1347:
1337:
1288:
1284:
1274:
1253:cite journal
1234:
1197:
1193:
1153:
1149:
1139:
1096:
1092:
1082:
1033:
1029:
1019:
1008:. Retrieved
1005:ResearchGate
1004:
995:
954:
950:
940:
905:
901:
845:
841:
831:
791:(1): 67–82.
788:
784:
726:
722:
712:
677:
673:
663:
620:
616:
554:
550:
484:
480:
438:
434:
380:Categorical
365:
342:
329:Permutation
317:
308:Categorical
305:Permutation
293:
257:Permutation
245:
212:
196:correlograms
189:
185:biodiversity
179:
146:
143:
106:
83:
62:
41:evolutionary
36:
35:
1833:Crown group
1795:Group types
1526:Systematics
957:: 475–505.
848:(1): 1–15.
358:Continuous
332:Continuous
286:Continuous
282:Permutation
260:Continuous
208:K-statistic
181:Quantifying
125:phenomenons
74:behavioural
1895:Categories
1511:Cladistics
1348:Biometrika
1156:: e01543.
1010:2021-08-30
406:References
368:statistic
296:statistic
268:Blomberg's
243:Abouheif's
237:Reference
176:Techniques
45:ecological
1848:Supertree
1812:Polyphyly
1807:Paraphyly
1802:Monophyly
1774:Apomorphy
1754:Primitive
1697:PhyloCode
1579:Cladogram
1447:205034365
1431:0028-0836
1368:0006-3444
1305:0888-8892
1172:2351-9894
1113:1415-4757
1058:1476-4687
971:0066-4162
924:1367-4803
862:0003-0147
805:2041-210X
745:1664-302X
696:0014-3820
674:Evolution
637:0962-8436
573:1076-836X
525:221735844
501:0014-3820
481:Evolution
457:2041-210X
377:Bayesian
225:Approach
161:assembly?
159:community
30:community
1867:Category
1770:Derived
1516:Taxonomy
1439:10553904
1384:15420245
1329:29107177
1321:20184650
1313:40864204
1245:14934629
1226:19843698
1131:23055808
1066:21326204
932:30358816
823:25780554
763:25368606
704:23461331
655:23569289
623:(1618).
581:18709597
517:12778543
389:See also
316:Moran's
102:quantify
1879:Commons
1605:Lineage
1411:Bibcode
1376:2332142
1217:2780941
1122:3459419
1074:4406120
1038:Bibcode
979:3069271
878:9731499
870:2461605
814:4358766
754:4201110
729:: 532.
646:3638444
589:2232680
509:3094610
340:Pagel's
26:mimicry
1445:
1437:
1429:
1403:Nature
1382:
1374:
1366:
1327:
1319:
1311:
1303:
1243:
1224:
1214:
1170:
1129:
1119:
1111:
1072:
1064:
1056:
1030:Nature
987:535590
985:
977:
969:
930:
922:
876:
868:
860:
821:
811:
803:
761:
751:
743:
702:
694:
653:
643:
635:
587:
579:
571:
523:
515:
507:
499:
455:
39:is an
1843:Basal
1668:UPGMA
1600:Grade
1596:Clade
1443:S2CID
1372:JSTOR
1325:S2CID
1309:JSTOR
1241:S2CID
1070:S2CID
983:S2CID
975:JSTOR
874:S2CID
866:JSTOR
585:S2CID
521:S2CID
505:JSTOR
248:mean
234:Data
129:clade
1435:PMID
1427:ISSN
1380:PMID
1364:ISSN
1317:PMID
1301:ISSN
1266:help
1222:PMID
1168:ISSN
1127:PMID
1109:ISSN
1062:PMID
1054:ISSN
967:ISSN
928:PMID
920:ISSN
858:ISSN
819:PMID
801:ISSN
759:PMID
741:ISSN
700:PMID
692:ISSN
651:PMID
633:ISSN
577:PMID
569:ISSN
513:PMID
497:ISSN
453:ISSN
140:Goal
90:taxa
43:and
20:The
1598:vs
1419:doi
1407:401
1356:doi
1293:doi
1212:PMC
1202:doi
1198:106
1158:doi
1117:PMC
1101:doi
1046:doi
1034:470
959:doi
910:doi
850:doi
846:125
809:PMC
793:doi
749:PMC
731:doi
682:doi
641:PMC
625:doi
621:368
559:doi
489:doi
443:doi
1897::
1441:.
1433:.
1425:.
1417:.
1405:.
1401:.
1378:.
1370:.
1362:.
1352:37
1350:.
1346:.
1323:.
1315:.
1307:.
1299:.
1289:24
1287:.
1283:.
1257::
1255:}}
1251:{{
1220:.
1210:.
1196:.
1192:.
1180:^
1166:.
1154:27
1152:.
1148:.
1125:.
1115:.
1107:.
1097:35
1095:.
1091:.
1068:.
1060:.
1052:.
1044:.
1032:.
1028:.
1003:.
981:.
973:.
965:.
955:33
953:.
949:.
926:.
918:.
906:35
904:.
900:.
886:^
872:.
864:.
856:.
844:.
840:.
817:.
807:.
799:.
787:.
783:.
771:^
757:.
747:.
739:.
725:.
721:.
698:.
690:.
678:67
676:.
672:.
649:.
639:.
631:.
619:.
615:.
597:^
583:.
575:.
567:.
555:57
553:.
549:.
533:^
519:.
511:.
503:.
495:.
485:57
483:.
479:.
465:^
451:.
437:.
433:.
413:^
374:✓
350:✓
326:X
302:✓
278:✓
254:X
119:,
55:.
1479:e
1472:t
1465:v
1449:.
1421::
1413::
1386:.
1358::
1331:.
1295::
1268:)
1264:(
1247:.
1228:.
1204::
1174:.
1160::
1133:.
1103::
1076:.
1048::
1040::
1013:.
989:.
961::
934:.
912::
880:.
852::
825:.
795::
789:6
765:.
733::
727:5
706:.
684::
657:.
627::
591:.
561::
527:.
491::
459:.
445::
439:3
366:δ
343:λ
318:I
294:D
271:K
246:C
Text is available under the Creative Commons Attribution-ShareAlike License. Additional terms may apply.