651:
also been detected in grains like barley, wheat, corn and their processed products as well as in shellfish. Dietary intake of patulin from apple juice has been estimated at between 0.03 and 0.26 μg per kg body weight per day in various age groups and populations. Content of patulin in apple juice is estimated to be less than 10–15 μg/L. A number of studies have looked into comparisons of organic vs conventional harvest of apples and levels of patulin contamination. For example, one study showed 0.9% of children drinking organic apple juice exceeded the
342:
229:
44:
503:
35:
682:
recommends a maximum concentration of 50 μg/L in apple juice. In the
European Union, the limit is also set at 50 micrograms per kilogram (μg/kg) in apple juice and cider, at 25 μg/kg in solid apple products, and at 10 μg/kg in products for infants and young children. These limits came
650:
Frequently, patulin is found in apples and apple products such as juices, jams, and ciders. It has also been detected in other fruits including cherries, blueberries, plums, bananas, strawberries, and grapes. Fungal growth leading to patulin production is most common on damaged fruits. Patulin has
841:
was done on apple juice to compare exposure and the PTDI. Without controls or an action limit, the 90th percentile of consumers would not be above the PTDI. However, the concentration in children 1–2 years old would be three times as high as the PDTI, hence an action limit of 50 μg/kg.
1413:
Baert, Katleen; De
Meulenaer, Bruno; Verdonck, Frederik; Huybrechts, Inge; De Henauw, Stefaan; Vanrolleghem, Peter A.; Debevere, Johan; Devlieghere, Frank (2007). "Variability and uncertainty assessment of patulin exposure for preschool children in Flanders".
602:, the amount of patulin in apple products is generally viewed as a measure of the quality of the apples used in production. In addition, patulin has been found in other foods such as grains, fruits, and vegetables. Its presence is highly regulated.
678:. Some theorize that it may be a carcinogen, although animal studies have remained inconclusive. Patulin has shown antimicrobial properties against some microorganisms. Several countries have instituted patulin restrictions in apple products. The
866:(EU) has set a maximum limit of 50 μg/kg on fruit juices and drinks, while solid apple products have a limit of 25 μg/kg. For certain foods intended for infants, an even lower limit of 10 μg/kg is observed.
637:
in 1943, it was specifically trialed to be used against the common cold. Patulin is used as a potassium-uptake inhibitor in laboratory applications. Kashif Jilani and co-workers reported that patulin stimulates suicidal
1303:
Piqué, E; Vargas-Murga, L; Gómez-Catalán, J; Lapuente, Jd; Llobet, JM (October 2013). "Occurrence of patulin in organic and conventional apple-based food marketed in
Catalonia and exposure assessment".
625:, so antioxidant and antimicrobial agents may be useful to destroy it. Levels of nitrogen, manganese, and pH as well as abundance of necessary enzymes regulate the biosynthetic pathway of patulin.
722:
Studies in rats showed decreased weight, and gastric, intestinal, and renal function changes, while repetitive doses lead to neurotoxicity. Reproductive toxicity in males was also reported. A
702:
range was reported between 50 and 170 mg/kg. Other routes of exposure are more toxic, yet less likely to occur. Major acute toxicity findings include gastrointestinal problems,
633:
Patulin was originally used as an antibiotic against Gram-positive and Gram-negative bacteria, but after several toxicity reports, it is no longer used for that purpose. Isolated by
1093:
Llewellyn, G.C; McCay, J.A; Brown, R.D; Musgrove, D.L; Butterworth, L.F; Munson, A.E; White, K.L (1998). "Immunological evaluation of the mycotoxin patulin in female b6C3F1 mice".
1252:
Piemontese, L.; Solfrizzo, M.; Visconti, A. (2005-05-01). "Occurrence of patulin in conventional and organic fruit products in Italy and subsequent exposure assessment".
1242:
Pique, E., et al. Occurrence of patulin in organic and conventional apple juice. Risk
Assessment. Recent Advances in Pharmaceutical Sciences, III, 2013: 131–144.
949:
655:(TDI) for patulin. A recent article described detection of patulin in marine strains of Penicillium, indicating a potential risk in shellfish consumption.
516:
621:
in the multi-step biosynthesis of patulin. Its gene is present in other fungi that may potentially produce the toxin. It is reactive with
391:
742:
1190:
671:
studies were primarily the cause for setting limits for patulin exposure, although a range of other types of toxicity also exist.
1454:
878:
146:
773:
in a number of animal and even human studies. Reduced cytokine secretion, oxidative burst in macrophages, increased splenic
781:
numbers are a few endpoints noticed. However, dietary relevant exposure would not be likely to alter immune response.
869:
To test for patulin contamination, a variety of methods and sample preparation methods have been employed, including
356:
957:
691:
Patulin is toxic primarily through affinity to sulfhydryl groups (SH), which results in inhibition of enzymes. Oral
511:
17:
523:
821:
such as removing mold, washing, and not using rotten or damaged apples for baking, canning, or juice production.
1229:
Wouters, FA, and
Speijers, GJA. JECFA Monograph on Patulin. World Health Organization Food Additives Series 35 (
915:
299:
224:
818:
569:
320:
186:
753:
Patulin decreased sperm count and altered sperm morphology in the rat. Also, it resulted in abortion of
882:
870:
851:
679:
236:
337:
1378:
Selmanoglu, G (2006). "Evaluation of the reproductive toxicity of patulin in growing male rats".
830:
652:
611:
62:
1230:
838:
707:
308:
206:
8:
1474:
552:
122:
112:
1194:
341:
228:
166:
1479:
1285:
1063:
1036:
999:
972:
874:
692:
1106:
1451:
1431:
1395:
1347:"Patulin: a Mycotoxin in Apples". Perishables Handling Quarterly (91): 5. August 1997
1321:
1277:
1269:
1169:
1110:
1068:
1004:
1289:
1423:
1387:
1313:
1261:
1159:
1102:
1058:
1048:
994:
984:
698:
in rodent models have ranged between 20 and 100 mg/kg. In poultry, the oral LD
539:
481:
414:
1458:
794:
557:
288:
833:(PTDI) for patulin was set at 0.43 μg/kg body weight by the FDA based on a
863:
806:
758:
634:
622:
565:
494:
1427:
1391:
1317:
1265:
789:
Although there are only very few reported cases and epidemiological data, the
1468:
1273:
774:
754:
703:
470:
217:
1435:
1399:
1325:
1281:
1173:
1072:
1008:
950:"Patulin in Apple Juice, Apple Juice Concentrates and Apple Juice Products"
738:
668:
594:
573:
1114:
1053:
989:
802:
770:
639:
588:
582:
1132:
Medical
Research Council. Clinical trial of patulin in the common cold.
778:
543:
442:
237:
197:
43:
1302:
1164:
1147:
1359:"Foodborne hazards (World Health Organization". Retrieved 2007-01-22.
798:
675:
577:
1035:
Puel, Olivier; Galtier, Pierre; Oswald, Isabelle P. (5 April 2010).
493:
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their
1412:
854:
recommends a maximum concentration of 50 μg/L in apple juice.
797:
and other reported adverse effects. In humans, it was tested as an
263:
757:
litters in rats and mice after i.p. injection. Embryotoxicity and
145:
561:
460:
275:
16:"Claviform" redirects here. For the botany and zoology term, see
1145:
793:
has set an action limit of 50 ppb in cider due to its potential
618:
599:
547:
177:
834:
723:
711:
664:
157:
135:
325:
1251:
1092:
741:
data, however it is considered a group 3 carcinogen by the
254:
817:
Patulin exposure can be successfully managed by following
605:
365:
InChI=1S/C7H6O4/c8-6-3-4-5(11-6)1-2-10-7(4)9/h1,3,7,9H,2H2
34:
1231:
http://www.inchem.org/documents/jecfa/jecmono/v26je10.htm
971:
Puel, Olivier; Galtier, Pierre; Oswald, Isabelle (2010).
790:
734:
375:
InChI=1/C7H6O4/c8-6-3-4-5(11-6)1-2-10-7(4)9/h1,3,7,9H,2H2
737:
concluded that patulin is genotoxic based on variable
726:
in rodents was observed at 43 μg/kg body weight.
556:. It is a white powder soluble in acidic water and in
1037:"Biosynthesis and Toxicological Effects of Patulin"
973:"Biosynthesis and Toxicological Effects of Patulin"
809:, yet also had negligible or no beneficial effect.
1146:Lupescu, A; Jilani, K; Zbidah, M; Lang, F (2013).
812:
674:While not a particularly potent toxin, patulin is
1034:
970:
1466:
617:Isoepoxydon dehydrogenase (IDH) is an important
287:
580:produced by a variety of molds, in particular,
564:that is heat-stable, so it is not destroyed by
121:
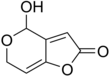
82:2-Hydroxy-3,7-dioxabicyclonona-5,9-dien-8-one
1148:"Patulin-induced suicidal erythrocyte death"
944:
1213:
1211:
1088:
1086:
1084:
1082:
942:
940:
938:
936:
934:
932:
930:
928:
926:
924:
743:International Agency for Research on Cancer
18:Glossary of entomology terms § clavate
1377:
1225:
1223:
642:death under physiological concentrations.
340:
227:
205:
1163:
1062:
1052:
998:
988:
307:
1355:
1353:
1208:
1185:
1183:
1079:
921:
837:of 0.3 mg/kg body weight per week.
1368:Patulin information leaf from Fermentek
1220:
911:
909:
899:
897:
748:
614:via multiple chemical transformations.
606:Biosynthesis, synthesis, and reactivity
336:
1467:
1030:
1028:
1026:
1024:
1022:
1020:
1018:
879:high-performance liquid chromatography
645:
475:110 °C (230 °F; 383 K)
218:
1350:
1180:
1128:
1126:
1124:
368:Key: ZRWPUFFVAOMMNM-UHFFFAOYSA-N
185:
165:
1152:Cellular Physiology and Biochemistry
906:
894:
745:(IARC) since data was inconclusive.
1015:
667:of 43 μg/kg body weight as well as
378:Key: ZRWPUFFVAOMMNM-UHFFFAOYAU
278:
262:
13:
1121:
761:were also reported in chick eggs.
42:
33:
14:
1491:
1445:
801:intranasally for use against the
764:
598:. Most commonly found in rotting
501:
426:
1406:
1371:
1362:
1341:
1332:
1296:
1254:Food Additives and Contaminants
1245:
1236:
903:Merck Index, 11th Edition, 7002
813:Risk management and regulations
784:
729:
683:into force on 1 November 2003.
610:Patulin is biosynthesized from
572:. However, stability following
497:(at 25 °C , 100 kPa).
1139:
964:
432:
420:
1:
1107:10.1016/s0278-6915(98)00084-2
888:
1416:Food and Chemical Toxicology
1306:Food and Chemical Toxicology
1095:Food and Chemical Toxicology
550:from which it was isolated,
7:
819:good agricultural practices
717:
658:
29:
10:
1496:
447:154.12 g/mol
15:
1428:10.1016/j.fct.2007.03.008
1392:10.1016/j.fct.2006.06.022
1318:10.1016/j.fct.2013.07.052
1266:10.1080/02652030500073550
1217:Pouchous et al. Shellfish
883:capillary electrophoresis
871:thin layer chromatography
852:World Health Organization
680:World Health Organization
491:
407:
387:
352:
105:
79:
61:
56:
28:
769:Patulin was found to be
686:
546:. It is named after the
399:O=C\1O/C2=C/COC(O)C2=C/1
628:
831:tolerable daily intake
653:tolerable daily intake
612:6-methylsalicylic acid
576:is lessened. It is a
47:
38:
1054:10.3390/toxins2040613
990:10.3390/toxins2040613
805:with few significant
46:
37:
839:Monte Carlo analysis
749:Reproduction studies
708:pulmonary congestion
706:(i.e. convulsions),
1461:, Food Safety Watch
646:Sources of exposure
553:Penicillium patulum
482:Solubility in water
25:
1457:2017-12-19 at the
1380:Food Chem. Toxicol
875:gas chromatography
663:A subacute rodent
524:Infobox references
48:
39:
23:
1386:(12): 2019–2024.
1165:10.1159/000354437
1101:(12): 1107–1115.
532:Chemical compound
530:
529:
321:CompTox Dashboard
147:Interactive image
52:
51:
1487:
1440:
1439:
1422:(9): 1745–1751.
1410:
1404:
1403:
1375:
1369:
1366:
1360:
1357:
1348:
1345:
1339:
1338:Beark et al 2007
1336:
1330:
1329:
1300:
1294:
1293:
1249:
1243:
1240:
1234:
1227:
1218:
1215:
1206:
1205:
1203:
1202:
1193:. Archived from
1187:
1178:
1177:
1167:
1143:
1137:
1136:1944; ii: 373-5.
1130:
1119:
1118:
1090:
1077:
1076:
1066:
1056:
1032:
1013:
1012:
1002:
992:
968:
962:
961:
956:. Archived from
946:
919:
918:sigmaaldrich.com
913:
904:
901:
829:The provisional
777:, and increased
558:organic solvents
542:classified as a
540:organic compound
514:
508:
505:
504:
434:
428:
422:
415:Chemical formula
345:
344:
329:
327:
311:
291:
280:
266:
239:
231:
220:
209:
189:
169:
149:
125:
30:
26:
22:
1495:
1494:
1490:
1489:
1488:
1486:
1485:
1484:
1465:
1464:
1459:Wayback Machine
1448:
1443:
1411:
1407:
1376:
1372:
1367:
1363:
1358:
1351:
1346:
1342:
1337:
1333:
1301:
1297:
1250:
1246:
1241:
1237:
1228:
1221:
1216:
1209:
1200:
1198:
1189:
1188:
1181:
1144:
1140:
1131:
1122:
1091:
1080:
1033:
1016:
969:
965:
948:
947:
922:
914:
907:
902:
895:
891:
815:
807:adverse effects
795:carcinogenicity
787:
767:
751:
732:
720:
701:
696:
689:
661:
648:
631:
608:
533:
526:
521:
520:
519: ?)
510:
506:
502:
498:
484:
455:Compact prisms
437:
431:
425:
417:
403:
400:
395:
394:
383:
380:
379:
376:
370:
369:
366:
360:
359:
348:
330:
323:
314:
294:
281:
269:
249:
212:
192:
172:
152:
139:
128:
115:
101:
99:
97:
95:
93:
91:
89:
87:
85:
83:
75:
21:
12:
11:
5:
1493:
1483:
1482:
1477:
1463:
1462:
1447:
1446:External links
1444:
1442:
1441:
1405:
1370:
1361:
1349:
1340:
1331:
1295:
1260:(5): 437–442.
1244:
1235:
1219:
1207:
1179:
1138:
1120:
1078:
1047:(4): 613–631.
1014:
983:(4): 613–631.
963:
960:on 2013-08-15.
920:
905:
892:
890:
887:
864:European Union
814:
811:
786:
783:
766:
765:Immunotoxicity
763:
759:teratogenicity
750:
747:
731:
728:
719:
716:
699:
694:
688:
685:
660:
657:
647:
644:
635:Nancy Atkinson
630:
627:
623:sulfur dioxide
607:
604:
566:pasteurization
531:
528:
527:
522:
500:
499:
495:standard state
492:
489:
488:
485:
480:
477:
476:
473:
467:
466:
463:
457:
456:
453:
449:
448:
445:
439:
438:
435:
429:
423:
418:
413:
410:
409:
405:
404:
402:
401:
398:
390:
389:
388:
385:
384:
382:
381:
377:
374:
373:
371:
367:
364:
363:
355:
354:
353:
350:
349:
347:
346:
333:
331:
319:
316:
315:
313:
312:
304:
302:
296:
295:
293:
292:
284:
282:
274:
271:
270:
268:
267:
259:
257:
251:
250:
248:
247:
243:
241:
233:
232:
222:
214:
213:
211:
210:
202:
200:
194:
193:
191:
190:
182:
180:
174:
173:
171:
170:
162:
160:
154:
153:
151:
150:
142:
140:
133:
130:
129:
127:
126:
118:
116:
111:
108:
107:
103:
102:
81:
77:
76:
70:-furopyran-2(6
65:
59:
58:
54:
53:
50:
49:
40:
9:
6:
4:
3:
2:
1492:
1481:
1478:
1476:
1473:
1472:
1470:
1460:
1456:
1453:
1450:
1449:
1437:
1433:
1429:
1425:
1421:
1417:
1409:
1401:
1397:
1393:
1389:
1385:
1381:
1374:
1365:
1356:
1354:
1344:
1335:
1327:
1323:
1319:
1315:
1311:
1307:
1299:
1291:
1287:
1283:
1279:
1275:
1271:
1267:
1263:
1259:
1255:
1248:
1239:
1232:
1226:
1224:
1214:
1212:
1197:on 2013-10-18
1196:
1192:
1186:
1184:
1175:
1171:
1166:
1161:
1157:
1153:
1149:
1142:
1135:
1129:
1127:
1125:
1116:
1112:
1108:
1104:
1100:
1096:
1089:
1087:
1085:
1083:
1074:
1070:
1065:
1060:
1055:
1050:
1046:
1042:
1038:
1031:
1029:
1027:
1025:
1023:
1021:
1019:
1010:
1006:
1001:
996:
991:
986:
982:
978:
974:
967:
959:
955:
951:
945:
943:
941:
939:
937:
935:
933:
931:
929:
927:
925:
917:
912:
910:
900:
898:
893:
886:
884:
880:
876:
872:
867:
865:
860:
859:
855:
853:
848:
847:
843:
840:
836:
832:
827:
826:
822:
820:
810:
808:
804:
800:
796:
792:
782:
780:
776:
775:T lymphocytes
772:
762:
760:
756:
746:
744:
740:
736:
727:
725:
715:
713:
709:
705:
704:neurotoxicity
697:
684:
681:
677:
672:
670:
666:
656:
654:
643:
641:
636:
626:
624:
620:
615:
613:
603:
601:
597:
596:
591:
590:
585:
584:
579:
575:
571:
567:
563:
559:
555:
554:
549:
545:
541:
537:
525:
518:
513:
496:
490:
486:
483:
479:
478:
474:
472:
471:Melting point
469:
468:
464:
462:
459:
458:
454:
451:
450:
446:
444:
441:
440:
419:
416:
412:
411:
406:
397:
396:
393:
386:
372:
362:
361:
358:
351:
343:
339:
338:DTXSID2021101
335:
334:
332:
322:
318:
317:
310:
306:
305:
303:
301:
298:
297:
290:
286:
285:
283:
277:
273:
272:
265:
261:
260:
258:
256:
253:
252:
245:
244:
242:
240:
235:
234:
230:
226:
223:
221:
219:ECHA InfoCard
216:
215:
208:
204:
203:
201:
199:
196:
195:
188:
184:
183:
181:
179:
176:
175:
168:
164:
163:
161:
159:
156:
155:
148:
144:
143:
141:
137:
132:
131:
124:
120:
119:
117:
114:
110:
109:
104:
78:
73:
69:
64:
60:
55:
45:
41:
36:
32:
31:
27:
19:
1419:
1415:
1408:
1383:
1379:
1373:
1364:
1343:
1334:
1309:
1305:
1298:
1257:
1253:
1247:
1238:
1199:. Retrieved
1195:the original
1158:(2): 291–9.
1155:
1151:
1141:
1133:
1098:
1094:
1044:
1040:
980:
976:
966:
958:the original
953:
881:(HPLC), and
868:
861:
857:
856:
849:
845:
844:
828:
824:
823:
816:
788:
785:Human health
768:
752:
739:genotoxicity
733:
730:Genotoxicity
721:
690:
673:
669:genotoxicity
662:
649:
632:
616:
609:
595:Byssochlamys
593:
587:
581:
574:fermentation
570:denaturation
551:
535:
534:
187:ChEMBL294018
106:Identifiers
80:Other names
71:
67:
1312:: 199–204.
954:www.fda.gov
803:common cold
771:immunotoxic
640:erythrocyte
589:Penicillium
583:Aspergillus
568:or thermal
452:Appearance
408:Properties
225:100.005.215
167:CHEBI:74926
84:Clairformin
66:4-hydroxy-4
1475:Mycotoxins
1469:Categories
1201:2013-11-25
889:References
779:neutrophil
560:. It is a
544:polyketide
465:1.52 g/mL
443:Molar mass
309:95X2BV4W8R
198:ChemSpider
134:3D model (
113:CAS Number
63:IUPAC name
1480:Furanones
1274:0265-203X
1191:"Patulin"
799:antiviral
676:genotoxic
578:mycotoxin
246:205-735-2
238:EC Number
88:Expansine
86:Claviform
1455:Archived
1436:17459555
1400:16905234
1326:23900007
1290:31155096
1282:16019815
1174:23942252
1073:22069602
1009:22069602
718:Subacute
659:Toxicity
487:Soluble
123:149-29-1
100:Patuline
98:Leucopin
96:Gigantin
94:Expansin
92:Clavatin
90:Clavacin
24:Patulin
1452:Patulin
1115:9862653
1064:3153204
1000:3153204
916:Patulin
873:(TLC),
562:lactone
536:Patulin
517:what is
515: (
461:Density
276:PubChem
1434:
1398:
1324:
1288:
1280:
1272:
1172:
1134:Lancet
1113:
1071:
1061:
1041:Toxins
1007:
997:
977:Toxins
877:(GC),
710:, and
619:enzyme
600:apples
548:fungus
538:is an
512:verify
509:
392:SMILES
264:C16748
178:ChEMBL
57:Names
1286:S2CID
835:NOAEL
724:NOAEL
712:edema
687:Acute
665:NOAEL
357:InChI
158:ChEBI
136:JSmol
74:)-one
1432:PMID
1396:PMID
1322:PMID
1278:PMID
1270:ISSN
1170:PMID
1111:PMID
1069:PMID
1005:PMID
862:The
850:The
629:Uses
592:and
586:and
300:UNII
289:4696
255:KEGG
207:4534
1424:doi
1388:doi
1314:doi
1262:doi
1160:doi
1103:doi
1059:PMC
1049:doi
995:PMC
985:doi
846:WHO
791:FDA
735:WHO
326:EPA
279:CID
1471::
1430:.
1420:45
1418:.
1394:.
1384:44
1382:.
1352:^
1320:.
1310:60
1308:.
1284:.
1276:.
1268:.
1258:22
1256:.
1222:^
1210:^
1182:^
1168:.
1156:32
1154:.
1150:.
1123:^
1109:.
1099:36
1097:.
1081:^
1067:.
1057:.
1043:.
1039:.
1017:^
1003:.
993:.
979:.
975:.
952:.
923:^
908:^
896:^
885:.
858:EU
825:US
755:F1
714:.
700:50
695:50
693:LD
1438:.
1426::
1402:.
1390::
1328:.
1316::
1292:.
1264::
1233:)
1204:.
1176:.
1162::
1117:.
1105::
1075:.
1051::
1045:2
1011:.
987::
981:2
507:N
436:4
433:O
430:6
427:H
424:7
421:C
328:)
324:(
138:)
72:H
68:H
20:.
Text is available under the Creative Commons Attribution-ShareAlike License. Additional terms may apply.