413:. The median eminence contains fiber terminals from many hypothalamic neuroendocrine neurons, secreting different neurotransmitters or neuropeptides, including vasopressin, corticotropin-releasing hormone (CRH), thyrotropin-releasing hormone (TRH), gonadotropin-releasing hormone (GnRH), growth hormone-releasing hormone (GHRH), dopamine (DA) and somatostatin (growth hormone release inhibiting hormone, GIH) into blood vessels in the hypophyseal portal system. The blood vessels carry the peptides to the anterior pituitary gland, where they regulate the secretion of hormones into the systemic circulation. The parvocellular neurosecretory cells include those that make:
62:
356:
42:
501:
Among these, inputs from neurons in structures adjacent to the anterior wall of the third ventricle (the "AV3V region") carry information about the electrolyte composition of the blood, and about circulating concentrations of such hormones as
408:
neurosecretory neurons of the PVN project to the median eminence, a neurohemal organ at the base of the brain, where their neurosecretory nerve terminals release their hormones at the primary capillary plexus of the
307:) beyond the blood–brain barrier. PVN is accounting for only about 1% of the brain volume.In the rat, the PVN consists of approximately 100,000 neurons located in a volume of about 0.5 cubic millimetre.
536:
coordinate metabolic regulation (via TRH secretion) with regulation of energy intake. Specifically, the projections from the arcuate nucleus seem to exert their effect on appetite via
763:
Chen, Chang-Rui; Zhong, Yu-Heng; Jiang, Shan; Xu, Wei; Xiao, Lei; Wang, Zan; Qu, Wei-Min; Huang, Zhi-Li (2021-11-17). Elmquist, Joel K; Wong, Ma-Li; Lazarus, Michael (eds.).
627:
Chen, Chang-Rui; Zhong, Yu-Heng; Jiang, Shan; Xu, Wei; Xiao, Lei; Wang, Zan; Qu, Wei-Min; Huang, Zhi-Li (2021-11-17). Elmquist, Joel K; Wong, Ma-Li; Lazarus, Michael (eds.).
160:
339:, and several populations of other cells that project to many different brain regions including parvocellular preautonomic cells that project to the
136:
1166:
824:"The hypothalamic paraventricular nucleus as a central hub for the estrogenic modulation of neuroendocrine function and behavior"
906:
Argiolas A, Melis MR (May 2005). "Central control of penile erection: role of the paraventricular nucleus of the hypothalamus".
949:
Russell JA, Blackburn RE, Leng G (June 1988). "The role of the AV3V region in the control of magnocellular oxytocin neurons".
460:
and populations of neurons that project centrally (i.e., to other brain regions). The centrally-projecting neurons include
580:"The paraventricular nucleus of the hypothalamus - a potential target for integrative treatment of autonomic dysfunction"
1176:
559:
479:, as well as to the brainstem and spinal cord (these are involved in blood pressure and temperature regulation), and
405:
367:
328:
316:
167:
555:
417:
228:
1042:
498:
The PVN receives afferent inputs from many brain regions and different parts of the body, by hormonal control.
389:
axons of the cells and released from neurosecretory nerve terminals residing in the posterior pituitary gland.
1073:"Regulation of the hypothalamic thyrotropin releasing hormone (TRH) neuron by neuronal and peripheral inputs"
514:
436:
232:
155:
46:
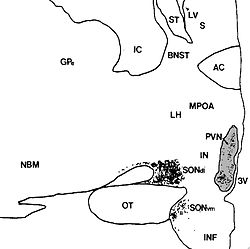
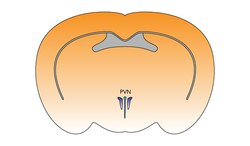
Human paraventricular nucleus (PVN) in this coronal section is indicated by the shaded area. Dots represent
688:"Case Report: Dysfunction of the Paraventricular Hypothalamic Nucleus Area Induces Hypersomnia in Patients"
433:, which also regulates ACTH secretion (vasopressin and CRH act synergistically to stimulate ACTH secretion)
1201:
440:
823:
410:
236:
1041:
Konturek PC, Konturek JW, Cześnikiewicz-Guzik M, Brzozowski T, Sito E, Konturek SJ (December 2005).
111:
425:
251:
for up to 20 hours per day. The PVN is thought to mediate many diverse functions through different
94:
26:
686:
Wang, Zan; Zhong, Yu-Heng; Jiang, Shan; Qu, Wei-Min; Huang, Zhi-Li; Chen, Chang-Rui (2022-03-14).
544:
537:
292:
284:
19:
200:
143:
131:
1196:
1122:"The Paraventricular Nucleus of the Hypothalamus: Development, Function, and Human Diseases"
480:
296:
247:
in mice. In humans, the dysfunction of the PVN and the other nuclei around it can lead to
8:
360:
324:
304:
216:
998:
Philosophical
Transactions of the Royal Society of London. Series B, Biological Sciences
489:
Parvocellular CRH neurons, which are thought to be involved in stress-related behaviors.
1097:
1072:
1018:
993:
974:
931:
799:
764:
722:
687:
663:
628:
604:
579:
393:
336:
240:
51:
475:
Parvocellular vasopressin cells, which project to many points in the hypothalamus and
1206:
1172:
1143:
1102:
1053:
1023:
966:
962:
923:
888:
851:
843:
804:
786:
765:"Dysfunctions of the paraventricular hypothalamic nucleus induce hypersomnia in mice"
727:
709:
668:
650:
629:"Dysfunctions of the paraventricular hypothalamic nucleus induce hypersomnia in mice"
609:
385:
These hormones are packaged into large vesicles, which are then transported down the
61:
935:
919:
1133:
1092:
1084:
1043:"Neuro-hormonal control of food intake: basic mechanisms and clinical implications"
1013:
1005:
978:
958:
915:
878:
835:
794:
776:
717:
699:
658:
640:
599:
591:
472:. These neurons are thought to have a role in gastric reflexes and penile erection,
371:
268:
533:
332:
300:
288:
280:
208:
124:
99:
1088:
839:
822:
Grassi, D.; Marraudino, M.; Garcia-Segura, L. M.; Panzica, G. C. (2022-04-01).
529:
256:
704:
595:
1190:
1040:
847:
790:
713:
654:
483:
476:
283:. It lies within the periventricular zone and is not to be confused with the
148:
994:"Neuropeptide Y in normal eating and in genetic and dietary-induced obesity"
883:
870:
1147:
1106:
1057:
1027:
1009:
927:
892:
855:
808:
731:
672:
613:
204:
1138:
1121:
970:
551:
522:
503:
469:
457:
430:
379:
344:
264:
244:
224:
47:
781:
645:
248:
106:
173:
517:) and the ventrolateral medulla carry information from the heart and
465:
444:
340:
821:
1171:. US Elsevier Health Bookshop, Mosby, Saunders, Netter & More.
375:
260:
220:
118:
550:
Inputs from glucose sensors within the brain stimulate release of
525:
to the CRH neurones are important regulators of stress responses.
518:
507:
396:
which also secrete vasopressin and a smaller amount of oxytocin.
252:
386:
212:
82:
421:
355:
320:
464:
Parvocellular oxytocin cells, which project mainly to the
291:. The PVN is highly vascularised and is protected by the
359:
Magnocellular neurons of the PVN and SON project to the
41:
577:
399:
350:
287:, which occupies a more medial position, beneath the
54:, SON). The medial surface is the 3rd ventricle (3V).
948:
456:
As well as neuroendocrine neurons, the PVN contains
66:
The paraventricular hypothalamus of the mouse brain
578:Ferguson AV, Latchford KJ, Samson WK (June 2008).
279:The paraventricular nucleus lies adjacent to the
1188:
762:
685:
626:
451:
392:Similar magnocellular neurons are found in the
1168:Guyton and Hall Textbook of Medical Physiology
868:
547:about levels of lighting (circadian rhythms).
905:
752:(Twelfth ed.). McGraw Hill. p. 665.
1064:
1034:
985:
540:-expressing oxytocinergic cells of the PVN.
899:
875:International Journal of Impotence Research
862:
370:cells in the PVN elaborate and secrete two
185:The paraventricular nucleus of hypothalamus
1164:
942:
60:
40:
1137:
1119:
1096:
1017:
882:
798:
780:
721:
703:
662:
644:
603:
510:, to regulate the magnocellular neurons.
235:(TRH). CRH and TRH are secreted into the
743:
741:
354:
35:Paraventricular nucleus of hypothalamus
1189:
1120:Qin C, Li J, Tang K (September 2018).
1070:
1050:Journal of Physiology and Pharmacology
239:, and target different neurons in the
738:
584:Expert Opinion on Therapeutic Targets
88:nucleus paraventricularis hypothalami
991:
869:Giuliano F, Allard J (August 2001).
400:Parvocellular neurosecretory neurons
351:Magnocellular neurosecretory neurons
243:. Dysfunctions of the PVN can cause
747:
13:
1165:Hall JE, Guyton AC (20 May 2015).
1157:
560:parvocellular neurosecretory cells
493:
329:parvocellular neurosecretory cells
317:magnocellular neurosecretory cells
267:, and the response of the body to
14:
1218:
168:Anatomical terms of neuroanatomy
50:(AVP) neurons (also seen in the
1113:
1077:Frontiers in Neuroendocrinology
920:10.1016/j.pneurobio.2005.06.002
828:Frontiers in Neuroendocrinology
556:corticotropin-releasing hormone
513:Inputs from the brainstem (the
418:Corticotropin-releasing hormone
335:, ultimately signalling to the
229:corticotropin-releasing hormone
871:"Dopamine and sexual function"
815:
756:
679:
620:
571:
1:
565:
515:nucleus of the solitary tract
437:Thyrotropin-releasing hormone
233:thyrotropin-releasing hormone
963:10.1016/0361-9230(88)90095-0
452:Centrally-projecting neurons
7:
1089:10.1016/j.yfrne.2010.01.001
840:10.1016/j.yfrne.2021.100974
532:-containing neurons in the
274:
10:
1223:
310:
223:, and a smaller amount of
24:
17:
705:10.3389/fnins.2022.830474
692:Frontiers in Neuroscience
596:10.1517/14728222.12.6.717
411:hypophyseal portal system
237:hypophyseal portal system
166:
154:
142:
130:
117:
105:
93:
81:
76:
71:
59:
39:
34:
1071:Nillni EA (April 2010).
908:Progress in Neurobiology
426:anterior pituitary gland
299:extend to sites (in the
227:. Other secretions are
207:, that lies next to the
27:Paraventricular thalamus
25:Not to be confused with
18:Not to be confused with
951:Brain Research Bulletin
884:10.1038/sj.ijir.3900719
545:suprachiasmatic nucleus
439:(TRH), which regulates
420:(CRH), which regulates
285:periventricular nucleus
20:Periventricular nucleus
1010:10.1098/rstb.2006.1855
877:. 13 Suppl 3: S18-28.
363:
1139:10.1210/en.2018-00453
358:
1052:. 56 Suppl 6: 5–25.
992:Beck B (July 2006).
331:that project to the
297:neuroendocrine cells
782:10.7554/eLife.69909
646:10.7554/eLife.69909
424:secretion from the
361:posterior pituitary
325:posterior pituitary
305:posterior pituitary
293:blood–brain barrier
219:where they secrete
217:posterior pituitary
1202:Neuroendocrinology
521:. Inputs from the
394:supraoptic nucleus
364:
337:anterior pituitary
241:anterior pituitary
52:supraoptic nucleus
1004:(1471): 1159–85.
404:The axons of the
315:The PVN contains
182:
181:
177:
1214:
1182:
1152:
1151:
1141:
1132:(9): 3458–3472.
1117:
1111:
1110:
1100:
1068:
1062:
1061:
1047:
1038:
1032:
1031:
1021:
989:
983:
982:
946:
940:
939:
903:
897:
896:
886:
866:
860:
859:
819:
813:
812:
802:
784:
760:
754:
753:
750:Human Physiology
745:
736:
735:
725:
707:
683:
677:
676:
666:
648:
624:
618:
617:
607:
575:
372:peptide hormones
323:extend into the
174:edit on Wikidata
171:
64:
44:
32:
31:
1222:
1221:
1217:
1216:
1215:
1213:
1212:
1211:
1187:
1186:
1185:
1179:
1160:
1158:Further reading
1155:
1118:
1114:
1069:
1065:
1045:
1039:
1035:
990:
986:
947:
943:
904:
900:
867:
863:
820:
816:
761:
757:
748:Fox SI (2011).
746:
739:
684:
680:
625:
621:
576:
572:
568:
534:arcuate nucleus
496:
494:Afferent inputs
454:
402:
353:
333:median eminence
313:
301:median eminence
295:, although its
289:third ventricle
281:third ventricle
277:
215:project to the
209:third ventricle
178:
67:
55:
30:
23:
12:
11:
5:
1220:
1210:
1209:
1204:
1199:
1184:
1183:
1177:
1161:
1159:
1156:
1154:
1153:
1112:
1063:
1033:
984:
941:
898:
861:
814:
755:
737:
678:
619:
569:
567:
564:
530:neuropeptide Y
495:
492:
491:
490:
487:
473:
453:
450:
449:
448:
434:
428:
401:
398:
352:
349:
312:
309:
276:
273:
257:osmoregulation
211:. Many of its
180:
179:
170:
164:
163:
158:
152:
151:
146:
140:
139:
134:
128:
127:
122:
115:
114:
109:
103:
102:
97:
91:
90:
85:
79:
78:
74:
73:
69:
68:
65:
57:
56:
45:
37:
36:
9:
6:
4:
3:
2:
1219:
1208:
1205:
1203:
1200:
1198:
1195:
1194:
1192:
1180:
1178:9781455770052
1174:
1170:
1169:
1163:
1162:
1149:
1145:
1140:
1135:
1131:
1127:
1126:Endocrinology
1123:
1116:
1108:
1104:
1099:
1094:
1090:
1086:
1083:(2): 134–56.
1082:
1078:
1074:
1067:
1059:
1055:
1051:
1044:
1037:
1029:
1025:
1020:
1015:
1011:
1007:
1003:
999:
995:
988:
980:
976:
972:
968:
964:
960:
957:(6): 803–10.
956:
952:
945:
937:
933:
929:
925:
921:
917:
913:
909:
902:
894:
890:
885:
880:
876:
872:
865:
857:
853:
849:
845:
841:
837:
833:
829:
825:
818:
810:
806:
801:
796:
792:
788:
783:
778:
774:
770:
766:
759:
751:
744:
742:
733:
729:
724:
719:
715:
711:
706:
701:
697:
693:
689:
682:
674:
670:
665:
660:
656:
652:
647:
642:
638:
634:
630:
623:
615:
611:
606:
601:
597:
593:
590:(6): 717–27.
589:
585:
581:
574:
570:
563:
561:
557:
553:
548:
546:
541:
539:
535:
531:
526:
524:
520:
516:
511:
509:
505:
499:
488:
485:
484:thermogenesis
482:
478:
477:limbic system
474:
471:
467:
463:
462:
461:
459:
446:
442:
438:
435:
432:
429:
427:
423:
419:
416:
415:
414:
412:
407:
406:parvocellular
397:
395:
390:
388:
383:
381:
377:
373:
369:
368:magnocellular
362:
357:
348:
346:
342:
338:
334:
330:
326:
322:
318:
308:
306:
302:
298:
294:
290:
286:
282:
272:
270:
266:
262:
258:
254:
250:
246:
242:
238:
234:
230:
226:
222:
218:
214:
210:
206:
202:
198:
194:
190:
186:
175:
169:
165:
162:
159:
157:
153:
150:
147:
145:
141:
138:
135:
133:
129:
126:
123:
120:
116:
113:
110:
108:
104:
101:
98:
96:
92:
89:
86:
84:
80:
75:
70:
63:
58:
53:
49:
43:
38:
33:
28:
21:
16:
1197:Hypothalamus
1167:
1129:
1125:
1115:
1080:
1076:
1066:
1049:
1036:
1001:
997:
987:
954:
950:
944:
911:
907:
901:
874:
864:
831:
827:
817:
772:
768:
758:
749:
695:
691:
681:
636:
632:
622:
587:
583:
573:
549:
543:Inputs from
542:
528:Inputs from
527:
512:
500:
497:
458:interneurons
455:
403:
391:
387:unmyelinated
384:
365:
314:
278:
255:, including
205:hypothalamus
196:
192:
188:
184:
183:
137:A14.1.08.909
125:birnlex_1407
87:
15:
914:(1): 1–21.
552:vasopressin
523:hippocampus
504:angiotensin
470:spinal cord
431:Vasopressin
380:vasopressin
345:spinal cord
303:and in the
265:wakefulness
245:hypersomnia
225:vasopressin
77:Identifiers
48:vasopressin
1191:Categories
834:: 100974.
775:: e69909.
639:: e69909.
566:References
249:drowsiness
231:(CRH) and
107:NeuroNames
848:0091-3022
791:2050-084X
714:1662-453X
655:2050-084X
481:brown fat
466:brainstem
447:secretion
445:prolactin
341:brainstem
1207:Hormones
1148:30052854
1107:20074584
1058:16340035
1028:16874931
936:24929538
928:16043278
893:11477488
856:34995643
809:34787078
732:35360167
673:34787078
614:18479218
376:oxytocin
275:Location
261:appetite
253:hormones
221:oxytocin
119:NeuroLex
1098:2849853
1019:1642692
979:4762486
971:3044525
800:8631797
723:8964012
664:8631797
605:2682920
519:stomach
508:relaxin
311:Neurons
213:neurons
203:in the
201:nucleus
100:D010286
72:Details
1175:
1146:
1105:
1095:
1056:
1026:
1016:
977:
969:
934:
926:
891:
854:
846:
807:
797:
789:
730:
720:
712:
671:
661:
653:
612:
602:
319:whose
269:stress
1046:(PDF)
975:S2CID
932:S2CID
769:eLife
633:eLife
558:from
321:axons
199:is a
195:, or
172:[
161:62320
83:Latin
1173:ISBN
1144:PMID
1103:PMID
1054:PMID
1024:PMID
967:PMID
924:PMID
889:PMID
852:PMID
844:ISSN
805:PMID
787:ISSN
728:PMID
710:ISSN
669:PMID
651:ISSN
610:PMID
554:and
538:MC4R
506:and
468:and
443:and
422:ACTH
378:and
366:The
343:and
197:PVH)
149:5722
132:TA98
95:MeSH
1134:doi
1130:159
1093:PMC
1085:doi
1014:PMC
1006:doi
1002:361
959:doi
916:doi
879:doi
836:doi
795:PMC
777:doi
718:PMC
700:doi
659:PMC
641:doi
600:PMC
592:doi
441:TSH
193:PVA
189:PVN
156:FMA
144:TA2
112:387
1193::
1142:.
1128:.
1124:.
1101:.
1091:.
1081:31
1079:.
1075:.
1048:.
1022:.
1012:.
1000:.
996:.
973:.
965:.
955:20
953:.
930:.
922:.
912:76
910:.
887:.
873:.
850:.
842:.
832:65
830:.
826:.
803:.
793:.
785:.
773:10
771:.
767:.
740:^
726:.
716:.
708:.
698:.
696:16
694:.
690:.
667:.
657:.
649:.
637:10
635:.
631:.
608:.
598:.
588:12
586:.
582:.
562:.
382:.
374::
347:.
327:,
271:.
263:,
259:,
191:,
121:ID
1181:.
1150:.
1136::
1109:.
1087::
1060:.
1030:.
1008::
981:.
961::
938:.
918::
895:.
881::
858:.
838::
811:.
779::
734:.
702::
675:.
643::
616:.
594::
486:.
187:(
176:]
29:.
22:.
Text is available under the Creative Commons Attribution-ShareAlike License. Additional terms may apply.