175:
199:
183:
142:
36:
351:(usually the earlobe, side or top) to straighten the ear canal, and then inserts the ear speculum side of the otoscope into the outer ear. It is important to brace the index or little finger of the hand holding the otoscope against the patient's head to avoid injuring the ear canal. The examiner then looks through the lens on the rear of the instrument to see inside the ear canal.
191:
426:(subspecialty ear doctors). Their widespread adoption in general medicine is hindered by cost and lack of familiarity among pediatric and general medicine professors in physician training programs. Studies have shown that reliance on a monocular otoscope to diagnose ear disease results in a more than 50% chance of misdiagnosis, as compared to binocular microscopic otoscopy.
446:. This is done by assessing the eardrum's contour (normal, retracted, full, or bulging), its color (gray, yellow, pink, amber, white, red, or blue), its translucency (translucent, semi-opaque, opaque), and its mobility (normal, increased, decreased, or absent). The pneumatic otoscope is the standard tool used in diagnosing
453:
The pneumatic otoscope has a pneumatic (diagnostic) head, which contains a lens, an enclosed light source, and a nipple for attaching a rubber bulb and tubing. By gently squeezing and releasing the bulb in rapid succession, the degree of eardrum mobility in response to positive and negative pressure
410:
and their head is tilted, which keeps the head stable and enables better lighting. The binocular view enables depth perception, which makes removal of earwax or other obstructing materials easier and less hazardous. The microscope also has up to 40× magnification, allowing more detailed viewing of
354:
In many models, the examiner can remove the lens and insert instruments like specialized suction tips through the otoscope into the ear canal, such as for removing earwax. Most models also have an insertion point for a bulb that pushes air through the speculum
367:
Many otoscopes for doctors' offices are wall-mounted, with an electrical cord providing power from an electric outlet. Portable otoscopes powered by batteries (usually rechargeable) in the handle are also available.
305:, and various ear diseases, can obscure the view of the eardrum and thus compromise the value of otoscopy done with a common otoscope, but can confirm the presence of obstructing symptoms.
462:. Using a rubber-tipped speculum or adding a small sleeve of rubber tubing at the end of a plastic speculum, can help improve the airtight seal and also help avoid injuring the patient.
402:
Another method of performing otoscopy (visualization of the ear) is by using a binocular (two-eyed) microscope in conjunction with a larger plastic or metal ear
406:, which provides a much larger field of view. The microscope is suspended from a stand, which frees up both of the examiner's hands; the patient is placed in a
690:
635:
955:
477:(creation of incision in the eardrum). The surgical head consists of an unenclosed light source and a lens that can swivel over a wide arc.
683:
337:
565:
676:
399:. These provide a two-dimensional view of the ear canal and its contents, and usually at least a portion of the eardrum.
610:
881:
100:
527:
119:
72:
1021:
79:
57:
517:
898:
642:
86:
755:
1149:
909:
465:
By replacing the pneumatic head with a surgical head, the pneumatic otoscope can also be used to clear
415:
of the canal skin). Subtle changes in the anatomy can also be more easily detected and interpreted.
68:
53:
760:
17:
1139:
874:
777:
324:
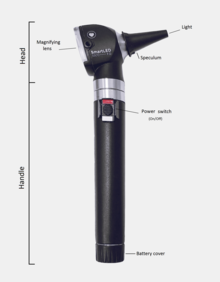
The most common otoscopes consist of a handle and a head. The head contains a light source and a
46:
636:"A View Through THE OTOSCOPE: Distinguishing Acute Otitis Media From Otitis Media With Effusion"
230:, or for evaluating specific ear complaints, such as earaches, sense of fullness in the ear, or
309:
784:
1072:
384:
227:
8:
1144:
772:
455:
403:
313:
308:
Otoscopes can also be used to examine patients' noses (avoiding the need for a separate
867:
841:
794:
668:
341:
279:
93:
1059:
965:
947:
602:
523:
519:
Medical-Surgical
Nursing - E-Book: Patient-Centered Collaborative Care, Single Volume
454:
can be observed. The head is designed so that an airtight chamber is produced when a
419:
252:
799:
555:
492:
388:
325:
174:
1087:
470:
407:
348:
722:
594:
372:
269:
215:
198:
1133:
993:
927:
750:
283:
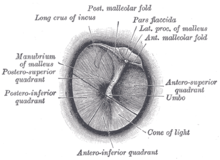
261:, its characteristics can indicate various diseases of the middle ear space.
182:
141:
1082:
1039:
1034:
1006:
983:
978:
846:
820:
789:
606:
447:
302:
264:
231:
1092:
1077:
1067:
1055:
1001:
937:
932:
922:
917:
767:
699:
560:
486:
474:
340:(front) end of the otoscope has an attachment for disposable plastic ear
1113:
1044:
1029:
1011:
973:
737:
727:
706:
662:
443:
392:
258:
164:
1108:
890:
714:
702:
495: – device used to take photos of the inside of a patient's mouth
459:
423:
411:
the entire ear canal, and of the entire eardrum (unless prevented by
396:
273:
248:
219:
257:
As the eardrum is the border between the external ear canal and the
35:
1118:
942:
815:
742:
439:
331:
290:
263:
Otoscopic examination can help diagnose conditions such as acute
223:
152:
466:
412:
298:
859:
190:
294:
698:
418:
Traditionally, binocular microscopes are only used by
497:
Pages displaying wikidata descriptions as a fallback
515:
336:to help illuminate and enlarge ear structures. The
247:An otoscope enables viewing and examination of the
60:. Unsourced material may be challenged and removed.
665:– Pictures and information about antique otoscopes
516:Ignatavicius, Donna D.; Workman, M. Linda (2013).
194:Right tympanic membrane as seen through a speculum
146:An otoscope, with a tube of disposable tips behind
593:Falkson, Samuel R.; Tadi, Prasanna (2022-10-31),
458:is attached and fitted snugly into the patient's
1131:
218:used by healthcare professionals to examine the
956:Endoscopic retrograde cholangiopancreatography
469:from the ear canal, and to perform diagnostic
875:
684:
592:
473:(drainage of fluid from the middle ear) or
882:
868:
691:
677:
522:. Elsevier Health Sciences. p. 1083.
378:
202:A doctor performs an otoscopy examination.
140:
120:Learn how and when to remove this message
422:(ear, nose, and throat specialists) and
197:
189:
181:
173:
356:
14:
1132:
226:. This may be done as part of routine
863:
672:
429:
312:) and upper throats (by removing the
27:Medical device for examining the ears
630:
628:
626:
588:
586:
584:
582:
550:
548:
546:
58:adding citations to reliable sources
29:
24:
25:
1161:
656:
623:
579:
543:
442:for assessing the health of the
359:) for testing eardrum mobility.
347:The examiner first pulls on the
319:
34:
613:from the original on 2024-06-09
568:from the original on 2024-06-09
450:(infection of the middle ear).
267:(infection of the middle ear),
45:needs additional citations for
641:. January 2000. Archived from
509:
371:Otoscopes are often sold with
13:
1:
889:
502:
7:
756:Eustachian tube dysfunction
480:
242:
10:
1166:
1022:Female reproductive system
910:Esophagogastroduodenoscopy
280:perforation of the eardrum
1101:
1053:
1020:
992:
964:
897:
829:
808:
736:
713:
601:, StatPearls Publishing,
489: – Diagnostic device
178:Components of an otoscope
161:
151:
139:
134:
761:Patulous Eustachian tube
362:
237:
186:Anatomy of the human ear
438:is used to examine the
383:Most otoscopes used in
379:Monocular and binocular
899:Gastrointestinal tract
556:"Otoscope examination"
203:
195:
187:
179:
785:Middle ear barotrauma
387:, pediatric offices,
375:as a diagnostic set.
293:(earwax), shed skin,
228:physical examinations
201:
193:
185:
177:
1073:Laparoscopic surgery
778:Gradenigo's syndrome
54:improve this article
334:(3× magnification),
330:typically around 8
795:Perforated eardrum
436:pneumatic otoscope
430:Pneumatic otoscope
357:pneumatic otoscopy
272:(infection of the
204:
196:
188:
180:
1150:Medical equipment
1127:
1126:
966:Respiratory tract
948:Capsule endoscopy
857:
856:
420:otolaryngologists
397:monocular devices
253:tympanic membrane
172:
171:
130:
129:
122:
104:
16:(Redirected from
1157:
884:
877:
870:
861:
860:
800:Tympanosclerosis
773:Bezold's abscess
693:
686:
679:
670:
669:
650:
649:
647:
640:
632:
621:
620:
619:
618:
590:
577:
576:
574:
573:
552:
541:
540:
538:
536:
513:
498:
493:Intraoral camera
389:general practice
335:
289:The presence of
277:
262:
165:edit on Wikidata
144:
132:
131:
125:
118:
114:
111:
105:
103:
62:
38:
30:
21:
1165:
1164:
1160:
1159:
1158:
1156:
1155:
1154:
1130:
1129:
1128:
1123:
1097:
1088:Mediastinoscopy
1049:
1016:
988:
960:
893:
888:
858:
853:
825:
804:
740:
732:
709:
700:Diseases of the
697:
659:
654:
653:
645:
638:
634:
633:
624:
616:
614:
591:
580:
571:
569:
554:
553:
544:
534:
532:
530:
514:
510:
505:
496:
483:
471:tympanocentesis
432:
408:supine position
385:emergency rooms
381:
373:ophthalmoscopes
365:
329:
326:magnifying lens
322:
268:
256:
245:
240:
168:
147:
126:
115:
109:
106:
63:
61:
51:
39:
28:
23:
22:
15:
12:
11:
5:
1163:
1153:
1152:
1147:
1142:
1140:Ear procedures
1125:
1124:
1122:
1121:
1116:
1111:
1105:
1103:
1099:
1098:
1096:
1095:
1090:
1085:
1080:
1075:
1070:
1064:
1062:
1051:
1050:
1048:
1047:
1042:
1037:
1032:
1026:
1024:
1018:
1017:
1015:
1014:
1009:
1004:
998:
996:
990:
989:
987:
986:
981:
976:
970:
968:
962:
961:
959:
958:
951:
950:
945:
940:
935:
930:
925:
920:
913:
912:
907:
903:
901:
895:
894:
887:
886:
879:
872:
864:
855:
854:
852:
851:
850:
849:
844:
833:
831:
827:
826:
824:
823:
818:
812:
810:
806:
805:
803:
802:
797:
792:
787:
782:
781:
780:
775:
765:
764:
763:
753:
747:
745:
734:
733:
731:
730:
725:
723:Otitis externa
719:
717:
711:
710:
696:
695:
688:
681:
673:
667:
666:
658:
657:External links
655:
652:
651:
648:on 2016-03-03.
622:
578:
564:. 2022-05-30.
542:
528:
507:
506:
504:
501:
500:
499:
490:
482:
479:
431:
428:
380:
377:
364:
361:
321:
318:
310:nasal speculum
303:foreign bodies
270:otitis externa
244:
241:
239:
236:
216:medical device
170:
169:
162:
159:
158:
155:
149:
148:
145:
137:
136:
128:
127:
42:
40:
33:
26:
9:
6:
4:
3:
2:
1162:
1151:
1148:
1146:
1143:
1141:
1138:
1137:
1135:
1120:
1117:
1115:
1112:
1110:
1107:
1106:
1104:
1100:
1094:
1091:
1089:
1086:
1084:
1081:
1079:
1076:
1074:
1071:
1069:
1066:
1065:
1063:
1061:
1057:
1052:
1046:
1043:
1041:
1038:
1036:
1033:
1031:
1028:
1027:
1025:
1023:
1019:
1013:
1010:
1008:
1005:
1003:
1000:
999:
997:
995:
994:Urinary tract
991:
985:
982:
980:
977:
975:
972:
971:
969:
967:
963:
957:
953:
952:
949:
946:
944:
941:
939:
936:
934:
931:
929:
928:Sigmoidoscopy
926:
924:
921:
919:
915:
914:
911:
908:
905:
904:
902:
900:
896:
892:
885:
880:
878:
873:
871:
866:
865:
862:
848:
845:
843:
840:
839:
838:
835:
834:
832:
828:
822:
819:
817:
814:
813:
811:
807:
801:
798:
796:
793:
791:
788:
786:
783:
779:
776:
774:
771:
770:
769:
766:
762:
759:
758:
757:
754:
752:
751:Cholesteatoma
749:
748:
746:
744:
739:
735:
729:
726:
724:
721:
720:
718:
716:
712:
708:
704:
701:
694:
689:
687:
682:
680:
675:
674:
671:
664:
661:
660:
644:
637:
631:
629:
627:
612:
608:
604:
600:
596:
589:
587:
585:
583:
567:
563:
562:
557:
551:
549:
547:
531:
529:9780323293440
525:
521:
520:
512:
508:
494:
491:
488:
485:
484:
478:
476:
472:
468:
463:
461:
457:
451:
449:
445:
441:
437:
427:
425:
421:
416:
414:
409:
405:
400:
398:
394:
390:
386:
376:
374:
369:
360:
358:
352:
350:
345:
343:
339:
333:
327:
320:Method of use
317:
315:
311:
306:
304:
300:
297:, canal skin
296:
292:
287:
285:
284:cholesteatoma
281:
275:
271:
266:
260:
254:
250:
235:
233:
229:
225:
221:
217:
213:
209:
200:
192:
184:
176:
166:
160:
156:
154:
150:
143:
138:
133:
124:
121:
113:
102:
99:
95:
92:
88:
85:
81:
78:
74:
71: –
70:
66:
65:Find sources:
59:
55:
49:
48:
43:This article
41:
37:
32:
31:
19:
1083:Thoracoscopy
1040:Falloposcopy
1035:Hysteroscopy
1007:Ureteroscopy
984:Bronchoscopy
979:Laryngoscopy
847:tympanometry
836:
821:Hearing loss
790:Otitis media
643:the original
615:, retrieved
598:
570:. Retrieved
559:
533:. Retrieved
518:
511:
464:
452:
448:otitis media
435:
433:
417:
401:
382:
370:
366:
353:
346:
323:
307:
288:
265:otitis media
246:
232:hearing loss
211:
207:
205:
116:
107:
97:
90:
83:
76:
64:
52:Please help
47:verification
44:
1093:Coelioscopy
1078:Arthroscopy
1068:Laparoscopy
1002:Nephroscopy
954:Accessory:
938:Proctoscopy
933:Pouchoscopy
923:Colonoscopy
918:Enteroscopy
768:Mastoiditis
561:MedlinePlus
487:Head mirror
475:myringotomy
255:(eardrum).
1145:Endoscopes
1134:Categories
1114:Angioscopy
1045:Culdoscopy
1030:Colposcopy
1012:Cystoscopy
974:Rhinoscopy
738:Middle ear
728:Otomycosis
707:middle ear
617:2024-06-09
599:StatPearls
595:"Otoscopy"
572:2024-06-09
503:References
444:middle ear
424:otologists
393:internists
278:traumatic
259:middle ear
80:newspapers
69:"Otoscope"
1109:Fetoscopy
891:Endoscopy
842:pneumatic
715:Outer ear
460:ear canal
391:, and by
274:outer ear
249:ear canal
220:ear canal
212:auriscope
157:auriscope
110:June 2024
1119:Otoscopy
1060:incision
943:Anoscopy
837:Otoscope
816:Ear pain
809:Symptoms
611:archived
607:32310550
566:Archived
481:See also
456:speculum
404:speculum
332:diopters
314:speculum
243:Function
208:otoscope
153:Synonyms
135:Otoscope
18:Otoscopy
1054:Closed
916:Lower:
743:mastoid
663:Phisick
440:eardrum
342:specula
291:cerumen
224:eardrum
94:scholar
1056:cavity
906:Upper:
605:
535:1 June
526:
467:earwax
338:distal
282:, and
96:
89:
82:
75:
67:
1102:Other
830:Tests
703:outer
646:(PDF)
639:(PDF)
413:edema
363:Types
349:pinna
344:.
316:).
299:edema
238:Usage
214:is a
163:[
101:JSTOR
87:books
1058:via
741:and
705:and
603:PMID
537:2019
524:ISBN
434:The
395:are
286:.
251:and
234:.
222:and
73:news
295:pus
210:or
206:An
56:by
1136::
625:^
609:,
597:,
581:^
558:.
545:^
328:,
301:,
276:),
883:e
876:t
869:v
692:e
685:t
678:v
575:.
539:.
355:(
167:]
123:)
117:(
112:)
108:(
98:·
91:·
84:·
77:·
50:.
20:)
Text is available under the Creative Commons Attribution-ShareAlike License. Additional terms may apply.