29:
272:
hydrolysis, performs a power stroke associated with release of hydrolysis products, and detaches from actin upon binding with new ATP. The detached myosin head then hydrolyses ATP, and performs a recovery stroke to restore its initial position. The strokes have been suggested to result from rotation of the lever arm domain around the converter domain, while the catalytic domain remains rigid.
271:
The globular head is well conserved, and is key to contraction. Muscle contraction results from an attachment–detachment cycle between the myosin heads extending from myosin filaments and the sites on actin filaments. The myosin head first attaches to actin together with the products of ATP
633:
Minoda H, Okabe T, Inayoshi Y, Miyakawa T, Miyauchi Y, Tanokura M, Katayama E, Wakabayashi T, Akimoto T, Sugi H (February 2011). "Electron microscopic evidence for the myosin head lever arm mechanism in hydrated myosin filaments using the gas environmental chamber".
435:
Rayment I, Rypniewski WR, Schmidt-Bäse K, Smith R, Tomchick DR, Benning MM, Winkelmann DA, Wesenberg G, Holden HM (July 1993). "Three-dimensional structure of myosin subfragment-1: a molecular motor".
478:
Rayment I, Holden HM, Whittaker M, Yohn CB, Lorenz M, Holmes KC, Milligan RA (July 1993). "Structure of the actin-myosin complex and its implications for muscle contraction".
165:
326:"Human embryonic myosin heavy chain cDNA. Interspecies sequence conservation of the myosin rod, chromosomal locus and isoform specific transcription of the gene"
289:
Hayashida M, Maita T, Matsuda G (July 1991). "The primary structure of skeletal muscle myosin heavy chain: I. Sequence of the amino-terminal 23 kDa fragment".
636:
521:
Molloy JE, Burns JE, Kendrick-Jones J, Tregear RT, White DC (November 1995). "Movement and force produced by a single myosin head".
221:
and most myosin molecules are composed of a head, neck, and tail domain; the myosin head binds to thin filamentous actin, and uses
101:
185:
324:
Eller M, Stedman HH, Sylvester JE, Fertels SH, Wu QL, Raychowdhury MK, Rubinstein NA, Kelly AM, Sarkar S (October 1989).
173:
261:
249:
169:
121:
114:
126:
691:
237:
rod-like tail at the C-terminal, although some forms have a globular region in their C-terminal.
233:
light chains. The heavy chain can be subdivided into the globular head at the N-terminal and the
225:
to generate force and "walk" along the thin filament. Myosin exists as a hexamer of two heavy
589:
532:
487:
444:
386:
152:
302:
8:
580:
593:
536:
491:
448:
390:
610:
575:
556:
355:
210:
409:
375:"Conserved protein domains in a myosin heavy chain gene from Dictyostelium discoideum"
374:
653:
615:
548:
503:
460:
414:
347:
342:
325:
306:
160:
106:
359:
264:
of the head portion of myosin has been determined and a model for the actin-myosin
57:
645:
605:
597:
560:
540:
523:
495:
452:
404:
394:
337:
298:
218:
148:
70:
677:
265:
230:
82:
601:
649:
222:
685:
499:
456:
399:
657:
619:
245:
552:
507:
464:
418:
351:
310:
110:
234:
202:
576:"Single-molecule measurement of the stiffness of the rigor myosin head"
94:
544:
673:
574:
Lewalle A, Steffen W, Stevenson O, Ouyang Z, Sleep J (March 2008).
373:
Warrick HM, De
Lozanne A, Leinwand LA, Spudich JA (December 1986).
241:
77:
434:
226:
89:
520:
372:
257:
206:
180:
28:
256:
to convert chemical energy, in the form of ATP, to mechanical
573:
253:
214:
323:
669:
632:
142:
64:
52:
477:
668:
This article incorporates text from the public domain
288:
637:
683:
430:
428:
217:. Myosin is the major component of the thick
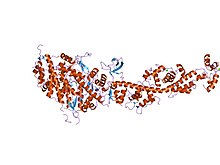
33:Scallop myosin in the near-rigor conformation
626:
567:
514:
471:
425:
366:
317:
282:
27:
609:
408:
398:
341:
213:, by sliding over thin myofilaments of
684:
303:10.1093/oxfordjournals.jbchem.a123543
248:for by a multi-gene family. Myosin
229:, two alkali light chains, and two
13:
14:
703:
1:
275:
240:There are many cell-specific
137:Available protein structures:
379:Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U.S.A
343:10.1016/0014-5793(89)81710-7
7:
602:10.1529/biophysj.107.119396
10:
708:
667:
650:10.1016/j.bbrc.2011.01.087
201:is the part of the thick
179:
159:
141:
136:
132:
120:
100:
88:
76:
63:
51:
43:
38:
26:
21:
244:of myosin heavy chains,
500:10.1126/science.8316858
457:10.1126/science.8316857
400:10.1073/pnas.83.24.9433
268:has been constructed.
16:Part of myofilaments
594:2008BpJ....94.2160L
581:Biophysical Journal
537:1995Natur.378..209M
492:1993Sci...261...58R
449:1993Sci...261...50R
391:1986PNAS...83.9433W
211:muscle contraction
195:
194:
191:
190:
186:structure summary
699:
662:
661:
630:
624:
623:
613:
571:
565:
564:
545:10.1038/378209a0
531:(6553): 209–12.
518:
512:
511:
475:
469:
468:
432:
423:
422:
412:
402:
370:
364:
363:
345:
321:
315:
314:
286:
134:
133:
31:
19:
18:
707:
706:
702:
701:
700:
698:
697:
696:
692:Protein domains
682:
681:
680:
666:
665:
631:
627:
572:
568:
519:
515:
486:(5117): 58–65.
476:
472:
433:
426:
371:
367:
322:
318:
287:
283:
278:
34:
17:
12:
11:
5:
705:
695:
694:
664:
663:
625:
566:
513:
470:
443:(5117): 50–8.
424:
385:(24): 9433–7.
365:
316:
280:
279:
277:
274:
223:ATP hydrolysis
193:
192:
189:
188:
183:
177:
176:
163:
157:
156:
146:
139:
138:
130:
129:
124:
118:
117:
104:
98:
97:
92:
86:
85:
80:
74:
73:
68:
61:
60:
55:
49:
48:
45:
41:
40:
36:
35:
32:
24:
23:
15:
9:
6:
4:
3:
2:
704:
693:
690:
689:
687:
679:
675:
671:
659:
655:
651:
647:
643:
639:
638:
629:
621:
617:
612:
607:
603:
599:
595:
591:
588:(6): 2160–9.
587:
583:
582:
577:
570:
562:
558:
554:
550:
546:
542:
538:
534:
530:
526:
525:
517:
509:
505:
501:
497:
493:
489:
485:
481:
474:
466:
462:
458:
454:
450:
446:
442:
438:
431:
429:
420:
416:
411:
406:
401:
396:
392:
388:
384:
380:
376:
369:
361:
357:
353:
349:
344:
339:
336:(1–2): 21–8.
335:
331:
327:
320:
312:
308:
304:
300:
296:
292:
285:
281:
273:
269:
267:
263:
259:
255:
251:
247:
243:
238:
236:
232:
228:
224:
220:
216:
212:
209:that acts in
208:
204:
200:
187:
184:
182:
178:
175:
171:
167:
164:
162:
158:
154:
150:
147:
144:
140:
135:
131:
128:
125:
123:
119:
116:
112:
108:
105:
103:
99:
96:
93:
91:
87:
84:
81:
79:
75:
72:
69:
66:
62:
59:
56:
54:
50:
46:
42:
37:
30:
25:
20:
644:(4): 651–6.
641:
635:
628:
585:
579:
569:
528:
522:
516:
483:
479:
473:
440:
436:
382:
378:
368:
333:
329:
319:
294:
290:
284:
270:
239:
198:
196:
297:(1): 54–9.
235:coiled-coil
205:made up of
203:myofilament
199:myosin head
47:Myosin_head
39:Identifiers
22:Myosin_head
291:J. Biochem
276:References
260:. The 3-D
231:regulatory
149:structures
678:IPR001609
330:FEBS Lett
262:structure
250:interacts
219:filaments
95:PDOC00017
83:IPR001609
686:Category
674:InterPro
658:21281603
620:18065470
360:12047829
242:isoforms
166:RCSB PDB
78:InterPro
611:2257899
590:Bibcode
561:4334476
553:7477328
533:Bibcode
508:8316858
488:Bibcode
480:Science
465:8316857
445:Bibcode
437:Science
419:3540939
387:Bibcode
352:2806546
311:1939027
266:complex
127:cd00124
90:PROSITE
58:PF00063
656:
618:
608:
559:
551:
524:Nature
506:
463:
417:
410:387152
407:
358:
350:
309:
258:energy
227:chains
207:myosin
181:PDBsum
155:
145:
115:SUPFAM
71:CL0023
44:Symbol
557:S2CID
356:S2CID
254:actin
252:with
246:coded
215:actin
111:SCOPe
102:SCOP2
672:and
670:Pfam
654:PMID
616:PMID
549:PMID
504:PMID
461:PMID
415:PMID
348:PMID
307:PMID
197:The
174:PDBj
170:PDBe
153:ECOD
143:Pfam
107:1mys
67:clan
65:Pfam
53:Pfam
646:doi
642:405
606:PMC
598:doi
541:doi
529:378
496:doi
484:261
453:doi
441:261
405:PMC
395:doi
338:doi
334:256
299:doi
295:110
161:PDB
122:CDD
688::
676::
652:.
640:.
614:.
604:.
596:.
586:94
584:.
578:.
555:.
547:.
539:.
527:.
502:.
494:.
482:.
459:.
451:.
439:.
427:^
413:.
403:.
393:.
383:83
381:.
377:.
354:.
346:.
332:.
328:.
305:.
293:.
172:;
168:;
151:/
113:/
109:/
660:.
648::
622:.
600::
592::
563:.
543::
535::
510:.
498::
490::
467:.
455::
447::
421:.
397::
389::
362:.
340::
313:.
301::
Text is available under the Creative Commons Attribution-ShareAlike License. Additional terms may apply.