1877:
95:. The coarse problem, while cheaper to solve, is similar to the fine grid problem in that it also has short- and long-wavelength errors. It can also be solved by a combination of relaxation and appeal to still coarser grids. This recursive process is repeated until a grid is reached where the cost of direct solution there is negligible compared to the cost of one relaxation sweep on the fine grid. This multigrid cycle typically reduces all error components by a fixed amount bounded well below one, independent of the fine grid mesh size. The typical application for multigrid is in the numerical solution of
136:
2394:
models in science and engineering described by partial differential equations. In view of the subspace correction framework, BPX preconditioner is a parallel subspace correction method where as the classic V-cycle is a successive subspace correction method. The BPX-preconditioner is known to be naturally more parallel and in some applications more robust than the classic V-cycle multigrid method. The method has been widely used by researchers and practitioners since 1990.
1547:
2459:
as well as quasi-optimal spaces was derived. Also, they proved that, under appropriate assumptions, the abstract two-level AMG method converges uniformly with respect to the size of the linear system, the coefficient variation, and the anisotropy. Their abstract framework covers most existing AMG methods, such as classical AMG, energy-minimization AMG, unsmoothed and smoothed aggregation AMG, and spectral AMGe.
2451:(AMG) construct their hierarchy of operators directly from the system matrix. In classical AMG, the levels of the hierarchy are simply subsets of unknowns without any geometric interpretation. (More generally, coarse grid unknowns can be particular linear combinations of fine grid unknowns.) Thus, AMG methods become black-box solvers for certain classes of
2605:
that appear in the nearly singular operator) independent convergence rate of the multigrid method applied to such nearly singular systems, i.e., in each grid, a space decomposition based on which the smoothing is applied, has to be constructed so that the null space of the singular part of the nearly
2455:. AMG is regarded as advantageous mainly where geometric multigrid is too difficult to apply, but is often used simply because it avoids the coding necessary for a true multigrid implementation. While classical AMG was developed first, a related algebraic method is known as smoothed aggregation (SA).
204:
There are many choices of multigrid methods with varying trade-offs between speed of solving a single iteration and the rate of convergence with said iteration. The 3 main types are V-Cycle, F-Cycle, and W-Cycle. These differ in which and how many coarse-grain cycles are performed per fine iteration.
2458:
In an overview paper by
Jinchao Xu and Ludmil Zikatanov, the "algebraic multigrid" methods are understood from an abstract point of view. They developed a unified framework and existing algebraic multigrid methods can be derived coherently. Abstract theory about how to construct optimal coarse space
2393:
Originally described in Xu's Ph.D. thesis and later published in
Bramble-Pasciak-Xu, the BPX-preconditioner is one of the two major multigrid approaches (the other is the classic multigrid algorithm such as V-cycle) for solving large-scale algebraic systems that arise from the discretization of
209:, F-Cycle takes 83% more time to compute than a V-Cycle iteration while a W-Cycle iteration takes 125% more. If the problem is set up in a 3D domain, then a F-Cycle iteration and a W-Cycle iteration take about 64% and 75% more time respectively than a V-Cycle iteration ignoring
232:
Any geometric multigrid cycle iteration is performed on a hierarchy of grids and hence it can be coded using recursion. Since the function calls itself with smaller sized (coarser) parameters, the coarsest grid is where the recursion stops. In cases where the system has a high
1554:
This approach has the advantage over other methods that it often scales linearly with the number of discrete nodes used. In other words, it can solve these problems to a given accuracy in a number of operations that is proportional to the number of unknowns.
2600:
operator. There were many works to attempt to design a robust and fast multigrid method for such nearly singular problems. A general guide has been provided as a design principle to achieve parameters (e.g., mesh size and physical parameters such as
106:
may be recast as a multigrid method. In these cases, multigrid methods are among the fastest solution techniques known today. In contrast to other methods, multigrid methods are general in that they can treat arbitrary regions and
2912:
2439:, that is, it adjusts the grid as the computation proceeds, in a manner dependent upon the computation itself. The idea is to increase resolution of the grid only in regions of the solution where it is needed.
3238:
Young-Ju Lee, Jinbiao Wu, Jinchao Xu and Ludmil
Zikatanov, Robust Subspace Correction Methods for Nearly Singular Systems, Mathematical Models and Methods in Applied Sciences, Vol. 17, No 11, pp. 1937-1963
205:
The V-Cycle algorithm executes one coarse-grain V-Cycle. F-Cycle does a coarse-grain V-Cycle followed by a coarse-grain F-Cycle, while each W-Cycle performs two coarse-grain W-Cycles per iteration. For a
2495:
Nearly singular problems arise in a number of important physical and engineering applications. Simple, but important example of nearly singular problems can be found at the displacement formulation of
2447:
Practically important extensions of multigrid methods include techniques where no partial differential equation nor geometrical problem background is used to construct the multilevel hierarchy. Such
2351:
time as well as in the case where the multigrid method is used as a solver. Multigrid preconditioning is used in practice even for linear systems, typically with one cycle per iteration, e.g., in
2109:
2200:
2362:
If the matrix of the original equation or an eigenvalue problem is symmetric positive definite (SPD), the preconditioner is commonly constructed to be SPD as well, so that the standard
1873:
1762:
1973:
2032:
2429:. These wavelet methods can be combined with multigrid methods. For example, one use of wavelets is to reformulate the finite element approach in terms of a multilevel method.
1676:
2526:
2606:
singular operator has to be included in the sum of the local null spaces, the intersection of the null space and the local spaces resulting from the space decompositions.
2546:
2308:
2370:
can still be used. Such imposed SPD constraints may complicate the construction of the preconditioner, e.g., requiring coordinated pre- and post-smoothing. However,
1911:
1630:
1603:
2349:
2261:
2232:
87:
The main idea of multigrid is to accelerate the convergence of a basic iterative method (known as relaxation, which generally reduces short-wavelength error) by a
2499:
for nearly incompressible materials. Typically, the major problem to solve such nearly singular systems boils down to treat the nearly singular operator given by
1702:
2594:
2566:
2136:
1805:
1782:
1576:
221:, W-Cycle can show superiority in its rate of convergence per iteration over F-Cycle. The choice of smoothing operators are extremely diverse as they include
115:
or other special properties of the equation. They have also been widely used for more-complicated non-symmetric and nonlinear systems of equations, like the
3399:
2378:
76:
exhibit different rates of convergence for short- and long-wavelength components, suggesting these different scales be treated differently, as in a
2862:
Bramble, James H., Joseph E. Pasciak, and
Jinchao Xu. "Parallel multilevel preconditioners." Mathematics of Computation 55, no. 191 (1990): 1–22.
3294:
3363:
206:
2791:
Efficient solution of symmetric eigenvalue problems using multigrid preconditioners in the locally optimal block conjugate gradient method
237:, the correction procedure is modified such that only a fraction of the prolongated coarser grid solution is added onto the finer grid.
3289:
3490:
2941:
Hyperbolic problems: theory, numerics, applications: proceedings of the Ninth
International Conference on Hyperbolic Problems of 2002
3440:
2411:
3869:
3416:
3390:
2403:
112:
96:
3714:
3484:
3332:
3149:
3122:
3093:
3064:
3037:
3010:
2977:
2948:
2922:
2894:
2774:
2747:
2691:
2660:
2633:
1550:
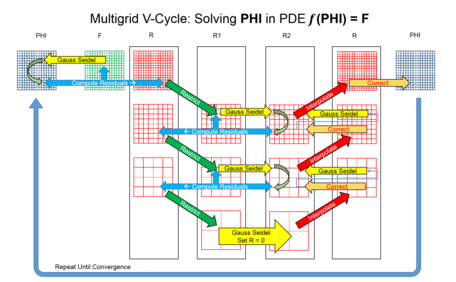
Assuming a 2-dimensional problem setup, the computation moves across grid hierarchy differently for various multigrid cycles.
3784:
3641:
3496:
2402:
Multigrid methods can be generalized in many different ways. They can be applied naturally in a time-stepping solution of
2040:
3315:
R. P. Fedorenko (1964), The speed of convergence of one iterative process. USSR Comput. Math. Math. Phys. 4, p. 227.
2144:
2871:
Xu, Jinchao. "Iterative methods by space decomposition and subspace correction." SIAM review 34, no. 4 (1992): 581-613.
2790:
3302:
3189:
214:
1764:
is the ratio of grid points on "neighboring" grids and is assumed to be constant throughout the grid hierarchy, and
3692:
3358:
102:
Multigrid methods can be applied in combination with any of the common discretization techniques. For example, the
3709:
3349:
Repository for multigrid, multilevel, multiscale, aggregation, defect correction, and domain decomposition methods
3843:
3629:
1558:
Assume that one has a differential equation which can be solved approximately (with a given accuracy) on a grid
1059:% Recursive W-cycle multigrid for solving the Poisson equation (\nabla^2 phi = f) on a uniform grid of spacing h
564:% Recursive F-cycle multigrid for solving the Poisson equation (\nabla^2 phi = f) on a uniform grid of spacing h
270:% Recursive V-Cycle Multigrid for solving the Poisson equation (\nabla^2 phi = f) on a uniform grid of spacing h
3610:
3599:
3576:
1813:
1707:
3582:
2407:
1919:
179:
169:
1981:
3699:
3664:
2569:
2355:. Its main advantage versus a purely multigrid solver is particularly clear for nonlinear problems, e.g.,
3864:
3704:
3383:
3821:
3806:
3682:
3368:
1635:
3468:
3448:
3430:
3263:
3252:
2502:
1787:
The following recurrence relation is then obtained for the effort of obtaining the solution on grid
3791:
3677:
3407:
2597:
2436:
542:. This multigrid cycle is slower than V-Cycle per iteration but does result in faster convergence.
143:
There are many variations of multigrid algorithms, but the common features are that a hierarchy of
65:
2531:
1033:
Similarly the procedures can modified as shown in the MATLAB style pseudo code for 1 iteration of
3833:
3811:
3796:
3779:
3687:
3672:
3588:
3453:
2573:
2476:
2472:
159:
124:
3027:
3001:. Vol. 20 of Lecture Notes in Computational Science and Engineering. Springer. p. 140
2650:
2266:
91:
correction of the fine grid solution approximation from time to time, accomplished by solving a
3753:
3524:
3376:
2487:
parallel-in-time integration method can also be reformulated as a two-level multigrid in time.
2471:. Of particular interest here are parallel-in-time multigrid methods: in contrast to classical
2385:
for symmetric eigenvalue problems are all shown to be robust if the preconditioner is not SPD.
3139:
3081:
2994:
2932:
2882:
2853:
Xu, Jinchao. Theory of multilevel methods. Vol. 8924558. Ithaca, NY: Cornell
University, 1989.
2677:
3801:
3647:
3563:
3110:
3054:
2965:
2623:
2468:
103:
53:
28:
3164:
Xu, J. and
Zikatanov, L., 2017. Algebraic multigrid methods. Acta Numerica, 26, pp.591-721.
1880:
Example of
Convergence Rates of Multigrid Cycles in comparison to other smoothing operators.
3838:
3511:
3264:
On the convergence of a relaxation method with natural constraints on the elliptic operator
2712:
1889:
1608:
1581:
210:
120:
2325:
2237:
2208:
8:
3605:
3519:
2419:
1681:
69:
2716:
3828:
3769:
2836:
2816:
2602:
2579:
2551:
2480:
2363:
2318:
A multigrid method with an intentionally reduced tolerance can be used as an efficient
2121:
1876:
1790:
1767:
1561:
108:
37:
3874:
3458:
3328:
3298:
3185:
3145:
3118:
3089:
3060:
3033:
3006:
2973:
2944:
2918:
2890:
2770:
2743:
2687:
2656:
2629:
2496:
2415:
2367:
116:
73:
3353:
3320:
2840:
2805:"Nonsymmetric Preconditioning for Conjugate Gradient and Steepest Descent Methods 1"
244:
These steps can be used as shown in the MATLAB style pseudo code for 1 iteration of
3774:
3653:
3621:
3221:
2826:
2374:
2115:
234:
213:. Typically, W-Cycle produces similar convergence to F-Cycle. However, in cases of
155:
77:
218:
3816:
3759:
3748:
2764:
2731:
2452:
2371:
2319:
1784:
is some constant modeling the effort of computing the result for one grid point.
222:
2831:
2804:
3594:
3541:
226:
144:
92:
81:
61:
3177:
2322:
for an external iterative solver, e.g., The solution may still be obtained in
3858:
3463:
186:
3635:
3552:
3529:
3319:
Press, W. H.; Teukolsky, S. A.; Vetterling, W. T.; Flannery, B. P. (2007).
3225:
2936:
2887:
Numerical solution of partial differential equations on parallel computers
194:– interpolating a correction computed on a coarser grid into a finer grid.
135:
3546:
3424:
3269:
139:
Visualization of iterative
Multigrid algorithm for fast O(n) convergence.
3398:
3137:
3079:
3025:
2648:
3309:
3273:
3165:
2880:
2356:
3259:
2803:
Bouwmeester, Henricus; Dougherty, Andrew; Knyazev, Andrew V. (2015).
57:
49:
3287:
William L. Briggs, Van Emden Henson, and Steve F. McCormick (2000),
1374:% stop recursion at smallest grid size, otherwise continue recursion
1173:% stop recursion at smallest grid size, otherwise continue recursion
879:% stop recursion at smallest grid size, otherwise continue recursion
678:% stop recursion at smallest grid size, otherwise continue recursion
384:% stop recursion at smallest grid size, otherwise continue recursion
80:
approach to multigrid. MG methods can be used as solvers as well as
2679:
Multigrid finite element methods for electromagnetic field modeling
2484:
2426:
2821:
3732:
2793:. Electronic Transactions on Numerical Analysis, 15, 38–55, 2003.
3318:
2263:
i.e. W-cycle multigrid used on a 1D problem; it would result in
2234:
time. It should be mentioned that there is one exception to the
1546:
3571:
2970:
Multiscale and multiresolution methods: theory and applications
2382:
200:– Adding prolongated coarser grid solution onto the finer grid.
2621:
3321:"Section 20.6. Multigrid Methods for Boundary Value Problems"
3310:
A relaxation method for solving elliptic difference equations
3212:
Horton, Graham (1992). "The time-parallel multigrid method".
2467:
Multigrid methods have also been adopted for the solution of
2352:
2930:
2675:
3726:
3720:
3535:
2802:
2528:
robustly with respect to the positive, but small parameter
1037:
for an even superior rate of convergence in certain cases:
2995:"Wavelet-based numerical homogenization with applications"
2992:
154:– reducing high frequency errors, for example using a few
3274:
Multi-Level
Adaptive Solutions to Boundary-Value Problems
3182:
Computing Methods in Applied Sciences and Engineering, VI
2914:
Computational fluid dynamics: principles and applications
2490:
3348:
2997:. In Timothy J. Barth; Tony Chan; Robert Haimes (eds.).
2968:. In Timothy J. Barth; Tony Chan; Robert Haimes (eds.).
2933:"Multigrid for Atmospheric Data Assimilation: Analysis"
3327:(3rd ed.). New York: Cambridge University Press.
2881:
F. Hülsemann; M. Kowarschik; M. Mohr; U. Rüde (2006).
2414:
is underway. Multigrid methods can also be applied to
64:. They are an example of a class of techniques called
3138:
U. Trottenberg; C. W. Oosterlee; A. Schüller (2001).
3080:
U. Trottenberg; C. W. Oosterlee; A. Schüller (2001).
3026:
U. Trottenberg; C. W. Oosterlee; A. Schüller (2001).
2649:
U. Trottenberg; C. W. Oosterlee; A. Schüller (2001).
2582:
2554:
2534:
2505:
2425:
Another set of multiresolution methods is based upon
2328:
2269:
2240:
2211:
2147:
2124:
2043:
1984:
1922:
1892:
1816:
1793:
1770:
1710:
1684:
1638:
1611:
1584:
1564:
3400:
Numerical methods for partial differential equations
3253:
An iterative method of solving elliptic net problems
2406:, or they can be applied directly to time-dependent
2388:
2104:{\displaystyle W_{1}=KN_{1}\sum _{p=0}^{n}\rho ^{p}}
2195:{\displaystyle W_{1}<KN_{1}{\frac {1}{1-\rho }}}
3325:Numerical Recipes: The Art of Scientific Computing
2588:
2560:
2540:
2520:
2343:
2302:
2255:
2226:
2194:
2130:
2103:
2026:
1967:
1905:
1867:
1799:
1776:
1756:
1696:
1670:
1624:
1597:
1570:
3312:. USSR Comput. Math. Math. Phys. 1, p. 1092.
1605:. Assume furthermore that a solution on any grid
3856:
2625:Practical Fourier analysis for multigrid methods
2397:
147:(grids) is considered. The important steps are:
3115:Matrix-based multigrid: theory and applications
1886:And in particular, we find for the finest grid
3295:Society for Industrial and Applied Mathematics
2885:. In Are Magnus Bruaset; Aslak Tveito (eds.).
3384:
3108:
3052:
2762:
2738:. McGraw-Hill Higher Education. p. 478
2736:Scientific Computing: An Introductory Survey
2462:
2442:
2313:
3255:. USSR Comp. Math. Math. Phys. 11, 171–182.
3214:Communications in Applied Numerical Methods
2966:"Multiscale scientific computation: review"
2963:
2729:
1978:Combining these two expressions (and using
3391:
3377:
2910:
3266:. USSR Comp. Math. Math. Phys. 6, 101–13.
3175:
2830:
2820:
2622:Roman Wienands; Wolfgang Joppich (2005).
2412:hyperbolic partial differential equations
2410:. Research on multilevel techniques for
1868:{\displaystyle W_{k}=W_{k+1}+\rho KN_{k}}
2404:parabolic partial differential equations
1875:
1757:{\displaystyle \rho =N_{i+1}/N_{i}<1}
1545:
134:
16:Method of solving differential equations
2676:Yu Zhu; Andreas C. Cangellaris (2006).
2205:that is, a solution may be obtained in
1968:{\displaystyle W_{1}=W_{2}+\rho KN_{1}}
97:elliptic partial differential equations
3857:
3211:
2999:Multiscale and Multiresolution Methods
2491:Multigrid for nearly singular problems
2483:in temporal direction. The well known
2027:{\displaystyle N_{k}=\rho ^{k-1}N_{1}}
1530:
3372:
3056:Numerical Analysis of Wavelet Methods
2993:Björn Engquist; Olof Runborg (2002).
2931:Achi Brandt and Rima Gandlin (2003).
1632:may be obtained with a given effort
72:of behavior. For example, many basic
68:, very useful in problems exhibiting
3642:Moving particle semi-implicit method
3553:Weighted essentially non-oscillatory
2766:An Introduction to Multigrid Methods
2706:
13:
3491:Finite-difference frequency-domain
2732:"Section 11.5.7 Multigrid Methods"
1678:from a solution on a coarser grid
14:
3886:
3342:
2789:Andrew V Knyazev, Klaus Neymeyr.
2389:Bramble–Pasciak–Xu preconditioner
1671:{\displaystyle W_{i}=\rho KN_{i}}
1578:with a given grid point density
172:after the smoothing operation(s).
2709:Analysis of the multigrid method
3844:Method of fundamental solutions
3630:Smoothed-particle hydrodynamics
3232:
3205:
3169:
3158:
3131:
3102:
3082:"Chapter 9: Adaptive Multigrid"
3073:
3046:
3019:
2986:
2957:
2903:
2874:
2865:
2856:
2707:Shah, Tasneem Mohammad (1989).
2521:{\displaystyle A+\varepsilon M}
3870:Partial differential equations
3485:Alternating direction-implicit
3178:"Parabolic multi-grid methods"
2883:"Parallel geometric multigrid"
2847:
2796:
2783:
2756:
2723:
2700:
2669:
2642:
2615:
2408:partial differential equations
2338:
2332:
2297:
2294:
2288:
2273:
2250:
2244:
2221:
2215:
1380:smallest_grid_size_is_achieved
1179:smallest_grid_size_is_achieved
885:smallest_grid_size_is_achieved
684:smallest_grid_size_is_achieved
390:smallest_grid_size_is_achieved
1:
3497:Finite-difference time-domain
3245:
2711:(Thesis). Oxford University.
2398:Generalized multigrid methods
1461:% Prolongation and correction
1260:% Prolongation and correction
966:% Prolongation and Correction
765:% Prolongation and Correction
471:% Prolongation and Correction
113:separability of the equations
3536:Advection upstream-splitting
3359:Algebraic multigrid tutorial
3176:Hackbusch, Wolfgang (1985).
2541:{\displaystyle \varepsilon }
130:
111:. They do not depend on the
7:
3547:Essentially non-oscillatory
3530:Monotonic upstream-centered
3251:G. P. Astrachancev (1971),
2889:. Birkhäuser. p. 165.
2832:10.1016/j.procs.2015.05.241
2449:algebraic multigrid methods
2381:for SPD linear systems and
2118:, we then find (for finite
99:in two or more dimensions.
10:
3891:
3807:Infinite difference method
3425:Forward-time central-space
3364:Links to AMG presentations
3278:Mathematics of Computation
2303:{\displaystyle O(Nlog(N))}
241:
3741:
3710:Poincaré–Steklov operator
3663:
3620:
3562:
3510:
3477:
3469:Method of characteristics
3439:
3415:
3406:
3293:(2nd ed.), Philadelphia:
2943:. Springer. p. 369.
2917:. Elsevier. p. 305.
2809:Procedia Computer Science
2628:. CRC Press. p. 17.
2463:Multigrid in time methods
2443:Algebraic multigrid (AMG)
2314:Multigrid preconditioning
1320:% Compute residual errors
1095:% Compute Residual Errors
825:% Compute residual errors
600:% Compute Residual Errors
538:The following represents
306:% Compute Residual Errors
24:
3727:Tearing and interconnect
3721:Balancing by constraints
3308:R. P. Fedorenko (1961),
3117:. Springer. p. 66.
3059:. Elsevier. p. 44.
2972:. Springer. p. 53.
2609:
2479:methods, they can offer
2437:adaptive mesh refinement
1039:
544:
250:
182:error to a coarser grid.
3834:Computer-assisted proof
3812:Infinite element method
3600:Gradient discretisation
125:Navier-Stokes equations
66:multiresolution methods
3822:Petrov–Galerkin method
3583:Discontinuous Galerkin
3226:10.1002/cnm.1630080906
2590:
2562:
2542:
2522:
2469:initial value problems
2345:
2304:
2257:
2228:
2196:
2132:
2105:
2090:
2028:
1969:
1907:
1881:
1869:
1801:
1778:
1758:
1698:
1672:
1626:
1599:
1572:
1551:
140:
54:differential equations
3802:Isogeometric analysis
3648:Material point method
3111:"Algebraic multigrid"
3109:Yair Shapira (2003).
3053:Albert Cohen (2003).
2763:P. Wesseling (1992).
2682:. Wiley. p. 132
2591:
2563:
2543:
2523:
2418:, or for problems in
2346:
2305:
2258:
2229:
2197:
2133:
2106:
2070:
2029:
1970:
1908:
1906:{\displaystyle N_{1}}
1879:
1870:
1802:
1779:
1759:
1699:
1673:
1627:
1625:{\displaystyle N_{i}}
1600:
1598:{\displaystyle N_{i}}
1573:
1549:
138:
104:finite element method
29:Differential equation
3839:Integrable algorithm
3665:Domain decomposition
3290:A Multigrid Tutorial
2964:Achi Brandt (2002).
2935:. In Thomas Y. Hou;
2730:M. T. Heath (2002).
2580:
2572:operator with large
2552:
2532:
2503:
2344:{\displaystyle O(N)}
2326:
2267:
2256:{\displaystyle O(N)}
2238:
2227:{\displaystyle O(N)}
2209:
2145:
2122:
2041:
1982:
1920:
1890:
1814:
1791:
1768:
1708:
1682:
1636:
1609:
1582:
1562:
215:convection-diffusion
166:Residual Computation
3683:Schwarz alternating
3606:Loubignac iteration
2911:J. Blaz̆ek (2001).
2717:1989STIN...9123418S
2420:statistical physics
2379:flexible CG methods
1697:{\displaystyle i+1}
1531:Computational cost
225:methods and can be
217:problems with high
207:discrete 2D problem
178:– downsampling the
160:Gauss–Seidel method
109:boundary conditions
21:
3865:Numerical analysis
3829:Validated numerics
3354:Multigrid tutorial
2655:. Academic Press.
2586:
2558:
2538:
2518:
2433:Adaptive multigrid
2416:integral equations
2364:conjugate gradient
2341:
2300:
2253:
2224:
2192:
2128:
2101:
2024:
1965:
1903:
1882:
1865:
1797:
1774:
1754:
1694:
1668:
1622:
1595:
1568:
1552:
1389:coarse_level_solve
1188:coarse_level_solve
894:coarse_level_solve
693:coarse_level_solve
399:coarse_level_solve
141:
74:relaxation methods
38:numerical analysis
19:
3852:
3851:
3792:Immersed boundary
3785:Method of moments
3700:Neumann–Dirichlet
3693:abstract additive
3678:Fictitious domain
3622:Meshless/Meshfree
3506:
3505:
3408:Finite difference
3334:978-0-521-88068-8
3151:978-0-12-701070-0
3124:978-1-4020-7485-1
3095:978-0-12-701070-0
3066:978-0-444-51124-9
3039:978-0-12-701070-0
3012:978-3-540-42420-8
2979:978-3-540-42420-8
2950:978-3-540-44333-9
2924:978-0-08-043009-6
2896:978-3-540-29076-6
2776:978-0-471-93083-9
2749:978-0-07-112229-0
2693:978-0-471-74110-7
2662:978-0-12-701070-0
2635:978-1-58488-492-7
2598:positive definite
2589:{\displaystyle M}
2561:{\displaystyle A}
2497:linear elasticity
2368:iterative methods
2190:
2131:{\displaystyle n}
1800:{\displaystyle k}
1777:{\displaystyle K}
1571:{\displaystyle i}
1528:
1527:
1035:W-cycle multigrid
540:F-cycle multigrid
246:V-Cycle Multigrid
34:
33:
3882:
3797:Analytic element
3780:Boundary element
3673:Schur complement
3654:Particle-in-cell
3589:Spectral element
3413:
3412:
3393:
3386:
3379:
3370:
3369:
3338:
3240:
3236:
3230:
3229:
3209:
3203:
3202:
3200:
3198:
3173:
3167:
3162:
3156:
3155:
3135:
3129:
3128:
3106:
3100:
3099:
3077:
3071:
3070:
3050:
3044:
3043:
3023:
3017:
3016:
2990:
2984:
2983:
2961:
2955:
2954:
2928:
2907:
2901:
2900:
2878:
2872:
2869:
2863:
2860:
2854:
2851:
2845:
2844:
2834:
2824:
2800:
2794:
2787:
2781:
2780:
2760:
2754:
2753:
2727:
2721:
2720:
2704:
2698:
2697:
2673:
2667:
2666:
2646:
2640:
2639:
2619:
2595:
2593:
2592:
2587:
2567:
2565:
2564:
2559:
2547:
2545:
2544:
2539:
2527:
2525:
2524:
2519:
2477:linear multistep
2375:steepest descent
2350:
2348:
2347:
2342:
2309:
2307:
2306:
2301:
2262:
2260:
2259:
2254:
2233:
2231:
2230:
2225:
2201:
2199:
2198:
2193:
2191:
2189:
2175:
2173:
2172:
2157:
2156:
2137:
2135:
2134:
2129:
2116:geometric series
2110:
2108:
2107:
2102:
2100:
2099:
2089:
2084:
2069:
2068:
2053:
2052:
2033:
2031:
2030:
2025:
2023:
2022:
2013:
2012:
1994:
1993:
1974:
1972:
1971:
1966:
1964:
1963:
1945:
1944:
1932:
1931:
1912:
1910:
1909:
1904:
1902:
1901:
1874:
1872:
1871:
1866:
1864:
1863:
1845:
1844:
1826:
1825:
1806:
1804:
1803:
1798:
1783:
1781:
1780:
1775:
1763:
1761:
1760:
1755:
1747:
1746:
1737:
1732:
1731:
1703:
1701:
1700:
1695:
1677:
1675:
1674:
1669:
1667:
1666:
1648:
1647:
1631:
1629:
1628:
1623:
1621:
1620:
1604:
1602:
1601:
1596:
1594:
1593:
1577:
1575:
1574:
1569:
1543:
1542:
1538:
1522:
1519:
1516:
1513:
1510:
1507:
1504:
1501:
1498:
1495:
1492:
1489:
1488:% Post-smoothing
1486:
1483:
1480:
1477:
1474:
1471:
1468:
1465:
1462:
1459:
1456:
1453:
1450:
1447:
1444:
1441:
1438:
1435:
1432:
1429:
1426:
1423:
1420:
1417:
1414:
1411:
1408:
1405:
1402:
1399:
1396:
1393:
1390:
1387:
1384:
1381:
1378:
1375:
1372:
1369:
1366:
1363:
1360:
1357:
1354:
1351:
1348:
1345:
1342:
1339:
1336:
1333:
1330:
1327:
1324:
1321:
1318:
1315:
1312:
1309:
1306:
1303:
1300:
1297:
1294:
1291:
1288:
1285:
1282:
1279:
1276:
1273:
1270:
1267:
1264:
1261:
1258:
1255:
1252:
1249:
1246:
1243:
1240:
1237:
1234:
1231:
1228:
1225:
1222:
1219:
1216:
1213:
1210:
1207:
1204:
1201:
1198:
1195:
1192:
1189:
1186:
1183:
1180:
1177:
1174:
1171:
1168:
1165:
1162:
1159:
1156:
1153:
1150:
1147:
1144:
1141:
1138:
1135:
1132:
1129:
1126:
1123:
1120:
1117:
1114:
1111:
1108:
1105:
1102:
1099:
1096:
1093:
1090:
1087:
1084:
1081:
1078:
1075:
1072:
1069:
1066:
1063:
1060:
1057:
1053:
1050:
1047:
1043:
1027:
1024:
1021:
1018:
1015:
1012:
1009:
1006:
1003:
1000:
997:
994:
993:% Post-smoothing
991:
988:
985:
982:
979:
976:
973:
970:
967:
964:
961:
958:
955:
952:
949:
946:
943:
940:
937:
934:
931:
928:
925:
922:
919:
916:
913:
910:
907:
904:
901:
898:
895:
892:
889:
886:
883:
880:
877:
874:
871:
868:
865:
862:
859:
856:
853:
850:
847:
844:
841:
838:
835:
832:
829:
826:
823:
820:
817:
814:
811:
808:
805:
802:
799:
796:
793:
790:
787:
784:
781:
778:
775:
772:
769:
766:
763:
760:
757:
754:
751:
748:
745:
742:
739:
736:
733:
730:
727:
724:
721:
718:
715:
712:
709:
706:
703:
700:
697:
694:
691:
688:
685:
682:
679:
676:
673:
670:
667:
664:
661:
658:
655:
652:
649:
646:
643:
640:
637:
634:
631:
628:
625:
622:
619:
616:
613:
610:
607:
604:
601:
598:
595:
592:
589:
586:
583:
580:
577:
574:
571:
568:
565:
562:
558:
555:
552:
548:
532:
529:
526:
523:
520:
517:
514:
511:
508:
505:
502:
499:
498:% Post-Smoothing
496:
493:
490:
487:
484:
481:
478:
475:
472:
469:
466:
463:
460:
457:
454:
451:
448:
445:
442:
439:
436:
433:
430:
427:
424:
421:
418:
415:
412:
409:
406:
403:
400:
397:
394:
391:
388:
385:
382:
379:
376:
373:
370:
367:
364:
361:
358:
355:
352:
349:
346:
343:
340:
337:
334:
331:
328:
325:
322:
319:
316:
313:
310:
307:
304:
301:
298:
295:
292:
289:
286:
283:
280:
277:
274:
271:
268:
264:
261:
258:
254:
240:
239:
235:condition number
78:Fourier analysis
42:multigrid method
22:
20:Multigrid method
18:
3890:
3889:
3885:
3884:
3883:
3881:
3880:
3879:
3855:
3854:
3853:
3848:
3817:Galerkin method
3760:Method of lines
3737:
3705:Neumann–Neumann
3659:
3616:
3558:
3525:High-resolution
3502:
3473:
3435:
3402:
3397:
3345:
3335:
3272:(April 1977), "
3248:
3243:
3237:
3233:
3210:
3206:
3196:
3194:
3192:
3174:
3170:
3163:
3159:
3152:
3144:. p. 417.
3136:
3132:
3125:
3107:
3103:
3096:
3088:. p. 356.
3078:
3074:
3067:
3051:
3047:
3040:
3024:
3020:
3013:
2991:
2987:
2980:
2962:
2958:
2951:
2925:
2908:
2904:
2897:
2879:
2875:
2870:
2866:
2861:
2857:
2852:
2848:
2801:
2797:
2788:
2784:
2777:
2761:
2757:
2750:
2728:
2724:
2705:
2701:
2694:
2674:
2670:
2663:
2647:
2643:
2636:
2620:
2616:
2612:
2603:Poisson's ratio
2596:is a symmetric
2581:
2578:
2577:
2553:
2550:
2549:
2533:
2530:
2529:
2504:
2501:
2500:
2493:
2465:
2453:sparse matrices
2445:
2400:
2391:
2327:
2324:
2323:
2316:
2268:
2265:
2264:
2239:
2236:
2235:
2210:
2207:
2206:
2179:
2174:
2168:
2164:
2152:
2148:
2146:
2143:
2142:
2123:
2120:
2119:
2095:
2091:
2085:
2074:
2064:
2060:
2048:
2044:
2042:
2039:
2038:
2018:
2014:
2002:
1998:
1989:
1985:
1983:
1980:
1979:
1959:
1955:
1940:
1936:
1927:
1923:
1921:
1918:
1917:
1897:
1893:
1891:
1888:
1887:
1859:
1855:
1834:
1830:
1821:
1817:
1815:
1812:
1811:
1792:
1789:
1788:
1769:
1766:
1765:
1742:
1738:
1733:
1721:
1717:
1709:
1706:
1705:
1683:
1680:
1679:
1662:
1658:
1643:
1639:
1637:
1634:
1633:
1616:
1612:
1610:
1607:
1606:
1589:
1585:
1583:
1580:
1579:
1563:
1560:
1559:
1544:
1540:
1536:
1534:
1533:
1524:
1523:
1520:
1517:
1514:
1511:
1508:
1505:
1502:
1499:
1496:
1493:
1490:
1487:
1484:
1481:
1478:
1475:
1472:
1469:
1466:
1463:
1460:
1457:
1454:
1451:
1448:
1445:
1442:
1439:
1436:
1433:
1430:
1427:
1424:
1421:
1418:
1415:
1412:
1409:
1406:
1403:
1400:
1397:
1394:
1391:
1388:
1385:
1382:
1379:
1376:
1373:
1370:
1367:
1364:
1361:
1358:
1355:
1352:
1349:
1346:
1343:
1340:
1337:
1334:
1331:
1328:
1325:
1322:
1319:
1316:
1313:
1310:
1307:
1304:
1301:
1298:
1295:
1292:
1289:
1286:
1283:
1280:
1277:
1274:
1271:
1268:
1265:
1262:
1259:
1256:
1253:
1250:
1247:
1244:
1241:
1238:
1235:
1232:
1229:
1226:
1223:
1220:
1217:
1214:
1211:
1208:
1205:
1202:
1199:
1196:
1193:
1190:
1187:
1184:
1181:
1178:
1175:
1172:
1169:
1166:
1163:
1160:
1157:
1154:
1151:
1148:
1145:
1142:
1139:
1136:
1133:
1130:
1127:
1124:
1121:
1118:
1115:
1112:
1109:
1106:
1103:
1100:
1097:
1094:
1091:
1088:
1085:
1082:
1079:
1076:
1073:
1070:
1067:
1064:
1062:% Pre-smoothing
1061:
1058:
1055:
1051:
1048:
1045:
1041:
1029:
1028:
1025:
1022:
1019:
1016:
1013:
1010:
1007:
1004:
1001:
998:
995:
992:
989:
986:
983:
980:
977:
974:
971:
968:
965:
962:
959:
956:
953:
950:
947:
944:
941:
938:
935:
932:
929:
926:
923:
920:
917:
914:
911:
908:
905:
902:
899:
896:
893:
890:
887:
884:
881:
878:
875:
872:
869:
866:
863:
860:
857:
854:
851:
848:
845:
842:
839:
836:
833:
830:
827:
824:
821:
818:
815:
812:
809:
806:
803:
800:
797:
794:
791:
788:
785:
782:
779:
776:
773:
770:
767:
764:
761:
758:
755:
752:
749:
746:
743:
740:
737:
734:
731:
728:
725:
722:
719:
716:
713:
710:
707:
704:
701:
698:
695:
692:
689:
686:
683:
680:
677:
674:
671:
668:
665:
662:
659:
656:
653:
650:
647:
644:
641:
638:
635:
632:
629:
626:
623:
620:
617:
614:
611:
608:
605:
602:
599:
596:
593:
590:
587:
584:
581:
578:
575:
572:
569:
567:% Pre-smoothing
566:
563:
560:
556:
553:
550:
546:
534:
533:
530:
527:
524:
521:
518:
515:
512:
509:
506:
503:
500:
497:
494:
491:
488:
485:
482:
479:
476:
473:
470:
467:
464:
461:
458:
455:
452:
449:
446:
443:
440:
437:
434:
431:
428:
425:
422:
419:
416:
413:
410:
407:
404:
401:
398:
395:
392:
389:
386:
383:
380:
377:
374:
371:
368:
365:
362:
359:
356:
353:
350:
347:
344:
341:
338:
335:
332:
329:
326:
323:
320:
317:
314:
311:
308:
305:
302:
299:
296:
293:
290:
287:
284:
281:
278:
275:
273:% Pre-Smoothing
272:
269:
266:
262:
259:
256:
252:
223:Krylov subspace
145:discretizations
133:
82:preconditioners
70:multiple scales
62:discretizations
17:
12:
11:
5:
3888:
3878:
3877:
3872:
3867:
3850:
3849:
3847:
3846:
3841:
3836:
3831:
3826:
3825:
3824:
3814:
3809:
3804:
3799:
3794:
3789:
3788:
3787:
3777:
3772:
3767:
3762:
3757:
3754:Pseudospectral
3751:
3745:
3743:
3739:
3738:
3736:
3735:
3730:
3724:
3718:
3712:
3707:
3702:
3697:
3696:
3695:
3690:
3680:
3675:
3669:
3667:
3661:
3660:
3658:
3657:
3651:
3645:
3639:
3633:
3626:
3624:
3618:
3617:
3615:
3614:
3608:
3603:
3597:
3592:
3586:
3580:
3574:
3568:
3566:
3564:Finite element
3560:
3559:
3557:
3556:
3550:
3544:
3542:Riemann solver
3539:
3533:
3527:
3522:
3516:
3514:
3508:
3507:
3504:
3503:
3501:
3500:
3494:
3488:
3481:
3479:
3475:
3474:
3472:
3471:
3466:
3461:
3456:
3451:
3449:Lax–Friedrichs
3445:
3443:
3437:
3436:
3434:
3433:
3431:Crank–Nicolson
3428:
3421:
3419:
3410:
3404:
3403:
3396:
3395:
3388:
3381:
3373:
3367:
3366:
3361:
3356:
3351:
3344:
3343:External links
3341:
3340:
3339:
3333:
3316:
3313:
3306:
3285:
3267:
3256:
3247:
3244:
3242:
3241:
3231:
3220:(9): 585–595.
3204:
3190:
3168:
3157:
3150:
3130:
3123:
3101:
3094:
3072:
3065:
3045:
3038:
3018:
3011:
2985:
2978:
2956:
2949:
2923:
2902:
2895:
2873:
2864:
2855:
2846:
2795:
2782:
2775:
2755:
2748:
2722:
2699:
2692:
2668:
2661:
2641:
2634:
2613:
2611:
2608:
2585:
2557:
2537:
2517:
2514:
2511:
2508:
2492:
2489:
2464:
2461:
2444:
2441:
2399:
2396:
2390:
2387:
2372:preconditioned
2340:
2337:
2334:
2331:
2320:preconditioner
2315:
2312:
2299:
2296:
2293:
2290:
2287:
2284:
2281:
2278:
2275:
2272:
2252:
2249:
2246:
2243:
2223:
2220:
2217:
2214:
2203:
2202:
2188:
2185:
2182:
2178:
2171:
2167:
2163:
2160:
2155:
2151:
2127:
2112:
2111:
2098:
2094:
2088:
2083:
2080:
2077:
2073:
2067:
2063:
2059:
2056:
2051:
2047:
2021:
2017:
2011:
2008:
2005:
2001:
1997:
1992:
1988:
1976:
1975:
1962:
1958:
1954:
1951:
1948:
1943:
1939:
1935:
1930:
1926:
1900:
1896:
1884:
1883:
1862:
1858:
1854:
1851:
1848:
1843:
1840:
1837:
1833:
1829:
1824:
1820:
1796:
1773:
1753:
1750:
1745:
1741:
1736:
1730:
1727:
1724:
1720:
1716:
1713:
1693:
1690:
1687:
1665:
1661:
1657:
1654:
1651:
1646:
1642:
1619:
1615:
1592:
1588:
1567:
1532:
1529:
1526:
1525:
1287:% Re-smoothing
1040:
1030:
792:% Re-smoothing
545:
535:
251:
227:preconditioned
219:Péclet numbers
202:
201:
195:
183:
173:
170:residual error
163:
132:
129:
117:Lamé equations
93:coarse problem
32:
31:
26:
15:
9:
6:
4:
3:
2:
3887:
3876:
3873:
3871:
3868:
3866:
3863:
3862:
3860:
3845:
3842:
3840:
3837:
3835:
3832:
3830:
3827:
3823:
3820:
3819:
3818:
3815:
3813:
3810:
3808:
3805:
3803:
3800:
3798:
3795:
3793:
3790:
3786:
3783:
3782:
3781:
3778:
3776:
3773:
3771:
3768:
3766:
3763:
3761:
3758:
3755:
3752:
3750:
3747:
3746:
3744:
3740:
3734:
3731:
3728:
3725:
3722:
3719:
3716:
3713:
3711:
3708:
3706:
3703:
3701:
3698:
3694:
3691:
3689:
3686:
3685:
3684:
3681:
3679:
3676:
3674:
3671:
3670:
3668:
3666:
3662:
3655:
3652:
3649:
3646:
3643:
3640:
3637:
3634:
3631:
3628:
3627:
3625:
3623:
3619:
3612:
3609:
3607:
3604:
3601:
3598:
3596:
3593:
3590:
3587:
3584:
3581:
3578:
3575:
3573:
3570:
3569:
3567:
3565:
3561:
3554:
3551:
3548:
3545:
3543:
3540:
3537:
3534:
3531:
3528:
3526:
3523:
3521:
3518:
3517:
3515:
3513:
3512:Finite volume
3509:
3498:
3495:
3492:
3489:
3486:
3483:
3482:
3480:
3476:
3470:
3467:
3465:
3462:
3460:
3457:
3455:
3452:
3450:
3447:
3446:
3444:
3442:
3438:
3432:
3429:
3426:
3423:
3422:
3420:
3418:
3414:
3411:
3409:
3405:
3401:
3394:
3389:
3387:
3382:
3380:
3375:
3374:
3371:
3365:
3362:
3360:
3357:
3355:
3352:
3350:
3347:
3346:
3336:
3330:
3326:
3322:
3317:
3314:
3311:
3307:
3304:
3303:0-89871-462-1
3300:
3296:
3292:
3291:
3286:
3283:
3279:
3275:
3271:
3268:
3265:
3261:
3257:
3254:
3250:
3249:
3235:
3227:
3223:
3219:
3215:
3208:
3193:
3191:9780444875976
3187:
3183:
3179:
3172:
3166:
3161:
3153:
3147:
3143:
3142:
3134:
3126:
3120:
3116:
3112:
3105:
3097:
3091:
3087:
3083:
3076:
3068:
3062:
3058:
3057:
3049:
3041:
3035:
3031:
3030:
3022:
3014:
3008:
3004:
3000:
2996:
2989:
2981:
2975:
2971:
2967:
2960:
2952:
2946:
2942:
2938:
2934:
2926:
2920:
2916:
2915:
2909:For example,
2906:
2898:
2892:
2888:
2884:
2877:
2868:
2859:
2850:
2842:
2838:
2833:
2828:
2823:
2818:
2814:
2810:
2806:
2799:
2792:
2786:
2778:
2772:
2768:
2767:
2759:
2751:
2745:
2741:
2737:
2733:
2726:
2718:
2714:
2710:
2703:
2695:
2689:
2685:
2681:
2680:
2672:
2664:
2658:
2654:
2653:
2645:
2637:
2631:
2627:
2626:
2618:
2614:
2607:
2604:
2599:
2583:
2575:
2571:
2568:is symmetric
2555:
2535:
2515:
2512:
2509:
2506:
2498:
2488:
2486:
2482:
2478:
2474:
2470:
2460:
2456:
2454:
2450:
2440:
2438:
2434:
2430:
2428:
2423:
2421:
2417:
2413:
2409:
2405:
2395:
2386:
2384:
2380:
2376:
2373:
2369:
2365:
2360:
2358:
2354:
2335:
2329:
2321:
2311:
2310:complexity.
2291:
2285:
2282:
2279:
2276:
2270:
2247:
2241:
2218:
2212:
2186:
2183:
2180:
2176:
2169:
2165:
2161:
2158:
2153:
2149:
2141:
2140:
2139:
2125:
2117:
2096:
2092:
2086:
2081:
2078:
2075:
2071:
2065:
2061:
2057:
2054:
2049:
2045:
2037:
2036:
2035:
2019:
2015:
2009:
2006:
2003:
1999:
1995:
1990:
1986:
1960:
1956:
1952:
1949:
1946:
1941:
1937:
1933:
1928:
1924:
1916:
1915:
1914:
1898:
1894:
1878:
1860:
1856:
1852:
1849:
1846:
1841:
1838:
1835:
1831:
1827:
1822:
1818:
1810:
1809:
1808:
1794:
1785:
1771:
1751:
1748:
1743:
1739:
1734:
1728:
1725:
1722:
1718:
1714:
1711:
1691:
1688:
1685:
1663:
1659:
1655:
1652:
1649:
1644:
1640:
1617:
1613:
1590:
1586:
1565:
1556:
1548:
1539:
1353:% Restriction
1128:% Restriction
1038:
1036:
1031:
858:% Restriction
633:% Restriction
543:
541:
536:
339:% Restriction
249:
247:
242:
238:
236:
230:
228:
224:
220:
216:
212:
208:
199:
196:
193:
189:
188:
187:Interpolation
184:
181:
177:
174:
171:
167:
164:
161:
157:
153:
150:
149:
148:
146:
137:
128:
126:
122:
118:
114:
110:
105:
100:
98:
94:
90:
85:
83:
79:
75:
71:
67:
63:
59:
55:
51:
47:
43:
39:
30:
27:
23:
3764:
3636:Peridynamics
3454:Lax–Wendroff
3324:
3288:
3281:
3277:
3234:
3217:
3213:
3207:
3195:. Retrieved
3181:
3171:
3160:
3140:
3133:
3114:
3104:
3085:
3075:
3055:
3048:
3028:
3021:
3002:
2998:
2988:
2969:
2959:
2940:
2937:Eitan Tadmor
2913:
2905:
2886:
2876:
2867:
2858:
2849:
2812:
2808:
2798:
2785:
2765:
2758:
2739:
2735:
2725:
2708:
2702:
2683:
2678:
2671:
2651:
2644:
2624:
2617:
2570:semidefinite
2494:
2466:
2457:
2448:
2446:
2432:
2431:
2424:
2401:
2392:
2361:
2317:
2204:
2113:
1977:
1885:
1786:
1557:
1553:
1476:prolongation
1275:prolongation
1034:
1032:
981:prolongation
780:prolongation
539:
537:
486:prolongation
245:
243:
231:
203:
197:
192:prolongation
191:
185:
175:
168:– computing
165:
151:
142:
101:
88:
86:
52:for solving
45:
41:
35:
3770:Collocation
3270:Achi Brandt
3184:: 189–197.
2815:: 276–285.
2481:concurrency
2473:Runge–Kutta
1362:restriction
1137:restriction
867:restriction
642:restriction
348:restriction
176:Restriction
3859:Categories
3459:MacCormack
3441:Hyperbolic
3246:References
2574:null space
2359:problems.
2357:eigenvalue
2114:Using the
198:Correction
156:iterations
121:elasticity
3775:Level-set
3765:Multigrid
3715:Balancing
3417:Parabolic
3284:: 333–90.
3260:Bakhvalov
3141:Multigrid
3086:Multigrid
3029:Multigrid
2822:1212.6680
2769:. Wiley.
2652:Multigrid
2536:ε
2513:ε
2435:exhibits
2187:ρ
2184:−
2093:ρ
2072:∑
2007:−
2000:ρ
1950:ρ
1850:ρ
1712:ρ
1653:ρ
1497:smoothing
1296:smoothing
1071:smoothing
1002:smoothing
801:smoothing
576:smoothing
507:smoothing
282:smoothing
211:overheads
152:Smoothing
131:Algorithm
58:hierarchy
50:algorithm
46:MG method
3875:Wavelets
3749:Spectral
3688:additive
3611:Smoothed
3577:Extended
3262:(1966),
3197:1 August
2939:(eds.).
2841:51978658
2576:, while
2485:Parareal
2427:wavelets
2034:) gives
1704:. Here,
1329:residual
1104:residual
1042:function
834:residual
609:residual
547:function
315:residual
253:function
180:residual
56:using a
48:) is an
3733:FETI-DP
3613:(S-FEM)
3532:(MUSCL)
3520:Godunov
2713:Bibcode
2548:. Here
1428:W_cycle
1227:W_cycle
1054:phi,f,h
1049:W_cycle
933:V_Cycle
732:F_Cycle
559:phi,f,h
554:F_Cycle
438:V_Cycle
265:phi,f,h
260:V_Cycle
158:of the
123:or the
3742:Others
3729:(FETI)
3723:(BDDC)
3595:Mortar
3579:(XFEM)
3572:hp-FEM
3555:(WENO)
3538:(AUSM)
3499:(FDTD)
3493:(FDFD)
3478:Others
3464:Upwind
3427:(FTCS)
3331:
3301:
3258:N. S.
3239:(2007)
3188:
3148:
3121:
3092:
3063:
3036:
3009:
2976:
2947:
2921:
2893:
2839:
2773:
2746:
2690:
2659:
2632:
2383:LOBPCG
1535:": -->
89:global
3756:(DVR)
3717:(BDD)
3656:(PIC)
3650:(MPM)
3644:(MPS)
3632:(SPH)
3602:(GDM)
3591:(SEM)
3549:(ENO)
3487:(ADI)
2837:S2CID
2817:arXiv
2610:Notes
2366:(CG)
2353:Hypre
1913:that
1155:zeros
660:zeros
366:zeros
25:Class
3638:(PD)
3585:(DG)
3329:ISBN
3299:ISBN
3199:2015
3186:ISBN
3146:ISBN
3119:ISBN
3090:ISBN
3061:ISBN
3034:ISBN
3007:ISBN
2974:ISBN
2945:ISBN
2929:and
2919:ISBN
2891:ISBN
2771:ISBN
2744:ISBN
2688:ISBN
2657:ISBN
2630:ISBN
2377:and
2159:<
1749:<
1537:edit
1419:else
1218:else
1161:size
924:else
723:else
666:size
429:else
372:size
40:, a
3276:",
3222:doi
2827:doi
2475:or
1521:end
1503:phi
1491:phi
1482:eps
1470:phi
1464:phi
1458:end
1440:rhs
1434:eps
1422:eps
1401:rhs
1395:eps
1383:eps
1356:rhs
1335:phi
1302:phi
1290:phi
1281:eps
1269:phi
1263:phi
1257:end
1239:rhs
1233:eps
1221:eps
1200:rhs
1194:eps
1182:eps
1170:));
1167:rhs
1149:eps
1131:rhs
1110:phi
1077:phi
1065:phi
1044:phi
1026:end
1008:phi
996:phi
987:eps
975:phi
969:phi
963:end
945:rhs
939:eps
927:eps
906:rhs
900:eps
888:eps
861:rhs
840:phi
807:phi
795:phi
786:eps
774:phi
768:phi
762:end
744:rhs
738:eps
726:eps
705:rhs
699:eps
687:eps
675:));
672:rhs
654:eps
636:rhs
615:phi
582:phi
570:phi
549:phi
531:end
513:phi
501:phi
492:eps
480:phi
474:phi
468:end
450:rhs
444:eps
432:eps
411:rhs
405:eps
393:eps
381:));
378:rhs
360:eps
342:rhs
321:phi
288:phi
276:phi
255:phi
190:or
119:of
60:of
36:In
3861::
3323:.
3297:,
3282:31
3280:,
3216:.
3180:.
3113:.
3084:.
3032:.
3005:.
3003:ff
2835:.
2825:.
2813:51
2811:.
2807:.
2742:.
2740:ff
2734:.
2686:.
2684:ff
2422:.
2138:)
1807::
1518:);
1485:);
1455:);
1416:);
1377:if
1371:);
1350:);
1317:);
1284:);
1254:);
1215:);
1176:if
1146:);
1125:);
1092:);
1023:);
990:);
960:);
921:);
882:if
876:);
855:);
822:);
789:);
759:);
720:);
681:if
651:);
630:);
597:);
528:);
495:);
465:);
426:);
387:if
357:);
336:);
303:);
248::
229:.
127:.
84:.
3392:e
3385:t
3378:v
3337:.
3305:.
3228:.
3224::
3218:8
3201:.
3154:.
3127:.
3098:.
3069:.
3042:.
3015:.
2982:.
2953:.
2927:.
2899:.
2843:.
2829::
2819::
2779:.
2752:.
2719:.
2715::
2696:.
2665:.
2638:.
2584:M
2556:A
2516:M
2510:+
2507:A
2339:)
2336:N
2333:(
2330:O
2298:)
2295:)
2292:N
2289:(
2286:g
2283:o
2280:l
2277:N
2274:(
2271:O
2251:)
2248:N
2245:(
2242:O
2222:)
2219:N
2216:(
2213:O
2181:1
2177:1
2170:1
2166:N
2162:K
2154:1
2150:W
2126:n
2097:p
2087:n
2082:0
2079:=
2076:p
2066:1
2062:N
2058:K
2055:=
2050:1
2046:W
2020:1
2016:N
2010:1
2004:k
1996:=
1991:k
1987:N
1961:1
1957:N
1953:K
1947:+
1942:2
1938:W
1934:=
1929:1
1925:W
1899:1
1895:N
1861:k
1857:N
1853:K
1847:+
1842:1
1839:+
1836:k
1832:W
1828:=
1823:k
1819:W
1795:k
1772:K
1752:1
1744:i
1740:N
1735:/
1729:1
1726:+
1723:i
1719:N
1715:=
1692:1
1689:+
1686:i
1664:i
1660:N
1656:K
1650:=
1645:i
1641:W
1618:i
1614:N
1591:i
1587:N
1566:i
1541:]
1515:h
1512:,
1509:f
1506:,
1500:(
1494:=
1479:(
1473:+
1467:=
1452:h
1449:*
1446:2
1443:,
1437:,
1431:(
1425:=
1413:h
1410:*
1407:2
1404:,
1398:,
1392:(
1386:=
1368:r
1365:(
1359:=
1347:h
1344:,
1341:f
1338:,
1332:(
1326:=
1323:r
1314:h
1311:,
1308:f
1305:,
1299:(
1293:=
1278:(
1272:+
1266:=
1251:h
1248:*
1245:2
1242:,
1236:,
1230:(
1224:=
1212:h
1209:*
1206:2
1203:,
1197:,
1191:(
1185:=
1164:(
1158:(
1152:=
1143:r
1140:(
1134:=
1122:h
1119:,
1116:f
1113:,
1107:(
1101:=
1098:r
1089:h
1086:,
1083:f
1080:,
1074:(
1068:=
1056:)
1052:(
1046:=
1020:h
1017:,
1014:f
1011:,
1005:(
999:=
984:(
978:+
972:=
957:h
954:*
951:2
948:,
942:,
936:(
930:=
918:h
915:*
912:2
909:,
903:,
897:(
891:=
873:r
870:(
864:=
852:h
849:,
846:f
843:,
837:(
831:=
828:r
819:h
816:,
813:f
810:,
804:(
798:=
783:(
777:+
771:=
756:h
753:*
750:2
747:,
741:,
735:(
729:=
717:h
714:*
711:2
708:,
702:,
696:(
690:=
669:(
663:(
657:=
648:r
645:(
639:=
627:h
624:,
621:f
618:,
612:(
606:=
603:r
594:h
591:,
588:f
585:,
579:(
573:=
561:)
557:(
551:=
525:h
522:,
519:f
516:,
510:(
504:=
489:(
483:+
477:=
462:h
459:*
456:2
453:,
447:,
441:(
435:=
423:h
420:*
417:2
414:,
408:,
402:(
396:=
375:(
369:(
363:=
354:r
351:(
345:=
333:h
330:,
327:f
324:,
318:(
312:=
309:r
300:h
297:,
294:f
291:,
285:(
279:=
267:)
263:(
257:=
162:.
44:(
Text is available under the Creative Commons Attribution-ShareAlike License. Additional terms may apply.