41:
147:
1719:
334:
324:
Differential diagnosis can be challenging due to the number of overlapping symptoms, shared between several motor neuron diseases. Frequently, the diagnosis is based on clinical findings (i.e. LMN vs. UMN signs and symptoms, patterns of weakness), family history of MND, and a variation of tests, many
166:
Signs and symptoms depend on the specific disease, but motor neuron diseases typically manifest as a group of movement-related symptoms. They come on slowly, and worsen over the course of more than three months. Various patterns of muscle weakness are seen, and muscle cramps and spasms may occur. One
137:
Symptoms of motor neuron diseases can be first seen at birth or can come on slowly later in life. Most of these diseases worsen over time; while some, such as ALS, shorten one's life expectancy, others do not. Currently, there are no approved treatments for the majority of motor neuron disorders, and
386:
UMNs are motor neurons that project from the cortex down to the brainstem or spinal cord. LMNs originate in the anterior horns of the spinal cord and synapse on peripheral muscles. Both motor neurons are necessary for the strong contraction of a muscle, but damage to an UMN can be distinguished from
219:
Various patterns of muscle weakness occur in different motor neuron diseases. Weakness can be symmetric or asymmetric, and it can occur in body parts that are distal, proximal, or both. According to
Statland et al., there are three main weakness patterns that are seen in motor neuron diseases, which
210:
Motor neuron diseases are seen both in children and adults. Those that affect children tend to be inherited or familial, and their symptoms are either present at birth or appear before learning to walk. Those that affect adults tend to appear after age 40. The clinical course depends on the specific
349:. The term "motor neuron disease" has varying meanings in different countries. Similarly, the literature inconsistently classifies which degenerative motor neuron disorders can be included under the umbrella term "motor neuron disease". The four main types of MND are marked (*) in the table below.
340:
Upper motor neurons originating in the primary motor cortex synapse to either lower motor neurons in the anterior horn of the central gray matter of the spinal cord (insert) or brainstem motor neurons (not shown). Motor neuron disease can affect either upper motor neurons (UMNs) or lower motor
303:
protein complex that then acts to repair double-strand breaks. About 95% of ALS patients have abnormalities in the nucleus-cytoplasmic localization in spinal motor neurons of TDP43. In TDP-43 depleted human neural stem cell-derived motor neurons, as well as in sporadic
199:) and cognitive and behavioural changes (e.g. problems in word fluency, decision-making, and memory) are also seen. There can be lower motor neuron findings (e.g. muscle wasting, muscle twitching), upper motor neuron findings (e.g. brisk reflexes,
1021:
239:
Motor neuron diseases are on a spectrum in terms of upper and lower motor neuron involvement. Some have just lower or upper motor neuron findings, while others have a mix of both. Lower motor neuron (LMN) findings include muscle
1788:
1773:
1758:
652:
2781:
1029:
515:(MRI): An MRI of the brain and spinal cord is recommended in patients with UMN signs and symptoms to explore other causes, such as a tumor, inflammation, or lack of blood supply (stroke).
371:
Sporadic or acquired MNDs occur in patients with no family history of degenerative motor neuron disease. Inherited or genetic MNDs adhere to one of the following inheritance patterns:
2304:
549:: Taking a small sample of a muscle or nerve may be necessary if the EMG/NCS is not specific enough to rule out other causes of progressive muscle weakness, but it is rarely used.
528:
For patients with MND affecting the LMNs, the EMG will show evidence of: (1) acute denervation, which is ongoing as motor neurons degenerate, and (2) chronic denervation and
2690:
2685:
124:. Most of these diseases seem to occur randomly without known causes, but some forms are inherited. Studies into these inherited forms have led to discoveries of various
2702:
2680:
1632:
746:
120:
Motor neuron diseases affect both children and adults. While each motor neuron disease affects patients differently, they all cause movement-related symptoms, mainly
1853:
1735:
346:
345:
Motor neuron disease describes a collection of clinical disorders, characterized by progressive muscle weakness and the degeneration of the motor neuron on
558:
There are no known curative treatments for the majority of motor neuron disorders. Please refer to the articles on individual disorders for more details.
1159:
383:. Some disorders, like ALS, can occur sporadically (85%) or can have a genetic cause (15%) with the same clinical symptoms and progression of disease.
19:
This article is about a group of muscle-wasting disorders. For the disease amyotrophic lateral sclerosis, also known as motor neuron(e) disease, see
269:
Most cases are sporadic and their causes are usually not known. It is thought that environmental, toxic, viral, or genetic factors may be involved.
2049:
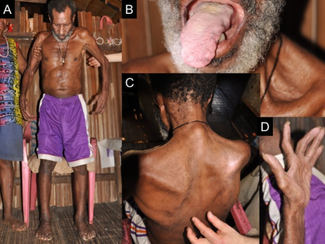
154:(ALS). (A) He needs assistance to stand. (B) Advanced atrophy of the tongue. (C) There is upper limb and truncal muscle atrophy with a positive
2044:
1682:
1007:
866:
525:(NCS): The EMG, which evaluates muscle function, and NCS, which evaluates nerve function, are performed together in patients with LMN signs.
1846:
2672:
295:-derived motor neurons. TDP-43 is rapidly recruited to double-strand breaks where it acts as a scaffold for the recruitment of the
2662:
1839:
669:
923:"Patterns of Weakness, Classification of Motor Neuron Disease, and Clinical Diagnosis of Sporadic Amyotrophic Lateral Sclerosis"
2642:
2315:
1723:
1621:
2667:
2299:
1658:
842:
705:
750:
509:(CSF) tests: Analysis of the fluid from around the brain and spinal cord could reveal signs of an infection or inflammation.
211:
disease, but most progress or worsen over the course of months. Some are fatal (e.g. ALS), while others are not (e.g. PLS).
2505:
2493:
1955:
1519:
1696:
2724:
2657:
2212:
2427:
2230:
979:
536:
288:
308:
patients' spinal cord specimens there is significant double-strand break accumulation and reduced levels of NHEJ.
2546:
1426:
1134:
2771:
2061:
2037:
1867:
1730:
2740:
2625:
2541:
2483:
2253:
2032:
1341:
Foster LA, Salajegheh MK (January 2019). "Motor Neuron
Disease: Pathophysiology, Diagnosis, and Management".
305:
195:), can also occur. Sensation, or the ability to feel, is typically not affected. Emotional disturbance (e.g.
151:
20:
1189:"Motor neuron disease-associated loss of nuclear TDP-43 is linked to DNA double-strand break repair defects"
2709:
2083:
1003:
102:
647:
that are referred to collectively as "motor neuron disorders", for instance the diseases belonging to the
2219:
2697:
2247:
1919:
1248:"Patterns of Weakness, Classification of Motor Neuron Disease & Clinical Diagnosis of Sporadic ALS"
1246:
Statland, Jeffrey M.; Barohn, Richard J.; McVey, April L.; Katz, Jonathan; Dimachkie, Mazen M. (2015).
512:
281:
277:
2647:
2615:
2589:
2567:
2416:
1995:
664:
648:
106:
2714:
2488:
1902:
1803:
747:"Motor Neuron Diseases Fact Sheet: National Institute of Neurological Disorders and Stroke (NINDS)"
296:
94:
1389:
640:
is used for amyotrophic lateral sclerosis, although is not uncommon to refer to the entire group.
632:
usually refers to the group of disorders while amyotrophic lateral sclerosis is frequently called
2719:
2652:
2408:
2226:
2078:
2068:
1912:
110:
1831:
643:
While MND refers to a specific subset of similar diseases, there are numerous other diseases of
2776:
2584:
2576:
2531:
2207:
2179:
2027:
522:
230:
Symmetric focal midline proximal weakness (neck, trunk, bulbar involvement; e.g. ALS, PBP, PLS)
693:
651:
group. However, they are not classified as "motor neuron diseases" by the 11th edition of the
2473:
2291:
2269:
2184:
2107:
2017:
2004:
1929:
1767:
261:
Motor neuron diseases with both UMN and LMN findings include both familial and sporadic ALS.
1160:"Motor Neuron Diseases Fact Sheet | National Institute of Neurological Disorders and Stroke"
805:
2536:
2353:
2242:
1200:
204:
114:
325:
of which are used to rule out disease mimics, which can manifest with identical symptoms.
8:
2465:
2112:
1967:
1907:
1792:
1187:
Mitra J, Guerrero EN, Hegde PM, Liachko NF, Wang H, Vasquez V, et al. (March 2019).
506:
376:
196:
176:
1204:
532:
of the muscle, as the remaining motor neurons attempt to fill in for lost motor neurons.
2635:
2620:
2608:
2358:
2309:
2146:
2009:
1897:
1676:
1595:
1570:
1366:
1280:
1247:
1223:
1188:
1077:
1052:
997:
947:
922:
860:
775:
372:
364:
360:
98:
1797:
2398:
2364:
2336:
2327:
2259:
2235:
2102:
1950:
1814:
1664:
1654:
1600:
1544:
1501:
1459:
1432:
1422:
1358:
1285:
1267:
1228:
1109:
1082:
985:
975:
952:
848:
838:
701:
86:
78:
53:
1370:
2521:
2392:
2387:
2172:
2167:
1590:
1582:
1493:
1350:
1275:
1259:
1218:
1208:
1072:
1064:
942:
934:
518:
2443:
2134:
1808:
1484:
Duleep A, Shefner J (February 2013). "Electrodiagnosis of motor neuron disease".
1354:
192:
121:
653:
International
Statistical Classification of Diseases and Related Health Problems
258:
Pure lower motor neuron diseases, or those with just LMN findings, include PMA.
255:
Pure upper motor neuron diseases, or those with just UMN findings, include PLS.
2500:
2449:
2277:
1986:
1863:
1571:"Molecular and cellular pathways of neurodegeneration in motor neurone disease"
1451:
1193:
Proceedings of the
National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America
1101:
566:
The table below lists life expectancy for patients who are diagnosed with MND.
540:
200:
1819:
1782:
1497:
1263:
1068:
938:
2765:
2526:
2478:
2348:
2117:
2073:
1924:
1668:
1586:
1271:
989:
852:
546:
529:
249:
245:
159:
155:
1436:
1213:
535:
By contrast, the NCS in these patients is usually normal. It can show a low
134:) that are thought to be important in understanding how the disease occurs.
2022:
1892:
1875:
1604:
1505:
1463:
1362:
1289:
1232:
1113:
1086:
956:
644:
82:
40:
1981:
1942:
1884:
974:. San Rafael, California (1537 Fourth Street, San Rafael, CA 94901 USA).
921:
Statland JM, Barohn RJ, McVey AL, Katz JS, Dimachkie MM (November 2015).
224:
Asymmetric distal weakness without sensory loss (e.g. ALS, PLS, PMA, MMA)
1750:
1609:
Many doctors use the terms motor neuron disease and ALS interchangeably.
352:
All types of MND can be differentiated by two defining characteristics:
2092:
1962:
300:
285:
184:
146:
2202:
2153:
2141:
2124:
2056:
1303:
292:
188:
172:
58:
2677:
Spinal muscular atrophy with lower extremity predominance (SMALED)
2382:
2374:
2340:
2194:
2097:
1135:"Progressive Muscular Atrophy – an overview | ScienceDirect Topics"
380:
168:
700:. Vol. 1 (8th ed.). London: Hodder Arnold. p. 947.
2782:
Systemic atrophies primarily affecting the central nervous system
1861:
1022:"Patient with amyotrophic lateral sclerosis (ALS) (case | Open-i"
241:
1649:
Schapira AH, Wszolek ZK, Dawson TM, Wood NW (13 February 2017).
2421:
2162:
2129:
1777:
1762:
1718:
451:
180:
539:(CMAP), which results from the loss of motor neurons, but the
1486:
Physical
Medicine and Rehabilitation Clinics of North America
1053:"Pattern-recognition approach to neuropathy and neuronopathy"
333:
655:(ICD-11), which is the definition followed in this article.
694:"Chapter 13: Diseases of movement and system degenerations"
130:
125:
1648:
1186:
696:. In Greenfield JG, Love S, Louis DN, Ellison DW (eds.).
692:
Ince PG, Clark B, Holton J, Revesz T, Wharton SB (2008).
90:
234:
1245:
970:
Cooper-Knock J, Jenkins T, Shaw PJ (1 September 2013).
969:
920:
833:
Cooper-Knock J, Jenkins T, Shaw PJ (1 September 2013).
832:
227:
Symmetric weakness without sensory loss (e.g. PMA, PLS)
16:
Group of neurological disorders affecting motor neurons
972:
Clinical and molecular aspects of motor neuron disease
835:
Clinical and molecular aspects of motor neuron disease
803:
316:
In adults, men are more commonly affected than women.
117:(MMA), as well as some rarer variants resembling ALS.
691:
1740:
1520:"NIH: ninds: Motor Neuron Diseases Information Page"
167:
can have difficulty breathing with climbing stairs (
252:, spasticity, muscle spasm, and abnormal reflexes.
1575:Journal of Neurology, Neurosurgery, and Psychiatry
2763:
1622:"An introduction to motor neurone disease (MND)"
1340:
799:
797:
636:. In the United Kingdom and Australia, the term
248:, and upper motor neuron (UMN) findings include
1458:. Treasure Island (FL): StatPearls Publishing.
1108:. Treasure Island (FL): StatPearls Publishing.
488:Familial amyotrophic lateral sclerosis (ALS)*
1847:
1701:ICD-11 for Mortality and Morbidity Statistics
1483:
794:
411:Sporadic amyotrophic lateral sclerosis (ALS)*
1182:
1180:
741:
739:
737:
2566:
1099:
1050:
735:
733:
731:
729:
727:
725:
723:
721:
719:
717:
1854:
1840:
1681:: CS1 maint: location missing publisher (
1416:
865:: CS1 maint: location missing publisher (
628:In the United States and Canada, the term
311:
39:
1594:
1452:"Neuroanatomy, Lower Motor Neuron Lesion"
1449:
1279:
1222:
1212:
1177:
1102:"Neuroanatomy, Upper Motor Neuron Lesion"
1076:
1006:) CS1 maint: location missing publisher (
946:
670:Hereditary motor and sensory neuropathies
280:(TDP-43), is a critical component of the
183:symptoms, including difficulty speaking (
171:), difficulty breathing when lying down (
804:Healthdirect Australia (17 April 2020).
714:
687:
685:
332:
145:
1549:Irish Motor Neurone Disease Association
214:
2764:
2643:Distal hereditary motor neuronopathies
2316:Template:Demyelinating diseases of CNS
1539:
1537:
1336:
1334:
1332:
1330:
1328:
1326:
1324:
179:if breathing muscles become involved.
1835:
1412:
1410:
1384:
1382:
1380:
916:
914:
912:
910:
908:
906:
904:
902:
900:
898:
896:
828:
826:
770:
768:
682:
356:Is the disease sporadic or inherited?
235:Lower and upper motor neuron findings
141:
2494:Idiopathic intracranial hypertension
1883:
1638:from the original on 9 October 2022.
1568:
894:
892:
890:
888:
886:
884:
882:
880:
878:
876:
582:Amyotrophic lateral sclerosis (ALS)
191:), and excessive saliva production (
1614:
1534:
1419:Neuroanatomy through clinical cases
1321:
598:Progressive muscular atrophy (PMA)
433:Progressive muscular atrophy (PMA)*
207:, increased muscle tone), or both.
13:
2725:Infantile progressive bulbar palsy
1562:
1407:
1377:
823:
765:
387:damage to a LMN by physical exam.
81:disorders that selectively affect
14:
2793:
2428:Template:Cerebrovascular diseases
2231:Frontotemporal lobar degeneration
1711:
1629:motor neurone disease association
963:
873:
328:
2448:For more detailed coverage, see
2426:For more detailed coverage, see
2397:For more detailed coverage, see
2363:For more detailed coverage, see
2314:For more detailed coverage, see
1717:
1343:The American Journal of Medicine
1051:Barohn RJ, Amato AA (May 2013).
590:Primary lateral sclerosis (PLS)
537:compound muscle action potential
422:Primary lateral sclerosis (PLS)*
1689:
1642:
1512:
1477:
1443:
1304:"Archive | Practical Neurology"
1296:
1239:
1152:
1127:
1093:
749:. ninds.nih.gov. Archived from
606:Progressive bulbar palsy (PBP)
444:Progressive bulbar palsy (PBP)*
1421:. Sunderland, Mass.: Sinauer.
1044:
1014:
623:
284:(NHEJ) enzymatic pathway that
1:
2741:Amyotrophic lateral sclerosis
2626:Hereditary spastic paraplegia
2484:Normal pressure hydrocephalus
806:"Motor neurone disease (MND)"
776:"Motor neurone disease – NHS"
675:
272:
152:amyotrophic lateral sclerosis
91:amyotrophic lateral sclerosis
21:Amyotrophic lateral sclerosis
2710:Progressive muscular atrophy
1703:. World Health Organisation.
1355:10.1016/j.amjmed.2018.07.012
561:
553:
359:Is there involvement of the
347:electrophysiological testing
319:
138:care is mostly symptomatic.
103:progressive muscular atrophy
7:
2220:Primary progressive aphasia
1697:"8B60 Motor neuron disease"
1653:. Chichester, West Sussex.
1390:"What forms does MND take?"
1100:Emos MC, Agarwal S (2022).
698:Greenfield's neuropathology
658:
470:Monomelic amyotrophy (MMA)
10:
2798:
2542:Hashimoto's encephalopathy
2248:Posterior cortical atrophy
2069:Striatonigral degeneration
1920:Cavernous sinus thrombosis
837:. San Rafael, California.
513:Magnetic resonance imaging
282:non-homologous end joining
278:TAR DNA-binding protein 43
187:), difficulty swallowing (
89:of the body. They include
85:, the cells which control
18:
2648:Spinal muscular atrophies
2616:Primary lateral sclerosis
2598:
2575:
2559:
2514:
2474:Intracranial hypertension
2464:
2436:
2407:
2373:
2335:
2324:
2290:
2268:
2254:Creutzfeldt–Jakob disease
2193:
2003:
1994:
1980:
1940:
1874:
1744:
1498:10.1016/j.pmr.2012.08.022
1450:Javed K, Daly DT (2022).
1264:10.1016/j.ncl.2015.07.006
1069:10.1016/j.ncl.2013.02.001
939:10.1016/j.ncl.2015.07.006
665:Spinal muscular atrophies
649:spinal muscular atrophies
543:should remain unaffected.
480:
403:
264:
107:primary lateral sclerosis
52:
47:
38:
33:
2715:Progressive bulbar palsy
2506:Intracranial hypotension
2489:Choroid plexus papilloma
1903:Herpesviral encephalitis
1587:10.1136/jnnp.2004.048652
1545:"Different types of MND"
1002:: CS1 maint: location (
500:
95:progressive bulbar palsy
2227:Frontotemporal dementia
1913:Encephalitis lethargica
1569:Shaw PJ (August 2005).
1214:10.1073/pnas.1818415116
638:motor neuron(e) disease
577:from start of symptoms
312:Associated risk factors
111:spinal muscular atrophy
2532:Hepatic encephalopathy
617:No change in survival
523:nerve conduction study
342:
163:
77:) are a group of rare
71:motor neurone diseases
2772:Motor neuron diseases
2590:Ataxia–telangiectasia
2547:Static encephalopathy
2270:Mitochondrial disease
2108:Spasmodic torticollis
2018:Basal ganglia disease
1731:Motor neuron diseases
1724:Motor neuron diseases
1417:Blumenfeld H (2002).
575:Median survival time
336:
149:
67:Motor neuron diseases
2537:Toxic encephalopathy
2243:Lewy bodies dementia
1726:at Wikimedia Commons
634:Lou Gehrig's disease
630:motor neuron disease
338:Corticospinal tract.
289:double-strand breaks
215:Patterns of weakness
115:monomelic amyotrophy
34:Motor neuron disease
2585:Friedreich's ataxia
1968:Meningoencephalitis
1908:Limbic encephalitis
1205:2019PNAS..116.4696M
1032:on 15 December 2018
810:healthdirect.gov.au
614:Pseudobulbar palsy
609:6 months – 3 years
507:Cerebrospinal fluid
377:autosomal recessive
365:lower motor neurons
361:upper motor neurons
197:pseudobulbar affect
177:respiratory failure
2621:Pseudobulbar palsy
2359:Status epilepticus
2310:Multiple sclerosis
2147:Myoclonic epilepsy
2010:movement disorders
1956:Acute disseminated
1898:Viral encephalitis
1252:Neurologic Clinics
1057:Neurologic Clinics
927:Neurologic Clinics
462:Yes, bulbar region
459:Pseudobulbar palsy
373:autosomal dominant
343:
164:
142:Signs and symptoms
99:pseudobulbar palsy
2759:
2758:
2755:
2754:
2751:
2750:
2555:
2554:
2460:
2459:
2399:Template:Headache
2365:Template:Epilepsy
2286:
2285:
2260:Vascular dementia
2103:Status dystonicus
1976:
1975:
1951:Encephalomyelitis
1829:
1828:
1722:Media related to
1660:978-1-118-66191-8
1651:Neurodegeneration
1199:(10): 4696–4705.
1139:sciencedirect.com
1026:openi.nlm.nih.gov
844:978-1-61504-429-0
782:. 15 January 2018
707:978-0-340-90681-1
621:
620:
498:
497:
399:LMN degeneration
87:voluntary muscles
79:neurodegenerative
64:
63:
28:Medical condition
2789:
2573:
2572:
2564:
2563:
2522:Brain herniation
2333:
2332:
2173:Intention tremor
2168:Essential tremor
2033:Postencephalitic
2001:
2000:
1992:
1991:
1881:
1880:
1862:Diseases of the
1856:
1849:
1842:
1833:
1832:
1742:
1741:
1721:
1705:
1704:
1693:
1687:
1686:
1680:
1672:
1646:
1640:
1639:
1637:
1626:
1618:
1612:
1611:
1598:
1581:(8): 1046–1057.
1566:
1560:
1559:
1557:
1555:
1541:
1532:
1531:
1529:
1527:
1516:
1510:
1509:
1481:
1475:
1474:
1472:
1470:
1447:
1441:
1440:
1414:
1405:
1404:
1402:
1400:
1386:
1375:
1374:
1338:
1319:
1318:
1316:
1314:
1300:
1294:
1293:
1283:
1243:
1237:
1236:
1226:
1216:
1184:
1175:
1174:
1172:
1170:
1156:
1150:
1149:
1147:
1145:
1131:
1125:
1124:
1122:
1120:
1097:
1091:
1090:
1080:
1048:
1042:
1041:
1039:
1037:
1028:. Archived from
1018:
1012:
1011:
1001:
993:
967:
961:
960:
950:
918:
871:
870:
864:
856:
830:
821:
820:
818:
816:
801:
792:
791:
789:
787:
772:
763:
762:
760:
758:
753:on 13 April 2014
743:
712:
711:
689:
569:
568:
396:UMN degeneration
390:
389:
205:Hoffman's reflex
43:
31:
30:
2797:
2796:
2792:
2791:
2790:
2788:
2787:
2786:
2762:
2761:
2760:
2747:
2673:Congenital DSMA
2594:
2551:
2510:
2456:
2444:Sleep disorders
2432:
2409:Cerebrovascular
2403:
2369:
2326:
2320:
2282:
2264:
2189:
2135:Choreoathetosis
2008:
1985:
1972:
1936:
1870:
1860:
1830:
1825:
1824:
1753:
1714:
1709:
1708:
1695:
1694:
1690:
1674:
1673:
1661:
1647:
1643:
1635:
1624:
1620:
1619:
1615:
1567:
1563:
1553:
1551:
1543:
1542:
1535:
1525:
1523:
1522:. 27 March 2019
1518:
1517:
1513:
1482:
1478:
1468:
1466:
1448:
1444:
1429:
1415:
1408:
1398:
1396:
1388:
1387:
1378:
1339:
1322:
1312:
1310:
1302:
1301:
1297:
1244:
1240:
1185:
1178:
1168:
1166:
1158:
1157:
1153:
1143:
1141:
1133:
1132:
1128:
1118:
1116:
1098:
1094:
1049:
1045:
1035:
1033:
1020:
1019:
1015:
995:
994:
982:
968:
964:
919:
874:
858:
857:
845:
831:
824:
814:
812:
802:
795:
785:
783:
774:
773:
766:
756:
754:
745:
744:
715:
708:
690:
683:
678:
661:
626:
576:
564:
556:
541:sensory neurons
503:
367:(LMN), or both?
341:neurons (LMNs).
331:
322:
314:
291:in pluripotent
275:
267:
237:
217:
201:Babinski reflex
158:. (D) Advanced
144:
122:muscle weakness
29:
24:
17:
12:
11:
5:
2795:
2785:
2784:
2779:
2774:
2757:
2756:
2753:
2752:
2749:
2748:
2746:
2745:
2744:
2743:
2732:
2731:
2730:
2729:
2728:
2727:
2722:
2712:
2707:
2706:
2705:
2700:
2695:
2694:
2693:
2688:
2683:
2675:
2670:
2665:
2660:
2655:
2645:
2631:
2630:
2629:
2628:
2623:
2618:
2604:
2602:
2596:
2595:
2593:
2592:
2587:
2581:
2579:
2570:
2561:
2557:
2556:
2553:
2552:
2550:
2549:
2544:
2539:
2534:
2529:
2524:
2518:
2516:
2512:
2511:
2509:
2508:
2503:
2501:Cerebral edema
2498:
2497:
2496:
2491:
2486:
2481:
2470:
2468:
2462:
2461:
2458:
2457:
2455:
2454:
2453:
2452:
2450:Template:Sleep
2440:
2438:
2434:
2433:
2431:
2430:
2424:
2419:
2413:
2411:
2405:
2404:
2402:
2401:
2395:
2390:
2385:
2379:
2377:
2371:
2370:
2368:
2367:
2361:
2356:
2351:
2345:
2343:
2330:
2322:
2321:
2319:
2318:
2312:
2307:
2302:
2296:
2294:
2288:
2287:
2284:
2283:
2281:
2280:
2278:Leigh syndrome
2274:
2272:
2266:
2265:
2263:
2262:
2251:
2250:
2245:
2240:
2239:
2238:
2224:
2223:
2222:
2217:
2216:
2215:
2199:
2197:
2191:
2190:
2188:
2187:
2182:
2177:
2176:
2175:
2170:
2159:
2158:
2157:
2156:
2151:
2150:
2149:
2139:
2138:
2137:
2127:
2122:
2121:
2120:
2115:
2110:
2105:
2089:
2088:
2087:
2086:
2081:
2076:
2071:
2066:
2065:
2064:
2054:
2053:
2052:
2042:
2041:
2040:
2035:
2030:
2014:
2012:
2005:Extrapyramidal
1998:
1989:
1987:encephalopathy
1978:
1977:
1974:
1973:
1971:
1970:
1965:
1960:
1959:
1958:
1947:
1945:
1938:
1937:
1935:
1934:
1933:
1932:
1922:
1917:
1916:
1915:
1910:
1905:
1900:
1889:
1887:
1878:
1872:
1871:
1864:nervous system
1859:
1858:
1851:
1844:
1836:
1827:
1826:
1823:
1822:
1811:
1800:
1785:
1770:
1754:
1749:
1748:
1746:
1745:Classification
1739:
1738:
1727:
1713:
1712:External links
1710:
1707:
1706:
1688:
1659:
1641:
1613:
1561:
1533:
1511:
1492:(1): 139–151.
1476:
1442:
1427:
1406:
1376:
1320:
1295:
1258:(4): 735–748.
1238:
1176:
1151:
1126:
1092:
1063:(2): 343–361.
1043:
1013:
980:
962:
933:(4): 735–748.
872:
843:
822:
793:
764:
713:
706:
680:
679:
677:
674:
673:
672:
667:
660:
657:
625:
622:
619:
618:
615:
611:
610:
607:
603:
602:
599:
595:
594:
591:
587:
586:
583:
579:
578:
573:
563:
560:
555:
552:
551:
550:
544:
533:
526:
519:Electromyogram
516:
510:
502:
499:
496:
495:
492:
489:
485:
484:
482:Inherited MNDs
478:
477:
474:
471:
467:
466:
463:
460:
456:
455:
448:
445:
441:
440:
437:
434:
430:
429:
426:
423:
419:
418:
415:
412:
408:
407:
401:
400:
397:
394:
369:
368:
357:
330:
329:Classification
327:
321:
318:
313:
310:
274:
271:
266:
263:
246:fasciculations
236:
233:
232:
231:
228:
225:
216:
213:
143:
140:
62:
61:
56:
50:
49:
48:spinal diagram
45:
44:
36:
35:
27:
15:
9:
6:
4:
3:
2:
2794:
2783:
2780:
2778:
2777:Rare diseases
2775:
2773:
2770:
2769:
2767:
2742:
2739:
2738:
2737:
2734:
2733:
2726:
2723:
2721:
2718:
2717:
2716:
2713:
2711:
2708:
2704:
2701:
2699:
2696:
2692:
2689:
2687:
2684:
2682:
2679:
2678:
2676:
2674:
2671:
2669:
2666:
2664:
2661:
2659:
2656:
2654:
2651:
2650:
2649:
2646:
2644:
2641:
2640:
2639:
2637:
2633:
2632:
2627:
2624:
2622:
2619:
2617:
2614:
2613:
2612:
2610:
2606:
2605:
2603:
2601:
2597:
2591:
2588:
2586:
2583:
2582:
2580:
2578:
2574:
2571:
2569:
2565:
2562:
2558:
2548:
2545:
2543:
2540:
2538:
2535:
2533:
2530:
2528:
2527:Reye syndrome
2525:
2523:
2520:
2519:
2517:
2513:
2507:
2504:
2502:
2499:
2495:
2492:
2490:
2487:
2485:
2482:
2480:
2479:Hydrocephalus
2477:
2476:
2475:
2472:
2471:
2469:
2467:
2463:
2451:
2447:
2446:
2445:
2442:
2441:
2439:
2435:
2429:
2425:
2423:
2420:
2418:
2415:
2414:
2412:
2410:
2406:
2400:
2396:
2394:
2391:
2389:
2386:
2384:
2381:
2380:
2378:
2376:
2372:
2366:
2362:
2360:
2357:
2355:
2352:
2350:
2347:
2346:
2344:
2342:
2338:
2334:
2331:
2329:
2323:
2317:
2313:
2311:
2308:
2306:
2303:
2301:
2298:
2297:
2295:
2293:
2292:Demyelinating
2289:
2279:
2276:
2275:
2273:
2271:
2267:
2261:
2258:
2257:
2256:
2255:
2249:
2246:
2244:
2241:
2237:
2234:
2233:
2232:
2228:
2225:
2221:
2218:
2214:
2211:
2210:
2209:
2206:
2205:
2204:
2201:
2200:
2198:
2196:
2192:
2186:
2183:
2181:
2180:Restless legs
2178:
2174:
2171:
2169:
2166:
2165:
2164:
2161:
2160:
2155:
2152:
2148:
2145:
2144:
2143:
2140:
2136:
2133:
2132:
2131:
2128:
2126:
2123:
2119:
2118:Blepharospasm
2116:
2114:
2111:
2109:
2106:
2104:
2101:
2100:
2099:
2096:
2095:
2094:
2091:
2090:
2085:
2082:
2080:
2077:
2075:
2074:Hemiballismus
2072:
2070:
2067:
2063:
2060:
2059:
2058:
2055:
2051:
2048:
2047:
2046:
2043:
2039:
2036:
2034:
2031:
2029:
2026:
2025:
2024:
2021:
2020:
2019:
2016:
2015:
2013:
2011:
2006:
2002:
1999:
1997:
1993:
1990:
1988:
1983:
1979:
1969:
1966:
1964:
1961:
1957:
1954:
1953:
1952:
1949:
1948:
1946:
1944:
1939:
1931:
1928:
1927:
1926:
1925:Brain abscess
1923:
1921:
1918:
1914:
1911:
1909:
1906:
1904:
1901:
1899:
1896:
1895:
1894:
1891:
1890:
1888:
1886:
1882:
1879:
1877:
1873:
1869:
1865:
1857:
1852:
1850:
1845:
1843:
1838:
1837:
1834:
1821:
1817:
1816:
1812:
1810:
1806:
1805:
1801:
1799:
1795:
1794:
1790:
1786:
1784:
1780:
1779:
1775:
1771:
1769:
1765:
1764:
1760:
1756:
1755:
1752:
1747:
1743:
1737:
1733:
1732:
1728:
1725:
1720:
1716:
1715:
1702:
1698:
1692:
1684:
1678:
1670:
1666:
1662:
1656:
1652:
1645:
1634:
1630:
1623:
1617:
1610:
1606:
1602:
1597:
1592:
1588:
1584:
1580:
1576:
1572:
1565:
1550:
1546:
1540:
1538:
1521:
1515:
1507:
1503:
1499:
1495:
1491:
1487:
1480:
1465:
1461:
1457:
1453:
1446:
1438:
1434:
1430:
1424:
1420:
1413:
1411:
1395:
1394:mndnsw.asn.au
1391:
1385:
1383:
1381:
1372:
1368:
1364:
1360:
1356:
1352:
1348:
1344:
1337:
1335:
1333:
1331:
1329:
1327:
1325:
1309:
1305:
1299:
1291:
1287:
1282:
1277:
1273:
1269:
1265:
1261:
1257:
1253:
1249:
1242:
1234:
1230:
1225:
1220:
1215:
1210:
1206:
1202:
1198:
1194:
1190:
1183:
1181:
1165:
1164:ninds.nih.gov
1161:
1155:
1140:
1136:
1130:
1115:
1111:
1107:
1103:
1096:
1088:
1084:
1079:
1074:
1070:
1066:
1062:
1058:
1054:
1047:
1031:
1027:
1023:
1017:
1009:
1005:
999:
991:
987:
983:
981:9781615044290
977:
973:
966:
958:
954:
949:
944:
940:
936:
932:
928:
924:
917:
915:
913:
911:
909:
907:
905:
903:
901:
899:
897:
895:
893:
891:
889:
887:
885:
883:
881:
879:
877:
868:
862:
854:
850:
846:
840:
836:
829:
827:
811:
807:
800:
798:
781:
777:
771:
769:
752:
748:
742:
740:
738:
736:
734:
732:
730:
728:
726:
724:
722:
720:
718:
709:
703:
699:
695:
688:
686:
681:
671:
668:
666:
663:
662:
656:
654:
650:
646:
645:motor neurons
641:
639:
635:
631:
616:
613:
612:
608:
605:
604:
600:
597:
596:
592:
589:
588:
584:
581:
580:
574:
571:
570:
567:
559:
548:
547:Tissue biopsy
545:
542:
538:
534:
531:
530:reinnervation
527:
524:
520:
517:
514:
511:
508:
505:
504:
493:
490:
487:
486:
483:
479:
475:
472:
469:
468:
464:
461:
458:
457:
453:
449:
446:
443:
442:
438:
435:
432:
431:
427:
424:
421:
420:
416:
413:
410:
409:
406:
405:Sporadic MNDs
402:
398:
395:
392:
391:
388:
384:
382:
378:
374:
366:
362:
358:
355:
354:
353:
350:
348:
339:
335:
326:
317:
309:
307:
302:
298:
294:
290:
287:
283:
279:
270:
262:
259:
256:
253:
251:
250:hyperreflexia
247:
243:
229:
226:
223:
222:
221:
212:
208:
206:
202:
198:
194:
190:
186:
182:
178:
174:
170:
161:
160:thenar muscle
157:
156:Babinski sign
153:
148:
139:
135:
133:
132:
127:
123:
118:
116:
112:
108:
104:
100:
96:
92:
88:
84:
83:motor neurons
80:
76:
72:
68:
60:
57:
55:
51:
46:
42:
37:
32:
26:
22:
2735:
2634:
2607:
2599:
2568:Degenerative
2305:Inflammatory
2252:
2185:Stiff-person
2023:Parkinsonism
1996:Degenerative
1893:Encephalitis
1876:Inflammation
1866:, primarily
1813:
1802:
1787:
1772:
1757:
1729:
1700:
1691:
1650:
1644:
1628:
1616:
1608:
1578:
1574:
1564:
1552:. Retrieved
1548:
1524:. Retrieved
1514:
1489:
1485:
1479:
1467:. Retrieved
1455:
1445:
1418:
1397:. Retrieved
1393:
1349:(1): 32–37.
1346:
1342:
1311:. Retrieved
1307:
1298:
1255:
1251:
1241:
1196:
1192:
1167:. Retrieved
1163:
1154:
1142:. Retrieved
1138:
1129:
1117:. Retrieved
1105:
1095:
1060:
1056:
1046:
1034:. Retrieved
1030:the original
1025:
1016:
971:
965:
930:
926:
834:
813:. Retrieved
809:
784:. Retrieved
779:
755:. Retrieved
751:the original
697:
642:
637:
633:
629:
627:
565:
557:
521:(EMG) &
481:
404:
385:
370:
351:
344:
337:
323:
315:
276:
268:
260:
257:
254:
238:
218:
209:
165:
136:
129:
119:
74:
70:
66:
65:
25:
2720:Fazio–Londe
2560:Both/either
2354:Generalised
2213:Early-onset
2208:Alzheimer's
1943:spinal cord
1554:12 December
1526:18 November
1428:087893060-4
1399:11 December
1036:12 December
624:Terminology
593:8–10 years
363:(UMN), the
286:repairs DNA
175:), or even
150:A man with
2766:Categories
2328:paroxysmal
2300:Autoimmune
2093:Dyskinesia
1963:Meningitis
1941:Brain and
1815:DiseasesDB
1456:StatPearls
1308:pn.bmj.com
1106:StatPearls
815:24 October
786:24 October
757:7 November
676:References
601:2–4 years
585:2–5 years
301:DNA ligase
273:DNA damage
193:sialorrhea
185:dysarthria
113:(SMA) and
2325:Episodic/
2203:Tauopathy
2154:Akathisia
2142:Myoclonus
2125:Athetosis
2057:Tauopathy
1677:cite book
1669:958876527
1272:0733-8619
998:cite book
990:860981760
861:cite book
853:860981760
562:Prognosis
554:Treatment
320:Diagnosis
293:stem cell
189:dysphagia
173:orthopnea
59:Neurology
54:Specialty
2691:SMALED2B
2686:SMALED2A
2383:Migraine
2375:Headache
2341:epilepsy
2337:Seizures
2195:Dementia
2098:Dystonia
1633:Archived
1631:. 2015.
1605:16024877
1506:23177036
1464:30969636
1437:44628054
1371:51910723
1363:30075105
1290:26515618
1233:30770445
1114:30725990
1087:23642713
957:26515618
659:See also
381:X-linked
169:exertion
162:atrophy.
2703:SMA-PME
2698:SMA-PCH
2681:SMALED1
2393:Tension
2388:Cluster
2113:Meige's
1930:Amoebic
1809:D016472
1596:1739758
1469:24 June
1313:24 June
1281:4629510
1224:6410842
1201:Bibcode
1169:24 June
1144:24 June
1119:24 June
1078:3922643
948:4629510
454:region
242:atrophy
109:(PLS),
105:(PMA),
97:(PBP),
93:(ALS),
2422:Stroke
2236:Pick's
2163:Tremor
2130:Chorea
1667:
1657:
1603:
1593:
1504:
1462:
1435:
1425:
1369:
1361:
1288:
1278:
1270:
1231:
1221:
1112:
1085:
1075:
988:
978:
955:
945:
851:
841:
780:nhs.uk
704:
452:bulbar
265:Causes
181:Bulbar
128:(e.g.
2736:both:
2668:DSMA1
2663:SMAX2
2658:SMAX1
2638:only:
2611:only:
2515:Other
2437:Other
2349:Focal
1982:Brain
1885:Brain
1798:335.2
1783:G12.2
1736:NINDS
1636:(PDF)
1625:(PDF)
1367:S2CID
572:Type
501:Tests
450:Yes,
379:, or
297:XRCC4
220:are:
126:genes
2339:and
2050:PKAN
2045:NBIA
1820:8358
1804:MeSH
1793:9-CM
1768:8B60
1683:link
1665:OCLC
1655:ISBN
1601:PMID
1556:2018
1528:2019
1502:PMID
1471:2022
1460:PMID
1433:OCLC
1423:ISBN
1401:2018
1359:PMID
1315:2022
1286:PMID
1268:ISSN
1229:PMID
1171:2022
1146:2022
1121:2022
1110:PMID
1083:PMID
1038:2018
1008:link
1004:link
986:OCLC
976:ISBN
953:PMID
867:link
849:OCLC
839:ISBN
817:2020
788:2020
759:2010
702:ISBN
494:Yes
491:Yes
476:Yes
439:Yes
417:Yes
393:Type
244:and
131:SOD1
75:MNDs
2653:SMA
2636:LMN
2609:UMN
2600:MND
2466:CSF
2417:TIA
2062:PSP
2038:NMS
2007:and
1868:CNS
1789:ICD
1774:ICD
1759:ICD
1734:at
1591:PMC
1583:doi
1494:doi
1351:doi
1347:132
1276:PMC
1260:doi
1219:PMC
1209:doi
1197:116
1073:PMC
1065:doi
943:PMC
935:doi
473:No
465:No
447:Yes
428:No
425:Yes
414:Yes
306:ALS
69:or
2768::
2577:SA
2084:OA
2079:HD
2028:PD
1818::
1807::
1796::
1781::
1778:10
1766::
1763:11
1699:.
1679:}}
1675:{{
1663:.
1627:.
1607:.
1599:.
1589:.
1579:76
1577:.
1573:.
1547:.
1536:^
1500:.
1490:24
1488:.
1454:.
1431:.
1409:^
1392:.
1379:^
1365:.
1357:.
1345:.
1323:^
1306:.
1284:.
1274:.
1266:.
1256:33
1254:.
1250:.
1227:.
1217:.
1207:.
1195:.
1191:.
1179:^
1162:.
1137:.
1104:.
1081:.
1071:.
1061:31
1059:.
1055:.
1024:.
1000:}}
996:{{
984:.
951:.
941:.
931:33
929:.
925:.
875:^
863:}}
859:{{
847:.
825:^
808:.
796:^
778:.
767:^
716:^
684:^
436:No
375:,
203:,
101:,
2229:/
1984:/
1855:e
1848:t
1841:v
1791:-
1776:-
1761:-
1751:D
1685:)
1671:.
1585::
1558:.
1530:.
1508:.
1496::
1473:.
1439:.
1403:.
1373:.
1353::
1317:.
1292:.
1262::
1235:.
1211::
1203::
1173:.
1148:.
1123:.
1089:.
1067::
1040:.
1010:)
992:.
959:.
937::
869:)
855:.
819:.
790:.
761:.
710:.
299:-
73:(
23:.
Text is available under the Creative Commons Attribution-ShareAlike License. Additional terms may apply.