397:). Calnexin acts to stabilize the class I MHC α chains prior to β2m binding. Following complete assembly of the MHC molecule, calnexin dissociates. The MHC molecule lacking a bound peptide is inherently unstable and requires the binding of the chaperones calreticulin and Erp57. Additionally, tapasin binds to the MHC molecule and serves to link it to the TAP proteins and facilitates the selection of peptide in an iterative process called peptide editing, thus facilitating enhanced peptide loading and colocalization.
466:(NK) cells are normally inactivated upon recognizing MHC I molecules on the surface of cells. Therefore, in the absence of MHC I molecules, NK cells are activated and recognize the cell as aberrant, suggesting that it may be infected by viruses attempting to evade immune destruction. Several human cancers also show down-regulation of MHC I, giving transformed cells the same survival advantage of being able to avoid normal immune surveillance designed to destroy any infected or transformed cells.
311:
31:
451:. As viruses induce cellular expression of viral proteins, some of these products are tagged for degradation, with the resulting peptide fragments entering the endoplasmic reticulum and binding to MHC I molecules. It is in this way, the MHC class I-dependent pathway of antigen presentation, that the virus infected cells signal T-cells that abnormal proteins are being produced as a result of infection.
330:
activity. The proteasome degrades intracellular proteins into small peptides that are then released into the cytosol. Proteasomes can also ligate distinct peptide fragments (termed spliced peptides), producing sequences that are noncontiguous and therefore not linearly templated in the genome. The
164:
A normal cell will display peptides from normal cellular protein turnover on its class I MHC, and CTLs will not be activated in response to them due to central and peripheral tolerance mechanisms. When a cell expresses foreign proteins, such as after viral infection, a fraction of the class I MHC
627:(death) of one copy of the gene, though sometimes this process results in two new genes with divergent function. It is likely that human MHC class Ib loci (HLA-E, -F, and -G) as well as MHC class I pseudogenes arose from MHC class Ia loci (HLA-A, -B, and -C) in this birth-and-death process.
462:, reducing the risk of infecting neighboring cells. As an evolutionary response to this method of immune surveillance, many viruses are able to down-regulate or otherwise prevent the presentation of MHC class I molecules on the cell surface. In contrast to cytotoxic T lymphocytes,
153:. The MHC I: peptide complex is then inserted via the endoplasmic reticulum into the external plasma membrane of the cell. The epitope peptide is bound on extracellular parts of the class I MHC molecule. Thus, the function of the class I MHC is to display intracellular proteins to
286:
domains fold to make up a groove for peptides to bind. MHC class I molecules bind peptides that are predominantly 8-10 amino acid in length (Parham 87), but the binding of longer peptides have also been reported.
587:, and have been found in all living jawed vertebrates that have been studied thus far. Since their emergence in jawed vertebrates, this gene family has been subjected to many divergent evolutionary paths as
1407:
Albring J, Koopmann JO, Hämmerling GJ, Momburg F (January 2004). "Retrotranslocation of MHC class I heavy chain from the endoplasmic reticulum to the cytosol is dependent on ATP supply to the ER lumen".
695:
Kulski JK, Shiina T, Anzai T, Kohara S, Inoko H (December 2002). "Comparative genomic analysis of the MHC: the evolution of class I duplication blocks, diversity and complexity from shark to man".
314:
Simplified diagram of cytoplasmic protein degradation by the proteasome, transport into endoplasmic reticulum by TAP complex, loading on MHC class I, and transport to the surface for presentation
102:; this will trigger an immediate response from the immune system against a particular non-self antigen displayed with the help of an MHC class I protein. Because MHC class I molecules present
1710:
331:
origin of spliced peptide segments can be from the same protein (cis-splicing) or different proteins (trans-splicing). The peptides have to be translocated from the cytosol into the
740:
1274:
Wearsch PA, Cresswell P (August 2007). "Selective loading of high-affinity peptides onto major histocompatibility complex class I molecules by the tapasin-ERp57 heterodimer".
1052:
Faridi P, Li C, Ramarathinam SH, Vivian JP, Illing PT, Mifsud NA, Ayala R, Song J, Gearing LJ, Hertzog PJ, Ternette N, Rossjohn J, Croft NP, Purcell AW (12 October 2018).
172:(NKs). Reduction in the normal levels of surface class I MHC, a mechanism employed by some viruses and certain tumors to evade CTL responses, activates NK cell killing.
366:. The two subunits form a peptide binding site and two ATP binding sites that face the cytosol. TAP binds peptides on the cytoplasmic side and translocates them under
1703:
428:
channel into the cytosol, where they might undergo further trimming in size, and might be translocated by TAP back into ER for binding to a MHC class I molecule.
1164:
Blees A, Januliene D, Hofmann T, Koller N, Schmidt C, Trowitzsch S, Moeller A, Tampé R (November 2017). "Structure of the human MHC-I peptide-loading complex".
1696:
1486:"Activation of CXCR4 triggers ubiquitination and down-regulation of major histocompatibility complex class I (MHC-I) on epithelioid carcinoma HeLa cells"
623:
events cause the genome to contain multiple copies of a gene which can then undergo separate evolutionary processes. Sometimes these processes result in
165:
will display these peptides on the cell surface. Consequently, CTLs specific for the MHC:peptide complex will recognize and kill presenting cells.
1527:"Trans-species polymorphism in humans and the great apes is generally maintained by balancing selection that modulates the host immune response"
1053:
351:
2091:
2096:
1445:"Exogenous antigens are processed through the endoplasmic reticulum-associated degradation (ERAD) in cross-presentation by dendritic cells"
2594:
1368:"Export of antigenic peptides from the endoplasmic reticulum intersects with retrograde protein translocation through the Sec61p channel"
893:
Ljunggren HG, Stam NJ, Öhlén C, Neefjes JJ, Höglund P, Heemels MT, Bastin J, Schumacher TN, Townsend A, Kärre K, Ploegh HL (1990-08-02).
737:
2177:
2172:
2104:
2222:
2202:
2192:
2187:
2157:
2265:
2144:
2232:
424:
Peptides that fail to bind MHC class I molecules in the lumen of the endoplasmic reticulum (ER) are removed from the ER via the
2323:
2018:
987:
Sun Y, Young MC, Woodward CH, Danon JN, Truong HV, Gupta S, Winters TJ, Font-Burgada J, Burslem GM, Sgourakis NG (2023-06-20).
370:
consumption into the lumen of the ER. The MHC class I molecule is then, in turn, loaded with peptides in the lumen of the ER.
807:
Syken J, Grandpre T, Kanold PO, Shatz CJ (September 2006). "PirB restricts ocular-dominance plasticity in visual cortex".
1688:
1096:
Liepe J, Marino F, Sidney J, Jeko A, Bunting DE, Sette A, Kloetzel PM, Stumpf MP, Heck AJ, Mishto M (21 October 2016).
1836:
404:
to reach the cell surface. The transport of the MHC class I molecules through the secretory pathway involves several
2523:
2332:
1981:
400:
Once the peptide is loaded onto the MHC class I molecule, the complex dissociates and it leaves the ER through the
71:
1366:
Koopmann JO, Albring J, Hüter E, Bulbuc N, Spee P, Neefjes J, Hämmerling GJ, Momburg F, et al. (July 2000).
1319:"Tapasin shapes immunodominance hierarchies according to the kinetic stability of peptide-MHC class I complexes"
858:
Burrows SR, Rossjohn J, McCluskey J (January 2006). "Have we cut ourselves too short in mapping CTL epitopes?".
180:
Paired-immunoglobulin-like receptor B (PirB), an MHCI-binding receptor, is involved in the regulation of visual
157:(CTLs). However, class I MHC can also present peptides generated from exogenous proteins, in a process known as
1668:
1097:
1054:"A subset of HLA-I peptides are not genomically templated: Evidence for cis- and trans-spliced peptide ligands"
405:
989:"Universal open MHC-I molecules for rapid peptide loading and enhanced complex stability across HLA allotypes"
757:
Hansen TH, Bouvier M (July 2009). "MHC class I antigen presentation: learning from viral evasion strategies".
294:
between the peptide, MHC I, and B2M, under subphysiological temperatures, stable, peptide-deficient MHC I/B2M
373:
The peptide-loading process involves several other molecules that form a large multimeric complex called the
599:
in an evolutionary related MHC class I gene remains in two species, likely due to strong pathogen-mediated
408:
of the MHC molecule. Some of the posttranslational modifications occur in the ER and involve change to the
2133:
2589:
2553:
2316:
1723:
738:
http://users.rcn.com/jkimball.ma.ultranet/BiologyPages/H/HLA.html#Class_I_Histocompatibility_Molecules
340:
2543:
298:
have been observed. Synthetic stable, peptide-receptive MHC I molecules have been generated using a
1682:
1672:
2518:
608:
374:
243:
122:
949:
2584:
2579:
2548:
1317:
Thirdborough SM, Roddick JS, Radcliffe JN, Howarth M, Stevenson FK, Elliott T (February 2008).
580:
459:
367:
185:
1745:
611:
evolution is one of the mechanistic explanations for the size of the MHC class I gene family.
564:
556:
544:
532:
520:
503:
491:
479:
206:
became more pronounced at all ages. PirB loss of function mutant mice also exhibited enhanced
2309:
1897:
1719:
1678:
592:
332:
290:
While a high-affinity peptide and the B2M subunit are normally required to maintain a stable
1807:
1774:
2301:
1797:
1593:
1228:
1173:
1112:
1000:
906:
816:
350:
The peptide translocation from the cytosol into the lumen of the ER is accomplished by the
247:
231:
169:
1643:
1626:
8:
600:
215:
54:
1718:
1232:
1177:
1116:
1029:
1004:
988:
910:
820:
1602:
1577:
1553:
1526:
1348:
1299:
1197:
1146:
950:"Direct binding of peptide to empty MHC class I molecules on intact cells and in vitro"
840:
782:
720:
669:
644:
326:. The proteasome is a macromolecule that consists of 28 subunits, of which half affect
158:
1384:
1367:
1251:
1216:
2528:
2123:
1648:
1607:
1558:
1507:
1466:
1425:
1389:
1340:
1291:
1256:
1189:
1138:
1078:
1034:
1016:
969:
965:
930:
922:
875:
832:
774:
712:
708:
674:
660:
584:
401:
230:
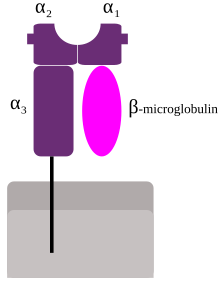
MHC class I molecules are heterodimers that consist of two polypeptide chains, α and
99:
98:. Their function is to display peptide fragments of proteins from within the cell to
1352:
1303:
1150:
724:
2076:
1638:
1597:
1589:
1548:
1538:
1497:
1456:
1417:
1379:
1330:
1283:
1246:
1236:
1201:
1181:
1128:
1120:
1098:"A large fraction of HLA class I ligands are proteasome-generated spliced peptides"
1068:
1024:
1008:
961:
948:
Schumacher TN, Heemels MT, Neefjes JJ, Kast W, Melief CJ, Ploegh HL (August 1990).
914:
867:
844:
824:
786:
766:
704:
664:
656:
645:"The MHC class I antigen presentation pathway: strategies for viral immune evasion"
620:
200:
189:
154:
1217:"Tapasin enhances MHC class I peptide presentation according to peptide half-life"
2490:
2009:
1872:
1726:
1421:
744:
443:
MHC class I molecules are loaded with peptides generated from the degradation of
413:
355:
336:
291:
267:
211:
207:
203:
196:
192:
181:
59:
2574:
1782:
1221:
Proceedings of the
National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America
1073:
591:
events have taken place. There are, however, documented cases of trans-species
463:
444:
358:
family and is a heterodimeric multimembrane-spanning polypeptide consisting of
299:
238:(B2M). The two chains are linked noncovalently via interaction of B2M and the α
95:
1543:
412:
regions of the protein, followed by extensive changes to the N-glycans in the
2568:
1763:
1020:
926:
871:
219:
1461:
1444:
1241:
1124:
1012:
828:
335:(ER) to meet the MHC class I molecule, whose peptide-binding site is in the
2384:
1991:
1611:
1562:
1511:
1502:
1485:
1470:
1429:
1393:
1344:
1295:
1260:
1193:
1142:
1133:
1082:
1038:
894:
879:
836:
778:
716:
678:
382:
295:
79:
75:
1652:
1335:
1318:
973:
934:
278:
heterodimer ligand, and checks the coupled peptide for antigenicity. The α
2538:
2038:
1882:
1820:
1736:
448:
327:
310:
1185:
199:
and adulthood. When the function of PirB was abolished in mutant mice,
168:
Alternatively, class I MHC itself can serve as an inhibitory ligand for
624:
588:
323:
214:. These results suggest that PirB may be involved in the modulation of
150:
87:
2050:
918:
455:
83:
1484:
Wang Z, Zhang L, Qiao A, Watson K, Zhang J, Fan GH (February 2008).
770:
2533:
2500:
2495:
2485:
2468:
2463:
2458:
2453:
2448:
2436:
2431:
2100:
2054:
1316:
1287:
604:
409:
386:
149:
generated mainly from the degradation of cytosolic proteins by the
91:
1753:
454:
The fate of the virus-infected cell is almost always induction of
110:
proteins, the pathway of MHC class I presentation is often called
2480:
2419:
2414:
2402:
2397:
2217:
2212:
2207:
2197:
2182:
2167:
2162:
2152:
1443:
Imai J, Hasegawa H, Maruya M, Koyasu S, Yahara I (January 2005).
432:
416:. The N-glycans mature fully before they reach the cell surface.
378:
319:
146:
107:
103:
1406:
2475:
2443:
2426:
2409:
2392:
2290:
2285:
2280:
2275:
2270:
2260:
2255:
2250:
2245:
2240:
1973:
1964:
1857:
1578:"Concerted and birth-and-death evolution of multigene families"
596:
259:
1214:
246:, while the B2M subunit is not polymorphic and encoded by the
30:
2374:
2369:
2364:
2359:
2354:
2349:
1945:
1941:
1215:
Howarth M, Williams A, Tolstrup AB, Elliott T (August 2004).
549:
537:
525:
508:
496:
484:
425:
394:
390:
266:-CD8 interaction holds the MHC I molecule in place while the
134:
130:
126:
2331:
1525:
Azevedo L, Serrano C, Amorim A, Cooper DN (September 2015).
947:
2086:
2081:
2028:
2023:
2013:
1949:
1921:
1905:
1901:
1815:
1792:
1787:
1759:
1163:
363:
359:
1524:
1365:
1051:
254:
domain is plasma membrane-spanning and interacts with the
2060:
2046:
892:
255:
242:
domain. Only the α chain is polymorphic and encoded by a
1442:
857:
806:
270:(TCR) on the surface of the cytotoxic T cell binds its α
694:
614:
1095:
986:
747:
Kimball's
Biology Pages, Histocompatibility Molecules
345:
1483:
895:"Empty MHC class I molecules come out in the cold"
1627:"Origin and evolution of HLA class I pseudogenes"
431:For example, an interaction of sec61 with bovine
2566:
1273:
993:Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences
302:between the MHC I and B2M, named "open MHC-I".
352:transporter associated with antigen processing
2317:
1704:
756:
579:The MHC class I genes originated in the most
175:
1436:
1400:
1359:
802:
800:
798:
796:
2324:
2310:
1711:
1697:
29:
1681:at the U.S. National Library of Medicine
1671:at the U.S. National Library of Medicine
1642:
1601:
1575:
1552:
1542:
1501:
1460:
1383:
1334:
1250:
1240:
1132:
1072:
1028:
793:
668:
595:in MHC class I genes, where a particular
318:The peptides are generated mainly in the
309:
619:Birth-and-death evolution asserts that
574:
339:of the ER. They have membrane proximal
210:after monocular deprivation during the
35:Schematic representation of MHC class I
2567:
1624:
1594:10.1146/annurev.genet.39.073003.112240
642:
2305:
1692:
1644:10.1093/oxfordjournals.molbev.a040201
469:
690:
688:
615:Birth-and-death of MHC class I genes
438:
1669:Histocompatibility+Antigens+Class+I
1490:The Journal of Biological Chemistry
13:
2595:Single-pass transmembrane proteins
419:
70:are one of two primary classes of
14:
2606:
1837:Polymeric immunoglobulin receptor
1662:
685:
346:Translocation and peptide loading
125:corresponding to MHC class I are
74:(MHC) molecules (the other being
2524:Minor histocompatibility antigen
2333:Major histocompatibility complex
709:10.1034/j.1600-065x.2002.19008.x
661:10.1046/j.1365-2567.2003.01738.x
72:major histocompatibility complex
1631:Molecular Biology and Evolution
1618:
1576:Nei M, Rooney AP (2005-11-14).
1569:
1518:
1477:
1310:
1267:
1208:
1157:
1089:
1045:
406:posttranslational modifications
2049:(with two glycoprotein chains
1323:European Journal of Immunology
980:
941:
886:
851:
750:
731:
636:
607:that can infect both species.
354:(TAP). TAP is a member of the
1:
2145:Killer-cell IG-like receptors
1385:10.1016/S1074-7613(00)00013-3
630:
1422:10.1016/j.molimm.2003.08.008
966:10.1016/0092-8674(90)90020-F
305:
225:
16:Protein of the immune system
7:
2233:Leukocyte IG-like receptors
184:. PirB is expressed in the
145:Class I MHC molecules bind
140:
10:
2611:
2554:Cluster of differentiation
1724:immunoglobulin superfamily
1074:10.1126/sciimmunol.aar3947
759:Nature Reviews. Immunology
643:Hewitt EW (October 2003).
176:PirB and visual plasticity
2544:Human blood group systems
2511:
2383:
2340:
2231:
2143:
2122:
2069:
2037:
2002:
1972:
1963:
1934:
1914:
1890:
1881:
1865:
1856:
1849:
1829:
1806:
1773:
1744:
1733:
1582:Annual Review of Genetics
1544:10.1186/s40246-015-0043-1
53:
45:
40:
28:
23:
1683:Medical Subject Headings
1673:Medical Subject Headings
1625:Hughes AL (March 1995).
1449:International Immunology
872:10.1016/j.it.2005.11.001
2549:Cell adhesion molecules
2519:Human leukocyte antigen
1720:Transmembrane receptors
1242:10.1073/pnas.0306294101
1125:10.1126/science.aaf4384
1013:10.1073/pnas.2304055120
829:10.1126/science.1128232
375:Peptide loading complex
86:cells in the bodies of
78:) and are found on the
1503:10.1074/jbc.m706848200
581:recent common ancestor
460:cell-mediated immunity
447:cytosolic proteins in
315:
186:central nervous system
1462:10.1093/intimm/dxh184
1336:10.1002/eji.200737832
697:Immunological Reviews
333:endoplasmic reticulum
313:
195:in the developmental
90:. They also occur on
68:MHC class I molecules
1410:Molecular Immunology
860:Trends in Immunology
575:Evolutionary history
248:Beta-2 microglobulin
170:natural killer cells
2070:Accessory molecules
1935:Accessory molecules
1233:2004PNAS..10111737H
1186:10.1038/nature24627
1178:2017Natur.551..525B
1117:2016Sci...354..354L
1005:2023PNAS..12004055S
999:(25): e2304055120.
911:1990Natur.346..476L
821:2006Sci...313.1795S
601:balancing selection
435:has been observed.
377:consisting of TAP,
216:synaptic plasticity
2134:cytokine receptors
1734:Antibody receptor:
1061:Science Immunology
815:(5794): 1795–800.
743:2016-02-04 at the
470:Genes and isotypes
316:
159:cross-presentation
116:endogenous pathway
2590:Protein targeting
2562:
2561:
2529:Blood transfusion
2299:
2298:
2124:Cytokine receptor
2118:
2117:
2114:
2113:
1959:
1958:
1930:
1929:
1845:
1844:
1679:MHC+Class+I+Genes
1276:Nature Immunology
1172:(7681): 525–528.
1111:(6310): 354–358.
905:(6283): 476–480.
585:jawed vertebrates
516:Less polymorphic
475:Very polymorphic
439:Effect of viruses
402:secretory pathway
155:cytotoxic T cells
100:cytotoxic T cells
65:
64:
2602:
2326:
2319:
2312:
2303:
2302:
2003:Antigen receptor
1970:
1969:
1888:
1887:
1866:Antigen receptor
1863:
1862:
1854:
1853:
1850:Antigen receptor
1808:Alpha (α)/mu (μ)
1742:
1741:
1727:immune receptors
1713:
1706:
1699:
1690:
1689:
1657:
1656:
1646:
1622:
1616:
1615:
1605:
1573:
1567:
1566:
1556:
1546:
1522:
1516:
1515:
1505:
1481:
1475:
1474:
1464:
1440:
1434:
1433:
1404:
1398:
1397:
1387:
1363:
1357:
1356:
1338:
1314:
1308:
1307:
1271:
1265:
1264:
1254:
1244:
1227:(32): 11737–42.
1212:
1206:
1205:
1161:
1155:
1154:
1136:
1102:
1093:
1087:
1086:
1076:
1067:(28): eaar3947.
1058:
1049:
1043:
1042:
1032:
984:
978:
977:
945:
939:
938:
919:10.1038/346476a0
890:
884:
883:
855:
849:
848:
804:
791:
790:
754:
748:
735:
729:
728:
692:
683:
682:
672:
640:
625:pseudogenization
621:gene duplication
201:ocular dominance
190:ocular dominance
33:
21:
20:
2610:
2609:
2605:
2604:
2603:
2601:
2600:
2599:
2565:
2564:
2563:
2558:
2507:
2379:
2336:
2330:
2300:
2295:
2227:
2139:
2110:
2065:
2033:
1998:
1955:
1926:
1910:
1877:
1841:
1825:
1802:
1769:
1735:
1729:
1717:
1665:
1660:
1623:
1619:
1574:
1570:
1523:
1519:
1482:
1478:
1441:
1437:
1405:
1401:
1364:
1360:
1315:
1311:
1272:
1268:
1213:
1209:
1162:
1158:
1100:
1094:
1090:
1056:
1050:
1046:
985:
981:
946:
942:
891:
887:
856:
852:
805:
794:
771:10.1038/nri2575
755:
751:
745:Wayback Machine
736:
732:
693:
686:
641:
637:
633:
617:
609:Birth-and-death
577:
472:
441:
422:
420:Peptide removal
414:Golgi apparatus
356:ABC transporter
348:
308:
292:ternary complex
285:
281:
277:
273:
268:T cell receptor
265:
258:co-receptor of
253:
241:
235:
228:
212:critical period
197:critical period
188:and diminishes
178:
143:
121:In humans, the
96:red blood cells
36:
17:
12:
11:
5:
2608:
2598:
2597:
2592:
2587:
2582:
2577:
2560:
2559:
2557:
2556:
2551:
2546:
2541:
2536:
2531:
2526:
2521:
2515:
2513:
2509:
2508:
2506:
2505:
2504:
2503:
2498:
2493:
2488:
2483:
2473:
2472:
2471:
2466:
2461:
2456:
2451:
2441:
2440:
2439:
2434:
2424:
2423:
2422:
2417:
2407:
2406:
2405:
2400:
2389:
2387:
2381:
2380:
2378:
2377:
2372:
2367:
2362:
2357:
2352:
2346:
2344:
2338:
2337:
2329:
2328:
2321:
2314:
2306:
2297:
2296:
2294:
2293:
2288:
2283:
2278:
2273:
2268:
2263:
2258:
2253:
2248:
2243:
2237:
2235:
2229:
2228:
2226:
2225:
2220:
2215:
2210:
2205:
2200:
2195:
2190:
2185:
2180:
2175:
2170:
2165:
2160:
2155:
2149:
2147:
2141:
2140:
2138:
2137:
2128:
2126:
2120:
2119:
2116:
2115:
2112:
2111:
2109:
2108:
2094:
2089:
2084:
2079:
2073:
2071:
2067:
2066:
2064:
2063:
2058:
2043:
2041:
2035:
2034:
2032:
2031:
2026:
2021:
2016:
2006:
2004:
2000:
1999:
1997:
1996:
1995:
1994:
1989:
1978:
1976:
1967:
1961:
1960:
1957:
1956:
1954:
1953:
1938:
1936:
1932:
1931:
1928:
1927:
1925:
1924:
1918:
1916:
1912:
1911:
1909:
1908:
1894:
1892:
1885:
1879:
1878:
1876:
1875:
1869:
1867:
1860:
1851:
1847:
1846:
1843:
1842:
1840:
1839:
1833:
1831:
1827:
1826:
1824:
1823:
1818:
1812:
1810:
1804:
1803:
1801:
1800:
1795:
1790:
1785:
1779:
1777:
1771:
1770:
1768:
1767:
1756:
1750:
1748:
1739:
1731:
1730:
1716:
1715:
1708:
1701:
1693:
1687:
1686:
1676:
1664:
1663:External links
1661:
1659:
1658:
1617:
1568:
1531:Human Genomics
1517:
1476:
1435:
1416:(10): 733–41.
1399:
1358:
1309:
1288:10.1038/ni1485
1266:
1207:
1156:
1088:
1044:
979:
960:(3): 563–567.
940:
885:
850:
792:
749:
730:
684:
634:
632:
629:
616:
613:
576:
573:
572:
571:
570:
569:
561:
553:
541:
529:
514:
513:
512:
500:
488:
471:
468:
464:natural killer
440:
437:
421:
418:
347:
344:
307:
304:
300:disulfide bond
283:
279:
275:
271:
263:
251:
239:
236:-microglobulin
233:
227:
224:
177:
174:
142:
139:
63:
62:
57:
51:
50:
47:
43:
42:
38:
37:
34:
26:
25:
15:
9:
6:
4:
3:
2:
2607:
2596:
2593:
2591:
2588:
2586:
2585:Glycoproteins
2583:
2581:
2580:Immune system
2578:
2576:
2573:
2572:
2570:
2555:
2552:
2550:
2547:
2545:
2542:
2540:
2537:
2535:
2532:
2530:
2527:
2525:
2522:
2520:
2517:
2516:
2514:
2510:
2502:
2499:
2497:
2494:
2492:
2489:
2487:
2484:
2482:
2479:
2478:
2477:
2474:
2470:
2467:
2465:
2462:
2460:
2457:
2455:
2452:
2450:
2447:
2446:
2445:
2442:
2438:
2435:
2433:
2430:
2429:
2428:
2425:
2421:
2418:
2416:
2413:
2412:
2411:
2408:
2404:
2401:
2399:
2396:
2395:
2394:
2391:
2390:
2388:
2386:
2382:
2376:
2373:
2371:
2368:
2366:
2363:
2361:
2358:
2356:
2353:
2351:
2348:
2347:
2345:
2343:
2339:
2334:
2327:
2322:
2320:
2315:
2313:
2308:
2307:
2304:
2292:
2289:
2287:
2284:
2282:
2279:
2277:
2274:
2272:
2269:
2267:
2264:
2262:
2259:
2257:
2254:
2252:
2249:
2247:
2244:
2242:
2239:
2238:
2236:
2234:
2230:
2224:
2221:
2219:
2216:
2214:
2211:
2209:
2206:
2204:
2201:
2199:
2196:
2194:
2191:
2189:
2186:
2184:
2181:
2179:
2176:
2174:
2171:
2169:
2166:
2164:
2161:
2159:
2156:
2154:
2151:
2150:
2148:
2146:
2142:
2136:
2135:
2130:
2129:
2127:
2125:
2121:
2106:
2102:
2099:(also called
2098:
2095:
2093:
2090:
2088:
2085:
2083:
2080:
2078:
2075:
2074:
2072:
2068:
2062:
2059:
2056:
2052:
2048:
2045:
2044:
2042:
2040:
2036:
2030:
2027:
2025:
2022:
2020:
2017:
2015:
2011:
2008:
2007:
2005:
2001:
1993:
1990:
1988:
1985:
1984:
1983:
1980:
1979:
1977:
1975:
1971:
1968:
1966:
1962:
1951:
1947:
1943:
1940:
1939:
1937:
1933:
1923:
1920:
1919:
1917:
1913:
1907:
1903:
1899:
1896:
1895:
1893:
1889:
1886:
1884:
1880:
1874:
1871:
1870:
1868:
1864:
1861:
1859:
1855:
1852:
1848:
1838:
1835:
1834:
1832:
1828:
1822:
1819:
1817:
1814:
1813:
1811:
1809:
1805:
1799:
1796:
1794:
1791:
1789:
1786:
1784:
1781:
1780:
1778:
1776:
1772:
1765:
1764:C-type lectin
1761:
1757:
1755:
1752:
1751:
1749:
1747:
1743:
1740:
1738:
1732:
1728:
1725:
1721:
1714:
1709:
1707:
1702:
1700:
1695:
1694:
1691:
1684:
1680:
1677:
1674:
1670:
1667:
1666:
1654:
1650:
1645:
1640:
1637:(2): 247–58.
1636:
1632:
1628:
1621:
1613:
1609:
1604:
1599:
1595:
1591:
1588:(1): 121–52.
1587:
1583:
1579:
1572:
1564:
1560:
1555:
1550:
1545:
1540:
1536:
1532:
1528:
1521:
1513:
1509:
1504:
1499:
1496:(7): 3951–9.
1495:
1491:
1487:
1480:
1472:
1468:
1463:
1458:
1454:
1450:
1446:
1439:
1431:
1427:
1423:
1419:
1415:
1411:
1403:
1395:
1391:
1386:
1381:
1378:(1): 117–27.
1377:
1373:
1369:
1362:
1354:
1350:
1346:
1342:
1337:
1332:
1328:
1324:
1320:
1313:
1305:
1301:
1297:
1293:
1289:
1285:
1282:(8): 873–81.
1281:
1277:
1270:
1262:
1258:
1253:
1248:
1243:
1238:
1234:
1230:
1226:
1222:
1218:
1211:
1203:
1199:
1195:
1191:
1187:
1183:
1179:
1175:
1171:
1167:
1160:
1152:
1148:
1144:
1140:
1135:
1134:10044/1/42330
1130:
1126:
1122:
1118:
1114:
1110:
1106:
1099:
1092:
1084:
1080:
1075:
1070:
1066:
1062:
1055:
1048:
1040:
1036:
1031:
1026:
1022:
1018:
1014:
1010:
1006:
1002:
998:
994:
990:
983:
975:
971:
967:
963:
959:
955:
951:
944:
936:
932:
928:
924:
920:
916:
912:
908:
904:
900:
896:
889:
881:
877:
873:
869:
865:
861:
854:
846:
842:
838:
834:
830:
826:
822:
818:
814:
810:
803:
801:
799:
797:
788:
784:
780:
776:
772:
768:
765:(7): 503–13.
764:
760:
753:
746:
742:
739:
734:
726:
722:
718:
714:
710:
706:
702:
698:
691:
689:
680:
676:
671:
666:
662:
658:
654:
650:
646:
639:
635:
628:
626:
622:
612:
610:
606:
602:
598:
594:
593:polymorphisms
590:
586:
582:
567:
566:
562:
559:
558:
554:
551:
547:
546:
542:
539:
535:
534:
530:
527:
523:
522:
518:
517:
515:
510:
506:
505:
501:
498:
494:
493:
489:
486:
482:
481:
477:
476:
474:
473:
467:
465:
461:
457:
452:
450:
446:
445:ubiquitinated
436:
434:
429:
427:
417:
415:
411:
407:
403:
398:
396:
392:
388:
384:
380:
376:
371:
369:
365:
361:
357:
353:
343:
342:
338:
334:
329:
325:
321:
312:
303:
301:
297:
293:
288:
269:
261:
257:
249:
245:
237:
223:
221:
220:visual cortex
217:
213:
209:
205:
202:
198:
194:
191:
187:
183:
173:
171:
166:
162:
160:
156:
152:
148:
138:
136:
132:
128:
124:
119:
117:
113:
109:
106:derived from
105:
101:
97:
94:, but not on
93:
89:
85:
81:
77:
73:
69:
61:
58:
56:
52:
48:
44:
39:
32:
27:
22:
19:
2385:MHC class II
2341:
2131:
2039:Co-receptors
1992:MHC class II
1986:
1634:
1630:
1620:
1585:
1581:
1571:
1534:
1530:
1520:
1493:
1489:
1479:
1455:(1): 45–53.
1452:
1448:
1438:
1413:
1409:
1402:
1375:
1371:
1361:
1329:(2): 364–9.
1326:
1322:
1312:
1279:
1275:
1269:
1224:
1220:
1210:
1169:
1165:
1159:
1108:
1104:
1091:
1064:
1060:
1047:
996:
992:
982:
957:
953:
943:
902:
898:
888:
863:
859:
853:
812:
808:
762:
758:
752:
733:
700:
696:
655:(2): 163–9.
652:
648:
638:
618:
578:
568:(pseudogene)
563:
560:(pseudogene)
555:
543:
531:
519:
502:
490:
478:
453:
442:
430:
423:
399:
383:calreticulin
372:
349:
317:
296:heterodimers
289:
229:
179:
167:
163:
144:
120:
115:
111:
80:cell surface
76:MHC class II
67:
66:
18:
2539:Calgranulin
2342:MHC class I
1987:MHC class I
1883:Co-receptor
1746:Epsilon (ε)
1737:Fc receptor
866:(1): 11–6.
449:proteasomes
328:proteolytic
250:gene. The α
88:vertebrates
49:MHC class I
41:Identifiers
24:MHC class I
2569:Categories
1891:stimulate:
703:: 95–122.
649:Immunology
631:References
589:speciation
324:proteasome
208:plasticity
204:plasticity
193:plasticity
182:plasticity
151:proteasome
55:Membranome
1830:Secretory
1775:Gamma (γ)
1537:(1): 21.
1021:0027-8424
927:0028-0836
605:pathogens
456:apoptosis
306:Synthesis
226:Structure
112:cytosolic
108:cytosolic
92:platelets
84:nucleated
2534:Arrestin
2178:KIR2DL5B
2173:KIR2DL5A
1915:inhibit:
1798:Neonatal
1612:16285855
1563:26337052
1512:18083706
1471:15546887
1430:14644099
1394:10933400
1372:Immunity
1353:28659293
1345:18196518
1304:29762957
1296:17603487
1261:15286279
1194:29107940
1151:41095551
1143:27846572
1083:30315122
1039:37310998
1030:10288639
880:16297661
837:16917027
779:19498380
741:Archived
725:41765680
717:12493009
679:14511229
458:through
410:N-glycan
387:calnexin
244:HLA gene
147:peptides
141:Function
104:peptides
2335:classes
2223:KIR3DS1
2218:KIR3DL3
2213:KIR3DL2
2208:KIR3DL1
2203:KIR2DS5
2198:KIR2DS4
2193:KIR2DS3
2188:KIR2DS2
2183:KIR2DS1
2168:KIR2DL4
2163:KIR2DL3
2158:KIR2DL2
2153:KIR2DL1
2097:ζ-chain
1974:Ligands
1965:T cells
1858:B cells
1793:FcγRIII
1653:7700152
1603:1464479
1554:4559023
1229:Bibcode
1202:4447406
1174:Bibcode
1113:Bibcode
1105:Science
1001:Bibcode
974:2199065
935:2198471
907:Bibcode
845:1860730
817:Bibcode
809:Science
787:9278263
670:1783040
583:of all
433:albumin
379:tapasin
341:Ig fold
322:by the
320:cytosol
262:. The α
260:T-cells
218:in the
82:of all
2476:HLA-DR
2444:HLA-DQ
2427:HLA-DP
2410:HLA-DO
2393:HLA-DM
2291:LILRB5
2286:LILRB4
2281:LILRB3
2276:LILRB2
2271:LILRB1
2266:LILRA6
2261:LILRA5
2256:LILRA4
2251:LILRA3
2246:LILRA2
2241:LILRA1
1821:Fcα/μR
1788:FcγRII
1760:FcεRII
1685:(MeSH)
1675:(MeSH)
1651:
1610:
1600:
1561:
1551:
1510:
1469:
1428:
1392:
1351:
1343:
1302:
1294:
1259:
1252:511045
1249:
1200:
1192:
1166:Nature
1149:
1141:
1081:
1037:
1027:
1019:
972:
933:
925:
899:Nature
878:
843:
835:
785:
777:
723:
715:
677:
667:
597:allele
389:, and
133:, and
46:Symbol
2575:Genes
2512:Other
2375:HLA-G
2370:HLA-F
2365:HLA-E
2360:HLA-C
2355:HLA-B
2350:HLA-A
1816:FcαRI
1783:FcγRI
1754:FcεRI
1349:S2CID
1300:S2CID
1198:S2CID
1147:S2CID
1101:(PDF)
1057:(PDF)
841:S2CID
783:S2CID
721:S2CID
565:HLA-L
557:HLA-K
550:HLA-G
545:HLA-G
538:HLA-F
533:HLA-F
526:HLA-E
521:HLA-E
509:HLA-C
504:HLA-C
497:HLA-B
492:HLA-B
485:HLA-A
480:HLA-A
426:sec61
395:PDIA3
391:Erp57
337:lumen
282:and α
135:HLA-C
131:HLA-B
127:HLA-A
2132:see
2105:TCRζ
2103:and
2101:CD3ζ
2092:CD3ε
2087:CD3δ
2082:CD3γ
2055:CD8β
2053:and
2051:CD8α
2029:TRG@
2024:TRD@
2019:TRB@
2014:TRA@
1950:CD79
1946:Ig-β
1942:Ig-α
1922:CD22
1906:CD81
1902:CD19
1898:CD21
1649:PMID
1608:PMID
1559:PMID
1508:PMID
1467:PMID
1426:PMID
1390:PMID
1341:PMID
1292:PMID
1257:PMID
1190:PMID
1139:PMID
1079:PMID
1035:PMID
1017:ISSN
970:PMID
954:Cell
931:PMID
923:ISSN
876:PMID
833:PMID
775:PMID
713:PMID
675:PMID
364:TAP2
362:and
360:TAP1
123:HLAs
2077:CD3
2061:CD4
2047:CD8
2010:TCR
1982:MHC
1873:BCR
1762:is
1639:doi
1598:PMC
1590:doi
1549:PMC
1539:doi
1498:doi
1494:283
1457:doi
1418:doi
1380:doi
1331:doi
1284:doi
1247:PMC
1237:doi
1225:101
1182:doi
1170:551
1129:hdl
1121:doi
1109:354
1069:doi
1025:PMC
1009:doi
997:120
962:doi
915:doi
903:346
868:doi
825:doi
813:313
767:doi
705:doi
701:190
665:PMC
657:doi
653:110
603:by
368:ATP
256:CD8
114:or
2571::
2501:β5
2496:β4
2491:β3
2486:β1
2469:β3
2464:β2
2459:β1
2454:α2
2449:α1
2437:β1
2432:α1
2012::
1722::
1647:.
1635:12
1633:.
1629:.
1606:.
1596:.
1586:39
1584:.
1580:.
1557:.
1547:.
1533:.
1529:.
1506:.
1492:.
1488:.
1465:.
1453:17
1451:.
1447:.
1424:.
1414:40
1412:.
1388:.
1376:13
1374:.
1370:.
1347:.
1339:.
1327:38
1325:.
1321:.
1298:.
1290:.
1278:.
1255:.
1245:.
1235:.
1223:.
1219:.
1196:.
1188:.
1180:.
1168:.
1145:.
1137:.
1127:.
1119:.
1107:.
1103:.
1077:.
1063:.
1059:.
1033:.
1023:.
1015:.
1007:.
995:.
991:.
968:.
958:62
956:.
952:.
929:.
921:.
913:.
901:.
897:.
874:.
864:27
862:.
839:.
831:.
823:.
811:.
795:^
781:.
773:.
761:.
719:.
711:.
699:.
687:^
673:.
663:.
651:.
647:.
385:,
381:,
274:-α
222:.
161:.
137:.
129:,
118:.
60:63
2481:α
2420:β
2415:α
2403:β
2398:α
2325:e
2318:t
2311:v
2107:)
2057:)
1952:)
1948:(
1944:/
1904:/
1900:/
1766:)
1758:(
1712:e
1705:t
1698:v
1655:.
1641::
1614:.
1592::
1565:.
1541::
1535:9
1514:.
1500::
1473:.
1459::
1432:.
1420::
1396:.
1382::
1355:.
1333::
1306:.
1286::
1280:8
1263:.
1239::
1231::
1204:.
1184::
1176::
1153:.
1131::
1123::
1115::
1085:.
1071::
1065:3
1041:.
1011::
1003::
976:.
964::
937:.
917::
909::
882:.
870::
847:.
827::
819::
789:.
769::
763:9
727:.
707::
681:.
659::
552:)
548:(
540:)
536:(
528:)
524:(
511:)
507:(
499:)
495:(
487:)
483:(
393:(
284:2
280:1
276:2
272:1
264:3
252:3
240:3
234:2
232:β
Text is available under the Creative Commons Attribution-ShareAlike License. Additional terms may apply.