474:
20:
152:
28:
420:
example, consider an input device connected to 8255 at port A. If from the previous operation, port A is initialized as an output port and if 8255 is not reset before using the current configuration, then there is a possibility of damage of either the input device connected or 8255 or both, since both 8255 and the device connected will be sending out data.
1297:
data transfer. This means that data can be input or output on the same eight lines (PA0 - PA7). Pins PC3 - PC7 are used as handshake lines for port A. The remaining pins of port C (PC0 - PC2) can be used as input/output lines if group B is initialized in mode 0 or as handshaking for port B if group B
1044:
In this mode, the ports can be used for simple I/O operations without handshaking signals. Port A, port B provide simple I/O operation. The two halves of port C can be either used together as an additional 8-bit port, or they can be used as individual 4-bit ports. Since the two halves of port C are
1217:
When we wish to use port A or port B for handshake (strobed) input or output operation, we initialise that port in mode 1 (port A and port B can be initialised to operate in different modes, i.e., for e.g., port A can operate in mode 0 and port B in mode 1). Some of the pins of port C function as
116:
family, also originally packaged as 40-pin DIL. The 8255 provides 24 I/O pins with four programmable direction bits: one for Port A(7:0) (i.e., all pins in the port), one for Port B(7:0), one for Port C(3:0) and one for Port C(7:4). By contrast, the
Motorola and MOS chips provide only 16 I/O pins
419:
input (pin 35) is connected to the RESET line of system like 8085, 8086, etc., so that when the system is reset, all the ports are initialized as input lines. This is done to prevent 8255 and/or any peripheral connected to it from being destroyed due to mismatch of port direction settings. As an
220:. The 8255 has 24 input/output pins. These are divided into three 8-bit ports (A, B, C). Port A and port B can be used as 8-bit input/output ports. Port C can be used as an 8-bit input/output port or as two 4-bit input/output ports or to produce handshake signals for ports A and B.
845:
1072:
The inputs are not latched because the CPU only has to read their current values, then store the data in a CPU register or memory if it needs to be referenced at a later time. If an input changes while the port is being read then the result may be indeterminate.
159:
The industrial grade version of Intel ID8255A was available for US$ 17.55 in quantities of 100 and up. The available Intel 8255A-5 version was for USD $ 6.55 in quantities of 100 or more. The available 82C55A CMOS version was outsourced to
117:
plus 4 control pins, but the
Motorola/MOS chips allow the direction (input or output) of all I/O pins to be individually programmed. Both have configurations that will do a certain amount of automatic handshaking and interrupt generation.
1068:
The 8255's outputs are latched to hold the last data written to them. This is required because the data only stays on the bus for one cycle. So, without latching, the outputs would become invalid as soon as the write cycle finishes.
1283:
4. INTE (Interrupt enable) - It is neither an input nor an output; it is an internal bit programmed to enable or disable the INTR pin. The INTE A bit is programmed using the PC6 bit and INTE B is programmed using the PC2
1405:
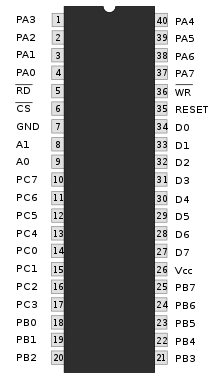
Intel
Corporation, "Microcomputer Component: New industrial grade product line answers the demand for high-reliability components to operate in industrial applications.", Intel Preview, March/April 1979, Pg.
1381:
1279:
3. INTR (Interrupt request) - It is a signal that often interrupts the microprocessor when the external device receives the data via the signal. this pin is qualified by the internal INTE(interrupt enable)
1258:
3. INTR (Interrupt request) - It is an output that requests an interrupt. The INTR pin becomes a logic 1 when the STB input returns to a logic 1, and is cleared when the data are input from the port by the
1626:
1272:
1. OBF (Output Buffer Full) - It is an output that goes low whenever data are output(OUT) to the port A or port B latch. This signal is set to a logic 1 whenever the ACK pulse returns from the external
470:) can be set or reset by writing a suitable value to the control word register. BSR mode and I/O mode are independent and selection of BSR mode does not affect the operation of other ports in I/O mode.
1616:
1276:
2. ACK (Acknowledge)-It causes the OBF pin to return to a logic 1 level. The ACK signal is a response from an external device, indicating that it has received the data from the 82C55A port.
423:
The control register (or the control logic, or the command word register) is an 8-bit register used to select the modes of operation and input/output designation of the ports.
1206:
1173:
1138:
1105:
413:
389:
280:
255:
1255:
2. STB (Strobed Input) - The strobe input loads data into the port latch, which holds the information until it is input to the microprocessor via the IN instruction.
1224:
If port A is initialised as mode 1 input port, then, PC3, PC4 and PC5 function as handshake signals. Pins PC6 and PC7 are available for use as input/output lines.
1208:
WR signal to write data to the selected port via the system data bus. This data is then received by the external peripheral device connected to the selected port.
1065:'Latched' means the bits are put into a storage register (array of flip-flops) which holds its output constant even if the inputs change after being latched.
1306:
controller. Acknowledgement and handshaking signals are provided to maintain proper data flow and synchronisation between the data transmitter and receiver.
1262:
4. INTE (Interrupt enable) - It is neither an input nor an output; it is an internal bit programmed via the port PC4(port A) or PC2(port B) bit position.
1613:
234:
Eight data lines (D0–D7) are available (with an 8-bit data buffer) to read/write data into the ports or control register under the status of the
1221:
For port B in this mode (irrespective of whether is acting as an input port or output port), PC0, PC1 and PC2 pins function as handshake lines.
995:
For example, if port B and upper port C have to be initialized as input ports and lower port C and port A as output ports (all in mode 0):
1150:
In the output mode, the CPU sends data to 8255 via system data bus and then the external peripheral ports receive this data via 8255 port.
1045:
independent, they may be used such that one-half is initialized as an input port while the other half is initialized as an output port.
1415:
Intel
Corporation, "Intel peripherals enhance 8086 system design", Intel Preview Special Issue: 16-Bit Solution, May/June 1980, Pg. 22
1652:
1601:
77:
packages. It found wide applicability in digital processing systems and was later cloned by other manufacturers. The 82C55 is a
1082:
In the input mode, the 8255 gets data from the external peripheral ports and the CPU reads the received data via its data bus.
1559:
1334:
1607:
1424:
Intel
Corporation, "NewsBit: Intel Licenses Oki on CMOS Version of Several Products", Solutions, July/August 1984, Page 1.
1433:
Ashborn, Jim; "Advanced
Packaging: A Little Goes A Long Way", Intel Corporation, Solutions, January/February 1986, Page 2
54:
microprocessor. The 8255 provides 24 parallel input/output lines with a variety of programmable operating modes.
1595:
1235:
Each port uses three lines of port c as handshake signal and remaining two signals can be used as i/o ports.
173:
109:
85:
47:
1647:
74:
168:
of sampling at fourth quarter of 1985. In
Eastern Europe, equivalent circuits were manufactured as the
1492:
165:
925:
are used for mode selection of Group A ( port A and upper port C). The selection is done as follows:
169:
1252:
1. IBF (Input Buffer Full) - It is an output indicating that the input latch contains information.
120:
Other comparable microprocessor I/O chips are the 2655 Programmable
Peripheral Interface from the
1642:
1298:
is initialized in mode 1. In this mode, the 8255 may be used to extend the system bus to a slave
871:
are assigned for port C lower, port B, port C upper and port A respectively. When these bits are
1324:
1189:
1156:
1121:
1088:
757:
Thus, as per the above values, 0B (Hex) will be loaded into the
Control Word Register (CWR).
396:
372:
263:
238:
161:
129:
125:
70:
50:(PPI) chip was developed and manufactured by Intel in the first half of the 1970s for the
8:
136:
93:
1032:
Hence, for the desired operation, the control word register will have to be loaded with
1140:
RD signal to read the data from the external peripheral device via the system data bus.
201:
140:
1629:, Intel 8080 Microcomputer Systems User's Manual (September 1975). Includes 8255 chip.
296:
allow to access a data register for each port or a control register, as listed below:
1555:
1509:
1330:
58:
143:
which had considerable additional functionality such as timers and shift registers.
1575:
284:(pin 36), which are active-low signals for read and write operations respectively.
1620:
1526:
1468:
1444:
1357:
462:
The Bit Set/Reset (BSR) mode is available on port C only. Each line of port C (PC
97:
473:
393:(pin 6) is used to enable the 8255 chip. It is an active-low signal, i.e., when
1299:
121:
1636:
185:
113:
285:
217:
184:
The 8255 was widely used in many microcomputer/microcontroller systems and
69:
microprocessors and their descendants. It was first available in a 40-pin
1303:
883:= 1, then lower port C and port A act as input ports. If these bits are
19:
904:
is used for mode selection of Group B (port B and lower port C). When D
216:
The 8255 gives a CPU or digital system access to programmable parallel
66:
62:
51:
44:
442:
The two modes are selected on the basis of the value present at the D
132:
1293:
Only port A can be initialized in this mode. Port A can be used for
887:, then the corresponding port acts as an output port. For e.g., if D
1288:
825:
bit of the
Control Word Register is 1. There are three I/O modes:
1020:
Port A and lower port C should operate as Output ports, hence, D
1009:
Port B and upper port C should operate as Input ports, hence, D
1006:
Mode selection bits, D2, D5, D6 are all 0 for mode 0 operation.
197:
189:
135:(equivalent to the Motorola 6820/6821), and the MOS Technology
84:
The functionality of the 8255 is now mostly embedded in larger
1227:
The mode 1 which supports handshaking has following features:
875:, the corresponding port acts as an input port. For e.g., if D
205:
1061:
With 4 ports, 16 different combinations of I/O are possible.
1350:
1232:
Two ports i.e. port A and B can be used as 8-bit i/o ports.
164:. The available package from Intel branded 82C55 in 44-pin
151:
89:
78:
844:
193:
1446:
Programmer's problem solver for the IBM PC, XT, & AT
81:
version for higher speed and lower current consumption.
1554:(second ed.). Techmax Publication. pp. 11–5.
27:
895:= 0, then port B and upper port C act as output ports.
230:
Group B consisting of port B and lower part of port C.
227:
Group A consisting of port A and upper part of port C.
1362:. Miller Freeman Publications. July 1996. p. 256
1212:
1192:
1159:
1124:
1091:
399:
375:
266:
241:
1058:
Ports do not have handshake or interrupt capability.
1048:
The input/output features in mode 0 are as follows:
1623:, Programming technical details and coding example
1200:
1167:
1132:
1099:
527:Selection of port C pin is determined as follows:
407:
383:
274:
249:
1634:
1461:
1289:Mode 2 - Strobed Bidirectional Input/Output mode
1175:CS low. It then selects the desired port using A
1107:CS low. Then it selects the desired port using A
523:is used to set/reset the selected pin of Port C.
223:The three ports are further grouped as follows:
1442:
431:There are two basic operational modes of 8255:
200:, PC/XT, PC/jr and clones, along with numerous
61:of chips, designed by Intel for use with their
1598:, Complete Description about the Intel 8255 IC
1316:
1085:The CPU first selects the 8255 chip by making
1322:
426:
1552:Microprocessor & Interfacing Techniques
1436:
457:
172:in the Soviet Union and as the MHB8255A by
92:version of the 8255 is still being made by
1153:CPU first selects the 8255 chip by making
450:= 1, 8255 operates in I/O mode, and when D
196:models. The 8255 was used in the original
1329:. New Age International. pp. 165–.
1302:or to transfer data bytes to and from a
843:
472:
446:bit of the control word register. When D
150:
112:(Peripheral Interface Adapter) from the
26:
18:
1144:
108:The 8255 has a similar function to the
1635:
1549:
1543:
1473:. Reed Business Pub. 1996. p. 947
1076:
1055:Input ports are buffered, not latched.
1039:
839:
684:As an example, if it is needed that PC
88:processing chips as a sub-function. A
16:Programmable Peripheral Interface chip
1627:bitsavers.informatik.uni-stuttgart.de
516:are used to select the pin of Port C.
96:but mostly used to expand the I/O of
1519:
1449:. Brady Communications Co. p. 3
816:
1326:Microprocessor And Its Applications
835:Mode 2 - Strobed Bi-directional I/O
13:
1241:Input and Output data are latched.
1213:Mode 1 - Strobed Input/output mode
1194:
1161:
1126:
1093:
908:= 0, mode 0 is selected and when D
688:be set, then in the control word,
454:= 0, it operates in the BSR mode.
401:
377:
268:
243:
14:
1664:
1589:
715:are not used, assume them to be '
415:CS = 0, the 8255 is enabled. The
1653:Input/output integrated circuits
1323:R Theagarajan (1 January 2004).
162:Oki Electronic Industry Co., Ltd
103:
1568:
1531:. McGraw-Hill. 1981. p. 40
1502:
1485:
368:The control signal chip select
179:
1427:
1418:
1409:
1399:
1374:
435:Bit Set/Reset mode (BSR mode).
1:
1382:"Product page for the 82C55A"
1309:
1238:Interrupt logic is supported.
486:bit is always 0 for BSR mode.
438:Input/Output mode (I/O mode).
1359:Embedded Systems Programming
821:This mode is selected when D
57:The 8255 is a member of the
7:
1493:"Intel 82c55 PPI Datasheet"
726:has to be selected, hence,
542:Bit/pin of port C selected
211:
146:
10:
1669:
1267:Output Handshaking signals
999:Since it is an I/O mode, D
1247:Input Handshaking signals
1052:Output ports are latched.
427:Operational modes of 8255
1443:Robert Jourdain (1986).
912:= 1, mode 1 is selected.
458:Bit Set/Reset (BSR) mode
1295:bidirectional handshake
1201:{\displaystyle {\neg }}
1168:{\displaystyle {\neg }}
1133:{\displaystyle {\neg }}
1118:The CPU then issues an
1100:{\displaystyle {\neg }}
848:I/O Control Word Format
408:{\displaystyle {\neg }}
384:{\displaystyle {\neg }}
275:{\displaystyle {\neg }}
250:{\displaystyle {\neg }}
1510:"PCI 82C55A Datasheet"
1202:
1169:
1134:
1101:
849:
749:has to be set, hence,
692:Since it is BSR mode,
478:
409:
385:
276:
251:
156:
32:
24:
1203:
1170:
1135:
1102:
1034:"10001010" = 8A (hex)
847:
476:
410:
386:
277:
252:
154:
130:Western Design Center
30:
22:
1610:, functions overview
1576:"i8255 introduction"
1190:
1157:
1145:Mode 0 - output mode
1122:
1089:
832:Mode 1 - Strobed I/O
501:are don't care bits.
397:
373:
264:
239:
1386:Renesas Electronics
1077:Mode 0 – input mode
1040:Mode 0 - simple I/O
984:As it is I/O mode,
840:Control Word format
829:Mode 0 - Simple I/O
202:homebuilt computers
176:in Czechoslovakia.
73:and later a 44-pin
1648:IBM PC compatibles
1619:2016-04-23 at the
1614:intel-assembler.it
1550:U. S. Shah. "11".
1198:
1186:CPU then issues a
1165:
1130:
1097:
850:
479:
405:
381:
272:
247:
157:
33:
25:
1596:drew.hickmans.net
1561:978-81-8492-305-6
1470:Electronics world
1336:978-81-224-1040-2
1218:handshake lines.
981:
980:
817:Input/Output mode
814:
813:
682:
681:
364:
363:
360:control register
155:MHB8255A by Tesla
110:Motorola 6820 PIA
1660:
1583:
1582:
1580:
1572:
1566:
1565:
1547:
1541:
1540:
1538:
1536:
1523:
1517:
1516:
1514:
1506:
1500:
1499:
1497:
1489:
1483:
1482:
1480:
1478:
1465:
1459:
1458:
1456:
1454:
1440:
1434:
1431:
1425:
1422:
1416:
1413:
1407:
1403:
1397:
1396:
1394:
1392:
1378:
1372:
1371:
1369:
1367:
1354:
1348:
1347:
1345:
1343:
1320:
1207:
1205:
1204:
1199:
1197:
1174:
1172:
1171:
1166:
1164:
1139:
1137:
1136:
1131:
1129:
1106:
1104:
1103:
1098:
1096:
929:
928:
760:
759:
530:
529:
414:
412:
411:
406:
404:
390:
388:
387:
382:
380:
301:
300:
281:
279:
278:
273:
271:
256:
254:
253:
248:
246:
98:microcontrollers
1668:
1667:
1663:
1662:
1661:
1659:
1658:
1657:
1633:
1632:
1621:Wayback Machine
1592:
1587:
1586:
1578:
1574:
1573:
1569:
1562:
1548:
1544:
1534:
1532:
1525:
1524:
1520:
1512:
1508:
1507:
1503:
1495:
1491:
1490:
1486:
1476:
1474:
1467:
1466:
1462:
1452:
1450:
1441:
1437:
1432:
1428:
1423:
1419:
1414:
1410:
1404:
1400:
1390:
1388:
1380:
1379:
1375:
1365:
1363:
1356:
1355:
1351:
1341:
1339:
1337:
1321:
1317:
1312:
1291:
1259:microprocessor.
1244:
1215:
1193:
1191:
1188:
1187:
1182:
1178:
1160:
1158:
1155:
1154:
1147:
1125:
1123:
1120:
1119:
1114:
1110:
1092:
1090:
1087:
1086:
1079:
1042:
1027:
1023:
1016:
1012:
1002:
989:
941:
935:
923:
919:
911:
907:
902:
894:
890:
882:
878:
869:
865:
861:
857:
842:
824:
819:
748:
739:
735:
731:
725:
714:
710:
706:
697:
687:
678:
661:
644:
627:
610:
593:
576:
559:
522:
515:
511:
507:
500:
496:
492:
485:
469:
465:
460:
453:
449:
445:
429:
400:
398:
395:
394:
376:
374:
371:
370:
313:
307:
295:
291:
267:
265:
262:
261:
242:
240:
237:
236:
214:
182:
149:
106:
43:) Programmable
31:Pinout of i8255
17:
12:
11:
5:
1666:
1656:
1655:
1650:
1645:
1643:Intel chipsets
1631:
1630:
1624:
1611:
1605:
1599:
1591:
1590:External links
1588:
1585:
1584:
1567:
1560:
1542:
1518:
1501:
1484:
1460:
1435:
1426:
1417:
1408:
1398:
1373:
1349:
1335:
1314:
1313:
1311:
1308:
1300:microprocessor
1290:
1287:
1286:
1285:
1281:
1277:
1274:
1264:
1263:
1260:
1256:
1253:
1243:
1242:
1239:
1236:
1233:
1229:
1214:
1211:
1210:
1209:
1196:
1184:
1180:
1176:
1163:
1151:
1146:
1143:
1142:
1141:
1128:
1116:
1112:
1108:
1095:
1083:
1078:
1075:
1063:
1062:
1059:
1056:
1053:
1041:
1038:
1030:
1029:
1025:
1021:
1018:
1014:
1010:
1007:
1004:
1000:
993:
992:
987:
979:
978:
975:
972:
968:
967:
964:
961:
957:
956:
953:
950:
946:
945:
942:
939:
936:
933:
927:
926:
921:
917:
913:
909:
905:
900:
896:
892:
888:
880:
876:
867:
863:
859:
855:
841:
838:
837:
836:
833:
830:
822:
818:
815:
812:
811:
808:
805:
802:
799:
796:
793:
790:
786:
785:
782:
779:
776:
773:
770:
767:
764:
755:
754:
746:
743:
737:
733:
729:
723:
720:
712:
708:
704:
701:
695:
685:
680:
679:
676:
673:
670:
667:
663:
662:
659:
656:
653:
650:
646:
645:
642:
639:
636:
633:
629:
628:
625:
622:
619:
616:
612:
611:
608:
605:
602:
599:
595:
594:
591:
588:
585:
582:
578:
577:
574:
571:
568:
565:
561:
560:
557:
554:
551:
548:
544:
543:
540:
537:
534:
525:
524:
520:
517:
513:
509:
505:
502:
498:
494:
490:
487:
483:
467:
463:
459:
456:
451:
447:
443:
440:
439:
436:
428:
425:
403:
379:
366:
365:
362:
361:
358:
355:
351:
350:
347:
344:
340:
339:
336:
333:
329:
328:
325:
322:
318:
317:
316:Port selected
314:
311:
308:
305:
293:
289:
270:
245:
232:
231:
228:
213:
210:
186:home computers
181:
178:
148:
145:
122:Signetics 2650
105:
102:
15:
9:
6:
4:
3:
2:
1665:
1654:
1651:
1649:
1646:
1644:
1641:
1640:
1638:
1628:
1625:
1622:
1618:
1615:
1612:
1609:
1606:
1603:
1602:ic-on-line.cn
1600:
1597:
1594:
1593:
1577:
1571:
1563:
1557:
1553:
1546:
1530:
1529:
1522:
1511:
1505:
1494:
1488:
1472:
1471:
1464:
1448:
1447:
1439:
1430:
1421:
1412:
1402:
1387:
1383:
1377:
1361:
1360:
1353:
1338:
1332:
1328:
1327:
1319:
1315:
1307:
1305:
1301:
1296:
1282:
1278:
1275:
1271:
1270:
1269:
1268:
1261:
1257:
1254:
1251:
1250:
1249:
1248:
1240:
1237:
1234:
1231:
1230:
1228:
1225:
1222:
1219:
1185:
1152:
1149:
1148:
1117:
1084:
1081:
1080:
1074:
1070:
1066:
1060:
1057:
1054:
1051:
1050:
1049:
1046:
1037:
1035:
1019:
1008:
1005:
998:
997:
996:
990:
983:
982:
976:
973:
970:
969:
965:
962:
959:
958:
954:
951:
948:
947:
943:
937:
931:
930:
924:
914:
903:
897:
886:
874:
870:
852:
851:
846:
834:
831:
828:
827:
826:
809:
806:
803:
800:
797:
794:
791:
788:
787:
783:
780:
777:
774:
771:
768:
765:
762:
761:
758:
752:
744:
741:
721:
718:
702:
699:
691:
690:
689:
674:
671:
668:
665:
664:
657:
654:
651:
648:
647:
640:
637:
634:
631:
630:
623:
620:
617:
614:
613:
606:
603:
600:
597:
596:
589:
586:
583:
580:
579:
572:
569:
566:
563:
562:
555:
552:
549:
546:
545:
541:
538:
535:
532:
531:
528:
518:
503:
488:
481:
480:
477:8255 BSR mode
475:
471:
455:
437:
434:
433:
432:
424:
421:
418:
392:
359:
356:
353:
352:
348:
345:
342:
341:
337:
334:
331:
330:
326:
323:
320:
319:
315:
309:
303:
302:
299:
298:
297:
287:
286:Address lines
283:
258:
229:
226:
225:
224:
221:
219:
209:
207:
203:
199:
195:
191:
187:
177:
175:
171:
167:
163:
153:
144:
142:
138:
134:
131:
127:
123:
118:
115:
114:Motorola 6800
111:
104:Similar chips
101:
99:
95:
91:
87:
82:
80:
76:
72:
68:
64:
60:
59:MCS-85 family
55:
53:
49:
46:
42:
38:
29:
21:
1570:
1551:
1545:
1533:. Retrieved
1527:
1521:
1504:
1487:
1475:. Retrieved
1469:
1463:
1451:. Retrieved
1445:
1438:
1429:
1420:
1411:
1401:
1389:. Retrieved
1385:
1376:
1364:. Retrieved
1358:
1352:
1340:. Retrieved
1325:
1318:
1294:
1292:
1266:
1265:
1246:
1245:
1226:
1223:
1220:
1216:
1071:
1067:
1064:
1047:
1043:
1033:
1031:
994:
985:
915:
898:
884:
872:
853:
820:
756:
750:
727:
716:
693:
683:
526:
461:
441:
430:
422:
416:
369:
367:
260:
259:(pin 5) and
235:
233:
222:
215:
204:such as the
188:such as the
183:
180:Applications
158:
124:family, the
119:
107:
83:
56:
40:
36:
34:
1608:sharpmz.org
1604:, Datasheet
1304:floppy disk
23:Intel D8255
1637:Categories
1391:11 January
1310:References
170:KR580VV55A
52:Intel 8080
45:Peripheral
37:Intel 8255
1195:¬
1162:¬
1127:¬
1094:¬
402:¬
378:¬
269:¬
244:¬
133:WDC 65C21
48:Interface
1617:Archived
751:D0 = '1'
736:= '0', D
732:= '1', D
212:Function
192:and all
147:Variants
141:6526 CIA
137:6522 VIA
1273:device.
920:& D
703:Since D
349:port C
338:port B
327:port A
126:Z80 PIO
94:Renesas
1558:
1535:3 June
1477:3 June
1453:3 June
1366:3 June
1342:3 June
1333:
1183:lines.
1115:lines.
504:Bits D
489:Bits D
198:IBM-PC
190:SV-328
128:, the
1579:(PDF)
1513:(PDF)
1496:(PDF)
1179:and A
1111:and A
944:Mode
740:= '1'
698:= '0'
519:Bit D
512:and D
497:and D
417:RESET
292:and A
206:N8VEM
174:Tesla
41:i8255
1556:ISBN
1537:2012
1528:Byte
1479:2012
1455:2012
1393:2023
1368:2012
1344:2012
1331:ISBN
1284:bit.
1280:bit.
1028:= 0.
1017:= 1.
1003:= 1.
991:= 1.
466:- PC
166:PLCC
139:and
90:CMOS
86:VLSI
79:CMOS
75:PLCC
67:8086
65:and
63:8085
39:(or
35:The
1024:= D
1013:= D
891:= D
879:= D
866:, D
862:, D
858:, D
784:D0
711:, D
707:, D
539:D1
536:D2
533:D3
508:, D
493:, D
218:I/O
194:MSX
71:DIP
1639::
1406:11
1384:.
1036:.
977:2
966:1
955:0
810:1
781:D1
778:D2
775:D3
772:D4
769:D5
766:D6
763:D7
745:PC
722:PC
717:0'
675:PC
658:PC
641:PC
624:PC
607:PC
590:PC
573:PC
556:PC
391:CS
282:WR
257:RD
208:.
100:.
1581:.
1564:.
1539:.
1515:.
1498:.
1481:.
1457:.
1395:.
1370:.
1346:.
1181:1
1177:0
1113:1
1109:0
1026:0
1022:4
1015:3
1011:1
1001:7
988:7
986:D
974:X
971:1
963:1
960:0
952:0
949:0
940:5
938:D
934:6
932:D
922:6
918:5
916:D
910:2
906:2
901:2
899:D
893:3
889:1
885:0
881:4
877:0
873:1
868:4
864:3
860:1
856:0
854:D
823:7
807:1
804:0
801:1
798:0
795:0
792:0
789:0
753:.
747:5
742:.
738:1
734:2
730:3
728:D
724:5
719:.
713:6
709:5
705:4
700:.
696:7
694:D
686:5
677:7
672:1
669:1
666:1
660:6
655:0
652:1
649:1
643:5
638:1
635:0
632:1
626:4
621:0
618:0
615:1
609:3
604:1
601:1
598:0
592:2
587:0
584:1
581:0
575:1
570:1
567:0
564:0
558:0
553:0
550:0
547:0
521:0
514:1
510:2
506:3
499:4
495:5
491:6
484:7
482:D
468:0
464:7
452:7
448:7
444:7
357:1
354:1
346:0
343:1
335:1
332:0
324:0
321:0
312:0
310:A
306:1
304:A
294:0
290:1
288:A
Text is available under the Creative Commons Attribution-ShareAlike License. Additional terms may apply.