601:
income inequality has increased (Milanovic 2011), remained relatively stable (Bourguignon and
Morrisson 2002), or decreased (Sala-i-Martin, 2002) since 1980. What Milanovic (2005) calls the “mother of all inequality disputes” emphasizes this debate by using the same data on Gini coefficient from 1950 to 2000 and showing that when countries’ GDP per capita incomes are unweighted by population income inequality increases, but when they are weighted inequality decreases. This has much to do with the recent average income rise in China and to some extent India, who represent almost two-fifths of the world. Notwithstanding, inter-country inequality is significant, for instance as a group the bottom 5% of US income distribution receives more income than over 68 percent of the world, and of the 60 million people that make up the top 1% of income distribution, 50 million of them are citizens of Western Europe, North America or Oceania (Milanovic 2011:116,156).
1007:
Institute of
Statistics claims that from 2004 to 2014, income inequality in Brazil declined. The Gini coefficient for household per capita income has gone down from 0,54 to 0,49. This decline is due to boosted income of the poor by sustained economic growth and implementation of social policies, for example increase in minimum wage or targeted social programs. In particular, the Bolsa Família program, introduced by reelected president Luiz Inácio Lula da Silva, whose goal is to support families in need. Although criticized, this program has not only helped reduce income inequality, but also increased literacy and lower child labor and mortality. In addition, progressive taxation, as well as schooling, demographic changes, and labor market segmentation, contributed to reducing inequality.
31:
968:
top decile’s share of income rose from 47 percent in 1994 to 60 percent in 2008 and 65 percent in 2017. The share of the poorest half of the population fell from 13 percent to 9 percent to 6 percent. An explanation for this trend is that South Africa governs a dual economy splitting the country into two different section. One section is built around an advanced capitalist economy while the other one is highly underdeveloped and mostly filled by black South
Africans, which further leads to racial division of local population. As a result, on average a black South African earns three times less than a white South African.
1046:
Gini coefficient is an income gap between rural and urban household. The share of the urban–rural income gap in total income inequality increased by 10 per cent over the period 1995–2007, rising from 38 to 48%. In China, constraints on migration limit the extent to which rural residents can move to urban areas in search of higher incomes and thereby reduce the urban–rural income gap. Although the urbanization rate has more than doubled in last 50 years, the prosses is still decelerated by various institutional and social barriers. As a result the share of national income of China's top 10% wealthiest people is 41%.
1081:
market institutions, and a culture of social cohesion which definitely contributes to them being notoriously the happiest in the world. Moreover, Nordic countries seem to be unaffected by the trends towards increasing inequality and higher unemployment observed in other countries, particularly the US and the UK Even though each of the Nordic countries have experienced termorarily rising income inequality, and they have all been affected by economic crises, they all shown a remarkable ability to recover and return to a persistent growth path and a stable relatively low income inequality.
428:: – it is weighted average of the mean level of earnings and education of certain occupations. It has advantages such a collecting important information about parents, which can be reported retrospectively by adult children. It also remains relatively stable in between the occupation career so single measuring provides adequate information of long run standing. On the other hand, it has also limitations for the mobility analyzing. Whereas occupational earning of men usually tends to be higher than by women, by the occupational education it is the other way around.
1642:... inequality continues to be a robust and powerful determinant both of the pace of medium-term growth and of the duration of growth spells, even controlling for the size of redistributive transfers. ... here is surprisingly little evidence for the growth-destroying effects of fiscal redistribution at a macroeconomic level. ... or non-extreme redistributions, there is no evidence of any adverse direct effect. The average redistribution, and the associated reduction in inequality, is thus associated with higher and more durable growth.
502:
889:: up to 40% of total income went into the pockets of the richest 5%. In the more recent years income distribution is still an issue. The UK experienced a large increase in inequality during the 1980s—the incomes of the highest deciles increase while everyone else was stagnant. Uneven growth in the years leading up to 1991 meant further increases in inequality. Throughout the 1990s and 2000s, more even growth across the distribution meant little changes in inequality, with rising incomes for everybody. In sight of
334:
same dollar amount of money (e.g. $ 100) has a greater economic impact on only one party—the poor. That same amount has little economic impact on a wealthy individual, so the disparity is addressed by ensuring the richest individuals are taxed a greater share of their wealth. The state then uses the tax revenue to find necessary and beneficial activities for the society at large. Every person in this system would have access to the same social benefits, but the rich pay more for it, so
133:
526:
1434:
2799:
188:
bargaining to improve wages for low- and middle-income workers. International
Perspectives on Income Distribution Income distribution varies greatly around the world. Comparing countries through tools like the World Income Inequality Database (WIID) or the Standardized World Income Inequality Database (SWIID) can provide insights into global patterns and the effectiveness of different policies.
201:
factor's market, and finally, are equal to the marginal productivity of the factors of production. A change in the quantity of any one of the factors will affect the marginal production, supply and demand of factors and eventually alter the income distribution from firms to households within the economy.
1130:. The income of any person in one year may depend on the income in the previous year and on a chance of progress. Assuming that to every "dying" income receiver, there is an heir to his or her income in the following year, and vice versa. This implies that the number of incomes is constant through time.
1080:
In the past, the income distribution in Nordic countries including
Denmark, Sweden, Norway, Finland, and Iceland was renowned for being relatively low compared to the rest of the world. This is caused by a combination of factors such as progressive taxation, strong social welfare system, strong labor
741:
economist
Duangmanee Laovakul in 2013 showed that the country's top 20 land owners owned 80 percent of the nation's land. The bottom 20 owned only 0.3 percent. Among those having bank deposits, 0.1 percent of bank accounts held 49 per cent of total bank deposits. As of 2019, Thai per capita income is
497:
is also widely used within the World Bank. It is an accurate and reliable index for measuring income distribution on a country by country level. The Gini index measurements go from 0 to 1 for 1 being perfect inequality and 0 being perfect equality. The world Gini index is measured at 0.52 as of 2016.
444:
mobility and the mobility of women: – Old economic analysis has been making one mistake, that they did analysis that focused mostly on the father-son pairs and their individual earnings. In the last two decades, they have expanded their research and now they focus more on the mother-daughter pairs as
187:
Progressive
Taxation: Taxing higher incomes at higher rates to redistribute income more evenly. Public Spending: Directing government expenditure towards education, healthcare, and social security to support lower-income groups. Wage Policies: Implementing minimum wage laws and encouraging collective
1010:
Even though Brazil has managed to lower its income inequality, it is still very high compared to the rest of the world, with around half of the total income being concentrated among the richest 10 per cent, a little above a fifth among the top 1 per cent, and close to one tenth among the top 0.1 per
958:
Occupying the 11th place in the ranking of income inequality in the world. USA TODAY stated: "Russia has a
Corruption Perceptions Index score of 28 – tied for the worst among OECD member states and affiliates and one of the lowest in the world. " The cause of the income gap are the close connections
607:
estimated in 2007 that the lower 80% of families were receiving $ 664 billion less income than they would be with a 1979 income distribution, or approximately $ 7,000 per family. Not receiving this income may have led many families to increase their debt burden, a significant factor in the 2007–2009
600:
Furthermore, increased inter-country income inequality over a long period is conclusive, with the Gini coefficient (using PPP exchange rate, unweighted by population) more than doubling between 1820 and the 1980s from .20 to .52 (Nolan 2009:63). However, scholars disagree about whether inter-country
572:
in the United States. The wealth gap between
Caucasian and African-American families studied nearly tripled, from $ 85,000 in 1984 to $ 236,500 in 2009. The study concluded that factors contributing to the inequality included years of home ownership (27%), household income (20%), education (5%), and
462:
et al. showed that unionization redressed the income inequality in
America and Canada, especially in their public sectors. For American male workers, the reduction of wage inequality was 1.7 percent in the private sector, while the reduction was 16.2 percent in the public sector. For American female
174:
Gini Coefficient: A measure that represents the income or wealth distribution among a nation's residents, with 0 expressing perfect equality and 1 indicating perfect inequality. Lorenz Curve: A graphical representation of income distribution, where a perfectly straight line (45-degree line) reflects
1045:
China is one the fastest growing economies in the world since its reform policies in late 1970s. However, this phenomenon is often accompanied by an increase in income inequality. China's Gini coefficient has risen from 0,31 to 0,491 between the years 1981 and 2008. The main reason for China's high
411:
stay always poor: people cannot easily change their economic status and inequality then seems as a permanent problem. 2) individuals can easily shift their income class, e.g. from middle earning class to upper class or from lower class to middle class. Inequality is "fluid" and temporary so it does
346:
Universal Access to Quality Education: Ensuring that all individuals have access to quality education can reduce income inequality by equipping people with the skills they need to succeed. Lifelong Learning and Retraining Programs: Support for ongoing education and retraining can help workers adapt
967:
South Africa is well known for being one of the most unequal societies in the world. The first democratic elections in 1994 were promising in terms of equal opportunities and living standards for South African population, but a few decades later the inequality is still very high. For instance, the
718:
The goal of social welfare initiatives like the Mahatma Gandhi National Rural Employment Guarantee Act (MGNREGA) is to provide jobs in rural areas. Public Distribution System (PDS) and other subsidized food programs help low-income households maintain food security. Economic changes like financial
333:
The progressive income tax takes a larger percentage of high incomes and a smaller percentage of low incomes. Effectively, the poorest pay the least of their earned incomes on taxes which allows them to keep a larger percentage of wealth. Justification can be illustrated by a simple heuristic: The
200:
According to this theory, the distribution of national income is determined by factor prices, the payment to each factor of production (wage for labor, rent for land, interest for capital, profit for entrepreneurship) which themselves are derived from the equilibrium of supply and demand in that
191:
Trends and Current Data Recent trends in income distribution show increasing income inequality in many parts of the world. This trend has been exacerbated by globalization and changes in the global economy. Current data from sources like the OECD can be used to update the article with the latest
693:
Addressing income inequality in Japan moving forward will require policies that tackle demographic challenges, ensure fair employment practices, and foster inclusive economic growth. Enhancing the social safety net and providing targeted assistance to vulnerable groups will be key to mitigating
1006:
Income distribution is typically higher is typically higher in developing economies than in advanced economies. In most major emerging economies, income inequality rose over the past three decades (2016), namely in China, Russia, South Africa and India. Although some might argue, the Brazilian
840:
The U.S. has the highest level of income inequality among its (post-)industrialized peers. When measured for all households, U.S. income inequality is comparable to other developed countries before taxes and transfers, but is among the highest after taxes and transfers, meaning the U.S. shifts
648:
These trends underscore the complexity of income distribution as a global challenge. While the specifics can vary greatly by region and country, the common themes of technological change, globalization, policy choices, and demographic shifts play pivotal roles in shaping the dynamics of income
544:
Across the board, a number of industries are stratified across the genders. This is the result of a variety of factors. These include differences in education choices, preferred job and industry, work experience, number of hours worked, and breaks in employment (such as for bearing and raising
662:
Despite these issues, Japan's Gini coefficient—a measure of income inequality—remains lower than in many OECD countries. Still, the relative poverty rate highlights significant economic hardship among certain population segments. The government has responded with policies aimed at converting
612:, as highly leveraged homeowners suffered a much larger reduction in their net worth during the crisis. Further, since lower income families tend to spend relatively more of their income than higher income families, shifting more of the income to wealthier families may slow economic growth.
754:
Australia was suffering from the global fallout from the 2008 financial crisis in 2011, but compared to many other industrialized countries, its economy remained comparatively strong, partly because of its solid mining industry and close trading relations with China.
312:
Addressing income inequality requires comprehensive policy interventions that consider these diverse causes, including improving access to education, reforming tax systems, ensuring fair labor practices, and implementing social policies that promote equity and
183:
Various economic theories address income distribution, from classical economics, which tends to focus on market mechanisms, to Keynesian economics, which emphasizes the role of government intervention. Policies to influence income distribution include:
105:). Modern economists have also addressed issues of income distribution, but have focused more on the distribution of income across individuals and households. Important theoretical and policy concerns include the balance between income inequality and
1125:
In a model by Champernowne, the author assumes that the income scale is divided into an enumerable infinity of income ranges, which have uniform proportionate distribution. The development through time of the DoI between ranges is regarded to be a
836:
Low unemployment rate and high GDP are signs of the health of the U.S. economy. But there is almost 18% of people living below the poverty line and the Gini coefficient is quite high. That ranks the United States 9th income inequal in the world.
383:
This provides actual money to the people with very low or no income and gives them an absolute freedom in decision-making how to use this benefit. This works best if we assume that they are rational and make decisions in their best interest.
588:
There are two ways of looking at income inequality, within country inequality (intra-country inequality) – which is inequality within a nation; or between country inequality (inter-country inequality) which is inequality between countries.
366:
If a cash is given to a poor person, he or she may not make "the best" choice in case, what to buy for this extra money. Then, there is the solution in form of the food stamps or directly the food as an in-kind transfer to the poorest.
770:
Australia's government prioritized resolving income inequities that were made worse by the global economic slump during this time, as well as maintaining economic stability. Among the measures taken to lessen income inequality were:
166:
among the participants in a particular economy, such as that of a specific country or of the world in general. While different theories may try to explain how income inequality comes about, income inequality metrics simply provide a
708:
Rate of unemployment: During this time, India's jobless rate was roughly 9%. GDP per capita: In 2011, the GDP per capita was approximately USD 1,500, indicating a significant income gap between developed countries and India.
746:) per year, driven by average GDP growth of five to six percent. Under the 20-year national plan stretching out to 2036, the government intends to narrow the income disparity gap to 15 times, down from 20 times in 2018.
1418:
596:
stated that the gap between rich and poor within OECD countries (most of which are "high income" economies) "has reached its highest level for over 30 years, and governments must act quickly to tackle inequality".
420:
Mobility is measured by the association between parents´ and adult children's socioeconomic standing, where higher association means less mobility. Socioeconomic standing is captured by four different measures:
1121:
It is difficult to create a realistic and not complicated theoretical model, because the forces determining the distribution of income (DoI) are varied and complex and they continuously interact and fluctuate.
782:
These measures were a part of Australia's larger strategy to guarantee that the country's economic expansion benefited all facets of society, especially in light of the unpredictability of the world economy.
437:
Earnings mobility: – Earning mobility evaluates the relationship between two certain generations by means of linear regression (upper math) of the long transformed measure of children's and parents' earnings.
2960:
Martela, F., Greve, B., Rothstein, B., & Saari, J. (2020). The Nordic exceptionalism: What explains why the Nordic countries are constantly among the happiest in the world. World happiness report, 2020,
2456:
250:
is noted for its systematic collection and review of available data, especially concerning income levels; not all aspects of historical wealth distribution are similarly attested in the available records.
845:
and $ 280,300 for the highest quintile. The degree of inequality accelerated within the top quintile, with the top 1% at $ 1.8 million, approximately 30 times the $ 59,300 income of the middle quintile.
541:. However, many prominent economists disagree with the need for inequality to increase as a country develops. Further, empirical data on the proclaimed subsequent decrease of inequality is conflicting.
896:
2019: The United Kingdom was doing a lot to reduce one of the widest gap between rich and poor citizens, what has led to getting on the 13th place in the ranking of income inequality in the world.
533:
Standard economic theory stipulates that inequality tends to increase over time as a country develops, and to decrease as a certain average income is attained. This theory is commonly known as the
1870:
355:
Work with other countries to establish international standards for labor rights, tax policies, and corporate governance to prevent a "race to the bottom" in terms of wages and working conditions.
778:
Introducing fiscal measures like progressive taxes that are intended to redistribute income. Encouraging work by taking steps to increase the number of jobs being created in different industries.
803:
2011: In the United States, income has become distributed more unequally over the past 30 years, with those in the top quintile (20 percent) earning more than the bottom 80 percent combined.
649:
inequality worldwide. Addressing these issues requires a nuanced understanding of both global trends and local contexts, as well as coordinated efforts across multiple sectors of society.
463:
workers, the reductions were 0.6 percent and 10.7 percent in the private and public sectors, respectively. In Canada, reduction effects were likewise more noticeable in the public sector.
545:
children). Men also typically go into higher paid and higher risk jobs when compared to women. These factors result in 60% to 75% difference between men's and women's average aggregate
175:
absolute equality. Quintile and Decile Ratios: These divide the population into equal parts (quintiles - fifths, deciles - tenths) to compare the income shares received by each group.
1240:
2643:
2592:
Were it not for those survey problems, the Census Bureau estimates, median household income would have risen just 3.8% and the poverty rate would have registered as 11.1%.
375:
The rent and upkeep of housing form a large portion of spending in the lower income families. Housing subsidies were designed to help the poor obtaining adequate housing.
553:, depending on the source. Various explanations for the remaining 25% to 40% have been suggested, including women's lower willingness and ability to negotiate salary and
434:: – Classes are instead categorical groupings based on specific occupational assets that determine life chances as expressed in outcomes such as income, health or wealth.
3615:
220:
The lack of a comprehensive measure about how the pretax income differs from the post-tax income makes hard to assess how government redistribution affects inequality.
1170:
2287:
1300:
1267:
1197:
3145:
INTERNATIONAL MONETARY FUND Research Department. Inequality and Unsustainable Growth: Two Sides of the Same Coin? Prepared by Andrew G. Berg and Jonathan D. Ostry1
2428:
2604:
885:
Inequality in the UK has been very high in the past, and did not change much until the onset of industrialization. Incomes used to be remarkably concentrated pre-
3580:
3138:
2574:
623:
1843:
3620:
3575:
1878:
705:
Post-tax Gini coefficient: In 2011, India's estimated Gini coefficient ranged from 0.33 to 0.36, indicating moderate to high levels of income inequality.
3161:
702:
India's economy was growing rapidly in 2011, but a big section of the population was still living in poverty, making income disparity a serious problem.
403:
over their lifetime. When someone improves his economic situation, this person is considered upwardly mobile. Mobility can vary between two extremes: 1)
2232:
3782:
3585:
3133:
758:
Post-tax Gini coefficient: In 2011, Australia's Gini coefficient was roughly 0.33, showing a moderate degree of income inequality by global standards.
2165:
2855:
634:
presented the distribution and change in income distribution of various nations over the course of a few decades along with other factors such as
3643:
3595:
2548:
209:
There exist some problems and limitations in the measurement of inequality as there is a large gap between the national accounts (which focus on
3168:. (This source presents data about long-run changes in the income distribution for 25 countries over the course of more than one hundred years.)
223:
There is not a clear view on how long-run trends in income concentration are shaped by the major changes in woman's labour force participation.
2868:
Derviş, K., & Qureshi, Z. (2016). Income distribution within countries: Rising in===Chiequality. Global Economy and Development. Brookings.
3653:
959:
of Russian oligarchs and the government, thanks to these relationships oligarchs get lucrative business deals and earn more and more money.
841:
relatively less income from higher income households to lower income households. In 2016, average market income was $ 15,600 for the lowest
3570:
3777:
1310:
2933:
3668:
3600:
2747:
733:
has been ranked the world's third most unequal nation after Russia and India, with a widening gap between rich and poor according to
445:
well. Generally earnings provides a stable measure of well-being independently of another financial assets or any kind of transfers.
3638:
2841:
712:
Rate of poverty: In 2011, more than 20% of Indians were living below the country's poverty line, making it a high rate of poverty.
3673:
1766:
Card D, Lemieux T, Riddell WC (Feb 2020). "Unions and wage inequality: The roles of gender, skill and public sector employment".
573:
familial financial support and/or inheritance (5%). In an analysis of the American Opportunity Accounts Act, a bill to introduce
3663:
3658:
3590:
798:
472:
3101:
3074:
3055:
3020:
2923:
Shi, L., & Renwei, Z. (2011). Market reform and the widening of the income gap. Social Sciences in China, 32(2), 140-158.
2508:
2197:
1948:
1676:
1543:
792:
645:
As of 2018, Albania has the smallest gap in wealth distribution with Zimbabwe having the largest gap in wealth distribution.
240:
is one aspect of economic inequality. Incomes levels can be studied through taxation records and other historical documents.
3565:
3542:
2027:
1488:
663:
non-regular positions to regular ones, increasing the minimum wage, and enhancing social security for low-income families.
490:
2403:
3011:
719:
inclusion programs that give underprivileged people access to banking services in an effort to promote inclusive growth.
242:
2214:
761:
Rate of unemployment: In 2011, Australia's unemployment rate was 5.1%, which was consistent with a stable labor market.
581:
reported that by 2019 white families had more than seven times the wealth of the average Black family, according to the
2154:
Milanovic, B., 2005. Worlds Apart: Measuring International and Global Inequality, Princeton University Press: Princeton
2050:
1473:
140:
for different income groups starting with the lowest quintile. Top 20% people take approximately 45% of the all income.
2816:
1133:
Under these assumptions any historical development of the DoI can be described by the following vectors and matrices.
568:
Institute on Assets and Social Policy which followed the same sets of families for 25 years found that there are vast
30:
3904:
3648:
3292:
2245:
1935:
569:
3557:
3193:
1523:
620:
116:
can represent the distribution of income within a society. The Lorenz curve is closely associated with measures of
17:
2315:
Narayanan, Sudha; Gerber, Nicolas (December 2017). "Social safety nets for food and nutrition security in India".
3839:
3376:
1993:
1964:
1900:
Blau, Francine D.; Kahn, Lawrence M. (February 2007). "The Gender Pay Gap: Have Women Gone as Far as They Can?".
1852:
877:, lower effective tax rates on higher incomes, and technology changes that reward higher educational attainment.
3253:
1468:
2351:
1109:
rate: 0,2% (3,65$ ) (2021), 0,8% (3,65$ ) (2021), 0,3% (3,65$ ) (2019), 0% (3,65$ ) (2021), 0% (3,65$ ) (2017)
2644:"Chairman Alan Krueger Discusses the Rise and Consequences of Inequality at the Center for American Progress"
1742:
1439:
3899:
3537:
3511:
3422:
1559:
1493:
3117:
1717:
1692:
1103:
per capita: $ 77,953.7 (2022), $ 68,178.0 (2022), $ 121,259.2 (2022), $ 62,823.0 (2022), $ 71,840.1 (2022)
3547:
3532:
3519:
582:
486:
3876:
3680:
3067:
The Secrets of Economic Indicators: Hidden Clues to Future Economic Trends and Investment Opportunities
2495:
2481:
764:
GDP per capita: In 2011, the GDP per capita was approximately USD 62,000, indicating a robust economy.
54:
have long seen income and its distribution as a central concern. Unequal distribution of income causes
2887:
3527:
3371:
1811:
510:
155:
145:
2497:
The Australian Economy in the 2000s: Proceedings of a Conference Held in Sydney on 15-16 August 2011
2273:
715:
The Indian government put in place a number of measures to alleviate economic disparity, including:
3260:
3248:
1498:
609:
395:
is another factor in the study of income inequality. It describes how people change their economic
82:
2097:
2083:
Bourguignon, François; Morrisson, Christian (2002). "Inequality Among World Citizens: 1820–1992".
3605:
3336:
2947:
2910:
2524:
Congressional Budget Office: Trends in the Distribution of Household Income Between 1979 and 2007
1483:
514:
2120:
Sala-i-Martin, Xavier (April 2002). The Disturbing 'Rise' of Global Income Inequality (Report).
1598:
1203:
254:
3722:
3445:
2092:
1785:
1654:
1535:
862:
858:
214:
168:
1139:
158:(or income distribution metrics) are used by social scientists to measure the distribution of
3853:
3704:
2141:
1272:
886:
554:
90:
3714:
2061:
Nolan, P., 2009. Crossroads: The End of Wild Capitalism Marshall Cavendish: London, New York
1622:
1527:
458:
reduces the income inequality in both private and public sectors, and research conducted by
3761:
3756:
3746:
3460:
3440:
3221:
3186:
3153:
3144:
2692:
2377:
2324:
1245:
1175:
870:
806:
2019: The wealthiest 10% of American households control nearly 75% of household net worth.
738:
592:
According to intra-country inequality at least in the OECD countries, a May 2011 report by
151:
8:
3831:
3728:
3485:
3415:
3366:
3341:
3238:
3233:
2004:
1994:"The Roots of the Widening Racial Wealth Gap: Explaining the Black-White Economic Divide"
1503:
565:
558:
425:
232:
163:
102:
66:
55:
2696:
2328:
849:
The economic and political impacts of inequality may include slower GDP growth, reduced
3026:
2988:
2728:
2715:
2682:
2668:
2261:
1917:
1553:
1127:
2900:
Piketty, T. 2014. Capital in the XXI century. Cambridge, MA: Harvard University Press.
3824:
3751:
3470:
3410:
3405:
3097:
3070:
3051:
3016:
2732:
2720:
2504:
2241:
2193:
2137:
1944:
1921:
1672:
1573:
1539:
1528:
1453:
850:
578:
314:
117:
81:(1772–1823) concentrated their attention on factor income-distribution, that is, the
2482:"Redistribution of * Income and Reducing Economic Inequality - IMF F&D Magazine"
1084:
The following data is for Denmark, Sweden, Norway, Finland and Iceland respectively
3388:
3226:
3089:
3043:
2980:
2710:
2700:
2673:
2332:
2288:"INCOME AND WEALTH INEQUALITY IN INDIA, 1922-2023: THE RISE OF THE BILLIONAIRE RAJ"
2129:
2121:
2102:
1909:
1463:
866:
616:
501:
478:
258:
137:
121:
98:
94:
767:
Poverty rate: Various estimates place the poverty rate between 12 and 13 percent.
3871:
3787:
3475:
3450:
3179:
1242:... matrix, that contains proportions of the occupants of r-th range in the year
1091:
coefficient: 0.283 (2021), 0.298 (2021), 0.277 (2019), 0.277 (2021), 0.261 (2017)
627:
392:
335:
274:
266:
106:
51:
3149:
2451:
2449:
3125:
2803:
2781:
2762:
2648:
2457:"The Australian economy and the global downturn Part 1: Reasons for resilience"
1989:
854:
639:
635:
482:
431:
247:
210:
74:
2336:
2106:
1913:
1743:"How do we characteristically measure and analyze intergenerational mobility?"
1172:... number of the income receivers in range r = 1, 2, ... in the initial year
3893:
3845:
3810:
3455:
3306:
3157:
3129:
3121:
2877:
World Inequality Database (WID.world) (2023) – processed by Our World in Data
2446:
2187:
1478:
1116:
874:
604:
561:
direct discrimination only explains a small part of gender wage differences.
538:
534:
441:
400:
294:
278:
78:
2051:
Society: Governments must tackle record gap between rich and poor, says OECD
1097:
rate: 4.892% (2024), 8.365% (2024), 3,8% (2024),4.892% (2024), 3.383% (2024)
132:
34:
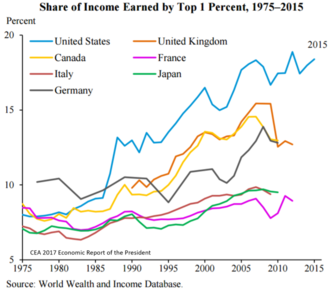
Share of income of the top 1% for selected developed countries, 1975 to 2015
3738:
3480:
3326:
3030:
2724:
2705:
1422:
The elements of proportion matrices can be estimated from historical data.
893:, there is more predicted income distribution discrepancies between wages.
631:
113:
3093:
3047:
998:
The highest income inequality is in the South Africa, based on 2019 data.
3804:
3465:
3395:
3361:
3331:
3301:
2523:
742:
US$ 8,000 a year. The government aims to raise it to US$ 15,000 (498,771
455:
298:
270:
2616:
3490:
3280:
2992:
1988:
1845:
An Analysis of Reasons for the Disparity in Wages Between Men and Women
1534:. Upper Saddle River, New Jersey 07458: Pearson Prentice Hall. p.
574:
494:
459:
396:
286:
282:
262:
70:
2934:"The Rise of Wealth, Private Property, and Income Inequality in China"
2605:"U.N. Report: With 40M in Poverty, U.S. Most Unequal Developed Nation"
3709:
3400:
3315:
3285:
3275:
3270:
3165:
2133:
1693:"Income Distribution: What can be done to improve income inequality?"
743:
517:
2018 that provides estimates of global income and wealth inequality.
290:
39:
2984:
2687:
2073:
Milanovic, B., 2011. Haves and the Have-Nots, Basic Books: New York
1413:{\displaystyle X_{s}(t+1)=\sum _{r=0}^{\infty }X_{r}(t)p'_{rs}(t).}
842:
730:
525:
2125:
3383:
3171:
2802:
Material was copied from this source, which is available under a
2667:
Stewart, Alexander J.; McCarty, Nolan; Bryson, Joanna J. (2020).
1458:
1448:
408:
306:
3817:
3432:
3203:
2549:"These 15 countries have the widest gaps between rich and poor"
1433:
890:
550:
404:
302:
159:
150:
The concept of inequality is distinct from that of poverty and
86:
27:
How a country's total GDP is distributed amongst its population
2971:
Champernowne, D. G. (1953). "A Model of Income Distribution".
3265:
2798:
1765:
775:
Bolstering the social safety net by raising welfare payments.
734:
652:
58:
which is a concern in almost all countries around the world.
178:
2669:"Polarization under rising inequality and economic decline"
2653:
2215:"Wealth Distribution and Income Inequality by Country 2022"
1768:
Canadian Journal of Economics/Revue canadienne d'économique
593:
546:
466:
50:
is distributed amongst its population. Economic theory and
1117:
Development of income distribution as a stochastic process
2579:
47:
1841:
257:
and of levels of economic equality/inequality include:
2804:
Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License
2575:"American Incomes Were Rising, Until The Pandemic Hit"
2378:"Government urged to help 1.2m desperately poor Thais"
1871:"On Equal Pay Day, key facts about the gender pay gap"
1522:
195:
2780:
Roser, Max; Ortiz-Ospina, Esteban (5 December 2013).
2761:
Roser, Max; Ortiz-Ospina, Esteban (5 December 2013).
2069:
2067:
1313:
1275:
1248:
1206:
1178:
1142:
2856:"Whites earn three times more than blacks: Stats SA"
2666:
2082:
1671:(9th ed.). Macmillan Learning. pp. 47–80.
1429:
378:
2842:"Poverty, Inequality and Policy in Southern Africa"
1943:. Publications Office of the European Union. 2013.
857:leading to increased risk of financial crises, and
320:
226:
3783:Socialism for the rich and capitalism for the poor
2064:
1412:
1294:
1261:
1234:
1191:
1164:
341:
3008:
2779:
2760:
2603:United Press International (UPI), June 22, 2018,
2179:
1937:Tackling the Gender Pay Gap in the European Union
347:to changing economic conditions and job markets.
136:Income before (green) and after (pink) taxes and
3891:
3086:Income Distribution Dynamics of Economic Systems
1740:
1269:shifted to the s-th range in the following year
3581:Largest financial services companies by revenue
2314:
1992:; Tatjana Meschede; Sam Osoro (February 2013).
1748:. The Stanford Center on Poverty and Inequality
1623:"Redistribution, Inequality, and Growth | Data"
213:totals) and inequality studies (which focus on
2888:"Inequality in Brazil: A Regional Perspective"
2817:"Brexit and wage inequality: before and after"
2566:
2028:"Can Baby Bonds Shrink the Racial Wealth Gap?"
1868:
3576:Largest corporations by market capitalization
3187:
2739:
2119:
171:used to determine the dispersion of incomes.
3009:Piketty, Thomas; Goldhammer, Arthur (2014).
2970:
2617:"The Distribution of Household Income, 2016"
1965:"What are the causes? - European Commission"
415:
350:
3778:The rich get richer and the poor get poorer
2635:
2395:
2166:"Harness market forces to share prosperity"
865:increasing relative to the average worker,
3586:Largest manufacturing companies by revenue
3194:
3180:
2948:"Unemployment Rates Around the World 2024"
2911:"Unemployment Rates Around the World 2024"
2349:
1718:"Income Distribution: Income Distribution"
1305:The vector of the DoI can be expressed as
653:Income distribution in different countries
570:differences in wealth across racial groups
3139:The Polarization of the U.S. Labor Market
2714:
2704:
2686:
2375:
2350:Sukprasert, Pattramon (6 February 2017).
2163:
2096:
1786:"GINI index (World Bank estimate) | Data"
1710:
853:, higher poverty rates, greater usage of
179:Economic Theories and Government Policies
3037:
2623:. Congressional Budget Office. July 2019
2609:
2401:
2185:
1982:
1899:
524:
500:
467:Distribution measurement internationally
412:not create a serious permanent problem.
131:
109:, and their often inverse relationship.
29:
3596:Largest technology companies by revenue
3083:
3064:
2641:
2597:
2572:
2404:"Steering the NESDB through transition"
2212:
2025:
489:(CIA), have measured income inequality
14:
3892:
3664:Income inequality in the United States
3659:Wealth inequality in the United States
2745:
2660:
2402:Theparat, Chatrudee (14 August 2018).
1666:
799:Income inequality in the United States
473:List of countries by income inequality
338:significantly reduces the inequality.
3591:Largest software companies by revenue
3175:
2746:Porter, Eduardo (November 12, 2013).
2542:
2540:
2538:
2536:
2534:
2532:
2007:Institute on Assets and Social Policy
793:Household income in the United States
481:, several organizations, such as the
3571:Largest corporate profits and losses
2573:Horsley, Scott (16 September 2020).
2547:Stebbins, Grant Suneson and Samuel.
2546:
2376:Chaitrong, Wichit (14 August 2019).
1893:
1809:
1489:Personal income in the United States
529:Idealized hypothetical Kuznets curve
370:
361:
3644:Countries by number of billionaires
3012:Capital in the Twenty-First Century
2748:"Rethinking the Rise of Inequality"
2517:
2503:. Reserve Bank of Australia. 2011.
1075:
861:. Causes of inequality may include
281:, abilities of individual workers,
243:Capital in the Twenty-First Century
196:Neoclassical theory of distribution
24:
3201:
3150:The Chartbook of Income Inequality
3002:
2642:Krueger, Alan (January 12, 2012).
2529:
1902:Academy of Management Perspectives
1667:MANKIW, N. GREGORY (22 May 2015).
1474:Kinetic exchange models of markets
1358:
387:
25:
3916:
3293:Primitive accumulation of capital
3111:
2213:Ventura, Luca (12 January 2022).
880:
379:Welfare and Unemployment benefits
3639:Cities by number of billionaires
2797:
2429:"Income inequality in Australia"
2026:Szapiro, Aron (6 October 2020).
1869:Patten, Eileen (14 April 2015).
1432:
786:
509:The World Inequality Lab at the
399:, i.e. move in the hierarchy of
321:How to improve income inequality
227:Income inequality and its causes
3840:The Theory of the Leisure Class
3715:Acquired situational narcissism
3084:Ribeiro, Marcelo Byrro (2020).
2964:
2954:
2940:
2926:
2917:
2903:
2894:
2880:
2871:
2862:
2848:
2834:
2809:
2773:
2754:
2488:
2474:
2421:
2369:
2352:"Thailand 'third most unequal'"
2343:
2308:
2280:
2225:
2206:
2186:Mian, Atif; Sufi, Amir (2014).
2157:
2148:
2113:
2076:
2055:
2044:
2019:
1957:
1928:
1862:
1835:
1829:
1803:
1778:
1759:
1530:Economics: Principles in Action
962:
513:published in December 2017 the
342:Education and Skill Development
3654:Countries by wealth inequality
3254:History of economic inequality
1734:
1685:
1660:
1647:
1615:
1591:
1574:"What is economic inequality?"
1566:
1526:; Sheffrin, Steven M. (2003).
1516:
1469:Affluence in the United States
1404:
1398:
1379:
1373:
1336:
1324:
1229:
1223:
1159:
1153:
449:
204:
127:
13:
1:
3118:The World Top Income Database
3038:Atkinson, Anthony B. (2015).
1842:CONSAD Research Corporation,
1510:
1440:Business and economics portal
1065:per capita: $ 21,482.6 (2022)
1030:per capita: $ 17,827.6 (2022)
694:income inequality's impacts.
46:covers how a country's total
3621:Number of billionaire alumni
3566:Largest companies by revenue
3015:. Harvard University Press.
1494:Poverty in the United States
749:
7:
1425:
725:
583:Survey of Consumer Finances
487:Central Intelligence Agency
277:& fiscal policies, the
255:Causes of income inequality
246:(2013) by French economist
10:
3921:
1235:{\displaystyle p'_{rs}(t)}
1036:rate: 1.4% (3,65$ ) (2023)
796:
790:
470:
273:policies, Federal Reserve
230:
143:
3867:
3796:
3770:
3737:
3700:
3693:
3649:Countries by total wealth
3631:
3556:
3528:List of centibillionaires
3510:
3503:
3431:
3372:High-net-worth individual
3354:
3217:
3210:
3065:Baumohl, Bernard (2005).
2337:10.1016/j.gfs.2017.05.001
2192:. University of Chicago.
2107:10.1257/00028280260344443
2001:Research and Policy Brief
1914:10.5465/AMP.2007.24286161
1741:Florencia Torche (2013).
1001:
926:
520:
511:Paris School of Economics
416:Measuring income mobility
351:International Cooperation
156:Income inequality metrics
146:Income inequality metrics
3905:Macroeconomic indicators
3261:International inequality
3249:Consumption distribution
2085:American Economic Review
1599:"Distribution of Income"
1558:: CS1 maint: location (
1499:Redistribution of wealth
1165:{\displaystyle X_{r}(0)}
1071:rate: 2% (3,65$ ) (2020)
1053:coefficient: 0.371(2020)
1040:
697:
657:
610:subprime mortgage crisis
328:
61:
3337:Conspicuous consumption
3141:, economics.harvard.edu
2219:Global Finance Magazine
1810:root (10 August 2008).
1484:Median household income
1295:{\displaystyle Y_{t+1}}
1018:coefficient: 0.52(2022)
515:World Inequality Report
3723:Argumentum ad crumenam
3069:. Wharton School Pub.
2706:10.1126/sciadv.abd4201
1414:
1362:
1296:
1263:
1236:
1193:
1166:
871:industry concentration
863:executive compensation
859:political polarization
530:
506:
141:
35:
3854:The Wealth of Nations
3705:Diseases of affluence
3094:10.1017/9781316136119
3048:10.4159/9780674287013
1415:
1342:
1297:
1264:
1262:{\displaystyle Y_{t}}
1237:
1194:
1192:{\displaystyle Y_{0}}
1167:
988:per capita: $ 12 287.
948:per capita: $ 24 417.
916:per capita: $ 39 425.
826:per capita: $ 53 632.
797:Further information:
683:per capita: $ 40 850.
555:sexual discrimination
528:
505:2018 World gini Index
504:
407:stay always rich and
169:system of measurement
135:
91:factors of production
33:
3762:Venture philanthropy
3757:Philanthrocapitalism
3669:Most expensive items
3543:Wealthiest Americans
3523:list of billionaires
3222:Capital accumulation
3154:University of Oxford
2973:The Economic Journal
2821:World Economic Forum
2317:Global Food Security
1311:
1273:
1246:
1204:
1176:
1140:
1024:rate: 8.032% (2024).
887:industrial evolution
739:Thammasat University
737:in 2016. A study by
192:figures and trends.
89:between the primary
67:Classical economists
3900:Income distribution
3818:Greek god of wealth
3729:Prosperity theology
3548:Wealthiest families
3533:Female billionaires
3367:Captain of industry
3342:Conspicuous leisure
3244:Income distribution
3239:Wealth distribution
3234:Economic inequality
2782:"Income Inequality"
2763:"Income Inequality"
2697:2020SciA....6.4201S
2329:2017GlFS...15...65N
2005:Brandeis University
1875:Pew Research Center
1504:Wealth distribution
1397:
1222:
566:Brandeis University
559:European Commission
557:. According to the
426:Occupational status
233:Economic inequality
164:economic inequality
56:economic inequality
44:income distribution
3681:Wealthiest animals
1790:data.worldbank.org
1524:O'Sullivan, Arthur
1410:
1382:
1292:
1259:
1232:
1207:
1189:
1162:
1128:stochastic process
976:coefficient: 0.62.
936:coefficient: 0.38.
904:coefficient: 0.35.
875:unionization rates
814:coefficient: 0.39.
671:coefficient: 0.32.
626:2014-03-01 at the
531:
507:
142:
36:
3887:
3886:
3863:
3862:
3752:The Giving Pledge
3689:
3688:
3499:
3498:
3162:Salvatore Morelli
3152:from INET at the
3103:978-1-316-13611-9
3076:978-0-13-145501-6
3057:978-0-674-28701-3
3022:978-0-674-43000-6
2786:Our World in Data
2767:Our World in Data
2654:National Archives
2510:978-0-9871488-5-8
2234:India Wage Report
2199:978-0-226-08194-6
1950:978-92-79-28821-0
1858:on 8 October 2013
1678:978-1-4641-8289-1
1545:978-0-13-063085-8
1454:Wage-price spiral
1059:rate: 5.1% (2024)
479:Gini coefficients
454:It is known that
371:Housing subsidies
362:In-kind transfers
315:economic mobility
275:monetary policies
267:economic policies
238:Income inequality
138:Transfer payments
118:income inequality
77:(1766–1834), and
16:(Redirected from
3912:
3747:Gospel of Wealth
3698:
3697:
3508:
3507:
3319:
3310:
3227:Overaccumulation
3215:
3214:
3196:
3189:
3182:
3173:
3172:
3158:Anthony Atkinson
3134:Facundo Alvaredo
3122:Anthony Atkinson
3107:
3080:
3061:
3034:
2997:
2996:
2979:(250): 318–351.
2968:
2962:
2958:
2952:
2951:
2950:. 18 April 2024.
2944:
2938:
2937:
2930:
2924:
2921:
2915:
2914:
2913:. 18 April 2024.
2907:
2901:
2898:
2892:
2891:
2884:
2878:
2875:
2869:
2866:
2860:
2859:
2852:
2846:
2845:
2838:
2832:
2831:
2829:
2827:
2813:
2807:
2801:
2796:
2794:
2792:
2777:
2771:
2770:
2758:
2752:
2751:
2743:
2737:
2736:
2718:
2708:
2690:
2681:(50): eabd4201.
2674:Science Advances
2664:
2658:
2657:
2639:
2633:
2632:
2630:
2628:
2613:
2607:
2601:
2595:
2594:
2589:
2587:
2570:
2564:
2563:
2561:
2559:
2544:
2527:
2521:
2515:
2514:
2502:
2492:
2486:
2485:
2478:
2472:
2471:
2469:
2468:
2453:
2444:
2443:
2441:
2440:
2425:
2419:
2418:
2416:
2414:
2399:
2393:
2392:
2390:
2388:
2373:
2367:
2366:
2364:
2362:
2347:
2341:
2340:
2312:
2306:
2305:
2303:
2302:
2292:
2284:
2278:
2277:
2271:
2267:
2265:
2257:
2255:
2254:
2239:
2229:
2223:
2222:
2210:
2204:
2203:
2183:
2177:
2176:
2174:
2172:
2161:
2155:
2152:
2146:
2145:
2117:
2111:
2110:
2100:
2080:
2074:
2071:
2062:
2059:
2053:
2048:
2042:
2041:
2039:
2038:
2023:
2017:
2016:
2014:
2012:
1998:
1986:
1980:
1979:
1977:
1975:
1961:
1955:
1954:
1942:
1932:
1926:
1925:
1897:
1891:
1890:
1888:
1886:
1881:on 16 April 2015
1877:. Archived from
1866:
1860:
1859:
1857:
1851:, archived from
1850:
1839:
1833:
1827:
1826:
1824:
1822:
1807:
1801:
1800:
1798:
1796:
1782:
1776:
1775:
1763:
1757:
1756:
1754:
1753:
1747:
1738:
1732:
1731:
1729:
1728:
1714:
1708:
1707:
1705:
1703:
1689:
1683:
1682:
1664:
1658:
1653:For poverty see
1651:
1645:
1644:
1639:
1637:
1632:. pp. 25–26
1627:
1619:
1613:
1612:
1610:
1609:
1595:
1589:
1588:
1586:
1584:
1570:
1564:
1563:
1557:
1549:
1533:
1520:
1464:Gini coefficient
1442:
1437:
1436:
1419:
1417:
1416:
1411:
1393:
1372:
1371:
1361:
1356:
1323:
1322:
1301:
1299:
1298:
1293:
1291:
1290:
1268:
1266:
1265:
1260:
1258:
1257:
1241:
1239:
1238:
1233:
1218:
1198:
1196:
1195:
1190:
1188:
1187:
1171:
1169:
1168:
1163:
1152:
1151:
1076:Nordic countries
867:financialization
485:(UN) and the US
279:market for labor
122:Gini coefficient
21:
18:Income disparity
3920:
3919:
3915:
3914:
3913:
3911:
3910:
3909:
3890:
3889:
3888:
3883:
3859:
3792:
3788:Too big to fail
3766:
3733:
3685:
3627:
3606:Philanthropists
3552:
3495:
3427:
3350:
3206:
3200:
3114:
3104:
3077:
3058:
3023:
3005:
3003:Further reading
3000:
2985:10.2307/2227127
2969:
2965:
2959:
2955:
2946:
2945:
2941:
2932:
2931:
2927:
2922:
2918:
2909:
2908:
2904:
2899:
2895:
2886:
2885:
2881:
2876:
2872:
2867:
2863:
2854:
2853:
2849:
2840:
2839:
2835:
2825:
2823:
2815:
2814:
2810:
2790:
2788:
2778:
2774:
2759:
2755:
2744:
2740:
2665:
2661:
2640:
2636:
2626:
2624:
2615:
2614:
2610:
2602:
2598:
2585:
2583:
2571:
2567:
2557:
2555:
2545:
2530:
2526:. October 2011.
2522:
2518:
2511:
2500:
2494:
2493:
2489:
2480:
2479:
2475:
2466:
2464:
2461:treasury.gov.au
2455:
2454:
2447:
2438:
2436:
2433:treasury.gov.au
2427:
2426:
2422:
2412:
2410:
2400:
2396:
2386:
2384:
2374:
2370:
2360:
2358:
2348:
2344:
2313:
2309:
2300:
2298:
2290:
2286:
2285:
2281:
2269:
2268:
2259:
2258:
2252:
2250:
2248:
2237:
2231:
2230:
2226:
2211:
2207:
2200:
2184:
2180:
2170:
2168:
2164:Larry Summers.
2162:
2158:
2153:
2149:
2118:
2114:
2081:
2077:
2072:
2065:
2060:
2056:
2049:
2045:
2036:
2034:
2032:Morningstar.com
2024:
2020:
2010:
2008:
1996:
1987:
1983:
1973:
1971:
1963:
1962:
1958:
1951:
1940:
1934:
1933:
1929:
1898:
1894:
1884:
1882:
1867:
1863:
1855:
1848:
1840:
1836:
1830:
1820:
1818:
1808:
1804:
1794:
1792:
1784:
1783:
1779:
1764:
1760:
1751:
1749:
1745:
1739:
1735:
1726:
1724:
1716:
1715:
1711:
1701:
1699:
1691:
1690:
1686:
1679:
1665:
1661:
1652:
1648:
1635:
1633:
1625:
1621:
1620:
1616:
1607:
1605:
1597:
1596:
1592:
1582:
1580:
1572:
1571:
1567:
1551:
1550:
1546:
1521:
1517:
1513:
1508:
1438:
1431:
1428:
1386:
1367:
1363:
1357:
1346:
1318:
1314:
1312:
1309:
1308:
1280:
1276:
1274:
1271:
1270:
1253:
1249:
1247:
1244:
1243:
1211:
1205:
1202:
1201:
1183:
1179:
1177:
1174:
1173:
1147:
1143:
1141:
1138:
1137:
1119:
1113:
1078:
1043:
1004:
965:
929:
883:
851:income mobility
801:
795:
789:
752:
728:
722:
700:
660:
655:
628:Wayback Machine
564:A study by the
523:
475:
469:
452:
418:
393:Income mobility
390:
388:Income mobility
381:
373:
364:
358:
353:
344:
336:progressive tax
331:
323:
259:labor economics
235:
229:
207:
198:
181:
148:
130:
107:economic growth
64:
52:economic policy
28:
23:
22:
15:
12:
11:
5:
3918:
3908:
3907:
3902:
3885:
3884:
3882:
3881:
3880:
3879:
3868:
3865:
3864:
3861:
3860:
3858:
3857:
3850:
3843:
3836:
3835:
3834:
3822:
3821:
3820:
3808:
3800:
3798:
3794:
3793:
3791:
3790:
3785:
3780:
3774:
3772:
3768:
3767:
3765:
3764:
3759:
3754:
3749:
3743:
3741:
3735:
3734:
3732:
3731:
3726:
3719:
3718:
3717:
3712:
3701:
3695:
3691:
3690:
3687:
3686:
3684:
3683:
3678:
3677:
3676:
3666:
3661:
3656:
3651:
3646:
3641:
3635:
3633:
3629:
3628:
3626:
3625:
3624:
3623:
3618:
3616:Endowment size
3610:
3609:
3608:
3598:
3593:
3588:
3583:
3578:
3573:
3568:
3562:
3560:
3554:
3553:
3551:
3550:
3545:
3540:
3538:Richest royals
3535:
3530:
3525:
3516:
3514:
3505:
3501:
3500:
3497:
3496:
3494:
3493:
3488:
3483:
3478:
3473:
3468:
3463:
3458:
3453:
3448:
3443:
3437:
3435:
3429:
3428:
3426:
3425:
3420:
3419:
3418:
3413:
3408:
3398:
3393:
3392:
3391:
3381:
3380:
3379:
3369:
3364:
3358:
3356:
3352:
3351:
3349:
3348:
3347:
3346:
3345:
3344:
3339:
3324:
3323:
3322:
3313:
3299:
3298:
3297:
3296:
3295:
3283:
3278:
3273:
3268:
3263:
3258:
3257:
3256:
3251:
3246:
3241:
3231:
3230:
3229:
3218:
3212:
3208:
3207:
3199:
3198:
3191:
3184:
3176:
3170:
3169:
3147:
3142:
3136:
3126:Thomas Piketty
3113:
3112:External links
3110:
3109:
3108:
3102:
3081:
3075:
3062:
3056:
3035:
3021:
3004:
3001:
2999:
2998:
2963:
2953:
2939:
2925:
2916:
2902:
2893:
2879:
2870:
2861:
2847:
2833:
2808:
2772:
2753:
2738:
2659:
2649:whitehouse.gov
2634:
2608:
2596:
2565:
2528:
2516:
2509:
2487:
2473:
2445:
2420:
2394:
2368:
2342:
2307:
2279:
2270:|website=
2246:
2224:
2205:
2198:
2178:
2156:
2147:
2112:
2091:(4): 727–744.
2075:
2063:
2054:
2043:
2018:
1990:Thomas Shapiro
1981:
1956:
1949:
1927:
1892:
1861:
1834:
1828:
1802:
1777:
1758:
1733:
1709:
1684:
1677:
1669:MACROECONOMICS
1659:
1646:
1614:
1590:
1565:
1544:
1514:
1512:
1509:
1507:
1506:
1501:
1496:
1491:
1486:
1481:
1476:
1471:
1466:
1461:
1456:
1451:
1445:
1444:
1443:
1427:
1424:
1409:
1406:
1403:
1400:
1396:
1392:
1389:
1385:
1381:
1378:
1375:
1370:
1366:
1360:
1355:
1352:
1349:
1345:
1341:
1338:
1335:
1332:
1329:
1326:
1321:
1317:
1303:
1302:
1289:
1286:
1283:
1279:
1256:
1252:
1231:
1228:
1225:
1221:
1217:
1214:
1210:
1199:
1186:
1182:
1161:
1158:
1155:
1150:
1146:
1118:
1115:
1111:
1110:
1104:
1098:
1092:
1077:
1074:
1073:
1072:
1066:
1060:
1054:
1042:
1039:
1038:
1037:
1031:
1025:
1019:
1003:
1000:
996:
995:
989:
983:
977:
964:
961:
956:
955:
949:
943:
937:
928:
925:
924:
923:
917:
911:
905:
882:
881:United Kingdom
879:
855:household debt
834:
833:
827:
821:
815:
791:Main article:
788:
785:
780:
779:
776:
751:
748:
727:
724:
699:
696:
691:
690:
684:
678:
672:
659:
656:
654:
651:
640:fertility rate
636:child survival
522:
519:
483:United Nations
471:Main article:
468:
465:
451:
448:
447:
446:
438:
435:
432:Class mobility
429:
417:
414:
389:
386:
380:
377:
372:
369:
363:
360:
352:
349:
343:
340:
330:
327:
322:
319:
248:Thomas Piketty
231:Main article:
228:
225:
206:
203:
197:
194:
180:
177:
144:Main article:
129:
126:
120:, such as the
75:Thomas Malthus
63:
60:
26:
9:
6:
4:
3:
2:
3917:
3906:
3903:
3901:
3898:
3897:
3895:
3878:
3875:
3874:
3873:
3870:
3869:
3866:
3856:
3855:
3851:
3849:
3848:
3844:
3842:
3841:
3837:
3833:
3830:
3829:
3828:
3827:
3823:
3819:
3816:
3815:
3814:
3813:
3809:
3807:
3806:
3802:
3801:
3799:
3795:
3789:
3786:
3784:
3781:
3779:
3776:
3775:
3773:
3769:
3763:
3760:
3758:
3755:
3753:
3750:
3748:
3745:
3744:
3742:
3740:
3736:
3730:
3727:
3725:
3724:
3720:
3716:
3713:
3711:
3708:
3707:
3706:
3703:
3702:
3699:
3696:
3692:
3682:
3679:
3675:
3672:
3671:
3670:
3667:
3665:
3662:
3660:
3657:
3655:
3652:
3650:
3647:
3645:
3642:
3640:
3637:
3636:
3634:
3630:
3622:
3619:
3617:
3614:
3613:
3612:Universities
3611:
3607:
3604:
3603:
3602:
3599:
3597:
3594:
3592:
3589:
3587:
3584:
3582:
3579:
3577:
3574:
3572:
3569:
3567:
3564:
3563:
3561:
3559:
3558:Organizations
3555:
3549:
3546:
3544:
3541:
3539:
3536:
3534:
3531:
3529:
3526:
3524:
3522:
3518:
3517:
3515:
3513:
3509:
3506:
3502:
3492:
3489:
3487:
3484:
3482:
3479:
3477:
3474:
3472:
3469:
3467:
3464:
3462:
3459:
3457:
3454:
3452:
3449:
3447:
3444:
3442:
3441:Concentration
3439:
3438:
3436:
3434:
3430:
3424:
3421:
3417:
3414:
3412:
3409:
3407:
3404:
3403:
3402:
3399:
3397:
3394:
3390:
3387:
3386:
3385:
3382:
3378:
3375:
3374:
3373:
3370:
3368:
3365:
3363:
3360:
3359:
3357:
3353:
3343:
3340:
3338:
3335:
3334:
3333:
3330:
3329:
3328:
3325:
3321:
3318:
3314:
3312:
3309:
3308:Nouveau riche
3305:
3304:
3303:
3300:
3294:
3291:
3290:
3289:
3288:
3287:
3284:
3282:
3279:
3277:
3274:
3272:
3269:
3267:
3264:
3262:
3259:
3255:
3252:
3250:
3247:
3245:
3242:
3240:
3237:
3236:
3235:
3232:
3228:
3225:
3224:
3223:
3220:
3219:
3216:
3213:
3209:
3205:
3197:
3192:
3190:
3185:
3183:
3178:
3177:
3174:
3167:
3163:
3159:
3155:
3151:
3148:
3146:
3143:
3140:
3137:
3135:
3131:
3130:Emmanuel Saez
3127:
3123:
3119:
3116:
3115:
3105:
3099:
3095:
3091:
3087:
3082:
3078:
3072:
3068:
3063:
3059:
3053:
3049:
3045:
3041:
3036:
3032:
3028:
3024:
3018:
3014:
3013:
3007:
3006:
2994:
2990:
2986:
2982:
2978:
2974:
2967:
2957:
2949:
2943:
2935:
2929:
2920:
2912:
2906:
2897:
2889:
2883:
2874:
2865:
2857:
2851:
2843:
2837:
2822:
2818:
2812:
2805:
2800:
2787:
2783:
2776:
2768:
2764:
2757:
2749:
2742:
2734:
2730:
2726:
2722:
2717:
2712:
2707:
2702:
2698:
2694:
2689:
2684:
2680:
2676:
2675:
2670:
2663:
2655:
2651:
2650:
2645:
2638:
2622:
2618:
2612:
2606:
2600:
2593:
2582:
2581:
2576:
2569:
2554:
2550:
2543:
2541:
2539:
2537:
2535:
2533:
2525:
2520:
2512:
2506:
2499:
2498:
2491:
2483:
2477:
2462:
2458:
2452:
2450:
2434:
2430:
2424:
2409:
2405:
2398:
2383:
2379:
2372:
2357:
2353:
2346:
2338:
2334:
2330:
2326:
2322:
2318:
2311:
2296:
2289:
2283:
2275:
2263:
2249:
2247:9789220311547
2243:
2236:
2235:
2228:
2220:
2216:
2209:
2201:
2195:
2191:
2190:
2189:House of Debt
2182:
2167:
2160:
2151:
2143:
2139:
2135:
2131:
2127:
2126:10.3386/w8904
2123:
2116:
2108:
2104:
2099:
2098:10.1.1.5.7307
2094:
2090:
2086:
2079:
2070:
2068:
2058:
2052:
2047:
2033:
2029:
2022:
2006:
2002:
1995:
1991:
1985:
1970:
1966:
1960:
1952:
1946:
1939:
1938:
1931:
1923:
1919:
1915:
1911:
1907:
1903:
1896:
1880:
1876:
1872:
1865:
1854:
1847:
1846:
1838:
1832:
1817:
1813:
1806:
1791:
1787:
1781:
1773:
1769:
1762:
1744:
1737:
1723:
1719:
1713:
1698:
1694:
1688:
1680:
1674:
1670:
1663:
1656:
1650:
1643:
1631:
1624:
1618:
1604:
1600:
1594:
1579:
1575:
1569:
1561:
1555:
1547:
1541:
1537:
1532:
1531:
1525:
1519:
1515:
1505:
1502:
1500:
1497:
1495:
1492:
1490:
1487:
1485:
1482:
1480:
1479:Median income
1477:
1475:
1472:
1470:
1467:
1465:
1462:
1460:
1457:
1455:
1452:
1450:
1447:
1446:
1441:
1435:
1430:
1423:
1420:
1407:
1401:
1394:
1390:
1387:
1383:
1376:
1368:
1364:
1353:
1350:
1347:
1343:
1339:
1333:
1330:
1327:
1319:
1315:
1306:
1287:
1284:
1281:
1277:
1254:
1250:
1226:
1219:
1215:
1212:
1208:
1200:
1184:
1180:
1156:
1148:
1144:
1136:
1135:
1134:
1131:
1129:
1123:
1114:
1108:
1105:
1102:
1099:
1096:
1093:
1090:
1087:
1086:
1085:
1082:
1070:
1067:
1064:
1061:
1058:
1055:
1052:
1049:
1048:
1047:
1035:
1032:
1029:
1026:
1023:
1020:
1017:
1014:
1013:
1012:
1008:
999:
993:
990:
987:
984:
981:
978:
975:
971:
970:
969:
960:
953:
950:
947:
944:
941:
938:
935:
931:
930:
921:
918:
915:
912:
909:
906:
903:
899:
898:
897:
894:
892:
888:
878:
876:
872:
868:
864:
860:
856:
852:
847:
844:
838:
831:
828:
825:
822:
819:
816:
813:
809:
808:
807:
804:
800:
794:
787:United States
784:
777:
774:
773:
772:
768:
765:
762:
759:
756:
747:
745:
740:
736:
732:
723:
720:
716:
713:
710:
706:
703:
695:
688:
685:
682:
679:
676:
673:
670:
666:
665:
664:
650:
646:
643:
641:
637:
633:
629:
625:
622:
619:presentation
618:
613:
611:
606:
605:Larry Summers
602:
598:
595:
590:
586:
584:
580:
576:
571:
567:
562:
560:
556:
552:
548:
542:
540:
539:Simon Kuznets
536:
535:Kuznets curve
527:
518:
516:
512:
503:
499:
496:
492:
488:
484:
480:
474:
464:
461:
457:
443:
442:family income
439:
436:
433:
430:
427:
424:
423:
422:
413:
410:
406:
402:
401:earning power
398:
394:
385:
376:
368:
359:
356:
348:
339:
337:
326:
318:
316:
310:
308:
304:
300:
296:
295:globalization
292:
288:
284:
280:
276:
272:
268:
264:
260:
256:
252:
249:
245:
244:
239:
234:
224:
221:
218:
216:
212:
211:macroeconomic
202:
193:
189:
185:
176:
172:
170:
165:
161:
157:
153:
147:
139:
134:
125:
123:
119:
115:
110:
108:
104:
100:
96:
92:
88:
84:
80:
79:David Ricardo
76:
73:(1723–1790),
72:
68:
59:
57:
53:
49:
45:
41:
32:
19:
3852:
3846:
3838:
3825:
3811:
3803:
3739:Philanthropy
3721:
3520:
3446:Distribution
3423:Robber baron
3332:Veblen goods
3327:Luxury goods
3316:
3307:
3243:
3085:
3066:
3039:
3010:
2976:
2972:
2966:
2956:
2942:
2928:
2919:
2905:
2896:
2882:
2873:
2864:
2850:
2836:
2824:. Retrieved
2820:
2811:
2789:. Retrieved
2785:
2775:
2766:
2756:
2741:
2678:
2672:
2662:
2652:– via
2647:
2637:
2625:. Retrieved
2620:
2611:
2599:
2591:
2586:16 September
2584:. Retrieved
2578:
2568:
2556:. Retrieved
2552:
2519:
2496:
2490:
2476:
2465:. Retrieved
2463:. 2012-04-02
2460:
2437:. Retrieved
2435:. 2013-11-18
2432:
2423:
2411:. Retrieved
2408:Bangkok Post
2407:
2397:
2385:. Retrieved
2381:
2371:
2359:. Retrieved
2356:Bangkok Post
2355:
2345:
2320:
2316:
2310:
2299:. Retrieved
2297:. March 2024
2294:
2282:
2251:. Retrieved
2233:
2227:
2218:
2208:
2188:
2181:
2171:21 September
2169:. Retrieved
2159:
2150:
2115:
2088:
2084:
2078:
2057:
2046:
2035:. Retrieved
2031:
2021:
2009:. Retrieved
2000:
1984:
1972:. Retrieved
1969:ec.europa.eu
1968:
1959:
1936:
1930:
1905:
1901:
1895:
1883:. Retrieved
1879:the original
1874:
1864:
1853:the original
1844:
1837:
1831:
1819:. Retrieved
1816:Investopedia
1815:
1812:"Gini Index"
1805:
1793:. Retrieved
1789:
1780:
1771:
1767:
1761:
1750:. Retrieved
1736:
1725:. Retrieved
1721:
1712:
1700:. Retrieved
1696:
1687:
1668:
1662:
1649:
1641:
1634:. Retrieved
1629:
1617:
1606:. Retrieved
1602:
1593:
1581:. Retrieved
1577:
1568:
1529:
1518:
1421:
1307:
1304:
1132:
1124:
1120:
1112:
1106:
1100:
1095:Unemployment
1094:
1088:
1083:
1079:
1068:
1062:
1057:Unemployment
1056:
1050:
1044:
1033:
1027:
1022:Unemployment
1021:
1015:
1009:
1005:
997:
994:rate: 26.6%.
991:
985:
982:rate: 27.3%.
980:Unemployment
979:
973:
966:
963:South Africa
957:
951:
945:
940:Unemployment
939:
933:
922:rate: 11.1%.
919:
913:
908:Unemployment
907:
901:
895:
884:
848:
839:
835:
832:rate: 11.1%.
829:
823:
818:Unemployment
817:
811:
805:
802:
781:
769:
766:
763:
760:
757:
753:
729:
721:
717:
714:
711:
707:
704:
701:
692:
686:
680:
675:Unemployment
674:
668:
661:
647:
644:
632:Hans Rosling
614:
603:
599:
591:
587:
563:
543:
532:
508:
476:
453:
419:
391:
382:
374:
365:
357:
354:
345:
332:
324:
311:
263:tax policies
253:
241:
237:
236:
222:
219:
215:distribution
208:
199:
190:
186:
182:
173:
149:
114:Lorenz curve
111:
83:distribution
65:
43:
37:
3805:Das Kapital
3674:by category
3396:Millionaire
3362:Billionaire
3320:(old money)
3317:Vieux riche
3311:(new money)
3302:Upper class
3031:j.ctt6wpqbc
2627:October 11,
2621:www.cbo.gov
1974:18 February
1908:(1): 7–23.
1885:11 November
1655:FGT metrics
1578:wol.iza.org
942:rate: 5.2%.
910:rate: 4.3%.
820:rate: 4.4%.
689:rate: 15.7%
677:rate: 2.6%.
579:Morningstar
456:labor union
450:Labor union
405:rich people
299:gender bias
271:labor union
205:Limitations
128:Measurement
3894:Categories
3877:by country
3826:Superclass
3471:Management
3281:Plutocracy
3040:Inequality
2826:23 October
2791:24 October
2688:1807.11477
2467:2024-04-21
2439:2024-04-21
2382:The Nation
2361:6 February
2301:2024-04-21
2253:2024-04-21
2037:2021-08-04
1821:4 December
1795:4 December
1752:2023-04-02
1727:2023-04-02
1722:SparkNotes
1697:SparkNotes
1608:2023-05-31
1511:References
869:, greater
621:shown here
575:Baby Bonds
495:Gini index
491:by country
460:David Card
397:well-being
287:automation
283:technology
71:Adam Smith
3710:Affluenza
3601:Charities
3466:Inherited
3461:Geography
3416:Ukrainian
3286:Plutonomy
3276:Overclass
3271:Oligarchy
3166:Max Roser
2733:216144890
2553:USA TODAY
2413:14 August
2387:14 August
2323:: 65–76.
2295:wid.world
2272:ignored (
2262:cite book
2134:10230/524
2093:CiteSeerX
1922:152531847
1636:18 August
1554:cite book
1359:∞
1344:∑
972:Post-tax
954:rate: NA.
932:Post-tax
900:Post-tax
810:Post-tax
750:Australia
667:Post-tax
291:education
40:economics
3872:Category
3486:Religion
3476:National
3451:Dynastic
3406:Business
3401:Oligarch
3389:Business
3211:Concepts
3202:Extreme
2961:129-146.
2725:33310855
2558:25 April
2240:. 2018.
2011:16 March
1702:25 April
1583:28 April
1426:See also
1395:′
1220:′
873:, lower
843:quintile
731:Thailand
726:Thailand
624:Archived
551:salaries
325:Source:
265:, other
152:fairness
69:such as
3771:Sayings
3694:Related
3411:Russian
3384:Magnate
2993:2227127
2716:7732181
2693:Bibcode
2325:Bibcode
1630:imf.org
1603:Econlib
1459:Poverty
1449:Subsidy
1107:Poverty
1069:Poverty
1034:Poverty
992:Poverty
952:Poverty
920:Poverty
830:Poverty
687:Poverty
307:culture
103:capital
3847:Wealth
3812:Plutus
3521:Forbes
3512:People
3456:Effect
3433:Wealth
3355:People
3204:wealth
3164:, and
3100:
3073:
3054:
3029:
3019:
2991:
2750:. NYT.
2731:
2723:
2713:
2507:
2244:
2196:
2142:311593
2140:
2095:
1947:
1920:
1675:
1542:
1011:cent.
1002:Brazil
927:Russia
891:Brexit
537:after
521:Trends
493:. The
477:Using
440:Total
305:, and
303:racism
162:, and
160:income
99:labour
87:income
3797:Media
3632:Other
3504:Lists
3481:Paper
3377:UHNWI
3266:Elite
3027:JSTOR
2989:JSTOR
2729:S2CID
2683:arXiv
2501:(PDF)
2291:(PDF)
2238:(PDF)
1997:(PDF)
1941:(PDF)
1918:S2CID
1856:(PDF)
1849:(PDF)
1746:(PDF)
1626:(PDF)
1041:China
735:Oxfam
698:India
658:Japan
615:In a
547:wages
329:Taxes
62:About
3832:List
3098:ISBN
3071:ISBN
3052:ISBN
3017:ISBN
2828:2019
2793:2019
2721:PMID
2629:2019
2588:2020
2560:2021
2505:ISBN
2415:2018
2389:2018
2363:2017
2274:help
2242:ISBN
2194:ISBN
2173:2015
2138:SSRN
2013:2013
1976:2016
1945:ISBN
1887:2023
1823:2016
1797:2016
1704:2021
1673:ISBN
1638:2020
1585:2022
1560:link
1540:ISBN
1089:Gini
1051:Gini
1016:Gini
974:Gini
934:Gini
902:Gini
812:Gini
744:baht
669:Gini
638:and
594:OECD
409:poor
285:and
112:The
101:and
95:land
3491:Tax
3156:by
3120:by
3090:doi
3044:doi
2981:doi
2711:PMC
2701:doi
2580:NPR
2333:doi
2130:hdl
2122:doi
2103:doi
1910:doi
1536:348
1101:GDP
1063:GDP
1028:GDP
986:GDP
946:GDP
914:GDP
824:GDP
681:GDP
617:TED
549:or
217:).
85:of
48:GDP
38:In
3896::
3160:,
3132:,
3128:,
3124:,
3096:.
3088:.
3050:.
3042:.
3025:.
2987:.
2977:63
2975:.
2819:.
2784:.
2765:.
2727:.
2719:.
2709:.
2699:.
2691:.
2677:.
2671:.
2646:.
2619:.
2590:.
2577:.
2551:.
2531:^
2459:.
2448:^
2431:.
2406:.
2380:.
2354:.
2331:.
2321:15
2319:.
2293:.
2266::
2264:}}
2260:{{
2217:.
2136:.
2128:.
2101:.
2089:92
2087:.
2066:^
2030:.
2003:.
1999:.
1967:.
1916:.
1906:21
1904:.
1873:.
1814:.
1788:.
1772:53
1770:.
1720:.
1695:.
1640:.
1628:.
1601:.
1576:.
1556:}}
1552:{{
1538:.
642:.
630:,
585:.
577:,
317:.
309:.
301:,
297:,
293:,
289:,
269:,
261:,
154:.
124:.
97:,
42:,
3195:e
3188:t
3181:v
3106:.
3092::
3079:.
3060:.
3046::
3033:.
2995:.
2983::
2936:.
2890:.
2858:.
2844:.
2830:.
2806:.
2795:.
2769:.
2735:.
2703::
2695::
2685::
2679:6
2656:.
2631:.
2562:.
2513:.
2484:.
2470:.
2442:.
2417:.
2391:.
2365:.
2339:.
2335::
2327::
2304:.
2276:)
2256:.
2221:.
2202:.
2175:.
2144:.
2132::
2124::
2109:.
2105::
2040:.
2015:.
1978:.
1953:.
1924:.
1912::
1889:.
1825:.
1799:.
1774:.
1755:.
1730:.
1706:.
1681:.
1657:.
1611:.
1587:.
1562:)
1548:.
1408:.
1405:)
1402:t
1399:(
1391:s
1388:r
1384:p
1380:)
1377:t
1374:(
1369:r
1365:X
1354:0
1351:=
1348:r
1340:=
1337:)
1334:1
1331:+
1328:t
1325:(
1320:s
1316:X
1288:1
1285:+
1282:t
1278:Y
1255:t
1251:Y
1230:)
1227:t
1224:(
1216:s
1213:r
1209:p
1185:0
1181:Y
1160:)
1157:0
1154:(
1149:r
1145:X
93:(
20:)
Text is available under the Creative Commons Attribution-ShareAlike License. Additional terms may apply.