265:
250:
216:
25:
235:
204:
180:
153:
126:
687:
earthquakes. These seismic events can reach greater than MW 8 and result in intense damage to infrastructure. The mid-crustal ramp in the
Himalayas is a key geologic feature in the history for both long-term and short-term seismic processes linked to deformation and shortening. Over the last 15 Ma, the ramp has gradually moved south due to duplexing, accretion, and tectonic undercutting.
1153:
forced back up through the channel they came down due to a space problem. The third model states that the thick continental crust of India further exacerbated the space problem and caused the corner flow of those rocks back up the channel. The fourth model includes the rocks being transported along the Main
Himalayan Thrust.
1149:
on top of lower grade metamorphic rocks still strongly debated, Kohn believes that it is due to long periods of transportation of higher grade metamorphic rocks on the Main
Himalayan Thrust. Essentially, the longer the higher grade rocks were spatially interacting with the thrust, the farther they were transported.
1392:
in the
Western Himalayas. Coulomb stress transfer is used to quantify how earthquakes release stress, identifying areas that are put under increased stress and those that have been unloaded. This study and those like it are important in understanding the current state of fault zones in the region, as
1152:
The exhumation of eclogite and granulite rocks can be explained by several different models. The first model includes slab tear where the lower plate tore off into the mantle leading to high amounts of rebound. The second model states that the rocks got to a certain point in subduction and then were
1148:
The metamorphic rocks of the
Himalaya can be very useful in deciphering and coming up with models of tectonic relationships. According to Kohn (2014), the exhumation of metamorphic rocks can be explained by the Main Himalayan Thrust. Although the mechanism of emplacing higher grade metamorphic rocks
686:
The
Himalayan tectonics result in long term deformation. This includes shortening across the Himalayas that range from 900 to 1,500 km. Said shortening is a product of the significant ongoing seismic activity. The continued convergence of the Indian plate with the Eurasian plate results in mega
617:
from very fast (18-19.5 cm/yr) to fast (4.5 cm/yr) at about 55 Ma is circumstantial support for collision then. Since then there has been about 2500 km of crustal shortening and rotating of India by 45° counterclockwise in the
Northwestern Himalaya to 10°-15° counterclockwise in
1368:
The modern day rate of convergence between the Indian and
Eurasian plates is measured to be approximately 17 mm/yr. This convergence is accommodated through seismic activity in active fault zones. As a result, the Himalayan range is one of the most seismically active regions in the world. This
186:
The earth in the
Cretaceous. The Cimmeridian Superterrane has accreted to Mega Laurasia, the oceanic crust of the Neotethys is subducted to the north along the Dras volcanic arc, the Shigatze Ocean opens as a consequence of back-arc spreading, India is separated from Africa and E. Gondwana and the
2748:
Steck, A.; Spring, L.; Vannay, J.C.; Masson, H.; Bucher, H.; Stutz, E.; Marchant, R.; Tieche, J.C. (1993b). Treloar, P. J.; Searle, M. P. (eds.). "The tectonic evolution of the northwestern
Himalaya in eastern Ladakh and Lahul, India, in Himalayan Tectonics".
682:
Even though it is more than reasonable to argue that this huge amount of crustal shortening most probably results from a combination of these three mechanisms, it is nevertheless the last mechanism which created the high topographic relief of the Himalaya.
2660:
Stampfli, G.M.; Mosar, J.; Favre, P.; Pillevuit, A.; Vannay, J.-C. (2001). "Permo-Mesozoic evolution of the western Tethyan realm: the Neotethys/East- Mediterranean connection". In P.A. Ziegler; W. Cavazza; A.H.F. Robertson; S. Crasquin-Soleau (eds.).
2129:
Burbank, Douglas W.; Leland, John; Fielding, Eric; Anderson, Robert S.; Brozovic, Nicholas; Reid, Mary R.; Duncan, Christopher (8 February 1996). "Bedrock incision, rock uplift and threshold hillslopes in the northwestern Himalayas".
210:
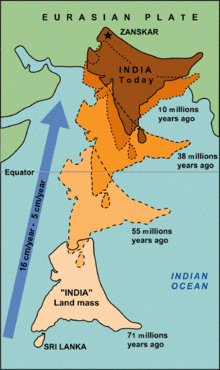
The northward drift of India from 71 Ma ago to present time. Note the simultaneous counter-clockwise rotation of India. Collision of the Indian continent with Eurasia occurred at about 55 million years ago. Source: www.usgs.org
245:. HHCS: High Himalayan Cristalline Sequence; ISZ: Indus Suture Zone; KW: Kishtwar Window; LKRW: Larji-Kulu-Rampur Window; MBT: Main Boundary Thrust; MCT: Main Central Thrust; SF: Sarchu Fault; ZSZ: Zanskar Shear Zone.
2706:
411:(LHCN)), Main Central thrust (MCT), Higher (or Greater) Himalayan crystallines (HHC), South Tibetan detachment system (STD), Tethys Himalaya (TH), and the Indus‐Tsangpo Suture Zone (ISZ). North of this lies the
403:(type of rocks and their layering) different from the adjacent zones. From south to north, the zones and the major faults separating them are the Main Frontal Thrust (MFT), Subhimalaya Zone (also called
629:
during the northward motion of India, at least three major mechanisms have been put forward, either separately or jointly, to explain what happened, since collision, to the 2500 km of "missing
2430:
Klootwijk, Chris T.; Gee, Jeff S.; Peirce, John W.; Smith, Guy M.; McFadden, Phil L. (May 1992). "An early India-Asia contact: Paleomagnetic constraints from Ninetyeast Ridge, ODP Leg 121".
2794:
Yin, An (May 2006). "Cenozoic tectonic evolution of the Himalayan orogen as constrained by along-strike variation of structural geometry, exhumation history, and foreland sedimentation".
1919:
Achache, José; Courtillot, Vincent; Xiu, Zhou Yao (1984). "Paleogeographic and tectonic evolution of southern Tibet since Middle Cretaceous time: New paleomagnetic data and synthesis".
2618:
Stampfli, G.M.; Mosar, J.; Favre, P.; Pillevuit, A.; Vannay, J.-C. (1998). "Permo-Triassic evolution of the western Tethyan realm: the Neotethys/east-Mediterranean basin connection".
2375:
Girard, M.; Bussy, F. (1998). "Late Pan-African magmatism in Himalaya: new geochronological and geochemical data from the Ordovician Tso Morari metagranites (Ladakh, NW India)".
1948:
Besse, J.; Courtillot, V.; Pozzi, J.P.; Westphal, M.; Zhou, Y.X. (18 October 1984). "Palaeomagnetic estimates of crustal shortening in the Himalayan thrusts and Zangbo Suture".
3108:
2401:
Klootwijk, C.T.; Conaghan, P.J.; Powell, C.McA. (October 1985). "The Himalayan Arc: large-scale continental subduction, oroclinal bending and back-arc spreading".
2496:
Patriat, Philippe; Achache, José (18 October 1984). "India-Eurasia collision chronology has implications for crustal shortening and driving mechanism of plates".
702:
One of the most striking aspects of the Himalayan orogen is the lateral continuity of its major tectonic elements. The Himalaya is classically divided into four
407:), Main Boundary Thrust (MBT), Lesser Himalaya (further subdivided into the "Lesser Himalayan Sedimentary Zone (LHSZ) and the Lesser Himalayan Crystalline
1878:"Coulomb Stress Modeling and Seismicity in the Western Himalaya, India Since 1905: Implications for the Incomplete Ruptures of the Main Himalayan Thrust"
750:
1180:
2870:
1092:
rocks. As with the HHCS, these metamorphic rocks represent the metamorphic equivalent of the sediments forming the base of the Tethys Himalaya. The
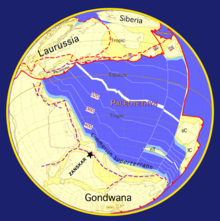
136:(290 million years ago) when India was part of Gondwana and bordered to the north by the Cimmerian Superterrane. Paleogeographic reconstruction by
1985:
Besse, Jean; Courtillot, Vincent (10 October 1988). "Paleogeographic maps of the continents bordering the Indian Ocean since the Early Jurassic".
2909:
2022:
Bingham, Douglas K.; Klootwijk, Chris T. (27 March 1980). "Palaeomagnetic constraints on Greater India's underthrusting of the Tibetan Plateau".
3083:
2730:"Geological Transect Across the Northwestern Himalaya in eastern Ladakh and Lahul (A Model for the Continental Collision of India and Asia)"
2672:"A plate tectonic model for the Paleozoic and Mesozoic constrained by dynamic plate boundaries and restored synthetic oceanic isochrons"
585:(84 Ma), the Indian plate began its very rapid northward drift covering a distance of about 6000 km, with the oceanic-oceanic
89:
562:(210 Ma), a major rifting episode split Gondwana in two parts. The Indian continent became part of East Gondwana, together with
61:
42:
2631:
Stampfli, G.M. (2000). E. Bozkurt; J.A. Winchester; J.D.A. Piper (eds.). "Tectonics and magmatism in Turkey and surrounding area".
2325:
Le Fort, P.; Cronin, V. S. (1 September 1988). "Granites in the Tectonic Evolution of the Himalaya, Karakoram and Southern Tibet".
1876:
Parija, Mahesh Prasad; Kumar, Sushil; Tiwari, V. M.; Biswal, Shubhasmita; Biswas, Arkoprovo; Velliyidathu, Arjun (September 2021).
2585:"Tethys reconstructed: plates, continental fragments and their Boundaries since 260 Ma from Central America to South-eastern Asia"
2282:
DiPietro, Joseph A.; Pogue, Kevin R. (September 2004). "Tectonostratigraphic subdivisions of the Himalaya: A view from the west".
283:) lies within the Transhimalayas in its east side. Bangong-Nujiang Suture Zone separates Qiangtang Terrane from the Lahsa Terrane
2362:
Frank, W.; Gansser, A.; Trommsdorff, V. (1977). "Geological observations in the Ladakh area (Himalayas); a preliminary report".
68:
2864:
2536:; Fournier, Marc; Jolivet, Laurent (1992). "Kinematics, topography, shortening, and extrusion in the India-Eurasia collision".
1038:
is usually progressive. But in many places along the Himalayan belt, this transition zone is marked by a major structure, the
2718:
1018:
of the TH. Stratigraphic analysis of these sediments yields important indications on the geological history of the northern
2853:"Geology and Petrographic study of the area from Chiraundi Khola to Thulo Khola, Dhading/Nawakot district, central Nepal".
863:
Approximately 30 different names exist in the literature to describe this unit; the most frequently found equivalents are
570:. However, the separation of East and West Gondwana, together with the formation of oceanic crust, occurred later, in the
75:
2902:
543:
ocean (Fig. 2). From that time on, the Cimmerian Superterranes drifted away from Gondwana towards the north. Nowadays,
399:
which extend across the length of Himalaya orogen. Each zone, flanked by the thrust faults on its north and south, has
361:
1512:
1492:
2995:
108:
57:
3159:
3154:
3149:
3129:
2707:"The TRANSMED Transects in Space and Time: Constraints on the Paleotectonic Evolution of the Mediterranean Domain"
256:
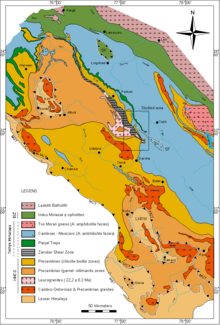
Simplified cross-section of the north-western Himalaya showing the main tectonic units and structural elements by
2985:
2975:
2955:
2451:
2895:
46:
2842:
Geochronologic and Thermobarometric Constraints on the Evolution of the Main Central Thrust, Himalayan Orogen
2728:
Steck, A.; Spring, L.; Vannay, J.C.; Masson, H.; Stutz, E.; Bucher, H.; Marchant, R.; Tièche, J.C. (1993a).
2199:
Dewey, J.F.; Cande, S.; Pitman III, W.C. (1989). "Tectonic evolution of the Indian/Eurasia Collision Zone".
1835:
3184:
1401:
Localized geology and geomorphology topics for various parts of the Himalaya are discussed on other pages:
3035:
756:
2388:
Heim, A.; Gansser, A. (1939). "Central Himalaya; geological observations of the Swiss expedition 1936".
2215:
Tectonic and metamorphic Evolution of the Central Himalayan Domain in Southeast Zanskar (Kashmir, India)
3164:
3005:
2935:
2327:
Philosophical Transactions of the Royal Society of London. Series A, Mathematical and Physical Sciences
2293:
1378:
1175:, Yarlung-Zangpo Suture Zone or Yarlung-Tsangpo Suture Zone, defines the zone of collision between the
280:
2241:"Paleocene-Eocene record of ophiolite obduction and initial India-Asia collision, south central Tibet"
82:
3194:
3189:
3179:
3174:
3169:
3040:
2878:
2459:
Molnar, P.; Tapponnier, P. (1975). "Cenozoic tectonics of Asia; effects of a continental collision".
1313:
1172:
660:
227:
2558:
3144:
3134:
3103:
2729:
1877:
1045:
455:
432:
3020:
3015:
3010:
2960:
2950:
2940:
1389:
1382:
1374:
35:
1295:
sediments derived mainly from the Ladakh batholith but also from the suture zone itself and the
3030:
3025:
2970:
2945:
2553:
2223:
1460:
1370:
637:
The first mechanism also calls upon the subduction of the Indian continental crust below Tibet.
505:
276:
574:(160-155 Ma). The Indian plate then broke off from Australia and Antarctica in the Early
242:
3093:
3050:
3045:
3000:
2990:
2980:
2965:
2100:
Brookfield, M.E. (1993). "The Himalaya passive margin from Precambrian to Cretaceous times".
1470:
1300:
1188:
832:
563:
272:
2687:
2414:
1369:
region has experienced many high magnitude earthquakes in the last 100 years, including the
2803:
2758:
2683:
2596:
2545:
2505:
2468:
2439:
2410:
2334:
2297:
2252:
2179:
2167:
2139:
2109:
2072:
2031:
1994:
1957:
1928:
1847:
1756:
1347:
884:
473:
2852:
1156:
694:
continental plates challenges one hypothesis for plate motion which relies on subduction.
8:
3098:
3088:
2284:
1317:, representing the northern limit of the Himalaya. Further to the North is the so-called
977:
764:
760:
528:
493:
469:
416:
392:
2807:
2762:
2600:
2549:
2509:
2472:
2443:
2338:
2301:
2256:
2183:
2143:
2113:
2076:
2035:
1998:
1961:
1932:
1859:
1851:
1760:
3139:
2782:
2648:
2571:
2521:
2350:
2313:
2270:
2155:
2088:
2047:
1973:
1780:
1449:
1019:
955:
839:(Kishtwar or Larji-Kulu-Rampur windows) within the High Himalaya Crystalline Sequence.
806:
645:
485:
428:
349:
317:
2696:
2671:
1743:
Dal Zilio, Luca; Hetényi, György; Hubbard, Judith; Bollinger, Laurent (2 March 2021).
2858:
2819:
2786:
2774:
2714:
2652:
2484:
2422:
2354:
2317:
2227:
2121:
2010:
1897:
1784:
1772:
1434:
1166:
1125:
895:(c. 22 Ma) age. Although most of the metasediments forming the HHCS are of late
630:
329:
2815:
2575:
2274:
2092:
2811:
2766:
2691:
2640:
2609:
2604:
2584:
2563:
2533:
2525:
2513:
2476:
2447:
2418:
2342:
2305:
2260:
2187:
2159:
2147:
2117:
2080:
2051:
2039:
2002:
1977:
1965:
1936:
1889:
1855:
1764:
1510:
A more modern paleogeographic reconstruction of the Permian-Triassic boundary, see
1405:
1343:
1229:
880:
443:
439:
345:
2770:
2644:
1490:
A more modern paleogeographic reconstruction of the Early Permian can be found at
842:
831:
are thrust over the Sub-himalayan range along the Main Boundary Thrust (MBT). The
353:
3060:
2882:
2840:
2480:
1445:
1424:
1414:
870:
836:
626:
606:
420:
369:
357:
333:
164:
1744:
958:. It is now generally accepted that the metasediments of the HHCS represent the
344:. The Himalaya-Tibet region supplies fresh water for more than one-fifth of the
3078:
1768:
1284:
848:
810:
691:
672:
668:
341:
298:
294:
391:
From south to north the Himalaya (Himalaya orogen) is divided into 4 parallel
264:
3123:
2823:
2778:
2231:
2014:
1901:
1776:
1331:
1319:
1184:
1162:
943:
919:
824:
622:
524:
412:
381:
2191:
2006:
1940:
373:
241:
Geological Map of the NW Himalaya; for references, see image description or
3073:
2488:
2346:
1516:
1496:
1464:
1428:
1354:
1339:
1280:
1276:
1176:
1133:
1129:
1117:
1089:
1003:
995:
991:
965:
959:
813:
675:
610:
497:
424:
400:
396:
337:
321:
314:
713:
520:
intrusions dated at around 500 Ma are also attributed to this event.
2309:
2265:
2240:
1893:
1530:
The fourfold division of Himalayan units has been used since the work of
1455:
1385:, all of which were recorded at magnitudes equal or greater than Mw 6.6.
1268:
1253:
1249:
1095:
1082:
1007:
903:
age, much younger metasediments can also be found in several areas, e.g.
896:
821:
799:
786:
and others), which demonstrates that the Himalaya is still a very active
783:
779:
733:
614:
578:(130-125 Ma) with the opening of the "South Indian Ocean" (Fig. 3).
548:
461:
2887:
1676:
1592:
1279:
sequence (with rare interbeds of marine saltwater sediments) comprising
962:
equivalents of the sedimentary series forming the base of the overlying
249:
215:
2921:
2665:. IGCP 369. Mém. Museum Nat. Hist. Nat. Vol. 186. pp. 51–108.
2663:
PeriTethys memoir 6: Peritethyan rift/wrench basins and passive margins
2377:
Schweizerische Mineralogische und Petrographische Mitteilungen Bulletin
2364:
Schweizerische Mineralogische und Petrographische Mitteilungen Bulletin
1439:
1351:
1292:
1233:
1157:
Indus Suture Zone (ISZ) (or Yarlung-Tsangpo Suture Zone) tectonic plate
1101:
1068:
939:
888:
852:
768:
586:
582:
575:
567:
501:
465:
384:. This last feature earned the Himalaya its name, originating from the
302:
271:
Indus-Yarlung suture zone separates Himalayas from the Transhimalayas.
133:
2567:
1568:
1201:
293:
is a record of the most dramatic and visible creations of the immense
2517:
2151:
2084:
2043:
1969:
1335:
1210:
1198:
1121:
1015:
828:
664:
649:
594:
590:
571:
540:
310:
160:
2060:
1803:
1724:
24:
2918:
2709:. In Cavazza W; Roure F; Spakman W; Stampfli GM; Ziegler P (eds.).
1791:
1700:
1640:
1237:
1086:
1023:
911:
904:
900:
803:
771:
725:
703:
598:
513:
509:
477:
442:, Central Himalaya, and Western Himalaya, which collectively house
385:
377:
1417:, which lies in the eastern half of the Indian union territory of
1030:. The transition between the generally low-grade sediments of the
855:
relief (highest peaks). It is commonly separated into four zones.
798:
The Lesser Himalaya (LH) tectonic plate is mainly formed by Upper
655:
The third proposed mechanism is that a large part (~1000 km (
415:
in Tibet which is outside the Himalayas. The Himalayas border the
2711:
The TRANSMED Atlas: the Mediterranean Region from Crust to Mantle
1410:
1288:
1271:
1027:
931:
927:
923:
892:
817:
740:
736:
729:
720:
The Sub-Himalayan tectonic plate is sometimes referred to as the
707:
532:
517:
481:
404:
365:
325:
306:
2876:
Wadia Institute of Himalayan Geology, Dehradun, India, main page
2865:
Reconstruction of the evolution of the Alpine-Himalayan orogeny.
2213:
1742:
1652:
1002:, have also been described within this unit. An almost complete
706:
units that can be followed for more than 2400 km along the
589:
continuing until the final closure of the oceanic basin and the
234:
203:
1418:
1325:
1245:
1241:
1206:
1137:
1113:
1074:
1061:
1011:
949:
843:
Central Himalayan Domain, (CHD) or High Himalaya tectonic plate
787:
775:
746:
559:
159:
The Earth at the Permian-Triassic boundary. The opening of the
1054:, which has indicators of both extension and compression. See
697:
2128:
1598:
1256:
971:
915:
908:
858:
552:
489:
408:
187:
Indian Ocean opens. Paleogeographic reconstructions based by
179:
152:
125:
1947:
1712:
1682:
438:
From east to west the Himalayas are divided into 3 regions,
2659:
2617:
2452:
10.1130/0091-7613(1992)020<0395:AEIACP>2.3.CO;2
1688:
1574:
1388:
A recent study (Parija et al, 2021) sought to quantify the
1223:
544:
536:
2875:
1745:"Building the Himalaya from tectonic to earthquake scales"
1664:
739:
sediments derived from the erosion of the Himalaya. These
324:
syntaxis at the western end, are the result of an ongoing
602:
2867:
Special Edition of "The Journal of the Virtual Explorer"
2861:
Special Edition of "The Journal of the Virtual Explorer"
2747:
2727:
2532:
1809:
1730:
1604:
1580:
222:
Geologic - Tectonic map of the Himalaya, modified after
2429:
2400:
2361:
1875:
1815:
1797:
1706:
1646:
847:
The Central Himalayan Domain forms the backbone of the
714:
Sub-Himalayan (Churia Hills or Sivaliks) tectonic plate
640:
Second is the extrusion or escape tectonics mechanism (
1836:"Himalayan Metamorphism and Its Tectonic Implications"
1628:
793:
728:
of the Himalayan Range and is essentially composed of
1918:
1658:
990:
The Tethys Himalaya is an approximately 100-km-wide
597:
onto India and the beginning of continent-continent
372:
rates at 2–12 mm/yr, the source of some of the
2239:Ding, Lin; Kapp, Paul; Wan, Xiaoqiao (6 May 2005).
1556:
1393:well as their potential for rupture in the future.
1034:and the underlying low- to high-grade rocks of the
974:which is thrust over the Lesser Himalaya along the
678:
together with the deformation of the Tibetan crust.
659:) or ~800 to ~1200 km) of the 2500 km of
488:(Fig. 1). During that period, the northern part of
49:. Unsourced material may be challenged and removed.
2633:Geological Society of London, Special Publications
1346:at the base of the Tibetan bloc, triggered by the
1143:
1107:
774:deposited by the rivers coming from the Himalaya (
531:and the Cimmerian Superterranes. During the Early
527:, an early stage of rifting developed between the
2058:
1531:
1431:is causing rapid uplifting of lower crustal rocks
1081:passes gradually to the north in a large dome of
994:formed by strongly folded and imbricated, weakly
887:which are intruded in many places by granites of
320:at the eastern end of the mountain range and the
3121:
2751:Geological Society, London, Special Publications
2670:Stampfli, G.M.; Borel, G.D. (28 February 2002).
2458:
2198:
2021:
1718:
1616:
1124:environment, on the northern part of the Indian
656:
641:
609:. The change of the relative speed between the
1984:
1694:
1191:) to the north. This suture zone is formed by:
998:sedimentary series. Several nappes, termed the
724:in the older literature. It forms the southern
690:The ongoing active collision of the Indian and
618:North Central Nepal relative to Asia (Fig. 4).
2495:
1670:
360:(nearly 10 mm/year at Nanga Parbat), the
313:, which stretch over 2400 km between the
196:
172:
145:
2903:
2859:Granitoids of the Himalayan Collisional Belt.
2704:
2669:
2324:
2281:
1840:Annual Review of Earth and Planetary Sciences
1610:
1586:
1473:- the root thrust that underlies the Himalaya
879:. It is a 30-km-thick, medium- to high-grade
223:
192:
168:
141:
1112:The Lamayuru and Markha Units are formed by
1062:Nyimaling-Tso Morari Metamorphic Dome (NTMD)
1026:evolution to its continental collision with
2387:
2374:
2238:
2170:(1988). "Extensional collapse of orogens".
1821:
1634:
1535:
851:and encompasses the areas with the highest
698:Major tectonic subdivisions of the Himalaya
348:, and accounts for a quarter of the global
16:Origins and structure of the mountain range
2910:
2896:
2099:
1442:- similar small scale erosion to the Indus
859:High Himalayan Crystalline Sequence (HHCS)
449:
2917:
2695:
2608:
2557:
2264:
1132:. The age of these sediments ranges from
109:Learn how and when to remove this message
2630:
2059:Blanford, W.T.; Medlicott, H.B. (1879).
1562:
1515:. Université de Lausanne. Archived from
1495:. Université de Lausanne. Archived from
263:
248:
233:
214:
202:
178:
151:
124:
2848:. PhD Thesis. University of California.
985:
3122:
2838:
1749:Nature Reviews Earth & Environment
1731:Le Pichon, Fournier & Jolivet 1992
1330:, which corresponds essentially to an
601:interaction starting at about 65
555:are partly made up of these terranes.
2891:
2839:Catlos, Elizabeth Jacqueline (2000).
2582:
2211:
2166:
1871:
1869:
1798:Frank, Gansser & Trommsdorff 1977
1707:Klootwijk, Conaghan & Powell 1985
1622:
1040:"Central Himalayan Detachment System"
1036:"High Himalayan Crystalline Sequence"
1022:of the Indian sub-continent from its
352:. Topographically, the belt has many
257:
188:
137:
1833:
644:) which sees the Indian plate as an
492:was affected by a late phase of the
47:adding citations to reliable sources
18:
2793:
2676:Earth and Planetary Science Letters
2403:Earth and Planetary Science Letters
1860:10.1146/annurev-earth-060313-055005
1363:
1240:volcanic island arc and consist of
794:Lesser Himalaya (LH) tectonic plate
13:
2061:"A manual of the geology of India"
1866:
1659:Achache, Courtillot & Xiu 1984
1205:, composed of an intercalation of
14:
3206:
2832:
1342:was caused by the melting of the
1213:from the Neotethys oceanic crust.
1100:is also here intruded by several
625:was "simply" subducted below the
376:and the highest concentration of
2705:Stampfli, GM; Borel, GD (2004).
2390:Schweizer. Naturf. Ges., Denksch
1448:to the North (also discussed in
368:Chomolangma), among the highest
23:
2816:10.1016/j.earscirev.2005.05.004
1987:Journal of Geophysical Research
1921:Journal of Geophysical Research
1827:
1736:
1532:Blanford & Medlicott (1879)
1524:
1303:and thus Eocene to post-Eocene.
1144:Exhumation of Metamorphic Rocks
1108:Lamayuru and Markha Units (LMU)
1046:South Tibetan Detachment System
34:needs additional citations for
2871:"Engineering Geology of Nepal"
2610:10.1080/09853111.1994.11105266
1504:
1484:
1079:"Tethys Himalaya synclinorium"
1052:"North Himalayan Normal Fault"
657:Dewey, Cande & Pitman 1989
472:, bounded to the north by the
1:
2855:MS Thesis by Gyanendra Gurung
2771:10.1144/GSL.SP.1993.074.01.19
2697:10.1016/S0012-821X(01)00588-X
2645:10.1144/GSL.SP.2000.173.01.01
1545:
388:for "the abode of the snow".
3109:North Himalayan Normal Fault
2737:Eclogae Geologicae Helvetiae
2481:10.1126/science.189.4201.419
2423:10.1016/0012-821X(85)90099-8
2222:(PhD thesis). Vol. 32.
2201:Eclogae Geologicae Helvetiae
2122:10.1016/0037-0738(93)90042-4
1719:Bingham & Klootwijk 1980
1550:
877:"High Himalayan Crystalline"
865:"Greater Himalayan Sequence"
755:, are internally folded and
722:Cis-Himalayan tectonic plate
642:Molnar & Tapponnier 1975
197:Patriat & Achache (1984)
173:Patriat & Achache (1984)
146:Patriat & Achache (1984)
7:
1695:Besse & Courtillot 1988
1396:
1334:of Andean type. Widespread
1104:(c. 480 Ma) granites.
891:(c. 500 Ma) and early
224:Le Fort & Cronin (1988)
193:Stampfli & Borel (2002)
169:Stampfli & Borel (2002)
142:Stampfli & Borel (2002)
10:
3213:
2294:American Geophysical Union
1911:
1769:10.1038/s43017-021-00143-1
1671:Patriat & Achache 1984
1467:system within the Himalaya
1379:1991 Uttarkashi Earthquake
1160:
827:(1840 ±70 Ma). These
453:
444:several nations and states
393:tectonostratigraphic zones
58:"Geology of the Himalayas"
3059:
2928:
1635:Ding, Kapp & Wan 2005
1611:DiPietro & Pogue 2004
1587:Stampfli & Borel 2002
1536:Heim & Gansser (1939)
1173:Indus-Yarlung suture zone
970:. The HHCS forms a major
228:Indus-Yarlung suture zone
3104:South Tibetan Detachment
3069:Geology of the Himalayas
2929:Notable Himalayan quakes
1477:
1413:is a subdistrict of the
1056:ongoing geologic studies
1014:is preserved within the
1006:record ranging from the
1000:"North Himalayan Nappes"
671:of the sediments of the
456:Pre-collisional Himalaya
291:geology of the Himalayas
167:from Gondwana. Based on
165:Cimmeridian Superterrane
3160:Natural history of Asia
3155:Landforms of South Asia
3150:Geography of South Asia
3130:Geology of the Himalaya
2881:30 October 2014 at the
2688:2002E&PSL.196...17S
2415:1985E&PSL..75..167K
2192:10.1029/TC007i006p01123
2007:10.1029/JB093iB10p11791
1941:10.1029/JB089iB12p10311
1822:Girard & Bussy 1998
1390:Coulomb Stress Transfer
1383:1999 Chamoli Earthquake
1375:1975 Kinnaur Earthquake
743:deposits, known as the
480:and was separated from
474:Cimmerian Superterranes
450:Making of the Himalayas
328:— the collision of the
301:forces and sculpted by
2347:10.1098/rsta.1988.0088
2224:University of Lausanne
2212:Dèzes, Pierre (1999).
2071:(504). Calcutta: 191.
1834:Kohn, Matthew (2014).
1461:Karakoram fault system
1371:1905 Kangra Earthquake
496:which is marked by an
356:: the highest rate of
284:
261:
246:
231:
212:
200:
176:
149:
3094:Main Himalayan Thrust
2796:Earth-Science Reviews
1647:Klootwijk et al. 1992
1471:Main Himalayan Thrust
1299:. These molasses are
1189:Karakoram-Lhasa Block
1128:and in the adjoining
885:metasedimentary rocks
811:passive Indian margin
710:(Fig. 5 and Fig. 7).
652:block out of its way.
267:
252:
237:
218:
206:
182:
155:
128:
2956:1833 Kathmandu–Bihar
2583:Ricou, L.M. (1994).
2310:10.1029/2003TC001554
2266:10.1029/2004TC001729
2220:Mémoires de Géologie
1993:(B10): 11791–11808.
1927:(B12): 10311–10340.
1894:10.1029/2020TC006204
1575:Stampfli et al. 2001
1355:Indian oceanic crust
1248:, volcanoclastites,
1042:, also known as the
986:Tethys Himalaya (TH)
881:metamorphic sequence
763:is thrust along the
663:was accommodated by
433:China–Myanmar border
364:(8848 m at Mt.
43:improve this article
3185:Geology of Pakistan
3099:Main Central Thrust
3089:Main Frontal Thrust
2808:2006ESRv...76....1Y
2763:1993GSLSP..74..265S
2713:. Springer Verlag.
2601:1994GeoAc...7..169R
2550:1992Tecto..11.1085L
2510:1984Natur.311..615P
2473:1975Sci...189..419M
2444:1992Geo....20..395K
2339:1988RSPTA.326..281F
2302:2004Tecto..23.5001D
2257:2005Tecto..24.3001D
2184:1988Tecto...7.1123D
2144:1996Natur.379..505B
2114:1993SedG...84....1B
2102:Sedimentary Geology
2077:1879Natur..20..191H
2036:1980Natur.284..336B
1999:1988JGR....9311791B
1962:1984Natur.311..621B
1933:1984JGR....8910311A
1852:2014AREPS..42..381K
1761:2021NRvEE...2..251D
1599:Burbank et al. 1996
1519:on 19 January 2011.
978:Main Central Thrust
809:sediments from the
765:Main Frontal Thrust
761:Sub-Himalayan Range
539:developed into the
529:Indian subcontinent
508:and the underlying
494:Pan-African orogeny
470:Indian subcontinent
431:to the east on the
417:Indo-Gangetic Plain
340:thrusting into the
281:Lhasa Block/Terrane
2996:1988 Myanmar-India
1810:Steck et al. 1993a
1450:Geography of Tibet
1323:, or more locally
1020:continental margin
956:Leh-Manali Highway
661:crustal shortening
648:that squeezed the
621:While most of the
486:Paleo-Tethys Ocean
429:Hengduan Mountains
350:sedimentary budget
285:
262:
247:
232:
213:
201:
177:
150:
3165:Geology of Bhutan
3117:
3116:
2720:978-3-540-22181-4
2568:10.1029/92TC01566
2534:Le Pichon, Xavier
2504:(5987): 615–621.
2467:(4201): 419–426.
2333:(1589): 281–299.
2138:(6565): 505–510.
2030:(5754): 336–338.
1956:(5987): 621–626.
1683:Besse et al. 1984
1427:- the erosion at
1314:Indus Suture Zone
1171:ISZ, also called
1167:Qiangtang terrane
1126:continental slope
1071:Metamorphic Dome"
1032:"Tethys Himalaya"
1008:Upper Proterozoic
835:often appears in
631:continental crust
330:continental crust
132:The Earth in the
119:
118:
111:
93:
3202:
3195:Regional geology
3190:Geology of Tibet
3180:Geology of Nepal
3175:Geology of India
3170:Geology of China
3036:April 2015 Nepal
2986:1950 Assam–Tibet
2912:
2905:
2898:
2889:
2888:
2849:
2847:
2827:
2790:
2744:
2734:
2724:
2701:
2699:
2666:
2656:
2627:
2614:
2612:
2589:Geodinamica Acta
2579:
2561:
2544:(6): 1085–1098.
2529:
2518:10.1038/311615a0
2492:
2455:
2426:
2409:(2–3): 167–183.
2397:
2384:
2371:
2358:
2321:
2278:
2268:
2235:
2208:
2195:
2178:(6): 1123–1139.
2163:
2152:10.1038/379505a0
2125:
2096:
2085:10.1038/020191a0
2055:
2044:10.1038/284336a0
2018:
1981:
1970:10.1038/311621a0
1944:
1906:
1905:
1873:
1864:
1863:
1831:
1825:
1819:
1813:
1807:
1801:
1795:
1789:
1788:
1740:
1734:
1728:
1722:
1716:
1710:
1704:
1698:
1692:
1686:
1680:
1674:
1668:
1662:
1656:
1650:
1644:
1638:
1632:
1626:
1620:
1614:
1608:
1602:
1596:
1590:
1584:
1578:
1572:
1566:
1560:
1539:
1528:
1522:
1520:
1508:
1502:
1500:
1488:
1406:Geology of Nepal
1364:Seismic activity
1301:post-collisional
1275:, a continental
1181:Ladakh Batholith
936:"Tschuldo slice"
849:Himalayan orogen
837:tectonic windows
607:Central Himalaya
440:Eastern Himalaya
346:world population
114:
107:
103:
100:
94:
92:
51:
27:
19:
3212:
3211:
3205:
3204:
3203:
3201:
3200:
3199:
3145:Plate tectonics
3135:Geology of Asia
3120:
3119:
3118:
3113:
3061:Plate tectonics
3055:
3006:1991 Uttarkashi
2936:1505 Lo Mustang
2924:
2916:
2883:Wayback Machine
2845:
2835:
2830:
2732:
2721:
2559:10.1.1.635.2173
2226:. p. 149.
1914:
1909:
1874:
1867:
1832:
1828:
1820:
1816:
1808:
1804:
1796:
1792:
1741:
1737:
1729:
1725:
1717:
1713:
1705:
1701:
1693:
1689:
1681:
1677:
1669:
1665:
1657:
1653:
1645:
1641:
1633:
1629:
1621:
1617:
1609:
1605:
1597:
1593:
1585:
1581:
1573:
1569:
1561:
1557:
1553:
1548:
1543:
1542:
1529:
1525:
1511:
1509:
1505:
1499:on 8 June 2011.
1491:
1489:
1485:
1480:
1446:Tibetan Plateau
1415:Kargil district
1399:
1366:
1297:Tethys Himalaya
1234:Late Cretaceous
1169:
1159:
1146:
1130:Neotethys basin
1120:deposited in a
1110:
1064:
1058:section below.
988:
966:Tethys Himalaya
861:
845:
833:Lesser Himalaya
796:
716:
700:
458:
452:
423:to the west in
421:Pamir Mountains
380:outside of the
374:greatest rivers
334:tectonic plates
287:
286:
226:. Green is the
115:
104:
98:
95:
52:
50:
40:
28:
17:
12:
11:
5:
3210:
3209:
3198:
3197:
3192:
3187:
3182:
3177:
3172:
3167:
3162:
3157:
3152:
3147:
3142:
3137:
3132:
3115:
3114:
3112:
3111:
3106:
3101:
3096:
3091:
3086:
3081:
3079:Eurasian Plate
3076:
3071:
3065:
3063:
3057:
3056:
3054:
3053:
3048:
3043:
3041:May 2015 Nepal
3038:
3033:
3028:
3023:
3018:
3013:
3008:
3003:
2998:
2993:
2988:
2983:
2978:
2973:
2968:
2963:
2958:
2953:
2948:
2943:
2938:
2932:
2930:
2926:
2925:
2915:
2914:
2907:
2900:
2892:
2886:
2885:
2873:
2868:
2862:
2856:
2850:
2834:
2833:External links
2831:
2829:
2828:
2802:(1–2): 1–131.
2791:
2757:(1): 265–276.
2745:
2725:
2719:
2702:
2667:
2657:
2628:
2615:
2595:(4): 169–218.
2580:
2530:
2493:
2456:
2438:(5): 395–398.
2427:
2398:
2385:
2372:
2359:
2322:
2296:Publications.
2279:
2236:
2209:
2196:
2164:
2126:
2097:
2056:
2019:
1982:
1945:
1915:
1913:
1910:
1908:
1907:
1865:
1846:(1): 381–419.
1826:
1814:
1802:
1790:
1755:(4): 251–268.
1735:
1723:
1711:
1699:
1687:
1675:
1663:
1651:
1639:
1627:
1615:
1603:
1591:
1579:
1567:
1554:
1552:
1549:
1547:
1544:
1541:
1540:
1523:
1503:
1482:
1481:
1479:
1476:
1475:
1474:
1468:
1458:
1453:
1443:
1437:
1432:
1422:
1408:
1398:
1395:
1365:
1362:
1361:
1360:
1359:
1358:
1307:
1306:
1305:
1304:
1285:braided stream
1262:
1261:
1260:
1259:
1217:
1216:
1215:
1214:
1158:
1155:
1145:
1142:
1109:
1106:
1098:Phe Formation"
1063:
1060:
987:
984:
860:
857:
844:
841:
795:
792:
715:
712:
699:
696:
680:
679:
653:
638:
476:, was part of
454:Main article:
451:
448:
419:to the south,
362:highest relief
342:Eurasian Plate
336:, namely, the
299:plate tectonic
295:mountain range
163:separates the
123:
122:
117:
116:
31:
29:
22:
15:
9:
6:
4:
3:
2:
3208:
3207:
3196:
3193:
3191:
3188:
3186:
3183:
3181:
3178:
3176:
3173:
3171:
3168:
3166:
3163:
3161:
3158:
3156:
3153:
3151:
3148:
3146:
3143:
3141:
3138:
3136:
3133:
3131:
3128:
3127:
3125:
3110:
3107:
3105:
3102:
3100:
3097:
3095:
3092:
3090:
3087:
3085:
3082:
3080:
3077:
3075:
3072:
3070:
3067:
3066:
3064:
3062:
3058:
3052:
3049:
3047:
3044:
3042:
3039:
3037:
3034:
3032:
3029:
3027:
3024:
3022:
3019:
3017:
3014:
3012:
3009:
3007:
3004:
3002:
2999:
2997:
2994:
2992:
2989:
2987:
2984:
2982:
2979:
2977:
2974:
2972:
2969:
2967:
2964:
2962:
2959:
2957:
2954:
2952:
2949:
2947:
2944:
2942:
2939:
2937:
2934:
2933:
2931:
2927:
2923:
2920:
2913:
2908:
2906:
2901:
2899:
2894:
2893:
2890:
2884:
2880:
2877:
2874:
2872:
2869:
2866:
2863:
2860:
2857:
2854:
2851:
2844:
2843:
2837:
2836:
2825:
2821:
2817:
2813:
2809:
2805:
2801:
2797:
2792:
2788:
2784:
2780:
2776:
2772:
2768:
2764:
2760:
2756:
2752:
2746:
2743:(1): 219–263.
2742:
2738:
2731:
2726:
2722:
2716:
2712:
2708:
2703:
2698:
2693:
2689:
2685:
2681:
2677:
2673:
2668:
2664:
2658:
2654:
2650:
2646:
2642:
2638:
2634:
2629:
2625:
2621:
2616:
2611:
2606:
2602:
2598:
2594:
2590:
2586:
2581:
2577:
2573:
2569:
2565:
2560:
2555:
2551:
2547:
2543:
2539:
2535:
2531:
2527:
2523:
2519:
2515:
2511:
2507:
2503:
2499:
2494:
2490:
2486:
2482:
2478:
2474:
2470:
2466:
2462:
2457:
2453:
2449:
2445:
2441:
2437:
2433:
2428:
2424:
2420:
2416:
2412:
2408:
2404:
2399:
2395:
2391:
2386:
2382:
2378:
2373:
2369:
2365:
2360:
2356:
2352:
2348:
2344:
2340:
2336:
2332:
2328:
2323:
2319:
2315:
2311:
2307:
2303:
2299:
2295:
2291:
2287:
2286:
2280:
2276:
2272:
2267:
2262:
2258:
2254:
2251:(3): TC3001.
2250:
2246:
2242:
2237:
2233:
2229:
2225:
2221:
2217:
2216:
2210:
2207:(3): 717–734.
2206:
2202:
2197:
2193:
2189:
2185:
2181:
2177:
2173:
2169:
2165:
2161:
2157:
2153:
2149:
2145:
2141:
2137:
2133:
2127:
2123:
2119:
2115:
2111:
2108:(1–4): 1–35.
2107:
2103:
2098:
2094:
2090:
2086:
2082:
2078:
2074:
2070:
2066:
2062:
2057:
2053:
2049:
2045:
2041:
2037:
2033:
2029:
2025:
2020:
2016:
2012:
2008:
2004:
2000:
1996:
1992:
1988:
1983:
1979:
1975:
1971:
1967:
1963:
1959:
1955:
1951:
1946:
1942:
1938:
1934:
1930:
1926:
1922:
1917:
1916:
1903:
1899:
1895:
1891:
1887:
1883:
1879:
1872:
1870:
1861:
1857:
1853:
1849:
1845:
1841:
1837:
1830:
1823:
1818:
1811:
1806:
1799:
1794:
1786:
1782:
1778:
1774:
1770:
1766:
1762:
1758:
1754:
1750:
1746:
1739:
1732:
1727:
1720:
1715:
1708:
1703:
1696:
1691:
1684:
1679:
1672:
1667:
1660:
1655:
1648:
1643:
1636:
1631:
1624:
1619:
1612:
1607:
1600:
1595:
1588:
1583:
1576:
1571:
1564:
1563:Stampfli 2000
1559:
1555:
1537:
1533:
1527:
1518:
1514:
1507:
1498:
1494:
1493:"Paleotethys"
1487:
1483:
1472:
1469:
1466:
1462:
1459:
1457:
1454:
1451:
1447:
1444:
1441:
1438:
1436:
1435:Mount Everest
1433:
1430:
1426:
1423:
1420:
1416:
1412:
1409:
1407:
1404:
1403:
1402:
1394:
1391:
1386:
1384:
1380:
1376:
1372:
1356:
1353:
1349:
1345:
1341:
1337:
1333:
1332:active margin
1329:
1327:
1322:
1321:
1320:Transhimalaya
1316:
1315:
1311:
1310:
1309:
1308:
1302:
1298:
1294:
1290:
1286:
1282:
1278:
1274:
1273:
1270:
1266:
1265:
1264:
1263:
1258:
1255:
1251:
1247:
1243:
1239:
1235:
1231:
1227:
1225:
1221:
1220:
1219:
1218:
1212:
1208:
1204:
1203:
1200:
1196:
1195:
1194:
1193:
1192:
1190:
1186:
1185:Transhimalaya
1182:
1178:
1174:
1168:
1164:
1163:Lhasa terrane
1154:
1150:
1141:
1139:
1135:
1131:
1127:
1123:
1119:
1115:
1105:
1103:
1099:
1097:
1091:
1088:
1084:
1080:
1076:
1072:
1070:
1059:
1057:
1053:
1049:
1047:
1041:
1037:
1033:
1029:
1025:
1021:
1017:
1013:
1009:
1005:
1004:stratigraphic
1001:
997:
996:metamorphosed
993:
983:
981:
979:
973:
969:
967:
961:
957:
953:
951:
945:
944:Carboniferous
941:
937:
933:
929:
925:
921:
920:Warwan Valley
917:
913:
910:
906:
902:
898:
894:
890:
886:
882:
878:
874:
872:
866:
856:
854:
850:
840:
838:
834:
830:
826:
823:
819:
815:
812:
808:
805:
801:
791:
789:
785:
781:
777:
773:
770:
766:
762:
758:
754:
752:
748:
742:
738:
735:
731:
727:
723:
718:
711:
709:
705:
695:
693:
688:
684:
677:
676:Indian margin
674:
670:
666:
662:
658:
654:
651:
647:
643:
639:
636:
635:
634:
632:
628:
627:Tibetan block
624:
623:oceanic crust
619:
616:
612:
608:
604:
600:
596:
592:
588:
584:
579:
577:
573:
569:
565:
561:
556:
554:
550:
546:
542:
538:
534:
530:
526:
525:Carboniferous
523:In the Early
521:
519:
515:
511:
507:
506:conglomerates
503:
499:
495:
491:
487:
483:
479:
475:
471:
467:
463:
457:
447:
445:
441:
436:
434:
430:
426:
422:
418:
414:
413:Transhimalaya
410:
406:
402:
398:
397:thrust faults
394:
389:
387:
383:
382:polar regions
379:
375:
371:
367:
363:
359:
355:
351:
347:
343:
339:
335:
331:
327:
323:
319:
316:
312:
308:
304:
300:
296:
292:
282:
278:
275:(also called
274:
273:Lhasa Terrane
270:
266:
259:
255:
251:
244:
240:
236:
229:
225:
221:
217:
209:
205:
198:
194:
190:
185:
181:
174:
170:
166:
162:
158:
154:
147:
143:
139:
135:
134:Early Permian
131:
127:
121:
113:
110:
102:
91:
88:
84:
81:
77:
74:
70:
67:
63:
60: –
59:
55:
54:Find sources:
48:
44:
38:
37:
32:This article
30:
26:
21:
20:
3084:Oldham Fault
3074:Indian Plate
3068:
3021:2008 Damxung
3016:2005 Kashmir
3011:1999 Chamoli
2961:1885 Kashmir
2951:1803 Garhwal
2941:1555 Kashmir
2841:
2799:
2795:
2754:
2750:
2740:
2736:
2710:
2682:(1): 17–33.
2679:
2675:
2662:
2636:
2632:
2623:
2619:
2592:
2588:
2541:
2537:
2501:
2497:
2464:
2460:
2435:
2431:
2406:
2402:
2393:
2389:
2380:
2376:
2370:(1): 89–113.
2367:
2363:
2330:
2326:
2289:
2283:
2248:
2244:
2219:
2214:
2204:
2200:
2175:
2171:
2135:
2131:
2105:
2101:
2068:
2064:
2027:
2023:
1990:
1986:
1953:
1949:
1924:
1920:
1885:
1881:
1843:
1839:
1829:
1817:
1805:
1793:
1752:
1748:
1738:
1726:
1714:
1702:
1690:
1678:
1666:
1654:
1642:
1630:
1618:
1606:
1594:
1582:
1570:
1558:
1526:
1517:the original
1506:
1497:the original
1486:
1465:active fault
1440:Sutlej River
1429:Nanga Parbat
1400:
1387:
1367:
1340:volcanic arc
1324:
1318:
1312:
1296:
1281:alluvial fan
1277:clastic rock
1267:
1250:pillow lavas
1222:
1197:
1177:Indian Plate
1170:
1151:
1147:
1134:Late Permian
1118:olistholiths
1111:
1093:
1078:
1077:region, the
1066:
1065:
1055:
1051:
1043:
1039:
1035:
1031:
999:
992:synclinorium
989:
975:
963:
947:
935:
876:
871:Tibetan Slab
868:
864:
862:
846:
814:intercalated
797:
744:
721:
719:
717:
701:
689:
685:
681:
620:
615:Asian plates
581:In the Late
580:
557:
522:
504:continental
498:unconformity
460:During Late
459:
437:
425:Central Asia
401:stratigraphy
390:
354:superlatives
338:Indian Plate
322:Nanga Parbat
315:Namcha Barwa
290:
288:
268:
258:Dèzes (1999)
253:
243:bibliography
238:
219:
207:
189:Dèzes (1999)
183:
156:
138:Dèzes (1999)
129:
120:
105:
96:
86:
79:
72:
65:
53:
41:Please help
36:verification
33:
3031:2011 Sikkim
3026:2009 Bhutan
2971:1905 Kangra
2946:1714 Bhutan
2922:earthquakes
2168:Dewey, J.F.
1513:"Neotethys"
1456:Paleotethys
1425:Indus River
1348:dehydration
1254:radiolarian
1096:Precambrian
1090:metamorphic
1083:greenschist
1067:"Nyimaling-
960:metamorphic
897:Proterozoic
853:topographic
800:Proterozoic
784:Brahmaputra
753:Formations"
734:Pleistocene
593:of oceanic
549:Afghanistan
516:. Numerous
462:Precambrian
140:, based on
3124:Categories
3051:2023 Nepal
3046:2021 Assam
3001:1988 Nepal
2991:1980 Nepal
2981:1947 Assam
2976:1934 Bihar
2966:1897 Assam
2620:PeriThetys
2383:: 399–418.
1623:Dèzes 1999
1546:References
1381:, and the
1352:subducting
1293:lacustrine
1252:and minor
1211:ophiolites
1161:See also:
1122:turbiditic
1102:Ordovician
1069:Tso Morari
1024:Gondwanian
940:Ordovician
889:Ordovician
816:with some
769:Quaternary
757:imbricated
587:subduction
583:Cretaceous
576:Cretaceous
568:Antarctica
502:Ordovician
466:Palaeozoic
427:, and the
303:weathering
297:formed by
211:(modified)
99:March 2024
69:newspapers
3140:Himalayas
2919:Himalayan
2824:0012-8252
2787:128420922
2779:0305-8719
2653:219202298
2554:CiteSeerX
2538:Tectonics
2396:(1): 245.
2355:202574726
2318:129138752
2285:Tectonics
2245:Tectonics
2232:1015-3578
2172:Tectonics
2015:0148-0227
1902:0278-7407
1882:Tectonics
1785:232084060
1777:2662-138X
1551:Citations
1336:volcanism
1328:Batholith
1226:Volcanics
1199:Ophiolite
1087:eclogitic
1016:sediments
899:to early
829:sediments
825:volcanics
802:to lower
767:over the
726:foothills
665:thrusting
650:Indochina
595:ophiolite
591:obduction
572:Callovian
564:Australia
541:Neotethys
514:sediments
311:Himalayas
277:Karakoram
161:Neotethys
2879:Archived
2639:: 1–23.
2576:36349751
2489:17781869
2275:39124270
2093:45807101
1463:- major
1397:See also
1338:in this
1238:Jurassic
1236:to Late
1202:Mélanges
1179:and the
912:syncline
905:Mesozoic
901:Cambrian
818:granites
807:detrital
804:Cambrian
772:alluvium
751:Sivaliks
737:molassic
704:tectonic
692:Eurasian
646:indenter
599:tectonic
518:granitic
510:Cambrian
500:between
478:Gondwana
464:and the
386:Sanskrit
378:glaciers
318:syntaxis
2804:Bibcode
2759:Bibcode
2684:Bibcode
2597:Bibcode
2546:Bibcode
2526:4315858
2506:Bibcode
2469:Bibcode
2461:Science
2440:Bibcode
2432:Geology
2411:Bibcode
2335:Bibcode
2298:Bibcode
2253:Bibcode
2180:Bibcode
2160:4362558
2140:Bibcode
2110:Bibcode
2073:Bibcode
2052:4279478
2032:Bibcode
1995:Bibcode
1978:4333485
1958:Bibcode
1929:Bibcode
1912:Sources
1848:Bibcode
1757:Bibcode
1411:Zanskar
1350:of the
1272:Molasse
1246:dacites
1242:basalts
1230:relicts
1114:flyschs
1073:in the
1028:Eurasia
1010:to the
982:(MCT).
946:in the
934:in the
932:Permian
928:Kashmir
924:Kistwar
907:in the
893:Miocene
741:molasse
730:Miocene
673:passive
669:folding
605:in the
558:In the
535:, this
533:Permian
512:marine
484:by the
482:Eurasia
405:Sivalik
370:erosion
366:Everest
332:of two
326:orogeny
307:erosion
83:scholar
2822:
2785:
2777:
2717:
2651:
2574:
2556:
2524:
2498:Nature
2487:
2353:
2316:
2273:
2230:
2158:
2132:Nature
2091:
2065:Nature
2050:
2024:Nature
2013:
1976:
1950:Nature
1900:
1783:
1775:
1419:Ladakh
1344:mantle
1326:Ladakh
1289:fluvio
1257:cherts
1207:flysch
1183:(also
1138:Eocene
1075:Ladakh
1012:Eocene
950:Sarchu
788:orogen
776:Ganges
759:. The
747:Murree
611:Indian
560:Norian
468:, the
409:Nappes
395:and 5
358:uplift
309:. The
269:Fig 8:
254:Fig 7:
239:Fig 6:
220:Fig 5:
208:Fig 4:
184:Fig 3:
157:Fig 2:
130:Fig 1:
85:
78:
71:
64:
56:
2846:(PDF)
2783:S2CID
2733:(PDF)
2649:S2CID
2572:S2CID
2522:S2CID
2351:S2CID
2314:S2CID
2292:(5).
2271:S2CID
2156:S2CID
2089:S2CID
2048:S2CID
1974:S2CID
1888:(9).
1781:S2CID
1478:Notes
1269:Indus
1232:of a
972:nappe
952:area"
916:Nepal
909:Tandi
780:Indus
553:Tibet
490:India
191:, on
90:JSTOR
76:books
2820:ISSN
2775:ISSN
2715:ISBN
2485:PMID
2228:ISSN
2011:ISSN
1898:ISSN
1773:ISSN
1534:and
1287:and
1224:Dras
1209:and
1165:and
1116:and
918:and
875:and
822:acid
820:and
749:and
708:belt
667:and
613:and
566:and
551:and
545:Iran
537:rift
305:and
289:The
195:and
171:and
144:and
62:news
2812:doi
2767:doi
2692:doi
2680:196
2641:doi
2637:173
2605:doi
2564:doi
2514:doi
2502:311
2477:doi
2465:189
2448:doi
2419:doi
2343:doi
2331:326
2306:doi
2261:doi
2188:doi
2148:doi
2136:379
2118:doi
2081:doi
2040:doi
2028:284
2003:doi
1966:doi
1954:311
1937:doi
1890:doi
1856:doi
1765:doi
1187:or
1136:to
1085:to
1050:or
954:on
942:to
926:in
922:of
914:of
883:of
732:to
633:".
175:.()
45:by
3126::
2818:.
2810:.
2800:76
2798:.
2781:.
2773:.
2765:.
2755:74
2753:.
2741:86
2739:.
2735:.
2690:.
2678:.
2674:.
2647:.
2635:.
2622:.
2603:.
2591:.
2587:.
2570:.
2562:.
2552:.
2542:11
2540:.
2520:.
2512:.
2500:.
2483:.
2475:.
2463:.
2446:.
2436:20
2434:.
2417:.
2407:75
2405:.
2394:73
2392:.
2381:79
2379:.
2368:57
2366:.
2349:.
2341:.
2329:.
2312:.
2304:.
2290:23
2288:.
2269:.
2259:.
2249:24
2247:.
2243:.
2218:.
2205:82
2203:.
2186:.
2174:.
2154:.
2146:.
2134:.
2116:.
2106:84
2104:.
2087:.
2079:.
2069:20
2067:.
2063:.
2046:.
2038:.
2026:.
2009:.
2001:.
1991:93
1989:.
1972:.
1964:.
1952:.
1935:.
1925:89
1923:.
1896:.
1886:40
1884:.
1880:.
1868:^
1854:.
1844:42
1842:.
1838:.
1779:.
1771:.
1763:.
1751:.
1747:.
1377:,
1373:,
1283:,
1244:,
1228:,
1140:.
938:,
930:,
867:,
790:.
782:,
778:,
603:Ma
547:,
446:.
435:.
2911:e
2904:t
2897:v
2826:.
2814::
2806::
2789:.
2769::
2761::
2723:.
2700:.
2694::
2686::
2655:.
2643::
2626:.
2624:3
2613:.
2607::
2599::
2593:7
2578:.
2566::
2548::
2528:.
2516::
2508::
2491:.
2479::
2471::
2454:.
2450::
2442::
2425:.
2421::
2413::
2357:.
2345::
2337::
2320:.
2308::
2300::
2277:.
2263::
2255::
2234:.
2194:.
2190::
2182::
2176:7
2162:.
2150::
2142::
2124:.
2120::
2112::
2095:.
2083::
2075::
2054:.
2042::
2034::
2017:.
2005::
1997::
1980:.
1968::
1960::
1943:.
1939::
1931::
1904:.
1892::
1862:.
1858::
1850::
1824:.
1812:.
1800:.
1787:.
1767::
1759::
1753:2
1733:.
1721:.
1709:.
1697:.
1685:.
1673:.
1661:.
1649:.
1637:.
1625:.
1613:.
1601:.
1589:.
1577:.
1565:.
1538:.
1521:.
1501:.
1452:)
1421:.
1357:.
1291:-
1094:"
1048:"
1044:"
980:"
976:"
968:"
964:"
948:"
873:"
869:"
745:"
279:-
260:.
230:.
199:.
148:.
112:)
106:(
101:)
97:(
87:·
80:·
73:·
66:·
39:.
Text is available under the Creative Commons Attribution-ShareAlike License. Additional terms may apply.