49:
339:
513:. Due to the fact that an embryo develops cranial to caudal, the formation of ectoderm does not happen at the same rate during development. The more inferior portion of the primitive streak will still have epiblast cells ingressing to make intraembryonic mesoderm, while the more superior portion has already stopped ingressing. However, eventually gastrulation finishes and the three germ layers are complete.
37:
375:(umbilical vesicle) is still debated. The main theory states that formation of the membranes of the yolk sac begins with an increase in production of hypoblast cells, followed by different patterns of migration. On day eight, the first portion of hypoblast cells begin their migration and make what is known as the primary yolk sac, or
479:
Also beginning on day 16, some of the ingressing epiblast cells make their way into the area between the epiblast and the newly forming definitive endoderm. This layer of cells becomes known as intraembryonic mesoderm. After the cells have moved bilaterally from the primitive streak and matured, four
403:
that surrounds a cavity. Formation of the definitive yolk sac occurs after the extraembryonic mesoderm splits, and it becomes a double layered structure with hypoblast-derived endoderm on the inside and mesoderm surrounding the outside. The definitive yolk sac contributes greatly to the embryo during
321:
into the two layers of the bilaminar embryonic disc. One of which is the epiblast, also known as the primitive ectoderm. The epiblast is the outer layer of the bilaminar embryonic disc and consists of columnar cells. The hypoblast, also known as the primitive endoderm, is the inner layer, closest to
382:
While the primary yolk sac is forming, extraembryonic mesoderm migrate into the blastocyst cavity and fill it with loosely packed cells. When the extraembryonic mesoderm is separated into two portions, a new gap arises called the gestational sac. This new cavity is responsible for detaching the
470:
On day 16, epiblast cells that are next to the primitive streak experience epithelial-to-mesenchymal transformation as they ingress through the primitive streak. The first wave of epiblast cells takes over the hypoblast, which slowly becomes replaced by new cells that eventually constitute the
387:. When the extraembryonic mesoderm splits into two layers, the amnion, yolk sac and chorion also become double-layered. The amnion and chorion are composed of extraembryonic ectoderm and mesoderm, whereas the yolk sac is composed of extraembryonic endoderm and mesoderm. By day 13, the
350:
is the first new cavity to form during the second week of development. Fluid collects between the epiblast and the hypoblast, which splits the epiblast into two portions. The layer at the embryonic pole grows around the amniotic sac, creating a barrier from the
504:
After the definitive endoderm and intraembryonic mesoderm formations are complete, the remaining epiblast cells do not ingress through the primitive streak; rather they remain on the outside and form the ectoderm. It is not long until the ectoderm becomes the
597:
359:, which is one of the four fetal membranes and the cells it comprises are referred to as amnioblasts. Although the amniotic sac is initially smaller than the blastocyst it becomes larger by week eight until the entire embryo is encompassed by the amnion.
235:(or the exocoelomic membrane), and they cover the blastocoel to form the yolk sac (or exocoelomic cavity). Cells of the hypoblast migrate along the outer edges of this reticulum and form the extraembryonic mesoderm; this disrupts the
297:. During these cellular divisions, the zygote remains the same size, but the number of cells increase. The morula enters the uterus after three or four days—during which a cavity, called the
416:. After the fourth week of development, the growing embryonic disc becomes much larger than the yolk sac and eventually involutes before birth. Uncommonly, the yolk sac may persist as the
379:(exocoelomic membrane). By day 12, the primary yolk sac has been disestablished by a new batch of migrating hypoblast cells that now contribute to the definitive yolk sac.
236:
223:
developed from the epiblast. The hypoblast is pushed down and forms the yolk sac (exocoelomic cavity) lining. Some hypoblast cells migrate along the inner
458:. During gastrulation, cells of the epiblast migrate towards the primitive streak, enter it, and then move apart from it through a process called
322:
the endometrium, which consists of cuboidal cells. The epiblast will develop into the 'embryo proper', and the hypoblast into the outer layer of
583:
645:
Schoenwolf, Gary C., and
William J. Larsen. Larsen's Human Embryology. 4th ed. Philadelphia: Churchill Livingstone/Elsevier, 2009. Print.
293:
to form two, then four, then eight and then 16 cells (typically by day four after fertilization), it becomes a ball of cells called a
219:
The epiblast migrates away from the trophoblast downwards, forming the amniotic cavity in between, the lining of which is formed from
404:
the fourth week of development, and executes critical functions for the embryo. One of which being the formation of blood, or
113:
48:
709:
736:
658:
471:
definitive endoderm. The definitive endoderm is what makes the lining of the gut and other associated gut structures.
567:
539:
342:
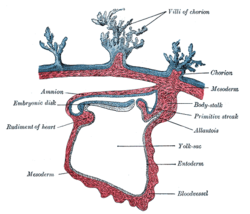
Image showing the bilaminar embryonic disc with its surrounding structures by day eight of embryonic development
654:"Bilaminar Embryonic Disc." Atlas of Human Embryology. Chronolab A.G. Switzerland, n.d. Web. 27 Nov. 2012. <
413:
17:
1021:
966:
745:
306:
181:. These two layers of cells are stretched between two fluid-filled cavities at either end: the primitive
154:
714:
338:
213:
108:
326:(extraembryonic membranes). The blastocyst serves as a source of nutrients for the growing cells by
1026:
938:
729:
421:
391:, a dense portion of extraembryonic mesoderm, restrains the embryonic disc in the gestational sac.
318:
790:
383:
embryo and, its amnion and yolk sac, from the far wall of the blastocyst, which is now named the
208:
forms between the layers. This distinction of layers of the bilaminar disc defines the primitive
161:, also known as the embryoblast, forms a bilaminar disc of two layers, an upper layer called the
1011:
910:
493:
443:
120:
674:"10.1 Early Development and Implantation." The Embryoblast. N.p., n.d. Web. 29 Nov. 2012. <
1016:
1006:
850:
489:
409:
274:
675:
481:
459:
376:
232:
228:
8:
1053:
760:
722:
577:
204:(blastocystic cavity) and made of cuboidal cells. As the two layers become evident, a
989:
775:
765:
563:
535:
485:
252:
205:
928:
891:
872:
510:
439:
388:
368:
197:
805:
662:
352:
323:
314:
262:
240:
224:
158:
84:
58:
655:
984:
882:
417:
400:
282:
1047:
933:
877:
534:(11th ed.). Philadelphia: Lippincott William & Wilkins. p. 54.
405:
290:
266:
209:
239:. Soon pockets form in the reticulum, which ultimately coalesce to form the
948:
903:
898:
506:
433:
347:
186:
96:
41:
Section through the embryo. (Bilaminar disc is labeled as embryonic disk.)
943:
868:
810:
310:
231:
along the way. These hypoblast cells and extracellular matrix are called
220:
193:
744:
126:
999:
886:
860:
800:
795:
780:
302:
298:
201:
91:
79:
832:
327:
170:
976:
958:
920:
837:
455:
451:
447:
372:
182:
174:
166:
162:
54:
420:
and cause a congenital out pouching of the digestive tract called
438:
In the third week, gastrulation begins with the formation of the
384:
278:
994:
785:
770:
688:
356:
294:
286:
270:
258:
150:
178:
149:
is the distinct two-layered structure of cells formed in an
362:
313:. During implantation the blastocyst, which contains the
36:
676:
http://www.embryology.ch/anglais/fplacenta/fecond04.html
474:
427:
157:
this takes place by day eight. It is formed when the
371:(chorionic cavity or extraembryonic coelom) and the
412:are first found in the wall of the yolk sac before
114:embryonic disc_by_E6.0.1.1.3.0.1 E6.0.1.1.3.0.1
465:
1045:
562:(Fifth ed.). Philadelphia, PA. p. 47.
480:divisions of intraembryonic mesoderm are made:
446:differentiate into the three germ cell layers:
394:
305:. Once the blastocyst is formed, it undergoes
730:
656:http://www.embryo.chronolab.com/formation.htm
598:"27.3B: Bilaminar Embryonic Disc Development"
737:
723:
582:: CS1 maint: location missing publisher (
557:
47:
35:
333:
53:Embryonic disc at implantation site with
553:
551:
337:
641:
639:
499:
227:lining of the blastocoel, secreting an
14:
1046:
637:
635:
633:
631:
629:
627:
625:
623:
621:
619:
529:
523:
363:Yolk sac and gestational sac formation
718:
590:
548:
367:The process of the formation of the
246:
668:
616:
475:Intraembryonic mesoderm development
399:Like the amnion, the yolk sac is a
177:), which will eventually form into
24:
648:
428:Epiblast cells during gastrulation
200:; the hypoblast is closest to the
25:
1065:
703:
192:The epiblast is adjacent to the
466:Definitive endoderm development
169:) and a lower layer called the
681:
414:primordial germ cell migration
13:
1:
516:
558:Schoenwolf, Gary C. (2015).
532:Langman's medical embryology
355:. This becomes known as the
346:Beginning on day eight, the
330:from the surrounding fluid.
153:. In the development of the
7:
1022:Splanchnopleuric mesenchyme
967:Splanchnopleuric mesenchyme
746:Human embryonic development
710:Diagram at manchester.ac.uk
442:. Gastrulation occurs when
395:Yolk sac during development
301:, is formed to produce the
10:
1070:
431:
289:. As the zygote undergoes
281:as it travels through the
250:
975:
957:
919:
859:
846:
819:
753:
560:Larsen's human embryology
243:(extraembryonic coelom).
214:polarity in embryogenesis
119:
107:
102:
90:
78:
70:
65:
46:
34:
29:
1027:Somatopleuric mesenchyme
939:Somatopleuric mesenchyme
748:in the first three weeks
319:cellular differentiation
277:, undergoes cleavage by
237:extraembryonic reticulum
139:bilaminar embryonic disc
30:Bilaminar embryonic disc
911:Regional specification
530:Sadler, T. W. (2010).
494:lateral plate mesoderm
444:pluripotent stem cells
343:
334:Amniotic sac formation
121:Anatomical terminology
1017:Intraembryonic coelom
490:intermediate mesoderm
422:Meckel's diverticulum
410:primordial germ cells
341:
275:embryonic development
196:and made of columnar
57:expanded to form the
500:Ectoderm development
482:cardiogenic mesoderm
229:extracellular matrix
143:bilaminar blastoderm
602:Medicine LibreTexts
661:2012-11-19 at the
344:
269:event between two
1041:
1040:
1037:
1036:
766:Oocyte activation
486:paraxial mesoderm
377:Heuser's membrane
253:Cleavage (embryo)
247:Initial formation
233:Heuser's membrane
206:basement membrane
135:
134:
130:
16:(Redirected from
1061:
929:Surface ectoderm
892:Primitive groove
873:Primitive streak
857:
856:
739:
732:
725:
716:
715:
697:
696:
693:gastrulation.org
685:
679:
672:
666:
652:
646:
643:
614:
613:
611:
609:
594:
588:
587:
581:
573:
555:
546:
545:
527:
511:surface ectoderm
440:primitive streak
389:connecting stalk
273:at the start of
241:chorionic cavity
198:epithelial cells
127:edit on Wikidata
124:
51:
39:
27:
26:
21:
1069:
1068:
1064:
1063:
1062:
1060:
1059:
1058:
1044:
1043:
1042:
1033:
971:
953:
915:
848:
842:
821:
815:
806:Inner cell mass
749:
743:
706:
701:
700:
687:
686:
682:
673:
669:
663:Wayback Machine
653:
649:
644:
617:
607:
605:
596:
595:
591:
575:
574:
570:
556:
549:
542:
528:
524:
519:
502:
477:
468:
436:
430:
397:
369:gestational sac
365:
353:cytotrophoblast
336:
324:fetal membranes
315:inner cell mass
263:eukaryotic cell
257:The one-celled
255:
249:
225:cytotrophoblast
159:inner cell mass
131:
85:Inner cell mass
61:
59:amniotic cavity
42:
23:
22:
15:
12:
11:
5:
1067:
1057:
1056:
1039:
1038:
1035:
1034:
1032:
1031:
1030:
1029:
1024:
1019:
1009:
1004:
1003:
1002:
997:
987:
985:Axial mesoderm
981:
979:
973:
972:
970:
969:
963:
961:
955:
954:
952:
951:
946:
941:
936:
931:
925:
923:
917:
916:
914:
913:
908:
907:
906:
896:
895:
894:
889:
883:Primitive node
880:
865:
863:
854:
844:
843:
841:
840:
835:
829:
827:
817:
816:
814:
813:
808:
803:
798:
793:
788:
783:
778:
773:
768:
763:
757:
755:
751:
750:
742:
741:
734:
727:
719:
713:
712:
705:
704:External links
702:
699:
698:
680:
667:
647:
615:
604:. 24 July 2018
589:
568:
547:
540:
521:
520:
518:
515:
501:
498:
476:
473:
467:
464:
432:Main article:
429:
426:
418:vitelline duct
401:fetal membrane
396:
393:
364:
361:
335:
332:
283:fallopian tube
251:Main article:
248:
245:
147:embryonic disc
133:
132:
123:
117:
116:
111:
105:
104:
100:
99:
94:
88:
87:
82:
76:
75:
72:
68:
67:
63:
62:
52:
44:
43:
40:
32:
31:
18:Embryonic disk
9:
6:
4:
3:
2:
1066:
1055:
1052:
1051:
1049:
1028:
1025:
1023:
1020:
1018:
1015:
1014:
1013:
1012:Lateral plate
1010:
1008:
1005:
1001:
998:
996:
993:
992:
991:
988:
986:
983:
982:
980:
978:
974:
968:
965:
964:
962:
960:
956:
950:
947:
945:
942:
940:
937:
935:
934:Neuroectoderm
932:
930:
927:
926:
924:
922:
918:
912:
909:
905:
902:
901:
900:
897:
893:
890:
888:
884:
881:
879:
878:Primitive pit
876:
875:
874:
870:
867:
866:
864:
862:
858:
855:
852:
845:
839:
836:
834:
831:
830:
828:
825:
818:
812:
809:
807:
804:
802:
799:
797:
794:
792:
789:
787:
784:
782:
779:
777:
774:
772:
769:
767:
764:
762:
761:Fertilization
759:
758:
756:
752:
747:
740:
735:
733:
728:
726:
721:
720:
717:
711:
708:
707:
694:
690:
684:
677:
671:
664:
660:
657:
651:
642:
640:
638:
636:
634:
632:
630:
628:
626:
624:
622:
620:
603:
599:
593:
585:
579:
571:
569:9781455706846
565:
561:
554:
552:
543:
541:9780781790697
537:
533:
526:
522:
514:
512:
508:
497:
495:
491:
487:
483:
472:
463:
461:
457:
453:
449:
445:
441:
435:
425:
423:
419:
415:
411:
407:
406:hematopoiesis
402:
392:
390:
386:
380:
378:
374:
370:
360:
358:
354:
349:
340:
331:
329:
325:
320:
316:
312:
308:
304:
300:
296:
292:
291:cell division
288:
284:
280:
276:
272:
268:
267:fertilization
264:
260:
254:
244:
242:
238:
234:
230:
226:
222:
217:
215:
211:
210:dorso ventral
207:
203:
199:
195:
190:
188:
184:
180:
176:
172:
168:
164:
160:
156:
152:
148:
144:
140:
128:
122:
118:
115:
112:
110:
106:
101:
98:
95:
93:
92:Gives rise to
89:
86:
83:
81:
77:
73:
69:
64:
60:
56:
50:
45:
38:
33:
28:
19:
1007:Intermediate
949:Neural crest
904:Gastrulation
823:
692:
683:
670:
650:
606:. Retrieved
601:
592:
559:
531:
525:
507:neural plate
503:
478:
469:
437:
434:Gastrulation
398:
381:
366:
348:amniotic sac
345:
317:, undergoes
307:implantation
265:formed by a
256:
218:
191:
187:amniotic sac
155:human embryo
146:
142:
138:
136:
97:Human embryo
944:Neurulation
869:Archenteron
861:Germ layers
811:Trophoblast
311:endometrium
221:amnioblasts
194:trophoblast
173:(primitive
165:(primitive
103:Identifiers
1054:Embryology
1000:Somitomere
887:Blastopore
851:Trilaminar
801:Blastocyst
796:Blastocoel
791:Cavitation
781:Blastomere
517:References
460:ingression
303:blastocyst
299:blastocoel
202:blastocoel
833:Hypoblast
824:Bilaminar
578:cite book
328:diffusion
309:into the
212:axis and
171:hypoblast
80:Precursor
1048:Category
990:Paraxial
977:Mesoderm
959:Endoderm
921:Ectoderm
899:Gastrula
838:Epiblast
776:Cleavage
659:Archived
456:endoderm
452:mesoderm
448:ectoderm
408:. Also,
373:yolk sac
185:and the
183:yolk sac
175:endoderm
167:ectoderm
163:epiblast
55:epiblast
847:Week 3
820:Week 2
608:12 June
385:chorion
285:to the
279:mitosis
271:gametes
66:Details
995:Somite
786:Morula
771:Zygote
754:Week 1
689:"Home"
566:
538:
357:amnion
295:morula
287:uterus
259:zygote
151:embryo
665:>.
179:fetus
125:[
678:>
610:2022
584:link
564:ISBN
536:ISBN
509:and
492:and
454:and
261:, a
137:The
71:Days
145:or
1050::
691:.
618:^
600:.
580:}}
576:{{
550:^
496:.
488:,
484:,
462:.
450:,
424:.
216:.
189:.
141:,
109:TE
74:13
885:/
871:/
853:)
849:(
826:)
822:(
738:e
731:t
724:v
695:.
612:.
586:)
572:.
544:.
129:]
20:)
Text is available under the Creative Commons Attribution-ShareAlike License. Additional terms may apply.