368:. It was demonstrated in the frog embryo that the first cleavage furrow widens in the animal hemisphere creating a small intercellular cavity that is sealed off via tight junctions. As cleavage continues, the cavity expands to become the developed blastocoel. The blastocoel is a crucial component of amphibian embryo development. It permits cell migration during gastrulation and prevents the cells beneath the blastocoel from interacting prematurely with the cells above the blastocoel. For instance, the blastocoel prevents the vegetal cells destined to become
41:
410:
cells surrounding it outwards. At this point, the cells have become specified and are ciliated on the opposite side of the blastocoel. The vegetal plate and animal hemisphere develop and secrete a hatching enzyme that digests the fertilization envelope and allows the embryo to now become a free-swimming hatched blastula.
404:
At the 120- cell stage, the sea urchin embryo is considered a blastula because of its developed blastocoel, which every embryonic cell surrounds and touches. Every cell is in contact with the proteinaceous fluid of the blastocoel on the inside and touches the hyaline layer on the outside. The loosely
409:
that create a seamless epithelium that completely encircles the blastocoel. Even as the blastomeres continue to divide, the blastula remains one-cell thick and thins out as the embryo expands outward. This is accomplished in part due to the influx of water that expands the blastocoel and pushes the
449:
cleavage. The blastoderm develops into the epiblast and hypoblast and it is between these layers that the blastocoel will form. The shape and formation of the avian blastodisc differs from amphibian, fish, and echinoderm blastulas, but the overall spatial relationship of the blastocoel remains the
29:
623:
Heasman, Janet; Crawford, Aaron; Goldstone, Kim; Garner-Hamrick, Peggy; Gumbiner, Barry; McCrea, Pierre; Kintner, Chris; Noro, Chikako
Yoshida; Wylie, Chris (1994). "Overexpression of cadherins and underexpression of β-catenin inhibit dorsal mesoderm induction in early Xenopus embryos".
331:
cells contain sodium (Na) pumps, Na/K- ATPase and Na/H exchangers, that pump sodium into the embryo. The oviduct cells stimulate these trophoblast sodium pumps as the fertilized egg travels down the fallopian tube towards the uterus. The accumulation of sodium pulls in water through
1056:(online). Amsterdam, NDE: Elsevier-Saunders. Retrieved 30 January 2016. "blastocoel... the fluid-filled cavity of the mass of cells (blastula) produced by cleavage of fertilized ovum. Sometimes spelled...alled...'Also' blastocoelic ...pertaining to the blastocoele.";
458:
The avian blastocoel is important during the development of the primitive streak. The ingression of the endodermal precursor cells form the epiblast into the blastocoel and the migration of lateral cells of the posterior epiblast towards the center form the early
430:. These cells then dissociate and ingress into the blastocoel and are called the primary mesenchyme. The cells move randomly along the inside of the blastocoel, until they become localized in the ventrolateral region of the blastocoel.
916:
Galileo, Deni S.; Morrill, John B. (1985). "Patterns of cells and extracellular material of the sea urchinLytechinus variegatus (Echinodermata; Echinoidea) embryo, from hatched blastula to late gastrula".
388:. If the mRNA is destroyed, then there’s no EP-cadherin, little to no blastomere adhesion and the blastocoel is non-existent. During the next stage of embryonic development, amphibian
360:
An amphibian embryo in the 128- cell stage is considered a blastula as the blastocoel in the embryo becomes apparent during this stage. The fluid-filled cavity forms in the
1488:
802:
Dumortier, Julien G.; Le Verge-Serandour, Mathieu; Tortorelli, Anna
Francesca; Mielke, Annette; De Plater, Ludmilla; Turlier, Hervé; Maître, Jean-Léon (2019).
771:
Dumortier, Julien G.; Le Verge-Serandour, Mathieu; Tortorelli, Anna
Francesca; Mielke, Annette; De Plater, Ludmilla; Turlier, Hervé; Maître, Jean-Léon (2019).
384:
The blastocoel can be damaged and abolished if the adhesion between blastomeres, provided by cell adhesion molecules like EP-cadherin, is destroyed as mRNA by
963:
Cherr, GN; Summers, RG; Baldwin, JD; Morrill, JB (15 June 1992). "Preservation and visualization of the sea urchin embryo blastocoelic extracellular matrix".
1006:
Kimmel, Charles B.; Ballard, William W.; Kimmel, Seth R.; Ullmann, Bonnie; Schilling, Thomas F. (1995). "Stages of embryonic development of the zebrafish".
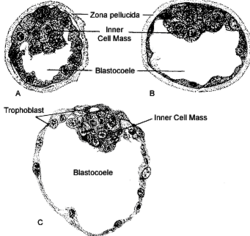
344:. The blastocoel further expands and the inner cell mass becomes positioned on one side of the trophoblast cells forming a mammalian blastula, called a
1481:
722:
295:
is a solid ball of cells that has a small group of internal cells surrounded by a larger group of external cells. Then blastomeres undergo
1474:
833:
Nieuwkoop, PD (1973). "The organization center of the amphibian embryo: its origin, spatial organization, and morphogenetic action".
483:
do not have a defined blastocoel. Rather, they have small, irregular extracellular spaces that are formed between the cells of the
467:
and functions as an opening through which cells travel into the blastocoel. As cells migrate into the blastocoel, they undergo an
1684:
681:
468:
1159:
426:
side of the blastula begins to flatten and thicken as a small cluster of these cells develop long, thin processes called
352:
and the blastocoel is the first axis of symmetry of mammalian embryo and determines its attachment point to the uterus.
736:
Wiley, Lynn M. (1984). "Cavitation in the mouse preimplantation embryo: and the origin of nascent blastocoele fluid".
1128:
1103:
1078:
878:
Purcell, SM; Keller, R (January 1993). "A different type of amphibian mesoderm morphogenesis in
Ceratophrys ornata".
854:
706:
542:
1057:
591:"The relationship between cleavage and blastocoel formation in Xenopus laevis. I. Light microscopic observations"
340:. To form a single lumen, the fluid from multiple water pockets collects into a single entity in process akin to
525:
Biggers, JD; Borland, RM; Powers, RD (1977). "Transport
Mechanisms in the Preimplantation Mammalian Embryo".
307:. The inner cell mass will go on to become the actual embryo. The external, surrounding cells develop into
1444:
1389:
1168:
78:
1137:
361:
572:
1526:
1449:
1361:
1246:
1152:
364:
of the frog. However, the early formation of the blastocoel has been traced back to the very first
296:
251:
1213:
316:
284:
1653:
1434:
1333:
122:
1439:
1429:
1273:
208:
396:, during mid-gastrulation. At the end of gastrulation, the blastocoel has been obliterated.
1648:
803:
772:
337:
438:
Similar to mammals, fertilization of the avian ovum occurs in the oviduct. From there the
8:
1521:
1183:
1145:
504:
1604:
1554:
1031:
988:
942:
846:
804:"Hydraulic fracturing and active coarsening position the lumen of the mouse blastocyst"
773:"Hydraulic fracturing and active coarsening position the lumen of the mouse blastocyst"
716:
649:
560:
419:
115:
1412:
1198:
1188:
1124:
1118:
1099:
1093:
1074:
1068:
1023:
980:
934:
895:
860:
850:
753:
749:
702:
677:
641:
637:
602:
548:
538:
443:
276:
235:
1466:
1035:
992:
946:
653:
1594:
1503:
1351:
1314:
1295:
1015:
972:
926:
887:
842:
815:
784:
745:
633:
530:
464:
460:
341:
311:
cells, which only contribute to extra-embryonic tissues. At this stage there is no
146:
590:
1663:
1569:
1550:
1516:
1228:
385:
365:
349:
324:
312:
300:
247:
224:
73:
51:
1658:
1599:
1589:
1581:
1543:
1407:
1305:
1089:
1064:
406:
323:
cells transport fluid into the embryo to create a blastocoel, the fluid-filled
1114:
534:
40:
1678:
1356:
1300:
328:
320:
304:
263:
a very small cavity has been described in the two-cell stage of development.
243:
220:
976:
930:
819:
788:
1564:
1371:
1326:
1321:
1019:
938:
801:
770:
423:
389:
254:
1027:
984:
899:
891:
864:
757:
645:
606:
1511:
1366:
1291:
1233:
552:
446:
442:, a small cluster of cells in the animal pole of the egg, then undergoes
393:
308:
59:
55:
1167:
1422:
1309:
1283:
1223:
1203:
484:
439:
345:
280:
216:
212:
105:
93:
47:
622:
250:
formed as the embryo enlarges, and is the essential precursor for the
128:
1533:
1255:
480:
427:
1622:
1399:
1381:
1343:
1260:
373:
369:
204:
110:
422:. After the blastula hatches from the fertilization envelope, the
1627:
1538:
333:
259:
28:
527:
Ciba
Foundation Symposium 52 - the Freezing of Mammalian Embryos
463:. As these cells converge inward, a depression forms called the
1559:
1417:
1208:
1193:
529:. Novartis Foundation Symposia. Vol. 52. pp. 129–53.
336:. The accumulation of water breaks open cell-cell contacts via
292:
288:
272:
239:
98:
418:
Important to the sea urchin blastula is the ingression of the
176:
16:
Fluid-filled or yolk-filled cavity that forms in the blastula
479:
Unlike amphibian, echinoderm, mammalian, and avian embryos,
405:
connected blastomeres are now tightly connected because of
167:
1005:
962:
203:
is a fluid-filled or yolk-filled cavity that forms in the
158:
701:(Fifth ed.). Oxford, United Kingdom. p. 375.
676:(9th ed.). Sunderland, Mass.: Sinauer Associates.
392:, the blastocoel is displaced by the formation of the
211:. At this stage in mammals the blastula is called the
1496:
173:
170:
161:
524:
413:
179:
164:
155:
152:
283:. At the 8- or 16-cell stage, the embryo undergoes
149:
595:Journal of Embryology and Experimental Morphology
1676:
1123:(6th ed.). Sunderland: Sinauer Associates.
1098:(6th ed.). Sunderland: Sinauer Associates.
1073:(6th ed.). Sunderland: Sinauer Associates.
453:
372:from coming in contact with those cells in the
915:
1482:
1153:
877:
376:fated to give rise to the skin and nerves.
1489:
1475:
1160:
1146:
911:
909:
721:: CS1 maint: location missing publisher (
279:divisions forming daughter cells known as
39:
27:
832:
826:
667:
665:
663:
618:
616:
246:. It is the first fluid-filled cavity or
1054:Dorland's Illustrated Medical Dictionary
958:
956:
469:epithelial-to-mesenchymal transformation
1112:
1087:
1062:
906:
871:
696:
690:
671:
379:
315:within the embryo. In a process called
1677:
1115:"The Early Development of Sea Urchins"
1052:Dorlands Staff (2004). "blastocoel ".
999:
660:
613:
584:
582:
520:
518:
1470:
1141:
953:
735:
303:fate and the external layer becoming
729:
588:
58:layer, alongside the surface of the
579:
515:
13:
1046:
847:10.1016/b978-0-12-028610-2.50005-8
497:
14:
1696:
1497:Membranes of the fetus and embryo
965:Microscopy Research and Technique
414:Development of primary mesenchyme
399:
299:with internal cells adopting the
355:
145:
474:
795:
764:
46:Schematic diagram showing the
1:
1090:"Early Amphibian Development"
1065:"Early Mammalian Development"
490:
454:Formation of primitive streak
266:
215:, which consists of an outer
52:embryoblast (inner cell mass)
1685:Animal developmental biology
750:10.1016/0012-1606(84)90290-2
638:10.1016/0092-8674(94)90069-8
275:undergoes several rounds of
7:
1445:Splanchnopleuric mesenchyme
1390:Splanchnopleuric mesenchyme
1169:Human embryonic development
433:
10:
1701:
672:Gilbert, Scott F. (2010).
505:"Definition of BLASTOCOEL"
1636:
1615:
1580:
1502:
1398:
1380:
1342:
1282:
1269:
1242:
1176:
1113:Gilbert, Scott F (2000).
1088:Gilbert, Scott F (2000).
1063:Gilbert, Scott F (2000).
835:Advances in Morphogenesis
699:Principles of development
535:10.1002/9780470720332.ch7
348:. The axis formed by the
271:After fertilization, the
121:
104:
92:
84:
72:
67:
38:
26:
21:
1527:Intermediate trophoblast
1450:Somatopleuric mesenchyme
1362:Somatopleuric mesenchyme
1171:in the first three weeks
589:Kalt, Marvin R. (1971).
297:cellular differentiation
977:10.1002/jemt.1070220104
931:10.1002/jmor.1051850310
820:10.1126/science.aaw7709
789:10.1126/science.aaw7709
697:Wolpert, Lewis (2015).
487:sitting atop the yolk.
327:. The membranes of the
1334:Regional specification
1020:10.1002/aja.1002030302
1008:Developmental Dynamics
234:It develops following
123:Anatomical terminology
1440:Intraembryonic coelom
1120:Developmental Biology
1095:Developmental Biology
1070:Developmental Biology
919:Journal of Morphology
892:10.1242/dev.117.1.307
738:Developmental Biology
674:Developmental biology
209:embryonic development
380:Damage to blastocoel
338:hydraulic fracturing
33:Mammalian blastocoel
1654:Reichert's membrane
1522:Syncytiotrophoblast
201:segmentation cavity
1555:Intervillous space
420:primary mesenchyme
291:. Eventually, the
207:during very early
195:, and also called
116:primitive yolk sac
1672:
1671:
1649:Heuser's membrane
1464:
1463:
1460:
1459:
1189:Oocyte activation
814:(6452): 465–468.
783:(6452): 465–468.
683:978-0-87893-384-6
362:animal hemisphere
223:, enveloping the
137:
136:
132:
1692:
1595:Umbilical artery
1491:
1484:
1477:
1468:
1467:
1352:Surface ectoderm
1315:Primitive groove
1296:Primitive streak
1280:
1279:
1162:
1155:
1148:
1139:
1138:
1134:
1109:
1084:
1040:
1039:
1003:
997:
996:
960:
951:
950:
913:
904:
903:
875:
869:
868:
830:
824:
823:
799:
793:
792:
768:
762:
761:
733:
727:
726:
720:
712:
694:
688:
687:
669:
658:
657:
620:
611:
610:
586:
577:
576:
570:
566:
564:
556:
522:
513:
512:
501:
465:primitive groove
461:primitive streak
386:oligonucleotides
342:Ostwald ripening
187:), also spelled
186:
185:
182:
181:
178:
175:
172:
169:
166:
163:
160:
157:
154:
151:
129:edit on Wikidata
126:
43:
31:
19:
18:
1700:
1699:
1695:
1694:
1693:
1691:
1690:
1689:
1675:
1674:
1673:
1668:
1664:Gestational sac
1632:
1611:
1605:Wharton's jelly
1576:
1551:Chorionic villi
1517:Cytotrophoblast
1498:
1495:
1465:
1456:
1394:
1376:
1338:
1271:
1265:
1244:
1238:
1229:Inner cell mass
1172:
1166:
1131:
1106:
1081:
1049:
1047:Further reading
1044:
1043:
1004:
1000:
961:
954:
914:
907:
876:
872:
857:
831:
827:
800:
796:
769:
765:
734:
730:
714:
713:
709:
695:
691:
684:
670:
661:
621:
614:
587:
580:
568:
567:
558:
557:
545:
523:
516:
509:Merriam-Webster
503:
502:
498:
493:
477:
456:
436:
416:
407:tight junctions
402:
382:
366:cleavage furrow
358:
350:inner cell mass
301:inner cell mass
269:
225:inner cell mass
197:cleavage cavity
148:
144:
133:
114:
63:
45:
34:
17:
12:
11:
5:
1698:
1688:
1687:
1670:
1669:
1667:
1666:
1661:
1659:Vitelline duct
1656:
1651:
1646:
1640:
1638:
1634:
1633:
1631:
1630:
1625:
1619:
1617:
1613:
1612:
1610:
1609:
1608:
1607:
1602:
1600:Umbilical vein
1597:
1590:Umbilical cord
1586:
1584:
1578:
1577:
1575:
1574:
1573:
1572:
1567:
1557:
1548:
1547:
1546:
1544:Decidual cells
1536:
1531:
1530:
1529:
1524:
1519:
1508:
1506:
1500:
1499:
1494:
1493:
1486:
1479:
1471:
1462:
1461:
1458:
1457:
1455:
1454:
1453:
1452:
1447:
1442:
1432:
1427:
1426:
1425:
1420:
1410:
1408:Axial mesoderm
1404:
1402:
1396:
1395:
1393:
1392:
1386:
1384:
1378:
1377:
1375:
1374:
1369:
1364:
1359:
1354:
1348:
1346:
1340:
1339:
1337:
1336:
1331:
1330:
1329:
1319:
1318:
1317:
1312:
1306:Primitive node
1303:
1288:
1286:
1277:
1267:
1266:
1264:
1263:
1258:
1252:
1250:
1240:
1239:
1237:
1236:
1231:
1226:
1221:
1216:
1211:
1206:
1201:
1196:
1191:
1186:
1180:
1178:
1174:
1173:
1165:
1164:
1157:
1150:
1142:
1136:
1135:
1129:
1110:
1104:
1085:
1079:
1060:
1048:
1045:
1042:
1041:
1014:(3): 253–310.
998:
952:
925:(3): 387–402.
905:
870:
855:
825:
794:
763:
728:
707:
689:
682:
659:
632:(5): 791–803.
612:
578:
569:|journal=
543:
514:
495:
494:
492:
489:
476:
473:
455:
452:
435:
432:
415:
412:
401:
400:In sea urchins
398:
381:
378:
357:
354:
287:and forms the
268:
265:
252:differentiated
135:
134:
125:
119:
118:
108:
102:
101:
96:
90:
89:
86:
82:
81:
76:
74:Carnegie stage
70:
69:
65:
64:
44:
36:
35:
32:
24:
23:
15:
9:
6:
4:
3:
2:
1697:
1686:
1683:
1682:
1680:
1665:
1662:
1660:
1657:
1655:
1652:
1650:
1647:
1645:
1642:
1641:
1639:
1635:
1629:
1626:
1624:
1621:
1620:
1618:
1614:
1606:
1603:
1601:
1598:
1596:
1593:
1592:
1591:
1588:
1587:
1585:
1583:
1579:
1571:
1568:
1566:
1563:
1562:
1561:
1558:
1556:
1552:
1549:
1545:
1542:
1541:
1540:
1537:
1535:
1532:
1528:
1525:
1523:
1520:
1518:
1515:
1514:
1513:
1510:
1509:
1507:
1505:
1501:
1492:
1487:
1485:
1480:
1478:
1473:
1472:
1469:
1451:
1448:
1446:
1443:
1441:
1438:
1437:
1436:
1435:Lateral plate
1433:
1431:
1428:
1424:
1421:
1419:
1416:
1415:
1414:
1411:
1409:
1406:
1405:
1403:
1401:
1397:
1391:
1388:
1387:
1385:
1383:
1379:
1373:
1370:
1368:
1365:
1363:
1360:
1358:
1357:Neuroectoderm
1355:
1353:
1350:
1349:
1347:
1345:
1341:
1335:
1332:
1328:
1325:
1324:
1323:
1320:
1316:
1313:
1311:
1307:
1304:
1302:
1301:Primitive pit
1299:
1298:
1297:
1293:
1290:
1289:
1287:
1285:
1281:
1278:
1275:
1268:
1262:
1259:
1257:
1254:
1253:
1251:
1248:
1241:
1235:
1232:
1230:
1227:
1225:
1222:
1220:
1217:
1215:
1212:
1210:
1207:
1205:
1202:
1200:
1197:
1195:
1192:
1190:
1187:
1185:
1184:Fertilization
1182:
1181:
1179:
1175:
1170:
1163:
1158:
1156:
1151:
1149:
1144:
1143:
1140:
1132:
1130:0-87893-243-7
1126:
1122:
1121:
1116:
1111:
1107:
1105:0-87893-243-7
1101:
1097:
1096:
1091:
1086:
1082:
1080:0-87893-243-7
1076:
1072:
1071:
1066:
1061:
1059:
1055:
1051:
1050:
1037:
1033:
1029:
1025:
1021:
1017:
1013:
1009:
1002:
994:
990:
986:
982:
978:
974:
970:
966:
959:
957:
948:
944:
940:
936:
932:
928:
924:
920:
912:
910:
901:
897:
893:
889:
886:(1): 307–17.
885:
881:
874:
866:
862:
858:
856:9780120286102
852:
848:
844:
840:
836:
829:
821:
817:
813:
809:
805:
798:
790:
786:
782:
778:
774:
767:
759:
755:
751:
747:
744:(2): 330–42.
743:
739:
732:
724:
718:
710:
708:9780199678143
704:
700:
693:
685:
679:
675:
668:
666:
664:
655:
651:
647:
643:
639:
635:
631:
627:
619:
617:
608:
604:
600:
596:
592:
585:
583:
574:
562:
554:
550:
546:
544:9780470720332
540:
536:
532:
528:
521:
519:
510:
506:
500:
496:
488:
486:
482:
472:
470:
466:
462:
451:
448:
445:
441:
431:
429:
425:
421:
411:
408:
397:
395:
391:
387:
377:
375:
371:
367:
363:
356:In amphibians
353:
351:
347:
343:
339:
335:
330:
329:trophectoderm
326:
322:
321:trophectoderm
318:
314:
310:
306:
305:trophectoderm
302:
298:
294:
290:
286:
282:
278:
274:
264:
262:
261:
256:
253:
249:
245:
244:fertilization
241:
237:
232:
230:
226:
222:
221:trophectoderm
218:
214:
210:
206:
202:
198:
194:
190:
184:
142:
130:
124:
120:
117:
112:
109:
107:
106:Gives rise to
103:
100:
97:
95:
91:
87:
83:
80:
77:
75:
71:
66:
61:
57:
53:
49:
42:
37:
30:
25:
20:
1643:
1430:Intermediate
1372:Neural crest
1327:Gastrulation
1218:
1119:
1094:
1069:
1058:Dorlands.com
1053:
1011:
1007:
1001:
971:(1): 11–22.
968:
964:
922:
918:
883:
879:
873:
838:
834:
828:
811:
807:
797:
780:
776:
766:
741:
737:
731:
698:
692:
673:
629:
625:
601:(1): 37–49.
598:
594:
526:
508:
499:
478:
475:In zebrafish
457:
437:
417:
403:
390:gastrulation
383:
359:
270:
258:
233:
228:
200:
196:
192:
188:
140:
138:
1616:Circulatory
1512:Trophoblast
1367:Neurulation
1292:Archenteron
1284:Germ layers
1234:Trophoblast
880:Development
447:meroblastic
394:archenteron
309:trophoblast
281:blastomeres
189:blastocoele
60:endometrium
56:trophoblast
50:, with its
1644:Blastocoel
1423:Somitomere
1310:Blastopore
1274:Trilaminar
1224:Blastocyst
1219:Blastocoel
1214:Cavitation
1204:Blastomere
491:References
485:blastodisc
440:blastodisc
346:blastocyst
317:cavitation
285:compaction
267:In mammals
229:blastocoel
217:epithelium
213:blastocyst
193:blastocele
141:blastocoel
48:blastocyst
22:Blastocoel
1534:Allantois
1256:Hypoblast
1247:Bilaminar
717:cite book
571:ignored (
561:cite book
481:zebrafish
444:discoidal
428:filopodia
257:. In the
94:Precursor
1679:Category
1623:Placenta
1413:Paraxial
1400:Mesoderm
1382:Endoderm
1344:Ectoderm
1322:Gastrula
1261:Epiblast
1199:Cleavage
1036:19327966
993:32044141
947:51615081
939:29991195
841:: 1–39.
654:33403560
434:In birds
374:ectoderm
370:endoderm
277:cleavage
255:gastrula
238:of the
236:cleavage
227:and the
205:blastula
111:Gastrula
54:and its
1628:Chorion
1539:Decidua
1270:Week 3
1243:Week 2
1028:8589427
985:1617206
900:8223254
865:4581327
808:Science
777:Science
758:6090240
646:7528101
607:5565077
424:vegetal
334:osmosis
260:Xenopus
68:Details
1570:cavity
1560:Amnion
1504:Embryo
1418:Somite
1209:Morula
1194:Zygote
1177:Week 1
1127:
1102:
1077:
1034:
1026:
991:
983:
945:
937:
898:
863:
853:
756:
705:
680:
652:
644:
605:
553:145938
551:
541:
450:same.
293:morula
289:morula
273:zygote
242:after
240:zygote
219:, the
99:Morula
1637:Other
1582:Fetus
1032:S2CID
989:S2CID
943:S2CID
650:S2CID
325:lumen
313:lumen
248:lumen
199:, or
127:[
1125:ISBN
1100:ISBN
1075:ISBN
1024:PMID
981:PMID
935:PMID
896:PMID
861:PMID
851:ISBN
754:PMID
723:link
703:ISBN
678:ISBN
642:PMID
626:Cell
603:PMID
573:help
549:PMID
539:ISBN
191:and
139:The
85:Days
1565:sac
1016:doi
1012:203
973:doi
927:doi
923:185
888:doi
884:117
843:doi
816:doi
812:365
785:doi
781:365
746:doi
742:105
634:doi
531:doi
1681::
1117:.
1092:.
1067:.
1030:.
1022:.
1010:.
987:.
979:.
969:22
967:.
955:^
941:.
933:.
921:.
908:^
894:.
882:.
859:.
849:.
839:10
837:.
810:.
806:.
779:.
775:.
752:.
740:.
719:}}
715:{{
662:^
648:.
640:.
630:79
628:.
615:^
599:26
597:.
593:.
581:^
565::
563:}}
559:{{
547:.
537:.
517:^
507:.
471:.
319:,
231:.
177:iː
113:,
1553:/
1490:e
1483:t
1476:v
1308:/
1294:/
1276:)
1272:(
1249:)
1245:(
1161:e
1154:t
1147:v
1133:.
1108:.
1083:.
1038:.
1018::
995:.
975::
949:.
929::
902:.
890::
867:.
845::
822:.
818::
791:.
787::
760:.
748::
725:)
711:.
686:.
656:.
636::
609:.
575:)
555:.
533::
511:.
183:/
180:l
174:s
171:ˌ
168:ə
165:t
162:s
159:æ
156:l
153:b
150:ˈ
147:/
143:(
131:]
88:5
79:3
62:.
Text is available under the Creative Commons Attribution-ShareAlike License. Additional terms may apply.