459:
623:
having higher rates among complex dislocations. Femoral head osteonecrosis happens in 5-40% of dislocations, with rates rising the longer time to reduction (>6 hours). Similarly increasing in rates with time to reduction, neurovascular injury with most notable being sciatic nerve injury, occurs in 8-20% of cases. Femoral head fractures accompany 10% of posterior dislocations and 25-75% of anterior dislocations. Lastly, recurrent dislocations can also occur, however is rare (<2%).
478:
556:
502:(ORIF) among other operative indications. Prognosis is worsened if reduction is delayed more than 6 hours. If the reduction is stable, the patient can proceed to protective weight bearing which includes crutch-assisted walking (ambulation) with weight bearing as tolerated for 4–6 weeks succeeding a short period of bed rest. If reduction is unstable, 4–6 weeks of skeletal traction is necessary before protective weight bearing.
548:
511:
bodies should be determined prior to reduction. Of note, femoral neck fractures, femoral head fractures, and incarcerated fracture fragments preventing joint reduction are contraindications. Common closed reduction methods include the Allis method, Stimson
Gravity Technique, and the Bigelow maneuvers. Once reduction is completed, management becomes less urgent and appropriate workup including CT scanning can be completed.
52:
606:- Standing, hold on to a nearby chair or surface. Swing one leg forwards away from you, and hold the position for three to five seconds. Then swing the leg slowly backwards and behind your body. Hold for three to five seconds. This exercise helps to increase range of motion, as well as strengthening the hip flexor and hip extensor muscles that control much of the hip joint.
632:
unrestrained. With the hip being inherently stable, dislocations are rare, however have high rates of associated injuries. For example, half of all hip dislocations are accompanied by a fracture. Refer to "Prognosis and
Complications" section for rates of other associated injuries. The condition was first described in the medical press in the early 1800s.
590:
Standing Hip abduction- Standing up and holding on to a nearby surface, slowly lift one leg away from the midline of the body and then lower it back to starting position. This is simply a more advanced way to do any of the lying hip abduction exercises, and should be done as the person progresses in
631:
Males are affected more often than females. Most common cause is high energy trauma such as from a motor vehicle collision or a high-level fall. Traumatic dislocations occur most commonly in those 16 to 40 years old. Of note, restrained passengers are at a lower risk for a hip dislocation than those
510:
The hip should be reduced as quickly as possible to reduce the risk of osteonecrosis of the femoral head. This is done through manual traction of the thigh inline with the dislocation under general anesthesia and muscle relaxation, or conscious sedation. Fractures of the femoral head and other loose
449:
also makes one more susceptible to hip dislocation. Hip dysplasia is a congenital condition in which the hip is deformed in a way that decreases the congruency between the head of the femur and the acetabulum of the pelvis. Bony congruence is a stabilizing factor to the hip joint, so the decrease in
618:
Hip dislocations can take anywhere from 2–3 months to fully heal, and even longer depending on associated injuries such as fracture. Moreover, the outcome ranges from a fully healthy hip to a painful, arthritic one. With simple posterior dislocations, literature reports great outcomes in 70%-80% of
543:
and receive professional prescriptive exercises based on their individual abilities, progress, and overall range of motion. The following are some typical recommended exercises used as rehabilitation for hip dislocation. It is important to understand that each individual has different capabilities
622:
Complications of hip dislocation that impact prognosis include post-traumatic arthritis, femoral head osteonecrosis, femoral head fracture, neurovascular injury, and recurrent dislocation. Post-traumatic arthritis is the most common long-term complication and happens in 20% of hip dislocations,
343:
For anterior dislocation, the affected limb will be in a position of abduction and external rotation. The degree of flexion depends on whether it is a superior or inferior dislocation, with the former resulting in hip extension and the latter, hip flexion. This is to say that with superior and
470:(AP) X-ray of the pelvis and a cross-table lateral X-ray of the effected hip are ordered for diagnosis. The size of the head of the femur is then compared across both sides of the pelvis. The affected femoral head will appear larger if the dislocation is anterior, and smaller if posterior. A
230:
Hip dislocations are classified by fracture association and by the positioning of the dislocated femoral head. A posteriorly positioned head is the most common dislocation type. Hip dislocations are a medical emergency, requiring prompt placement of the femoral head back into the acetabulum
239:
on the thighbone in line with the dislocation. If this is unsuccessful or if there is an associated fracture in need of repair, surgery is required. It often takes 2–3 months for a dislocated hip to fully heal, and it can take even longer depending on associated injuries such as fracture.
300:
is when the femoral head lies anteriorly after dislocation. Anterior dislocations are subdivided into two types being inferior (obturator) dislocation and superior (iliac or pubic) dislocation. There is also a
Thompson and Epstein classification system for anterior hip dislocations.
619:
cases. With complex dislocations, the outcome is often governed by the associated fracture. Anterior dislocations are noted to have worse outcomes with their higher likelihood of being associated with femoral head injuries. Those without associated femoral head injuries do better.
321:
The affected leg is usually extremely painful, precluding weight-bearing and movement. Nerve injuries also can accompany dislocations, necessitating careful neurovascular examination. Deformity is also present, which is based on concomitant injuries and the type of dislocation:
1469:
498:) in order to reduce the risk of osteonecrosis of the femoral head. Most professionals recommend closed reduction (nonoperative) barring operative indications such as irreducible dislocation, delayed presentation, non-concentric reduction, fracture requiring excision and/or
243:
Typically, people with hip dislocations present with severe pain and an inability to move the affected leg. Diagnosis is made by physical exam and plain X-rays of the hips. A CT scan is recommended following reduction to rule out complications. Complications include
344:
inferior anterior dislocations, the affected leg will be bent at the hip backwards and upwards respectively, while being shifted and pointed away from the body. Femoral nerve palsies can also be present, conferring leg numbness and weakness, however are uncommon.
594:
Knee raises- While standing and holding onto a chair, slowly lift one leg off the ground and bring it closer to the body while bending the knee. Then lower the leg back down slowly. This helps to strengthen the hip flexor muscles and retain stability in the
413:. About 65% of cases are related to motor vehicle collisions, with falls from elevation and sports injuries causing the majority of the rest. Moreover, wear and tear of the body with aging increases the older population's susceptibility to hip dislocation.
308:
is an outdated term for displacement of the femoral head towards the body's center into a fractured acetabulum and is no longer used. Moreover, the term "congenital" dislocation is no longer recommended, except for very rare conditions, in which there is a
259:
Males are affected more often than females. Traumatic dislocations occurs most commonly in those 16 to 40 years old. Half of all hip dislocations are accompanied by a fracture. The condition was first described in the medical press in the early 1800s.
569:
Bridge- Lie flat on back. Place arms with palms down beside body. Keep feet hip distance apart and bend knees. Slowly lift hips upward. Hold position for three to five seconds. This helps strengthen the glutes and increase stability of the hip
330:
For posterior dislocation, the affected limb will be in a position of flexion, adduction, and internal rotation. This is to say, the affected leg will be bent upwards at the hip, while being shifted and pointed towards the middle of the body.
1972:
1965:
400:
or annular ligament which encases the femoral neck, stabilizing the joint capsule. The strength of a healthy hip, reinforced and stabilized by the aforementioned structures can withstand over 1000 lbs. of force.
1872:
1849:
268:
Dislocations are categorized as simple if there is no associated fracture, and complex if there is. In addition, hip dislocations are classified depending on the location of the head of the femur as follows:
280:
is when the femoral head lies posteriorly after dislocation. It is the most common pattern of dislocation accounting for 90% of hip dislocations, and those with an associated fracture are categorized by the
1958:
580:- Lie flat on back. Slowly slide leg away from body and then back in, keeping the knees straight. This exercises the gluteus medius and helps to maintain stability in the hip while walking.
1774:
524:
2666:
3020:
423:) knee as is the case with a dashboard injury in a motor vehicle accident. The positioning of the hip at the time of impact determines associated injuries, with
519:
Open (surgical) reduction indications include an irreducible dislocation, fracture with fragments preventing congruent reduction, fracture requiring an
207:) is very stable, secured by both bony and soft-tissue constraints. With that, dislocation would require significant force which typically results from
1950:
877:
523:, delayed presentation, and non-concentric reduction. Approaches to surgical reductions include the posterior approach for posterior dislocations (
2659:
235:). This reduction of the femoral head back into the hip socket is typically done under sedation and without surgery, through maneuvers including
1044:
528:
1664:
3025:
2652:
2552:
587:- Lie on one side with one leg on top of the other. Slowly lift the top leg towards the ceiling and then lower it back down slowly.
2045:
2493:
531:) approach for anterior dislocations. A CT scan or Judet views should be obtained prior to transfer to the surgical suite.
1887:
282:
708:
Beebe MJ, Bauer JM, Mir HR (July 2016). "Treatment of Hip
Dislocations and Associated Injuries: Current State of Care".
861:
17:
1494:
2854:
1980:
1403:
1020:
982:
759:
544:
that can best be assessed by a physical therapist or medical professional, and that these are simply recommendations.
462:
Reimer's migration index can be used to indicate hip dislocation. The migration index (MI) is normally less than 33%.
2901:
499:
494:
Hip dislocations are a medical emergency, requiring timely placement of the femoral head back into the acetabulum (
441:
and abduction of the hip. In the setting of forced external rotation and abduction of the hip, the hip flexed and
2447:
2166:
1604:
1190:
495:
374:
232:
161:
1638:
641:
91:
2282:
1985:
467:
2452:
2171:
2001:
1989:
335:
injury is also present in 8%-20% of cases, conferring numbness and weakness to aspects of the lower leg.
2483:
1427:
2537:
2457:
682:
393:
1686:
2392:
2035:
1898:
1339:"Case of Injury of the Hip Confounded with Dislocation, and Fracture of the Neck of the Thigh-Bone"
2990:
2985:
2758:
2644:
2429:
2063:
2040:
603:
584:
577:
212:
86:
972:
385:
358:
236:
134:
749:
481:
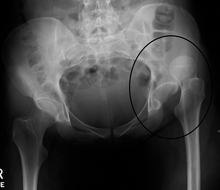
Dislocation of the left hip, secondary to developmental hip dysplasia. Closed arrow marks the
2805:
2332:
1997:
362:
286:
361:
of the spherical femoral head (of femur) and the concave acetabulum (of pelvis). It forms a
2864:
2547:
946:
389:
381:
8:
2752:
2726:
2365:
1981:
1876:
442:
424:
165:
1814:
609:
Adding ankle weights to any exercises can be done as progress is made in rehabilitation.
445:
leads to the inferior and superior sub-types of anterior hip dislocation, respectively.
2762:
2748:
2721:
2227:
1734:
1701:
1674:
1605:"Hip subluxation and dislocation in cerebral palsy: outcome of bone surgery in 21 hips"
1578:
1421:
1363:
1338:
1158:
1140:
1038:
871:
216:
76:
1104:
2941:
2895:
2675:
2562:
2542:
1909:
1758:
1739:
1721:
1619:
1409:
1399:
1368:
1350:
1316:
1308:
1260:
1224:
1132:
1124:
1120:
1080:
1076:
1026:
1016:
978:
857:
755:
725:
438:
121:
64:
1938:
1881:
1639:"Hip (horizontal beam lateral view) | Radiology Reference Article | Radiopaedia.org"
1144:
2963:
2869:
2849:
2609:
2604:
2525:
2517:
2437:
2401:
2209:
2161:
2118:
1729:
1713:
1551:
1444:
1398:. Sarwark, John F. Rosemont, Ill.: American Academy of Orthopaedic Surgeons. 2010.
1358:
1300:
1116:
1072:
717:
540:
397:
30:
This article is about acute hip dislocation. For developmental hip dysplasia, see
2687:
2625:
2360:
2190:
2156:
1903:
220:
2891:
2778:
2488:
2419:
2383:
2355:
2277:
2181:
2055:
1288:
1252:
1216:
458:
253:
1914:
1866:
1862:
1858:
1717:
1304:
721:
365:
that is encased by an articular capsule, reinforced and stabilized by muscle,
3014:
2859:
2498:
2442:
2409:
2292:
2113:
1725:
1603:
Persiani P, Molayem I, Calistri A, Rosi S, Bove M, Villani C (October 2008).
1413:
1354:
1312:
1128:
1030:
446:
332:
245:
224:
143:
114:
31:
2995:
2800:
2768:
2580:
2473:
2315:
2287:
2073:
2068:
1743:
1623:
1372:
1320:
1264:
1228:
1136:
1084:
729:
450:
this conferred by hip dysplasia makes one more susceptible to dislocation.
249:
208:
196:
139:
477:
2679:
2503:
2270:
2261:
2146:
2078:
1063:
Goddard NJ (August 2000). "Classification of traumatic hip dislocation".
856:(4th ed.). Philadelphia: Wolters Kluwer Health. p. Chapter 27.
69:
1526:
2709:
2478:
2414:
2327:
2321:
2297:
2265:
2232:
2201:
2151:
2123:
482:
310:
200:
1841:
2977:
2933:
2841:
2773:
2740:
2585:
2530:
2337:
2222:
2215:
2196:
2128:
2092:
1933:
1819:
428:
204:
199:) separates from its cup–shaped socket in the hip bone, known as the
172:
95:
1013:
Skeletal trauma : basic science, management, and reconstruction
555:
2929:
2736:
2700:
2027:
2023:
2005:
1287:
Beebe, Michael J.; Bauer, Jennifer M.; Mir, Hassan R. (July 2016).
373:. Even so, the joint is quite flexible in movement, allowing three
370:
2674:
1579:"Congenital Hip Dysplasia Symptoms & Treatments | Orthopedics"
1011:
Browner BD, Jupiter JB, Krettek C, Anderson PA (9 December 2014).
547:
380:
Major ligaments conferring stability to the hip joint include the
2792:
2595:
2253:
1763:. The Library of Congress. Philadelphia, H.C. Lea's son & co.
599:
471:
420:
1892:
2920:
2915:
2683:
1853:
573:
427:
of the hip making a complex hip dislocation more likely, while
409:
With this, to dislocate a healthy hip requires a great deal of
366:
285:
system, the
Stewart and Milford classification system, and the
192:
127:
1251:
Graber, Matthew; Marino, Dominic V.; Johnson, Dean E. (2021),
195:). Specifically it is when the ball–shaped head of the femur (
2955:
2879:
2819:
2788:
2695:
1215:
Masiewicz, Spencer; Mabrouk, Ahmed; Johnson, Dean E. (2021),
1010:
410:
188:
219:
from elevation. Hip dislocations can also occur following a
2973:
2883:
2837:
2713:
2138:
1602:
520:
51:
2951:
2815:
2571:
2101:
2014:
970:
431:
and flexion of the hip favors a simple hip dislocation.
1289:"Treatment of Hip Dislocations and Associated Injuries"
1214:
539:
Individuals with hip dislocation should participate in
289:
system (when associated with femoral head fractures).
474:
may also be ordered to clarify the fracture pattern.
1831:
1250:
977:. Lippincott Williams & Wilkins. p. 1032.
59:X-ray showing a joint dislocation of the left hip.
751:Diagnostic Imaging: Musculoskeletal Trauma E-Book
747:
3012:
1103:Foulk, David M.; Mullis, Brian H. (April 2010).
1259:, Treasure Island (FL): StatPearls Publishing,
1223:, Treasure Island (FL): StatPearls Publishing,
852:Egol Kenneth A, Koval KJ, Zuckerman JD (2010).
313:" fixed dislocation location present at birth.
3021:Congenital disorders of musculoskeletal system
1775:"Kocher-Langenbeck approach to the acetabulum"
1544:
971:Callaghan JJ, Rosenberg AG, Rubash HE (2007).
2660:
1966:
1809:
1807:
1805:
1803:
1801:
1799:
1797:
1795:
1286:
707:
223:or from a developmental abnormality known as
1700:Ross, James R.; Gardner, Michael J. (2012).
1105:"Hip Dislocation: Evaluation and Management"
876:: CS1 maint: multiple names: authors list (
1706:Current Reviews in Musculoskeletal Medicine
1699:
1666:Chapter 86. Hip Joint Dislocation Reduction
1102:
2667:
2653:
1973:
1959:
1815:Hip Dislocation Treatment & Management
1792:
1189:Publishing, Harvard Health (17 May 2019).
1188:
1065:Clinical Orthopaedics and Related Research
1043:: CS1 maint: location missing publisher (
847:
845:
843:
841:
839:
837:
835:
833:
831:
829:
827:
825:
823:
821:
819:
817:
815:
813:
811:
809:
807:
805:
803:
801:
799:
797:
795:
793:
791:
325:
50:
1733:
1362:
1163:Colorado Center of Orthopaedic Excellence
947:"Hip Dislocation - Trauma - Orthobullets"
789:
787:
785:
783:
781:
779:
777:
775:
773:
771:
754:. Elsevier Health Sciences. p. 495.
743:
741:
739:
677:
675:
338:
1662:
673:
671:
669:
667:
665:
663:
661:
659:
657:
655:
554:
546:
476:
457:
272:
1756:
1343:The London Medical and Physical Journal
1336:
1109:American Academy of Orthopaedic Surgeon
1062:
710:The Orthopedic Clinics of North America
292:
14:
3013:
1332:
1330:
1246:
1244:
768:
736:
701:
396:. The former three ligaments form the
2648:
1954:
1573:
1571:
1569:
1521:
1519:
1517:
1515:
1439:
1437:
1390:
1388:
1386:
1384:
1382:
1282:
1280:
1184:
1182:
1180:
941:
939:
937:
935:
933:
931:
929:
927:
925:
923:
921:
919:
917:
915:
913:
911:
909:
907:
652:
419:happen with direct trauma to a bent (
352:
316:
203:. The joint of the femur and pelvis (
2494:Greig cephalopolysyndactyly syndrome
1098:
1096:
1094:
1058:
1056:
1054:
1015:(Fifth ed.). Philadelphia, PA.
1006:
1004:
1002:
1000:
998:
996:
994:
905:
903:
901:
899:
897:
895:
893:
891:
889:
887:
851:
1327:
1293:Orthopedic Clinics of North America
1241:
283:Thompson and Epstein classification
24:
1984:malformations and deformations of
1636:
1566:
1552:"Hip Dislocation-OrthoInfo - AAOS"
1512:
1445:"Hip Dislocation-OrthoInfo - AAOS"
1434:
1396:Essentials of musculoskeletal care
1379:
1277:
1191:"Traumatic Dislocation of the Hip"
1177:
748:Blankenbaker DG, Davis KW (2016).
263:
25:
3037:
3026:Dislocations, sprains and strains
2855:Anterior cruciate ligament injury
1827:
1554:. Orthoinfo.aaos.org. 1 June 2014
1159:"Recovering from Hip Dislocation"
1091:
1051:
991:
884:
534:
394:ligament of the head of the femur
1121:10.5435/00124635-201004000-00003
1077:10.1097/00003086-200008000-00004
635:
500:open reduction internal fixation
81:Hip pain, trouble moving the hip
2167:Congenital patellar dislocation
2046:Wallis–Zieff–Goldblatt syndrome
1767:
1750:
1693:
1656:
1630:
1596:
1487:
1462:
1208:
1151:
626:
505:
191:) separates from the hip bone (
1337:Yeatman, John C. (June 1815).
964:
485:, open arrow the femoral head.
13:
1:
646:
642:Dislocation of hip in animals
489:
164:of the hip carried out under
92:Avascular necrosis of the hip
1669:. The McGraw-Hill Companies.
1583:Hospital for Special Surgery
1495:"How Does a Hip Joint Move?"
613:
563:
514:
453:
347:
7:
2453:Oto-palato-digital syndrome
2448:Hallermann–Streiff syndrome
2172:Congenital knee dislocation
1990:musculoskeletal abnormality
1527:"Hip joint - Joints health"
1217:"Posterior Hip Dislocation"
437:happen with trauma forcing
357:The hip joint includes the
10:
3042:
2484:Craniodiaphyseal dysplasia
1663:Reichman, Eric F. (2013).
1253:"Anterior Hip Dislocation"
639:
29:
2972:
2950:
2928:
2914:
2878:
2836:
2814:
2787:
2735:
2708:
2694:
2618:
2594:
2570:
2561:
2516:
2466:
2458:Treacher Collins syndrome
2428:
2400:
2391:
2382:
2348:
2309:reduction deficits / limb
2308:
2252:
2245:
2180:
2137:
2100:
2091:
2054:
2022:
2013:
1996:
1924:
1835:
1718:10.1007/s12178-012-9129-8
1612:Acta Orthopaedica Belgica
1305:10.1016/j.ocl.2016.02.002
722:10.1016/j.ocl.2016.02.002
171:
157:
149:
133:
120:
109:
101:
85:
75:
63:
58:
49:
44:
2283:Cenani–Lenz syndactylism
2036:Cleidocranial dysostosis
1702:"Femoral head fractures"
1470:"Understanding your hip"
404:
2991:Achilles tendon rupture
2986:Patellar tendon rupture
2430:Craniofacial dysostosis
1760:A treatise on fractures
551:A set of ankle weights.
213:motor vehicle collision
187:is when the thighbone (
1986:musculoskeletal system
1426:: CS1 maint: others (
560:
552:
486:
463:
417:Posterior dislocations
386:ischiofemoral ligament
278:Posterior dislocations
250:femoral head fractures
135:Differential diagnosis
2538:Klippel–Feil syndrome
854:Handbook of fractures
558:
550:
527:), and the anterior (
480:
461:
435:Anterior dislocations
363:ball-and-socket joint
326:Posterior dislocation
298:Anterior dislocations
273:Posterior dislocation
2865:Patellar dislocation
2548:Spina bifida occulta
2064:Madelung's deformity
2041:Sprengel's deformity
1474:www.allinahealth.org
951:www.orthobullets.com
559:Modified side plank.
390:pubofemoral ligament
382:iliofemoral ligament
339:Anterior dislocation
293:Anterior dislocation
252:, and posttraumatic
2753:Dislocated shoulder
2366:RAPADILINO syndrome
1757:Stimson LA (1883).
1531:joints-health.co.uk
306:Central dislocation
166:procedural sedation
105:Anterior, posterior
2806:Gamekeeper's thumb
2763:Separated shoulder
2722:Dislocation of jaw
2228:Rocker bottom foot
1925:External resources
1449:orthoinfo.aaos.org
561:
553:
487:
468:anterior-posterior
464:
375:degrees of freedom
353:Functional anatomy
317:Signs and symptoms
209:significant trauma
45:Dislocation of hip
18:Dislocation of hip
3008:
3007:
3004:
3003:
2942:Rotator cuff tear
2910:
2909:
2896:High ankle sprain
2642:
2641:
2638:
2637:
2634:
2633:
2563:Thoracic skeleton
2543:Spondylolisthesis
2512:
2511:
2378:
2377:
2374:
2373:
2241:
2240:
2087:
2086:
1948:
1947:
683:"Hip Dislocation"
525:Kocher-Langenbeck
439:external rotation
181:
180:
122:Diagnostic method
39:Medical condition
27:Orthopedic injury
16:(Redirected from
3033:
2964:Pulled hamstring
2926:
2925:
2870:Knee dislocation
2850:Tear of meniscus
2706:
2705:
2669:
2662:
2655:
2646:
2645:
2610:Pectus carinatum
2605:Pectus excavatum
2568:
2567:
2526:Spinal curvature
2518:Vertebral column
2438:Crouzon syndrome
2402:Craniosynostosis
2398:
2397:
2389:
2388:
2254:fingers and toes
2250:
2249:
2162:Discoid meniscus
2119:Upington disease
2098:
2097:
2020:
2019:
2011:
2010:
1975:
1968:
1961:
1952:
1951:
1833:
1832:
1822:
1811:
1790:
1789:
1787:
1785:
1771:
1765:
1764:
1754:
1748:
1747:
1737:
1697:
1691:
1690:
1684:
1680:
1678:
1670:
1660:
1654:
1653:
1651:
1649:
1637:Murphy, Andrew.
1634:
1628:
1627:
1609:
1600:
1594:
1593:
1591:
1589:
1575:
1564:
1563:
1561:
1559:
1548:
1542:
1541:
1539:
1537:
1523:
1510:
1509:
1507:
1505:
1491:
1485:
1484:
1482:
1480:
1466:
1460:
1459:
1457:
1455:
1441:
1432:
1431:
1425:
1417:
1392:
1377:
1376:
1366:
1349:(196): 469–471.
1334:
1325:
1324:
1284:
1275:
1274:
1273:
1271:
1248:
1239:
1238:
1237:
1235:
1212:
1206:
1205:
1203:
1201:
1186:
1175:
1174:
1172:
1170:
1155:
1149:
1148:
1100:
1089:
1088:
1060:
1049:
1048:
1042:
1034:
1008:
989:
988:
968:
962:
961:
959:
957:
943:
882:
881:
875:
867:
849:
766:
765:
745:
734:
733:
705:
699:
698:
696:
694:
679:
541:physical therapy
398:zona orbicularis
54:
42:
41:
21:
3041:
3040:
3036:
3035:
3034:
3032:
3031:
3030:
3011:
3010:
3009:
3000:
2968:
2946:
2919:
2906:
2874:
2832:
2828:Hip dislocation
2810:
2783:
2731:
2699:
2690:
2673:
2643:
2630:
2626:Poland syndrome
2614:
2590:
2557:
2508:
2462:
2424:
2370:
2361:Larsen syndrome
2349:multiple joints
2344:
2304:
2237:
2176:
2157:Genu recurvatum
2133:
2110:Hip dislocation
2083:
2050:
2000:
1992:
1979:
1949:
1944:
1943:
1920:
1919:
1844:
1830:
1825:
1812:
1793:
1783:
1781:
1773:
1772:
1768:
1755:
1751:
1698:
1694:
1682:
1681:
1672:
1671:
1661:
1657:
1647:
1645:
1635:
1631:
1607:
1601:
1597:
1587:
1585:
1577:
1576:
1567:
1557:
1555:
1550:
1549:
1545:
1535:
1533:
1525:
1524:
1513:
1503:
1501:
1493:
1492:
1488:
1478:
1476:
1468:
1467:
1463:
1453:
1451:
1443:
1442:
1435:
1419:
1418:
1406:
1394:
1393:
1380:
1335:
1328:
1285:
1278:
1269:
1267:
1249:
1242:
1233:
1231:
1213:
1209:
1199:
1197:
1187:
1178:
1168:
1166:
1157:
1156:
1152:
1101:
1092:
1061:
1052:
1036:
1035:
1023:
1009:
992:
985:
969:
965:
955:
953:
945:
944:
885:
869:
868:
864:
850:
769:
762:
746:
737:
706:
702:
692:
690:
681:
680:
653:
649:
644:
638:
629:
616:
583:Side Lying Leg
566:
537:
517:
508:
492:
456:
407:
355:
350:
341:
328:
319:
295:
275:
266:
264:Classifications
221:hip replacement
211:such as from a
185:hip dislocation
40:
35:
28:
23:
22:
15:
12:
11:
5:
3039:
3029:
3028:
3023:
3006:
3005:
3002:
3001:
2999:
2998:
2993:
2988:
2982:
2980:
2970:
2969:
2967:
2966:
2960:
2958:
2948:
2947:
2945:
2944:
2938:
2936:
2923:
2912:
2911:
2908:
2907:
2905:
2904:
2899:
2892:Sprained ankle
2888:
2886:
2876:
2875:
2873:
2872:
2867:
2862:
2857:
2852:
2846:
2844:
2834:
2833:
2831:
2830:
2824:
2822:
2812:
2811:
2809:
2808:
2803:
2797:
2795:
2785:
2784:
2782:
2781:
2779:Bankart lesion
2776:
2771:
2766:
2756:
2745:
2743:
2733:
2732:
2730:
2729:
2724:
2718:
2716:
2703:
2692:
2691:
2672:
2671:
2664:
2657:
2649:
2640:
2639:
2636:
2635:
2632:
2631:
2629:
2628:
2622:
2620:
2616:
2615:
2613:
2612:
2607:
2601:
2599:
2592:
2591:
2589:
2588:
2583:
2577:
2575:
2565:
2559:
2558:
2556:
2555:
2550:
2545:
2540:
2535:
2534:
2533:
2522:
2520:
2514:
2513:
2510:
2509:
2507:
2506:
2501:
2496:
2491:
2489:Dolichocephaly
2486:
2481:
2476:
2470:
2468:
2464:
2463:
2461:
2460:
2455:
2450:
2445:
2440:
2434:
2432:
2426:
2425:
2423:
2422:
2420:Trigonocephaly
2417:
2412:
2406:
2404:
2395:
2393:Skull and face
2386:
2380:
2379:
2376:
2375:
2372:
2371:
2369:
2368:
2363:
2358:
2356:Arthrogryposis
2352:
2350:
2346:
2345:
2343:
2342:
2341:
2340:
2335:
2330:
2318:
2312:
2310:
2306:
2305:
2303:
2302:
2301:
2300:
2290:
2285:
2280:
2278:Arachnodactyly
2275:
2274:
2273:
2258:
2256:
2247:
2243:
2242:
2239:
2238:
2236:
2235:
2230:
2225:
2220:
2219:
2218:
2206:
2205:
2204:
2199:
2186:
2184:
2182:foot deformity
2178:
2177:
2175:
2174:
2169:
2164:
2159:
2154:
2149:
2143:
2141:
2135:
2134:
2132:
2131:
2126:
2121:
2116:
2106:
2104:
2095:
2089:
2088:
2085:
2084:
2082:
2081:
2076:
2071:
2066:
2060:
2058:
2056:hand deformity
2052:
2051:
2049:
2048:
2043:
2038:
2032:
2030:
2017:
2008:
1994:
1993:
1978:
1977:
1970:
1963:
1955:
1946:
1945:
1942:
1941:
1929:
1928:
1926:
1922:
1921:
1918:
1917:
1906:
1895:
1884:
1869:
1845:
1840:
1839:
1837:
1836:Classification
1829:
1828:External links
1826:
1824:
1823:
1791:
1766:
1749:
1712:(3): 199–205.
1692:
1683:|website=
1655:
1629:
1595:
1565:
1543:
1511:
1486:
1461:
1433:
1404:
1378:
1326:
1299:(3): 527–549.
1276:
1240:
1207:
1195:Harvard Health
1176:
1165:. 2 March 2018
1150:
1115:(4): 199–209.
1090:
1050:
1021:
990:
983:
963:
883:
863:978-1605477602
862:
767:
760:
735:
700:
650:
648:
645:
640:Main article:
637:
634:
628:
625:
615:
612:
611:
610:
607:
596:
592:
588:
581:
571:
565:
562:
536:
535:Rehabilitation
533:
529:Smith-Petersen
516:
513:
507:
504:
491:
488:
455:
452:
406:
403:
354:
351:
349:
346:
340:
337:
327:
324:
318:
315:
294:
291:
274:
271:
265:
262:
254:osteoarthritis
179:
178:
175:
169:
168:
159:
155:
154:
151:
147:
146:
137:
131:
130:
124:
118:
117:
111:
107:
106:
103:
99:
98:
89:
83:
82:
79:
73:
72:
67:
61:
60:
56:
55:
47:
46:
38:
26:
9:
6:
4:
3:
2:
3038:
3027:
3024:
3022:
3019:
3018:
3016:
2997:
2994:
2992:
2989:
2987:
2984:
2983:
2981:
2979:
2975:
2971:
2965:
2962:
2961:
2959:
2957:
2953:
2949:
2943:
2940:
2939:
2937:
2935:
2931:
2927:
2924:
2922:
2917:
2913:
2903:
2900:
2897:
2893:
2890:
2889:
2887:
2885:
2881:
2877:
2871:
2868:
2866:
2863:
2861:
2860:Unhappy triad
2858:
2856:
2853:
2851:
2848:
2847:
2845:
2843:
2839:
2835:
2829:
2826:
2825:
2823:
2821:
2817:
2813:
2807:
2804:
2802:
2799:
2798:
2796:
2794:
2790:
2786:
2780:
2777:
2775:
2772:
2770:
2767:
2764:
2760:
2757:
2754:
2750:
2747:
2746:
2744:
2742:
2738:
2734:
2728:
2725:
2723:
2720:
2719:
2717:
2715:
2711:
2707:
2704:
2702:
2697:
2693:
2689:
2685:
2681:
2677:
2670:
2665:
2663:
2658:
2656:
2651:
2650:
2647:
2627:
2624:
2623:
2621:
2617:
2611:
2608:
2606:
2603:
2602:
2600:
2597:
2593:
2587:
2584:
2582:
2579:
2578:
2576:
2573:
2569:
2566:
2564:
2560:
2554:
2553:Sacralization
2551:
2549:
2546:
2544:
2541:
2539:
2536:
2532:
2529:
2528:
2527:
2524:
2523:
2521:
2519:
2515:
2505:
2502:
2500:
2499:Plagiocephaly
2497:
2495:
2492:
2490:
2487:
2485:
2482:
2480:
2477:
2475:
2472:
2471:
2469:
2465:
2459:
2456:
2454:
2451:
2449:
2446:
2444:
2443:Hypertelorism
2441:
2439:
2436:
2435:
2433:
2431:
2427:
2421:
2418:
2416:
2413:
2411:
2410:Scaphocephaly
2408:
2407:
2405:
2403:
2399:
2396:
2394:
2390:
2387:
2385:
2381:
2367:
2364:
2362:
2359:
2357:
2354:
2353:
2351:
2347:
2339:
2336:
2334:
2331:
2329:
2326:
2325:
2324:
2323:
2319:
2317:
2314:
2313:
2311:
2307:
2299:
2296:
2295:
2294:
2293:Brachydactyly
2291:
2289:
2286:
2284:
2281:
2279:
2276:
2272:
2269:
2268:
2267:
2263:
2260:
2259:
2257:
2255:
2251:
2248:
2246:Either / both
2244:
2234:
2231:
2229:
2226:
2224:
2221:
2217:
2214:
2213:
2212:
2211:
2207:
2203:
2200:
2198:
2195:
2194:
2193:
2192:
2188:
2187:
2185:
2183:
2179:
2173:
2170:
2168:
2165:
2163:
2160:
2158:
2155:
2153:
2150:
2148:
2145:
2144:
2142:
2140:
2136:
2130:
2127:
2125:
2122:
2120:
2117:
2115:
2114:Hip dysplasia
2111:
2108:
2107:
2105:
2103:
2099:
2096:
2094:
2090:
2080:
2077:
2075:
2072:
2070:
2067:
2065:
2062:
2061:
2059:
2057:
2053:
2047:
2044:
2042:
2039:
2037:
2034:
2033:
2031:
2029:
2025:
2021:
2018:
2016:
2012:
2009:
2007:
2003:
1999:
1995:
1991:
1987:
1983:
1976:
1971:
1969:
1964:
1962:
1957:
1956:
1953:
1940:
1936:
1935:
1931:
1930:
1927:
1923:
1916:
1912:
1911:
1907:
1905:
1901:
1900:
1896:
1894:
1890:
1889:
1885:
1883:
1879:
1878:
1874:
1870:
1868:
1864:
1860:
1856:
1855:
1851:
1847:
1846:
1843:
1838:
1834:
1821:
1817:
1816:
1810:
1808:
1806:
1804:
1802:
1800:
1798:
1796:
1780:
1776:
1770:
1762:
1761:
1753:
1745:
1741:
1736:
1731:
1727:
1723:
1719:
1715:
1711:
1707:
1703:
1696:
1688:
1676:
1668:
1667:
1659:
1644:
1640:
1633:
1625:
1621:
1618:(5): 609–14.
1617:
1613:
1606:
1599:
1584:
1580:
1574:
1572:
1570:
1553:
1547:
1532:
1528:
1522:
1520:
1518:
1516:
1500:
1496:
1490:
1475:
1471:
1465:
1450:
1446:
1440:
1438:
1429:
1423:
1415:
1411:
1407:
1405:9780892035793
1401:
1397:
1391:
1389:
1387:
1385:
1383:
1374:
1370:
1365:
1360:
1356:
1352:
1348:
1344:
1340:
1333:
1331:
1322:
1318:
1314:
1310:
1306:
1302:
1298:
1294:
1290:
1283:
1281:
1266:
1262:
1258:
1254:
1247:
1245:
1230:
1226:
1222:
1218:
1211:
1196:
1192:
1185:
1183:
1181:
1164:
1160:
1154:
1146:
1142:
1138:
1134:
1130:
1126:
1122:
1118:
1114:
1110:
1106:
1099:
1097:
1095:
1086:
1082:
1078:
1074:
1071:(377): 11–4.
1070:
1066:
1059:
1057:
1055:
1046:
1040:
1032:
1028:
1024:
1022:9781455776283
1018:
1014:
1007:
1005:
1003:
1001:
999:
997:
995:
986:
984:9780781750929
980:
976:
975:
974:The Adult Hip
967:
952:
948:
942:
940:
938:
936:
934:
932:
930:
928:
926:
924:
922:
920:
918:
916:
914:
912:
910:
908:
906:
904:
902:
900:
898:
896:
894:
892:
890:
888:
879:
873:
865:
859:
855:
848:
846:
844:
842:
840:
838:
836:
834:
832:
830:
828:
826:
824:
822:
820:
818:
816:
814:
812:
810:
808:
806:
804:
802:
800:
798:
796:
794:
792:
790:
788:
786:
784:
782:
780:
778:
776:
774:
772:
763:
761:9780323442954
757:
753:
752:
744:
742:
740:
731:
727:
723:
719:
716:(3): 527–49.
715:
711:
704:
688:
684:
678:
676:
674:
672:
670:
668:
666:
664:
662:
660:
658:
656:
651:
643:
636:Other animals
633:
624:
620:
608:
605:
601:
597:
593:
589:
586:
582:
579:
575:
572:
568:
567:
557:
549:
545:
542:
532:
530:
526:
522:
512:
503:
501:
497:
484:
479:
475:
473:
469:
460:
451:
448:
447:Hip dysplasia
444:
440:
436:
432:
430:
426:
422:
418:
414:
412:
402:
399:
395:
391:
387:
383:
378:
376:
372:
368:
364:
360:
345:
336:
334:
333:Sciatic nerve
323:
314:
312:
307:
302:
299:
290:
288:
284:
279:
270:
261:
257:
255:
251:
247:
246:osteonecrosis
241:
238:
234:
228:
226:
225:hip dysplasia
222:
218:
214:
210:
206:
202:
198:
194:
190:
186:
176:
174:
170:
167:
163:
160:
156:
152:
148:
145:
144:hip dysplasia
141:
138:
136:
132:
129:
126:Confirmed by
125:
123:
119:
116:
115:hip dysplasia
112:
108:
104:
100:
97:
93:
90:
88:
87:Complications
84:
80:
78:
74:
71:
68:
66:
62:
57:
53:
48:
43:
37:
33:
32:Hip dysplasia
19:
2996:Shin splints
2827:
2801:Pulled elbow
2769:ALPSA lesion
2680:subluxations
2676:Dislocations
2474:Macrocephaly
2320:
2316:Acheiropodia
2288:Ectrodactyly
2208:
2189:
2109:
2074:Oligodactyly
2069:Clinodactyly
1998:Appendicular
1932:
1908:
1897:
1886:
1871:
1848:
1813:
1782:. Retrieved
1778:
1769:
1759:
1752:
1709:
1705:
1695:
1665:
1658:
1646:. Retrieved
1642:
1632:
1615:
1611:
1598:
1586:. Retrieved
1582:
1556:. Retrieved
1546:
1534:. Retrieved
1530:
1502:. Retrieved
1499:Brainlab.org
1498:
1489:
1477:. Retrieved
1473:
1464:
1452:. Retrieved
1448:
1395:
1346:
1342:
1296:
1292:
1268:, retrieved
1256:
1232:, retrieved
1220:
1210:
1198:. Retrieved
1194:
1167:. Retrieved
1162:
1153:
1112:
1108:
1068:
1064:
1012:
973:
966:
954:. Retrieved
950:
853:
750:
713:
709:
703:
691:. Retrieved
686:
630:
627:Epidemiology
621:
617:
538:
518:
509:
506:Nonoperative
493:
465:
434:
433:
416:
415:
408:
379:
359:articulation
356:
342:
329:
320:
305:
303:
297:
296:
277:
276:
267:
258:
242:
229:
197:femoral head
184:
182:
140:Hip fracture
36:
2504:Saddle nose
2271:Webbed toes
2262:Polydactyly
2147:Genu valgum
2079:Polydactyly
1643:Radiopaedia
689:. June 2014
311:teratologic
70:Orthopedics
3015:Categories
2479:Platybasia
2415:Oxycephaly
2328:Phocomelia
2322:Ectromelia
2298:Stub thumb
2266:Syndactyly
2233:Hammer toe
2202:Pigeon toe
2152:Genu varum
2124:Coxa valga
1982:Congenital
1910:DiseasesDB
1257:StatPearls
1221:StatPearls
647:References
604:extensions
490:Management
483:acetabulum
392:, and the
215:or from a
201:acetabulum
153:Seat-belts
150:Prevention
2934:upper arm
2774:SLAP tear
2741:upper arm
2701:ligaments
2531:Scoliosis
2338:Hemimelia
2223:Pes cavus
2216:Flat feet
2197:Club foot
2129:Coxa vara
1939:emerg/144
1934:eMedicine
1820:eMedicine
1779:site name
1726:1935-9748
1685:ignored (
1675:cite book
1454:1 October
1422:cite book
1414:706805938
1355:0267-0259
1313:0030-5898
1129:1067-151X
1039:cite book
1031:898159499
872:cite book
614:Prognosis
585:abduction
578:abduction
564:Exercises
515:Operative
496:reduction
454:Diagnosis
429:adduction
425:abduction
371:ligaments
348:Mechanism
304:To note,
233:reduction
205:hip joint
173:Prognosis
162:Reduction
158:Treatment
96:arthritis
65:Specialty
2930:Shoulder
2902:Turf toe
2737:Shoulder
2727:Whiplash
2581:Cervical
2028:shoulder
2024:clavicle
2006:dysmelia
1744:22628176
1648:24 March
1624:19058693
1588:17 March
1536:22 March
1504:22 March
1479:22 March
1373:30493665
1321:27241377
1270:17 March
1265:29939591
1234:17 March
1229:29083669
1200:23 March
1169:23 March
1145:24913294
1137:20357229
1085:10943180
956:17 March
730:27241377
443:extended
237:traction
177:Variable
113:Trauma,
77:Symptoms
2921:tendons
2916:Muscles
2793:forearm
2688:strains
2684:sprains
2596:sternum
1904:D006618
1784:4 April
1735:3535084
1558:1 March
1364:5581659
600:flexion
472:CT scan
2696:Joints
2619:other:
2333:Amelia
2210:valgus
1893:142700
1742:
1732:
1724:
1622:
1412:
1402:
1371:
1361:
1353:
1319:
1311:
1263:
1227:
1143:
1135:
1127:
1083:
1029:
1019:
981:
860:
758:
728:
693:7 June
591:rehab.
574:Supine
570:joint.
421:flexed
388:, the
384:, the
369:, and
367:tendon
287:Pipkin
193:pelvis
128:X-rays
110:Causes
2956:thigh
2880:Ankle
2820:thigh
2789:Elbow
2586:Bifid
2467:other
2384:Axial
2191:varus
1867:Q65.2
1863:Q65.0
1859:S73.0
1608:(PDF)
1141:S2CID
411:force
405:Cause
189:femur
102:Types
2976:and
2974:Knee
2954:and
2932:and
2884:foot
2882:and
2840:and
2838:Knee
2818:and
2791:and
2739:and
2714:neck
2712:and
2710:Head
2686:and
2572:ribs
2139:knee
2015:Arms
2002:limb
1915:3056
1899:MeSH
1888:OMIM
1877:9-CM
1786:2021
1740:PMID
1722:ISSN
1687:help
1650:2021
1620:PMID
1590:2021
1560:2015
1538:2021
1506:2021
1481:2021
1456:2017
1428:link
1410:OCLC
1400:ISBN
1369:PMID
1351:ISSN
1317:PMID
1309:ISSN
1272:2021
1261:PMID
1236:2021
1225:PMID
1202:2021
1171:2021
1133:PMID
1125:ISSN
1081:PMID
1045:link
1027:OCLC
1017:ISBN
979:ISBN
958:2021
878:link
858:ISBN
756:ISBN
726:PMID
695:2018
687:AAOS
602:and
598:Hip
595:hip.
576:leg
521:ORIF
217:fall
2978:leg
2952:Hip
2918:and
2842:leg
2816:Hip
2698:and
2102:hip
2093:Leg
1882:835
1873:ICD
1850:ICD
1818:at
1730:PMC
1714:doi
1359:PMC
1301:doi
1117:doi
1073:doi
1069:377
718:doi
466:An
3017::
2759:AC
2749:GH
2682:,
2264:/
2112:/
2026:/
2004:/
1988:/
1937::
1913::
1902::
1891::
1880::
1861:,
1857::
1854:10
1794:^
1777:.
1738:.
1728:.
1720:.
1708:.
1704:.
1679::
1677:}}
1673:{{
1641:.
1616:74
1614:.
1610:.
1581:.
1568:^
1529:.
1514:^
1497:.
1472:.
1447:.
1436:^
1424:}}
1420:{{
1408:.
1381:^
1367:.
1357:.
1347:33
1345:.
1341:.
1329:^
1315:.
1307:.
1297:47
1295:.
1291:.
1279:^
1255:,
1243:^
1219:,
1193:.
1179:^
1161:.
1139:.
1131:.
1123:.
1113:18
1111:.
1107:.
1093:^
1079:.
1067:.
1053:^
1041:}}
1037:{{
1025:.
993:^
949:.
886:^
874:}}
870:{{
770:^
738:^
724:.
714:47
712:.
685:.
654:^
377:.
256:.
248:,
227:.
183:A
142:,
94:,
2898:)
2894:(
2765:)
2761:(
2755:)
2751:(
2678:/
2668:e
2661:t
2654:v
2598::
2574::
1974:e
1967:t
1960:v
1875:-
1865:-
1852:-
1842:D
1788:.
1746:.
1716::
1710:5
1689:)
1652:.
1626:.
1592:.
1562:.
1540:.
1508:.
1483:.
1458:.
1430:)
1416:.
1375:.
1323:.
1303::
1204:.
1173:.
1147:.
1119::
1087:.
1075::
1047:)
1033:.
987:.
960:.
880:)
866:.
764:.
732:.
720::
697:.
309:"
231:(
34:.
20:)
Text is available under the Creative Commons Attribution-ShareAlike License. Additional terms may apply.