212:: These cells migrate, during the fourth to the fifth week of fetal development in humans, on both sides of the spinal cord toward the region just behind the dorsal aorta forming the two chains of sympathetic ganglia (Sympathetic chain). From these ganglia, the post synaptic sympathetic fibers will arise and extend toward their target organ. Some of these cells will migrate to the adrenal medulla to form sympathetic ganglia cells within the adrenal medulla (without postsynaptic sympathetic fibers). A tumor arising from these cells is called neuroblastoma.
325:(which are secreted from the pituitary); all of these peptides bind to opioid receptors and produce analgesic (and other) responses. The hormones are secreted from chromaffin granules; this is where the enzyme dopamine β-hydroxylase catalyses the conversion of dopamine to noradrenaline. Distinct N and E cell forms exist (also Na and A cells in British nomenclature - noradrenaline and adrenaline); the former produce norepinephrine, the latter arise out of N cells through interaction with glucocorticoids, and convert norepinephrine into epinephrine.
329:
282:
270:
368:. This increased sympathetic activity leads to chronically increased synthesis and secretion of catecholamines from the adrenal chromaffin cells. This chronic increase of epinephrine and norepinephrine secretion causes desensitization of the chromaffin cells to catecholamines resulting in a decrease in production and presence of α
227:. These terms can be used interchangeably but usually paraganglioma refer to a tumor originating from chromaffin cells outside the adrenal gland, which can also be called extra-adrenal pheochromocytoma, whereas pheochromocytoma typically refer to a tumor originating from the chromaffin cells within the adrenal gland.
388:
that normally prevents the cells from over producing the catecholamines and replaces it with a positive feedback loop in which increased secretion further elicits more secretion. This upregulation of GRK2 is also accompanied by upregulation and increased production of the enzyme
219:(or pheochromocytes): These cells will migrate to the area adjacent to the sympathetic ganglia (hence the name paraganglia) and to the adrenal medulla where they will be the most abundant type of cells. The largest extra-adrenal cluster of chromaffin cells in mammals is the
29:
152:. These cells serve a variety of functions such as serving as a response to stress, monitoring carbon dioxide and oxygen concentrations in the body, maintenance of respiration and the regulation of blood pressure. They are in close proximity to pre-synaptic
428:
are so named because of their histological similarity to chromaffin cells (they stain yellow when treated with chromium salts), but their function is quite different and they are not derivatives of the neural crest.
562:
164:
of the sympathetic nervous system releases acetylcholine, which then binds to nicotinic acetylcholine receptors on the adrenal medulla. This causes the release of catecholamines. The chromaffin cells release
533:
640:
Perry, SF; Capaldo, A (Nov 16, 2011). "The autonomic nervous system and chromaffin tissue: neuroendocrine regulation of catecholamine secretion in non-mammalian vertebrates".
863:"Reduction of Sympathetic Activity via Adrenal-targeted GRK2 Gene Deletion Attenuates Heart Failure Progression and Improves Cardiac Function after Myocardial Infarction"
570:
253:
In non-mammals, chromaffin cells are found in a variety of places, generally not organised as an individual organ, and may be without innervation, relying only on
205:
There are two types of cells that originate from the neural crest and are related to the sympathetic nervous system (originate from a cell called sympathogonia):
101:
541:
453:
591:
Schober, Andreas; Parlato, Rosanna; Huber, Katrin; Kinscherf, Ralf; Hartleben, Björn; Huber, Tobias B.; Schütz, Günther; Unsicker, Klaus (1 January 2013).
944:
448:
981:
160:, with which they communicate, and structurally they are similar to post-synaptic sympathetic neurons. In order to activate chromaffin cells, the
929:
473:
Schober, Andreas; Parlato, Rosanna; Huber, Katrin; Kinscherf, Ralf; Hartleben, Björn; Huber, Tobias B; Schütz, Günther; Unsicker, Klaus (2013).
352:
of glomus cells). Sometimes only neoplasms of adrenal origin are named pheochromocytomas, while others are named extra-adrenal paragangliomas.
317:
stream. The secreted adrenaline and noradrenaline play an important role in the sympathetic nervous system response, commonly called the
1378:
804:
Jafferjee, Malika; Reyes Valero, Thairy; Marrero, Christine; McCrink, Katie A.; Brill, Ava; Lymperopoulos, Anastasios (2016-03-01).
974:
788:
421:
to form a brown color, most strongly in the cells secreting noradrenaline. Chromaffin cells are also called pheochromocytes.
563:"Chapter 164. The Autonomic Nervous System: The Sympathetic System - Review of Medical Embryology Book - LifeMap Discovery"
684:
364:, the body increases sympathetic activity to the adrenal medulla as the compensatory mechanism to increase heart rate and
1373:
593:"Cell Loss and Autophagy in the Extra-Adrenal Chromaffin Organ of Zuckerkandl are Regulated by Glucocorticoid Signalling"
475:"Cell Loss and Autophagy in the Extra-Adrenal Chromaffin Organ of Zuckerkandl are Regulated by Glucocorticoid Signalling"
950:
861:
Lymperopoulos, Anastasios; Rengo, Giuseppe; Gao, Erhe; Ebert, Steven N.; Dorn, Gerald W.; Koch, Walter J. (2010-05-21).
967:
926: – Histology Learning System at Boston University - "Endocrine System: adrenal gland, reticularis and medulla"
108:
945:
Rat
Chromaffin cells primary cultures: Standardization and quality assessment for single-cell assays (a protocol)
534:"Chapter 179. The Paraganglionic System: The Paraganglia - Review of Medical Embryology Book - LifeMap Discovery"
381:
321:. The enkephalins and enkephalin-containing peptides are related to, but distinct from endogenous peptides named
328:
1399:
96:
732:
1302:
934:
348:(also called chromaffin or sympathetic paragangliomas, in contrast to non-chromaffin or parasympathetic
1163:
157:
806:"GRK2 Up-Regulation Creates a Positive Feedback Loop for Catecholamine Production in Chromaffin Cells"
89:
1026:
380:
receptors is caused by the upregulation of the enzyme
Adrenal G protein coupled receptor kinase 2 (
318:
84:
72:
939:
1135:
1046:
1409:
1158:
425:
923:
1404:
1361:
1351:
390:
220:
186:
8:
1140:
1093:
1085:
373:
153:
137:
372:
adrenergic receptors on their cell membrane. This desensitization and downregulation of
1058:
1008:
897:
862:
838:
805:
665:
617:
592:
507:
474:
1284:
1150:
1063:
1036:
951:
https://pscientifics.com/adrenal-chromaffin-cell-stain-giemsa-staining-method/Adrenal
902:
884:
843:
825:
784:
747:
699:
657:
622:
608:
512:
494:
490:
385:
161:
669:
1335:
1200:
1195:
1190:
1075:
1068:
1041:
991:
892:
874:
833:
817:
649:
612:
604:
590:
502:
486:
345:
294:
235:
224:
959:
1210:
1103:
1098:
1016:
999:
653:
141:
77:
189:
for systemic effects on multiple organs (similarly to secretory neurones of the
1267:
1182:
1113:
1031:
1021:
707:
418:
365:
302:
286:
182:
1393:
1272:
1262:
1173:
1053:
888:
829:
498:
361:
349:
238:. In lower concentrations, extra-adrenal chromaffin cells also reside in the
178:
166:
145:
48:
879:
1356:
1322:
1312:
1250:
906:
847:
751:
661:
626:
516:
190:
703:
1330:
1245:
821:
436:
432:
298:
274:
231:
174:
1307:
1292:
730:
310:
170:
313:
and enkephalin-containing peptides, and a few other hormones into the
114:
1297:
1108:
731:
Szewczyk, A; Lobanov, NA; Kicińska, A; Wójcik, G; Nałecz, MJ (2001).
393:, which catalyzes the rate limiting step of catecholamine synthesis.
322:
258:
254:
194:
1368:
1240:
803:
414:
341:
306:
243:
1127:
755:
281:
239:
149:
409:
ity. They are named as such because they can be visualised by
293:
Chromaffin cells of the adrenal medulla are innervated by the
269:
223:. Tumors arising from these cell are called paragangliomas or
1257:
1232:
410:
314:
247:
60:
472:
733:"ATP-sensitive K+ transport in adrenal chromaffin granules"
28:
860:
384:) which effectively eliminates the normal autocrine-type
16:
Neuroendocrine cells found in adrenal medulla in mammals
935:
UC-San Diego
Chromaffin Cell and Hypertension Research
778:
454:
List of human cell types derived from the germ layers
197:
signals. Hence they are called neuroendocrine cells.
682:
989:
449:
List of distinct cell types in the adult human body
783:(5th ed.). Edinburgh: Churchill Livingstone.
401:The word "chromaffin" comes from a portmanteau of
685:"Adrenocortical control of epinephrine synthesis"
33:Adrenal gland. (Medulla labeled at bottom right.)
1391:
639:
953:Chromaffin Cell Stain (Giemsa Staining Method)
975:
930:Secretion Control in Adrenal Chromaffin Cells
417:salts. Chromium salts oxidise and polymerise
327:
435:are clusters of either chromaffin cells or
1379:List of human endocrine organs and actions
982:
968:
779:Young; Lowe; Stevens; Heath, eds. (2006).
642:Autonomic Neuroscience: Basic and Clinical
27:
896:
878:
837:
616:
506:
336:
280:
268:
683:Pohorecky, LA; Wurtman, RJ (Mar 1971).
1392:
230:Chromaffin cells also settle near the
963:
528:
526:
13:
740:Acta Neurobiologiae Experimentalis
14:
1421:
917:
523:
609:10.1111/j.1365-2826.2012.02367.x
491:10.1111/j.1365-2826.2012.02367.x
355:
109:Anatomical terms of microanatomy
867:Journal of Biological Chemistry
854:
797:
781:Wheater's Functional Histology
772:
724:
676:
633:
584:
555:
466:
1:
597:Journal of Neuroendocrinology
479:Journal of Neuroendocrinology
459:
344:arising from these cells are
940:A Primer on Chromaffin Cells
654:10.1016/j.autneu.2010.04.006
200:
7:
442:
264:
10:
1426:
439:near sympathetic ganglia.
396:
332:Catecholamine biosynthesis
158:sympathetic nervous system
1344:
1321:
1283:
1231:
1209:
1181:
1172:
1149:
1126:
1084:
1007:
998:
924:Histology image: 14507loa
107:
95:
83:
71:
66:endocrinocytus medullaris
59:
54:
43:
38:
26:
22:Medullary chromaffin cell
21:
319:fight-or-flight response
297:and secrete adrenaline (
1047:Somatomammotrophic cell
880:10.1074/jbc.M109.077859
810:Molecular Endocrinology
692:Pharmacological Reviews
567:discovery.lifemapsc.com
538:discovery.lifemapsc.com
261:signals for secretion.
426:enterochromaffin cells
333:
290:
278:
337:Clinical significance
331:
284:
272:
193:), and can also send
1400:Neuroendocrine cells
1362:Organ of Zuckerkandl
1352:Enteroendocrine cell
822:10.1210/me.2015-1305
391:tyrosine hydroxylase
221:organ of Zuckerkandl
187:systemic circulation
140:found mostly in the
138:neuroendocrine cells
1141:Parafollicular cell
873:(21): 16378–16386.
154:sympathetic ganglia
1285:Islets of pancreas
1059:Corticotropic cell
334:
301:), noradrenaline (
291:
279:
90:H3.08.02.6.00015
1387:
1386:
1227:
1226:
1151:Parathyroid gland
1122:
1121:
1064:Gonadotropic cell
1037:Somatotropic cell
790:978-0-443-06850-8
386:negative feedback
346:pheochromocytomas
246:, and behind the
225:pheochromocytomas
123:
122:
118:
1417:
1336:Corpora arenacea
1201:Zona reticularis
1196:Zona fasciculata
1191:Zona glomerulosa
1179:
1178:
1076:Chromophobe cell
1069:Thyrotropic cell
1005:
1004:
992:endocrine system
984:
977:
970:
961:
960:
911:
910:
900:
882:
858:
852:
851:
841:
801:
795:
794:
776:
770:
769:
767:
766:
760:
754:. Archived from
737:
728:
722:
721:
719:
718:
712:
706:. Archived from
689:
680:
674:
673:
637:
631:
630:
620:
588:
582:
581:
579:
578:
569:. Archived from
559:
553:
552:
550:
549:
540:. Archived from
530:
521:
520:
510:
470:
295:splanchnic nerve
236:carotid arteries
217:Chromaffin cells
162:splanchnic nerve
134:phaeochromocytes
126:Chromaffin cells
115:edit on Wikidata
112:
31:
19:
18:
1425:
1424:
1420:
1419:
1418:
1416:
1415:
1414:
1390:
1389:
1388:
1383:
1340:
1317:
1279:
1223:
1219:Chromaffin cell
1205:
1168:
1145:
1136:Follicular cell
1118:
1099:Median eminence
1080:
1017:Pars intermedia
1000:Pituitary gland
994:
990:Anatomy of the
988:
920:
915:
914:
859:
855:
802:
798:
791:
777:
773:
764:
762:
758:
735:
729:
725:
716:
714:
710:
687:
681:
677:
638:
634:
589:
585:
576:
574:
561:
560:
556:
547:
545:
532:
531:
524:
471:
467:
462:
445:
399:
377:
371:
358:
339:
285:Noradrenaline (
267:
203:
177:) and ~20% of
130:pheochromocytes
119:
34:
17:
12:
11:
5:
1423:
1413:
1412:
1407:
1402:
1385:
1384:
1382:
1381:
1376:
1371:
1366:
1365:
1364:
1354:
1348:
1346:
1342:
1341:
1339:
1338:
1333:
1327:
1325:
1319:
1318:
1316:
1315:
1310:
1305:
1300:
1295:
1289:
1287:
1281:
1280:
1278:
1277:
1276:
1275:
1270:
1268:Granulosa cell
1265:
1255:
1254:
1253:
1248:
1237:
1235:
1229:
1228:
1225:
1224:
1222:
1221:
1215:
1213:
1207:
1206:
1204:
1203:
1198:
1193:
1187:
1185:
1176:
1170:
1169:
1167:
1166:
1161:
1155:
1153:
1147:
1146:
1144:
1143:
1138:
1132:
1130:
1124:
1123:
1120:
1119:
1117:
1116:
1114:Herring bodies
1111:
1106:
1101:
1096:
1090:
1088:
1082:
1081:
1079:
1078:
1073:
1072:
1071:
1066:
1061:
1051:
1050:
1049:
1044:
1042:Prolactin cell
1039:
1032:Acidophil cell
1029:
1024:
1022:Pars tuberalis
1019:
1013:
1011:
1002:
996:
995:
987:
986:
979:
972:
964:
955:
954:
947:
942:
937:
932:
927:
919:
918:External links
916:
913:
912:
853:
816:(3): 372–381.
796:
789:
771:
723:
675:
632:
583:
554:
522:
464:
463:
461:
458:
457:
456:
451:
444:
441:
419:catecholamines
398:
395:
375:
369:
366:cardiac output
357:
354:
350:paragangliomas
338:
335:
303:norepinephrine
287:norepinephrine
266:
263:
202:
199:
183:norepinephrine
167:catecholamines
146:adrenal glands
128:, also called
121:
120:
111:
105:
104:
99:
93:
92:
87:
81:
80:
75:
69:
68:
63:
57:
56:
52:
51:
45:
41:
40:
36:
35:
32:
24:
23:
15:
9:
6:
4:
3:
2:
1422:
1411:
1410:Adrenal gland
1408:
1406:
1403:
1401:
1398:
1397:
1395:
1380:
1377:
1375:
1372:
1370:
1367:
1363:
1360:
1359:
1358:
1355:
1353:
1350:
1349:
1347:
1343:
1337:
1334:
1332:
1329:
1328:
1326:
1324:
1320:
1314:
1311:
1309:
1306:
1304:
1301:
1299:
1296:
1294:
1291:
1290:
1288:
1286:
1282:
1274:
1273:Corpus luteum
1271:
1269:
1266:
1264:
1263:Theca interna
1261:
1260:
1259:
1256:
1252:
1249:
1247:
1244:
1243:
1242:
1239:
1238:
1236:
1234:
1230:
1220:
1217:
1216:
1214:
1212:
1208:
1202:
1199:
1197:
1194:
1192:
1189:
1188:
1186:
1184:
1180:
1177:
1175:
1174:Adrenal gland
1171:
1165:
1162:
1160:
1157:
1156:
1154:
1152:
1148:
1142:
1139:
1137:
1134:
1133:
1131:
1129:
1125:
1115:
1112:
1110:
1107:
1105:
1102:
1100:
1097:
1095:
1092:
1091:
1089:
1087:
1083:
1077:
1074:
1070:
1067:
1065:
1062:
1060:
1057:
1056:
1055:
1054:Basophil cell
1052:
1048:
1045:
1043:
1040:
1038:
1035:
1034:
1033:
1030:
1028:
1027:Pars distalis
1025:
1023:
1020:
1018:
1015:
1014:
1012:
1010:
1006:
1003:
1001:
997:
993:
985:
980:
978:
973:
971:
966:
965:
962:
958:
952:
948:
946:
943:
941:
938:
936:
933:
931:
928:
925:
922:
921:
908:
904:
899:
894:
890:
886:
881:
876:
872:
868:
864:
857:
849:
845:
840:
835:
831:
827:
823:
819:
815:
811:
807:
800:
792:
786:
782:
775:
761:on 2017-08-09
757:
753:
749:
745:
741:
734:
727:
713:on 2016-03-05
709:
705:
701:
697:
693:
686:
679:
671:
667:
663:
659:
655:
651:
647:
643:
636:
628:
624:
619:
614:
610:
606:
602:
598:
594:
587:
573:on 2017-05-05
572:
568:
564:
558:
544:on 2016-12-20
543:
539:
535:
529:
527:
518:
514:
509:
504:
500:
496:
492:
488:
484:
480:
476:
469:
465:
455:
452:
450:
447:
446:
440:
438:
434:
430:
427:
422:
420:
416:
412:
408:
404:
394:
392:
387:
383:
379:
367:
363:
362:heart failure
356:Heart failure
353:
351:
347:
343:
330:
326:
324:
320:
316:
312:
308:
304:
300:
296:
288:
283:
276:
271:
262:
260:
256:
251:
249:
245:
241:
237:
233:
228:
226:
222:
218:
213:
211:
206:
198:
196:
192:
188:
184:
180:
179:noradrenaline
176:
172:
168:
163:
159:
155:
151:
147:
143:
139:
135:
131:
127:
116:
110:
106:
103:
100:
98:
94:
91:
88:
86:
82:
79:
76:
74:
70:
67:
64:
62:
58:
53:
50:
49:adrenal gland
46:
42:
37:
30:
25:
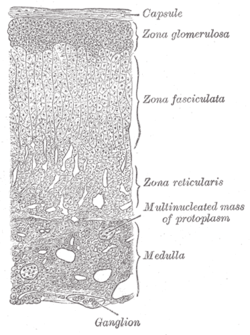
20:
1323:Pineal gland
1313:Epsilon cell
1251:Sertoli cell
1218:
1164:Oxyphil cell
1094:Pars nervosa
956:
870:
866:
856:
813:
809:
799:
780:
774:
763:. Retrieved
756:the original
743:
739:
726:
715:. Retrieved
708:the original
695:
691:
678:
648:(1): 54–66.
645:
641:
635:
603:(1): 34–47.
600:
596:
586:
575:. Retrieved
571:the original
566:
557:
546:. Retrieved
542:the original
537:
485:(1): 34–47.
482:
478:
468:
437:glomus cells
431:
423:
406:
402:
400:
359:
340:
292:
273:Adrenaline (
252:
229:
216:
214:
209:
207:
204:
191:hypothalamus
133:
129:
125:
124:
65:
1405:Human cells
1374:Development
1357:Paraganglia
1331:Pinealocyte
1246:Leydig cell
746:(1): 1–12.
698:(1): 1–35.
433:Paraganglia
299:epinephrine
275:epinephrine
232:vagus nerve
210:Neuroblasts
175:epinephrine
55:Identifiers
1394:Categories
1308:Delta cell
1293:Alpha cell
1159:Chief cell
765:2013-02-25
717:2013-03-01
577:2017-06-03
548:2017-06-03
460:References
378:adrenergic
360:Following
323:endorphins
311:enkephalin
171:adrenaline
169:: ~80% of
1298:Beta cell
1109:Pituicyte
1086:Posterior
889:0021-9258
830:0888-8809
499:0953-8194
342:Neoplasms
259:paracrine
255:endocrine
201:Structure
195:paracrine
1369:Placenta
1241:Testicle
1009:Anterior
907:20351116
848:26849467
752:11315316
670:42402600
662:20547474
627:23078542
517:23078542
443:See also
415:chromium
411:staining
405:ium and
307:dopamine
305:), some
265:Function
244:prostate
47:Medulla
44:Location
1303:PP cell
1211:Medulla
1128:Thyroid
898:2871505
839:5414648
704:4941407
618:3564403
508:3564403
397:History
240:bladder
185:) into
156:of the
150:mammals
144:of the
142:medulla
136:), are
78:D019439
39:Details
1233:Gonads
1183:Cortex
905:
895:
887:
846:
836:
828:
787:
750:
702:
668:
660:
625:
615:
515:
505:
497:
242:wall,
1345:Other
1258:Ovary
1104:Stalk
759:(PDF)
736:(PDF)
711:(PDF)
688:(PDF)
666:S2CID
413:with
407:affin
403:chrom
315:blood
248:liver
113:[
102:69263
61:Latin
903:PMID
885:ISSN
844:PMID
826:ISSN
785:ISBN
748:PMID
700:PMID
658:PMID
623:PMID
513:PMID
495:ISSN
424:The
382:GRK2
234:and
132:(or
73:MeSH
893:PMC
875:doi
871:285
834:PMC
818:doi
650:doi
646:165
613:PMC
605:doi
503:PMC
487:doi
257:or
215:2)
208:1)
148:in
97:FMA
1396::
957:]
901:.
891:.
883:.
869:.
865:.
842:.
832:.
824:.
814:30
812:.
808:.
744:61
742:.
738:.
696:23
694:.
690:.
664:.
656:.
644:.
621:.
611:.
601:25
599:.
595:.
565:.
536:.
525:^
511:.
501:.
493:.
483:25
481:.
477:.
309:,
250:.
85:TH
983:e
976:t
969:v
949:[
909:.
877::
850:.
820::
793:.
768:.
720:.
672:.
652::
629:.
607::
580:.
551:.
519:.
489::
376:2
374:α
370:2
289:)
277:)
181:(
173:(
117:]
Text is available under the Creative Commons Attribution-ShareAlike License. Additional terms may apply.