675:"ASA/ACCF/AHA/AANN/AANS/ACR/ASNR/CNS/SAIP/SCAI/SIR/SNIS/SVM/SVS Guideline on the Management of Patients With Extracranial Carotid and Vertebral Artery Disease: Executive Summary A Report of the American College of Cardiology Foundation/American Heart Association Task Force on Practice Guidelines, and the American Stroke Association, American Association of Neuroscience Nurses, American Association of Neurological Surgeons, American College of Radiology, American Society of Neuroradiology, Congress of Neurological Surgeons, Society of Atherosclerosis Imaging and Prevention, Society for Cardiovascular Angiography and Interventions, Society of Interventional Radiology, Society of NeuroInterventional Surgery, Society for Vascular Medicine, and Society for Vascular Surgery Developed in Collaboration With the American Academy of Neurology and Society of Cardiovascular Computed Tomography"
337:
372:(EEG), transcranial doppler analysis, cerebral oximetry, or carotid artery stump pressure monitoring can guide the placement of a shunt, or a shunt may be routinely used. At present there is still ongoing debate related to difference in outcome between local and general anaesthesia, and methods of determining the need for a shunt. However, excellent outcomes can be achieved by performing carotid endarterectomy under local local
29:
144:
401:, UK. Eastcott's procedure was not strictly an endarterectomy as we now understand it; he excised the diseased part of the artery and then resutured the healthy ends together. Carotid endarterectomy was finally shown to be effective in stroke prevention after a landmark clinical trial spearheaded by the Canadian clinical scientist
348:. The incision is between 5 and 10 cm (2.0 and 3.9 in) in length. The internal, common and external carotid arteries are carefully identified, controlled with vessel loops, and clamped. The lumen of the internal carotid artery is opened, and the atheromatous plaque substance removed. The artery is closed using
215:
ulcerated plaques. This low rate of stroke means that there is less potential stroke risk-reduction from endarterectomy for asymptomatic patients relative to symptomatic patients. However, for asymptomatic patients with severe carotid stenosis (80-99%), carotid endarterectomy plus treatment with a
214:
Asymptomatic people have narrowing of their carotid arteries, but have not experienced a transient ischemic attack or stroke. The annual risk of stroke in patients with asymptomatic carotid disease is between 1% and 2%, although some patients are considered to be at higher risk, such as those with
560:
Verhoeven, B; Hellings, WE; Moll, FL; de Vries, JP; de Kleijn, DP; de Bruin, P; Busser, E; Schoneveld, AH; Pasterkamp, G (December 2005). "Carotid atherosclerotic plaques in patients with transient ischemic attacks and stroke have unstable characteristics compared with plaques in asymptomatic and
197:
Unlike asymptomatic patients, symptomatic people with moderate carotid stenosis (50–69%) still benefit from endarterectomy, albeit to a lesser degree, with a number needed to treat of 22 at five years. Recent evidence demonstrated that unstable carotid atherosclerotic plaques are responsible for
749:
Bhattathiri, PS; Ramakrishnan, Y; Vivar, RA; Bell, K; Bullock, RE; Mitchell, P; Gregson, B; Mendelow, AD (August 2005). "Effect of awake
Carotid Endarterectomy under local anaesthesia on peri-operative blood pressure: blood pressure is normalised when carotid stenosis is treated under local
596:
Sef, D; Kovacevic, M; Jernej, B; Novacic, K; Slavica, M; Petrak, J; Medved, I; Milosevic, M (November 2022). "Immunohistochemical analysis of MMP-9 and COX-2 expression in carotid atherosclerotic plaques among patients undergoing carotid endarterectomy: A prospective study".
396:
in
Houston, TX, although the technique was not reported in the medical literature until 1975. The first case to be recorded in the medical literature was in The Lancet in 1954; the surgeon was Felix Eastcott, a consultant surgeon and deputy director of the surgical unit at
139:
Carotid endarterectomy itself can cause strokes, so to be of benefit in preventing strokes over time, the risks for combined 30-day mortality and stroke risk following surgery should be < 3% for asymptomatic people and ≤ 6% for symptomatic people.
882:
Barnett, HJM; Taylor, DW; Haynes, RB; Sackett, DL; Peerless, SJ; Ferguson, GG; Fox, AJ; Rankin, RN; Hachinski, VC; Wiebers, DO; Eliasziw, M (1991). "Beneficial effect of carotid endarterectomy in symptomatic patients with high-grade carotid stenosis".
135:
over time. Carotid stenosis can either have symptoms (i.e., be symptomatic), or be found by a doctor in the absence of symptoms (asymptomatic) - and the risk-reduction from endarterectomy is greater for symptomatic than asymptomatic patients.
405:. Since then, evidence for its effectiveness in different patient groups has accumulated. In 2003 nearly 140,000 carotid endarterectomies were performed in the US, however, the number of procedures has continued to decrease over time.
462:
Watanabe, J; Ogata, T; Hamada, O; Nonaka, M; Abe, H; Higashi, T; Shiota, E; Inoue, T (July 2014). "Improvement of cognitive function after carotid endarterectomy--a new strategy for the evaluation of cognitive function".
368:. The latter allows for direct monitoring of neurological status by intra-operative verbal contact and neurological assessment. With general anaesthesia, indirect methods of assessing cerebral perfusion must be used.
918:
Lichtman, Judith H.; Jones, Michael R.; Leifheit, Erica C.; Sheffet, Alice J.; Howard, George; Lal, Brajesh K.; Howard, Virginia J.; Wang, Yun; Curtis, Jeptha; Brott, Thomas G. (2017-09-19).
714:
Sef, D; Skopljanac-Macina, A; Milosevic, M; Skrtic, A; Vidjak, V (May 2018). "Cerebral
Neuromonitoring during Carotid Endarterectomy and Impact of Contralateral Internal Carotid Occlusion".
206:
and hence benefit less from the procedure. For maximum benefit people should be operated on soon after a stroke or transient ischemic attack, preferably within the first 2 weeks.
231:
The most feared complication of carotid endarterectomy is stroke. Risks of stroke at the time of surgery are higher for symptomatic (3–5%) than asymptomatic patients (1–3%).
360:
is achieved, and the overlying layers closed with suture. The skin can be closed with suture which may be visible or invisible (absorbable). Many surgeons place a temporary
384:
The endarterectomy procedure was developed and first done by the
Portuguese surgeon Joao Cid dos Santos in 1946, when he operated an occluded subsartorial artery, at the
175:
Carotid endarterectomy does not treat symptoms of prior strokes. It is controversial if carotid endarterectomy can improve cognitive function in some patients.
245:
Long term complications include restenosis of the endarterectomy bed, although the clinical significance of this is controversial in asymptomatic patients.
829:
Eastcott, HH; Pickering, GW; Rob, CG (13 November 1954). "Reconstruction of internal carotid artery in a patient with intermittent attacks of hemiplegia".
264:
and complete cerebrovascular territory side severe neurologic deficits (NIHSS>15), because there is no brain tissue at risk for further stroke damage.
388:. In 1951 an Argentinian surgeon repaired a carotid artery occlusion using a bypass procedure. The first endarterectomy was successfully performed by
202:) in these patients . In addition, co-morbidity adversely affects the outcome: people with multiple medical problems have a higher post-operative
60:
992:
190:
In symptomatic patients with a 70–99% stenosis, for every six people treated, one major stroke would be prevented at two years (i.e., a
261:
1190:
634:"Carotid Stenting Versus Endarterectomy for Asymptomatic Carotid Artery Stenosis: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis"
1185:
112:, the surgeon opens the artery and removes the plaque. The plaque forms and thickens the inner layer of the artery, or
1344:
985:
171:. Plaque often builds up at that division, and a carotid endarterectomy cuts open the artery and removes the plaque.
242:, also known as reperfusion syndrome, which is associated with headache and high blood pressure following surgery.
239:
1248:
364:
to ensure blood supply to the brain during the procedure. The procedure may be performed under general or local
1273:
423:"Atherosclerotic Peripheral Vascular Disease Symposium II: controversies in carotid artery revascularization"
398:
1014:
1154:
978:
116:, hence the name of the procedure which simply means removal of part of the internal layers of the artery.
864:
716:
Journal of stroke and cerebrovascular diseases : the official journal of
National Stroke Association
599:
Journal of stroke and cerebrovascular diseases : the official journal of
National Stroke Association
345:
1370:
1023:
503:
Rerkasem, Amaraporn; Orrapin, Saritphat; Howard, Dominic Pj; Rerkasem, Kittipan (12 September 2020).
199:
184:
1314:
1268:
328:
is an alternative to carotid endarterectomy in cases where endarterectomy is considered too risky.
67:
1319:
1263:
325:
168:
164:
132:
105:
101:
46:
42:
1298:
1175:
1083:
727:
610:
476:
393:
369:
191:
238:
injury are also risks at the time of surgery. Following surgery, a rare early complication is
1375:
920:"Carotid Endarterectomy and Carotid Artery Stenting in the US Medicare Population, 1999-2014"
152:
38:
223:
does reduces stroke risk further than medication alone in the five years following surgery.
1253:
385:
8:
1212:
1207:
1159:
632:
Moresoli, P; Habib, B; Reynier, P; Secrest, MH; Eisenberg, MJ; Filion, KB (August 2017).
402:
952:
919:
537:
504:
389:
842:
439:
422:
336:
1202:
1145:
957:
939:
900:
846:
811:
767:
731:
696:
655:
614:
578:
542:
524:
480:
444:
220:
160:
55:
1063:
1009:
1001:
947:
931:
892:
838:
801:
759:
723:
686:
645:
606:
570:
532:
520:
516:
472:
434:
421:
White CJ, Beckman JA, Cambria RP, Comerota AJ, Gray WA, Hobson RW, Iyer SS (2008).
120:
1380:
1231:
1197:
1141:
1031:
650:
633:
361:
353:
349:
73:
34:
896:
267:
People deemed unfit for the operation by the surgeon or anesthesiologist due to
1217:
1121:
1098:
1075:
1046:
691:
674:
203:
148:
109:
806:
789:
763:
574:
1364:
1093:
1088:
943:
528:
235:
935:
1349:
1180:
961:
850:
815:
771:
735:
700:
659:
618:
582:
546:
484:
448:
904:
1293:
1258:
1240:
1126:
1041:
1036:
373:
365:
268:
33:
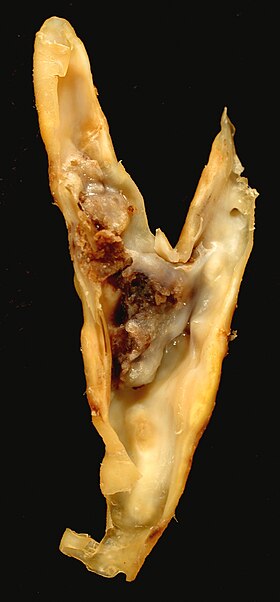
Carotid endarterectomy specimen. The specimen is removed from within the
83:
1339:
1285:
1131:
357:
131:
Carotid endarterectomy is used to reduce the risk of strokes caused by
275:
High risk criteria for carotid endarterectomy include the following:
1058:
970:
713:
97:
28:
748:
1108:
216:
123:, which can also reduce the risk of stroke for some patients.
559:
502:
260:
The person has a previous complete hemispheric stroke on the
156:
151:
is the large vertical artery in red. The blood supply to the
917:
300:
Severe lung disease or chronic obstructive pulmonary disease
1112:
631:
420:
881:
143:
595:
505:"Carotid endarterectomy for symptomatic carotid stenosis"
461:
673:
Brott TG, Halperin JL, Abbara S, et al. (2011).
828:
352:
with or without a patch to increase the size of the
163:(right). The common carotid artery divides into the
672:
257:
There is complete internal carotid artery occlusion
288:Left main or multi vessel coronary artery disease
198:cerebral ischemic events and symptoms (stroke or
100:procedure used to reduce the risk of stroke from
1362:
1022:
783:
781:
344:An incision is made on the midline side of the
340:Illustration depicting a Carotid Endarterectomy
309:Prior radical neck surgery or radiation therapy
183:Symptomatic people have had either a stroke or
465:Journal of Stroke and Cerebrovascular Diseases
986:
778:
666:
625:
509:The Cochrane Database of Systematic Reviews
993:
979:
728:10.1016/j.jstrokecerebrovasdis.2017.12.030
611:10.1016/j.jstrokecerebrovasdis.2022.106731
477:10.1016/j.jstrokecerebrovasdis.2013.11.004
306:High cervical (C2) or intrathoracic lesion
294:Left ventricular ejection fraction of ≤30%
291:Need for open heart surgery within 30 days
27:
951:
805:
690:
649:
536:
438:
315:Prior ipsilateral carotic endarterectomy.
787:
335:
142:
1363:
312:Contralateral carotid artery occlusion
253:The procedure should be avoided when:
974:
282:Class III/IV congestive heart failure
1000:
498:
496:
494:
318:Contralateral laryngeal nerve injury
1191:Extracorporeal membrane oxygenation
248:
13:
1186:Isolated organ perfusion technique
865:"Felix Eastcott, arterial surgeon"
790:"The first carotid endarterectomy"
14:
1392:
491:
440:10.1161/circulationaha.108.191175
240:cerebral hyperperfusion syndrome
226:
1249:Digital subtraction angiography
911:
885:New England Journal of Medicine
875:
857:
822:
209:
126:
1274:Magnetic resonance angiography
788:Friedman, SG (December 2014).
742:
707:
589:
553:
521:10.1002/14651858.CD001081.pub4
455:
414:
297:Recent (≤30 days) heart attack
178:
1:
1345:Ankle–brachial pressure index
843:10.1016/S0140-6736(54)90544-9
408:
1155:Endovascular aneurysm repair
651:10.1161/STROKEAHA.117.016824
331:
285:Class III/IV angina pectoris
119:An alternative procedure is
7:
897:10.1056/NEJM199108153250701
794:Journal of Vascular Surgery
563:Journal of vascular surgery
561:amaurosis fugax patients".
10:
1397:
692:10.1016/j.jacc.2010.11.005
399:St Mary's Hospital, London
379:
346:sternocleidomastoid muscle
155:starts at the arch of the
1332:
1307:
1284:
1239:
1230:
1168:
1140:
1107:
1074:
1008:
807:10.1016/j.jvs.2014.08.059
764:10.1007/s00701-005-0548-9
575:10.1016/j.jvs.2005.08.009
234:Bleeding, infection, and
200:transient ischemic attack
185:transient ischemic attack
80:
66:
54:
26:
21:
1315:Intravascular ultrasound
1269:Radionuclide angiography
1320:Carotid ultrasonography
1264:Fluorescein angiography
936:10.1001/jama.2017.12882
326:Carotid artery stenting
169:external carotid artery
165:internal carotid artery
133:carotid artery stenosis
106:internal carotid artery
102:carotid artery stenosis
47:external carotid artery
43:internal carotid artery
1299:Impedance phlebography
1176:Cardiopulmonary bypass
1084:Ambulatory phlebectomy
1052:Carotid endarterectomy
370:Electroencephalography
341:
192:number needed to treat
172:
94:Carotid endarterectomy
22:Carotid endarterectomy
871:. London. 2009-12-31.
339:
221:anti-platelet therapy
153:common carotid artery
146:
39:common carotid artery
1254:Cerebral angiography
1015:Endovascular surgery
752:Acta neurochirurgica
392:around 1953, at the
386:University of Lisbon
303:Severe renal disease
187:or amaurosis fugax.
1213:Seldinger technique
1208:First rib resection
1160:Open aortic surgery
800:(6): 1703–8.e1–4.
394:Methodist Hospital
342:
173:
41:(bottom), and the
16:Surgical procedure
1358:
1357:
1328:
1327:
1226:
1225:
1203:Revascularization
930:(11): 1035–1046.
679:J Am Coll Cardiol
433:(25): 2852–2859.
403:Dr. Henry Barnett
161:subclavian artery
91:
90:
1388:
1371:Vascular surgery
1333:Other diagnostic
1237:
1236:
1064:Carotid stenting
1024:Arterial disease
1020:
1019:
1002:Vascular surgery
995:
988:
981:
972:
971:
966:
965:
955:
915:
909:
908:
879:
873:
872:
861:
855:
854:
826:
820:
819:
809:
785:
776:
775:
746:
740:
739:
722:(5): 1395–1402.
711:
705:
704:
694:
670:
664:
663:
653:
644:(8): 2150–2157.
629:
623:
622:
593:
587:
586:
557:
551:
550:
540:
500:
489:
488:
459:
453:
452:
442:
418:
249:Reasons to avoid
121:carotid stenting
84:edit on Wikidata
76:
31:
19:
18:
1396:
1395:
1391:
1390:
1389:
1387:
1386:
1385:
1361:
1360:
1359:
1354:
1324:
1303:
1280:
1232:Medical imaging
1222:
1198:Vascular access
1164:
1142:Aortic aneurysm
1136:
1103:
1070:
1032:Vascular bypass
1013:
1004:
999:
969:
916:
912:
880:
876:
863:
862:
858:
837:(6846): 994–6.
827:
823:
786:
779:
747:
743:
712:
708:
671:
667:
630:
626:
594:
590:
558:
554:
515:(9): CD001081.
501:
492:
460:
456:
419:
415:
411:
390:Michael DeBakey
382:
334:
251:
229:
212:
181:
129:
104:(narrowing the
87:
72:
50:
17:
12:
11:
5:
1394:
1384:
1383:
1378:
1373:
1356:
1355:
1353:
1352:
1347:
1342:
1336:
1334:
1330:
1329:
1326:
1325:
1323:
1322:
1317:
1311:
1309:
1305:
1304:
1302:
1301:
1296:
1290:
1288:
1282:
1281:
1279:
1278:
1277:
1276:
1271:
1266:
1261:
1256:
1245:
1243:
1234:
1228:
1227:
1224:
1223:
1221:
1220:
1218:Vascular snare
1215:
1210:
1205:
1200:
1195:
1194:
1193:
1183:
1178:
1172:
1170:
1166:
1165:
1163:
1162:
1157:
1151:
1149:
1138:
1137:
1135:
1134:
1129:
1124:
1122:Venous cutdown
1118:
1116:
1105:
1104:
1102:
1101:
1099:Vein stripping
1096:
1091:
1086:
1080:
1078:
1076:Venous disease
1072:
1071:
1069:
1068:
1067:
1066:
1056:
1055:
1054:
1047:Endarterectomy
1044:
1039:
1034:
1028:
1026:
1017:
1006:
1005:
998:
997:
990:
983:
975:
968:
967:
910:
891:(7): 445-453.
874:
856:
821:
777:
750:anaesthesia".
741:
706:
685:(8): 1002–44.
665:
624:
605:(11): 106731.
588:
569:(6): 1075–81.
552:
490:
454:
412:
410:
407:
381:
378:
333:
330:
323:
322:
319:
316:
313:
310:
307:
304:
301:
298:
295:
292:
289:
286:
283:
280:
273:
272:
265:
258:
250:
247:
228:
225:
211:
208:
204:mortality rate
180:
177:
159:(left) or the
149:carotid artery
128:
125:
110:endarterectomy
89:
88:
81:
78:
77:
70:
64:
63:
58:
52:
51:
32:
24:
23:
15:
9:
6:
4:
3:
2:
1393:
1382:
1379:
1377:
1374:
1372:
1369:
1368:
1366:
1351:
1348:
1346:
1343:
1341:
1338:
1337:
1335:
1331:
1321:
1318:
1316:
1313:
1312:
1310:
1306:
1300:
1297:
1295:
1292:
1291:
1289:
1287:
1283:
1275:
1272:
1270:
1267:
1265:
1262:
1260:
1257:
1255:
1252:
1251:
1250:
1247:
1246:
1244:
1242:
1238:
1235:
1233:
1229:
1219:
1216:
1214:
1211:
1209:
1206:
1204:
1201:
1199:
1196:
1192:
1189:
1188:
1187:
1184:
1182:
1179:
1177:
1174:
1173:
1171:
1167:
1161:
1158:
1156:
1153:
1152:
1150:
1147:
1143:
1139:
1133:
1130:
1128:
1125:
1123:
1120:
1119:
1117:
1114:
1110:
1106:
1100:
1097:
1095:
1094:Sclerotherapy
1092:
1090:
1089:Laser surgery
1087:
1085:
1082:
1081:
1079:
1077:
1073:
1065:
1062:
1061:
1060:
1057:
1053:
1050:
1049:
1048:
1045:
1043:
1040:
1038:
1035:
1033:
1030:
1029:
1027:
1025:
1021:
1018:
1016:
1011:
1007:
1003:
996:
991:
989:
984:
982:
977:
976:
973:
963:
959:
954:
949:
945:
941:
937:
933:
929:
925:
921:
914:
906:
902:
898:
894:
890:
886:
878:
870:
866:
860:
852:
848:
844:
840:
836:
832:
825:
817:
813:
808:
803:
799:
795:
791:
784:
782:
773:
769:
765:
761:
758:(8): 839–45.
757:
753:
745:
737:
733:
729:
725:
721:
717:
710:
702:
698:
693:
688:
684:
680:
676:
669:
661:
657:
652:
647:
643:
639:
635:
628:
620:
616:
612:
608:
604:
600:
592:
584:
580:
576:
572:
568:
564:
556:
548:
544:
539:
534:
530:
526:
522:
518:
514:
510:
506:
499:
497:
495:
486:
482:
478:
474:
471:(6): 1332–6.
470:
466:
458:
450:
446:
441:
436:
432:
428:
424:
417:
413:
406:
404:
400:
395:
391:
387:
377:
375:
371:
367:
363:
359:
355:
351:
347:
338:
329:
327:
320:
317:
314:
311:
308:
305:
302:
299:
296:
293:
290:
287:
284:
281:
279:Age ≥80 years
278:
277:
276:
270:
269:comorbidities
266:
263:
259:
256:
255:
254:
246:
243:
241:
237:
236:cranial nerve
232:
227:Complications
224:
222:
219:medicine and
218:
207:
205:
201:
195:
193:
188:
186:
176:
170:
166:
162:
158:
154:
150:
145:
141:
137:
134:
124:
122:
117:
115:
111:
107:
103:
99:
95:
85:
79:
75:
71:
69:
65:
62:
59:
57:
53:
48:
44:
40:
36:
30:
25:
20:
1376:Neurosurgery
1350:Toe pressure
1181:Cardioplegia
1051:
927:
923:
913:
888:
884:
877:
868:
859:
834:
830:
824:
797:
793:
755:
751:
744:
719:
715:
709:
682:
678:
668:
641:
637:
627:
602:
598:
591:
566:
562:
555:
512:
508:
468:
464:
457:
430:
426:
416:
383:
343:
324:
321:Tracheostoma
274:
252:
244:
233:
230:
213:
210:Asymptomatic
196:
189:
182:
174:
138:
130:
127:Medical uses
118:
113:
93:
92:
1294:Portography
1259:Aortography
1241:Angiography
1127:Arteriotomy
1042:Atherectomy
1037:Angioplasty
427:Circulation
374:anaesthesia
366:anaesthesia
262:ipsilateral
179:Symptomatic
45:(left) and
1365:Categories
1340:Angioscopy
1308:Ultrasound
1286:Venography
1146:dissection
1132:Phlebotomy
409:References
358:Hemostasis
944:0098-7484
869:The Times
529:1469-493X
332:Procedure
194:of six).
1109:Arterial
1059:Stenting
1010:Vascular
962:28975306
851:13213095
816:25238726
772:15959858
736:29397311
701:21288680
660:28679848
619:36075131
583:16376194
547:32918282
485:24462461
449:19106407
167:and the
98:surgical
56:ICD-9-CM
49:(right).
953:5818799
905:1852179
538:8536099
380:History
74:D016894
37:of the
1381:Stroke
1115:access
1113:venous
960:
950:
942:
903:
849:
831:Lancet
814:
770:
734:
699:
658:
638:Stroke
617:
581:
545:
535:
527:
483:
447:
350:suture
217:statin
114:intima
108:). In
1169:Other
362:shunt
354:lumen
157:aorta
96:is a
82:[
35:lumen
1111:and
1012:and
958:PMID
940:ISSN
924:JAMA
901:PMID
847:PMID
812:PMID
768:PMID
732:PMID
697:PMID
656:PMID
615:PMID
579:PMID
543:PMID
525:ISSN
513:2020
481:PMID
445:PMID
147:The
68:MeSH
61:38.1
948:PMC
932:doi
928:318
893:doi
889:325
839:doi
835:267
802:doi
760:doi
756:147
724:doi
687:doi
646:doi
607:doi
571:doi
533:PMC
517:doi
473:doi
435:doi
431:118
1367::
1144:/
956:.
946:.
938:.
926:.
922:.
899:.
887:.
867:.
845:.
833:.
810:.
798:60
796:.
792:.
780:^
766:.
754:.
730:.
720:27
718:.
695:.
683:57
681:.
677:.
654:.
642:48
640:.
636:.
613:.
603:31
601:.
577:.
567:42
565:.
541:.
531:.
523:.
511:.
507:.
493:^
479:.
469:23
467:.
443:.
429:.
425:.
376:.
356:.
1148::
994:e
987:t
980:v
964:.
934::
907:.
895::
853:.
841::
818:.
804::
774:.
762::
738:.
726::
703:.
689::
662:.
648::
621:.
609::
585:.
573::
549:.
519::
487:.
475::
451:.
437::
271:.
86:]
Text is available under the Creative Commons Attribution-ShareAlike License. Additional terms may apply.