568:
776:
918:
is open and competent, that breathing is unlabored, and that circulation—i.e. pulses that can be felt—is present. This is sometimes described as the "A, B, C's"—Airway, Breathing, and
Circulation—and is the first step in any resuscitation or triage. Then, the history of the accident or injury is amplified with any medical, dietary (timing of last oral intake) and history, from whatever sources that might be available such as family, friends, and previous treating physicians. This method is sometimes given the mnemonic "
427:
458:
202:
506:
581:
556:. The recovery of brain function following a traumatic injury is highly variable and depends upon the specific intracranial injuries that occur. However, there is a significant correlation between the severity of the initial insult as well as the level of neurologic function during the initial assessment and the level of lasting neurologic deficits. Initial treatment may be targeted at reducing the
935:
to acquire images, although this gets shorter with each generation of scanners, and the removal of the patient from the immediate view of the emergency or surgical staff. Many providers use the aid of an algorithm such as the ATLS guidelines to determine which images to obtain following the initial assessment. These algorithms take into account the mechanism of injury,
327:, due to the greater precision in identifying the mechanism of injury. The priority in assessing blunt trauma in sports injuries is separating contusions and musculo-tendinous injuries from injuries to solid organs and the gut. It is also crucial to recognize the potential for developing blood loss and to react accordingly. Blunt injuries to the
529:(TBI) is a significant cause of morbidity and mortality and is most commonly caused by falls, motor vehicle crashes, sports- and work-related injuries, and assaults. It is the most common cause of death in patients under the age of 25. TBI is graded from mild to severe, with greater severity correlating with increased morbidity and mortality.
1087:. If surgery is indicated, there are numerous options available. A comprehensive discussion between the patient and the surgeon will take place to carefully evaluate the best approach, tailored to the patient's specific condition and injury. Conservative measures such as maintaining a clear and open airway, oxygen support,
469:, or chest tube. This tube is typically installed because it helps restore a certain balance in pressures (usually due to misplaced air or surrounding blood) that are impeding the lungs' ability to inflate and thus exchange vital gases that allow the body to function. A less common procedure that may be employed is a
335:
1038:
The treatment of blunt cranial trauma is dependent on the extent of the injury. A discussion between the patient and healthcare professionals will take place in order to carefully assess the patient's condition and determine the best approach for treatment. When considering the management of cranial
917:
publishes the
Advanced Trauma Life Support guidelines, which provide a step-by-step approach to the initial assessment, stabilization, diagnostic reasoning, and treatment of traumatic injuries that codifies this general principle. The assessment typically begins by ensuring that the subject's airway
934:
if required. If time and the patient's stability permit, a CT examination may be carried out if available. Its advantages include superior definition of the injury, leading to grading of the injury and sometimes the confidence to avoid or postpone surgery. Its disadvantages include the time taken
1095:
are often given to manage blunt thoracic trauma. Oftentimes, pain control is the most basic and effective treatment approach because the presence of severe pain may lead to impairment of proper breathing, further exacerbating impaired lungs. Pain management in thoracic trauma patients improves the
493:
may be placed if there is suspicion of trauma to the neck. Evaluation of blunt trauma to the head continues with the secondary survey for evidence of cranial trauma, including bruises, contusions, lacerations, and abrasions. In addition to noting external injury, a comprehensive neurologic exam is
819:
or CT scan to detect fractures; however, if there is concern for life-threatening bleeding, patients should receive an X-ray of the pelvis. Following initial treatment of the patient, fractures may need to be treated surgically if significant, while some minor fractures may heal without requiring
814:
on patients to stabilize the patient's pelvis and prevent further damage to these structures while patients are transported to a hospital. During the evaluation of trauma patients in an emergency department, the stability of the pelvis is typically assessed by the healthcare provider to determine
888:
experienced by most patients. To evaluate the spectrum of cardiac injury, the
American Association for the Surgery of Trauma (AAST) organ injury scale may be used to aid in determining the extent of the injury (see Evaluation and Diagnosis below). BCI may be broken down into
411:) which can reliably detect a significant amount of blood around the heart or in the lung by using a special machine that visualizes sound waves sent through the body. Only 10–15% of thoracic traumas require surgery, but they can have serious impacts on the
311:. Although these are rare examples, it has been suggested that they are caused by applying excessive pressure when performing these life-saving techniques. Finally, the occurrence of splenic rupture with mild blunt abdominal trauma in those recovering from
226:
pressure in the more serious, depending on the force applied. Initially, there may be few indications that serious internal abdominal injury has occurred, making assessment more challenging and requiring a high degree of clinical suspicion.
209:
Blunt abdominal trauma (BAT) represents 75% of all blunt trauma and is the most common example of this injury. Seventy-five percent of BAT occurs in motor vehicle crashes, in which rapid deceleration may propel the driver into the
863:
Blunt cardiac trauma, also known as Blunt
Cardiac Injury (BCI), encompasses a spectrum of cardiac injuries resulting from blunt force trauma to the chest. While BCIs necessitate a substantial amount of force to occur because the
608:
injuries. The most common mechanism for solely upper extremity injuries is machine operation or tool use. Work-related accidents and vehicle crashes are also common causes. The injured extremity is examined for four major
649:, essentially asking, "Does blood seem to be getting through the injured area in a way that enough is getting to the parts past the injury?" When it is not obvious that the answer is "yes", an injured extremity index or
1555:
Brophy RH, Gamradt SC, Barnes RP, Powell JW, DelPizzo JJ, Rodeo SA, Warren RF (January 2008). "Kidney injuries in professional
American football: implications for management of an athlete with 1 functioning kidney".
913:
In most settings, the initial evaluation and stabilization of traumatic injury follows the same general principles of identifying and treating immediately life-threatening injuries. In the US, the
660:. This uses a special scanner and a substance that makes it easier to examine the vessels in finer detail than what the human hand can feel or the human eye can see. Soft tissue damage can lead to
843:
that is often performed following traumatic injuries. Should a patient appear hemodynamically unstable in the absence of obvious blood on the FAST scan, there may be concern for bleeding into the
494:
typically performed to assess for damage to the brain. Depending on the mechanism of injury and examination, a CT scan of the skull and brain may be ordered. This is typically done to assess for
238:. The former occurs from a direct blow, such as a punch, or compression against a non-yielding object such as a seat belt or steering column. This force may deform a hollow organ, increasing its
748:
and multiple-story falls, and thus pelvic injuries are commonly associated with additional traumatic injuries in other locations. In the pelvis specifically, the structures at risk include the
971:
When blunt trauma is significant enough to require evaluation by a healthcare provider, treatment is typically aimed at treating life-threatening injuries, such as maintaining the patient's
355:. Broadly, this also includes damage caused by direct blunt force (such as a fist or a bat in an assault), acceleration or deceleration (such as that from a rear-end automotive crash),
946:
In 2011, criteria were defined that might allow patients with blunt abdominal trauma to be discharged safely without further evaluation. The characteristics of such patients include:
2029:
407:
may prove useful in such instances. Those experiencing more obvious complications from a blunt chest injury will likely undergo a focused assessment with sonography for trauma (
58:
1055:
may be indicated. Mechanical ventilation will add oxygen and remove carbon dioxide in the blood. It is also critically important to avoid low blood pressure in the setting of
2319:
1063:
greater than or equal to 120mmHg. Lastly, healthcare professionals should conduct consecutive neurological examinations to allow for early identification of elevated
987:. The management of patients with blunt force trauma necessitates the collaboration of an interpersonal healthcare team, which may include but is not limited to; a
876:, the majority of patients are asymptomatic. Clinical presentations may range from minor, clinically insignificant changes to heartbeat or may progress to severe
473:, which, by removing blood surrounding the heart, permits the heart to regain some ability to appropriately pump blood. In certain dire circumstances an emergent
1282:
Bansal V, Conroy C, Tominaga GT, Coimbra R (December 2009). "The utility of seat belt signs to predict intra-abdominal injury following motor vehicle crashes".
922:". The amount of time spent on diagnosis should be minimized and expedited by a combination of clinical assessment and appropriate use of technology, such as
852:
403:
at the time the trauma initially occurs or even until hours after. A high degree of clinical suspicion may sometimes be required to identify such injuries, a
323:
The supervised environment in which most sports injuries occur allows for mild deviations from the traditional trauma treatment algorithms, such as
1199:
835:
in the pelvis. The majority of bleeding due to pelvic trauma is due to injury to the veins. Fluid (often blood) may be detected in the pelvis via
1896:
de
Mestral C, Sharma S, Haas B, Gomez D, Nathens AB (February 2013). "A contemporary analysis of the management of the mangled lower extremity".
331:
from helmets, shoulder pads, and knees are described in
American football, association football, martial arts, and all-terrain vehicle crashes.
3092:
927:
408:
485:
The primary clinical concern with blunt trauma to the head is damage to the brain, although other structures, including the skull, face,
2667:
2037:
1124:
Worldwide, a significant cause of disability and death in people under the age of 35 is trauma, of which most are due to blunt trauma.
113:, describes a physical trauma due to a forceful impact without penetration of the body's surface. Blunt trauma stands in contrast with
2230:
Geeraerts, Thomas; Chhor, Vibol; Cheisson, Gaëlle; Martin, Laurent; Bessoud, Bertrand; Ozanne, Augustin; Duranteau, Jacques (2007).
395:
organs may have been affected. Blunt thoracic trauma is not always visible from the outside and such internal injuries may not show
1039:
trauma, it is crucial to ensure that the patient can breathe effectively. Effective breathing can be monitored using the patient's
1463:
Mack L, Forbes TL, Harris KA (January 2002). "Acute aortic thrombosis following incorrect application of the
Heimlich maneuver".
567:
2327:
692:
or computed tomography if deformity (misshapen), bruising, or joint laxity (looser or more flexible than usual) are observed.
2458:
Marco GG, Diego S, Giulio A, Luca S (October 2005). "Screening US and CT for blunt abdominal trauma: a retrospective study".
1715:
1338:
1096:
ability to breathe properly on their own, encourages the excretion of pulmonary secretions, and decreases the aggravation of
1067:
and subsequent implementation of interventions to improve blood flow and reduce stress to the body. Of note, patients taking
304:
2060:"Can Doppler pressure measurement replace "exclusion" arteriography in the diagnosis of occult extremity arterial trauma?"
3422:
1105:
31:
2544:"Blunt abdominal trauma patients are at very low risk for intra-abdominal injury after emergency department observation"
17:
1662:
650:
584:
The Ankle-Brachial Index is depicted here. Note: ultrasound enhancement of pulses is not required but may be helpful.
532:
Most patients with more severe traumatic brain injury have a combination of intracranial injuries, which can include
2209:
1429:
3427:
2983:
2384:
Morley, Eric J.; English, Bryan; Cohen, David B.; Paolo, William F.; Nusbaum, Jeffrey; Gupta, Nachi (2019-03-01).
3478:
2660:
380:
86:
757:
1325:
Fitzgerald JE, Larvin M (2009). "Chapter 15: Management of
Abdominal Trauma". In Baker Q, Aldoori M (eds.).
1015:
is a serious concern due to its tremendous infectious potential. In these cases, it is essential to perform
3514:
3119:
3087:
1008:
923:
914:
642:
324:
1782:
Platz JJ, Fabricant L, Norotsky M (August 2017). "Thoracic Trauma: Injuries, Evaluation, and
Treatment".
1075:
therapy during the time of blunt cranial trauma should undergo rapid reversal of anticoagulating agents.
553:
489:, and neck are also at risk. Following assessment of the patient's airway, circulation, and breathing, a
315:
or 'mono' (also known as 'glandular fever' in non-U.S. countries, specifically the UK) is well reported.
230:
There are two basic physical mechanisms at play with the potential of injury to intra-abdominal organs:
2807:
430:
This table depicts mechanisms of blunt thoracic trauma and the most common injuries from each mechanism
1190:
3442:
3160:
2653:
1684:
884:. Oftentimes, chest wall injuries are seen in conjunction with BCI, which confounds the presence of
560:
if there is concern for swelling or bleeding within this skull. This may require surgery, such as a
3519:
3056:
3048:
2232:"Clinical review: Initial management of blunt pelvic trauma patients with haemodynamic instability"
1023:
848:
693:
312:
3287:
3282:
2832:
1508:"Return to contact sports following infectious mononucleosis: the role of serial ultrasonography"
745:
541:
270:
3483:
3292:
3129:
3124:
1056:
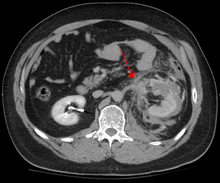
1052:
526:
517:, a variety of intracranial bleeding commonly associated with blunt trauma to the temple region
254:
130:
798:, which itself is associated with a myriad of complications including bleeding, damage to the
3524:
3471:
3257:
3217:
3061:
3031:
2802:
2359:
1064:
1019:
to assess the internal damage, drain infected fluid in the abdomen, and clean the wound with
844:
589:
557:
533:
231:
138:
1871:
815:
whether a fracture may have occurred. Providers may then decide to order imaging such as an
3432:
3071:
2976:
2600:
Dogrul, Bekir Nihat; Kiliccalan, Ibrahim; Asci, Ekrem Samet; Peker, Selim Can (June 2020).
1051:
in the blood. If the patient cannot maintain appropriate blood oxygen levels on their own,
936:
902:
673:
289:
2386:"Points & Pearls: Blunt cardiac injury: emergency department diagnosis and management"
8:
3267:
3237:
2914:
1257:"Assessment of abdominal trauma – Differential diagnosis of symptoms | BMJ Best Practice"
1027:
1016:
765:
721:
681:
3402:
3381:
3340:
3207:
2882:
2792:
2695:
2626:
2601:
2568:
2543:
2519:
2494:
2436:
2266:
2231:
2084:
2059:
1970:
1921:
1764:
1672:
1627:
1581:
1537:
1488:
1395:
1370:
1307:
1040:
622:
593:
537:
495:
470:
451:
246:
153:
114:
73:
3509:
3252:
3247:
3202:
2631:
2573:
2524:
2475:
2440:
2405:
2397:
2271:
2253:
2159:
2124:
2089:
2075:
2011:
2006:
1989:
1962:
1913:
1845:
1799:
1756:
1721:
1711:
1658:
1619:
1573:
1529:
1480:
1400:
1334:
1299:
1238:
1163:
1101:
1092:
1072:
1048:
1020:
972:
894:
549:
545:
514:
447:
376:
308:
300:
161:
82:
1974:
1925:
1768:
1631:
1585:
1492:
184:
and may require immediate medical attention. Blunt trauma to the head and/or severe
3397:
3361:
2950:
2858:
2797:
2777:
2745:
2740:
2621:
2613:
2563:
2555:
2514:
2506:
2467:
2432:
2293:
2261:
2243:
2186:
2151:
2116:
2079:
2071:
2001:
1990:"Objective criteria accurately predict amputation following lower extremity trauma"
1952:
1905:
1791:
1748:
1703:
1650:
1611:
1565:
1541:
1519:
1472:
1390:
1382:
1311:
1291:
1230:
1113:
1083:
Nine out of ten patients with thoracic trauma can be treated effectively without a
788:
118:
943:
to determine whether patients should have imaging or proceed directly to surgery.
810:. If pelvic trauma is suspected, emergency medical services personnel may place a
2969:
2750:
2730:
2700:
2559:
1654:
1256:
1012:
1004:
898:
795:
729:
605:
601:
561:
490:
426:
299:
In rare cases, this injury has been attributed to medical techniques such as the
239:
126:
2617:
2510:
2471:
2190:
2142:
Bosch X, Poch E, Grau JM (July 2009). "Rhabdomyolysis and acute kidney injury".
1909:
1837:
1155:
1026:
are often necessary. In the case of multiple holes or significant damage to the
3454:
3449:
3272:
3139:
1739:
Bhargava M, Wazni OM, Saliba WI (March 2016). "Interventional Pericardiology".
1524:
1507:
1060:
1044:
992:
988:
919:
697:
661:
626:
618:
499:
388:
211:
94:
2919:
2645:
2542:
Kendall JL, Kestler AM, Whitaker KT, Adkisson MM, Haukoos JS (November 2011).
1795:
1752:
1725:
1707:
1476:
1295:
1234:
963:
To be considered low-risk, patients would need to meet all low-risk criteria.
3503:
3488:
3371:
3335:
3330:
3192:
3134:
3026:
2904:
2735:
2720:
2401:
2257:
1569:
1068:
984:
877:
811:
761:
717:
713:
420:
265:
that travel within the mesentery. Classic examples of these mechanisms are a
169:
2385:
775:
465:
The injuries may necessitate a procedure, most commonly the insertion of an
222:
in less serious cases, or rupture of internal organs from briefly increased
3466:
3366:
3325:
3310:
3232:
3016:
3011:
2945:
2891:
2782:
2725:
2635:
2577:
2528:
2479:
2409:
2275:
2177:
Kennedy RH (September 1932). "Emergency Treatment of Extremity Fractures".
2163:
2128:
2120:
1966:
1917:
1849:
1803:
1760:
1623:
1577:
1533:
1484:
1404:
1303:
1242:
1167:
1097:
1003:
In cases of blunt abdominal injury, the most frequent damage occurs in the
807:
784:
749:
725:
705:
701:
630:
457:
435:
396:
364:
360:
274:
262:
235:
223:
2444:
2155:
2093:
2015:
3437:
3376:
3222:
3144:
2940:
2935:
2837:
2827:
1438:
940:
890:
689:
657:
614:
474:
443:
384:
356:
188:
are the most likely causes of death due to blunt force traumatic injury.
177:
165:
90:
1386:
371:
of some sort). Common signs and symptoms include something as simple as
334:
201:
3345:
3227:
3066:
3006:
2863:
2772:
1088:
931:
885:
836:
824:
709:
571:
A fracture, an injury to the skeletal component of the upper extremity.
466:
439:
157:
149:
1615:
3197:
2909:
2900:
2842:
2787:
2602:"Blunt trauma related chest wall and pulmonary injuries: An overview"
1957:
1940:
1330:
840:
368:
293:
280:
When blunt abdominal trauma is complicated by 'internal injury,' the
258:
215:
181:
180:
of the affected individual. In some cases, blunt force trauma can be
145:
66:
2877:
1371:"Intestinal Injury from Blunt Abdominal Trauma: A Study of 47 Cases"
434:
The most immediate life-threatening injuries that may occur include
3461:
2868:
2768:
2248:
1221:
Isenhour JL, Marx J (August 2007). "Advances in abdominal trauma".
983:
criteria have shown improved outcomes when they are cared for in a
976:
869:
677:
646:
634:
597:
505:
185:
134:
129:
or impactful force to a body part. Such incidents often occur with
2886:
2423:
Woods SD (February 1995). "Assessment of blunt abdominal trauma".
1030:, the affected segment of tissue may need to be removed entirely.
2712:
1084:
873:
803:
799:
736:
treatment may be necessary, but many are managed nonoperatively.
733:
654:
510:
404:
400:
266:
250:
176:
of the impact, the area of the body affected, and the underlying
172:. The severity of these injuries depends on factors such as the
137:, and sports-related injuries, and are notably common among the
3181:
3021:
2992:
2819:
2760:
2681:
1988:
Johansen K, Daines M, Howey T, Helfet D, Hansen ST (May 1990).
1831:
1829:
1827:
1825:
1823:
1821:
1819:
1817:
1815:
1813:
1109:
1059:. Studies have demonstrated improved outcomes in patients with
1007:, and in severe situations, this can result in small intestine
980:
769:
688:
and vessels in the same compartment). Bones are evaluated with
669:
665:
610:
392:
372:
352:
328:
285:
219:
78:
2541:
1505:
580:
57:
2677:
1318:
881:
865:
832:
828:
816:
780:
753:
732:. Depending on the extent of injury and involved structures,
696:
evaluation involves testing the major nerve functions of the
685:
638:
412:
338:
A depiction of flail chest, a very serious blunt chest injury
281:
173:
122:
2229:
2225:
2223:
2107:
Egan AF, Cahill KC (November 2017). "Compartment Syndrome".
1810:
1437:(9th ed.). American College of Surgeons. Archived from
1154:
Simon, Leslie V.; Lopez, Richard A.; King, Kevin C. (2020).
979:. Patients who have suffered blunt trauma and meet specific
144:
Blunt trauma can lead to a wide range of injuries including
117:, which occurs when an object pierces the skin, enters body
3320:
2896:
2204:
2202:
2200:
1506:
O'Connor TE, Skinner LJ, Kiely P, Fenton JE (August 2011).
1281:
416:
1697:
953:
no evidence of lowered blood pressure or raised pulse rate
653:
may be used to help guide whether further evaluation with
2961:
2599:
2220:
1987:
1895:
1554:
486:
30:"Blunt force trauma" redirects here. For other uses, see
2197:
2383:
2030:"Annual Report of the National Trauma Data Bank (NTDB)"
245:
Deceleration, on the other hand, causes stretching and
1781:
242:
or internal pressure and possibly leading to rupture.
1424:
1422:
1420:
1418:
1416:
1414:
1364:
1362:
1360:
1358:
1356:
1354:
1352:
1350:
1078:
347:
The term blunt thoracic trauma, or, more informally,
2457:
1698:
Maisch B, Ristić AD, Seferović PM, Tsang TS (2011).
1033:
855:
or surgery, depending on the location and severity.
592:(like arms, legs, hands, feet) is extremely common.
1738:
318:
2364:The American Association for the Surgery of Trauma
1431:Advanced Trauma Life Support Student Course Manual
1411:
1347:
1189:
744:The most common causes of blunt pelvic trauma are
363:(such as a heavy object falling on a person), and
359:(a combination of acceleration and deceleration),
27:Trauma to the body without penetration of the skin
3501:
2492:
2287:
2285:
1462:
1324:
998:
292:) are most frequently involved, followed by the
2675:
1112:, or regional pain management methods, such as
521:
2595:
2593:
2591:
2589:
2587:
2326:. American College of Surgeons. Archived from
1368:
1187:
1153:
575:
257:, are anchored. This can cause tearing of the
3093:Focused assessment with sonography for trauma
2977:
2661:
2282:
2141:
2057:
1597:
1595:
1181:
205:Abdominal CT showing left renal artery injury
2493:Jansen JO, Yule SR, Loudon MA (April 2008).
2354:
2352:
2350:
2348:
2346:
2344:
1898:The Journal of Trauma and Acute Care Surgery
1732:
1220:
51:Blunt injury, non-penetrating trauma, trauma
2584:
1863:
1835:
1223:Emergency Medicine Clinics of North America
1149:
1147:
1145:
1143:
1141:
1139:
1137:
1047:. The goal is to maintain greater than 90%
908:
794:One of the primary concerns is the risk of
351:, encompasses a variety of injuries to the
249:at the points where mobile contents in the
2984:
2970:
2668:
2654:
2106:
1644:
1592:
995:, and emergency and trauma nursing staff.
56:
2625:
2567:
2518:
2495:"Investigation of blunt abdominal trauma"
2341:
2265:
2247:
2083:
2005:
1956:
1836:Haydel, Micelle; Scott, Dulebohn (2021).
1602:Blyth A (March 2014). "Thoracic trauma".
1523:
1394:
564:, in which part of the skull is removed.
196:
2422:
2320:"Initial Management of Pelvic Fractures"
1134:
774:
579:
566:
504:
456:
425:
342:
333:
200:
2176:
1938:
1558:The American Journal of Sports Medicine
858:
540:, and intracranial bleeding, including
480:
14:
3502:
1649:. Springer, London. pp. 105–111.
1249:
1188:Cimino-Fiallos, Nicole (28 May 2020).
827:, which may result from damage to the
739:
2965:
2649:
2058:Lynch K, Johansen K (December 1991).
1784:The Surgical Clinics of North America
1601:
928:bedside ultrasound examination (FAST)
375:, but occasionally as complicated as
1106:Nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs
851:. Stopping the bleeding may require
125:. Blunt trauma occurs due to direct
3423:Acute respiratory distress syndrome
2291:
2144:The New England Journal of Medicine
2109:The New England Journal of Medicine
1869:
1327:Clinical Surgery: A Practical Guide
24:
2437:10.1111/j.1445-2197.1995.tb07263.x
1079:Treatment of blunt thoracic trauma
991:, emergency department physician,
756:, major blood vessels such as the
645:pulse exam, and signs/symptoms of
25:
3536:
2317:
1647:Intercostal Chest Drain Insertion
1034:Treatment of blunt cranial trauma
191:
3428:Chronic traumatic encephalopathy
2076:10.1097/00000658-199112000-00016
2007:10.1097/00005373-199005000-00007
2000:(5): 568–572, discussion 572–3.
1116:, can be used for pain control.
785:inferior and superior pubic rami
319:Blunt abdominal trauma in sports
2606:Chinese Journal of Traumatology
2535:
2486:
2451:
2416:
2377:
2311:
2179:New England Journal of Medicine
2170:
2135:
2100:
2051:
2022:
1981:
1932:
1889:
1775:
1691:
1638:
1548:
1499:
1369:Mukhopadhyay M (October 2009).
1202:from the original on 2017-09-24
1191:"Hard Hits: Blunt Force Trauma"
1119:
956:no abdominal pain or tenderness
307:and manual thrusts to clear an
261:of the bowel and injury to the
3479:Post-traumatic stress disorder
1945:The British Journal of Surgery
1941:"Epidemiology of major trauma"
1456:
1275:
1214:
1028:blood supply of the intestines
1011:. Perforation of the small or
823:A life-threatening concern is
664:(a rapid breakdown of injured
600:, making up as much as 30% of
381:ventilation-perfusion mismatch
87:ventilation-perfusion mismatch
81:, occasionally complicated as
13:
1:
1700:Interventional Pericardiology
1127:
999:Treatment of abdominal trauma
672:) or may potentially develop
3120:Advanced trauma life support
3088:Diagnostic peritoneal lavage
2560:10.5811/westjem.2010.11.2016
1655:10.1007/978-1-4471-2259-3_10
966:
924:diagnostic peritoneal lavage
915:American College of Surgeons
522:Traumatic brain injury (TBI)
139:elderly who experience falls
7:
2618:10.1016/j.cjtee.2020.04.003
2511:10.1136/bmj.39534.686192.80
2472:10.1016/j.ejrad.2005.02.001
2390:Emergency Medicine Practice
2191:10.1056/NEJM193209012070903
1910:10.1097/TA.0b013e31827a05e3
893:injury, valvular injuries,
787:in a patient with previous
633:are examined for expanding
576:Blunt trauma to extremities
554:intraparenchymal hemorrhage
500:fracture of the skull bones
10:
3541:
2991:
2808:Retroperitoneal hemorrhage
1741:Current Cardiology Reports
1525:10.1177/014556131109000819
783:showing a fracture of the
461:An example of a chest tube
452:airway obstruction/rupture
29:
3415:
3390:
3354:
3303:
3180:
3173:
3161:Resuscitative thoracotomy
3153:
3112:
3105:
3080:
3049:Clinical prediction rules
3047:
3040:
2999:
2928:
2851:
2818:
2759:
2711:
2688:
1796:10.1016/j.suc.2017.03.004
1753:10.1007/s11886-016-0698-9
1708:10.1007/978-3-642-11335-2
1645:Falter F, Nair S (2012).
1477:10.1007/s10016-001-0147-z
1296:10.1080/15389580903191450
1284:Traffic Injury Prevention
1235:10.1016/j.emc.2007.06.002
1162:. StatPearls Publishing.
868:is well-protected by the
853:endovascular intervention
72:
64:
55:
47:
42:
3057:Abbreviated Injury Scale
1872:"Traumatic Brain Injury"
1570:10.1177/0363546507308940
1057:traumatic brain injuries
1024:Prophylactic antibiotics
909:Evaluation and diagnosis
849:retroperitoneal hematoma
313:infectious mononucleosis
3288:Penetrating head injury
3283:Intracranial hemorrhage
1939:Søreide K (July 2009).
1061:systolic blood pressure
975:and preventing ongoing
950:absence of intoxication
668:that can overwhelm the
542:subarachnoid hemorrhage
218:, or seatbelt, causing
131:road traffic collisions
3484:Subcutaneous emphysema
3443:Volkmann's contracture
3293:Traumatic brain injury
3130:Early appropriate care
3125:Damage control surgery
2425:ANZ Journal of Surgery
2360:"Blunt Cardiac Injury"
2121:10.1056/NEJMicm1701729
1053:mechanical ventilation
959:no blood in the urine.
791:
585:
572:
527:Traumatic brain injury
518:
496:blood within the skull
462:
431:
339:
206:
197:Blunt abdominal trauma
121:, and creates an open
111:non-penetrating trauma
3258:Thoracic aorta injury
3218:Diaphragmatic rupture
3062:Injury Severity Score
3032:Trauma triad of death
2915:Occupational injuries
2298:Life in the Fast Lane
2156:10.1056/NEJMra0801327
1994:The Journal of Trauma
1876:Life in the Fast Lane
1065:intracranial pressure
930:before proceeding to
845:retroperitoneal space
831:, iliac arteries, or
778:
746:motor vehicle crashes
611:functional components
583:
570:
558:intracranial pressure
534:diffuse axonal injury
508:
460:
438:, open pneumothorax,
429:
343:Blunt thoracic trauma
337:
204:
3433:Compartment syndrome
3072:Revised Trauma Score
2920:Traumatic amputation
1702:. Berlin: Springer.
1333:. pp. 192–204.
1261:bestpractice.bmj.com
1156:"Blunt Force Trauma"
1093:volume resuscitation
937:physical examination
903:myocardial contusion
859:Blunt cardiac trauma
674:compartment syndrome
651:ankle-brachial index
596:are the most common
481:Blunt cranial trauma
436:tension pneumothorax
290:blunt splenic trauma
273:and injuries to the
3515:Medical emergencies
3268:Blunt kidney trauma
3238:Pulmonary contusion
1838:"Blunt Head Trauma"
1444:on 21 December 2018
1387:10.5001/omj.2009.52
1017:exploratory surgery
766:reproductive organs
740:Blunt pelvic trauma
682:muscle compartments
655:computed tomography
538:cerebral contusions
391:due to the way the
3382:Spinal cord injury
3341:Penetrating trauma
3208:Soft tissue injury
2883:Penetrating trauma
2803:Grey Turner's sign
2793:Subungual hematoma
1229:(3): 713–733, ix.
1196:login.medscape.com
1085:surgical operation
792:
586:
573:
519:
471:pericardiocentesis
463:
432:
349:blunt chest injury
340:
207:
115:penetrating trauma
107:blunt force trauma
32:Blunt Force Trauma
18:Blunt-force trauma
3497:
3496:
3411:
3410:
3253:Internal bleeding
3248:Cardiac tamponade
3203:Joint dislocation
3169:
3168:
3101:
3100:
2959:
2958:
2505:(7650): 938–942.
2064:Annals of Surgery
1717:978-3-642-11334-5
1616:10.1136/bmj.g1137
1512:Ear Nose Throat J
1340:978-1-4441-0962-7
1102:low oxygen levels
1089:tube thoracostomy
1049:oxygen saturation
550:epidural hematoma
546:subdural hematoma
515:epidural hematoma
477:may be employed.
467:intercostal drain
448:cardiac tamponade
301:Heimlich maneuver
100:
99:
37:Medical condition
16:(Redirected from
3532:
3403:Pediatric trauma
3398:Geriatric trauma
3362:Abdominal trauma
3178:
3177:
3110:
3109:
3045:
3044:
2986:
2979:
2972:
2963:
2962:
2951:Abdominal trauma
2859:Ballistic trauma
2746:Friction blister
2741:Fracture blister
2670:
2663:
2656:
2647:
2646:
2640:
2639:
2629:
2597:
2582:
2581:
2571:
2548:West J Emerg Med
2539:
2533:
2532:
2522:
2490:
2484:
2483:
2455:
2449:
2448:
2420:
2414:
2413:
2396:(Suppl 3): 1–2.
2381:
2375:
2374:
2372:
2371:
2356:
2339:
2338:
2336:
2335:
2315:
2309:
2308:
2306:
2304:
2292:Nickson, Chris.
2289:
2280:
2279:
2269:
2251:
2227:
2218:
2217:
2214:www.uptodate.com
2206:
2195:
2194:
2174:
2168:
2167:
2139:
2133:
2132:
2104:
2098:
2097:
2087:
2055:
2049:
2048:
2046:
2045:
2036:. Archived from
2026:
2020:
2019:
2009:
1985:
1979:
1978:
1960:
1958:10.1002/bjs.6643
1936:
1930:
1929:
1893:
1887:
1886:
1884:
1882:
1870:Nickson, Chris.
1867:
1861:
1860:
1858:
1856:
1833:
1808:
1807:
1779:
1773:
1772:
1736:
1730:
1729:
1695:
1689:
1688:
1682:
1678:
1676:
1668:
1642:
1636:
1635:
1599:
1590:
1589:
1552:
1546:
1545:
1527:
1503:
1497:
1496:
1460:
1454:
1453:
1451:
1449:
1443:
1436:
1426:
1409:
1408:
1398:
1366:
1345:
1344:
1322:
1316:
1315:
1279:
1273:
1272:
1270:
1268:
1263:. 14 August 2018
1253:
1247:
1246:
1218:
1212:
1211:
1209:
1207:
1193:
1185:
1179:
1178:
1176:
1174:
1151:
1114:local anesthetic
1013:large intestines
1005:small intestines
993:anesthesiologist
939:, and patient's
789:hip replacements
690:plain film X-ray
271:ligamentum teres
182:life-threatening
105:, also known as
60:
40:
39:
21:
3540:
3539:
3535:
3534:
3533:
3531:
3530:
3529:
3520:Causes of death
3500:
3499:
3498:
3493:
3407:
3386:
3350:
3299:
3174:Pathophysiology
3165:
3149:
3097:
3076:
3036:
2995:
2990:
2960:
2955:
2924:
2847:
2814:
2755:
2751:Sucking blister
2731:Delayed blister
2707:
2684:
2674:
2644:
2643:
2598:
2585:
2540:
2536:
2491:
2487:
2456:
2452:
2421:
2417:
2382:
2378:
2369:
2367:
2358:
2357:
2342:
2333:
2331:
2318:Croce, Martin.
2316:
2312:
2302:
2300:
2294:"Pelvic Trauma"
2290:
2283:
2228:
2221:
2208:
2207:
2198:
2175:
2171:
2140:
2136:
2105:
2101:
2056:
2052:
2043:
2041:
2028:
2027:
2023:
1986:
1982:
1937:
1933:
1894:
1890:
1880:
1878:
1868:
1864:
1854:
1852:
1834:
1811:
1780:
1776:
1737:
1733:
1718:
1696:
1692:
1680:
1679:
1670:
1669:
1665:
1643:
1639:
1600:
1593:
1553:
1549:
1504:
1500:
1461:
1457:
1447:
1445:
1441:
1434:
1428:
1427:
1412:
1367:
1348:
1341:
1323:
1319:
1280:
1276:
1266:
1264:
1255:
1254:
1250:
1219:
1215:
1205:
1203:
1186:
1182:
1172:
1170:
1152:
1135:
1130:
1122:
1081:
1036:
1001:
969:
911:
899:cardiac chamber
895:coronary artery
878:cardiac failure
861:
796:pelvic fracture
742:
730:lower extremity
712:as well as the
710:upper extremity
606:lower extremity
578:
562:hemicraniectomy
524:
491:cervical collar
483:
345:
321:
294:small intestine
269:tear along the
199:
194:
127:physical trauma
65:A woman with a
38:
35:
28:
23:
22:
15:
12:
11:
5:
3538:
3528:
3527:
3522:
3517:
3512:
3495:
3494:
3492:
3491:
3486:
3481:
3476:
3475:
3474:
3469:
3459:
3458:
3457:
3455:Rhabdomyolysis
3450:Crush syndrome
3447:
3446:
3445:
3435:
3430:
3425:
3419:
3417:
3413:
3412:
3409:
3408:
3406:
3405:
3400:
3394:
3392:
3388:
3387:
3385:
3384:
3379:
3374:
3369:
3364:
3358:
3356:
3352:
3351:
3349:
3348:
3343:
3338:
3333:
3328:
3323:
3318:
3313:
3307:
3305:
3301:
3300:
3298:
3297:
3296:
3295:
3290:
3285:
3277:
3276:
3275:
3273:Splenic injury
3270:
3262:
3261:
3260:
3255:
3250:
3242:
3241:
3240:
3235:
3230:
3225:
3220:
3212:
3211:
3210:
3205:
3200:
3195:
3186:
3184:
3175:
3171:
3170:
3167:
3166:
3164:
3163:
3157:
3155:
3151:
3150:
3148:
3147:
3142:
3140:Trauma surgery
3137:
3132:
3127:
3122:
3116:
3114:
3107:
3103:
3102:
3099:
3098:
3096:
3095:
3090:
3084:
3082:
3081:Investigations
3078:
3077:
3075:
3074:
3069:
3064:
3059:
3053:
3051:
3042:
3038:
3037:
3035:
3034:
3029:
3024:
3019:
3014:
3009:
3003:
3001:
2997:
2996:
2989:
2988:
2981:
2974:
2966:
2957:
2956:
2954:
2953:
2948:
2943:
2938:
2932:
2930:
2926:
2925:
2923:
2922:
2917:
2912:
2907:
2894:
2889:
2880:
2871:
2866:
2861:
2855:
2853:
2849:
2848:
2846:
2845:
2840:
2835:
2830:
2824:
2822:
2816:
2815:
2813:
2812:
2811:
2810:
2805:
2800:
2795:
2790:
2785:
2780:
2765:
2763:
2757:
2756:
2754:
2753:
2748:
2743:
2738:
2733:
2728:
2723:
2717:
2715:
2709:
2708:
2706:
2705:
2704:
2703:
2692:
2690:
2686:
2685:
2673:
2672:
2665:
2658:
2650:
2642:
2641:
2612:(3): 125–138.
2583:
2554:(4): 496–504.
2534:
2485:
2450:
2415:
2376:
2340:
2310:
2281:
2249:10.1186/cc5157
2219:
2196:
2185:(9): 393–395.
2169:
2134:
2099:
2070:(6): 737–741.
2050:
2021:
1980:
1951:(7): 697–698.
1931:
1904:(2): 597–603.
1888:
1862:
1809:
1790:(4): 783–799.
1774:
1731:
1716:
1690:
1663:
1637:
1591:
1547:
1498:
1471:(1): 130–133.
1455:
1410:
1381:(4): 256–259.
1346:
1339:
1317:
1290:(6): 567–572.
1274:
1248:
1213:
1180:
1132:
1131:
1129:
1126:
1121:
1118:
1104:in the blood.
1080:
1077:
1045:pulse oximeter
1043:content via a
1035:
1032:
1000:
997:
989:trauma surgeon
968:
965:
961:
960:
957:
954:
951:
910:
907:
860:
857:
758:iliac arteries
754:proximal femur
741:
738:
728:nerves in the
708:nerves in the
662:rhabdomyolysis
613:which include
577:
574:
523:
520:
482:
479:
389:cardiac output
387:, and reduced
344:
341:
320:
317:
303:, attempts at
275:renal arteries
212:steering wheel
198:
195:
193:
192:Classification
190:
170:bone fractures
98:
97:
95:cardiac output
76:
70:
69:
62:
61:
53:
52:
49:
45:
44:
36:
26:
9:
6:
4:
3:
2:
3537:
3526:
3523:
3521:
3518:
3516:
3513:
3511:
3508:
3507:
3505:
3490:
3489:Wound healing
3487:
3485:
3482:
3480:
3477:
3473:
3470:
3468:
3465:
3464:
3463:
3460:
3456:
3453:
3452:
3451:
3448:
3444:
3441:
3440:
3439:
3436:
3434:
3431:
3429:
3426:
3424:
3421:
3420:
3418:
3416:Complications
3414:
3404:
3401:
3399:
3396:
3395:
3393:
3389:
3383:
3380:
3378:
3375:
3373:
3372:Facial trauma
3370:
3368:
3365:
3363:
3360:
3359:
3357:
3353:
3347:
3344:
3342:
3339:
3337:
3336:Gunshot wound
3334:
3332:
3331:Electrocution
3329:
3327:
3324:
3322:
3319:
3317:
3314:
3312:
3309:
3308:
3306:
3302:
3294:
3291:
3289:
3286:
3284:
3281:
3280:
3278:
3274:
3271:
3269:
3266:
3265:
3263:
3259:
3256:
3254:
3251:
3249:
3246:
3245:
3243:
3239:
3236:
3234:
3231:
3229:
3226:
3224:
3221:
3219:
3216:
3215:
3213:
3209:
3206:
3204:
3201:
3199:
3196:
3194:
3193:Bone fracture
3191:
3190:
3188:
3187:
3185:
3183:
3179:
3176:
3172:
3162:
3159:
3158:
3156:
3152:
3146:
3143:
3141:
3138:
3136:
3135:Trauma center
3133:
3131:
3128:
3126:
3123:
3121:
3118:
3117:
3115:
3111:
3108:
3104:
3094:
3091:
3089:
3086:
3085:
3083:
3079:
3073:
3070:
3068:
3065:
3063:
3060:
3058:
3055:
3054:
3052:
3050:
3046:
3043:
3039:
3033:
3030:
3028:
3027:Resuscitation
3025:
3023:
3020:
3018:
3015:
3013:
3010:
3008:
3005:
3004:
3002:
2998:
2994:
2987:
2982:
2980:
2975:
2973:
2968:
2967:
2964:
2952:
2949:
2947:
2944:
2942:
2939:
2937:
2934:
2933:
2931:
2927:
2921:
2918:
2916:
2913:
2911:
2908:
2906:
2905:Chemical burn
2902:
2898:
2895:
2893:
2890:
2888:
2884:
2881:
2879:
2876:/superficial/
2875:
2872:
2870:
2867:
2865:
2862:
2860:
2857:
2856:
2854:
2850:
2844:
2841:
2839:
2836:
2834:
2831:
2829:
2826:
2825:
2823:
2821:
2817:
2809:
2806:
2804:
2801:
2799:
2798:Cullen's sign
2796:
2794:
2791:
2789:
2786:
2784:
2781:
2779:
2778:Battle's sign
2776:
2775:
2774:
2770:
2767:
2766:
2764:
2762:
2758:
2752:
2749:
2747:
2744:
2742:
2739:
2737:
2736:Edema blister
2734:
2732:
2729:
2727:
2724:
2722:
2721:Blood blister
2719:
2718:
2716:
2714:
2710:
2702:
2699:
2698:
2697:
2694:
2693:
2691:
2687:
2683:
2679:
2671:
2666:
2664:
2659:
2657:
2652:
2651:
2648:
2637:
2633:
2628:
2623:
2619:
2615:
2611:
2607:
2603:
2596:
2594:
2592:
2590:
2588:
2579:
2575:
2570:
2565:
2561:
2557:
2553:
2549:
2545:
2538:
2530:
2526:
2521:
2516:
2512:
2508:
2504:
2500:
2496:
2489:
2481:
2477:
2473:
2469:
2466:(1): 97–101.
2465:
2461:
2454:
2446:
2442:
2438:
2434:
2430:
2426:
2419:
2411:
2407:
2403:
2399:
2395:
2391:
2387:
2380:
2365:
2361:
2355:
2353:
2351:
2349:
2347:
2345:
2330:on 2015-04-21
2329:
2325:
2321:
2314:
2299:
2295:
2288:
2286:
2277:
2273:
2268:
2263:
2259:
2255:
2250:
2245:
2241:
2237:
2236:Critical Care
2233:
2226:
2224:
2215:
2211:
2205:
2203:
2201:
2192:
2188:
2184:
2180:
2173:
2165:
2161:
2157:
2153:
2149:
2145:
2138:
2130:
2126:
2122:
2118:
2114:
2110:
2103:
2095:
2091:
2086:
2081:
2077:
2073:
2069:
2065:
2061:
2054:
2040:on 2015-04-23
2039:
2035:
2031:
2025:
2017:
2013:
2008:
2003:
1999:
1995:
1991:
1984:
1976:
1972:
1968:
1964:
1959:
1954:
1950:
1946:
1942:
1935:
1927:
1923:
1919:
1915:
1911:
1907:
1903:
1899:
1892:
1877:
1873:
1866:
1851:
1847:
1843:
1839:
1832:
1830:
1828:
1826:
1824:
1822:
1820:
1818:
1816:
1814:
1805:
1801:
1797:
1793:
1789:
1785:
1778:
1770:
1766:
1762:
1758:
1754:
1750:
1746:
1742:
1735:
1727:
1723:
1719:
1713:
1709:
1705:
1701:
1694:
1686:
1674:
1666:
1664:9781447122586
1660:
1656:
1652:
1648:
1641:
1633:
1629:
1625:
1621:
1617:
1613:
1609:
1605:
1598:
1596:
1587:
1583:
1579:
1575:
1571:
1567:
1563:
1559:
1551:
1543:
1539:
1535:
1531:
1526:
1521:
1518:(8): E21–24.
1517:
1513:
1509:
1502:
1494:
1490:
1486:
1482:
1478:
1474:
1470:
1466:
1465:Ann Vasc Surg
1459:
1440:
1433:
1432:
1425:
1423:
1421:
1419:
1417:
1415:
1406:
1402:
1397:
1392:
1388:
1384:
1380:
1376:
1372:
1365:
1363:
1361:
1359:
1357:
1355:
1353:
1351:
1342:
1336:
1332:
1328:
1321:
1313:
1309:
1305:
1301:
1297:
1293:
1289:
1285:
1278:
1262:
1258:
1252:
1244:
1240:
1236:
1232:
1228:
1224:
1217:
1201:
1197:
1192:
1184:
1169:
1165:
1161:
1157:
1150:
1148:
1146:
1144:
1142:
1140:
1138:
1133:
1125:
1117:
1115:
1111:
1107:
1103:
1099:
1094:
1090:
1086:
1076:
1074:
1070:
1069:anticoagulant
1066:
1062:
1058:
1054:
1050:
1046:
1042:
1031:
1029:
1025:
1022:
1018:
1014:
1010:
1006:
996:
994:
990:
986:
985:trauma center
982:
978:
974:
964:
958:
955:
952:
949:
948:
947:
944:
942:
938:
933:
929:
925:
921:
916:
906:
904:
901:rupture, and
900:
896:
892:
887:
883:
879:
875:
871:
867:
856:
854:
850:
846:
842:
838:
834:
830:
826:
821:
818:
813:
812:pelvic binder
809:
805:
801:
797:
790:
786:
782:
777:
773:
771:
767:
763:
762:urinary tract
759:
755:
751:
747:
737:
735:
731:
727:
723:
722:deep peroneal
719:
715:
711:
707:
703:
699:
695:
691:
687:
683:
680:builds up in
679:
675:
671:
667:
663:
659:
658:arteriography
656:
652:
648:
644:
640:
636:
632:
628:
624:
620:
616:
612:
607:
603:
599:
595:
591:
582:
569:
565:
563:
559:
555:
551:
547:
543:
539:
535:
530:
528:
516:
512:
507:
503:
501:
497:
492:
488:
478:
476:
472:
468:
459:
455:
453:
449:
445:
441:
437:
428:
424:
422:
421:great vessels
418:
414:
410:
406:
402:
398:
394:
390:
386:
382:
378:
374:
370:
366:
362:
358:
354:
350:
336:
332:
330:
326:
316:
314:
310:
306:
302:
297:
295:
291:
287:
283:
278:
276:
272:
268:
264:
263:blood vessels
260:
256:
252:
248:
243:
241:
237:
233:
228:
225:
221:
217:
213:
203:
189:
187:
183:
179:
178:comorbidities
175:
171:
167:
163:
159:
155:
151:
147:
142:
140:
136:
132:
128:
124:
120:
116:
112:
108:
104:
96:
92:
88:
84:
80:
77:
75:
71:
68:
63:
59:
54:
50:
46:
41:
33:
19:
3525:Trauma types
3367:Chest injury
3326:Crush injury
3316:Blunt trauma
3315:
3311:Blast injury
3233:Pneumothorax
3017:Traumatology
3012:Major trauma
2946:Chest trauma
2892:Aerosol burn
2874:Blunt trauma
2873:
2783:Raccoon eyes
2726:Coma blister
2609:
2605:
2551:
2547:
2537:
2502:
2498:
2488:
2463:
2460:Eur J Radiol
2459:
2453:
2431:(2): 75–76.
2428:
2424:
2418:
2393:
2389:
2379:
2368:. Retrieved
2366:. 2013-01-14
2363:
2332:. Retrieved
2328:the original
2323:
2313:
2301:. Retrieved
2297:
2239:
2235:
2213:
2182:
2178:
2172:
2150:(1): 62–72.
2147:
2143:
2137:
2115:(19): 1877.
2112:
2108:
2102:
2067:
2063:
2053:
2042:. Retrieved
2038:the original
2034:www.facs.org
2033:
2024:
1997:
1993:
1983:
1948:
1944:
1934:
1901:
1897:
1891:
1879:. Retrieved
1875:
1865:
1853:. Retrieved
1841:
1787:
1783:
1777:
1744:
1740:
1734:
1699:
1693:
1646:
1640:
1607:
1603:
1564:(1): 85–90.
1561:
1557:
1550:
1515:
1511:
1501:
1468:
1464:
1458:
1446:. Retrieved
1439:the original
1430:
1378:
1374:
1326:
1320:
1287:
1283:
1277:
1265:. Retrieved
1260:
1251:
1226:
1222:
1216:
1204:. Retrieved
1198:. Medscape.
1195:
1183:
1171:. Retrieved
1159:
1123:
1120:Epidemiology
1098:inflammation
1082:
1073:antiplatelet
1041:blood oxygen
1037:
1002:
970:
962:
945:
912:
862:
822:
808:nerve damage
793:
750:pelvic bones
743:
684:damages the
615:soft tissues
587:
531:
525:
484:
464:
433:
367:(such as an
348:
346:
322:
298:
279:
244:
240:intraluminal
236:deceleration
229:
224:intraluminal
208:
164:or external
143:
110:
106:
103:Blunt trauma
102:
101:
43:Blunt trauma
3438:Contracture
3391:Demographic
3377:Head injury
3223:Flail chest
3145:Trauma team
2941:Head injury
2936:Hand injury
2303:20 December
1881:13 December
1855:11 December
1681:|work=
1448:17 December
1009:perforation
941:vital signs
891:pericardial
847:, known as
839:during the
604:and 60% of
590:extremities
513:showing an
475:thoracotomy
444:flail chest
385:hypovolemia
361:compression
357:shear force
253:, like the
232:compression
166:hemorrhages
158:lacerations
150:concussions
91:hypovolemia
48:Other names
3504:Categories
3346:Stab wound
3228:Hemothorax
3154:Procedures
3113:Principles
3106:Management
3067:NACA score
3041:Assessment
3007:Polytrauma
3000:Principles
2864:Stab wound
2773:Ecchymosis
2370:2023-09-22
2334:2018-12-20
2242:(1): 204.
2210:"UpToDate"
2044:2018-12-16
1842:StatPearls
1726:1036224056
1375:Oman Med J
1160:StatPearls
1128:References
977:blood loss
932:laparotomy
926:(DPL), or
897:injuries,
886:chest pain
837:ultrasound
825:hemorrhage
768:, and the
694:Neurologic
588:Injury to
440:hemothorax
220:contusions
186:blood loss
146:contusions
93:, reduced
3304:Mechanism
3198:Degloving
2929:By region
2910:Frostbite
2901:Corrosion
2788:Black eye
2689:Abrasions
2402:1559-3908
2258:1364-8535
1747:(3): 31.
1683:ignored (
1673:cite book
1610:: g1137.
1331:CRC Press
1267:1 January
1206:1 January
1173:1 January
967:Treatment
841:FAST scan
820:surgery.
369:explosion
259:mesentery
216:dashboard
154:abrasions
67:black eye
3510:Injuries
3462:Embolism
2869:Splinter
2769:Hematoma
2713:Blisters
2701:Avulsion
2696:Abrasion
2682:injuries
2676:General
2636:32417043
2578:22224146
2529:18436949
2480:16168270
2410:30821949
2276:17300738
2164:19571284
2129:29117495
1975:10670345
1967:19526611
1926:44503022
1918:23354257
1850:28613521
1804:28728716
1769:27688193
1761:26908116
1632:44608099
1624:24609501
1586:25602860
1578:17986635
1534:21853428
1493:46698020
1485:11904818
1405:22216378
1304:19916127
1243:17826214
1200:Archived
1168:29262209
870:rib cage
734:surgical
698:axillary
678:pressure
647:ischemia
635:hematoma
598:etiology
401:symptoms
393:thoracic
373:bruising
247:shearing
162:internal
135:assaults
79:bruising
74:Symptoms
3244:Cardio
2761:Bruises
2627:7296362
2569:3236146
2520:2335258
2445:7857232
2267:2151899
2094:1741655
2085:1358501
2016:2342140
1542:7530057
1396:3243872
1312:9040242
1110:opioids
1021:saline.
874:sternum
804:bladder
800:urethra
718:sciatic
714:femoral
670:kidneys
631:Vessels
623:vessels
511:CT scan
405:CT scan
377:hypoxia
267:hepatic
251:abdomen
83:hypoxia
3355:Region
3279:Neuro
3182:Injury
3022:Triage
2993:Trauma
2878:closed
2852:Other:
2838:Spider
2833:Insect
2828:Animal
2820:Biting
2678:wounds
2634:
2624:
2576:
2566:
2527:
2517:
2478:
2443:
2408:
2400:
2274:
2264:
2256:
2162:
2127:
2092:
2082:
2014:
1973:
1965:
1924:
1916:
1848:
1802:
1767:
1759:
1724:
1714:
1661:
1630:
1622:
1584:
1576:
1540:
1532:
1491:
1483:
1403:
1393:
1337:
1310:
1302:
1241:
1166:
1091:, and
981:triage
973:airway
920:SAMPLE
806:, and
770:rectum
760:, the
752:, the
726:tibial
724:, and
706:median
704:, and
702:radial
686:nerves
676:(when
666:muscle
643:distal
625:, and
619:nerves
552:, and
487:orbits
450:, and
419:, and
365:blasts
329:kidney
309:airway
286:spleen
168:, and
119:tissue
3214:Resp
2843:Snake
1971:S2CID
1922:S2CID
1765:S2CID
1628:S2CID
1582:S2CID
1538:S2CID
1489:S2CID
1442:(PDF)
1435:(PDF)
1308:S2CID
882:death
866:heart
833:veins
829:aorta
817:X-ray
781:X-ray
639:bruit
627:bones
602:upper
594:Falls
417:lungs
413:heart
397:signs
353:chest
288:(see
282:liver
255:bowel
174:force
123:wound
3321:Burn
3189:MSK
2897:Burn
2887:open
2680:and
2632:PMID
2574:PMID
2525:PMID
2476:PMID
2441:PMID
2406:PMID
2398:ISSN
2324:FACS
2305:2018
2272:PMID
2254:ISSN
2160:PMID
2125:PMID
2090:PMID
2012:PMID
1963:PMID
1914:PMID
1883:2018
1857:2018
1846:PMID
1800:PMID
1757:PMID
1722:OCLC
1712:ISBN
1685:help
1659:ISBN
1620:PMID
1574:PMID
1530:PMID
1481:PMID
1450:2018
1401:PMID
1335:ISBN
1300:PMID
1269:2021
1239:PMID
1208:2021
1175:2021
1164:PMID
1100:and
880:and
872:and
802:and
409:FAST
325:ATLS
284:and
234:and
3472:fat
3467:air
3264:GI
2622:PMC
2614:doi
2564:PMC
2556:doi
2515:PMC
2507:doi
2503:336
2499:BMJ
2468:doi
2433:doi
2262:PMC
2244:doi
2187:doi
2183:207
2152:doi
2148:361
2117:doi
2113:377
2080:PMC
2072:doi
2068:214
2002:doi
1953:doi
1906:doi
1792:doi
1749:doi
1704:doi
1651:doi
1612:doi
1608:348
1604:BMJ
1566:doi
1520:doi
1473:doi
1391:PMC
1383:doi
1292:doi
1231:doi
1071:or
779:An
498:or
399:or
305:CPR
109:or
3506::
2630:.
2620:.
2610:23
2608:.
2604:.
2586:^
2572:.
2562:.
2552:12
2550:.
2546:.
2523:.
2513:.
2501:.
2497:.
2474:.
2464:56
2462:.
2439:.
2429:65
2427:.
2404:.
2394:21
2392:.
2388:.
2362:.
2343:^
2322:.
2296:.
2284:^
2270:.
2260:.
2252:.
2240:11
2238:.
2234:.
2222:^
2212:.
2199:^
2181:.
2158:.
2146:.
2123:.
2111:.
2088:.
2078:.
2066:.
2062:.
2032:.
2010:.
1998:30
1996:.
1992:.
1969:.
1961:.
1949:96
1947:.
1943:.
1920:.
1912:.
1902:74
1900:.
1874:.
1844:.
1840:.
1812:^
1798:.
1788:97
1786:.
1763:.
1755:.
1745:18
1743:.
1720:.
1710:.
1677::
1675:}}
1671:{{
1657:.
1626:.
1618:.
1606:.
1594:^
1580:.
1572:.
1562:36
1560:.
1536:.
1528:.
1516:90
1514:.
1510:.
1487:.
1479:.
1469:16
1467:.
1413:^
1399:.
1389:.
1379:24
1377:.
1373:.
1349:^
1329:.
1306:.
1298:.
1288:10
1286:.
1259:.
1237:.
1227:25
1225:.
1194:.
1158:.
1136:^
1108:,
905:.
772:.
764:,
720:,
716:,
700:,
641:,
637:,
629:.
621:,
617:,
548:,
544:,
536:,
509:A
502:.
454:.
446:,
442:,
423:.
415:,
383:,
379:,
296:.
277:.
214:,
160:,
156:,
152:,
148:,
141:.
133:,
89:,
85:,
2985:e
2978:t
2971:v
2903:/
2899:/
2885:/
2771:/
2669:e
2662:t
2655:v
2638:.
2616::
2580:.
2558::
2531:.
2509::
2482:.
2470::
2447:.
2435::
2412:.
2373:.
2337:.
2307:.
2278:.
2246::
2216:.
2193:.
2189::
2166:.
2154::
2131:.
2119::
2096:.
2074::
2047:.
2018:.
2004::
1977:.
1955::
1928:.
1908::
1885:.
1859:.
1806:.
1794::
1771:.
1751::
1728:.
1706::
1687:)
1667:.
1653::
1634:.
1614::
1588:.
1568::
1544:.
1522::
1495:.
1475::
1452:.
1407:.
1385::
1343:.
1314:.
1294::
1271:.
1245:.
1233::
1210:.
1177:.
34:.
20:)
Text is available under the Creative Commons Attribution-ShareAlike License. Additional terms may apply.