178:
argument put forward is that the process of seafloor spreading is the same in both cases, but the movement of seafloor spreading centers in the basin causes the asymmetry in the magnetic anomalies. This process can be seen in the Lau back-arc basin. Though the magnetic anomalies are more complex to decipher, the rocks sampled from back-arc basin spreading centers do not differ very much from those at mid-ocean ridges. In contrast, the volcanic rocks of the nearby island arc differ significantly from those in the basin.
2250:
433:
20:
3138:
3159:
182:
229:). As the subduction zone and its associated trench pull backward, the overriding plate is stretched, thinning the crust and forming a back-arc basin. In some cases, extension is triggered by the entrance of a buoyant feature in the subduction zone, which locally slows down subduction and induces the subducting plate to rotate adjacent to it. This rotation is associated with trench retreat and overriding plate extension.
2239:
71:
3148:
499:
theory, geologists thought that convergent plate margins were zones of compression, thus zones of strong extension above subduction zones (back-arc basins) were not expected. The hypothesis that some convergent plate margins were actively spreading was developed by Dan Karig in 1970, while a graduate
411:
is the most common sediment type recovered from the back-arc basins of the western
Pacific. This sediment type made up 23.8% of the total thickness of sediment recovered by the DSDP. The pelagic carbonates consist of ooze, chalk, and limestone. Nanofossils and foraminifera make up the majority of the
189:
Back-arc basins are different from normal mid-ocean ridges because they are characterized by asymmetric seafloor spreading, but this is quite variable even within single basins. For example, in the central
Mariana Trough, current spreading rates are 2–3 times greater on the western flank, whereas at
84:
Back-arc basins are typically very long and relatively narrow, often thousands of kilometers long while only being a few hundred kilometers wide at most. For back-arc extension to form, a subduction zone is required, but not all subduction zones have a back-arc extension feature. Back-arc basins are
74:
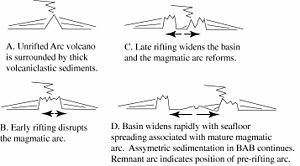
Cross-section sketch showing the development of a back-arc basin by rifting the arc longitudinally. The rift matures to the point of seafloor spreading, allowing a new magmatic arc to form on the trenchward side of the basin (to the right in this image) and stranding a remnant arc on the far side of
232:
The age of the subducting crust needed to establish back-arc spreading has been found to be 55 million years old or older. This is why back-arc spreading centers appear concentrated in the western
Pacific. The dip angle of the subducting slab may also be significant, as is shown to be greater
193:
Other back-arc basins such as the Lau Basin have undergone large rift jumps and propagation events (sudden changes in relative rift motion) that have transferred spreading centers from arc-distal to more arc-proximal positions. Conversely, study of recent spreading rates appear to be relatively
173:
of the crust that had formed in back-arc basins deviated in form from the crust formed at mid-ocean ridges. In many areas the anomalies do not appear parallel, as well as the profiles of the magnetic anomalies in the basin lacking symmetry or a central anomaly as a traditional ocean basin does,
210:
it sheds water, causing mantle melting, volcanism, and the formation of island arcs. Another result of this is a convection cell is formed. The rising magma and heat along with the outwards tension in the crust in contact with the convection cell cause a region of melt to form, resulting in a
177:
This has prompted some to characterize the spreading in back-arc basins to be more diffused and less uniform than at mid-ocean ridges. The idea that back-arc basin spreading is inherently different from mid-ocean ridge spreading is controversial and has been debated through the years. Another
190:
the southern end of the
Mariana Trough the position of the spreading center adjacent to the volcanic front suggests that overall crustal accretion has been nearly entirely asymmetric there. This situation is mirrored to the north where a large spreading asymmetry is also developed.
194:
symmetric with perhaps small rift jumps. The cause of asymmetric spreading in back-arc basins remains poorly understood. General ideas invoke asymmetries relative to the spreading axis in arc melt generation processes and heat flow, hydration gradients with distance from the slab,
412:
sediment. Resedimented carbonates made up 9.5% of the total thickness of sediment recovered by the DSDP. This sediment type had the same composition as the biogenic pelagic carbonated, but it had been reworked with well-developed sedimentary structures. Pyroclastics consisting of
89:
is very old. The restricted width of back-arc basins is due to magmatic activity being reliant on water and induced mantle convection, limiting their formation to along subduction zones. Spreading rates vary from only a few centimeters per year (as in the
215:. This process drives the island arc toward the subduction zone and the rest of the plate away from the subduction zone. The backward motion of the subduction zone relative to the motion of the plate which is being subducted is called
316:
style. These systems are inner and midfan subsystem and the outer fan subsystem. The inner and midfan system contains interbedded thin to medium bedded sandstones and mudstones. Structures that are found in these sandstones include
168:
that collected in the basin decreased toward the center of the basin, indicating a younger surface. The idea that thickness and age of sediment on the sea floor is related to the age of the oceanic crust was proposed by Harry Hess.
341:
and mudstones are found in this system. Sedimentary structures found in this system include parallel laminae, micro-cross laminae, and graded bedding. Partial Bouma sequences can be identified in this subsystem.
424:, quartz, plant debris, and glass made up 9.5% of the sediment recovered. These volcanic sediments were sourced form the regional tectonic controlled volcanism and the nearby island arc sources.
1626:
Parson, L.M.; Pearce, J.A.; Murton, B.J.; Hodkinson, R.A. (1990). "Role of ridge jumps and ridge propagation in the tectonic evolution of the Lau back-arc basin, southwest
Pacific".
337:
can be found within the subsystem. The outer fan subsystem generally consists of finer sediments when compared to the inner and midfan system. Well sorted volcanoclastic sandstones,
1093:
67:, as convergent boundaries were expected to universally be zones of compression. However, in 1970, Dan Karig published a model of back-arc basins consistent with plate tectonics.
255:
is strongly asymmetric, with most of the sediment supplied from the active volcanic arc which regresses in step with the rollback of the trench. From cores collected during the
23:
Cross-section through the shallow part of a subduction zone showing the relative positions of an active magmatic arc and back-arc basin, such as the southern part of the
1495:
Klein, G.D. (1985). "The
Control of Depositional Depth, Tectonic Uplift, and Volcanism on Sedimentation Processes in the Back-Arc Basins of the Western Pacific Ocean".
1231:
Klein, G.D. (1985). "The
Control of Depositional Depth, Tectonic Uplift, and Volcanism on Sedimentation Processes in the Back-Arc Basins of the Western Pacific Ocean".
206:
The extension of the crust behind volcanic arcs is believed to be caused by processes in association with subduction. As the subducting plate descends into the
233:
than 30° in areas of back-arc spreading; this is most likely because as oceanic crust gets older it becomes denser, resulting in a steeper angle of descent.
2878:
118:
O). The high water contents of back-arc basin basalt magmas is derived from water carried down the subduction zone and released into the overlying
1597:
Molnar, P.; Atwater, T. (1978). "Interarc spreading and
Cordilleran tectonics as alternates related to the age of subducted oceanic lithosphere".
1145:
Molnar, P.; Atwater, T. (1978). "Interarc spreading and
Cordilleran tectonics as alternates related to the age of subducted oceanic lithosphere".
2868:
1927:
1422:
Gill, J.B. (1976). "Composition and age of Lau Basin and Ridge volcanic rocks: Implications for evolution of an interarc basin and remnant arc".
809:
Gill, J.B. (1976). "Composition and age of Lau Basin and Ridge volcanic rocks: Implications for evolution of an interarc basin and remnant arc".
263:
account for 1.2% of sediments collected by the DSDP. The average size of the sediments in the conglomerates are pebble sized but can range from
300:
made up 20% of the total thickness of sediment recovered by the DSDP. The fans can be divided into two sub-systems based on the differences in
236:
The thinning of the overriding plate from back-arc rifting can lead to the formation of new oceanic crust (i.e., back-arc spreading). As the
1121:
259:(DSDP) nine sediment types were found in the back-arc basins of the western Pacific. Debris flows of thick to medium bedded massive
2784:
151:
3151:
2199:
1967:
2431:
1796:"Collisional model for rapid fore-arc block rotations, arc curvature, and episodic back-arc rifting in subduction settings"
326:
464:
regions, but most are found in the western
Pacific. Not all subduction zones have back-arc basins; some, like the central
400:
at each site it was found. This sediment type consisted of 4.2% of the total thickness of sediment recovered by the DSDP.
1920:
501:
63:, where a subduction zone moves towards the subducting plate. Back-arc basins were initially an unexpected phenomenon in
2321:
3026:
2453:
2341:
2873:
2144:
1706:
2331:
2291:
1532:
Martinez, F.; Fryer, P.; Baker, N.A.; Yamazaki, T. (1995). "Evolution of backarc rifting: Mariana Trough, 20–24N".
971:"Role of ridge jumps and ridge propagation in the tectonic evolution of the Lau back-arc basin, southwest Pacific"
3061:
2047:
1647:
994:
3141:
2734:
1913:
1443:
830:
445:
1721:
Taylor, B.; Zellmer, K.; Martinez, F.; Goodliffe, A. (1996). "Sea-floor spreading in the Lau back-arc basin".
24:
2189:
771:
Taylor, B; Zellmer, K; Martinez, F; Goodliffe, A (1996). "Sea-floor spreading in the Lau back-arc basin".
2249:
2386:
1791:
2921:
2326:
2286:
1787:
256:
3194:
3184:
3051:
2426:
2416:
2356:
1992:
1962:
1358:
Deschamps, A.; Fujiwara, T. (2003). "Asymmetric accretion along the slow-spreading Mariana Ridge".
970:
844:
Deschamps, A.; Fujiwara, T. (2003). "Asymmetric accretion along the slow-spreading Mariana Ridge".
469:
3189:
3088:
3071:
2908:
2401:
2266:
2204:
2194:
2087:
475:
There are a number of extinct or fossil back-arc basins, such as the Parece Vela-Shikoku Basin,
3199:
3083:
3021:
2448:
2134:
309:
260:
217:
60:
240:
stretches, the asthenosphere below rises to shallow depths and partially melts as a result of
2916:
2898:
2406:
2301:
1936:
397:
1734:
1610:
1158:
784:
712:
3103:
2936:
2639:
2496:
2361:
2072:
1873:
1842:
1807:
1759:
1730:
1668:
1635:
1606:
1575:
1541:
1504:
1475:
1431:
1400:
1367:
1330:
1287:
1240:
1154:
1105:
1058:
1021:
1009:
982:
937:
896:
853:
818:
780:
708:
659:
609:
565:
8:
3098:
2983:
2978:
2704:
2376:
2336:
2052:
1864:
Zellmer, K.E.; Taylor, B. (2001). "A three-plate kinematic model for Lau Basin opening".
114:
O), whereas mid-ocean ridge basalt magmas are very dry (typically <0.3 weight % H
40:
1877:
1846:
1831:"Spreading process of the northern Mariana Trough: Rifting-spreading transition at 22 N"
1811:
1763:
1672:
1639:
1579:
1545:
1508:
1479:
1435:
1404:
1371:
1334:
1291:
1244:
1109:
1062:
1025:
986:
941:
926:"Spreading process of the northern Mariana Trough: Rifting-spreading transition at 22 N"
900:
857:
822:
663:
613:
569:
3041:
2754:
2744:
2709:
2609:
2594:
2491:
1899:
1829:
Yamazaki, T.; Seama, N.; Okino, K.; Kitada, K.; Joshima, M.; Oda, H.; Naka, J. (2003).
1775:
1686:
1520:
1413:
1388:
1346:
1256:
1074:
966:
924:
Yamazaki, T.; Seama, N.; Okino, K.; Kitada, K.; Joshima, M.; Oda, H.; Naka, J. (2003).
677:
578:
553:
157:
3123:
3113:
3056:
3036:
2719:
2684:
2619:
2599:
2589:
2471:
2159:
2017:
1779:
1742:
1710:
1702:
1690:
1618:
1524:
1466:
Karig, Daniel E (1970). "Ridges and basins of the Tonga-Kermadec island arc system".
1455:
1260:
1166:
792:
746:
720:
696:
681:
504:. This was the result of several marine geologic expeditions to the western Pacific.
305:
264:
241:
135:
56:
407:, and chert. It makes up 4.3% of the sediment thickness recovered. Biogenic pelagic
3078:
3046:
3016:
2825:
2810:
2679:
2614:
2506:
2421:
2351:
2276:
2057:
2027:
1957:
1952:
1881:
1850:
1815:
1767:
1738:
1676:
1643:
1614:
1583:
1567:
1549:
1512:
1483:
1439:
1408:
1375:
1350:
1338:
1321:
1295:
1248:
1162:
1113:
1078:
1066:
1049:
1029:
990:
945:
904:
888:
861:
826:
788:
716:
667:
617:
600:
Karig, Daniel (1970). "Ridges and basins of the Tonga-Kermadec island arc system".
573:
457:
349:
345:
268:
170:
36:
2883:
2779:
2729:
2694:
2654:
2546:
2516:
2366:
2316:
2226:
2184:
2117:
2042:
2002:
1750:
Uyeda S (1984). "Subduction zones: their diversity, mechanism and human impact".
523:
513:
496:
479:, and Kurile Basin. Compressional back-arc basins are found, for example, in the
441:
373:
322:
103:
86:
64:
2993:
2988:
2893:
2888:
2724:
2664:
2659:
2391:
2281:
2102:
2037:
2012:
461:
432:
408:
404:
393:
369:
334:
330:
139:
123:
107:
91:
2238:
3178:
3163:
3011:
2931:
2820:
2739:
2714:
2649:
2579:
2486:
2381:
2258:
2179:
2139:
2112:
2022:
1972:
313:
252:
207:
185:
The islands of Japan were separated from mainland Asia by back-arc spreading.
52:
19:
1487:
1319:
Barker, P.F.; Hill, I.A. (1980). "Asymmetric spreading in back-arc basins".
1047:
Barker, P.F.; Hill, I.A. (1980). "Asymmetric spreading in back-arc basins".
621:
3118:
3066:
3006:
2957:
2835:
2830:
2805:
2789:
2764:
2481:
2371:
2311:
2097:
2007:
1982:
1902:
in EGU GIFT2017: Shaping the Mediterranean from the Inside Out, via YouTube
476:
453:
449:
413:
385:
283:
195:
119:
750:
134:
in the subducting slab. Similar to mid-ocean ridges, back-arc basins have
106:; the main difference being back-arc basin basalts are often very rich in
3108:
2840:
2769:
2634:
2574:
2541:
2531:
2526:
2411:
2346:
2306:
2296:
2271:
2154:
2127:
2107:
2067:
2032:
1885:
1855:
1830:
1820:
1795:
1714:
1681:
1656:
1588:
1562:
1379:
1300:
1275:
1033:
950:
925:
909:
883:
865:
672:
647:
357:
289:
244:
decompression melting. As this melt nears the surface, spreading begins.
237:
161:
1905:
2926:
2774:
2749:
2644:
2624:
2551:
2536:
2521:
2511:
2476:
2396:
2216:
2211:
2174:
2169:
2164:
2062:
1771:
1459:
484:
361:
48:
44:
43:. Presently all back-arc basins are submarine features associated with
3158:
1553:
1117:
2998:
2860:
2845:
2759:
2604:
2443:
2438:
2221:
2149:
2077:
1997:
1987:
1944:
1900:
Animation of subduction, trench rollback and back-arc basin expansion
1563:"Geophysical Characteristics of the Southern Mariana Trough, 11N–13N"
1342:
1070:
884:"Geophysical Characteristics of the Southern Mariana Trough, 11N–13N"
365:
338:
318:
301:
293:
280:
272:
127:
95:
3093:
2815:
2674:
2566:
2556:
2501:
1977:
1516:
1389:"On the Relative Importance of the Driving Forces of Plate Motion*"
1252:
480:
381:
297:
181:
165:
16:
Submarine features associated with island arcs and subduction zones
554:"On the Relative Importance of the Driving Forces of Plate Motion"
2962:
2952:
2122:
2092:
1276:"Kinematics of back-arc inversion of the Western Black Sea Basin"
518:
70:
2669:
2082:
421:
389:
377:
353:
99:
1720:
770:
694:
3031:
2850:
2629:
2584:
695:
Taylor, B.; Zellmer, K.; Martinez, F.; Goodliffe, A. (1996).
465:
276:
2463:
1648:
10.1130/0091-7613(1990)018<0470:RORJAR>2.3.CO;2
1625:
1092:
Martinez, F.; Fryer, P.; Baker, N.A.; Yamazaki, T. (1995).
995:
10.1130/0091-7613(1990)018<0470:RORJAR>2.3.CO;2
965:
Parson, L.M.; Pearce, J.A.; Murton, B.J.; Hodkinson, R.A.;
964:
417:
212:
131:
1531:
1444:
10.1130/0016-7606(1976)87<1384:caaolb>2.0.co;2
1091:
831:
10.1130/0016-7606(1976)87<1384:CAAOLB>2.0.CO;2
1828:
1452:
Petrological Studies: A Volume to Honor A .F. Buddington
923:
743:
Petrological Studies: A Volume to Honor A .F. Buddington
420:
and a host of other constituents including nanofossils,
1094:"Evolution of backarc rifting: Mariana Trough, 20–24N"
1010:"A three-plate kinematic model for Lau Basin opening"
85:
found in areas where the subducting plate of oceanic
1560:
881:
1450:Hess, Henry H. (1962). "History of Ocean Basins".
333:, and gradational tops of sandstone beds. Partial
198:effects, and evolution from rifting to spreading.
2879:North West Shelf Operational Oceanographic System
1357:
843:
741:Hess, Henry H (1962). "History of Ocean Basins".
405:radiolarian, diatomaceous, silicoflagellate oozes
3176:
1786:
2869:Deep-ocean Assessment and Reporting of Tsunamis
1312:
697:"Sea-floor Spreading in the Lau Back-arc Basin"
1654:
645:
1921:
1863:
1596:
1144:
1007:
403:Biogenic pelagic silica sediments consist of
79:
1561:Martinez, F.; Fryer, P.; Becker, N. (2000).
1386:
882:Martinez, F.; Fryer, P.; Becker, N. (2000).
551:
122:. Additional sources of water could be the
102:that are similar to those erupted from the
98:. Spreading ridges within the basins erupt
1928:
1914:
1318:
1046:
201:
174:indicating asymmetric seafloor spreading.
1935:
1854:
1819:
1680:
1587:
1412:
1299:
949:
908:
671:
577:
1699:Backarc Basins: Tectonics and Magmatism.
1273:
440:Active back-arc basins are found in the
431:
180:
69:
18:
1749:
1657:"Controls on back-arc basin formations"
648:"Controls on back-arc basin formations"
436:The active back-arc basins of the world
3177:
2200:one-dimensional Saint-Venant equations
1226:
1224:
1222:
1220:
1218:
1216:
1214:
1212:
1210:
1208:
1206:
1204:
1202:
1200:
1198:
1196:
75:the basin (to the left in this image).
51:zones, with many found in the western
1909:
1494:
1465:
1230:
1194:
1192:
1190:
1188:
1186:
1184:
1182:
1180:
1178:
1176:
1140:
1138:
599:
490:
164:of the basin floor. The thickness of
145:
3147:
1800:Geochemistry, Geophysics, Geosystems
1661:Geochemistry, Geophysics, Geosystems
1421:
877:
875:
808:
804:
802:
766:
764:
762:
760:
740:
652:Geochemistry, Geophysics, Geosystems
641:
639:
637:
635:
633:
631:
595:
593:
591:
589:
547:
545:
543:
541:
539:
1723:Earth and Planetary Science Letters
1655:Sdrolias, M.; Muller, R.D. (2006).
773:Earth and Planetary Science Letters
701:Earth and Planetary Science Letters
502:Scripps Institution of Oceanography
13:
3027:National Oceanographic Data Center
2454:World Ocean Circulation Experiment
2342:Global Ocean Data Analysis Project
1414:10.1111/j.1365-246x.1975.tb00631.x
1274:Munteanu, I.; et al. (2011).
1173:
1135:
1008:Zellmer, K.E.; Taylor, B. (2001).
646:Sdrolias, M; Muller, R.D. (2006).
579:10.1111/j.1365-246X.1975.tb00631.x
14:
3211:
2874:Global Sea Level Observing System
1893:
1393:Geophysical Journal International
872:
799:
757:
628:
586:
558:Geophysical Journal International
536:
3157:
3146:
3137:
3136:
2332:Geochemical Ocean Sections Study
2248:
2237:
247:
110:(typically 1–1.5 weight % H
3062:Ocean thermal energy conversion
2785:Vine–Matthews–Morley hypothesis
1468:Journal of Geophysical Research
1387:Forsyth, D.; Uyeda, S. (1975).
1267:
1085:
1040:
1001:
958:
917:
602:Journal of Geophysical Research
152:Vine–Matthews–Morley hypothesis
59:, caused by a process known as
837:
734:
688:
271:. Accessory materials include
1:
552:Forsyth, D; Uyeda, S (1975).
94:), to 15 cm/year in the
2322:El Niño–Southern Oscillation
2292:Craik–Leibovich vortex force
2048:Luke's variational principle
1743:10.1016/0012-821x(96)00148-3
1619:10.1016/0012-821X(78)90187-5
1313:General and cited references
1167:10.1016/0012-821X(78)90187-5
793:10.1016/0012-821x(96)00148-3
721:10.1016/0012-821X(96)00148-3
529:
427:
279:, shallow water fossils and
7:
507:
55:. Most of them result from
41:convergent plate boundaries
10:
3216:
2387:Ocean dynamical thermostat
2235:
348:containing iron-manganese
149:
80:Structural characteristics
3132:
2971:
2945:
2922:Ocean acoustic tomography
2907:
2859:
2798:
2735:Mohorovičić discontinuity
2693:
2565:
2462:
2327:General circulation model
2257:
1963:Benjamin–Feir instability
1943:
1866:Geochem. Geophys. Geosyst
1835:Geochem. Geophys. Geosyst
1360:Geochem. Geophys. Geosyst
1014:Geochem. Geophys. Geosyst
969:Scientific Party (1990).
930:Geochem. Geophys. Geosyst
846:Geochem. Geophys. Geosyst
329:, dewatering structures,
257:Deep Sea Drilling Project
3052:Ocean surface topography
2427:Thermohaline circulation
2417:Subsurface ocean current
2357:Hydrothermal circulation
2190:Wave–current interaction
1968:Boussinesq approximation
1701:New York: Plenum Press.
495:With the development of
3089:Sea surface temperature
3072:Outline of oceanography
2267:Atmospheric circulation
2205:shallow water equations
2195:Waves and shallow water
2088:Significant wave height
1735:1996E&PSL.144...35T
1611:1978E&PSL..41..330M
1599:Earth Planet. Sci. Lett
1488:10.1029/JB075i002p00239
1159:1978E&PSL..41..330M
1147:Earth Planet. Sci. Lett
785:1996E&PSL.144...35T
713:1996E&PSL.144...35T
622:10.1029/JB075i002p00239
292:systems of interbedded
202:Formation and tectonics
61:oceanic trench rollback
3084:Sea surface microlayer
2449:Wind generated current
1697:Taylor, Brian (1995).
468:, are associated with
437:
396:made up the uppermost
310:sedimentary structures
186:
76:
35:is a type of geologic
28:
2917:Deep scattering layer
2899:World Geodetic System
2407:Princeton Ocean Model
2287:Coriolis–Stokes force
1937:Physical oceanography
1794:; Mann, Paul (2009).
435:
398:stratigraphic section
386:foraminiferal remains
327:convolute laminations
184:
150:Further information:
73:
25:Izu–Bonin–Mariana Arc
22:
2937:Underwater acoustics
2497:Perigean spring tide
2362:Langmuir circulation
2073:Rossby-gravity waves
1886:10.1029/2000GC000106
1856:10.1029/2002GC000492
1821:10.1029/2008gc002220
1682:10.1029/2005GC001090
1589:10.1029/2000JB900117
1380:10.1029/2003GC000537
1301:10.1029/2011tc002865
1034:10.1029/2000GC000106
951:10.1029/2002GC000492
910:10.1029/2000JB900117
866:10.1029/2003GC000537
745:. pp. 599–620.
673:10.1029/2005GC001090
470:rear-arc compression
3099:Science On a Sphere
2705:Convergent boundary
2377:Modular Ocean Model
2337:Geostrophic current
2053:Mild-slope equation
1878:2001GGG.....2.1020Z
1847:2003GGG.....4.1075Y
1812:2009GGG....10.5001W
1764:1984GeoJo...8..381U
1673:2006GGG.....7.4016S
1640:1990Geo....18..470P
1580:2000JGR...10516591M
1574:(B7): 16591–16607.
1546:1995JGR...100.3807M
1509:1985JG.....93....1D
1480:1970JGR....75..239K
1436:1976GSAB...87.1384G
1405:1975GeoJ...43..163F
1372:2003GGG.....4.8622D
1335:1980Natur.285..652B
1292:2011Tecto..30.5004M
1245:1985JG.....93....1D
1110:1995JGR...100.3807M
1063:1980Natur.285..652B
1026:2001GGG.....2.1020Z
987:1990Geo....18..470P
942:2003GGG.....4.1075Y
901:2000JGR...10516591M
895:(B7): 16591–16607.
858:2003GGG.....4.8622D
823:1976GSAB...87.1384G
664:2006GGG.....7.4016S
614:1970JGR....75..239K
570:1975GeoJ...43..163F
2755:Seafloor spreading
2745:Outer trench swell
2710:Divergent boundary
2610:Continental margin
2595:Carbonate platform
2492:Lunitidal interval
1772:10.1007/BF00185938
1497:Journal of Geology
1233:Journal of Geology
967:RRS Charles Darwin
491:History of thought
438:
187:
171:Magnetic anomalies
158:seafloor spreading
146:Seafloor spreading
136:hydrothermal vents
77:
29:
3172:
3171:
3164:Oceans portal
3124:World Ocean Atlas
3114:Underwater glider
3057:Ocean temperature
2720:Hydrothermal vent
2685:Submarine volcano
2620:Continental shelf
2600:Coastal geography
2590:Bathymetric chart
2472:Amphidromic point
2160:Wave nonlinearity
2018:Infragravity wave
1788:Wallace, Laura M.
1554:10.1029/94JB02466
1540:(B3): 3807–3827.
1430:(10): 1384–1395.
1329:(5767): 652–654.
1118:10.1029/94JB02466
1104:(B3): 3807–3827.
1057:(5767): 652–654.
817:(10): 1384–1395.
160:has been seen in
3207:
3162:
3161:
3150:
3149:
3140:
3139:
3079:Pelagic sediment
3017:Marine pollution
2811:Deep ocean water
2680:Submarine canyon
2615:Continental rise
2507:Rule of twelfths
2422:Sverdrup balance
2352:Humboldt Current
2277:Boundary current
2252:
2241:
2058:Radiation stress
2028:Iribarren number
2003:Equatorial waves
1958:Ballantine scale
1953:Airy wave theory
1930:
1923:
1916:
1907:
1906:
1889:
1860:
1858:
1825:
1823:
1783:
1746:
1694:
1684:
1651:
1622:
1593:
1591:
1568:J. Geophys. Res.
1557:
1528:
1491:
1447:
1418:
1416:
1383:
1354:
1343:10.1038/285652a0
1306:
1305:
1303:
1271:
1265:
1264:
1228:
1171:
1170:
1142:
1133:
1132:
1130:
1129:
1120:. Archived from
1089:
1083:
1082:
1071:10.1038/285652a0
1044:
1038:
1037:
1005:
999:
998:
962:
956:
955:
953:
921:
915:
914:
912:
889:J. Geophys. Res.
879:
870:
869:
841:
835:
834:
806:
797:
796:
768:
755:
754:
738:
732:
731:
729:
727:
692:
686:
685:
675:
643:
626:
625:
597:
584:
583:
581:
549:
104:mid-ocean ridges
57:tensional forces
39:, found at some
3215:
3214:
3210:
3209:
3208:
3206:
3205:
3204:
3195:Plate tectonics
3185:Back-arc basins
3175:
3174:
3173:
3168:
3156:
3128:
2967:
2941:
2903:
2884:Sea-level curve
2855:
2794:
2780:Transform fault
2730:Mid-ocean ridge
2696:
2689:
2655:Oceanic plateau
2561:
2547:Tidal resonance
2517:Theory of tides
2458:
2367:Longshore drift
2317:Ekman transport
2253:
2247:
2246:
2245:
2244:
2243:
2242:
2233:
2185:Wave turbulence
2118:Trochoidal wave
2043:Longshore drift
1939:
1934:
1896:
1534:J. Geophys. Res
1315:
1310:
1309:
1272:
1268:
1229:
1174:
1143:
1136:
1127:
1125:
1098:J. Geophys. Res
1090:
1086:
1045:
1041:
1036:. 2000GC000106.
1006:
1002:
963:
959:
922:
918:
880:
873:
842:
838:
807:
800:
769:
758:
739:
735:
725:
723:
693:
689:
644:
629:
598:
587:
550:
537:
532:
524:Intra-arc basin
514:Back-arc region
510:
500:student at the
493:
430:
394:sponge spicules
374:montmorillonite
335:Bouma sequences
325:, slump folds,
250:
221:(also known as
218:trench rollback
204:
154:
148:
138:and associated
117:
113:
82:
65:plate tectonics
17:
12:
11:
5:
3213:
3203:
3202:
3197:
3192:
3190:Marine geology
3187:
3170:
3169:
3167:
3166:
3154:
3144:
3133:
3130:
3129:
3127:
3126:
3121:
3116:
3111:
3106:
3104:Stratification
3101:
3096:
3091:
3086:
3081:
3076:
3075:
3074:
3064:
3059:
3054:
3049:
3044:
3039:
3034:
3029:
3024:
3019:
3014:
3009:
3004:
2996:
2994:Color of water
2991:
2989:Benthic lander
2986:
2981:
2975:
2973:
2969:
2968:
2966:
2965:
2960:
2955:
2949:
2947:
2943:
2942:
2940:
2939:
2934:
2929:
2924:
2919:
2913:
2911:
2905:
2904:
2902:
2901:
2896:
2894:Sea level rise
2891:
2889:Sea level drop
2886:
2881:
2876:
2871:
2865:
2863:
2857:
2856:
2854:
2853:
2848:
2843:
2838:
2833:
2828:
2823:
2818:
2813:
2808:
2802:
2800:
2796:
2795:
2793:
2792:
2787:
2782:
2777:
2772:
2767:
2762:
2757:
2752:
2747:
2742:
2737:
2732:
2727:
2725:Marine geology
2722:
2717:
2712:
2707:
2701:
2699:
2691:
2690:
2688:
2687:
2682:
2677:
2672:
2667:
2665:Passive margin
2662:
2660:Oceanic trench
2657:
2652:
2647:
2642:
2637:
2632:
2627:
2622:
2617:
2612:
2607:
2602:
2597:
2592:
2587:
2582:
2577:
2571:
2569:
2563:
2562:
2560:
2559:
2554:
2549:
2544:
2539:
2534:
2529:
2524:
2519:
2514:
2509:
2504:
2499:
2494:
2489:
2484:
2479:
2474:
2468:
2466:
2460:
2459:
2457:
2456:
2451:
2446:
2441:
2436:
2435:
2434:
2424:
2419:
2414:
2409:
2404:
2399:
2394:
2392:Ocean dynamics
2389:
2384:
2379:
2374:
2369:
2364:
2359:
2354:
2349:
2344:
2339:
2334:
2329:
2324:
2319:
2314:
2309:
2304:
2299:
2294:
2289:
2284:
2282:Coriolis force
2279:
2274:
2269:
2263:
2261:
2255:
2254:
2236:
2234:
2232:
2231:
2230:
2229:
2219:
2214:
2209:
2208:
2207:
2202:
2192:
2187:
2182:
2177:
2172:
2167:
2162:
2157:
2152:
2147:
2142:
2137:
2132:
2131:
2130:
2120:
2115:
2110:
2105:
2103:Stokes problem
2100:
2095:
2090:
2085:
2080:
2075:
2070:
2065:
2060:
2055:
2050:
2045:
2040:
2038:Kinematic wave
2035:
2030:
2025:
2020:
2015:
2010:
2005:
2000:
1995:
1990:
1985:
1980:
1975:
1970:
1965:
1960:
1955:
1949:
1947:
1941:
1940:
1933:
1932:
1925:
1918:
1910:
1904:
1903:
1895:
1894:External links
1892:
1891:
1890:
1861:
1826:
1784:
1758:(1): 381–406.
1747:
1729:(1–2): 35–40.
1718:
1695:
1652:
1634:(5): 470–473.
1623:
1605:(3): 330–340.
1594:
1558:
1529:
1517:10.1086/628916
1492:
1474:(2): 239–254.
1463:
1448:
1419:
1399:(1): 163–200.
1384:
1355:
1314:
1311:
1308:
1307:
1266:
1253:10.1086/628916
1172:
1153:(3): 330–340.
1134:
1084:
1039:
1000:
981:(5): 470–473.
957:
916:
871:
836:
798:
779:(1–2): 35–40.
756:
733:
707:(1–2): 35–40.
687:
627:
608:(2): 239–254.
585:
564:(4): 163–200.
534:
533:
531:
528:
527:
526:
521:
516:
509:
506:
497:plate tectonic
492:
489:
462:Tyrrhenian Sea
446:Kermadec-Tonga
429:
426:
370:volcanic glass
331:graded bedding
296:sandstone and
249:
246:
223:hinge rollback
203:
200:
147:
144:
140:chemosynthetic
124:eclogitization
115:
111:
108:magmatic water
92:Mariana Trough
81:
78:
33:back-arc basin
15:
9:
6:
4:
3:
2:
3212:
3201:
3200:Sedimentology
3198:
3196:
3193:
3191:
3188:
3186:
3183:
3182:
3180:
3165:
3160:
3155:
3153:
3145:
3143:
3135:
3134:
3131:
3125:
3122:
3120:
3117:
3115:
3112:
3110:
3107:
3105:
3102:
3100:
3097:
3095:
3092:
3090:
3087:
3085:
3082:
3080:
3077:
3073:
3070:
3069:
3068:
3065:
3063:
3060:
3058:
3055:
3053:
3050:
3048:
3045:
3043:
3040:
3038:
3035:
3033:
3030:
3028:
3025:
3023:
3020:
3018:
3015:
3013:
3012:Marine energy
3010:
3008:
3005:
3003:
3002:
2997:
2995:
2992:
2990:
2987:
2985:
2982:
2980:
2979:Acidification
2977:
2976:
2974:
2970:
2964:
2961:
2959:
2956:
2954:
2951:
2950:
2948:
2944:
2938:
2935:
2933:
2932:SOFAR channel
2930:
2928:
2925:
2923:
2920:
2918:
2915:
2914:
2912:
2910:
2906:
2900:
2897:
2895:
2892:
2890:
2887:
2885:
2882:
2880:
2877:
2875:
2872:
2870:
2867:
2866:
2864:
2862:
2858:
2852:
2849:
2847:
2844:
2842:
2839:
2837:
2834:
2832:
2829:
2827:
2824:
2822:
2819:
2817:
2814:
2812:
2809:
2807:
2804:
2803:
2801:
2797:
2791:
2788:
2786:
2783:
2781:
2778:
2776:
2773:
2771:
2768:
2766:
2763:
2761:
2758:
2756:
2753:
2751:
2748:
2746:
2743:
2741:
2740:Oceanic crust
2738:
2736:
2733:
2731:
2728:
2726:
2723:
2721:
2718:
2716:
2715:Fracture zone
2713:
2711:
2708:
2706:
2703:
2702:
2700:
2698:
2692:
2686:
2683:
2681:
2678:
2676:
2673:
2671:
2668:
2666:
2663:
2661:
2658:
2656:
2653:
2651:
2650:Oceanic basin
2648:
2646:
2643:
2641:
2638:
2636:
2633:
2631:
2628:
2626:
2623:
2621:
2618:
2616:
2613:
2611:
2608:
2606:
2603:
2601:
2598:
2596:
2593:
2591:
2588:
2586:
2583:
2581:
2580:Abyssal plain
2578:
2576:
2573:
2572:
2570:
2568:
2564:
2558:
2555:
2553:
2550:
2548:
2545:
2543:
2540:
2538:
2535:
2533:
2530:
2528:
2525:
2523:
2520:
2518:
2515:
2513:
2510:
2508:
2505:
2503:
2500:
2498:
2495:
2493:
2490:
2488:
2487:Internal tide
2485:
2483:
2480:
2478:
2475:
2473:
2470:
2469:
2467:
2465:
2461:
2455:
2452:
2450:
2447:
2445:
2442:
2440:
2437:
2433:
2430:
2429:
2428:
2425:
2423:
2420:
2418:
2415:
2413:
2410:
2408:
2405:
2403:
2400:
2398:
2395:
2393:
2390:
2388:
2385:
2383:
2382:Ocean current
2380:
2378:
2375:
2373:
2370:
2368:
2365:
2363:
2360:
2358:
2355:
2353:
2350:
2348:
2345:
2343:
2340:
2338:
2335:
2333:
2330:
2328:
2325:
2323:
2320:
2318:
2315:
2313:
2310:
2308:
2305:
2303:
2300:
2298:
2295:
2293:
2290:
2288:
2285:
2283:
2280:
2278:
2275:
2273:
2270:
2268:
2265:
2264:
2262:
2260:
2256:
2251:
2240:
2228:
2225:
2224:
2223:
2220:
2218:
2215:
2213:
2210:
2206:
2203:
2201:
2198:
2197:
2196:
2193:
2191:
2188:
2186:
2183:
2181:
2180:Wave shoaling
2178:
2176:
2173:
2171:
2168:
2166:
2163:
2161:
2158:
2156:
2153:
2151:
2148:
2146:
2143:
2141:
2140:Ursell number
2138:
2136:
2133:
2129:
2126:
2125:
2124:
2121:
2119:
2116:
2114:
2111:
2109:
2106:
2104:
2101:
2099:
2096:
2094:
2091:
2089:
2086:
2084:
2081:
2079:
2076:
2074:
2071:
2069:
2066:
2064:
2061:
2059:
2056:
2054:
2051:
2049:
2046:
2044:
2041:
2039:
2036:
2034:
2031:
2029:
2026:
2024:
2023:Internal wave
2021:
2019:
2016:
2014:
2011:
2009:
2006:
2004:
2001:
1999:
1996:
1994:
1991:
1989:
1986:
1984:
1981:
1979:
1976:
1974:
1973:Breaking wave
1971:
1969:
1966:
1964:
1961:
1959:
1956:
1954:
1951:
1950:
1948:
1946:
1942:
1938:
1931:
1926:
1924:
1919:
1917:
1912:
1911:
1908:
1901:
1898:
1897:
1887:
1883:
1879:
1875:
1871:
1867:
1862:
1857:
1852:
1848:
1844:
1840:
1836:
1832:
1827:
1822:
1817:
1813:
1809:
1805:
1801:
1797:
1793:
1789:
1785:
1781:
1777:
1773:
1769:
1765:
1761:
1757:
1753:
1748:
1744:
1740:
1736:
1732:
1728:
1724:
1719:
1716:
1712:
1708:
1707:9780306449376
1704:
1700:
1696:
1692:
1688:
1683:
1678:
1674:
1670:
1666:
1662:
1658:
1653:
1649:
1645:
1641:
1637:
1633:
1629:
1624:
1620:
1616:
1612:
1608:
1604:
1600:
1595:
1590:
1585:
1581:
1577:
1573:
1570:
1569:
1564:
1559:
1555:
1551:
1547:
1543:
1539:
1535:
1530:
1526:
1522:
1518:
1514:
1510:
1506:
1502:
1498:
1493:
1489:
1485:
1481:
1477:
1473:
1469:
1464:
1461:
1457:
1453:
1449:
1445:
1441:
1437:
1433:
1429:
1425:
1420:
1415:
1410:
1406:
1402:
1398:
1394:
1390:
1385:
1381:
1377:
1373:
1369:
1365:
1361:
1356:
1352:
1348:
1344:
1340:
1336:
1332:
1328:
1324:
1323:
1317:
1316:
1302:
1297:
1293:
1289:
1285:
1281:
1277:
1270:
1262:
1258:
1254:
1250:
1246:
1242:
1238:
1234:
1227:
1225:
1223:
1221:
1219:
1217:
1215:
1213:
1211:
1209:
1207:
1205:
1203:
1201:
1199:
1197:
1195:
1193:
1191:
1189:
1187:
1185:
1183:
1181:
1179:
1177:
1168:
1164:
1160:
1156:
1152:
1148:
1141:
1139:
1124:on 2011-08-27
1123:
1119:
1115:
1111:
1107:
1103:
1099:
1095:
1088:
1080:
1076:
1072:
1068:
1064:
1060:
1056:
1052:
1051:
1043:
1035:
1031:
1027:
1023:
1019:
1015:
1011:
1004:
996:
992:
988:
984:
980:
976:
972:
968:
961:
952:
947:
943:
939:
935:
931:
927:
920:
911:
906:
902:
898:
894:
891:
890:
885:
878:
876:
867:
863:
859:
855:
851:
847:
840:
832:
828:
824:
820:
816:
812:
805:
803:
794:
790:
786:
782:
778:
774:
767:
765:
763:
761:
752:
748:
744:
737:
722:
718:
714:
710:
706:
702:
698:
691:
683:
679:
674:
669:
665:
661:
658:(4): Q04016.
657:
653:
649:
642:
640:
638:
636:
634:
632:
623:
619:
615:
611:
607:
603:
596:
594:
592:
590:
580:
575:
571:
567:
563:
559:
555:
548:
546:
544:
542:
540:
535:
525:
522:
520:
519:Forearc basin
517:
515:
512:
511:
505:
503:
498:
488:
486:
482:
478:
473:
471:
467:
463:
459:
455:
451:
447:
443:
434:
425:
423:
419:
415:
410:
406:
401:
399:
395:
391:
387:
383:
379:
375:
371:
367:
363:
359:
355:
351:
347:
346:Pelagic clays
343:
340:
336:
332:
328:
324:
320:
315:
311:
307:
303:
299:
295:
291:
290:Submarine fan
287:
285:
282:
278:
274:
270:
266:
262:
261:conglomerates
258:
254:
253:Sedimentation
248:Sedimentation
245:
243:
239:
234:
230:
228:
227:hinge retreat
224:
220:
219:
214:
209:
208:asthenosphere
199:
197:
191:
183:
179:
175:
172:
167:
163:
159:
153:
143:
142:communities.
141:
137:
133:
129:
125:
121:
109:
105:
101:
97:
93:
88:
72:
68:
66:
62:
58:
54:
53:Pacific Ocean
50:
46:
42:
38:
34:
26:
21:
3119:Water column
3067:Oceanography
3042:Observations
3037:Explorations
3007:Marginal sea
3000:
2958:OSTM/Jason-2
2790:Volcanic arc
2765:Slab suction
2482:Head of tide
2372:Loop Current
2312:Ekman spiral
2098:Stokes drift
2008:Gravity wave
1983:Cnoidal wave
1869:
1865:
1838:
1834:
1803:
1799:
1792:Ellis, Susan
1755:
1751:
1726:
1722:
1698:
1664:
1660:
1631:
1627:
1602:
1598:
1571:
1566:
1537:
1533:
1500:
1496:
1471:
1467:
1451:
1427:
1424:GSA Bulletin
1423:
1396:
1392:
1366:(10): 8622.
1363:
1359:
1326:
1320:
1283:
1279:
1269:
1236:
1232:
1150:
1146:
1126:. Retrieved
1122:the original
1101:
1097:
1087:
1054:
1048:
1042:
1017:
1013:
1003:
978:
974:
960:
933:
929:
919:
892:
887:
852:(10): 8622.
849:
845:
839:
814:
811:GSA Bulletin
810:
776:
772:
742:
736:
724:. Retrieved
704:
700:
690:
655:
651:
605:
601:
561:
557:
494:
477:Sea of Japan
474:
450:South Scotia
439:
414:volcanic ash
402:
350:micronodules
344:
288:
251:
235:
231:
226:
222:
216:
205:
196:mantle wedge
192:
188:
176:
156:Evidence of
155:
120:mantle wedge
83:
32:
30:
3109:Thermocline
2826:Mesopelagic
2799:Ocean zones
2770:Slab window
2635:Hydrography
2575:Abyssal fan
2542:Tidal range
2532:Tidal power
2527:Tidal force
2412:Rip current
2347:Gulf Stream
2307:Ekman layer
2297:Downwelling
2272:Baroclinity
2259:Circulation
2155:Wave height
2145:Wave action
2128:megatsunami
2108:Stokes wave
2068:Rossby wave
2033:Kelvin wave
2013:Green's law
1872:(5): 1020.
1841:(9): 1075.
1667:(4): 1–40.
1503:(1): 1–25.
1454:. 599–620.
1239:(1): 1–25.
1020:(5): 1020.
936:(9): 1075.
726:26 December
358:plagioclase
319:load clasts
275:fragments,
238:lithosphere
45:island arcs
3179:Categories
3047:Reanalysis
2946:Satellites
2927:Sofar bomb
2775:Subduction
2750:Ridge push
2645:Ocean bank
2625:Contourite
2552:Tide gauge
2537:Tidal race
2522:Tidal bore
2512:Slack tide
2477:Earth tide
2397:Ocean gyre
2217:Wind setup
2212:Wind fetch
2175:Wave setup
2170:Wave radar
2165:Wave power
2063:Rogue wave
1993:Dispersion
1806:(5): n/a.
1752:GeoJournal
1286:(5): n/a.
1128:2010-05-08
485:Swiss Alps
458:North Fiji
409:carbonates
362:orthoclase
339:siltstones
128:amphiboles
49:subduction
2909:Acoustics
2861:Sea level
2760:Slab pull
2697:tectonics
2605:Cold seep
2567:Landforms
2444:Whirlpool
2439:Upwelling
2222:Wind wave
2150:Wave base
2078:Sea state
1998:Edge wave
1988:Cross sea
1780:128986436
1691:129068818
1525:129527339
1280:Tectonics
1261:129527339
682:129068818
530:Citations
428:Locations
366:magnetite
302:lithology
294:turbidite
281:sandstone
273:limestone
242:adiabatic
96:Lau Basin
3142:Category
3094:Seawater
2821:Littoral
2816:Deep sea
2675:Seamount
2557:Tideline
2502:Rip tide
2432:shutdown
2402:Overflow
2135:Undertow
1978:Clapotis
1715:32464941
508:See also
483:and the
481:Pyrenees
442:Marianas
382:smectite
321:, micro-
298:mudstone
265:granules
166:sediment
3152:Commons
3022:Mooring
2972:Related
2963:Jason-3
2953:Jason-1
2836:Pelagic
2831:Oceanic
2806:Benthic
2123:Tsunami
2093:Soliton
1874:Bibcode
1843:Bibcode
1808:Bibcode
1760:Bibcode
1731:Bibcode
1669:Bibcode
1636:Bibcode
1628:Geology
1607:Bibcode
1576:Bibcode
1542:Bibcode
1505:Bibcode
1476:Bibcode
1432:Bibcode
1401:Bibcode
1368:Bibcode
1351:4233630
1331:Bibcode
1288:Bibcode
1241:Bibcode
1155:Bibcode
1106:Bibcode
1079:4233630
1059:Bibcode
1022:Bibcode
983:Bibcode
975:Geology
938:Bibcode
897:Bibcode
854:Bibcode
819:Bibcode
781:Bibcode
709:Bibcode
660:Bibcode
610:Bibcode
566:Bibcode
390:diatoms
314:bedding
306:texture
269:cobbles
100:basalts
2841:Photic
2670:Seabed
2083:Seiche
1778:
1713:
1705:
1689:
1523:
1460:881288
1458:
1349:
1322:Nature
1259:
1077:
1050:Nature
751:881288
749:
680:
460:, and
422:pyrite
392:, and
378:illite
354:quartz
323:faults
312:, and
284:clasts
3032:Ocean
3001:Alvin
2851:Swash
2695:Plate
2640:Knoll
2630:Guyot
2585:Atoll
2464:Tides
2227:model
2113:Swell
1945:Waves
1776:S2CID
1687:S2CID
1521:S2CID
1347:S2CID
1257:S2CID
1075:S2CID
678:S2CID
466:Andes
454:Manus
277:chert
162:cores
132:micas
87:crust
37:basin
2999:DSV
2984:Argo
2846:Surf
2302:Eddy
1711:OCLC
1703:ISBN
1456:OCLC
747:OCLC
728:2016
418:tuff
213:rift
130:and
47:and
1882:doi
1851:doi
1816:doi
1768:doi
1739:doi
1727:144
1677:doi
1644:doi
1615:doi
1584:doi
1572:105
1550:doi
1538:100
1513:doi
1484:doi
1440:doi
1409:doi
1376:doi
1339:doi
1327:285
1296:doi
1249:doi
1163:doi
1114:doi
1102:100
1067:doi
1055:285
1030:doi
991:doi
946:doi
905:doi
893:105
862:doi
827:doi
789:doi
777:144
717:doi
705:144
668:doi
618:doi
574:doi
472:.
267:to
225:or
126:of
3181::
1880:.
1868:.
1849:.
1837:.
1833:.
1814:.
1804:10
1802:.
1798:.
1790:;
1774:.
1766:.
1754:.
1737:.
1725:.
1709:.
1685:.
1675:.
1663:.
1659:.
1642:.
1632:18
1630:.
1613:.
1603:41
1601:.
1582:.
1565:.
1548:.
1536:.
1519:.
1511:.
1501:93
1499:.
1482:.
1472:75
1470:.
1438:.
1428:87
1426:.
1407:.
1397:43
1395:.
1391:.
1374:.
1362:.
1345:.
1337:.
1325:.
1294:.
1284:30
1282:.
1278:.
1255:.
1247:.
1237:93
1235:.
1175:^
1161:.
1151:41
1149:.
1137:^
1112:.
1100:.
1096:.
1073:.
1065:.
1053:.
1028:.
1016:.
1012:.
989:.
979:18
977:.
973:.
944:.
932:.
928:.
903:.
886:.
874:^
860:.
848:.
825:.
815:87
813:.
801:^
787:.
775:.
759:^
715:.
703:.
699:.
676:.
666:.
654:.
650:.
630:^
616:.
606:75
604:.
588:^
572:.
560:.
556:.
538:^
487:.
456:,
452:,
448:,
444:,
416:,
388:,
384:,
380:,
376:,
372:,
368:,
364:,
360:,
356:,
352:,
308:,
304:,
286:.
31:A
1929:e
1922:t
1915:v
1888:.
1884::
1876::
1870:2
1859:.
1853::
1845::
1839:4
1824:.
1818::
1810::
1782:.
1770::
1762::
1756:8
1745:.
1741::
1733::
1717:.
1693:.
1679::
1671::
1665:7
1650:.
1646::
1638::
1621:.
1617::
1609::
1592:.
1586::
1578::
1556:.
1552::
1544::
1527:.
1515::
1507::
1490:.
1486::
1478::
1462:.
1446:.
1442::
1434::
1417:.
1411::
1403::
1382:.
1378::
1370::
1364:4
1353:.
1341::
1333::
1304:.
1298::
1290::
1263:.
1251::
1243::
1169:.
1165::
1157::
1131:.
1116::
1108::
1081:.
1069::
1061::
1032::
1024::
1018:2
997:.
993::
985::
954:.
948::
940::
934:4
913:.
907::
899::
868:.
864::
856::
850:4
833:.
829::
821::
795:.
791::
783::
753:.
730:.
719::
711::
684:.
670::
662::
656:7
624:.
620::
612::
582:.
576::
568::
562:7
116:2
112:2
27:.
Text is available under the Creative Commons Attribution-ShareAlike License. Additional terms may apply.