151:
highlight safety and efficacy of aDBS vs cDBS using this a new generation of DBS IPG in PD (AlphaDBS system by
Newronika SpA, Milan, Italy). The Medtronic PC+S device was also developed in a commercial IPG allowing stimulation and sensing, the Percept PC, which is approved for aDBS delivery in Japan. Nobutaka Hattori and the group performed a research study, focused on exploring the case of a 51-year-old man with Parkinson's disease (PD) presenting with motor fluctuations, who received bilateral subthalamic deep brain stimulation (DBS) the Percept PC device, showing the feasibility of the approach. While these new devices seem to have various applications in terms of facilitating condition-dependent stimulation, and providing new insights into the pathophysiological mechanisms of PD, they are currently under investigation in larger clinical studies, to definitely allow their use in clinical practice
230:
safety and effectiveness of aDBS stimulation compared to cDBS in a daily session, both in terms of motor performance and TEED to the patient. Simon Little has regarded aDBS approach to be superior to conventional DBS in PD in primates using cortical neuronal spike triggering and in humans employing local field potential biomarkers. While presenting a protocol for a pseudo-randomised clinical study for adaptive deep brain stimulation as advanced
Parkinson's disease treatment, it was shown that aDBS do not induce dysarthria, in contrast to cDBS. Also it has been suggested that aDBS and cDBS can improve patient's axial symptoms to a similar extent, but compared with cDBS, aDBS significantly improves its main symptom, bradykinesia.
203:. A 2017 research study presented a review on the available literature supporting the feasibility of an LFP-based aDBS approach in patients with TS. In addition to that, researchers have put forward several explorative findings regarding LFP data recently acquired and analysed in patients with TS after DBS electrode implantation at rest, during voluntary and involuntary movements (tics), and during ongoing DBS. It was found out that LFPs recorded from DBS targets can be used to control new aDBS devices capable of adaptive stimulation responsive to the symptoms of TS.
143:, in a public-private partnership with Medtronic. The researchers inserted the device into two patients with Parkinson's disease who had traditional DBS but continued to experience dyskinesia after adjustment by a neurologist. Later on, they compared the results of the adaptive stimulation system with traditional stimulation set manually on two patients, and found that the adaptive approach was as effective at controlling symptoms as constant stimulation. The AlphaDBS implantable system by Newronika was developed and
20:
212:
characteristics of pallidal low-frequency and beta bursts can be helpful in implementing adaptive brain stimulation in the context of parkinsonian and dystonic internal globus pallidus. A significant amount of scientific research to date on pathological oscillations in dystonia has been focused to address potential biomarkers that might be used as a feedback signal for controlling aDBS in patients with dystonia.
138:
published the architecture of an implantable aDBS device for application in humans. This design was embedded in
Medtronic's Activa PC + S research device, allowing LFP sensing and recording while delivering targeted DBS therapy. This device was used in 2018 by a research team led by Philip A. Starr
229:
In a 2021 research study conducted by
Alberto Priori, a comparative analysis was presented between the impacts on motor symptoms between conventional deep brain stimulation (cDBS) and closed-loop adaptive deep brain stimulation (aDBS) in patients with Parkinson's disease. This work highlighted the
167:(STN), on account of which it has the capability to change the current depending on the strength of the beta band oscillation, and can, therefore, overcome conventional DBS (cDBS) therapy limitations, including stimulation-induced long term side effects, such as dyskinesia or speech deterioration.
211:
The applications of aDBS in the treatment of dystonia have significantly evolved over the past few years. Low-frequency oscillations (LFO) detected in the internal globus pallidus of dystonia patients have been identified as a physiomarker for adaptive Deep Brain
Stimulation (aDBS). Moreover, the
121:
Keeping in view this unwanted side effect of DBS, concepts that have the capability to sense brain activity and automatically adjust the stimulation in response to fluctuating biomarkers, were re-introduced by multiple teams, with a first peer-reviewed publication in modern times by the teams of
220:
Adaptive deep brain stimulation (aDBS) may be an effective tool in the treatment of essential tremor (ET), which is one of the most common neurological movement disorders. aDBS for ET is however more focused on a closed-loop technology based on external sensors. In a recent study, H J Chizeck
150:
The AlphaDBS represents a new generation commercially available DBS implantable pulse generator (IPG) for DBS and sensing, with aDBS capabilities. A systematic multicentre international study consisted of six investigational sites (in Italy, Poland and The
Netherlands) was also conducted to
56:
based on what the patient is doing and the medication they take over time to optimize the patient's symptoms. However, it can lead to side effects. aDBS and differs from conventional DBS systems (that provide constant stimulation) in that it can both sense the brain activity and deliver the
1051:
Arlotti, Mattia; Colombo, Matteo; Bonfanti, Andrea; Mandat, Tomasz; Lanotte, Michele Maria; Pirola, Elena; Borellini, Linda; Rampini, Paolo; Eleopra, Roberto; Rinaldo, Sara; Romito, Luigi; Janssen, Marcus L. F.; Priori, Alberto; Marceglia, Sara (November 18, 2021).
1206:
Little, Simon; Tripoliti, Elina; Beudel, Martijn; Pogosyan, Alek; Cagnan, Hayriye; Herz, Damian; Bestmann, Sven; Aziz, Tipu; Cheeran, Binith; Zrinzo, Ludvic; Hariz, Marwan; Hyam, Jonathan; Limousin, Patricia; Foltynie, Tom; Brown, Peter (December 18, 2016).
1256:
Bocci, T.; Arlotti, M.; Marceglia, S.; Prenassi, M.; Ardolino, G.; Cogiamanian, F.; Borrellini, L.; Rampini, P.; Locatelli, M.; Barbieri, S.; Priori, A. (January 2019). "Adaptive Deep Brain
Stimulation for Parkinson's disease: Safety and effectiveness".
247:
Marceglia, Sara; Guidetti, Matteo; Harmsen, Irene E; Loh, Aaron; Meoni, Sara; Foffani, Guglielmo; Lozano, Andres M; Volkmann, Jens; Moro, Elena; Priori, Alberto (December 2021). "Deep brain stimulation: is it time to change gears by closing the loop?".
788:
Arlotti, Mattia; Marceglia, Sara; Foffani, Guglielmo; Volkmann, Jens; Lozano, Andres M.; Moro, Elena; Cogiamanian, Filippo; Prenassi, Marco; Bocci, Tommaso; Cortese, Francesca; Rampini, Paolo; Barbieri, Sergio; Priori, Alberto (March 13, 2018).
130:
in the same year. The study, followed by others testing more patients in longer time windows (up to 24 hours) supported the hypothesis that aDBS is effective in controlling PD symptoms while reducing side effects of constant stimulation.
605:
Little, Simon; Pogosyan, Alex; Neal, Spencer; Zavala, Baltazar; Zrinzo, Ludvic; Hariz, Marwan; Foltynie, Thomas; Limousin, Patricia; Ashkan, Keyoumars; FitzGerald, James; Green, Alexander L.; Aziz, Tipu Z.; Brown, Peter (September 2013).
838:
Rosa, Manuela; Arlotti, Mattia; Marceglia, Sara; Cogiamanian, Filippo; Ardolino, Gianluca; Fonzo, Alessio Di; Lopiano, Leonardo; Scelzo, Emma; Merola, Aristide; Locatelli, Marco; Rampini, Paolo M.; Priori, Alberto (April 18, 2017).
163:(LFP) of the target structure recorded through the implanted electrodes that deliver stimulation. The present application of adaptive DBS (aDBS) technique is primarily based on the detection of increased beta oscillations in the
566:
Rosin, Boris; Slovik, Maya; Mitelman, Rea; Rivlin-Etzion, Michal; Haber, Suzanne N.; Israel, Zvi; Vaadia, Eilon; Bergman, Hagai (October 2011). "Closed-Loop Deep Brain
Stimulation Is Superior in Ameliorating Parkinsonism".
1392:
Fra̧czek, Tomasz M.; Ferleger, Benjamin I.; Brown, Timothy E.; Thompson, Margaret C.; Haddock, Andrew J.; Houston, Brady C.; Ojemann, Jeffrey G.; Ko, Andrew L.; Herron, Jeffrey A.; Chizeck, Howard J. (November 18, 2021).
77:
long before the advent of 'modern' DBS. Perhaps the earliest closed-loop experiment in an animal model was performed by
Delgado and colleagues in 1969. In the modern era of DBS following the introduction of the method by
118:. However, the working mechanism of conventional DBS involved the continuous stimulation of the target structure, which is an approach that cannot adapt to patients' changing symptoms or functional status in real-time.
312:
Bocci, Tommaso; Prenassi, Marco; Arlotti, Mattia; Cogiamanian, Filippo Maria; Borellini, Linda; Moro, Elena; Lozano, Andres M.; Volkmann, Jens; Barbieri, Sergio; Priori, Alberto; Marceglia, Sara (September 28, 2021).
1485:
Ferleger, B I; Houston, B; Thompson, M C; Cooper, S S; Sonnet, K S; Ko, A L; Herron, J A; Chizeck, H J (October 2020). "Fully implanted adaptive deep brain stimulation in freely moving essential tremor patients".
473:
Bechtereva, N.P.; Bondartchuk, A.N.; Smirnov, V.M.; Meliutcheva, L.A.; Shandurina, A.N. (1975). "Method of
Electrostimulation of the Deep Brain Structures in Treatment of Some Chronic Diseases".
994:
Swann, Nicole C.; de Hemptinne, Coralie; Thompson, Margaret C.; Miocinovic, Svjetlana; Miller, Andrew M.; Gilron, Ro'ee; Ostrem, Jill L.; Chizeck, Howard J.; Starr, Philip A. (August 18, 2018).
187:(LFPs) as target to adapt DBS parameters to motor fluctuations. Results of the experiments proved that aDBS is highly effective in controlling the patients PD symptoms in addition to the normal
888:
Prenassi, Marco; Arlotti, Mattia; Borellini, Linda; Bocci, Tommaso; Cogiamanian, Filippo; Locatelli, Marco; Rampini, Paolo; Barbieri, Sergio; Priori, Alberto; Marceglia, Sara (May 31, 2021).
726:
Guidetti, Matteo; Marceglia, Sara; Loh, Aaron; Harmsen, Irene E.; Meoni, Sara; Foffani, Guglielmo; Lozano, Andres M.; Moro, Elena; Volkmann, Jens; Priori, Alberto (September 1, 2021).
1537:
Rosa, Manuela; Arlotti, Mattia; Ardolino, Gianluca; Cogiamanian, Filippo; Marceglia, Sara; Di Fonzo, Alessio; Cortese, Francesca; Rampini, Paolo M.; Priori, Alberto (June 18, 2015).
48:
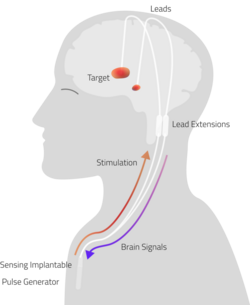
to regions of the brain that control movement through a surgically implanted wire, or lead, that is connected to an implantable pulse generator (IPG). Programming adjustments to the
890:"The Relationship Between Electrical Energy Delivered by Deep Brain Stimulation and Levodopa-Induced Dyskinesias in Parkinson's Disease: A Retrospective Preliminary Analysis"
658:
Priori, Alberto; Foffani, Guglielmo; Rossi, Lorenzo; Marceglia, Sara (July 2013). "Adaptive deep brain stimulation (aDBS) controlled by local field potential oscillations".
74:
958:
940:
184:
1343:
Molina, Rene; Okun, Michael S.; Shute, Jonathan B.; Opri, Enrico; Rossi, P. Justin; Martinez-Ramirez, Daniel; Foote, Kelly D.; Gunduz, Aysegul (August 18, 2018).
221:
presented the first translation-ready training procedure for a fully embedded aDBS control system for MDs and one of the first examples of such a system in ET.
1444:
Priori, Alberto; Maiorana, Natale; Dini, Michelangelo; Guidetti, Matteo; Marceglia, Sara; Ferrucci, Roberta (2021). "Adaptive deep brain stimulation (ADBS)".
1103:
Nakajima, Asuka; Shimo, Yasushi; Fuse, Atsuhito; Tokugawa, Joji; Hishii, Makoto; Iwamuro, Hirokazu; Umemura, Atsushi; Hattori, Nobutaka (November 18, 2021).
1209:"Adaptive deep brain stimulation for Parkinson's disease demonstrates reduced speech side effects compared to conventional stimulation in the acute setting"
175:
Adaptive Deep Brain Stimulation (aDBS) is a treatment modality that is being studied for the treatment of multiple neuropsychiatric and movement disorders.
188:
500:
134:
The device used in these studies was the external component of the AlphaDBS system developed by Newronika. While these advancements were ongoing,
403:
Delgado, J. M.; Johnston, V. S.; Wallace, J. D.; Bradley, R. J. (September 1969). "Operant conditioning of EEG in the unrestrained chimpanzee".
147:
in 2021. A systematic study was also conducted to highlight safety and efficacy of aDBS vs cDBS using this new generation of DBS IPG in PD.
1159:"Adaptive deep brain stimulation as advanced Parkinson's disease treatment (ADAPT study): protocol for a pseudo-randomised clinical study"
976:
1395:"Closing the Loop With Cortical Sensing: The Development of Adaptive Deep Brain Stimulation for Essential Tremor Using the Activa PC+S"
1292:
Marceglia, Sara; Rosa, Manuela; Servello, Domenico; Porta, Mauro; Barbieri, Sergio; Moro, Elena; Priori, Alberto (January 18, 2018).
140:
183:
Since 2015, several experiments were carried out to assess the efficacy of aDBS, that uses beta-band power of the subthalamic
1461:
710:
384:
86:
in 2011, the first in-human application of aDBS was carried out by the team of Peter Brown in 2013, followed by the team of
1157:
Piña-Fuentes, Dan; Beudel, Martijn; Little, Simon; Brown, Peter; Oterdoom, D L Marinus; van Dijk, J Marc C (June 2019).
62:
1607:
111:
315:"Eight-hours conventional versus adaptive deep brain stimulation of the subthalamic nucleus in Parkinson's disease"
1345:"Report of a patient undergoing chronic responsive deep brain stimulation for Tourette syndrome: proof of concept"
1602:
438:
Heath, Robert G.; Cox, Aris W.; Lustick, Leonard S. (August 1974). "Brain Activity During Emotional States".
365:
Beudel, Martijn; Cagnan, Hayriye; Little, Simon (2018). "Adaptive Brain Stimulation for Movement Disorders".
199:
Adaptive deep brain stimulation (aDBS) is currently being studied to be used as a potential treatment for
1105:"Case Report: Chronic Adaptive Deep Brain Stimulation Personalizing Therapy Based on Parkinsonian State"
38:
1612:
1597:
1152:
1150:
1054:"A New Implantable Closed-Loop Clinical Neural Interface: First Application in Parkinson's Disease"
1592:
841:"Adaptive deep brain stimulation controls levodopa-induced side effects in Parkinsonian patients"
1147:
103:
66:
58:
494:
160:
37:(clDBS), is a neuro-modulatory technique currently under investigation for the treatment of
1495:
1007:
257:
514:
Krook-Magnuson, Esther; Gelinas, Jennifer N.; Soltesz, Ivan; Buzsáki, György (July 2015).
8:
164:
45:
1499:
1011:
261:
1563:
1538:
1519:
1421:
1394:
1369:
1344:
1320:
1293:
1274:
1233:
1208:
1183:
1158:
1131:
1104:
1080:
1053:
1028:
995:
916:
889:
865:
840:
815:
790:
767:
693:
Speelman, J. D. Hans; Schuurman, Rick (2020). "The History of Deep Brain Stimulation".
632:
607:
540:
515:
339:
314:
291:
99:
79:
70:
1568:
1523:
1511:
1467:
1457:
1426:
1374:
1325:
1238:
1188:
1136:
1085:
1033:
921:
870:
820:
771:
759:
706:
675:
637:
584:
545:
455:
420:
416:
380:
344:
295:
283:
200:
1278:
996:"Adaptive deep brain stimulation for Parkinson's disease using motor cortex sensing"
671:
516:"Neuroelectronics and Biooptics: Closed-Loop Technologies in Neurological Disorders"
102:
in the 1980ies, DBS received recognition as a treatment method for tremor and later
1558:
1550:
1503:
1449:
1416:
1406:
1364:
1356:
1315:
1305:
1266:
1228:
1220:
1178:
1170:
1126:
1116:
1075:
1065:
1023:
1015:
911:
901:
860:
852:
810:
802:
749:
739:
698:
667:
627:
619:
576:
535:
527:
482:
447:
412:
372:
334:
326:
273:
265:
1446:
Emerging Horizons in Neuromodulation: New Frontiers in Brain and Spine Stimulation
366:
98:
After being developed in the 1950s, and modern versions introduced by the team of
19:
1270:
806:
580:
531:
159:
In order to adapt to the stimulation parameters, adaptive DBS (aDBS) employs the
49:
1174:
791:"Eight-hours adaptive deep brain stimulation in patients with Parkinson disease"
702:
1507:
1453:
1019:
330:
269:
127:
87:
16:
Neurosurgical treatment involving implantation of an 'adaptive neurostimularot'
1411:
1121:
1070:
906:
744:
727:
1586:
1224:
123:
83:
1360:
1310:
1572:
1515:
1471:
1430:
1378:
1329:
1242:
1192:
1140:
1089:
1037:
941:"Medtronic Trial Assessing Safety, Efficacy of New Parkinson's DBS Feature"
925:
874:
824:
763:
679:
641:
588:
549:
348:
287:
459:
451:
424:
82:, after a demonstration of efficacy of aDBS in the macaque by the team of
61:, closed loop applications were carried out by multiple pioneers, such as
1539:"Adaptive deep brain stimulation in a freely moving parkinsonian patient"
1448:. International Review of Neurobiology. Vol. 159. pp. 111–127.
53:
754:
472:
278:
144:
1554:
856:
623:
486:
376:
135:
371:. Progress in Neurological Surgery. Vol. 33. pp. 230–242.
57:
appropriate stimulation in real time. Of note, in the early days of
993:
513:
126:(in primates) and Peter Brown (in humans), followed by the team of
115:
107:
565:
837:
787:
608:"Adaptive deep brain stimulation in advanced Parkinson disease"
311:
1536:
1294:"Adaptive Deep Brain Stimulation (aDBS) for Tourette Syndrome"
1484:
1391:
1255:
1205:
1156:
887:
402:
1050:
725:
657:
246:
1443:
1291:
728:"Clinical perspectives of adaptive deep brain stimulation"
224:
1102:
977:"Adaptive deep brain stimulation for Parkinson's disease"
604:
28:
1342:
405:
Electroencephalography and Clinical Neurophysiology
1213:Journal of Neurology, Neurosurgery, and Psychiatry
959:"Deep Brain Stimulation Systems - Activa Platform"
695:Fundamentals and Clinics of Deep Brain Stimulation
364:
692:
93:
1584:
368:Current Concepts in Movement Disorder Management
437:
499:: CS1 maint: DOI inactive as of August 2024 (
178:
1562:
1420:
1410:
1368:
1319:
1309:
1232:
1182:
1130:
1120:
1079:
1069:
1027:
915:
905:
864:
814:
753:
743:
631:
539:
338:
277:
194:
938:
475:Stereotactic and Functional Neurosurgery
215:
18:
225:Comparison with conventional DBS (cDBS)
141:University of California, San Francisco
1585:
783:
781:
154:
653:
651:
360:
358:
307:
305:
600:
598:
561:
559:
398:
396:
52:are frequently made by the treating
1096:
981:National Institutes of Health (NIH)
939:Carvalho, Joana (18 January 2021).
778:
44:Conventional DBS delivers constant
13:
648:
355:
302:
35:Closed Loop Deep Brain stimulation
14:
1624:
595:
556:
393:
27:Adaptive Deep Brain Stimulation (
1530:
1478:
1437:
1385:
1336:
1285:
1249:
1199:
1109:Frontiers in Human Neuroscience
1044:
987:
969:
951:
932:
881:
831:
719:
686:
672:10.1016/j.expneurol.2012.09.013
507:
466:
440:American Journal of Psychiatry
431:
240:
170:
94:History in Parkinson's disease
1:
1488:Journal of Neural Engineering
1000:Journal of Neural Engineering
250:Journal of Neural Engineering
233:
112:obsessive–compulsive disorder
1271:10.1016/j.clinph.2018.09.098
807:10.1212/WNL.0000000000005121
581:10.1016/j.neuron.2011.08.023
532:10.1001/jamaneurol.2015.0608
417:10.1016/0013-4694(69)91347-9
7:
1175:10.1136/bmjopen-2019-029652
703:10.1007/978-3-030-36346-8_1
206:
10:
1629:
1454:10.1016/bs.irn.2021.06.006
331:10.1038/s41531-021-00229-z
39:neurodegenerative diseases
1412:10.3389/fnins.2021.749705
1399:Frontiers in Neuroscience
1122:10.3389/fnhum.2021.702961
1071:10.3389/fnins.2021.763235
1058:Frontiers in Neuroscience
907:10.3389/fneur.2021.643841
745:10.1016/j.brs.2021.07.063
75:Carl Wilhelm Sem-Jacobsen
1608:Neurosurgical procedures
1508:10.1088/1741-2552/abb416
1259:Clinical Neurophysiology
1225:10.1136/jnnp-2016-313518
1020:10.1088/1741-2552/aabc9b
270:10.1088/1741-2552/ac3267
191:, reducing dyskinesias.
179:Parkinson's disease (PD)
1361:10.3171/2017.6.JNS17626
1349:Journal of Neurosurgery
1311:10.3390/brainsci8010004
319:npj Parkinson's Disease
945:Parkinson's News Today
894:Frontiers in Neurology
660:Experimental Neurology
489:(inactive 2024-08-17).
195:Tourette syndrome (TS)
185:Local Field Potentials
59:Deep Brain Stimulation
46:electrical stimulation
23:
452:10.1176/ajp.131.8.858
216:Essential tremor (ET)
161:local field potential
22:
1603:Neurology procedures
1500:2020JNEng..17e6026F
1012:2018JNEng..15d6006S
612:Annals of Neurology
262:2021JNEng..18f1001M
165:subthalamic nucleus
155:Mechanism of action
104:Parkinson's disease
1543:Movement Disorders
845:Movement Disorders
100:Alim Louis Benabid
90:in the same year.
80:Alim Louis Benabid
71:Natalia Bechtereva
24:
1555:10.1002/mds.26241
1463:978-0-12-822298-0
1219:(12): 1388–1389.
857:10.1002/mds.26953
801:(11): e971–e976.
732:Brain Stimulation
712:978-3-030-36345-1
697:. pp. 3–13.
624:10.1002/ana.23951
487:10.1159/000102727
386:978-3-318-06201-4
377:10.1159/000481107
1620:
1577:
1576:
1566:
1549:(7): 1003–1005.
1534:
1528:
1527:
1482:
1476:
1475:
1441:
1435:
1434:
1424:
1414:
1389:
1383:
1382:
1372:
1340:
1334:
1333:
1323:
1313:
1289:
1283:
1282:
1253:
1247:
1246:
1236:
1203:
1197:
1196:
1186:
1154:
1145:
1144:
1134:
1124:
1100:
1094:
1093:
1083:
1073:
1048:
1042:
1041:
1031:
991:
985:
984:
973:
967:
966:
955:
949:
948:
936:
930:
929:
919:
909:
885:
879:
878:
868:
835:
829:
828:
818:
785:
776:
775:
757:
747:
738:(5): 1238–1247.
723:
717:
716:
690:
684:
683:
655:
646:
645:
635:
602:
593:
592:
563:
554:
553:
543:
511:
505:
504:
498:
490:
481:(1–3): 136–140.
470:
464:
463:
435:
429:
428:
400:
391:
390:
362:
353:
352:
342:
309:
300:
299:
281:
244:
189:Levodopa therapy
33:, also known as
30:
1628:
1627:
1623:
1622:
1621:
1619:
1618:
1617:
1613:Neurotechnology
1598:Medical devices
1583:
1582:
1581:
1580:
1535:
1531:
1483:
1479:
1464:
1442:
1438:
1390:
1386:
1341:
1337:
1290:
1286:
1254:
1250:
1204:
1200:
1155:
1148:
1101:
1097:
1049:
1045:
992:
988:
983:. June 4, 2018.
975:
974:
970:
957:
956:
952:
937:
933:
886:
882:
836:
832:
786:
779:
724:
720:
713:
691:
687:
656:
649:
603:
596:
564:
557:
512:
508:
492:
491:
471:
467:
436:
432:
401:
394:
387:
363:
356:
310:
303:
245:
241:
236:
227:
218:
209:
197:
181:
173:
157:
96:
50:pulse generator
17:
12:
11:
5:
1626:
1616:
1615:
1610:
1605:
1600:
1595:
1593:Electrotherapy
1579:
1578:
1529:
1477:
1462:
1436:
1384:
1355:(2): 308–314.
1335:
1298:Brain Sciences
1284:
1248:
1198:
1169:(6): e029652.
1146:
1095:
1043:
986:
968:
950:
931:
880:
851:(4): 628–629.
830:
777:
718:
711:
685:
647:
618:(3): 449–457.
594:
575:(2): 370–384.
555:
526:(7): 823–829.
520:JAMA Neurology
506:
465:
446:(8): 858–862.
430:
411:(7): 701–702.
392:
385:
354:
301:
238:
237:
235:
232:
226:
223:
217:
214:
208:
205:
196:
193:
180:
177:
172:
169:
156:
153:
128:Alberto Priori
95:
92:
88:Alberto Priori
15:
9:
6:
4:
3:
2:
1625:
1614:
1611:
1609:
1606:
1604:
1601:
1599:
1596:
1594:
1591:
1590:
1588:
1574:
1570:
1565:
1560:
1556:
1552:
1548:
1544:
1540:
1533:
1525:
1521:
1517:
1513:
1509:
1505:
1501:
1497:
1494:(5): 056026.
1493:
1489:
1481:
1473:
1469:
1465:
1459:
1455:
1451:
1447:
1440:
1432:
1428:
1423:
1418:
1413:
1408:
1404:
1400:
1396:
1388:
1380:
1376:
1371:
1366:
1362:
1358:
1354:
1350:
1346:
1339:
1331:
1327:
1322:
1317:
1312:
1307:
1303:
1299:
1295:
1288:
1280:
1276:
1272:
1268:
1264:
1260:
1252:
1244:
1240:
1235:
1230:
1226:
1222:
1218:
1214:
1210:
1202:
1194:
1190:
1185:
1180:
1176:
1172:
1168:
1164:
1160:
1153:
1151:
1142:
1138:
1133:
1128:
1123:
1118:
1114:
1110:
1106:
1099:
1091:
1087:
1082:
1077:
1072:
1067:
1063:
1059:
1055:
1047:
1039:
1035:
1030:
1025:
1021:
1017:
1013:
1009:
1006:(4): 046006.
1005:
1001:
997:
990:
982:
978:
972:
964:
960:
954:
946:
942:
935:
927:
923:
918:
913:
908:
903:
899:
895:
891:
884:
876:
872:
867:
862:
858:
854:
850:
846:
842:
834:
826:
822:
817:
812:
808:
804:
800:
796:
792:
784:
782:
773:
769:
765:
761:
756:
751:
746:
741:
737:
733:
729:
722:
714:
708:
704:
700:
696:
689:
681:
677:
673:
669:
665:
661:
654:
652:
643:
639:
634:
629:
625:
621:
617:
613:
609:
601:
599:
590:
586:
582:
578:
574:
570:
562:
560:
551:
547:
542:
537:
533:
529:
525:
521:
517:
510:
502:
496:
488:
484:
480:
476:
469:
461:
457:
453:
449:
445:
441:
434:
426:
422:
418:
414:
410:
406:
399:
397:
388:
382:
378:
374:
370:
369:
361:
359:
350:
346:
341:
336:
332:
328:
324:
320:
316:
308:
306:
297:
293:
289:
285:
280:
275:
271:
267:
263:
259:
256:(6): 061001.
255:
251:
243:
239:
231:
222:
213:
204:
202:
192:
190:
186:
176:
168:
166:
162:
152:
148:
146:
142:
137:
132:
129:
125:
124:Hagai Bergman
119:
117:
113:
109:
105:
101:
91:
89:
85:
84:Hagai Bergman
81:
76:
72:
68:
64:
60:
55:
51:
47:
42:
40:
36:
32:
21:
1546:
1542:
1532:
1491:
1487:
1480:
1445:
1439:
1402:
1398:
1387:
1352:
1348:
1338:
1301:
1297:
1287:
1262:
1258:
1251:
1216:
1212:
1201:
1166:
1162:
1112:
1108:
1098:
1061:
1057:
1046:
1003:
999:
989:
980:
971:
962:
953:
944:
934:
897:
893:
883:
848:
844:
833:
798:
794:
735:
731:
721:
694:
688:
663:
659:
615:
611:
572:
568:
523:
519:
509:
495:cite journal
478:
474:
468:
443:
439:
433:
408:
404:
367:
322:
318:
253:
249:
242:
228:
219:
210:
198:
182:
174:
158:
149:
133:
120:
97:
67:Robert Heath
63:José Delgado
43:
34:
26:
25:
755:2434/865610
279:2434/877893
171:Medical use
54:neurologist
1587:Categories
1405:: 749705.
1265:(1): e17.
1115:: 702961.
1064:: 763235.
900:: 643841.
234:References
1524:219166717
963:Medtronic
795:Neurology
772:236949013
666:: 77–86.
325:(1): 88.
296:239472558
145:CE-marked
136:Medtronic
1573:25999288
1516:33055369
1472:34446243
1431:34955714
1379:28960154
1330:29295486
1304:(1): 4.
1279:56569946
1243:27530809
1193:31201193
1163:BMJ Open
1141:34483867
1090:34949982
1038:29741160
926:34135846
875:28211585
825:29444973
764:34371211
680:23022916
642:23852650
589:22017994
550:25961887
349:34584095
288:34678794
207:Dystonia
116:epilepsy
108:dystonia
1564:5032989
1496:Bibcode
1422:8695120
1370:7007215
1321:5789335
1234:5136720
1184:6575861
1132:8414587
1081:8689059
1029:6021210
1008:Bibcode
917:8200487
866:5412843
816:5858949
633:3886292
541:4501886
460:4209918
425:4187397
340:8478873
258:Bibcode
139:at the
1571:
1561:
1522:
1514:
1470:
1460:
1429:
1419:
1377:
1367:
1328:
1318:
1277:
1241:
1231:
1191:
1181:
1139:
1129:
1088:
1078:
1036:
1026:
924:
914:
873:
863:
823:
813:
770:
762:
709:
678:
640:
630:
587:
569:Neuron
548:
538:
458:
423:
383:
347:
337:
294:
286:
1520:S2CID
1275:S2CID
768:S2CID
292:S2CID
1569:PMID
1512:PMID
1468:PMID
1458:ISBN
1427:PMID
1375:PMID
1326:PMID
1239:PMID
1189:PMID
1137:PMID
1086:PMID
1034:PMID
922:PMID
871:PMID
821:PMID
760:PMID
707:ISBN
676:PMID
638:PMID
585:PMID
546:PMID
501:link
456:PMID
421:PMID
381:ISBN
345:PMID
284:PMID
114:and
73:and
29:aDBS
1559:PMC
1551:doi
1504:doi
1450:doi
1417:PMC
1407:doi
1365:PMC
1357:doi
1353:129
1316:PMC
1306:doi
1267:doi
1263:130
1229:PMC
1221:doi
1179:PMC
1171:doi
1127:PMC
1117:doi
1076:PMC
1066:doi
1024:PMC
1016:doi
912:PMC
902:doi
861:PMC
853:doi
811:PMC
803:doi
750:hdl
740:doi
699:doi
668:doi
664:245
628:PMC
620:doi
577:doi
536:PMC
528:doi
483:doi
448:doi
444:131
413:doi
373:doi
335:PMC
327:doi
274:hdl
266:doi
1589::
1567:.
1557:.
1547:30
1545:.
1541:.
1518:.
1510:.
1502:.
1492:17
1490:.
1466:.
1456:.
1425:.
1415:.
1403:15
1401:.
1397:.
1373:.
1363:.
1351:.
1347:.
1324:.
1314:.
1300:.
1296:.
1273:.
1261:.
1237:.
1227:.
1217:87
1215:.
1211:.
1187:.
1177:.
1165:.
1161:.
1149:^
1135:.
1125:.
1113:15
1111:.
1107:.
1084:.
1074:.
1062:15
1060:.
1056:.
1032:.
1022:.
1014:.
1004:15
1002:.
998:.
979:.
961:.
943:.
920:.
910:.
898:12
896:.
892:.
869:.
859:.
849:32
847:.
843:.
819:.
809:.
799:90
797:.
793:.
780:^
766:.
758:.
748:.
736:14
734:.
730:.
705:.
674:.
662:.
650:^
636:.
626:.
616:74
614:.
610:.
597:^
583:.
573:72
571:.
558:^
544:.
534:.
524:72
522:.
518:.
497:}}
493:{{
479:37
477:.
454:.
442:.
419:.
409:27
407:.
395:^
379:.
357:^
343:.
333:.
321:.
317:.
304:^
290:.
282:.
272:.
264:.
254:18
252:.
201:TS
110:,
106:,
69:,
65:,
41:.
1575:.
1553::
1526:.
1506::
1498::
1474:.
1452::
1433:.
1409::
1381:.
1359::
1332:.
1308::
1302:8
1281:.
1269::
1245:.
1223::
1195:.
1173::
1167:9
1143:.
1119::
1092:.
1068::
1040:.
1018::
1010::
965:.
947:.
928:.
904::
877:.
855::
827:.
805::
774:.
752::
742::
715:.
701::
682:.
670::
644:.
622::
591:.
579::
552:.
530::
503:)
485::
462:.
450::
427:.
415::
389:.
375::
351:.
329::
323:7
298:.
276::
268::
260::
31:)
Text is available under the Creative Commons Attribution-ShareAlike License. Additional terms may apply.