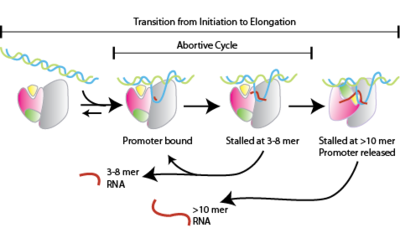
141:-addition step in initial transcription, RNA polymerase, stochastically, can proceed on the pathway toward promoter escape (productive initiation) or can release the RNA product and revert to the RNA polymerase-promoter open complex (abortive initiation). During this early stage of transcription, RNA polymerase enters a phase during which dissociation of the transcription complex energetically competes with the elongation process. Abortive cycling is not caused by strong binding between the initiation complex and the promoter.
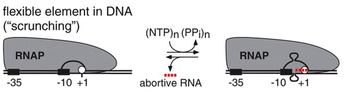
167:"scrunching". In abortive initiation, RNA polymerase re-winds and ejects the downstream portion of the unwound DNA, releasing the RNA, and reverting to the RNA polymerase-promoter open complex; in contrast, in productive initiation, RNA polymerase re-winds and ejects the upstream portion of the unwound DNA, breaking RNA polymerase-promoter interactions, escaping the promoter, and forming a transcription elongation complex.
150:
183:
abortive transcription in the presence of ATP, UTP, and GTP, a complex is formed that has a much lower capacity for abortive recycling and a much higher rate of synthesis of the full-length RNA transcript. A study in 2010 found evidence that these truncated transcripts inhibit termination of RNA synthesis by a
166:
in which RNA polymerase remains stationary while it unwinds and pulls downstream DNA into the transcription complex to pass the nucleotides through the polymerase active site, thereby transcribing the DNA without moving. This causes the unwound DNA to accumulate within the enzyme, hence the name DNA
182:
There are no widely accepted functions for the resulting truncated RNA transcripts. However, a study in 1981 found evidence that there was a relationship between the number of abortive transcripts produced and the time until long RNA strands are successfully produced. When RNA polymerase undergoes
170:
A 2006 paper that demonstrated the involvement of DNA scrunching in initial transcription proposed the idea that the stress incurred during DNA scrunching provides the driving force for both abortive initiation and productive initiation. A companion paper published the same year confirmed that
157:
For many years, the mechanism by which RNA polymerase moves along the DNA strand during abortive initiation remained elusive. It had been observed that RNA polymerase did not escape from the promoter during transcription initiation, so it was unknown how the enzyme could read the DNA strand to
171:
detectable DNA scrunching occurs in 80% of transcription cycles, and is actually estimated to be 100%, given the limitation of the ability to detect rapid scrunching (20% of scrunches have a duration of less than 1 second).
28:
667:
153:
DNA scrunching mechanism. During initial transcription, RNA polymerase (RNAP) remains stationary on the promoter and unwinds and reels in downstream DNA.
615:
1002:
17:
1148:
783:
113:
RNA polymerase enters into abortive cycles of synthesis and releases short RNA products (contains less than 10 nucleotides)
1380:
106:
RNA polymerase then unwinds one turn of DNA surrounding the transcription start site to yield an RNA polymerase-promoter
647:
550:"Tiny abortive initiation transcripts exert antitermination activity on an RNA hairpin-dependent intrinsic terminator"
92:
755:
174:
A 2016 paper showed that DNA scrunching also occurs before RNA synthesis during transcription start site selection.
1352:
909:
853:
61:
transcripts which are released before the transcription complex leaves the promoter. This process occurs in both
1405:
848:
361:
Martin CT, Muller DK, Coleman JE (1988). "Processivity in early stages of transcription by T7 RNA polymerase".
1347:
456:
Winkelman JT, Vvedenskaya IO, Zhang Y, Zhang Y, Bird JG, Taylor DM, Gourse RL, Ebright RH, Nickels BE (2016).
1400:
936:
867:
608:
159:
1368:
1342:
672:
995:
1450:
1028:
887:
1225:
1161:
1131:
1109:
1445:
1019:
1011:
931:
719:
632:
601:
205:
46:
1326:
1015:
892:
709:
694:
210:
1235:
988:
897:
822:
714:
1419:
1414:
1282:
1184:
812:
797:
677:
188:
1316:
1230:
1196:
1090:
919:
817:
735:
513:
Munson LM, Reznikoff WS (1981). "Abortive initiation and long ribonucleic acid synthesis".
469:
412:
317:
252:
8:
1299:
1267:
1153:
1127:
745:
458:"Multiplexed protein-DNA cross-linking: Scrunching in transcription start site selection"
54:
980:
473:
416:
321:
256:
241:"Abortive initiation and productive initiation by RNA polymerase involve DNA scrunching"
116:
RNA polymerase escapes the promoter and enters into the elongation step of transcription
1068:
880:
763:
574:
549:
490:
457:
433:
400:
338:
301:
297:
273:
240:
236:
1387:
579:
530:
495:
438:
401:"Initial transcription by RNA polymerase proceeds through a DNA-scrunching mechanism"
378:
343:
278:
70:
32:
964:
1309:
1292:
569:
561:
522:
485:
477:
428:
420:
370:
333:
325:
268:
260:
162:. Within the last decade, studies have revealed that abortive initiation involves
1173:
941:
778:
624:
200:
1383:
1371:
1321:
768:
740:
50:
1439:
1085:
969:
656:
74:
58:
481:
424:
329:
264:
843:
773:
642:
583:
499:
442:
399:
Kapanidis AN, Margeat E, Ho SO, Kortkhonjia E, Weiss S, Ebright RH (2006).
347:
282:
534:
382:
1272:
1240:
1143:
946:
875:
565:
125:
Abortive initiation is a normal process of transcription and occurs both
66:
526:
374:
99:
RNA polymerase binds to promoter DNA to form an RNA polymerase-promoter
1424:
1118:
1073:
1063:
1058:
1053:
1048:
904:
138:
62:
1080:
184:
1287:
1277:
924:
914:
838:
127:
27:
593:
1247:
1114:
660:
149:
133:
79:
1043:
455:
1304:
1156:
682:
398:
1375:
1205:
1136:
1010:
652:
69:. Abortive initiation is typically studied in the T3 and
234:
295:
360:
1437:
512:
394:
392:
302:"Direct detection of abortive RNA transcripts
230:
228:
226:
996:
609:
547:
57:and enters into cycles of synthesis of short
541:
389:
223:
1003:
989:
764:Precursor mRNA (pre-mRNA / hnRNA)
616:
602:
506:
354:
573:
489:
432:
337:
272:
449:
148:
26:
14:
1438:
289:
1149:Histone acetylation and deacetylation
984:
784:Histone acetylation and deacetylation
597:
849:Ribosome-nascent chain complex (RNC)
91:Abortive initiation occurs prior to
623:
24:
86:
25:
1462:
548:Lee S, Nguyen HM, Kang C (2010).
144:
1353:Archaeal transcription factor B
854:Post-translational modification
13:
1:
216:
158:transcribe it without moving
120:
7:
194:
177:
10:
1467:
1029:Transcriptional regulation
1396:
1361:
1335:
1260:
1226:Transcription coregulator
1218:
1195:
1172:
1162:Histone acetyltransferase
1132:Histone methyltransferase
1110:Histone-modifying enzymes
1108:
1101:
1036:
1027:
957:
866:
831:
805:
796:
754:
728:
702:
693:
631:
45:, is an early process of
915:sequestration (P-bodies)
206:Eukaryotic transcription
1327:Internal control region
893:Gene regulatory network
482:10.1126/science.aad6881
425:10.1126/science.1131399
330:10.1126/science.1169237
265:10.1126/science.1131398
211:Bacterial transcription
898:cis-regulatory element
154:
43:abortive transcription
35:
18:Abortive transcription
1420:Intrinsic termination
1185:DNA methyltransferase
152:
47:genetic transcription
30:
1197:Chromatin remodeling
920:alternative splicing
910:Post-transcriptional
736:Transcription factor
300:, Nickels B (2009).
239:, Strick TR (2006).
189:intrinsic terminator
31:Abortive cycling by
1154:Histone deacetylase
1144:Histone demethylase
1128:Histone methylation
844:Transfer RNA (tRNA)
527:10.1021/bi00511a003
474:2016Sci...351.1090W
417:2006Sci...314.1144K
375:10.1021/bi00411a012
322:2009Sci...324..927G
257:2006Sci...314.1139R
235:Revyakin A, Liu C,
39:Abortive initiation
958:Influential people
937:Post-translational
756:Post-transcription
566:10.1093/nar/gkq450
155:
93:promoter clearance
71:T7 RNA polymerases
36:
1451:Molecular biology
1433:
1432:
1388:RNA polymerase II
1256:
1255:
1214:
1213:
978:
977:
862:
861:
792:
791:
668:Special transfers
554:Nucleic Acids Res
316:(5929): 927–928.
251:(5802): 1139–43.
33:T7 RNA polymerase
16:(Redirected from
1458:
1310:Response element
1293:Response element
1106:
1105:
1034:
1033:
1005:
998:
991:
982:
981:
803:
802:
700:
699:
618:
611:
604:
595:
594:
588:
587:
577:
545:
539:
538:
510:
504:
503:
493:
468:(6277): 1090–3.
453:
447:
446:
436:
411:(5802): 1144–7.
396:
387:
386:
358:
352:
351:
341:
293:
287:
286:
276:
232:
41:, also known as
21:
1466:
1465:
1461:
1460:
1459:
1457:
1456:
1455:
1446:Gene expression
1436:
1435:
1434:
1429:
1404:
1398:
1392:
1357:
1331:
1252:
1210:
1191:
1174:DNA methylation
1168:
1112:
1097:
1023:
1009:
979:
974:
953:
888:Transcriptional
858:
827:
788:
779:Polyadenylation
750:
724:
689:
683:Protein→Protein
634:
627:
625:Gene expression
622:
592:
591:
560:(18): 6045–53.
546:
542:
511:
507:
454:
450:
397:
390:
369:(11): 3966–74.
359:
355:
294:
290:
233:
224:
219:
201:Oligonucleotide
197:
180:
164:DNA scrunching,
147:
123:
89:
87:Overall process
23:
22:
15:
12:
11:
5:
1464:
1454:
1453:
1448:
1431:
1430:
1428:
1427:
1422:
1417:
1411:
1409:
1394:
1393:
1391:
1390:
1384:RNA polymerase
1378:
1372:RNA polymerase
1365:
1363:
1359:
1358:
1356:
1355:
1350:
1345:
1339:
1337:
1333:
1332:
1330:
1329:
1324:
1319:
1314:
1313:
1312:
1307:
1297:
1296:
1295:
1290:
1285:
1280:
1275:
1264:
1262:
1258:
1257:
1254:
1253:
1251:
1250:
1245:
1244:
1243:
1238:
1233:
1222:
1220:
1216:
1215:
1212:
1211:
1209:
1208:
1202:
1200:
1193:
1192:
1190:
1189:
1188:
1187:
1179:
1177:
1170:
1169:
1167:
1166:
1165:
1164:
1159:
1146:
1141:
1140:
1139:
1124:
1122:
1103:
1099:
1098:
1096:
1095:
1094:
1093:
1088:
1078:
1077:
1076:
1071:
1066:
1061:
1056:
1051:
1040:
1038:
1031:
1025:
1024:
1008:
1007:
1000:
993:
985:
976:
975:
973:
972:
967:
965:François Jacob
961:
959:
955:
954:
952:
951:
950:
949:
944:
934:
929:
928:
927:
922:
917:
907:
902:
901:
900:
895:
885:
884:
883:
872:
870:
864:
863:
860:
859:
857:
856:
851:
846:
841:
835:
833:
829:
828:
826:
825:
820:
815:
809:
807:
800:
794:
793:
790:
789:
787:
786:
781:
776:
771:
766:
760:
758:
752:
751:
749:
748:
743:
741:RNA polymerase
738:
732:
730:
726:
725:
723:
722:
717:
712:
706:
704:
697:
691:
690:
688:
687:
686:
685:
680:
675:
665:
664:
663:
645:
639:
637:
629:
628:
621:
620:
613:
606:
598:
590:
589:
540:
505:
448:
388:
353:
288:
221:
220:
218:
215:
214:
213:
208:
203:
196:
193:
179:
176:
146:
145:DNA scrunching
143:
137:. After each
122:
119:
118:
117:
114:
111:
104:
88:
85:
75:bacteriophages
51:RNA polymerase
9:
6:
4:
3:
2:
1463:
1452:
1449:
1447:
1444:
1443:
1441:
1426:
1423:
1421:
1418:
1416:
1413:
1412:
1410:
1407:
1402:
1395:
1389:
1385:
1382:
1379:
1377:
1373:
1370:
1367:
1366:
1364:
1360:
1354:
1351:
1349:
1346:
1344:
1341:
1340:
1338:
1334:
1328:
1325:
1323:
1320:
1318:
1315:
1311:
1308:
1306:
1303:
1302:
1301:
1298:
1294:
1291:
1289:
1286:
1284:
1281:
1279:
1276:
1274:
1271:
1270:
1269:
1266:
1265:
1263:
1259:
1249:
1246:
1242:
1239:
1237:
1234:
1232:
1229:
1228:
1227:
1224:
1223:
1221:
1217:
1207:
1204:
1203:
1201:
1198:
1194:
1186:
1183:
1182:
1181:
1180:
1178:
1175:
1171:
1163:
1160:
1158:
1155:
1152:
1151:
1150:
1147:
1145:
1142:
1138:
1135:
1134:
1133:
1129:
1126:
1125:
1123:
1120:
1116:
1111:
1107:
1104:
1100:
1092:
1091:trp repressor
1089:
1087:
1086:lac repressor
1084:
1083:
1082:
1079:
1075:
1072:
1070:
1067:
1065:
1062:
1060:
1057:
1055:
1052:
1050:
1047:
1046:
1045:
1042:
1041:
1039:
1035:
1032:
1030:
1026:
1021:
1017:
1013:
1012:Transcription
1006:
1001:
999:
994:
992:
987:
986:
983:
971:
970:Jacques Monod
968:
966:
963:
962:
960:
956:
948:
945:
943:
940:
939:
938:
935:
933:
932:Translational
930:
926:
923:
921:
918:
916:
913:
912:
911:
908:
906:
903:
899:
896:
894:
891:
890:
889:
886:
882:
879:
878:
877:
874:
873:
871:
869:
865:
855:
852:
850:
847:
845:
842:
840:
837:
836:
834:
830:
824:
821:
819:
816:
814:
811:
810:
808:
804:
801:
799:
795:
785:
782:
780:
777:
775:
772:
770:
767:
765:
762:
761:
759:
757:
753:
747:
744:
742:
739:
737:
734:
733:
731:
727:
721:
718:
716:
713:
711:
708:
707:
705:
701:
698:
696:
695:Transcription
692:
684:
681:
679:
676:
674:
671:
670:
669:
666:
662:
658:
654:
651:
650:
649:
648:Central dogma
646:
644:
641:
640:
638:
636:
630:
626:
619:
614:
612:
607:
605:
600:
599:
596:
585:
581:
576:
571:
567:
563:
559:
555:
551:
544:
536:
532:
528:
524:
521:(8): 2081–5.
520:
516:
509:
501:
497:
492:
487:
483:
479:
475:
471:
467:
463:
459:
452:
444:
440:
435:
430:
426:
422:
418:
414:
410:
406:
402:
395:
393:
384:
380:
376:
372:
368:
364:
357:
349:
345:
340:
335:
331:
327:
323:
319:
315:
311:
307:
305:
299:
292:
284:
280:
275:
270:
266:
262:
258:
254:
250:
246:
242:
238:
231:
229:
227:
222:
212:
209:
207:
204:
202:
199:
198:
192:
190:
186:
175:
172:
168:
165:
161:
151:
142:
140:
136:
135:
130:
129:
115:
112:
109:
105:
102:
98:
97:
96:
94:
84:
82:
81:
76:
72:
68:
64:
60:
56:
52:
48:
44:
40:
34:
29:
19:
947:irreversible
832:Key elements
729:Key elements
643:Genetic code
633:Introduction
557:
553:
543:
518:
515:Biochemistry
514:
508:
465:
461:
451:
408:
404:
366:
363:Biochemistry
362:
356:
313:
309:
303:
291:
248:
244:
181:
173:
169:
163:
156:
132:
126:
124:
107:
100:
90:
78:
55:DNA promoter
42:
38:
37:
1397:Termination
1273:Pribnow box
1241:Corepressor
1236:Coactivator
1037:prokaryotic
798:Translation
635:to genetics
296:Goldman S,
187:-dependent
185:RNA hairpin
67:prokaryotes
53:binds to a
1440:Categories
1425:Rho factor
1415:Terminator
1406:eukaryotic
1381:eukaryotic
1362:Elongation
1348:Eukaryotic
1336:Initiation
1119:nucleosome
1102:eukaryotic
1074:gal operon
1069:ara operon
1064:Gua Operon
1059:gab operon
1054:trp operon
1049:lac operon
1020:Eukaryotic
942:reversible
905:lac operon
881:imprinting
876:Epigenetic
868:Regulation
823:Eukaryotic
769:5' capping
720:Eukaryotic
298:Ebright RH
237:Ebright RH
217:References
160:downstream
139:nucleotide
63:eukaryotes
1401:bacterial
1369:bacterial
1343:Bacterial
1317:Insulator
1261:Promotion
1231:Activator
1081:Repressor
1016:Bacterial
813:Bacterial
710:Bacterial
121:Mechanism
49:in which
1322:Silencer
1300:Enhancer
1288:CAAT box
1278:TATA box
1268:Promoter
925:microRNA
839:Ribosome
818:Archaeal
774:Splicing
746:Promoter
715:Archaeal
659: →
655: →
584:20507918
500:26941320
443:17110578
348:19443781
283:17110577
195:See also
178:Function
128:in vitro
1248:Inducer
1115:histone
678:RNA→DNA
673:RNA→RNA
661:Protein
575:2952870
535:6165380
491:4797950
470:Bibcode
462:Science
434:2754788
413:Bibcode
405:Science
383:3415967
339:2718712
318:Bibcode
310:Science
304:in vivo
274:2754787
253:Bibcode
245:Science
134:in vivo
110:complex
103:complex
80:E. coli
77:and in
1044:Operon
582:
572:
533:
498:
488:
441:
431:
381:
346:
336:
281:
271:
101:closed
1305:E-box
1157:HDAC1
806:Types
703:Types
1376:rpoB
1219:both
1206:CHD7
1137:EZH2
580:PMID
531:PMID
496:PMID
439:PMID
379:PMID
344:PMID
279:PMID
131:and
108:open
65:and
59:mRNA
1283:BRE
657:RNA
653:DNA
570:PMC
562:doi
523:doi
486:PMC
478:doi
466:351
429:PMC
421:doi
409:314
371:doi
334:PMC
326:doi
314:324
269:PMC
261:doi
249:314
95:.
73:in
1442::
1386::
1374::
1121:):
1018:,
578:.
568:.
558:38
556:.
552:.
529:.
519:20
517:.
494:.
484:.
476:.
464:.
460:.
437:.
427:.
419:.
407:.
403:.
391:^
377:.
367:27
365:.
342:.
332:.
324:.
312:.
308:.
277:.
267:.
259:.
247:.
243:.
225:^
191:.
83:.
1408:)
1403:,
1399:(
1199::
1176::
1130:/
1117:/
1113:(
1022:)
1014:(
1004:e
997:t
990:v
617:e
610:t
603:v
586:.
564::
537:.
525::
502:.
480::
472::
445:.
423::
415::
385:.
373::
350:.
328::
320::
306:"
285:.
263::
255::
20:)
Text is available under the Creative Commons Attribution-ShareAlike License. Additional terms may apply.