1079:, a colleague of Fisher, claimed to be able to tell whether the tea or the milk was added first to a cup. Fisher proposed to give her eight cups, four of each variety, in random order. One could then ask what the probability was for her getting the number she got correct, but just by chance. The null hypothesis was that the Lady had no such ability. The test statistic was a simple count of the number of successes in selecting the 4 cups. The critical region was the single case of 4 successes of 4 possible based on a conventional probability criterion (< 5%). A pattern of 4 successes corresponds to 1 out of 70 possible combinations (p≈ 1.4%). Fisher asserted that no alternative hypothesis was (ever) required. The lady correctly identified every cup, which would be considered a statistically significant result.
816:
4856:"The emphasis given to formal tests of significance throughout Statistical Methods ... has caused scientific research workers to pay undue attention to the results of the tests of significance they perform on their data, particularly data derived from experiments, and too little to the estimates of the magnitude of the effects they are investigating." ... "The emphasis on tests of significance and the consideration of the results of each experiment in isolation, have had the unfortunate consequence that scientific workers have often regarded the execution of a test of significance on an experiment as the ultimate objective."
258:; Mathematicians have generalized and refined the theory for decades). Fisher thought that it was not applicable to scientific research because often, during the course of the experiment, it is discovered that the initial assumptions about the null hypothesis are questionable due to unexpected sources of error. He believed that the use of rigid reject/accept decisions based on models formulated before data is collected was incompatible with this common scenario faced by scientists and attempts to apply this method to scientific research would lead to mass confusion.
8101:
2503:
422:
aspects of statistical inference) that persisted among instructors. While the problem was addressed more than a decade ago, and calls for educational reform continue, students still graduate from statistics classes holding fundamental misconceptions about hypothesis testing. Ideas for improving the teaching of hypothesis testing include encouraging students to search for statistical errors in published papers, teaching the history of statistics and emphasizing the controversy in a generally dry subject.
20:
1004:
restrictive parametric assumptions, but rather on empirical approximate methods with asymptotic guarantees. Traditional parametric hypothesis tests are more computationally efficient but make stronger structural assumptions. In situations where computing the probability of the test statistic under the null hypothesis is hard or impossible (due to perhaps inconvenience or lack of knowledge of the underlying distribution), the bootstrap offers a viable method for statistical inference.
402:
thinking clearly about problems involving mass data, as well as the effective reporting of trends and inferences from said data, but caution that writers for a broad public should have a solid understanding of the field in order to use the terms and concepts correctly. An introductory college statistics class places much emphasis on hypothesis testing – perhaps half of the course. Such fields as literature and divinity now include findings based on statistical analysis (see the
9273:
8087:
1946:
2313:
cancel out completely, the chance of finding statistical significance in either direction approaches 100%. However, this absurd assumption that the mean difference between two groups cannot be zero implies that the data cannot be independent and identically distributed (i.i.d.) because the expected difference between any two subgroups of i.i.d. random variates is zero; therefore, the i.i.d. assumption is also absurd.
9297:
8125:
2225:
radioactive sources. The hypotheses become 0,1,2,3... grains of radioactive sand. There is little distinction between none or some radiation (Fisher) and 0 grains of radioactive sand versus all of the alternatives (Neyman–Pearson). The major Neyman–Pearson paper of 1933 also considered composite hypotheses (ones whose distribution includes an unknown parameter). An example proved the optimality of the (Student's)
9285:
8113:
4559:"Until we go through the accounts of testing hypotheses, separating decision elements from conclusion elements, the intimate mixture of disparate elements will be a continual source of confusion." ... "There is a place for both "doing one's best" and "saying only what is certain," but it is important to know, in each instance, both which one is being done, and which one ought to be done."
284:, for example, still uses the Neyman/Pearson formulation). Great conceptual differences and many caveats in addition to those mentioned above were ignored. Neyman and Pearson provided the stronger terminology, the more rigorous mathematics and the more consistent philosophy, but the subject taught today in introductory statistics has more similarities with Fisher's method than theirs.
668:. For example, Lehmann (1992) in a review of the fundamental paper by Neyman and Pearson (1933) says: "Nevertheless, despite their shortcomings, the new paradigm formulated in the 1933 paper, and the many developments carried out within its framework continue to play a central role in both the theory and practice of statistics and can be expected to do so in the foreseeable future".
2356:) has been created to publish such results exclusively. Textbooks have added some cautions, and increased coverage of the tools necessary to estimate the size of the sample required to produce significant results. Few major organizations have abandoned use of significance tests although some have discussed doing so. For instance, in 2023, the editors of the
1667:
5623:"...the proper application of statistics to scientific inference is irrevocably committed to extensive consideration of inverse probabilities..." It was acknowledged, with regret, that a priori probability distributions were available "only as a subjective feel, differing from one person to the next" "in the more immediate future, at least".
5259:"Hypothesis tests. It is hard to imagine a situation in which a dichotomous accept-reject decision is better than reporting an actual p value or, better still, a confidence interval." (p 599). The committee used the cautionary term "forbearance" in describing its decision against a ban of hypothesis testing in psychology reporting. (p 603)
220:. Neyman (who teamed with the younger Pearson) emphasized mathematical rigor and methods to obtain more results from many samples and a wider range of distributions. Modern hypothesis testing is an inconsistent hybrid of the Fisher vs Neyman/Pearson formulation, methods and terminology developed in the early 20th century.
2204:). A simple method of solution is to select the hypothesis with the highest probability for the Geiger counts observed. The typical result matches intuition: few counts imply no source, many counts imply two sources and intermediate counts imply one source. Notice also that usually there are problems for
1310:
consideration of a real population and a real sample produced an imaginary bag. The philosopher was considering logic rather than probability. To be a real statistical hypothesis test, this example requires the formalities of a probability calculation and a comparison of that probability to a standard.
2252:
The dispute over formulations is unresolved. Science primarily uses Fisher's (slightly modified) formulation as taught in introductory statistics. Statisticians study Neyman–Pearson theory in graduate school. Mathematicians are proud of uniting the formulations. Philosophers consider them separately.
1313:
A simple generalization of the example considers a mixed bag of beans and a handful that contain either very few or very many white beans. The generalization considers both extremes. It requires more calculations and more comparisons to arrive at a formal answer, but the core philosophy is unchanged;
622:
In the "lady tasting tea" example (below), Fisher required the lady to properly categorize all of the cups of tea to justify the conclusion that the result was unlikely to result from chance. His test revealed that if the lady was effectively guessing at random (the null hypothesis), there was a 1.4%
2316:
Layers of philosophical concerns. The probability of statistical significance is a function of decisions made by experimenters/analysts. If the decisions are based on convention they are termed arbitrary or mindless while those not so based may be termed subjective. To minimize type II errors, large
2215:
Neyman–Pearson theory can accommodate both prior probabilities and the costs of actions resulting from decisions. The former allows each test to consider the results of earlier tests (unlike Fisher's significance tests). The latter allows the consideration of economic issues (for example) as well as
1344:
If the null hypothesis is valid, the only thing the test person can do is guess. For every card, the probability (relative frequency) of any single suit appearing is 1/4. If the alternative is valid, the test subject will predict the suit correctly with probability greater than 1/4. We will call the
421:
An academic study states that the cookbook method of teaching introductory statistics leaves no time for history, philosophy or controversy. Hypothesis testing has been taught as received unified method. Surveys showed that graduates of the class were filled with philosophical misconceptions (on all
401:
Statistics is increasingly being taught in schools with hypothesis testing being one of the elements taught. Many conclusions reported in the popular press (political opinion polls to medical studies) are based on statistics. Some writers have stated that statistical analysis of this kind allows for
2340:
The continuing controversy concerns the selection of the best statistical practices for the near-term future given the existing practices. However, adequate research design can minimize this issue. Critics would prefer to ban NHST completely, forcing a complete departure from those practices, while
1646:
740:
Those making critical decisions based on the results of a hypothesis test are prudent to look at the details rather than the conclusion alone. In the physical sciences most results are fully accepted only when independently confirmed. The general advice concerning statistics is, "Figures never lie,
250:
Neyman & Pearson considered a different problem to Fisher (which they called "hypothesis testing"). They initially considered two simple hypotheses (both with frequency distributions). They calculated two probabilities and typically selected the hypothesis associated with the higher probability
99:
importance of the choice of null hypothesis has gone largely unacknowledged. When the null hypothesis is predicted by theory, a more precise experiment will be a more severe test of the underlying theory. When the null hypothesis defaults to "no difference" or "no effect", a more precise experiment
3128:
We are quite in danger of sending highly trained and highly intelligent young men out into the world with tables of erroneous numbers under their arms, and with a dense fog in the place where their brains ought to be. In this century, of course, they will be working on guided missiles and advising
2312:
When used to detect whether a difference exists between groups, a paradox arises. As improvements are made to experimental design (e.g. increased precision of measurement and sample size), the test becomes more lenient. Unless one accepts the absurd assumption that all sources of noise in the data
2260:
Fisher thought that hypothesis testing was a useful strategy for performing industrial quality control, however, he strongly disagreed that hypothesis testing could be useful for scientists. Hypothesis testing provides a means of finding test statistics used in significance testing. The concept of
1309:
The beans in the bag are the population. The handful are the sample. The null hypothesis is that the sample originated from the population. The criterion for rejecting the null-hypothesis is the "obvious" difference in appearance (an informal difference in the mean). The interesting result is that
2232:
Fisher's significance testing has proven a popular flexible statistical tool in application with little mathematical growth potential. Neyman–Pearson hypothesis testing is claimed as a pillar of mathematical statistics, creating a new paradigm for the field. It also stimulated new applications in
2195:
An example of Neyman–Pearson hypothesis testing (or null hypothesis statistical significance testing) can be made by a change to the radioactive suitcase example. If the "suitcase" is actually a shielded container for the transportation of radioactive material, then a test might be used to select
1472:
When the test subject correctly predicts all 25 cards, we will consider them clairvoyant, and reject the null hypothesis. Thus also with 24 or 23 hits. With only 5 or 6 hits, on the other hand, there is no cause to consider them so. But what about 12 hits, or 17 hits? What is the critical number,
1003:
methods can be used for null hypothesis testing. A bootstrap creates numerous simulated samples by randomly resampling (with replacement) the original, combined sample data, assuming the null hypothesis is correct. The bootstrap is very versatile as it is distribution-free and it does not rely on
940:
if a sample was sufficiently inconsistent with the (null) hypothesis. This was variously considered common sense, a pragmatic heuristic for identifying meaningful experimental results, a convention establishing a threshold of statistical evidence or a method for drawing conclusions from data. The
631:
Statistics are helpful in analyzing most collections of data. This is equally true of hypothesis testing which can justify conclusions even when no scientific theory exists. In the Lady tasting tea example, it was "obvious" that no difference existed between (milk poured into tea) and (tea poured
600:-value is the probability that a test statistic which is at least as extreme as the one obtained would occur under the null hypothesis. At a significance level of 0.05, a fair coin would be expected to (incorrectly) reject the null hypothesis (that it is fair) in 1 out of 20 tests on average. The
223:
Fisher popularized the "significance test". He required a null-hypothesis (corresponding to a population frequency distribution) and a sample. His (now familiar) calculations determined whether to reject the null-hypothesis or not. Significance testing did not utilize an alternative hypothesis so
2403:
Critics of significance testing have advocated basing inference less on p-values and more on confidence intervals for effect sizes for importance, prediction intervals for confidence, replications and extensions for replicability, meta-analyses for generality :. But none of these suggested
3460:'Statistical methods and statistical terms are necessary in reporting the mass data of social and economic trends, business conditions, "opinion" polls, the census. But without writers who use the words with honesty and readers who know what they mean, the result can only be semantic nonsense.'
1286:
A criminal trial can be regarded as either or both of two decision processes: guilty vs not guilty or evidence vs a threshold ("beyond a reasonable doubt"). In one view, the defendant is judged; in the other view the performance of the prosecution (which bears the burden of proof) is judged. A
1317:
The statement also relies on the inference that the sampling was random. If someone had been picking through the bag to find white beans, then it would explain why the handful had so many white beans, and also explain why the number of white beans in the bag was depleted (although the bag is
4949:
Thirty years later, Meehl acknowledged statistical significance theory to be mathematically sound while continuing to question the default choice of null hypothesis, blaming instead the "social scientists' poor understanding of the logical relation between theory and fact" in "The
Problem Is
683:. When theory is only capable of predicting the sign of a relationship, a directional (one-sided) hypothesis test can be configured so that only a statistically significant result supports theory. This form of theory appraisal is the most heavily criticized application of hypothesis testing.
965:
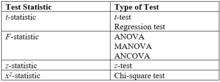
for examples) to a threshold. The test statistic (the formula found in the table below) is based on optimality. For a fixed level of Type I error rate, use of these statistics minimizes Type II error rates (equivalent to maximizing power). The following terms describe tests in terms of such
109:
compares the birthrates of boys and girls in multiple
European cities. He states: "it is natural to conclude that these possibilities are very nearly in the same ratio". Thus, the null hypothesis in this case that the birthrates of boys and girls should be equal given "conventional wisdom".
2224:
the former produces a conclusion on the basis of only strong evidence while the latter produces a decision on the basis of available evidence. While the two tests seem quite different both mathematically and philosophically, later developments lead to the opposite claim. Consider many tiny
5286:
Editors should seriously consider for publication any carefully done study of an important question, relevant to their readers, whether the results for the primary or any additional outcome are statistically significant. Failure to submit or publish findings because of lack of statistical
841:
of a statistical test are the boundaries of the acceptance region of the test. The acceptance region is the set of values of the test statistic for which the null hypothesis is not rejected. Depending on the shape of the acceptance region, there can be one or more than one critical value.
123:
to determine "whether a given form of frequency curve will effectively describe the samples drawn from a given population." Thus the null hypothesis is that a population is described by some distribution predicted by theory. He uses as an example the numbers of five and sixes in the
1941:{\displaystyle P({\text{reject }}H_{0}\mid H_{0}{\text{ is valid}})=P\left(X\geq 10\mid p={\frac {1}{4}}\right)=\sum _{k=10}^{25}P\left(X=k\mid p={\frac {1}{4}}\right)=\sum _{k=10}^{25}{\binom {25}{k}}\left(1-{\frac {1}{4}}\right)^{25-k}\left({\frac {1}{4}}\right)^{k}\approx 0.0713}
1046:-value. Arbuthnot concluded that this is too small to be due to chance and must instead be due to divine providence: "From whence it follows, that it is Art, not Chance, that governs." In modern terms, he rejected the null hypothesis of equally likely male and female births at the
2404:
alternatives inherently produces a decision. Lehmann said that hypothesis testing theory can be presented in terms of conclusions/decisions, probabilities, or confidence intervals: "The distinction between the ... approaches is largely one of reporting and interpretation."
1042:. In every year, the number of males born in London exceeded the number of females. Considering more male or more female births as equally likely, the probability of the observed outcome is 0.5, or about 1 in 4,836,000,000,000,000,000,000,000; in modern terms, this is the
1489:=10. In the first case almost no test subjects will be recognized to be clairvoyant, in the second case, a certain number will pass the test. In practice, one decides how critical one will be. That is, one decides how often one accepts an error of the first kind – a
3476:"...the basic ideas in statistics assist us in thinking clearly about the problem, provide some guidance about the conditions that must be satisfied if sound inferences are to be made, and enable us to detect many inferences that have no good logical foundation."
2083:
1314:
If the composition of the handful is greatly different from that of the bag, then the sample probably originated from another bag. The original example is termed a one-sided or a one-tailed test while the generalization is termed a two-sided or two-tailed test.
145:
of a given categorical factor. Here the null hypothesis is by default that two things are unrelated (e.g. scar formation and death rates from smallpox). The null hypothesis in this case is no longer predicted by theory or conventional wisdom, but is instead the
5657:
In listing the competing definitions of "objective" Bayesian analysis, "A major goal of statistics (indeed science) is to find a completely coherent objective
Bayesian methodology for learning from data." The author expressed the view that this goal "is not
330:
Report the exact level of significance (e.g. p = 0.051 or p = 0.049). Do not refer to "accepting" or "rejecting" hypotheses. If the result is "not significant", draw no conclusions and make no decisions, but suspend judgement until further data is available.
2295:
and definition of multiple comparison. The former often changes during the course of a study and the latter is unavoidably ambiguous. (i.e. "p values depend on both the (data) observed and on the other possible (data) that might have been observed but
941:
statistical hypothesis test added mathematical rigor and philosophical consistency to the concept by making the alternative hypothesis explicit. The term is loosely used for the modern version which is now part of statistical hypothesis testing.
2269:) produce the same mathematical answer. The preferred answer is context dependent. While the existing merger of Fisher and Neyman–Pearson theories has been heavily criticized, modifying the merger to achieve Bayesian goals has been considered.
345:
The usefulness of the procedure is limited among others to situations where you have a disjunction of hypotheses (e.g. either μ1 = 8 or μ2 = 10 is true) and where you can make meaningful cost-benefit trade-offs for choosing alpha and beta.
2368:
to convey the precision of that estimate), saying "Ultimately, it is the physiological importance of the data that those publishing in The
Journal of Physiology should be most concerned with, rather than the statistical significance."
819:
Suppose the data can be realized from an N(0,1) distribution. For example, with a chosen significance level α = 0.05, from the Z-table, a one-tailed critical value of approximately 1.645 can be obtained. The one-tailed critical value
1964:) is determined. Typically, values in the range of 1% to 5% are selected. (If the maximum acceptable error rate is zero, an infinite number of correct guesses is required.) Depending on this Type 1 error rate, the critical value
272:
provided an intermission in the debate. The dispute between Fisher and Neyman terminated (unresolved after 27 years) with Fisher's death in 1962. Neyman wrote a well-regarded eulogy. Some of Neyman's later publications reported
1504:
2171:, attempt to balance the consequences of incorrect decisions across all possibilities, rather than concentrating on a single null hypothesis. A number of other approaches to reaching a decision based on data are available via
1091:; a defendant is considered not guilty as long as his or her guilt is not proven. The prosecutor tries to prove the guilt of the defendant. Only when there is enough evidence for the prosecution is the defendant convicted.
406:). An introductory statistics class teaches hypothesis testing as a cookbook process. Hypothesis testing is also taught at the postgraduate level. Statisticians learn how to create good statistical test procedures (like
2256:
The terminology is inconsistent. Hypothesis testing can mean any mixture of two formulations that both changed with time. Any discussion of significance testing vs hypothesis testing is doubly vulnerable to confusion.
691:"If the government required statistical procedures to carry warning labels like those on drugs, most inference methods would have long labels indeed." This caution applies to hypothesis tests and alternatives to them.
611:-value is less than the chosen significance threshold (equivalently, if the observed test statistic is in the critical region), then we say the null hypothesis is rejected at the chosen level of significance. If the
2179:, some of which have desirable properties. Hypothesis testing, though, is a dominant approach to data analysis in many fields of science. Extensions to the theory of hypothesis testing include the study of the
321:
Set up two statistical hypotheses, H1 and H2, and decide about α, β, and sample size before the experiment, based on subjective cost-benefit considerations. These define a rejection region for each hypothesis.
9083:
2219:
The two forms of hypothesis testing are based on different problem formulations. The original test is analogous to a true/false question; the Neyman–Pearson test is more like multiple choice. In the view of
4097:
Martin, M.A., 2007. Bootstrap hypothesis testing for some common statistical problems: A critical evaluation of size and power properties. Computational
Statistics & Data Analysis, 51(12), pp.6321-6342.
890:
rate. For composite hypotheses this is the supremum of the probability of rejecting the null hypothesis over all cases covered by the null hypothesis. The complement of the false positive rate is termed
2253:
Learned opinions deem the formulations variously competitive (Fisher vs Neyman), incompatible or complementary. The dispute has become more complex since
Bayesian inference has achieved respectability.
619:
less than the chosen significance threshold (equivalently, if the observed test statistic is outside the critical region), then the null hypothesis is not rejected at the chosen level of significance.
1405:
2798:"On the criterion that a given system of deviations from the probable in the case of a correlated system of variables is such that it can be reasonably supposed to have arisen from random sampling"
1023:
The earliest use of statistical hypothesis testing is generally credited to the question of whether male and female births are equally likely (null hypothesis), which was addressed in the 1700s by
1466:
2317:
samples are recommended. In psychology practically all null hypotheses are claimed to be false for sufficiently large samples so "...it is usually nonsensical to perform an experiment with the
447:
Derive the distribution of the test statistic under the null hypothesis from the assumptions. In standard cases this will be a well-known result. For example, the test statistic might follow a
280:
The modern version of hypothesis testing is a hybrid of the two approaches that resulted from confusion by writers of statistical textbooks (as predicted by Fisher) beginning in the 1940s (but
2433:. Bayesian methods could be criticized for requiring information that is seldom available in the cases where significance testing is most heavily used. Neither the prior probabilities nor the
1979:
1341:
As we try to find evidence of their clairvoyance, for the time being the null hypothesis is that the person is not clairvoyant. The alternative is: the person is (more or less) clairvoyant.
2144:) is incorrect. The procedure is based on how likely it would be for a set of observations to occur if the null hypothesis were true. This probability of making an incorrect decision is
334:
If the data falls into the rejection region of H1, accept H2; otherwise accept H1. Accepting a hypothesis does not mean that you believe in it, but only that you act as if it were true.
701:
The conclusion of the test is only as solid as the sample upon which it is based. The design of the experiment is critical. A number of unexpected effects have been observed including:
35:
is a method of statistical inference used to decide whether the data sufficiently supports a particular hypothesis. A statistical hypothesis test typically involves a calculation of a
2332:
Critics and supporters are largely in factual agreement regarding the characteristics of null hypothesis significance testing (NHST): While it can provide critical information, it is
261:
The dispute between Fisher and Neyman–Pearson was waged on philosophical grounds, characterized by a philosopher as a dispute over the proper role of models in statistical inference.
3294:
Halpin, P F; Stam, HJ (Winter 2006). "Inductive
Inference or Inductive Behavior: Fisher and Neyman: Pearson Approaches to Statistical Testing in Psychological Research (1940–1960)".
342:
Use this procedure only if little is known about the problem at hand, and only to draw provisional conclusions in the context of an attempt to understand the experimental situation.
737:
Multiple testing: When multiple true null hypothesis tests are conducted at once without adjustment, the overall probability of Type I error is higher than the nominal alpha level.
2321:
aim of rejecting the null hypothesis." "Statistically significant findings are often misleading" in psychology. Statistical significance does not imply practical significance, and
2429:
and has also contrasted
Bayesian estimation for assessing null values with Bayesian model comparison for hypothesis testing. Two competing models/hypotheses can be compared using
369:
reflect philosophical differences. The most common application of hypothesis testing is in the scientific interpretation of experimental data, which is naturally studied by the
235:-value was devised as an informal, but objective, index meant to help a researcher determine (based on other knowledge) whether to modify future experiments or strengthen one's
731:
for example, there is no agreement on a measure of forecast accuracy. In the absence of a consensus measurement, no decision based on measurements will be without controversy.
2229:-test, "there can be no better test for the hypothesis under consideration" (p 321). Neyman–Pearson theory was proving the optimality of Fisherian methods from its inception.
376:
Fisher and Neyman opposed the subjectivity of probability. Their views contributed to the objective definitions. The core of their historical disagreement was philosophical.
251:(the hypothesis more likely to have generated the sample). Their method always selected a hypothesis. It also allowed the calculation of both types of error probabilities.
209:(son of Karl). Ronald Fisher began his life in statistics as a Bayesian (Zabell 1992), but Fisher soon grew disenchanted with the subjectivity involved (namely use of the
3409:
254:
Fisher and Neyman/Pearson clashed bitterly. Neyman/Pearson considered their formulation to be an improved generalization of significance testing (the defining paper was
9338:
524:
Not rejecting the null hypothesis does not mean the null hypothesis is "accepted" per se (though Neyman and
Pearson used that word in their original writings; see the
2935:
2196:
among three hypotheses: no radioactive source present, one present, two (all) present. The test could be required for safety, with actions required in each case. The
591:
571:
4950:
Epistemology, Not
Statistics: Replace Significance Tests by Confidence Intervals and Quantify Accuracy of Risky Numerical Predictions" (Chapter 14 in Harlow (1997)).
4125:
2136:, although the two types of inference have notable differences. Statistical hypothesis tests define a procedure that controls (fixes) the probability of incorrectly
1206:
1173:
1146:
1119:
2118:
5790:
1215:
The hypothesis of innocence is rejected only when an error is very unlikely, because one does not want to convict an innocent defendant. Such an error is called
3936:
Hubbard, R.; Parsa, A. R.; Luthy, M. R. (1997). "The Spread of Statistical Significance Testing in Psychology: The Case of the Journal of Applied Psychology".
1053:
Laplace considered the statistics of almost half a million births. The statistics showed an excess of boys compared to girls. He concluded by calculation of a
1641:{\displaystyle P({\text{reject }}H_{0}\mid H_{0}{\text{ is valid}})=P\left(X=25\mid p={\frac {1}{4}}\right)=\left({\frac {1}{4}}\right)^{25}\approx 10^{-15}}
2148:
the probability that the null hypothesis is true, nor whether any specific alternative hypothesis is true. This contrasts with other possible techniques of
553:
When the null hypothesis is true and statistical assumptions are met, the probability that the p-value will be less than or equal to the significance level
100:
is a less severe test of the theory that motivated performing the experiment. An examination of the origins of the latter practice may therefore be useful:
1221:(i.e., the conviction of an innocent person), and the occurrence of this error is controlled to be rare. As a consequence of this asymmetric behaviour, an
978:, the test with the greatest power (probability of rejection) for a given value of the parameter(s) being tested, contained in the alternative hypothesis.
5798:
Statistical Analysis based Hypothesis Testing Method in Biological Knowledge Discovery; Md. Naseef-Ur-Rahman Chowdhury, Suvankar Paul, Kazi Zakia Sultana
1295:
The following example was produced by a philosopher describing scientific methods generations before hypothesis testing was formalized and popularized.
9078:
9068:
5725:
2997:
2183:
of tests, i.e. the probability of correctly rejecting the null hypothesis given that it is false. Such considerations can be used for the purpose of
2352:
publishers have recognized the obligation to publish some results that are not statistically significant to combat publication bias, and a journal (
5395:
2410:
is one proposed alternative to significance testing. (Nickerson cited 10 sources suggesting it, including Rozeboom (1960)). For example, Bayesian
4797:
2756:
2389:
A unifying position of critics is that statistics should not lead to an accept-reject conclusion or decision, but to an estimated value with an
239:
in the null hypothesis. Hypothesis testing (and Type I/II errors) was devised by Neyman and Pearson as a more objective alternative to Fisher's
7222:
3129:
the medical profession on the control of disease, and there is no limit to the extent to which they could impede every sort of national effort.
418:
and chi-squared). Statistical hypothesis testing is considered a mature area within statistics, but a limited amount of development continues.
361:, which includes hypothesis testing, is applied probability. Both probability and its application are intertwined with philosophy. Philosopher
7727:
4346:
679:). Significance testing is used as a substitute for the traditional comparison of predicted value and experimental result at the core of the
5785:
5472:
2460:
hypothesis testing can provide this information, and do not claim to. The probability a hypothesis is true can only be derived from use of
5703:
Lehmann E.L. (1992) "Introduction to Neyman and Pearson (1933) On the Problem of the Most Efficient Tests of Statistical Hypotheses". In:
521:
The former report is adequate, the latter gives a more detailed explanation of the data and the reason why the suitcase is being checked.
7877:
9118:
7501:
6142:
3337:
Gigerenzer, Gerd; Zeno Swijtink; Theodore Porter; Lorraine Daston; John Beatty; Lorenz Kruger (1989). "Part 3: The Inference Experts".
773:
Test statistic: A value calculated from a sample without any unknown parameters, often to summarize the sample for comparison purposes.
3406:
593:. This ensures that the hypothesis test maintains its specified false positive rate (provided that statistical assumptions are met).
68:
While hypothesis testing was popularized early in the 20th century, early forms were used in the 1700s. The first use is credited to
2309:. Most of the criticism is indirect. Rather than being wrong, statistical hypothesis testing is misunderstood, overused and misused.
7275:
4910:
604:-value does not provide the probability that either the null hypothesis or its opposite is correct (a common source of confusion).
4838:
Yates, Frank (1951). "The Influence of Statistical Methods for Research Workers on the Development of the Science of Statistics".
9323:
9151:
9123:
8163:
7714:
4088:
Tibshirani, R.J. and Efron, B., 1993. An introduction to the bootstrap. Monographs on statistics and applied probability, 57(1).
9128:
8444:
2090:
From all the numbers c, with this property, we choose the smallest, in order to minimize the probability of a Type II error, a
944:
Conservative test: A test is conservative if, when constructed for a given nominal significance level, the true probability of
750:
2905:
1356:
899:. ("This is a specific test. Because the result is positive, we can confidently say that the patient has the condition.") See
9186:
9093:
5763:
5330:
4780:
4727:
4702:
4652:
4496:
4447:
4392:
4362:
4326:
4228:
4204:
4179:
3843:
3802:
3777:
3740:
3524:"Students' Misconceptions of Statistical Inference: A Review of the Empirical Evidence from Research on Statistics Education"
3453:
3346:
2703:
2678:
2651:
671:
Significance testing has been the favored statistical tool in some experimental social sciences (over 90% of articles in the
5514:
5269:
5102:
This paper lead to the review of statistical practices by the APA. Cohen was a member of the Task Force that did the review.
2344:
Controversy over significance testing, and its effects on publication bias in particular, has produced several results. The
2283:
Criticism of statistical hypothesis testing fills volumes. Much of the criticism can be summarized by the following issues:
2205:
727:
A statistical analysis of misleading data produces misleading conclusions. The issue of data quality can be more subtle. In
9176:
6137:
5837:
4256:
2322:
1653:
and hence, very small. The probability of a false positive is the probability of randomly guessing correctly all 25 times.
380:
1418:
734:
Publication bias: Statistically nonsignificant results may be less likely to be published, which can bias the literature.
379:
Many of the philosophical criticisms of hypothesis testing are discussed by statisticians in other contexts, particularly
9133:
8697:
8285:
6741:
5889:
2384:
2200:
of hypothesis testing says that a good criterion for the selection of hypotheses is the ratio of their probabilities (a
2078:{\displaystyle P({\text{reject }}H_{0}\mid H_{0}{\text{ is valid}})=P\left(X\geq c\mid p={\frac {1}{4}}\right)\leq 0.01}
8201:
4677:
4521:
3920:
2345:
265:
2360:"strongly recommend the use of estimation methods for those publishing in The Journal" (meaning the magnitude of the
2299:
Confusion resulting (in part) from combining the methods of Fisher and Neyman–Pearson which are conceptually distinct.
517:"The Geiger-counter reading is high; 97% of safe suitcases have lower readings. The limit is 95%. Check the suitcase."
9191:
8717:
8300:
7524:
7416:
5712:
5348:"Moving beyond P values in The Journal of Physiology: A primer on the value of effect sizes and confidence intervals"
4755:
4471:
4064:
3980:
3704:
936:: A predecessor to the statistical hypothesis test (see the Origins section). An experimental result was said to be
8129:
7702:
7576:
5117:
Nickerson, Raymond S. (2000). "Null Hypothesis Significance Tests: A Review of an Old and Continuing Controversy".
2585:
268:
in 1938, breaking his partnership with Pearson and separating the disputants (who had occupied the same building).
8834:
8462:
8439:
7760:
7421:
7166:
6537:
6127:
3362:
Mayo, D. G.; Spanos, A. (2006). "Severe Testing as a Basic Concept in a Neyman–Pearson Philosophy of Induction".
3146:
Lenhard, Johannes (2006). "Models and Statistical Inference: The Controversy between Fisher and Neyman–Pearson".
3084:
Lehmann, E. L. (December 1993). "The Fisher, Neyman–Pearson Theories of Testing Hypotheses: One Theory or Two?".
2590:
213:
when determining prior probabilities), and sought to provide a more "objective" approach to inductive inference.
9328:
9289:
9108:
9058:
8870:
8767:
8528:
8429:
8342:
7811:
7023:
6830:
6719:
6677:
2615:
2605:
6751:
2414:
can provide rich information about the data from which researchers can draw inferences, while using uncertain
2167:, but this fails when comparing point and continuous hypotheses. Other approaches to decision making, such as
9333:
9301:
8941:
8712:
8054:
7013:
5916:
5773:
2643:
100 Statistical Tests in R: What to Choose, how to Easily Calculate, with Over 300 Illustrations and Examples
2580:
2302:
Emphasis on statistical significance to the exclusion of estimation and confirmation by repeated experiments.
174:
4118:"An argument for Divine Providence, taken from the constant regularity observed in the births of both sexes"
1485:=25 (i.e. we only accept clairvoyance when all cards are predicted correctly) we're more critical than with
1477:, of hits, at which point we consider the subject to be clairvoyant? How do we determine the critical value
8806:
8533:
7605:
7554:
7539:
7529:
7398:
7270:
7237:
7063:
7018:
6848:
2610:
981:
3523:
2261:
power is useful in explaining the consequences of adjusting the significance level and is heavily used in
815:
8953:
8846:
8757:
8570:
8558:
8467:
8156:
8117:
7949:
7750:
7674:
6975:
6729:
6398:
5862:
5768:
4079:
Hall, P. and Wilson, S.R., 1991. Two guidelines for bootstrap hypothesis testing. Biometrics, pp.757-762.
2720:"Appraising and Amending Theories: The Strategy of Lakatosian Defense and Two Principles That Warrant It"
2543:
2234:
900:
538:
It is particularly critical that appropriate sample sizes be estimated before conducting the experiment.
448:
216:
Fisher emphasized rigorous experimental design and methods to extract a result from few samples assuming
182:
125:
40:
4106:
Horowitz, J.L., 2019. Bootstrap methods in econometrics. Annual Review of Economics, 11, pp.193-224. I'm
3234:"Hypothetical explanations of the negative apparent effects of cloud seeding in the Whitetop Experiment"
694:
The successful hypothesis test is associated with a probability and a type-I error rate. The conclusion
287:
Sometime around 1940, authors of statistical text books began combining the two approaches by using the
9023:
8948:
8853:
8389:
7834:
7806:
7801:
7549:
7308:
7214:
7194:
7102:
6813:
6631:
6114:
5986:
2532:
2527:
2522:
1034:
Arbuthnot examined birth records in London for each of the 82 years from 1629 to 1710, and applied the
994:
3557:
2951:
2771:
2364:(to allow readers to judge whether a finding has practical, physiological, or clinical relevance) and
1330:. They are shown the back face of a randomly chosen playing card 25 times and asked which of the four
9145:
9140:
9008:
8707:
8414:
8372:
8336:
8243:
7566:
7334:
7055:
6980:
6909:
6838:
6758:
6746:
6616:
6604:
6597:
6305:
6026:
5233:
Wilkinson, Leland (1999). "Statistical Methods in Psychology Journals; Guidelines and Explanations".
4866:
Begg, Colin B.; Berlin, Jesse A. (1988). "Publication bias: a problem in interpreting medical data".
2262:
2184:
904:
318:
Set up a statistical null hypothesis. The null need not be a nil hypothesis (i.e., zero difference).
210:
147:
51:
5601:
5531:
4297:
3602:(2006). "Why We Don't Really Know What Statistical Significance Means: Implications for Educators".
3376:
2325:. Casting doubt on the null hypothesis is thus far from directly supporting the research hypothesis.
8983:
8682:
8394:
8290:
8049:
7816:
7679:
7364:
7329:
7293:
7078:
6520:
6429:
6388:
6300:
5991:
5830:
2565:
2562:
2457:
2437:
of the test statistic under the alternative hypothesis are often available in the social sciences.
2434:
2197:
2168:
1287:
hypothesis test can be regarded as either a judgment of a hypothesis or as a judgment of evidence.
1223:
937:
484:
255:
198:
142:
3034:
Goodman, S N (June 15, 1999). "Toward evidence-based medical statistics. 1: The P Value Fallacy".
2464:, which was unsatisfactory to both the Fisher and Neyman–Pearson camps due to the explicit use of
9254:
9181:
9013:
7958:
7571:
7511:
7448:
7086:
7070:
6808:
6670:
6660:
6510:
6424:
5563:
3682:"The Null Ritual What You Always Wanted to Know About Significant Testing but Were Afraid to Ask"
1217:
1000:
3425:
2440:
Advocates of a Bayesian approach sometimes claim that the goal of a researcher is most often to
2249:. Both formulations have been successful, but the successes have been of a different character.
755:
The following definitions are mainly based on the exposition in the book by Lehmann and Romano:
531:
The processes described here are perfectly adequate for computation. They seriously neglect the
9277:
9249:
9028:
8752:
8238:
8149:
7996:
7926:
7719:
7656:
7411:
7298:
6295:
6192:
6099:
5978:
5877:
5780:
5596:
5526:
5416:
5322:
5316:
5305:. Volume 1 number 1 was published in 2002, and all articles are on psychology-related subjects.
4484:
3371:
2153:
804:
763:
716:. Industrial workers were more productive in better illumination, and most productive in worse.
358:
63:
4773:
The Cult of Statistical Significance: How the Standard Error Costs Us Jobs, Justice, and Lives
4318:
4312:
4248:
4171:
483:
Decide to either reject the null hypothesis in favor of the alternative or not reject it. The
9234:
9018:
8553:
8454:
8347:
8196:
8021:
7963:
7906:
7732:
7625:
7534:
7260:
7144:
7003:
6995:
6885:
6877:
6692:
6588:
6566:
6525:
6490:
6457:
6403:
6378:
6333:
6272:
6232:
6034:
5857:
5581:
5389:
3047:
2920:
2575:
2441:
2418:
that exert only minimal influence on the results when enough data is available. Psychologist
2394:
2378:
2357:
2201:
2164:
2129:
1960:
Before the test is actually performed, the maximum acceptable probability of a Type I error (
665:
576:
556:
532:
384:
370:
217:
4163:
3445:
3439:
2338:
Successfully rejecting the null hypothesis may offer no support for the research hypothesis.
9209:
8993:
8858:
8824:
8772:
8597:
8592:
8538:
8494:
8384:
8322:
8211:
8206:
7944:
7519:
7468:
7444:
7406:
7324:
7303:
7255:
7134:
7112:
7081:
6990:
6867:
6818:
6736:
6709:
6665:
6621:
6383:
6159:
6039:
5786:
Critique of classical hypothesis testing highlighting long-standing qualms of statisticians
5734:
4117:
4056:
3875:
3681:
3245:
3190:
3112:
3006:
2600:
2411:
2365:
2216:
probabilities. A likelihood ratio remains a good criterion for selecting among hypotheses.
1184:
1151:
1124:
1097:
1028:
396:
194:
178:
73:
3647:
Sotos, Ana Elisa Castro; Vanhoof, Stijn; Noortgate, Wim Van den; Onghena, Patrick (2009).
3522:
Sotos, Ana Elisa Castro; Vanhoof, Stijn; Noortgate, Wim Van den; Onghena, Patrick (2007).
2797:
2097:
8:
9219:
9214:
8988:
8787:
8777:
8612:
8221:
8091:
8016:
7939:
7620:
7384:
7377:
7339:
7247:
7227:
7199:
6932:
6798:
6793:
6783:
6775:
6593:
6554:
6444:
6434:
6343:
6122:
6078:
5996:
5921:
5823:
4491:(3rd ed.). Eagan, MN; Washington, D.C.: West National Academies Press. p. 259.
2423:
2160:
1039:
664:
Statistical hypothesis testing plays an important role in the whole of statistics and in
510:
The difference in the two processes applied to the radioactive suitcase example (below):
463:
452:
366:
244:
5738:
4941:
3879:
3249:
3194:
3010:
2305:
Rigidly requiring statistical significance as a criterion for publication, resulting in
430:
The typical steps involved in performing a frequentist hypothesis test in practice are:
365:
wrote, "All knowledge degenerates into probability." Competing practical definitions of
8841:
8424:
8273:
8105:
7916:
7770:
7666:
7615:
7491:
7388:
7372:
7349:
7126:
6860:
6843:
6803:
6714:
6609:
6571:
6542:
6502:
6462:
6408:
6325:
6011:
6006:
5809:
5544:
5495:
5447:
5377:
5250:
5212:
5208:
5177:
5160:
Branch, Mark (2014). "Malignant side effects of null hypothesis significance testing".
5142:
5093:
5039:
4933:
4891:
4883:
4816:
4592:
4285:
4144:
4024:
3997:
3953:
3720:
3629:
3599:
3580:
3389:
3311:
3214:
3163:
3059:
2970:
2876:
2558:
2508:
2407:
2328:"t does not tell us what we want to know". Lists of dozens of complaints are available.
2133:
910:
767:
706:
236:
3268:
3233:
675:
during the early 1990s). Other fields have favored the estimation of parameters (e.g.
9003:
8998:
8926:
8875:
8649:
8629:
8617:
8577:
8548:
8516:
8434:
8327:
8295:
8191:
8100:
8011:
7981:
7973:
7793:
7784:
7709:
7640:
7496:
7481:
7456:
7344:
7285:
7151:
7139:
6765:
6682:
6626:
6549:
6393:
6315:
6094:
5968:
5708:
5614:
5540:
5499:
5439:
5381:
5369:
5326:
5216:
5134:
5043:
4977:
4895:
4820:
4776:
4751:
4723:
4698:
4673:
4648:
4517:
4492:
4467:
4443:
4388:
4358:
4322:
4252:
4224:
4200:
4175:
4164:
4148:
4060:
4029:
3976:
3957:
3916:
3893:
3839:
3798:
3773:
3746:
3736:
3700:
3449:
3342:
3336:
3319:
3273:
3206:
3051:
2832:"On the Theory of Contingency and Its Relation to Association and Normal Correlation"
2699:
2674:
2647:
2570:
2502:
2469:
2461:
2415:
2390:
2180:
877:
866:
680:
138:
5181:
5146:
4937:
4717:
4273:
4162:
Brian, Éric; Jaisson, Marie (2007). "Physico-Theology and Mathematics (1710–1794)".
3633:
3218:
3167:
860:: The set of values of the test statistic for which the null hypothesis is rejected.
9168:
8921:
8880:
8692:
8667:
8479:
8409:
8253:
8036:
7991:
7755:
7742:
7635:
7610:
7544:
7476:
7354:
6962:
6855:
6788:
6701:
6648:
6467:
6338:
6132:
6016:
5931:
5898:
5742:
5681:
5646:
5606:
5548:
5536:
5487:
5468:
5451:
5431:
5412:
5359:
5242:
5204:
5169:
5126:
5085:
5031:
5004:
4969:
4925:
4875:
4851:
4847:
4812:
4748:
Beyond Significance Testing: Reforming Data Analysis Methods in Behavioral Research
4623:
4582:
4554:
4550:
4134:
4019:
4009:
3945:
3883:
3765:
3728:
3692:
3665:
3660:
3648:
3619:
3611:
3572:
3538:
3502:
3393:
3381:
3303:
3263:
3253:
3198:
3155:
3097:
3093:
3063:
3043:
3014:
2966:
2902:
2866:
2812:
2734:
2419:
2306:
2238:
2176:
1066:
713:
281:
120:
5254:
5097:
4049:
3202:
9229:
8931:
8734:
8727:
8662:
8602:
8484:
8474:
8404:
8377:
8362:
8317:
8307:
8258:
7953:
7697:
7559:
7486:
7161:
7035:
7008:
6985:
6954:
6581:
6576:
6530:
6260:
5911:
5273:
3542:
2909:
2668:
2641:
2537:
2349:
2242:
2172:
2149:
2141:
1177:
1018:
791:
190:
96:
77:
7443:
5089:
5008:
4410:"Illustrations of the Logic of Science VI: Deduction, Induction, and Hypothesis"
243:-value, also meant to determine researcher behaviour, but without requiring any
8916:
8702:
8639:
8624:
8607:
8565:
8367:
8248:
7902:
7897:
6360:
6290:
5936:
5246:
5035:
3238:
Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America
2831:
2805:
The London, Edinburgh, and Dublin Philosophical Magazine and Journal of Science
2738:
2553:
2398:
2209:
2091:
1490:
1076:
1024:
887:
720:
438:
403:
292:
106:
69:
36:
24:
19:
5130:
2816:
9317:
9224:
9103:
8911:
8885:
8762:
8722:
8687:
8677:
8657:
8399:
8357:
8332:
8280:
8268:
8263:
8172:
8059:
8026:
7889:
7850:
7661:
7630:
7094:
7048:
6653:
6355:
6182:
5946:
5941:
5491:
5173:
4342:
4014:
3949:
3750:
3615:
3413:
2897:
2453:
2430:
2292:
896:
801:
Positive data: Data that enable the investigator to reject a null hypothesis.
542:
225:
186:
151:
4628:
4611:
4587:
4570:
3649:"How Confident Are Students in Their Misconceptions about Hypothesis Tests?"
3507:
3490:
3407:
Mathematics > High School: Statistics & Probability > Introduction
3258:
2871:
2854:
824:≈ 1.645 corresponds to the chosen significance level. The critical region [C
9244:
8672:
8521:
8511:
8489:
8419:
8312:
8226:
8001:
7934:
7911:
7826:
7156:
6452:
6350:
6285:
6227:
6212:
6149:
6104:
5747:
5720:
5618:
5443:
5373:
5138:
4960:
Bakan, David (1966). "The test of significance in psychological research".
4670:
Statistical Inference: A Commentary for the Social and Behavioural Sciences
4139:
4033:
3897:
3859:
3323:
3277:
3210:
3055:
3019:
2992:
2913:. A working paper that explains the difference between Fisher's evidential
2595:
2465:
1331:
1327:
501:
is in the critical region, and not to reject the null hypothesis otherwise.
269:
206:
202:
163:
134:
116:
5195:
Hunter, John E. (January 1997). "Needed: A Ban on the Significance Test".
4981:
3732:
3696:
3385:
3159:
9239:
8936:
8634:
8543:
8506:
8044:
8006:
7689:
7590:
7452:
7265:
7232:
6724:
6641:
6636:
6280:
6237:
6217:
6197:
6187:
5956:
4824:
3998:"Common pitfalls in statistical analysis: The perils of multiple testing"
2548:
2445:
2361:
2246:
1088:
728:
676:
3315:
2278:
781:: Any hypothesis which specifies the population distribution completely.
8865:
8587:
6890:
6370:
6070:
6001:
5951:
5926:
5846:
4887:
4718:
Harlow, Lisa Lavoie; Stanley A. Mulaik; James H. Steiger, eds. (1997).
4596:
3584:
3339:
The Empire of Chance: How Probability Changed Science and Everyday Life
2880:
2719:
2517:
2449:
2221:
951:
723:. Pills with no medically active ingredients were remarkably effective.
514:"The Geiger-counter reading is 10. The limit is 9. Check the suitcase."
425:
362:
92:
39:. Then a decision is made, either by comparing the test statistic to a
5721:"On the Problem of the Most Efficient Tests of Statistical Hypotheses"
4317:. Cambridge, Mass: Belknap Press of Harvard University Press. p.
2993:"On the Problem of the most Efficient Tests of Statistical Hypotheses"
2348:
has strengthened its statistical reporting requirements after review,
948:
rejecting the null hypothesis is never greater than the nominal level.
623:
chance that the observed results (perfectly ordered tea) would occur.
8963:
8782:
8352:
8233:
7043:
6895:
6515:
6310:
6222:
6207:
6202:
6167:
5686:
5669:
5651:
5634:
5610:
5435:
5364:
5347:
4973:
4314:
The History of Statistics: The Measurement of Uncertainty before 1900
4245:
The History of Statistics: The Measurement of Uncertainty Before 1900
3689:
The SAGE Handbook of Quantitative Methodology for the Social Sciences
3307:
2265:. The two methods remain philosophically distinct. They usually (but
1035:
4911:"Theory-Testing in Psychology and Physics: A Methodological Paradox"
4879:
3888:
3863:
3624:
3576:
2397:. Estimation statistics can be accomplished with either frequentist
8829:
8582:
8216:
8186:
6559:
6177:
6054:
6049:
6044:
4929:
4409:
3935:
2620:
295:(or data) to test against the Neyman–Pearson "significance level".
5796:
5057:
Lykken, David T. (1991). "What's wrong with psychology, anyway?".
3996:
Ranganathan, Priya; Pramesh, C. S; Buyse, Marc (April–June 2016).
3763:
8501:
8064:
7765:
3910:
3474:(6 ed.). Ames, Iowa: Iowa State University Press. p. 3.
2473:
1334:
it belongs to. The number of hits, or correct answers, is called
920:
828:, ∞) is realized as the tail of the standard normal distribution.
648:
Determining the range at which a bat can detect an insect by echo
167:
44:
8141:
5473:"Rejecting or Accepting Parameter Values in Bayesian Estimation"
5076:
Jacob Cohen (December 1994). "The Earth Is Round (p < .05)".
3416:
Common Core State Standards Initiative (relates to USA students)
3232:
Losavich, J. L.; Neyman, J.; Scott, E. L.; Wells, M. A. (1971).
3181:
Neyman, Jerzy (1967). "RA Fisher (1890—1962): An Appreciation".
387:. Hypothesis testing is of continuing interest to philosophers.
8796:
7986:
6967:
6941:
6921:
6172:
5963:
5022:
Nunnally, Jum (1960). "The place of statistics in psychology".
1227:(acquitting a person who committed the crime), is more common.
1968:
is calculated. For example, if we select an error rate of 1%,
1318:
probably intended to be assumed much larger than one's hand).
1212:. It is the alternative hypothesis that one hopes to support.
651:
Deciding whether hospital carpeting results in more infections
8958:
5815:
5569:(Report). Department of Statistics, University of Washington.
4642:
2696:
in Statisticians of the Centuries by C.C. Heyde and E. Seneta
2640:
Lewis, Nancy D.; Lewis, Nigel Da Costa; Lewis, N. D. (2013).
1303:
Therefore: Probably, these beans were taken from another bag.
988:
541:
The phrase "test of significance" was coined by statistician
299:
A comparison between Fisherian, frequentist (Neyman–Pearson)
5345:
3646:
3521:
2422:
has suggested Bayesian estimation as an alternative for the
1057:-value that the excess was a real, but unexplained, effect.
709:. A horse appeared to be capable of doing simple arithmetic.
9084:
Committee on the Environment, Public Health and Food Safety
8890:
5906:
4612:"Could Fisher, Jeffreys and Neyman Have Agreed on Testing?"
2163:
approach to hypothesis testing is to base decisions on the
882:: For simple hypotheses, this is the test's probability of
657:
Checking whether bumper stickers reflect car owner behavior
23:
The above image shows a table with some of the most common
5480:
Advances in Methods and Practices in Psychological Science
4770:
2393:; this data-analysis philosophy is broadly referred to as
2128:
Statistical hypothesis testing is a key technique of both
1957:= 10 yields a much greater probability of false positive.
639:
Testing whether more men than women suffer from nightmares
154:
and others to dismiss the use of "inverse probabilities".
4695:
Statistical Significance: Rationale, Validity and Utility
4442:(5. print. ed.). Cambridge : Cambridge Univ. Press.
4126:
Philosophical Transactions of the Royal Society of London
2385:
Confidence interval § Statistical hypothesis testing
1087:
A statistical test procedure is comparable to a criminal
957:
A statistical hypothesis test compares a test statistic (
434:
Define a hypothesis (claim which is testable using data).
5302:
4798:"Recent Methodological Contributions to Clinical Trials"
4750:. Washington, D.C.: American Psychological Association.
3231:
2452:
is true based on the data they have collected. Neither
1400:{\displaystyle {\text{:}}\qquad H_{0}:p={\tfrac {1}{4}}}
1094:
In the start of the procedure, there are two hypotheses
1071:
In a famous example of hypothesis testing, known as the
5287:
significance is an important cause of publication bias.
3995:
3673:
635:
Real world applications of hypothesis testing include:
157:
5582:"The fallacy of the null-hypothesis significance test"
4995:
Gigerenzer, G (November 2004). "Mindless statistics".
3558:"New Pedagogy and New Content: The Case of Statistics"
3355:
1447:
1386:
162:
Modern significance testing is largely the product of
5299:
Journal of Articles in Support of the Null Hypothesis
5116:
3491:"Testing Statistical Hypotheses: The Story of a Book"
3426:
College Board Tests > AP: Subjects > Statistics
2923:
2354:
Journal of Articles in Support of the Null Hypothesis
2100:
1982:
1670:
1507:
1421:
1359:
1187:
1154:
1127:
1100:
579:
559:
264:
Events intervened: Neyman accepted a position in the
7728:
Autoregressive conditional heteroskedasticity (ARCH)
4195:
Conover, W.J. (1999), "Chapter 3.4: The Sign Test",
2945:
2943:
2855:"R. A. Fisher on the History of Inverse Probability"
2498:
2334:
inadequate as the sole tool for statistical analysis
2190:
1461:{\displaystyle {\text{:}}H_{1}:p>{\tfrac {1}{4}}}
426:
Performing a frequentist hypothesis test in practice
5512:
4541:Tukey, John W. (1960). "Conclusions vs decisions".
2764:
Mémoires de l'Académie Royale des Sciences de Paris
437:Select a relevant statistical test with associated
7190:
5707:, (Eds Kotz, S., Johnson, N.L.), Springer-Verlag.
4988:
4868:Journal of the Royal Statistical Society, Series A
4170:. Springer Science & Business Media. pp.
4048:
2959:Journal of the Royal Statistical Society, Series B
2929:
2836:Drapers' Company Research Memoirs Biometric Series
2112:
2077:
1940:
1640:
1460:
1399:
1200:
1167:
1140:
1113:
645:Evaluating the effect of the full moon on behavior
585:
565:
9339:Mathematical and quantitative methods (economics)
5781:Bayesian critique of classical hypothesis testing
5726:Philosophical Transactions of the Royal Society A
5515:"Significance tests harm progress in forecasting"
5346:Williams S, Carson R, Tóth K (October 10, 2023).
5232:
4771:McCloskey, Deirdre N.; Stephen T. Ziliak (2008).
3470:Snedecor, George W.; Cochran, William G. (1967).
3364:The British Journal for the Philosophy of Science
3289:
3287:
2998:Philosophical Transactions of the Royal Society A
2986:
2984:
2982:
2980:
2940:
2487:, while Neyman–Pearson devised their approach of
2472:. Fisher's strategy is to sidestep this with the
1862:
1849:
632:into milk). The data contradicted the "obvious".
469:Compute from the observations the observed value
9315:
5463:
5461:
5407:
5405:
5339:
3913:Statistics in the Real World: a book of examples
3597:
2917:-value and the Neyman–Pearson Type I error rate
784:Composite hypothesis: Any hypothesis which does
762:: A statement about the parameters describing a
7276:Multivariate adaptive regression splines (MARS)
5270:"ICMJE: Obligation to Publish Negative Studies"
4840:Journal of the American Statistical Association
4643:Morrison, Denton; Henkel, Ramon, eds. (2006) .
3772:. Vol. I and II (Second ed.). Wiley.
3469:
3341:. Cambridge University Press. pp. 70–122.
3086:Journal of the American Statistical Association
2892:
2890:
2639:
788:specify the population distribution completely.
487:decision rule is to reject the null hypothesis
4440:Probability theory : the logic of science
4115:
3975:. New York: W.H. Freeman and Co. p. 426.
3284:
2977:
2952:"Statistical Methods and Scientific Induction"
2750:
2748:
201:"), while hypothesis testing was developed by
50:computed from the test statistic. Roughly 100
8157:
5831:
5718:
5458:
5402:
4046:
3833:
3488:
2991:Neyman, J; Pearson, E. S. (January 1, 1933).
2990:
2123:
357:Hypothesis testing and philosophy intersect.
141:" in order to determine whether outcomes are
5394:: CS1 maint: multiple names: authors list (
5228:
5226:
5159:
5112:
5110:
5108:
4482:
4407:
4265:
4161:
3911:Richard J. Larsen; Donna Fox Stroup (1976).
3484:
3482:
3079:
3077:
3075:
3073:
2887:
2687:
1148:: "the defendant is guilty". The first one,
87:
5424:Journal of Experimental Psychology: General
5417:"Bayesian Estimation Supersedes the T Test"
5075:
4483:Kaye, David H.; Freedman, David A. (2011).
4199:(Third ed.), Wiley, pp. 157–176,
4188:
4047:Hughes, Ann J.; Grawoig, Dennis E. (1971).
3428:The College Board (relates to USA students)
2823:
2789:
2745:
2341:supporters suggest a less absolute change.
9119:Centers for Disease Control and Prevention
8164:
8150:
5876:
5838:
5824:
5793:How to choose the correct statistical test
5670:"R. A. Fisher on Bayes and Bayes' theorem"
5635:"The Case for Objective Bayesian Analysis"
5506:
4994:
4865:
4536:
4534:
4212:
4055:. Reading, Mass.: Addison-Wesley. p.
3973:Introduction to the Practice of Statistics
3834:Lehmann, E. L.; Romano, Joseph P. (2005).
3811:
3792:
3679:
3361:
3330:
3293:
3141:
3139:
3137:
1497:= 25 the probability of such an error is:
989:Nonparametric bootstrap hypothesis testing
660:Testing the claims of handwriting analysts
9079:Centre for Disease Prevention and Control
9069:Center for Disease Control and Prevention
6489:
5764:"Statistical hypotheses, verification of"
5746:
5685:
5650:
5600:
5530:
5363:
5223:
5105:
5024:Educational and Psychological Measurement
4795:
4764:
4720:What If There Were No Significance Tests?
4627:
4586:
4221:Applied Nonparametric Statistical Methods
4138:
4023:
4013:
3887:
3821:, Edinburgh: Oliver and Boyd, 1925, p.43.
3664:
3623:
3506:
3479:
3375:
3267:
3257:
3070:
3018:
2870:
2693:
5579:
5467:
5411:
5021:
4741:
4739:
4636:
4274:"Mémoire sur les probabilités (XIX, XX)"
3819:Statistical Methods for Research Workers
3048:10.7326/0003-4819-130-12-199906150-00008
2694:Bellhouse, P. (2001), "John Arbuthnot",
1321:
814:
654:Selecting the best means to stop smoking
27:and their corresponding tests or models.
18:
9124:Health departments in the United States
5810:p-value and hypothesis test calculators
5667:
5069:
4953:
4568:
4531:
4489:Reference Manual on Scientific Evidence
4310:
4271:
4242:
4223:(Second ed.), Chapman & Hall,
4194:
4166:The Descent of Human Sex Ratio at Birth
3929:
3864:"Scientific method: Statistical errors"
3463:
3145:
3134:
3083:
3033:
2829:
2795:
2754:
1407: (just guessing)
9316:
9129:Council on Education for Public Health
7802:Kaplan–Meier estimator (product limit)
5632:
5314:
5194:
5153:
5056:
4711:
4609:
4437:
4341:
4335:
4218:
3904:
3180:
3110:
2949:
2852:
1290:
751:Notation in probability and statistics
744:
9187:Professional degrees of public health
9094:Ministry of Health and Family Welfare
8145:
7875:
7442:
7189:
6488:
6258:
5875:
5819:
5802:
5715:(followed by reprinting of the paper)
5705:Breakthroughs in Statistics, Volume 1
5292:
4959:
4908:
4837:
4745:
4736:
4667:
4540:
4247:. Harvard University Press. pp.
4051:Statistics: A Foundation for Analysis
3970:
3964:
3858:
3829:
3827:
3555:
3431:
2717:
2666:
2483:based on the data alone) followed by
2208:. Null hypotheses should be at least
1468: (true clairvoyant).
1326:A person (the subject) is tested for
1121:: "the defendant is not guilty", and
1050: = 1/2 significance level.
626:
9284:
9177:Bachelor of Science in Public Health
8112:
7812:Accelerated failure time (AFT) model
5561:
5519:International Journal of Forecasting
4692:
4686:
4385:R.A. Fisher, The Life of a Scientist
3437:
2903:P Values are not Error Probabilities
2323:correlation does not imply causation
2094:. For the above example, we select:
1299:Few beans of this handful are white.
642:Establishing authorship of documents
505:
451:with known degrees of freedom, or a
381:correlation does not imply causation
158:Modern origins and early controversy
81:
9296:
8445:Workers' right to access the toilet
8286:Human right to water and sanitation
8124:
7407:Analysis of variance (ANOVA, anova)
6259:
5564:Bayes factors and model uncertainty
4571:"The History of Statistics in 1933"
4569:Stigler, Stephen M. (August 1996).
4511:
4505:
4382:
4357:]. Courier Dover Publications.
4347:"Mathematics of a Lady Tasting Tea"
3838:(3E ed.). New York: Springer.
2156:are treated on a more equal basis.
1305:This is an hypothetical inference.
1060:
886:rejecting the null hypothesis. The
525:
13:
7502:Cochran–Mantel–Haenszel statistics
6128:Pearson product-moment correlation
5719:Neyman, J.; Pearson, E.S. (1933).
5697:
5318:Statistical Methods for Psychology
5209:10.1111/j.1467-9280.1997.tb00534.x
4817:10.1093/oxfordjournals.aje.a112313
4351:The World of Mathematics, volume 3
4197:Practical Nonparametric Statistics
3824:
3795:Design and analysis of experiments
3770:Design and Analysis of Experiments
3296:The American Journal of Psychology
2971:10.1111/j.2517-6161.1955.tb00180.x
2346:American Psychological Association
1853:
1345:probability of guessing correctly
1255:Do not reject the null hypothesis
1082:
1012:
266:University of California, Berkeley
14:
9350:
8718:Commercial determinants of health
8171:
5756:
5059:Thinking Clearly About Psychology
4645:The Significance Test Controversy
2191:Neyman–Pearson hypothesis testing
2187:prior to the collection of data.
1301:Most beans in this bag are white.
548:
277:-values and significance levels.
9295:
9283:
9272:
9271:
8301:National public health institute
8123:
8111:
8099:
8086:
8085:
7876:
5541:10.1016/j.ijforecast.2007.03.004
4805:American Journal of Epidemiology
4775:. University of Michigan Press.
4387:. New York: Wiley. p. 134.
4280:. Vol. 9. pp. 429–438.
3721:"Testing Statistical Hypotheses"
3565:International Statistical Review
2667:Kanji, Gopal K. (18 July 2006).
2586:Modifiable temporal unit problem
2501:
970:Most powerful test: For a given
307:Fisher's null hypothesis testing
43:or equivalently by evaluating a
8698:Open-source healthcare software
8440:Sociology of health and illness
7761:Least-squares spectral analysis
5661:
5626:
5573:
5555:
5321:(5 ed.). Duxbury. p.
5308:
5262:
5188:
5050:
5015:
4902:
4859:
4831:
4789:
4722:. Lawrence Erlbaum Associates.
4661:
4603:
4562:
4485:"Reference Guide on Statistics"
4476:
4456:
4431:
4401:
4376:
4304:
4236:
4155:
4109:
4100:
4091:
4082:
4073:
4040:
3989:
3852:
3786:
3757:
3713:
3653:Journal of Statistics Education
3640:
3591:
3549:
3515:
3419:
3400:
3225:
3174:
3104:
3027:
2591:Multivariate hypothesis testing
2372:
1365:
741:but liars figure" (anonymous).
310:Neyman–Pearson decision theory
16:Method of statistical inference
9324:Statistical hypothesis testing
9059:Caribbean Public Health Agency
8871:Sexually transmitted infection
8768:Statistical hypothesis testing
8529:Occupational safety and health
8430:Sexual and reproductive health
8343:Occupational safety and health
6742:Mean-unbiased minimum-variance
5845:
4997:The Journal of Socio-Economics
4852:10.1080/01621459.1951.10500764
4672:. Chichester New York: Wiley.
4555:10.1080/00401706.1960.10489909
4369:Originally from Fisher's book
3836:Testing Statistical Hypotheses
3666:10.1080/10691898.2009.11889514
3604:Journal of Marketing Education
3098:10.1080/01621459.1993.10476404
2846:
2757:"Mémoire sur les probabilités"
2711:
2660:
2633:
2616:Bayesian information criterion
2606:Almost sure hypothesis testing
2022:
1986:
1710:
1674:
1547:
1511:
466:. Common values are 5% and 1%.
1:
8713:Social determinants of health
8055:Geographic information system
7271:Simultaneous equations models
4349:. In James Roy Newman (ed.).
3203:10.1126/science.156.3781.1456
2627:
2581:Modifiable areal unit problem
2456:'s significance testing, nor
1349:. The hypotheses, then, are:
932:Statistical significance test
673:Journal of Applied Psychology
458:Select a significance level (
455:with known mean and variance.
352:
52:specialized statistical tests
8773:Analysis of variance (ANOVA)
8534:Human factors and ergonomics
7238:Coefficient of determination
6849:Uniformly most powerful test
5580:Rozeboom, William W (1960).
5513:Armstrong, J. Scott (2007).
4408:C. S. Peirce (August 1878).
4311:Stigler, Stephen M. (1986).
4278:Oeuvres complètes de Laplace
4243:Stigler, Stephen M. (1986).
3793:Montgomery, Douglas (2009).
3725:Springer Texts in Statistics
3543:10.1016/j.edurev.2007.04.001
3444:. New York: Norton. p.
2698:, Springer, pp. 39–42,
2611:Akaike information criterion
2272:
1268:
1253:
982:Uniformly most powerful test
390:
7:
8954:Good manufacturing practice
8758:Randomized controlled trial
7807:Proportional hazards models
7751:Spectral density estimation
7733:Vector autoregression (VAR)
7167:Maximum posterior estimator
6399:Randomized controlled trial
5791:Statistical Tests Overview:
5769:Encyclopedia of Mathematics
5090:10.1037/0003-066X.49.12.997
5009:10.1016/j.socec.2004.09.033
3531:Educational Research Review
3113:"The Nature of Probability"
2544:Complete spatial randomness
2494:
2235:statistical process control
1007:
907:for exhaustive definitions.
901:sensitivity and specificity
686:
33:statistical hypothesis test
10:
9355:
9024:Theory of planned behavior
8949:Good agricultural practice
8854:Public health surveillance
8746:epidemiological statistics
8390:Public health intervention
7567:Multivariate distributions
5987:Average absolute deviation
5247:10.1037/0003-066X.54.8.594
5036:10.1177/001316446002000401
4796:Cornfield, Jerome (1976).
3441:How to lie with statistics
2908:September 4, 2013, at the
2739:10.1207/s15327965pli0102_1
2533:Checking if a coin is fair
2528:Bootstrapping (statistics)
2382:
2376:
2276:
2124:Variations and sub-classes
1656:Being less critical, with
1064:
1016:
995:Bootstrapping (statistics)
992:
748:
462:), the maximum acceptable
394:
224:there was no concept of a
175:Pearson's chi-squared test
76:(1770s), in analyzing the
61:
57:
9267:
9202:
9161:
9146:World Toilet Organization
9141:World Health Organization
9048:
9037:
8974:
8899:
8815:
8743:
8708:Public health informatics
8648:
8453:
8415:Right to rest and leisure
8244:Globalization and disease
8179:
8081:
8035:
7972:
7925:
7888:
7884:
7871:
7843:
7825:
7792:
7783:
7741:
7688:
7649:
7598:
7589:
7555:Structural equation model
7510:
7467:
7463:
7438:
7397:
7363:
7317:
7284:
7246:
7213:
7209:
7185:
7125:
7034:
6953:
6917:
6908:
6891:Score/Lagrange multiplier
6876:
6829:
6774:
6700:
6691:
6501:
6497:
6484:
6443:
6417:
6369:
6324:
6306:Sample size determination
6271:
6267:
6254:
6158:
6113:
6087:
6069:
6025:
5977:
5897:
5888:
5884:
5871:
5853:
5131:10.1037/1082-989X.5.2.241
4610:Berger, James O. (2003).
4383:Box, Joan Fisher (1978).
2817:10.1080/14786440009463897
2770:: 227–332. Archived from
2291:-value is dependent upon
2263:sample size determination
2185:sample size determination
2140:that a default position (
938:statistically significant
905:type I and type II errors
211:principle of indifference
148:principle of indifference
137:develops the concept of "
88:Choice of null hypothesis
9192:Schools of public health
8984:Diffusion of innovations
8683:Health impact assessment
8395:Public health laboratory
8291:Management of depression
8050:Environmental statistics
7572:Elliptical distributions
7365:Generalized linear model
7294:Simple linear regression
7064:Hodges–Lehmann estimator
6521:Probability distribution
6430:Stochastic approximation
5992:Coefficient of variation
5492:10.1177/2515245918771304
5174:10.1177/0959354314525282
4514:Basic probability theory
4015:10.4103/2229-3485.179436
3950:10.1177/0959354397074006
3797:. Hoboken, N.J.: Wiley.
3616:10.1177/0273475306288399
3556:Moore, David S. (1997).
2435:probability distribution
2287:The interpretation of a
2169:Bayesian decision theory
1493:, or Type I error. With
1224:error of the second kind
449:Student's t distribution
183:Student's t-distribution
9255:Social hygiene movement
9182:Doctor of Public Health
9014:Social cognitive theory
8816:Infectious and epidemic
8598:Fecal–oral transmission
7710:Cross-correlation (XCF)
7318:Non-standard predictors
6752:Lehmann–Scheffé theorem
6425:Adaptive clinical trial
5162:Theory & Psychology
4909:Meehl, Paul E. (1967).
4668:Oakes, Michael (1986).
4414:Popular Science Monthly
4116:John Arbuthnot (1710).
3680:Gigerenzer, G. (2004).
3259:10.1073/pnas.68.11.2643
2930:{\displaystyle \alpha }
2646:. Heather Hills Press.
1415:alternative hypothesis
1270:Reject null hypothesis
1218:error of the first kind
586:{\displaystyle \alpha }
566:{\displaystyle \alpha }
291:-value in place of the
9250:Germ theory of disease
9029:Transtheoretical model
8106:Mathematics portal
7927:Engineering statistics
7835:Nelson–Aalen estimator
7412:Analysis of covariance
7299:Ordinary least squares
7223:Pearson product-moment
6627:Statistical functional
6538:Empirical distribution
6371:Controlled experiments
6100:Frequency distribution
5878:Descriptive statistics
5748:10.1098/rsta.1933.0009
5633:Berger, James (2006).
5589:Psychological Bulletin
5315:Howell, David (2002).
4962:Psychological Bulletin
4647:. Aldine Transaction.
4438:Jaynes, E. T. (2007).
4140:10.1098/rstl.1710.0011
3489:E. L. Lehmann (1997).
3438:Huff, Darrell (1993).
3020:10.1098/rsta.1933.0009
2931:
2523:Behrens–Fisher problem
2154:alternative hypothesis
2152:in which the null and
2114:
2079:
1942:
1845:
1780:
1642:
1462:
1401:
1307:
1210:alternative hypothesis
1202:
1169:
1142:
1115:
829:
805:Alternative hypothesis
760:Statistical hypothesis
587:
567:
494:if the observed value
476:of the test statistic
359:Inferential statistics
218:Gaussian distributions
126:Weldon dice throw data
82:§ Human sex ratio
64:History of probability
28:
9329:Design of experiments
9134:Public Health Service
9019:Social norms approach
9009:PRECEDE–PROCEED model
8455:Preventive healthcare
8348:Pharmaceutical policy
8197:Chief Medical Officer
8022:Population statistics
7964:System identification
7698:Autocorrelation (ACF)
7626:Exponential smoothing
7540:Discriminant analysis
7535:Canonical correlation
7399:Partition of variance
7261:Regression validation
7105:(Jonckheere–Terpstra)
7004:Likelihood-ratio test
6693:Frequentist inference
6605:Location–scale family
6526:Sampling distribution
6491:Statistical inference
6458:Cross-sectional study
6445:Observational studies
6404:Randomized experiment
6233:Stem-and-leaf display
6035:Central limit theorem
5235:American Psychologist
5197:Psychological Science
5119:Psychological Methods
5078:American Psychologist
4918:Philosophy of Science
4697:. SAGE Publications.
4693:Chow, Siu L. (1997).
4629:10.1214/ss/1056397485
4588:10.1214/ss/1032280216
4371:Design of Experiments
4355:Design of Experiments
4343:Fisher, Sir Ronald A.
3971:Moore, David (2003).
3938:Theory and Psychology
3733:10.1007/0-387-27605-x
3697:10.4135/9781412986311
3508:10.1214/ss/1029963261
2932:
2872:10.1214/ss/1177012488
2727:Psychological Inquiry
2670:100 Statistical Tests
2576:Look-elsewhere effect
2566:tests of significance
2400:or Bayesian methods.
2395:estimation statistics
2379:Estimation statistics
2358:Journal of Physiology
2279:p-value § Misuse
2165:posterior probability
2130:frequentist inference
2115:
2080:
1943:
1825:
1760:
1643:
1463:
1402:
1322:Clairvoyant card game
1297:
1203:
1201:{\displaystyle H_{1}}
1170:
1168:{\displaystyle H_{0}}
1143:
1141:{\displaystyle H_{1}}
1116:
1114:{\displaystyle H_{0}}
1027:(1710), and later by
818:
666:statistical inference
588:
568:
533:design of experiments
385:design of experiments
371:philosophy of science
22:
9334:Logic and statistics
9210:Sara Josephine Baker
9109:Public Health Agency
8994:Health communication
8859:Disease surveillance
8825:Asymptomatic carrier
8807:Statistical software
8495:Preventive nutrition
8323:Medical anthropology
8212:Environmental health
7945:Probabilistic design
7530:Principal components
7373:Exponential families
7325:Nonlinear regression
7304:General linear model
7266:Mixed effects models
7256:Errors and residuals
7233:Confounding variable
7135:Bayesian probability
7113:Van der Waerden test
7103:Ordered alternative
6868:Multiple comparisons
6747:Rao–Blackwellization
6710:Estimating equations
6666:Statistical distance
6384:Factorial experiment
5917:Arithmetic-Geometric
5733:(694–706): 289–337.
5562:Kass, R. E. (1993).
4947:on December 3, 2013.
4512:Ash, Robert (1970).
4464:Theory of Statistics
4462:Schervish, M (1996)
4272:Laplace, P. (1778).
4133:(325–336): 186–190.
3817:R. A. Fisher (1925).
3691:. pp. 391–408.
3111:Fisher, R N (1958).
3005:(694–706): 289–337.
2921:
2755:Laplace, P. (1778).
2601:Dichotomous thinking
2412:parameter estimation
2366:confidence intervals
2198:Neyman–Pearson lemma
2113:{\displaystyle c=13}
2098:
1980:
1972:is calculated thus:
1668:
1505:
1419:
1357:
1185:
1152:
1125:
1098:
1029:Pierre-Simon Laplace
577:
557:
397:Statistics education
195:analysis of variance
179:William Sealy Gosset
95:has argued that the
74:Pierre-Simon Laplace
72:(1710), followed by
9220:Carl Rogers Darnall
9215:Samuel Jay Crumbine
8989:Health belief model
8842:Notifiable diseases
8778:Regression analysis
8613:Waterborne diseases
8202:Cultural competence
8017:Official statistics
7940:Methods engineering
7621:Seasonal adjustment
7389:Poisson regressions
7309:Bayesian regression
7248:Regression analysis
7228:Partial correlation
7200:Regression analysis
6799:Prediction interval
6794:Likelihood interval
6784:Confidence interval
6776:Interval estimation
6737:Unbiased estimators
6555:Model specification
6435:Up-and-down designs
6123:Partial correlation
6079:Index of dispersion
5997:Interquartile range
5739:1933RSPTA.231..289N
5668:Aldrich, J (2008).
4746:Kline, Rex (2004).
4616:Statistical Science
4575:Statistical Science
4516:. New York: Wiley.
4466:, p. 218. Springer
4219:Sprent, P. (1989),
3880:2014Natur.506..150N
3764:Hinkelmann, Klaus;
3600:Armstrong, J. Scott
3495:Statistical Science
3472:Statistical Methods
3386:10.1093/bjps/axl003
3250:1971PNAS...68.2643L
3195:1967Sci...156.1456N
3189:(3781): 1456–1460.
3160:10.1093/bjps/axi152
3011:1933RSPTA.231..289N
2859:Statistical Science
2830:Pearson, K (1904).
2796:Pearson, K (1900).
2489:inductive behaviour
2485:inductive inference
2468:in the form of the
1291:Philosopher's beans
1040:non-parametric test
848:Region of rejection
745:Definition of terms
464:false positive rate
453:normal distribution
300:
247:by the researcher.
245:inductive inference
54:have been defined.
8818:disease prevention
8753:Case–control study
8425:Security of person
8274:Health care reform
8037:Spatial statistics
7917:Medical statistics
7817:First hitting time
7771:Whittle likelihood
7422:Degrees of freedom
7417:Multivariate ANOVA
7350:Heteroscedasticity
7162:Bayesian estimator
7127:Bayesian inference
6976:Kolmogorov–Smirnov
6861:Randomization test
6831:Testing hypotheses
6804:Tolerance interval
6715:Maximum likelihood
6610:Exponential family
6543:Density estimation
6503:Statistical theory
6463:Natural experiment
6409:Scientific control
6326:Survey methodology
6012:Standard deviation
5803:Online calculators
3598:Hubbard, Raymond;
3412:July 28, 2012, at
3148:Br. J. Philos. Sci
3092:(424): 1242–1249.
2950:Fisher, R (1955).
2927:
2853:Zabell, S (1989).
2540:test decision tree
2509:Mathematics portal
2408:Bayesian inference
2206:proving a negative
2134:Bayesian inference
2110:
2075:
1938:
1638:
1481:? With the choice
1458:
1456:
1397:
1395:
1198:
1181:. The second one,
1165:
1138:
1111:
976:significance level
911:Significance level
830:
707:clever Hans effect
627:Use and importance
583:
563:
298:
228:(false negative).
29:
9311:
9310:
9263:
9262:
9173:Higher education
9004:Positive deviance
8999:Health psychology
8975:Health behavioral
8902:safety management
8876:Social distancing
8650:Population health
8630:Smoking cessation
8578:Pharmacovigilance
8549:Injury prevention
8517:Infection control
8435:Social psychology
8385:Prisoners' rights
8328:Medical sociology
8296:Public health law
8192:Biological hazard
8139:
8138:
8077:
8076:
8073:
8072:
8012:National accounts
7982:Actuarial science
7974:Social statistics
7867:
7866:
7863:
7862:
7859:
7858:
7794:Survival function
7779:
7778:
7641:Granger causality
7482:Contingency table
7457:Survival analysis
7434:
7433:
7430:
7429:
7286:Linear regression
7181:
7180:
7177:
7176:
7152:Credible interval
7121:
7120:
6904:
6903:
6720:Method of moments
6589:Parametric family
6550:Statistical model
6480:
6479:
6476:
6475:
6394:Random assignment
6316:Statistical power
6250:
6249:
6246:
6245:
6095:Contingency table
6065:
6064:
5932:Generalized/power
5674:Bayesian Analysis
5639:Bayesian Analysis
5358:(23): 5131–5133.
5332:978-0-534-37770-0
4782:978-0-472-05007-9
4729:978-0-8058-2634-0
4704:978-0-7619-5205-3
4654:978-0-202-30879-1
4498:978-0-309-21421-6
4449:978-0-521-59271-0
4394:978-0-471-09300-8
4364:978-0-486-41151-4
4328:978-0-674-40340-6
4230:978-0-412-44980-2
4206:978-0-471-16068-7
4181:978-1-4020-6036-6
4002:Perspect Clin Res
3874:(7487): 150–152.
3845:978-0-387-98864-1
3804:978-0-470-12866-4
3779:978-0-470-38551-7
3766:Kempthorne, Oscar
3742:978-0-387-98864-1
3455:978-0-393-31072-6
3348:978-0-521-39838-1
3244:(11): 2643–2646.
3120:Centennial Review
2896:Raymond Hubbard,
2777:on April 27, 2015
2718:Meehl, P (1990).
2705:978-0-387-95329-8
2680:978-1-4462-2250-8
2653:978-1-4840-5299-0
2571:Granger causality
2470:prior probability
2391:interval estimate
2177:optimal decisions
2062:
2020:
1992:
1920:
1888:
1860:
1815:
1750:
1708:
1680:
1610:
1587:
1545:
1517:
1455:
1425:
1394:
1363:
1284:
1283:
1241:Truly not guilty
778:Simple hypothesis
681:scientific method
506:Practical example
350:
349:
199:significance test
9346:
9299:
9298:
9287:
9286:
9275:
9274:
9169:Health education
9046:
9045:
8900:Food hygiene and
8881:Tropical disease
8693:Infant mortality
8668:Community health
8544:Controlled Drugs
8480:Health promotion
8410:Right to housing
8254:Health economics
8166:
8159:
8152:
8143:
8142:
8127:
8126:
8115:
8114:
8104:
8103:
8089:
8088:
7992:Crime statistics
7886:
7885:
7873:
7872:
7790:
7789:
7756:Fourier analysis
7743:Frequency domain
7723:
7670:
7636:Structural break
7596:
7595:
7545:Cluster analysis
7492:Log-linear model
7465:
7464:
7440:
7439:
7381:
7355:Homoscedasticity
7211:
7210:
7187:
7186:
7106:
7098:
7090:
7089:(Kruskal–Wallis)
7074:
7059:
7014:Cross validation
6999:
6981:Anderson–Darling
6928:
6915:
6914:
6886:Likelihood-ratio
6878:Parametric tests
6856:Permutation test
6839:1- & 2-tails
6730:Minimum distance
6702:Point estimation
6698:
6697:
6649:Optimal decision
6600:
6499:
6498:
6486:
6485:
6468:Quasi-experiment
6418:Adaptive designs
6269:
6268:
6256:
6255:
6133:Rank correlation
5895:
5894:
5886:
5885:
5873:
5872:
5840:
5833:
5826:
5817:
5816:
5777:
5752:
5750:
5692:
5691:
5689:
5687:10.1214/08-BA306
5665:
5659:
5656:
5654:
5652:10.1214/06-ba115
5630:
5624:
5622:
5611:10.1037/h0042040
5604:
5586:
5577:
5571:
5570:
5568:
5559:
5553:
5552:
5534:
5510:
5504:
5503:
5477:
5465:
5456:
5455:
5436:10.1037/a0029146
5421:
5415:(July 9, 2012).
5409:
5400:
5399:
5393:
5385:
5367:
5365:10.1113/JP285575
5343:
5337:
5336:
5312:
5306:
5296:
5290:
5289:
5283:
5281:
5276:on July 16, 2012
5272:. Archived from
5266:
5260:
5258:
5230:
5221:
5220:
5192:
5186:
5185:
5157:
5151:
5150:
5114:
5103:
5101:
5084:(12): 997–1003.
5073:
5067:
5066:
5054:
5048:
5047:
5019:
5013:
5012:
4992:
4986:
4985:
4974:10.1037/h0020412
4957:
4951:
4948:
4946:
4940:. Archived from
4915:
4906:
4900:
4899:
4863:
4857:
4855:
4835:
4829:
4828:
4802:
4793:
4787:
4786:
4768:
4762:
4761:
4743:
4734:
4733:
4715:
4709:
4708:
4690:
4684:
4683:
4665:
4659:
4658:
4640:
4634:
4633:
4631:
4607:
4601:
4600:
4590:
4566:
4560:
4558:
4538:
4529:
4527:
4509:
4503:
4502:
4480:
4474:
4460:
4454:
4453:
4435:
4429:
4428:
4426:
4424:
4405:
4399:
4398:
4380:
4374:
4368:
4339:
4333:
4332:
4308:
4302:
4301:
4295:
4291:
4289:
4281:
4269:
4263:
4262:
4258:978-0-67440341-3
4240:
4234:
4233:
4216:
4210:
4209:
4192:
4186:
4185:
4169:
4159:
4153:
4152:
4142:
4122:
4113:
4107:
4104:
4098:
4095:
4089:
4086:
4080:
4077:
4071:
4070:
4054:
4044:
4038:
4037:
4027:
4017:
3993:
3987:
3986:
3968:
3962:
3961:
3933:
3927:
3926:
3908:
3902:
3901:
3891:
3856:
3850:
3849:
3831:
3822:
3815:
3809:
3808:
3790:
3784:
3783:
3761:
3755:
3754:
3717:
3711:
3710:
3686:
3677:
3671:
3670:
3668:
3644:
3638:
3637:
3627:
3595:
3589:
3588:
3562:
3553:
3547:
3546:
3528:
3519:
3513:
3512:
3510:
3486:
3477:
3475:
3467:
3461:
3459:
3435:
3429:
3423:
3417:
3404:
3398:
3397:
3379:
3359:
3353:
3352:
3334:
3328:
3327:
3308:10.2307/20445367
3291:
3282:
3281:
3271:
3261:
3229:
3223:
3222:
3178:
3172:
3171:
3143:
3132:
3131:
3117:
3108:
3102:
3101:
3081:
3068:
3067:
3042:(12): 995–1004.
3031:
3025:
3024:
3022:
2988:
2975:
2974:
2956:
2947:
2938:
2936:
2934:
2933:
2928:
2894:
2885:
2884:
2874:
2850:
2844:
2843:
2827:
2821:
2820:
2802:
2793:
2787:
2786:
2784:
2782:
2776:
2761:
2752:
2743:
2742:
2724:
2715:
2709:
2708:
2691:
2685:
2684:
2664:
2658:
2657:
2637:
2511:
2506:
2505:
2420:John K. Kruschke
2307:publication bias
2239:detection theory
2202:likelihood ratio
2119:
2117:
2116:
2111:
2086:
2084:
2082:
2081:
2076:
2068:
2064:
2063:
2055:
2021:
2018:
2016:
2015:
2003:
2002:
1993:
1990:
1949:
1947:
1945:
1944:
1939:
1931:
1930:
1925:
1921:
1913:
1906:
1905:
1894:
1890:
1889:
1881:
1867:
1866:
1865:
1852:
1844:
1839:
1821:
1817:
1816:
1808:
1779:
1774:
1756:
1752:
1751:
1743:
1709:
1706:
1704:
1703:
1691:
1690:
1681:
1678:
1649:
1647:
1645:
1644:
1639:
1637:
1636:
1621:
1620:
1615:
1611:
1603:
1593:
1589:
1588:
1580:
1546:
1543:
1541:
1540:
1528:
1527:
1518:
1515:
1467:
1465:
1464:
1459:
1457:
1448:
1436:
1435:
1426:
1423:
1406:
1404:
1403:
1398:
1396:
1387:
1375:
1374:
1364:
1361:
1353:null hypothesis
1230:
1229:
1208:, is called the
1207:
1205:
1204:
1199:
1197:
1196:
1175:, is called the
1174:
1172:
1171:
1166:
1164:
1163:
1147:
1145:
1144:
1139:
1137:
1136:
1120:
1118:
1117:
1112:
1110:
1109:
1073:Lady tasting tea
1067:Lady tasting tea
1061:Lady tasting tea
999:Bootstrap-based
934:
933:
858:
857:
850:
849:
838:
837:
780:
779:
714:Hawthorne effect
592:
590:
589:
584:
572:
570:
569:
564:
535:considerations.
301:
297:
282:signal detection
121:chi squared test
9354:
9353:
9349:
9348:
9347:
9345:
9344:
9343:
9314:
9313:
9312:
9307:
9259:
9230:Margaret Sanger
9198:
9157:
9041:
9039:
9033:
8976:
8970:
8942:Safety scandals
8901:
8895:
8817:
8811:
8745:
8739:
8735:Social medicine
8728:Race and health
8663:Child mortality
8644:
8603:Open defecation
8485:Human nutrition
8475:Family planning
8463:Behavior change
8449:
8405:Right to health
8318:Maternal health
8308:Health politics
8259:Health literacy
8175:
8170:
8140:
8135:
8098:
8069:
8031:
7968:
7954:quality control
7921:
7903:Clinical trials
7880:
7855:
7839:
7827:Hazard function
7821:
7775:
7737:
7721:
7684:
7680:Breusch–Godfrey
7668:
7645:
7585:
7560:Factor analysis
7506:
7487:Graphical model
7459:
7426:
7393:
7379:
7359:
7313:
7280:
7242:
7205:
7204:
7173:
7117:
7104:
7096:
7088:
7072:
7057:
7036:Rank statistics
7030:
7009:Model selection
6997:
6955:Goodness of fit
6949:
6926:
6900:
6872:
6825:
6770:
6759:Median unbiased
6687:
6598:
6531:Order statistic
6493:
6472:
6439:
6413:
6365:
6320:
6263:
6261:Data collection
6242:
6154:
6109:
6083:
6061:
6021:
5973:
5890:Continuous data
5880:
5867:
5849:
5844:
5805:
5762:
5759:
5700:
5698:Further reading
5695:
5666:
5662:
5631:
5627:
5602:10.1.1.398.9002
5584:
5578:
5574:
5566:
5560:
5556:
5532:10.1.1.343.9516
5511:
5507:
5475:
5471:(May 8, 2018).
5466:
5459:
5419:
5410:
5403:
5387:
5386:
5344:
5340:
5333:
5313:
5309:
5297:
5293:
5279:
5277:
5268:
5267:
5263:
5231:
5224:
5193:
5189:
5158:
5154:
5115:
5106:
5074:
5070:
5055:
5051:
5020:
5016:
4993:
4989:
4958:
4954:
4944:
4913:
4907:
4903:
4880:10.2307/2982993
4864:
4860:
4836:
4832:
4800:
4794:
4790:
4783:
4769:
4765:
4758:
4744:
4737:
4730:
4716:
4712:
4705:
4691:
4687:
4680:
4666:
4662:
4655:
4641:
4637:
4608:
4604:
4567:
4563:
4539:
4532:
4524:
4510:
4506:
4499:
4481:
4477:
4461:
4457:
4450:
4436:
4432:
4422:
4420:
4406:
4402:
4395:
4381:
4377:
4365:
4340:
4336:
4329:
4309:
4305:
4293:
4292:
4283:
4282:
4270:
4266:
4259:
4241:
4237:
4231:
4217:
4213:
4207:
4193:
4189:
4182:
4160:
4156:
4120:
4114:
4110:
4105:
4101:
4096:
4092:
4087:
4083:
4078:
4074:
4067:
4045:
4041:
3994:
3990:
3983:
3969:
3965:
3934:
3930:
3923:
3909:
3905:
3889:10.1038/506150a
3857:
3853:
3846:
3832:
3825:
3816:
3812:
3805:
3791:
3787:
3780:
3762:
3758:
3743:
3719:
3718:
3714:
3707:
3684:
3678:
3674:
3645:
3641:
3596:
3592:
3577:10.2307/1403333
3560:
3554:
3550:
3526:
3520:
3516:
3487:
3480:
3468:
3464:
3456:
3436:
3432:
3424:
3420:
3405:
3401:
3377:10.1.1.130.8131
3360:
3356:
3349:
3335:
3331:
3292:
3285:
3230:
3226:
3179:
3175:
3144:
3135:
3115:
3109:
3105:
3082:
3071:
3032:
3028:
2989:
2978:
2954:
2948:
2941:
2922:
2919:
2918:
2910:Wayback Machine
2895:
2888:
2851:
2847:
2828:
2824:
2811:(50): 157–175.
2800:
2794:
2790:
2780:
2778:
2774:
2759:
2753:
2746:
2722:
2716:
2712:
2706:
2692:
2688:
2681:
2665:
2661:
2654:
2638:
2634:
2630:
2625:
2559:Fisher's method
2538:Comparing means
2507:
2500:
2497:
2387:
2381:
2375:
2350:medical journal
2281:
2275:
2243:decision theory
2193:
2173:decision theory
2150:decision theory
2142:null hypothesis
2126:
2099:
2096:
2095:
2054:
2035:
2031:
2017:
2011:
2007:
1998:
1994:
1989:
1981:
1978:
1977:
1976:
1926:
1912:
1908:
1907:
1895:
1880:
1873:
1869:
1868:
1861:
1848:
1847:
1846:
1840:
1829:
1807:
1788:
1784:
1775:
1764:
1742:
1723:
1719:
1705:
1699:
1695:
1686:
1682:
1677:
1669:
1666:
1665:
1664:
1629:
1625:
1616:
1602:
1598:
1597:
1579:
1560:
1556:
1542:
1536:
1532:
1523:
1519:
1514:
1506:
1503:
1502:
1501:
1446:
1431:
1427:
1422:
1420:
1417:
1416:
1385:
1370:
1366:
1360:
1358:
1355:
1354:
1324:
1304:
1302:
1300:
1293:
1280:Right decision
1276:
1275:Wrong decision
1271:
1264:
1263:Wrong decision
1260:Right decision
1256:
1249:
1247:
1240:
1238:
1192:
1188:
1186:
1183:
1182:
1178:null hypothesis
1159:
1155:
1153:
1150:
1149:
1132:
1128:
1126:
1123:
1122:
1105:
1101:
1099:
1096:
1095:
1085:
1083:Courtroom trial
1069:
1063:
1021:
1019:Human sex ratio
1015:
1013:Human sex ratio
1010:
997:
991:
931:
930:
869:(1 −
867:Power of a test
856:Critical region
855:
854:
847:
846:
835:
834:
827:
823:
810:
797:
792:Null hypothesis
777:
776:
753:
747:
689:
629:
578:
575:
574:
558:
555:
554:
551:
508:
500:
497:
493:
490:
479:
475:
472:
443:
428:
399:
393:
355:
191:null hypothesis
160:
97:epistemological
90:
78:human sex ratio
66:
60:
25:test statistics
17:
12:
11:
5:
9352:
9342:
9341:
9336:
9331:
9326:
9309:
9308:
9306:
9305:
9293:
9281:
9268:
9265:
9264:
9261:
9260:
9258:
9257:
9252:
9247:
9242:
9237:
9232:
9227:
9222:
9217:
9212:
9206:
9204:
9200:
9199:
9197:
9196:
9195:
9194:
9189:
9184:
9179:
9171:
9165:
9163:
9159:
9158:
9156:
9155:
9148:
9143:
9138:
9137:
9136:
9131:
9126:
9121:
9113:
9112:
9111:
9106:
9098:
9097:
9096:
9088:
9087:
9086:
9081:
9073:
9072:
9071:
9063:
9062:
9061:
9052:
9050:
9043:
9038:Organizations,
9035:
9034:
9032:
9031:
9026:
9021:
9016:
9011:
9006:
9001:
8996:
8991:
8986:
8980:
8978:
8972:
8971:
8969:
8968:
8967:
8966:
8961:
8951:
8946:
8945:
8944:
8939:
8934:
8929:
8924:
8919:
8914:
8905:
8903:
8897:
8896:
8894:
8893:
8888:
8883:
8878:
8873:
8868:
8863:
8862:
8861:
8851:
8850:
8849:
8839:
8838:
8837:
8827:
8821:
8819:
8813:
8812:
8810:
8809:
8804:
8803:
8802:
8794:
8785:
8780:
8775:
8765:
8760:
8755:
8749:
8747:
8744:Biological and
8741:
8740:
8738:
8737:
8732:
8731:
8730:
8725:
8720:
8710:
8705:
8703:Multimorbidity
8700:
8695:
8690:
8685:
8680:
8675:
8670:
8665:
8660:
8654:
8652:
8646:
8645:
8643:
8642:
8640:Vector control
8637:
8632:
8627:
8625:School hygiene
8622:
8621:
8620:
8615:
8610:
8608:Sanitary sewer
8605:
8600:
8595:
8585:
8580:
8575:
8574:
8573:
8566:Patient safety
8563:
8562:
8561:
8556:
8551:
8546:
8541:
8536:
8526:
8525:
8524:
8519:
8514:
8509:
8499:
8498:
8497:
8492:
8482:
8477:
8472:
8471:
8470:
8459:
8457:
8451:
8450:
8448:
8447:
8442:
8437:
8432:
8427:
8422:
8417:
8412:
8407:
8402:
8397:
8392:
8387:
8382:
8381:
8380:
8375:
8370:
8365:
8360:
8350:
8345:
8340:
8330:
8325:
8320:
8315:
8310:
8305:
8304:
8303:
8298:
8288:
8283:
8278:
8277:
8276:
8271:
8261:
8256:
8251:
8249:Harm reduction
8246:
8241:
8236:
8231:
8230:
8229:
8224:
8214:
8209:
8204:
8199:
8194:
8189:
8183:
8181:
8177:
8176:
8169:
8168:
8161:
8154:
8146:
8137:
8136:
8134:
8133:
8121:
8109:
8095:
8082:
8079:
8078:
8075:
8074:
8071:
8070:
8068:
8067:
8062:
8057:
8052:
8047:
8041:
8039:
8033:
8032:
8030:
8029:
8024:
8019:
8014:
8009:
8004:
7999:
7994:
7989:
7984:
7978:
7976:
7970:
7969:
7967:
7966:
7961:
7956:
7947:
7942:
7937:
7931:
7929:
7923:
7922:
7920:
7919:
7914:
7909:
7900:
7898:Bioinformatics
7894:
7892:
7882:
7881:
7869:
7868:
7865:
7864:
7861:
7860:
7857:
7856:
7854:
7853:
7847:
7845:
7841:
7840:
7838:
7837:
7831:
7829:
7823:
7822:
7820:
7819:
7814:
7809:
7804:
7798:
7796:
7787:
7781:
7780:
7777:
7776:
7774:
7773:
7768:
7763:
7758:
7753:
7747:
7745:
7739:
7738:
7736:
7735:
7730:
7725:
7717:
7712:
7707:
7706:
7705:
7703:partial (PACF)
7694:
7692:
7686:
7685:
7683:
7682:
7677:
7672:
7664:
7659:
7653:
7651:
7650:Specific tests
7647:
7646:
7644:
7643:
7638:
7633:
7628:
7623:
7618:
7613:
7608:
7602:
7600:
7593:
7587:
7586:
7584:
7583:
7582:
7581:
7580:
7579:
7564:
7563:
7562:
7552:
7550:Classification
7547:
7542:
7537:
7532:
7527:
7522:
7516:
7514:
7508:
7507:
7505:
7504:
7499:
7497:McNemar's test
7494:
7489:
7484:
7479:
7473:
7471:
7461:
7460:
7436:
7435:
7432:
7431:
7428:
7427:
7425:
7424:
7419:
7414:
7409:
7403:
7401:
7395:
7394:
7392:
7391:
7375:
7369:
7367:
7361:
7360:
7358:
7357:
7352:
7347:
7342:
7337:
7335:Semiparametric
7332:
7327:
7321:
7319:
7315:
7314:
7312:
7311:
7306:
7301:
7296:
7290:
7288:
7282:
7281:
7279:
7278:
7273:
7268:
7263:
7258:
7252:
7250:
7244:
7243:
7241:
7240:
7235:
7230:
7225:
7219:
7217:
7207:
7206:
7203:
7202:
7197:
7191:
7183:
7182:
7179:
7178:
7175:
7174:
7172:
7171:
7170:
7169:
7159:
7154:
7149:
7148:
7147:
7142:
7131:
7129:
7123:
7122:
7119:
7118:
7116:
7115:
7110:
7109:
7108:
7100:
7092:
7076:
7073:(Mann–Whitney)
7068:
7067:
7066:
7053:
7052:
7051:
7040:
7038:
7032:
7031:
7029:
7028:
7027:
7026:
7021:
7016:
7006:
7001:
6998:(Shapiro–Wilk)
6993:
6988:
6983:
6978:
6973:
6965:
6959:
6957:
6951:
6950:
6948:
6947:
6939:
6930:
6918:
6912:
6910:Specific tests
6906:
6905:
6902:
6901:
6899:
6898:
6893:
6888:
6882:
6880:
6874:
6873:
6871:
6870:
6865:
6864:
6863:
6853:
6852:
6851:
6841:
6835:
6833:
6827:
6826:
6824:
6823:
6822:
6821:
6816:
6806:
6801:
6796:
6791:
6786:
6780:
6778:
6772:
6771:
6769:
6768:
6763:
6762:
6761:
6756:
6755:
6754:
6749:
6734:
6733:
6732:
6727:
6722:
6717:
6706:
6704:
6695:
6689:
6688:
6686:
6685:
6680:
6675:
6674:
6673:
6663:
6658:
6657:
6656:
6646:
6645:
6644:
6639:
6634:
6624:
6619:
6614:
6613:
6612:
6607:
6602:
6586:
6585:
6584:
6579:
6574:
6564:
6563:
6562:
6557:
6547:
6546:
6545:
6535:
6534:
6533:
6523:
6518:
6513:
6507:
6505:
6495:
6494:
6482:
6481:
6478:
6477:
6474:
6473:
6471:
6470:
6465:
6460:
6455:
6449:
6447:
6441:
6440:
6438:
6437:
6432:
6427:
6421:
6419:
6415:
6414:
6412:
6411:
6406:
6401:
6396:
6391:
6386:
6381:
6375:
6373:
6367:
6366:
6364:
6363:
6361:Standard error
6358:
6353:
6348:
6347:
6346:
6341:
6330:
6328:
6322:
6321:
6319:
6318:
6313:
6308:
6303:
6298:
6293:
6291:Optimal design
6288:
6283:
6277:
6275:
6265:
6264:
6252:
6251:
6248:
6247:
6244:
6243:
6241:
6240:
6235:
6230:
6225:
6220:
6215:
6210:
6205:
6200:
6195:
6190:
6185:
6180:
6175:
6170:
6164:
6162:
6156:
6155:
6153:
6152:
6147:
6146:
6145:
6140:
6130:
6125:
6119:
6117:
6111:
6110:
6108:
6107:
6102:
6097:
6091:
6089:
6088:Summary tables
6085:
6084:
6082:
6081:
6075:
6073:
6067:
6066:
6063:
6062:
6060:
6059:
6058:
6057:
6052:
6047:
6037:
6031:
6029:
6023:
6022:
6020:
6019:
6014:
6009:
6004:
5999:
5994:
5989:
5983:
5981:
5975:
5974:
5972:
5971:
5966:
5961:
5960:
5959:
5954:
5949:
5944:
5939:
5934:
5929:
5924:
5922:Contraharmonic
5919:
5914:
5903:
5901:
5892:
5882:
5881:
5869:
5868:
5866:
5865:
5860:
5854:
5851:
5850:
5843:
5842:
5835:
5828:
5820:
5814:
5813:
5804:
5801:
5800:
5799:
5794:
5788:
5783:
5778:
5758:
5757:External links
5755:
5754:
5753:
5716:
5699:
5696:
5694:
5693:
5680:(1): 161–170.
5660:
5645:(3): 385–402.
5625:
5595:(5): 416–428.
5572:
5554:
5525:(2): 321–327.
5505:
5486:(2): 270–280.
5457:
5430:(2): 573–603.
5401:
5338:
5331:
5307:
5303:JASNH homepage
5291:
5261:
5241:(8): 594–604.
5222:
5187:
5168:(2): 256–277.
5152:
5125:(2): 241–301.
5104:
5068:
5049:
5030:(4): 641–650.
5014:
5003:(5): 587–606.
4987:
4968:(6): 423–437.
4952:
4930:10.1086/288135
4924:(2): 103–115.
4901:
4874:(3): 419–463.
4858:
4846:(253): 19–34.
4830:
4811:(4): 408–421.
4788:
4781:
4763:
4756:
4735:
4728:
4710:
4703:
4685:
4679:978-0471104438
4678:
4660:
4653:
4635:
4602:
4581:(3): 244–252.
4561:
4549:(4): 423–433.
4530:
4523:978-0471034506
4522:
4504:
4497:
4475:
4455:
4448:
4430:
4400:
4393:
4375:
4363:
4334:
4327:
4303:
4294:|journal=
4264:
4257:
4235:
4229:
4211:
4205:
4187:
4180:
4154:
4108:
4099:
4090:
4081:
4072:
4065:
4039:
4008:(2): 106–107.
3988:
3981:
3963:
3944:(4): 545–554.
3928:
3922:978-0023677205
3921:
3903:
3851:
3844:
3823:
3810:
3803:
3785:
3778:
3756:
3741:
3712:
3705:
3672:
3639:
3610:(2): 114–120.
3590:
3571:(2): 123–165.
3548:
3514:
3478:
3462:
3454:
3430:
3418:
3399:
3370:(2): 323–357.
3354:
3347:
3329:
3302:(4): 625–653.
3283:
3224:
3173:
3133:
3103:
3069:
3036:Ann Intern Med
3026:
2976:
2939:
2926:
2886:
2865:(3): 247–256.
2845:
2822:
2788:
2744:
2733:(2): 108–141.
2710:
2704:
2686:
2679:
2659:
2652:
2631:
2629:
2626:
2624:
2623:
2618:
2613:
2608:
2603:
2598:
2593:
2588:
2583:
2578:
2573:
2568:
2561:for combining
2556:
2554:Falsifiability
2551:
2546:
2541:
2535:
2530:
2525:
2520:
2514:
2513:
2512:
2496:
2493:
2479:(an objective
2462:Bayes' Theorem
2458:Neyman–Pearson
2377:Main article:
2374:
2371:
2330:
2329:
2326:
2314:
2310:
2303:
2300:
2297:
2274:
2271:
2192:
2189:
2125:
2122:
2109:
2106:
2103:
2092:false negative
2088:
2087:
2074:
2071:
2067:
2061:
2058:
2053:
2050:
2047:
2044:
2041:
2038:
2034:
2030:
2027:
2024:
2019: is valid
2014:
2010:
2006:
2001:
1997:
1988:
1985:
1951:
1950:
1937:
1934:
1929:
1924:
1919:
1916:
1911:
1904:
1901:
1898:
1893:
1887:
1884:
1879:
1876:
1872:
1864:
1859:
1856:
1851:
1843:
1838:
1835:
1832:
1828:
1824:
1820:
1814:
1811:
1806:
1803:
1800:
1797:
1794:
1791:
1787:
1783:
1778:
1773:
1770:
1767:
1763:
1759:
1755:
1749:
1746:
1741:
1738:
1735:
1732:
1729:
1726:
1722:
1718:
1715:
1712:
1707: is valid
1702:
1698:
1694:
1689:
1685:
1676:
1673:
1651:
1650:
1635:
1632:
1628:
1624:
1619:
1614:
1609:
1606:
1601:
1596:
1592:
1586:
1583:
1578:
1575:
1572:
1569:
1566:
1563:
1559:
1555:
1552:
1549:
1544: is valid
1539:
1535:
1531:
1526:
1522:
1513:
1510:
1491:false positive
1470:
1469:
1454:
1451:
1445:
1442:
1439:
1434:
1430:
1409:
1408:
1393:
1390:
1384:
1381:
1378:
1373:
1369:
1323:
1320:
1292:
1289:
1282:
1281:
1278:
1273:
1267:
1266:
1265:Type II Error
1261:
1258:
1252:
1251:
1245:
1242:
1236:
1233:
1195:
1191:
1162:
1158:
1135:
1131:
1108:
1104:
1084:
1081:
1077:Muriel Bristol
1065:Main article:
1062:
1059:
1025:John Arbuthnot
1017:Main article:
1014:
1011:
1009:
1006:
993:Main article:
990:
987:
986:
985:
979:
955:
954:
949:
942:
927:
917:
908:
888:false positive
875:
863:
862:
861:
836:Critical value
825:
821:
813:
812:
808:
802:
799:
795:
789:
782:
774:
771:
746:
743:
725:
724:
721:placebo effect
717:
710:
688:
685:
662:
661:
658:
655:
652:
649:
646:
643:
640:
628:
625:
582:
562:
550:
549:Interpretation
547:
526:Interpretation
519:
518:
515:
507:
504:
503:
502:
498:
495:
491:
488:
485:Neyman-Pearson
481:
477:
473:
470:
467:
456:
445:
441:
439:test statistic
435:
427:
424:
404:Bible Analyzer
395:Main article:
392:
389:
354:
351:
348:
347:
343:
340:
336:
335:
332:
328:
324:
323:
319:
316:
312:
311:
308:
305:
293:test statistic
159:
156:
107:Pierre Laplace
89:
86:
80:at birth; see
70:John Arbuthnot
59:
56:
41:critical value
37:test statistic
15:
9:
6:
4:
3:
2:
9351:
9340:
9337:
9335:
9332:
9330:
9327:
9325:
9322:
9321:
9319:
9304:
9303:
9294:
9292:
9291:
9282:
9280:
9279:
9270:
9269:
9266:
9256:
9253:
9251:
9248:
9246:
9243:
9241:
9238:
9236:
9233:
9231:
9228:
9226:
9225:Joseph Lister
9223:
9221:
9218:
9216:
9213:
9211:
9208:
9207:
9205:
9201:
9193:
9190:
9188:
9185:
9183:
9180:
9178:
9175:
9174:
9172:
9170:
9167:
9166:
9164:
9160:
9153:
9149:
9147:
9144:
9142:
9139:
9135:
9132:
9130:
9127:
9125:
9122:
9120:
9117:
9116:
9114:
9110:
9107:
9105:
9104:Health Canada
9102:
9101:
9099:
9095:
9092:
9091:
9089:
9085:
9082:
9080:
9077:
9076:
9074:
9070:
9067:
9066:
9064:
9060:
9057:
9056:
9054:
9053:
9051:
9049:Organizations
9047:
9044:
9036:
9030:
9027:
9025:
9022:
9020:
9017:
9015:
9012:
9010:
9007:
9005:
9002:
9000:
8997:
8995:
8992:
8990:
8987:
8985:
8982:
8981:
8979:
8973:
8965:
8962:
8960:
8957:
8956:
8955:
8952:
8950:
8947:
8943:
8940:
8938:
8935:
8933:
8930:
8928:
8925:
8923:
8920:
8918:
8915:
8913:
8910:
8909:
8907:
8906:
8904:
8898:
8892:
8889:
8887:
8886:Vaccine trial
8884:
8882:
8879:
8877:
8874:
8872:
8869:
8867:
8864:
8860:
8857:
8856:
8855:
8852:
8848:
8845:
8844:
8843:
8840:
8836:
8833:
8832:
8831:
8828:
8826:
8823:
8822:
8820:
8814:
8808:
8805:
8801:
8799:
8795:
8793:
8791:
8786:
8784:
8781:
8779:
8776:
8774:
8771:
8770:
8769:
8766:
8764:
8763:Relative risk
8761:
8759:
8756:
8754:
8751:
8750:
8748:
8742:
8736:
8733:
8729:
8726:
8724:
8723:Health equity
8721:
8719:
8716:
8715:
8714:
8711:
8709:
8706:
8704:
8701:
8699:
8696:
8694:
8691:
8689:
8688:Health system
8686:
8684:
8681:
8679:
8678:Global health
8676:
8674:
8671:
8669:
8666:
8664:
8661:
8659:
8658:Biostatistics
8656:
8655:
8653:
8651:
8647:
8641:
8638:
8636:
8633:
8631:
8628:
8626:
8623:
8619:
8616:
8614:
8611:
8609:
8606:
8604:
8601:
8599:
8596:
8594:
8591:
8590:
8589:
8586:
8584:
8581:
8579:
8576:
8572:
8569:
8568:
8567:
8564:
8560:
8557:
8555:
8552:
8550:
8547:
8545:
8542:
8540:
8537:
8535:
8532:
8531:
8530:
8527:
8523:
8520:
8518:
8515:
8513:
8510:
8508:
8505:
8504:
8503:
8500:
8496:
8493:
8491:
8488:
8487:
8486:
8483:
8481:
8478:
8476:
8473:
8469:
8466:
8465:
8464:
8461:
8460:
8458:
8456:
8452:
8446:
8443:
8441:
8438:
8436:
8433:
8431:
8428:
8426:
8423:
8421:
8418:
8416:
8413:
8411:
8408:
8406:
8403:
8401:
8400:Right to food
8398:
8396:
8393:
8391:
8388:
8386:
8383:
8379:
8376:
8374:
8371:
8369:
8366:
8364:
8361:
8359:
8356:
8355:
8354:
8351:
8349:
8346:
8344:
8341:
8338:
8334:
8333:Mental health
8331:
8329:
8326:
8324:
8321:
8319:
8316:
8314:
8311:
8309:
8306:
8302:
8299:
8297:
8294:
8293:
8292:
8289:
8287:
8284:
8282:
8281:Housing First
8279:
8275:
8272:
8270:
8269:Health system
8267:
8266:
8265:
8264:Health policy
8262:
8260:
8257:
8255:
8252:
8250:
8247:
8245:
8242:
8240:
8237:
8235:
8232:
8228:
8225:
8223:
8220:
8219:
8218:
8215:
8213:
8210:
8208:
8205:
8203:
8200:
8198:
8195:
8193:
8190:
8188:
8185:
8184:
8182:
8178:
8174:
8173:Public health
8167:
8162:
8160:
8155:
8153:
8148:
8147:
8144:
8132:
8131:
8122:
8120:
8119:
8110:
8108:
8107:
8102:
8096:
8094:
8093:
8084:
8083:
8080:
8066:
8063:
8061:
8060:Geostatistics
8058:
8056:
8053:
8051:
8048:
8046:
8043:
8042:
8040:
8038:
8034:
8028:
8027:Psychometrics
8025:
8023:
8020:
8018:
8015:
8013:
8010:
8008:
8005:
8003:
8000:
7998:
7995:
7993:
7990:
7988:
7985:
7983:
7980:
7979:
7977:
7975:
7971:
7965:
7962:
7960:
7957:
7955:
7951:
7948:
7946:
7943:
7941:
7938:
7936:
7933:
7932:
7930:
7928:
7924:
7918:
7915:
7913:
7910:
7908:
7904:
7901:
7899:
7896:
7895:
7893:
7891:
7890:Biostatistics
7887:
7883:
7879:
7874:
7870:
7852:
7851:Log-rank test
7849:
7848:
7846:
7842:
7836:
7833:
7832:
7830:
7828:
7824:
7818:
7815:
7813:
7810:
7808:
7805:
7803:
7800:
7799:
7797:
7795:
7791:
7788:
7786:
7782:
7772:
7769:
7767:
7764:
7762:
7759:
7757:
7754:
7752:
7749:
7748:
7746:
7744:
7740:
7734:
7731:
7729:
7726:
7724:
7722:(Box–Jenkins)
7718:
7716:
7713:
7711:
7708:
7704:
7701:
7700:
7699:
7696:
7695:
7693:
7691:
7687:
7681:
7678:
7676:
7675:Durbin–Watson
7673:
7671:
7665:
7663:
7660:
7658:
7657:Dickey–Fuller
7655:
7654:
7652:
7648:
7642:
7639:
7637:
7634:
7632:
7631:Cointegration
7629:
7627:
7624:
7622:
7619:
7617:
7614:
7612:
7609:
7607:
7606:Decomposition
7604:
7603:
7601:
7597:
7594:
7592:
7588:
7578:
7575:
7574:
7573:
7570:
7569:
7568:
7565:
7561:
7558:
7557:
7556:
7553:
7551:
7548:
7546:
7543:
7541:
7538:
7536:
7533:
7531:
7528:
7526:
7523:
7521:
7518:
7517:
7515:
7513:
7509:
7503:
7500:
7498:
7495:
7493:
7490:
7488:
7485:
7483:
7480:
7478:
7477:Cohen's kappa
7475:
7474:
7472:
7470:
7466:
7462:
7458:
7454:
7450:
7446:
7441:
7437:
7423:
7420:
7418:
7415:
7413:
7410:
7408:
7405:
7404:
7402:
7400:
7396:
7390:
7386:
7382:
7376:
7374:
7371:
7370:
7368:
7366:
7362:
7356:
7353:
7351:
7348:
7346:
7343:
7341:
7338:
7336:
7333:
7331:
7330:Nonparametric
7328:
7326:
7323:
7322:
7320:
7316:
7310:
7307:
7305:
7302:
7300:
7297:
7295:
7292:
7291:
7289:
7287:
7283:
7277:
7274:
7272:
7269:
7267:
7264:
7262:
7259:
7257:
7254:
7253:
7251:
7249:
7245:
7239:
7236:
7234:
7231:
7229:
7226:
7224:
7221:
7220:
7218:
7216:
7212:
7208:
7201:
7198:
7196:
7193:
7192:
7188:
7184:
7168:
7165:
7164:
7163:
7160:
7158:
7155:
7153:
7150:
7146:
7143:
7141:
7138:
7137:
7136:
7133:
7132:
7130:
7128:
7124:
7114:
7111:
7107:
7101:
7099:
7093:
7091:
7085:
7084:
7083:
7080:
7079:Nonparametric
7077:
7075:
7069:
7065:
7062:
7061:
7060:
7054:
7050:
7049:Sample median
7047:
7046:
7045:
7042:
7041:
7039:
7037:
7033:
7025:
7022:
7020:
7017:
7015:
7012:
7011:
7010:
7007:
7005:
7002:
7000:
6994:
6992:
6989:
6987:
6984:
6982:
6979:
6977:
6974:
6972:
6970:
6966:
6964:
6961:
6960:
6958:
6956:
6952:
6946:
6944:
6940:
6938:
6936:
6931:
6929:
6924:
6920:
6919:
6916:
6913:
6911:
6907:
6897:
6894:
6892:
6889:
6887:
6884:
6883:
6881:
6879:
6875:
6869:
6866:
6862:
6859:
6858:
6857:
6854:
6850:
6847:
6846:
6845:
6842:
6840:
6837:
6836:
6834:
6832:
6828:
6820:
6817:
6815:
6812:
6811:
6810:
6807:
6805:
6802:
6800:
6797:
6795:
6792:
6790:
6787:
6785:
6782:
6781:
6779:
6777:
6773:
6767:
6764:
6760:
6757:
6753:
6750:
6748:
6745:
6744:
6743:
6740:
6739:
6738:
6735:
6731:
6728:
6726:
6723:
6721:
6718:
6716:
6713:
6712:
6711:
6708:
6707:
6705:
6703:
6699:
6696:
6694:
6690:
6684:
6681:
6679:
6676:
6672:
6669:
6668:
6667:
6664:
6662:
6659:
6655:
6654:loss function
6652:
6651:
6650:
6647:
6643:
6640:
6638:
6635:
6633:
6630:
6629:
6628:
6625:
6623:
6620:
6618:
6615:
6611:
6608:
6606:
6603:
6601:
6595:
6592:
6591:
6590:
6587:
6583:
6580:
6578:
6575:
6573:
6570:
6569:
6568:
6565:
6561:
6558:
6556:
6553:
6552:
6551:
6548:
6544:
6541:
6540:
6539:
6536:
6532:
6529:
6528:
6527:
6524:
6522:
6519:
6517:
6514:
6512:
6509:
6508:
6506:
6504:
6500:
6496:
6492:
6487:
6483:
6469:
6466:
6464:
6461:
6459:
6456:
6454:
6451:
6450:
6448:
6446:
6442:
6436:
6433:
6431:
6428:
6426:
6423:
6422:
6420:
6416:
6410:
6407:
6405:
6402:
6400:
6397:
6395:
6392:
6390:
6387:
6385:
6382:
6380:
6377:
6376:
6374:
6372:
6368:
6362:
6359:
6357:
6356:Questionnaire
6354:
6352:
6349:
6345:
6342:
6340:
6337:
6336:
6335:
6332:
6331:
6329:
6327:
6323:
6317:
6314:
6312:
6309:
6307:
6304:
6302:
6299:
6297:
6294:
6292:
6289:
6287:
6284:
6282:
6279:
6278:
6276:
6274:
6270:
6266:
6262:
6257:
6253:
6239:
6236:
6234:
6231:
6229:
6226:
6224:
6221:
6219:
6216:
6214:
6211:
6209:
6206:
6204:
6201:
6199:
6196:
6194:
6191:
6189:
6186:
6184:
6183:Control chart
6181:
6179:
6176:
6174:
6171:
6169:
6166:
6165:
6163:
6161:
6157:
6151:
6148:
6144:
6141:
6139:
6136:
6135:
6134:
6131:
6129:
6126:
6124:
6121:
6120:
6118:
6116:
6112:
6106:
6103:
6101:
6098:
6096:
6093:
6092:
6090:
6086:
6080:
6077:
6076:
6074:
6072:
6068:
6056:
6053:
6051:
6048:
6046:
6043:
6042:
6041:
6038:
6036:
6033:
6032:
6030:
6028:
6024:
6018:
6015:
6013:
6010:
6008:
6005:
6003:
6000:
5998:
5995:
5993:
5990:
5988:
5985:
5984:
5982:
5980:
5976:
5970:
5967:
5965:
5962:
5958:
5955:
5953:
5950:
5948:
5945:
5943:
5940:
5938:
5935:
5933:
5930:
5928:
5925:
5923:
5920:
5918:
5915:
5913:
5910:
5909:
5908:
5905:
5904:
5902:
5900:
5896:
5893:
5891:
5887:
5883:
5879:
5874:
5870:
5864:
5861:
5859:
5856:
5855:
5852:
5848:
5841:
5836:
5834:
5829:
5827:
5822:
5821:
5818:
5811:
5807:
5806:
5797:
5795:
5792:
5789:
5787:
5784:
5782:
5779:
5775:
5771:
5770:
5765:
5761:
5760:
5749:
5744:
5740:
5736:
5732:
5728:
5727:
5722:
5717:
5714:
5713:0-387-94037-5
5710:
5706:
5702:
5701:
5688:
5683:
5679:
5675:
5671:
5664:
5653:
5648:
5644:
5640:
5636:
5629:
5620:
5616:
5612:
5608:
5603:
5598:
5594:
5590:
5583:
5576:
5565:
5558:
5550:
5546:
5542:
5538:
5533:
5528:
5524:
5520:
5516:
5509:
5501:
5497:
5493:
5489:
5485:
5481:
5474:
5470:
5469:Kruschke, J K
5464:
5462:
5453:
5449:
5445:
5441:
5437:
5433:
5429:
5425:
5418:
5414:
5413:Kruschke, J K
5408:
5406:
5397:
5391:
5383:
5379:
5375:
5371:
5366:
5361:
5357:
5353:
5349:
5342:
5334:
5328:
5324:
5320:
5319:
5311:
5304:
5300:
5295:
5288:
5275:
5271:
5265:
5256:
5252:
5248:
5244:
5240:
5236:
5229:
5227:
5218:
5214:
5210:
5206:
5202:
5198:
5191:
5183:
5179:
5175:
5171:
5167:
5163:
5156:
5148:
5144:
5140:
5136:
5132:
5128:
5124:
5120:
5113:
5111:
5109:
5099:
5095:
5091:
5087:
5083:
5079:
5072:
5064:
5060:
5053:
5045:
5041:
5037:
5033:
5029:
5025:
5018:
5010:
5006:
5002:
4998:
4991:
4983:
4979:
4975:
4971:
4967:
4963:
4956:
4943:
4939:
4935:
4931:
4927:
4923:
4919:
4912:
4905:
4897:
4893:
4889:
4885:
4881:
4877:
4873:
4869:
4862:
4853:
4849:
4845:
4841:
4834:
4826:
4822:
4818:
4814:
4810:
4806:
4799:
4792:
4784:
4778:
4774:
4767:
4759:
4757:9781591471189
4753:
4749:
4742:
4740:
4731:
4725:
4721:
4714:
4706:
4700:
4696:
4689:
4681:
4675:
4671:
4664:
4656:
4650:
4646:
4639:
4630:
4625:
4621:
4617:
4613:
4606:
4598:
4594:
4589:
4584:
4580:
4576:
4572:
4565:
4556:
4552:
4548:
4544:
4543:Technometrics
4537:
4535:
4525:
4519:
4515:
4508:
4500:
4494:
4490:
4486:
4479:
4473:
4472:0-387-94546-6
4469:
4465:
4459:
4451:
4445:
4441:
4434:
4419:
4415:
4411:
4404:
4396:
4390:
4386:
4379:
4372:
4366:
4360:
4356:
4352:
4348:
4344:
4338:
4330:
4324:
4320:
4316:
4315:
4307:
4299:
4287:
4279:
4275:
4268:
4260:
4254:
4250:
4246:
4239:
4232:
4226:
4222:
4215:
4208:
4202:
4198:
4191:
4183:
4177:
4173:
4168:
4167:
4158:
4150:
4146:
4141:
4136:
4132:
4128:
4127:
4119:
4112:
4103:
4094:
4085:
4076:
4068:
4066:0-201-03021-7
4062:
4058:
4053:
4052:
4043:
4035:
4031:
4026:
4021:
4016:
4011:
4007:
4003:
3999:
3992:
3984:
3982:9780716796572
3978:
3974:
3967:
3959:
3955:
3951:
3947:
3943:
3939:
3932:
3924:
3918:
3915:. Macmillan.
3914:
3907:
3899:
3895:
3890:
3885:
3881:
3877:
3873:
3869:
3865:
3861:
3860:Nuzzo, Regina
3855:
3847:
3841:
3837:
3830:
3828:
3820:
3814:
3806:
3800:
3796:
3789:
3781:
3775:
3771:
3767:
3760:
3752:
3748:
3744:
3738:
3734:
3730:
3726:
3722:
3716:
3708:
3706:9780761923596
3702:
3698:
3694:
3690:
3683:
3676:
3667:
3662:
3658:
3654:
3650:
3643:
3635:
3631:
3626:
3621:
3617:
3613:
3609:
3605:
3601:
3594:
3586:
3582:
3578:
3574:
3570:
3566:
3559:
3552:
3544:
3540:
3537:(2): 98–113.
3536:
3532:
3525:
3518:
3509:
3504:
3500:
3496:
3492:
3485:
3483:
3473:
3466:
3457:
3451:
3447:
3443:
3442:
3434:
3427:
3422:
3415:
3414:archive.today
3411:
3408:
3403:
3395:
3391:
3387:
3383:
3378:
3373:
3369:
3365:
3358:
3350:
3344:
3340:
3333:
3325:
3321:
3317:
3313:
3309:
3305:
3301:
3297:
3290:
3288:
3279:
3275:
3270:
3265:
3260:
3255:
3251:
3247:
3243:
3239:
3235:
3228:
3220:
3216:
3212:
3208:
3204:
3200:
3196:
3192:
3188:
3184:
3177:
3169:
3165:
3161:
3157:
3153:
3149:
3142:
3140:
3138:
3130:
3125:
3121:
3114:
3107:
3099:
3095:
3091:
3087:
3080:
3078:
3076:
3074:
3065:
3061:
3057:
3053:
3049:
3045:
3041:
3037:
3030:
3021:
3016:
3012:
3008:
3004:
3000:
2999:
2994:
2987:
2985:
2983:
2981:
2972:
2968:
2964:
2960:
2953:
2946:
2944:
2924:
2916:
2912:
2911:
2907:
2904:
2899:
2898:M. J. Bayarri
2893:
2891:
2882:
2878:
2873:
2868:
2864:
2860:
2856:
2849:
2841:
2837:
2833:
2826:
2818:
2814:
2810:
2806:
2799:
2792:
2773:
2769:
2765:
2758:
2751:
2749:
2740:
2736:
2732:
2728:
2721:
2714:
2707:
2701:
2697:
2690:
2682:
2676:
2672:
2671:
2663:
2655:
2649:
2645:
2644:
2636:
2632:
2622:
2619:
2617:
2614:
2612:
2609:
2607:
2604:
2602:
2599:
2597:
2594:
2592:
2589:
2587:
2584:
2582:
2579:
2577:
2574:
2572:
2569:
2567:
2564:
2560:
2557:
2555:
2552:
2550:
2547:
2545:
2542:
2539:
2536:
2534:
2531:
2529:
2526:
2524:
2521:
2519:
2516:
2515:
2510:
2504:
2499:
2492:
2490:
2486:
2482:
2478:
2476:
2471:
2467:
2463:
2459:
2455:
2451:
2447:
2443:
2438:
2436:
2432:
2431:Bayes factors
2428:
2426:
2421:
2417:
2413:
2409:
2405:
2401:
2399:
2396:
2392:
2386:
2380:
2370:
2367:
2363:
2359:
2355:
2351:
2347:
2342:
2339:
2335:
2327:
2324:
2320:
2315:
2311:
2308:
2304:
2301:
2298:
2294:
2293:stopping rule
2290:
2286:
2285:
2284:
2280:
2270:
2268:
2264:
2258:
2254:
2250:
2248:
2244:
2240:
2236:
2230:
2228:
2223:
2217:
2213:
2211:
2207:
2203:
2199:
2188:
2186:
2182:
2178:
2174:
2170:
2166:
2162:
2157:
2155:
2151:
2147:
2143:
2139:
2135:
2131:
2121:
2107:
2104:
2101:
2093:
2072:
2069:
2065:
2059:
2056:
2051:
2048:
2045:
2042:
2039:
2036:
2032:
2028:
2025:
2012:
2008:
2004:
1999:
1995:
1983:
1975:
1974:
1973:
1971:
1967:
1963:
1958:
1956:
1935:
1932:
1927:
1922:
1917:
1914:
1909:
1902:
1899:
1896:
1891:
1885:
1882:
1877:
1874:
1870:
1857:
1854:
1841:
1836:
1833:
1830:
1826:
1822:
1818:
1812:
1809:
1804:
1801:
1798:
1795:
1792:
1789:
1785:
1781:
1776:
1771:
1768:
1765:
1761:
1757:
1753:
1747:
1744:
1739:
1736:
1733:
1730:
1727:
1724:
1720:
1716:
1713:
1700:
1696:
1692:
1687:
1683:
1671:
1663:
1662:
1661:
1660:= 10, gives:
1659:
1654:
1633:
1630:
1626:
1622:
1617:
1612:
1607:
1604:
1599:
1594:
1590:
1584:
1581:
1576:
1573:
1570:
1567:
1564:
1561:
1557:
1553:
1550:
1537:
1533:
1529:
1524:
1520:
1508:
1500:
1499:
1498:
1496:
1492:
1488:
1484:
1480:
1476:
1452:
1449:
1443:
1440:
1437:
1432:
1428:
1414:
1413:
1412:
1391:
1388:
1382:
1379:
1376:
1371:
1367:
1352:
1351:
1350:
1348:
1342:
1339:
1337:
1333:
1329:
1319:
1315:
1311:
1306:
1296:
1288:
1279:
1277:Type I Error
1274:
1269:
1262:
1259:
1254:
1250:Truly guilty
1243:
1234:
1232:
1231:
1228:
1226:
1225:
1220:
1219:
1213:
1211:
1193:
1189:
1180:
1179:
1160:
1156:
1133:
1129:
1106:
1102:
1092:
1090:
1080:
1078:
1074:
1068:
1058:
1056:
1051:
1049:
1045:
1041:
1037:
1032:
1030:
1026:
1020:
1005:
1002:
996:
983:
980:
977:
973:
969:
968:
967:
964:
960:
953:
950:
947:
943:
939:
935:
928:
926:
925:
923:
918:
916:
912:
909:
906:
902:
898:
897:biostatistics
894:
889:
885:
881:
880:
876:
874:
872:
868:
864:
859:
851:
844:
843:
840:
832:
831:
817:
806:
803:
800:
793:
790:
787:
783:
775:
772:
769:
765:
761:
758:
757:
756:
752:
742:
738:
735:
732:
730:
722:
718:
715:
711:
708:
704:
703:
702:
699:
697:
692:
684:
682:
678:
674:
669:
667:
659:
656:
653:
650:
647:
644:
641:
638:
637:
636:
633:
624:
620:
618:
614:
610:
605:
603:
599:
594:
580:
560:
546:
544:
543:Ronald Fisher
539:
536:
534:
529:
527:
522:
516:
513:
512:
511:
486:
482:
468:
465:
461:
457:
454:
450:
446:
440:
436:
433:
432:
431:
423:
419:
417:
413:
409:
405:
398:
388:
386:
382:
377:
374:
372:
368:
364:
360:
344:
341:
338:
337:
333:
329:
326:
325:
320:
317:
314:
313:
309:
306:
303:
302:
296:
294:
290:
285:
283:
278:
276:
271:
267:
262:
259:
257:
252:
248:
246:
242:
238:
234:
229:
227:
226:Type II error
221:
219:
214:
212:
208:
204:
200:
196:
192:
188:
187:Ronald Fisher
184:
180:
176:
172:
170:
165:
155:
153:
149:
144:
140:
136:
133:
129:
127:
122:
119:develops the
118:
115:
111:
108:
105:
101:
98:
94:
85:
83:
79:
75:
71:
65:
55:
53:
49:
47:
42:
38:
34:
26:
21:
9300:
9288:
9276:
9245:Radium Girls
9240:Typhoid Mary
8927:Microbiology
8797:
8789:
8673:Epidemiology
8571:Organization
8522:Oral hygiene
8512:Hand washing
8490:Healthy diet
8420:Right to sit
8313:Labor rights
8128:
8116:
8097:
8090:
8002:Econometrics
7952: /
7935:Chemometrics
7912:Epidemiology
7905: /
7878:Applications
7720:ARIMA model
7667:Q-statistic
7616:Stationarity
7512:Multivariate
7455: /
7451: /
7449:Multivariate
7447: /
7387: /
7383: /
7157:Bayes factor
7056:Signed rank
6968:
6942:
6934:
6922:
6617:Completeness
6453:Cohort study
6351:Opinion poll
6286:Missing data
6273:Study design
6228:Scatter plot
6150:Scatter plot
6143:Spearman's ρ
6105:Grouped data
5767:
5730:
5724:
5704:
5677:
5673:
5663:
5658:attainable".
5642:
5638:
5628:
5592:
5588:
5575:
5557:
5522:
5518:
5508:
5483:
5479:
5427:
5423:
5390:cite journal
5355:
5351:
5341:
5317:
5310:
5298:
5294:
5285:
5280:September 3,
5278:. Retrieved
5274:the original
5264:
5238:
5234:
5200:
5196:
5190:
5165:
5161:
5155:
5122:
5118:
5081:
5077:
5071:
5062:
5058:
5052:
5027:
5023:
5017:
5000:
4996:
4990:
4965:
4961:
4955:
4942:the original
4921:
4917:
4904:
4871:
4867:
4861:
4843:
4839:
4833:
4808:
4804:
4791:
4772:
4766:
4747:
4719:
4713:
4694:
4688:
4669:
4663:
4644:
4638:
4619:
4615:
4605:
4578:
4574:
4564:
4546:
4542:
4513:
4507:
4488:
4478:
4463:
4458:
4439:
4433:
4421:. Retrieved
4417:
4413:
4403:
4384:
4378:
4370:
4354:
4350:
4337:
4313:
4306:
4277:
4267:
4244:
4238:
4220:
4214:
4196:
4190:
4165:
4157:
4130:
4124:
4111:
4102:
4093:
4084:
4075:
4050:
4042:
4005:
4001:
3991:
3972:
3966:
3941:
3937:
3931:
3912:
3906:
3871:
3867:
3854:
3835:
3818:
3813:
3794:
3788:
3769:
3759:
3724:
3715:
3688:
3675:
3656:
3652:
3642:
3607:
3603:
3593:
3568:
3564:
3551:
3534:
3530:
3517:
3501:(1): 48–52.
3498:
3494:
3471:
3465:
3440:
3433:
3421:
3402:
3367:
3363:
3357:
3338:
3332:
3299:
3295:
3241:
3237:
3227:
3186:
3182:
3176:
3151:
3147:
3127:
3123:
3119:
3106:
3089:
3085:
3039:
3035:
3029:
3002:
2996:
2965:(1): 69–78.
2962:
2958:
2914:
2901:
2862:
2858:
2848:
2839:
2835:
2825:
2808:
2804:
2791:
2781:September 5,
2779:. Retrieved
2772:the original
2767:
2763:
2730:
2726:
2713:
2695:
2689:
2669:
2662:
2642:
2635:
2596:Omnibus test
2488:
2484:
2480:
2474:
2466:subjectivity
2439:
2424:
2406:
2402:
2388:
2373:Alternatives
2353:
2343:
2337:
2333:
2331:
2318:
2288:
2282:
2266:
2259:
2255:
2251:
2231:
2226:
2218:
2214:
2194:
2158:
2145:
2137:
2127:
2089:
1991:reject
1969:
1965:
1961:
1959:
1954:
1952:
1679:reject
1657:
1655:
1652:
1516:reject
1494:
1486:
1482:
1478:
1474:
1471:
1410:
1346:
1343:
1340:
1335:
1328:clairvoyance
1325:
1316:
1312:
1308:
1298:
1294:
1285:
1222:
1216:
1214:
1209:
1176:
1093:
1086:
1072:
1070:
1054:
1052:
1047:
1043:
1033:
1022:
998:
975:
971:
966:optimality:
962:
958:
956:
945:
929:
921:
919:
914:
892:
883:
878:
870:
865:
853:
845:
833:
785:
759:
754:
739:
736:
733:
726:
700:
695:
693:
690:
672:
670:
663:
634:
630:
621:
616:
612:
608:
606:
601:
597:
595:
552:
540:
537:
530:
523:
520:
509:
459:
429:
420:
415:
411:
410:, Student's
407:
400:
378:
375:
356:
288:
286:
279:
274:
270:World War II
263:
260:
253:
249:
240:
232:
230:
222:
215:
207:Egon Pearson
203:Jerzy Neyman
168:
164:Karl Pearson
161:
135:Karl Pearson
131:
130:
117:Karl Pearson
113:
112:
103:
102:
91:
67:
45:
32:
30:
9302:WikiProject
9042:and history
8922:Engineering
8635:Vaccination
8507:Food safety
8130:WikiProject
8045:Cartography
8007:Jurimetrics
7959:Reliability
7690:Time domain
7669:(Ljung–Box)
7591:Time-series
7469:Categorical
7453:Time-series
7445:Categorical
7380:(Bernoulli)
7215:Correlation
7195:Correlation
6991:Jarque–Bera
6963:Chi-squared
6725:M-estimator
6678:Asymptotics
6622:Sufficiency
6389:Interaction
6301:Replication
6281:Effect size
6238:Violin plot
6218:Radar chart
6198:Forest plot
6188:Correlogram
6138:Kendall's τ
4622:(1): 1–32.
4528:Section 8.2
3126:: 261–274.
2563:independent
2549:Counternull
2446:probability
2444:assess the
2442:objectively
2362:effect size
2247:game theory
2210:falsifiable
1272:Conviction
1038:, a simple
946:incorrectly
913:of a test (
893:specificity
884:incorrectly
729:forecasting
677:effect size
573:is at most
367:probability
143:independent
139:contingency
9318:Categories
9055:Caribbean
8932:Processing
8866:Quarantine
8788:Student's
8588:Sanitation
8222:History of
7997:Demography
7715:ARMA model
7520:Regression
7097:(Friedman)
7058:(Wilcoxon)
6996:Normality
6986:Lilliefors
6933:Student's
6809:Resampling
6683:Robustness
6671:divergence
6661:Efficiency
6599:(monotone)
6594:Likelihood
6511:Population
6344:Stratified
6296:Population
6115:Dependence
6071:Count data
6002:Percentile
5979:Dispersion
5912:Arithmetic
5847:Statistics
5203:(1): 3–7.
2628:References
2518:Statistics
2450:hypothesis
2383:See also:
2296:weren't").
2277:See also:
2267:not always
2159:One naïve
1257:Acquittal
1001:resampling
952:Exact test
764:population
749:See also:
698:be wrong.
615:-value is
528:section).
363:David Hume
353:Philosophy
93:Paul Meehl
62:See also:
9235:John Snow
9162:Education
9152:Full list
9040:education
8964:ISO 22000
8917:Chemistry
8830:Epidemics
8783:ROC curve
8593:Emergency
8373:Radiation
8353:Pollution
8337:Ministers
8234:Euthenics
7378:Logistic
7145:posterior
7071:Rank sum
6819:Jackknife
6814:Bootstrap
6632:Bootstrap
6567:Parameter
6516:Statistic
6311:Statistic
6223:Run chart
6208:Pie chart
6203:Histogram
6193:Fan chart
6168:Bar chart
6050:L-moments
5937:Geometric
5774:EMS Press
5597:CiteSeerX
5527:CiteSeerX
5500:125788648
5382:263827430
5352:J Physiol
5301:website:
5217:145422959
5044:144813784
4896:121054702
4423:March 30,
4345:(1956) .
4296:ignored (
4286:cite book
4149:186209819
3958:145576828
3751:1431-875X
3372:CiteSeerX
3154:: 69–91.
2925:α
2273:Criticism
2070:≤
2046:∣
2040:≥
2005:∣
1933:≈
1900:−
1878:−
1827:∑
1799:∣
1762:∑
1734:∣
1728:≥
1693:∣
1631:−
1623:≈
1571:∣
1530:∣
1036:sign test
1031:(1770s).
581:α
561:α
391:Education
150:that led
9278:Category
8977:sciences
8912:Additive
8583:Safe sex
8554:Medicine
8468:Theories
8239:Genomics
8217:Eugenics
8207:Deviance
8187:Auxology
8092:Category
7785:Survival
7662:Johansen
7385:Binomial
7340:Isotonic
6927:(normal)
6572:location
6379:Blocking
6334:Sampling
6213:Q–Q plot
6178:Box plot
6160:Graphics
6055:Skewness
6045:Kurtosis
6017:Variance
5947:Heronian
5942:Harmonic
5619:13744252
5444:22774788
5374:37815959
5182:40712136
5147:28340967
5139:10937333
4938:96422880
4034:27141478
3898:24522584
3862:(2014).
3768:(2008).
3727:. 2005.
3634:34729227
3625:2092/413
3410:Archived
3324:17286092
3316:20445367
3278:16591951
3219:44708120
3211:17741062
3168:14136146
3056:10383371
2906:Archived
2673:. SAGE.
2621:E-values
2495:See also
2161:Bayesian
2138:deciding
1248:is true
1239:is true
1008:Examples
687:Cautions
383:and the
256:abstract
9290:Commons
9203:History
9100:Canada
9075:Europe
8559:Nursing
8539:Hygiene
8502:Hygiene
8227:Liberal
8180:General
8118:Commons
8065:Kriging
7950:Process
7907:studies
7766:Wavelet
7599:General
6766:Plug-in
6560:L space
6339:Cluster
6040:Moments
5858:Outline
5776:, 2001
5735:Bibcode
5549:1550979
5452:5610231
5065:: 3–39.
4982:5974619
4888:2982993
4597:2246117
4249:225–226
4025:4840791
3876:Bibcode
3585:1403333
3394:7176653
3246:Bibcode
3191:Bibcode
3183:Science
3064:7534212
3007:Bibcode
2881:2245634
2842:: 1–35.
2448:that a
766:(not a
607:If the
185:), and
58:History
9090:India
9065:China
8937:Safety
8618:Worker
7987:Census
7577:Normal
7525:Manova
7345:Robust
7095:2-way
7087:1-way
6925:-test
6596:
6173:Biplot
5964:Median
5957:Lehmer
5899:Center
5711:
5617:
5599:
5547:
5529:
5498:
5450:
5442:
5380:
5372:
5329:
5255:428023
5253:
5215:
5180:
5145:
5137:
5098:380942
5096:
5042:
4980:
4936:
4894:
4886:
4825:788503
4823:
4779:
4754:
4726:
4701:
4676:
4651:
4595:
4520:
4495:
4470:
4446:
4391:
4361:
4325:
4255:
4227:
4203:
4178:
4147:
4063:
4032:
4022:
3979:
3956:
3919:
3896:
3868:Nature
3842:
3801:
3776:
3749:
3739:
3703:
3632:
3583:
3452:
3392:
3374:
3345:
3322:
3314:
3276:
3269:389491
3266:
3217:
3209:
3166:
3062:
3054:
2879:
2702:
2677:
2650:
2477:-value
2454:Fisher
2416:priors
1953:Thus,
1936:0.0713
1075:, Dr.
924:-value
768:sample
171:-value
152:Fisher
48:-value
9115:U.S.
8959:HACCP
8908:Food
8800:-test
8792:-test
8378:Light
8363:Water
7611:Trend
7140:prior
7082:anova
6971:-test
6945:-test
6937:-test
6844:Power
6789:Pivot
6582:shape
6577:scale
6027:Shape
6007:Range
5952:Heinz
5927:Cubic
5863:Index
5808:Some
5585:(PDF)
5567:(PDF)
5545:S2CID
5496:S2CID
5476:(PDF)
5448:S2CID
5420:(PDF)
5378:S2CID
5251:S2CID
5213:S2CID
5178:S2CID
5143:S2CID
5094:S2CID
5040:S2CID
4945:(PDF)
4934:S2CID
4914:(PDF)
4892:S2CID
4884:JSTOR
4801:(PDF)
4593:JSTOR
4353:[
4174:–25.
4145:S2CID
4121:(PDF)
3954:S2CID
3685:(PDF)
3659:(2).
3630:S2CID
3581:JSTOR
3561:(PDF)
3527:(PDF)
3390:S2CID
3312:JSTOR
3215:S2CID
3164:S2CID
3116:(PDF)
3060:S2CID
2955:(PDF)
2877:JSTOR
2801:(PDF)
2775:(PDF)
2760:(PDF)
2723:(PDF)
2481:index
2427:-test
2222:Tukey
2181:power
1332:suits
1089:trial
984:(UMP)
696:might
237:faith
132:1904:
114:1900:
104:1778:
8891:WASH
8847:List
8835:List
8368:Soil
7844:Test
7044:Sign
6896:Wald
5969:Mode
5907:Mean
5709:ISBN
5615:PMID
5440:PMID
5396:link
5370:PMID
5327:ISBN
5282:2012
5135:PMID
4978:PMID
4821:PMID
4777:ISBN
4752:ISBN
4724:ISBN
4699:ISBN
4674:ISBN
4649:ISBN
4518:ISBN
4493:ISBN
4468:ISBN
4444:ISBN
4425:2012
4389:ISBN
4359:ISBN
4323:ISBN
4298:help
4253:ISBN
4225:ISBN
4201:ISBN
4176:ISBN
4061:ISBN
4030:PMID
3977:ISBN
3917:ISBN
3894:PMID
3840:ISBN
3799:ISBN
3774:ISBN
3747:ISSN
3737:ISBN
3701:ISBN
3450:ISBN
3343:ISBN
3320:PMID
3274:PMID
3207:PMID
3052:PMID
2783:2013
2700:ISBN
2675:ISBN
2648:ISBN
2319:sole
2245:and
2175:and
2132:and
2073:0.01
1444:>
1411:and
972:size
903:and
879:Size
719:The
712:The
705:The
596:The
231:The
205:and
8358:Air
7024:BIC
7019:AIC
5743:doi
5731:231
5682:doi
5647:doi
5607:doi
5537:doi
5488:doi
5432:doi
5428:142
5360:doi
5356:601
5243:doi
5205:doi
5170:doi
5127:doi
5086:doi
5032:doi
5005:doi
4970:doi
4926:doi
4876:doi
4872:151
4848:doi
4813:doi
4809:104
4624:doi
4583:doi
4551:doi
4319:134
4135:doi
4057:191
4020:PMC
4010:doi
3946:doi
3884:doi
3872:506
3729:doi
3693:doi
3661:doi
3620:hdl
3612:doi
3573:doi
3539:doi
3503:doi
3382:doi
3304:doi
3300:119
3264:PMC
3254:doi
3199:doi
3187:156
3156:doi
3094:doi
3044:doi
3040:130
3015:doi
3003:231
2967:doi
2867:doi
2813:doi
2735:doi
2146:not
974:or
961:or
895:in
786:not
617:not
499:obs
474:obs
197:, "
193:",
177:),
9320::
5772:,
5766:,
5741:.
5729:.
5723:.
5676:.
5672:.
5641:.
5637:.
5613:.
5605:.
5593:57
5591:.
5587:.
5543:.
5535:.
5523:23
5521:.
5517:.
5494:.
5482:.
5478:.
5460:^
5446:.
5438:.
5426:.
5422:.
5404:^
5392:}}
5388:{{
5376:.
5368:.
5354:.
5350:.
5325:.
5323:94
5284:.
5249:.
5239:54
5237:.
5225:^
5211:.
5199:.
5176:.
5166:24
5164:.
5141:.
5133:.
5121:.
5107:^
5092:.
5082:49
5080:.
5061:.
5038:.
5028:20
5026:.
5001:33
4999:.
4976:.
4966:66
4964:.
4932:.
4922:34
4920:.
4916:.
4890:.
4882:.
4870:.
4844:46
4842:.
4819:.
4807:.
4803:.
4738:^
4620:18
4618:.
4614:.
4591:.
4579:11
4577:.
4573:.
4547:26
4545:.
4533:^
4487:.
4418:13
4416:.
4412:.
4321:.
4290::
4288:}}
4284:{{
4276:.
4251:.
4143:.
4131:27
4129:.
4123:.
4059:.
4028:.
4018:.
4004:.
4000:.
3952:.
3940:.
3892:.
3882:.
3870:.
3866:.
3826:^
3745:.
3735:.
3723:.
3699:.
3687:.
3657:17
3655:.
3651:.
3628:.
3618:.
3608:28
3606:.
3579:.
3569:65
3567:.
3563:.
3533:.
3529:.
3499:12
3497:.
3493:.
3481:^
3448:.
3388:.
3380:.
3368:57
3366:.
3318:.
3310:.
3298:.
3286:^
3272:.
3262:.
3252:.
3242:68
3240:.
3236:.
3213:.
3205:.
3197:.
3185:.
3162:.
3152:57
3150:.
3136:^
3122:.
3118:.
3090:88
3088:.
3072:^
3058:.
3050:.
3038:.
3013:.
3001:.
2995:.
2979:^
2963:17
2961:.
2957:.
2942:^
2900:,
2889:^
2875:.
2861:.
2857:.
2838:.
2834:.
2807:.
2803:.
2766:.
2762:.
2747:^
2729:.
2725:.
2491:.
2336:.
2241:,
2237:,
2212:.
2120:.
2108:13
1897:25
1855:25
1842:25
1837:10
1777:25
1772:10
1731:10
1634:15
1627:10
1618:25
1568:25
1338:.
915:α)
852:/
807:(H
794:(H
770:).
545:.
414:,
373:.
339:3
327:2
315:1
304:#
189:("
173:,
128:.
84:.
31:A
9154:)
9150:(
8798:Z
8790:t
8339:)
8335:(
8165:e
8158:t
8151:v
6969:G
6943:F
6935:t
6923:Z
6642:V
6637:U
5839:e
5832:t
5825:v
5812:.
5751:.
5745::
5737::
5690:.
5684::
5678:3
5655:.
5649::
5643:1
5621:.
5609::
5551:.
5539::
5502:.
5490::
5484:1
5454:.
5434::
5398:)
5384:.
5362::
5335:.
5257:.
5245::
5219:.
5207::
5201:8
5184:.
5172::
5149:.
5129::
5123:5
5100:.
5088::
5063:1
5046:.
5034::
5011:.
5007::
4984:.
4972::
4928::
4898:.
4878::
4854:.
4850::
4827:.
4815::
4785:.
4760:.
4732:.
4707:.
4682:.
4657:.
4632:.
4626::
4599:.
4585::
4557:.
4553::
4526:.
4501:.
4452:.
4427:.
4397:.
4373:.
4367:.
4331:.
4300:)
4261:.
4184:.
4172:1
4151:.
4137::
4069:.
4036:.
4012::
4006:7
3985:.
3960:.
3948::
3942:7
3925:.
3900:.
3886::
3878::
3848:.
3807:.
3782:.
3753:.
3731::
3709:.
3695::
3669:.
3663::
3636:.
3622::
3614::
3587:.
3575::
3545:.
3541::
3535:2
3511:.
3505::
3458:.
3446:8
3396:.
3384::
3351:.
3326:.
3306::
3280:.
3256::
3248::
3221:.
3201::
3193::
3170:.
3158::
3124:2
3100:.
3096::
3066:.
3046::
3023:.
3017::
3009::
2973:.
2969::
2937:.
2915:p
2883:.
2869::
2863:4
2840:1
2819:.
2815::
2809:5
2785:.
2768:9
2741:.
2737::
2731:1
2683:.
2656:.
2475:p
2425:t
2289:p
2227:t
2105:=
2102:c
2085:.
2066:)
2060:4
2057:1
2052:=
2049:p
2043:c
2037:X
2033:(
2029:P
2026:=
2023:)
2013:0
2009:H
2000:0
1996:H
1987:(
1984:P
1970:c
1966:c
1962:α
1955:c
1948:.
1928:k
1923:)
1918:4
1915:1
1910:(
1903:k
1892:)
1886:4
1883:1
1875:1
1871:(
1863:)
1858:k
1850:(
1834:=
1831:k
1823:=
1819:)
1813:4
1810:1
1805:=
1802:p
1796:k
1793:=
1790:X
1786:(
1782:P
1769:=
1766:k
1758:=
1754:)
1748:4
1745:1
1740:=
1737:p
1725:X
1721:(
1717:P
1714:=
1711:)
1701:0
1697:H
1688:0
1684:H
1675:(
1672:P
1658:c
1648:,
1613:)
1608:4
1605:1
1600:(
1595:=
1591:)
1585:4
1582:1
1577:=
1574:p
1565:=
1562:X
1558:(
1554:P
1551:=
1548:)
1538:0
1534:H
1525:0
1521:H
1512:(
1509:P
1495:c
1487:c
1483:c
1479:c
1475:c
1453:4
1450:1
1441:p
1438::
1433:1
1429:H
1424::
1392:4
1389:1
1383:=
1380:p
1377::
1372:0
1368:H
1362::
1347:p
1336:X
1246:1
1244:H
1237:0
1235:H
1194:1
1190:H
1161:0
1157:H
1134:1
1130:H
1107:0
1103:H
1055:p
1048:p
1044:p
963:t
959:z
922:p
873:)
871:β
839:s
826:α
822:α
820:C
811:)
809:1
798:)
796:0
613:p
609:p
602:p
598:p
496:t
492:0
489:H
480:.
478:T
471:t
460:α
444:.
442:T
416:F
412:t
408:z
289:p
275:p
241:p
233:p
181:(
169:p
166:(
46:p
Text is available under the Creative Commons Attribution-ShareAlike License. Additional terms may apply.