415:
857:
379:
391:
427:
403:
533:
47:
56:
337:
are often characterized as supratentorial (above the tentorium) and infratentorial (below the tentorium). The location of the tumor can help in determining the type of tumor, as different tumors occur with different frequencies at each location. Additionally, most childhood primary brain tumors are
235:. The free border of each side extends anteriorly beyond the medial end of the superior petrosal sinus (i.e. the apex of the petrous part of the temporal bone) to overlap the attached margin, thenceforth forming a ridge of dura matter upon the roof of the
877:
248:
The tentorium slopes superior-ward so that the free border is situated at a more superior level than its bony attachment, thus conforming to the shape of the surfaces of the cerebrum and cerebellum with which it is in
357:. Tentorial herniation is a serious symptom, especially since the brainstem is likely to be compressed as well if the intracranial pressure rises further. A common type of herniation is
378:
341:
Since the tentorium is a hard structure, if there is an expansion of the volume of the brain or its surrounding matter above the tentorium, such as because of a tumour or
139:
414:
338:
infratentorial, while most adult primary brain tumors are supratentorial. The location of the tumor may have prognostic significance as well.
115:
367:
within the cerebellar tentorium are not very common in elderly people; they are not accompanied by any disease and have no known cause.
390:
17:
402:
493:
598:
724:
146:
570:
286:
510:
134:
734:
282:
542:
847:
307:
294:
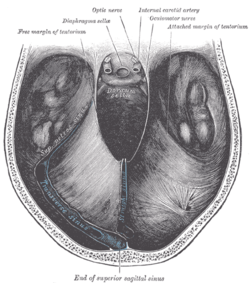
It is attached, behind, by its convex border, to the transverse ridges upon the inner surface of the
103:
384:
Dura mater and its processes exposed by removing part of the right half of the skull, and the brain.
739:
240:
30:
This article is about the vertebrate brain structure. For the arthropod anatomical structure, see
714:
426:
264:
591:
122:
110:
761:
695:
680:
200:
196:
180:
685:
8:
832:
643:
561:
856:
576:
827:
776:
719:
565:
299:
260:
882:
653:
584:
547:
489:
878:
Knowledge articles incorporating text from the 20th edition of Gray's
Anatomy (1918)
511:"Normal intracranial calcifications | Radiology Reference Article | Radiopaedia.org"
729:
358:
354:
792:
709:
668:
658:
236:
228:
451:
861:
822:
817:
771:
766:
704:
648:
323:
295:
271:
259:
The attached margin of the tentorium cerebelli is attached at the edges of the
184:
871:
797:
538:
364:
345:, the brain can get pushed down partly through the tentorium. This is called
303:
275:
127:
27:
Vertebrate brain structure separating the cerebellum from the occipital lobes
187:
into four (incomplete) compartments. The cerebellar tentorium separates the
638:
319:
615:
611:
334:
227:
The free border of the tentorium is U-shaped; it forms an aperture - the
152:
630:
346:
267:(here, the two layers of the tentorium diverge to embrace the sinuses);
188:
176:
98:
753:
350:
322:
attaches onto the midline of the upper surface of the tentorium; the
211:
31:
203:; the cerebrum is supratentorial and the cerebellum infratentorial.
607:
342:
232:
207:
192:
74:
274:
posteriorly, and (the superior angle of) the petrous part of the
46:
408:
Sagittal section of the skull, showing the sinuses of the dura.
302:; in front, to the superior angle of the petrous part of the
172:
86:
396:
Tentorium cerebelli seen cut out in the back of the skull.
55:
606:
206:
The free border of the tentorium gives passage to the
845:
869:
592:
353:on the affected side, due to pressure on the
239:, terminating anteriorly by attaching at the
573:at the University of Michigan Health System
599:
585:
483:
449:
281:Anteriorly, its attachment extends to the
54:
45:
502:
450:Ita, Michael I.; Bordoni, Bruno (2024).
329:
479:
477:
475:
473:
14:
870:
537:This article incorporates text in the
580:
488:(12th ed.). Elsevier Australia.
60:Cerebellar tentorium seen from above.
470:
420:Human brain dura mater (reflections)
370:
229:tentorial notch (tentorial incisure)
452:"Neuroanatomy, Tentorium Cerebelli"
24:
443:
326:runs along this line of junction.
254:
25:
894:
555:
508:
285:; posteriorly, it extends to the
855:
531:
425:
413:
401:
389:
377:
147:Anatomical terms of neuroanatomy
287:internal occipital protuberance
484:Sinnatamby, Chummy S. (2011).
306:on either side, enclosing the
222:
13:
1:
437:
231:- which gives passage to the
313:
217:
210:(the upper-most part of the
7:
545:of the 20th edition of
283:posterior clinoid processes
10:
899:
270:it thus attaches onto the
29:
810:
785:
752:
725:Of lateral cerebral fossa
694:
676:
667:
629:
622:
318:The posterior end of the
308:superior petrosal sinuses
298:, and there encloses the
145:
133:
121:
109:
97:
85:
80:
70:
65:
53:
44:
39:
740:Cerebellopontine cistern
349:and will often cause an
241:anterior clinoid process
18:Infratentorial neoplasms
715:Interpeduncular cistern
458:. StatPearls Publishing
265:superior petrosal sinus
762:Denticulate ligaments
696:Subarachnoid cisterns
681:Arachnoid granulation
330:Clinical significance
201:infratentorial region
735:Of lamina terminalis
686:Arachnoid trabeculae
165:cerebellar tentorium
40:Cerebellar tentorium
833:Cerebrospinal fluid
644:Tentorium cerebelli
571:Atlas image: n2a3p2
432:Tentorium cerebelli
169:tentorium cerebelli
92:tentorium cerebelli
828:Subarachnoid space
777:Perivascular space
720:Chiasmatic cistern
566:Indiana University
300:transverse sinuses
261:transverse sinuses
183:that separate the
179:") is one of four
843:
842:
806:
805:
748:
747:
654:Diaphragma sellae
509:Muzio, Bruno Di.
495:978-0-7295-3752-0
371:Additional images
175:for "tent of the
161:
160:
156:
16:(Redirected from
890:
860:
859:
851:
730:Superior cistern
674:
673:
627:
626:
601:
594:
587:
578:
577:
535:
534:
526:
525:
523:
521:
506:
500:
499:
481:
468:
467:
465:
463:
447:
429:
417:
405:
393:
381:
359:uncal herniation
355:oculomotor nerve
153:edit on Wikidata
150:
58:
49:
37:
36:
21:
898:
897:
893:
892:
891:
889:
888:
887:
868:
867:
866:
854:
846:
844:
839:
802:
793:Filum terminale
781:
744:
710:Pontine cistern
690:
669:Arachnoid mater
663:
659:Trigeminal cave
618:
605:
558:
532:
529:
519:
517:
507:
503:
496:
482:
471:
461:
459:
448:
444:
440:
433:
430:
421:
418:
409:
406:
397:
394:
385:
382:
373:
332:
316:
257:
255:Attached border
237:cavernous sinus
225:
220:
157:
61:
35:
28:
23:
22:
15:
12:
11:
5:
896:
886:
885:
880:
865:
864:
841:
840:
838:
837:
836:
835:
825:
823:Subdural space
820:
818:Epidural space
814:
812:
808:
807:
804:
803:
801:
800:
795:
789:
787:
783:
782:
780:
779:
774:
772:Choroid plexus
769:
767:Tela choroidea
764:
758:
756:
750:
749:
746:
745:
743:
742:
737:
732:
727:
722:
717:
712:
707:
705:Cisterna magna
701:
699:
692:
691:
689:
688:
683:
677:
671:
665:
664:
662:
661:
656:
651:
649:Falx cerebelli
646:
641:
635:
633:
624:
620:
619:
604:
603:
596:
589:
581:
575:
574:
568:
557:
556:External links
554:
548:Gray's Anatomy
528:
527:
501:
494:
486:Last's Anatomy
469:
441:
439:
436:
435:
434:
431:
424:
422:
419:
412:
410:
407:
400:
398:
395:
388:
386:
383:
376:
372:
369:
365:Calcifications
351:enlarged pupil
331:
328:
324:straight sinus
315:
312:
296:occipital bone
272:occipital bone
256:
253:
224:
221:
219:
216:
197:supratentorial
185:cranial cavity
159:
158:
149:
143:
142:
137:
131:
130:
125:
119:
118:
113:
107:
106:
101:
95:
94:
89:
83:
82:
78:
77:
72:
68:
67:
63:
62:
59:
51:
50:
42:
41:
26:
9:
6:
4:
3:
2:
895:
884:
881:
879:
876:
875:
873:
863:
858:
853:
852:
849:
834:
831:
830:
829:
826:
824:
821:
819:
816:
815:
813:
809:
799:
798:Leptomeninges
796:
794:
791:
790:
788:
784:
778:
775:
773:
770:
768:
765:
763:
760:
759:
757:
755:
751:
741:
738:
736:
733:
731:
728:
726:
723:
721:
718:
716:
713:
711:
708:
706:
703:
702:
700:
697:
693:
687:
684:
682:
679:
678:
675:
672:
670:
666:
660:
657:
655:
652:
650:
647:
645:
642:
640:
637:
636:
634:
632:
628:
625:
621:
617:
613:
609:
602:
597:
595:
590:
588:
583:
582:
579:
572:
569:
567:
563:
560:
559:
553:
552:
549:
546:
544:
540:
539:public domain
516:
512:
505:
497:
491:
487:
480:
478:
476:
474:
457:
453:
446:
442:
428:
423:
416:
411:
404:
399:
392:
387:
380:
375:
374:
368:
366:
362:
360:
356:
352:
348:
344:
339:
336:
327:
325:
321:
311:
309:
305:
304:temporal bone
301:
297:
292:
291:
288:
284:
279:
277:
276:temporal bone
273:
269:
266:
262:
252:
251:
246:
245:
242:
238:
234:
230:
215:
213:
209:
204:
202:
198:
194:
190:
186:
182:
178:
174:
170:
166:
154:
148:
144:
141:
138:
136:
132:
129:
126:
124:
120:
117:
114:
112:
108:
105:
102:
100:
96:
93:
90:
88:
84:
79:
76:
73:
69:
64:
57:
52:
48:
43:
38:
33:
19:
639:Falx cerebri
550:
536:
530:
518:. Retrieved
514:
504:
485:
460:. Retrieved
455:
445:
363:
340:
335:Brain tumors
333:
320:falx cerebri
317:
293:
290:
280:
278:anteriorly.
268:
258:
250:
247:
244:
226:
205:
168:
164:
162:
116:A14.1.01.104
91:
616:spinal cord
515:Radiopaedia
223:Free border
181:dural folds
81:Identifiers
872:Categories
631:Dura mater
456:StatPearls
438:References
347:herniation
195:forming a
189:cerebellum
177:cerebellum
99:NeuroNames
754:Pia mater
314:Relations
218:Structure
212:brainstem
191:from the
32:tentorium
883:Meninges
786:Combined
608:Meninges
543:page 874
520:9 August
462:9 August
343:bleeding
249:contact.
233:midbrain
208:midbrain
193:cerebrum
75:Meninges
862:Anatomy
610:of the
199:and an
71:Part of
66:Details
848:Portal
811:Spaces
623:Layers
551:(1918)
492:
612:brain
562:Photo
541:from
173:Latin
151:[
140:83966
87:Latin
614:and
522:2024
490:ISBN
464:2024
263:and
163:The
128:5375
111:TA98
104:1240
564:at
214:).
167:or
135:FMA
123:TA2
874::
513:.
472:^
454:.
361:.
310:.
850::
698::
600:e
593:t
586:v
524:.
498:.
466:.
289:.
243:.
171:(
155:]
34:.
20:)
Text is available under the Creative Commons Attribution-ShareAlike License. Additional terms may apply.