46:
33:
785:
282:
Studying environmental changes: Brachionus calyciflorus can serve as an indicator of environmental changes in water bodies. Monitoring population dynamics of
Brachionus calyciflorus can help assess the health of aquatic systems and detect any changes that may occur as a result of pollution or climate
245:
During the life cycle of
Brachionus calyciflorus, there are several stages and instars, including neonate, juvenile, pre-adult, and adult stages. The duration of each stage can vary depending on environmental factors such as temperature, food supply, and population density. In ideal conditions, the
233:
The life cycle of
Brachionus calyciflorus begins with the hatching of eggs, which are either fertilized or produced by parthenogenesis. The juveniles that hatch from these eggs, called "amictic" females, are diploid and develop into reproductive females without undergoing meiosis, meaning that they
262:
Brachionus calyciflorus is a cosmopolitan species, meaning it is found in many regions of the world, including North and South
America, Europe, Asia, Australia, and Africa. It has been reported in a range of countries, including the United States, Canada, Brazil, Spain, France, Sweden, Russia, and
217:
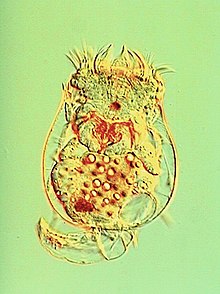
One of the most distinctive features of
Brachionus calyciflorus is its lorica, or outer shell. The lorica of Brachionus calyciflorus is formed from two separate plates, with the upper plate forming a calyx-like structure over the head region of the body. The lower plate is elliptical in shape and
204:
The taxonomy of
Brachionus calyciflorus is well-established based on morphological and molecular characteristics. As a member of the phylum Rotifera, it shares many features with other rotifers, including a ciliated corona and a characteristic rotary motion. Within the genus Brachionus, there are
237:
Once the food supply becomes scarce, some amictic females switch to a meiotic mode of reproduction, producing haploid male offspring. These males then fertilize the haploid eggs, laid by the female offspring, leading to the production of diploid resting eggs, which remain dormant in the sediment
213:
Brachionus calyciflorus has a characteristic morphology that distinguishes it from other rotifer species. The body of
Brachionus calyciflorus is elongated and cylindrical in shape, measuring about 160 to 350 μm in length and 80 to 160 μm in width. The head region of the body is retractable and
266:
In addition to its natural distribution, Brachionus calyciflorus is commonly used in aquaculture, where it is reared in laboratory cultures to feed fish and other aquatic organisms. It is also used in ecotoxicology studies as a test organism due to its short life cycle and sensitivity to
286:
Toxicity testing: Brachionus calyciflorus is widely used in ecotoxicological studies due to its sensitivity to toxic substances. It is used to test the effects of different substances on aquatic organisms, and to assess the potential risk to human health and the
318:
Feeding: Brachionus calyciflorus feeds on microalgae and bacteria, and thus, it is important to provide a food source. Some commonly used microalgae for
Brachionus calyciflorus cultivation include Chlorella vulgaris, Scenedesmus sp., and Nannochloropsis
221:
Brachionus calyciflorus has a well-developed digestive system, with an elongated pharynx and a muscular stomach. The reproductive system of the rotifer is also well-developed, with a pair of ovaries and testes located in the posterior part of the body.
311:
Temperature: The optimal temperature for culturing
Brachionus calyciflorus is between 20 °C to 28 °C. Higher temperatures can lead to a decrease in growth rate and reproduction, while lower temperatures can lead to a decrease in overall
258:
This species is euryhaline, meaning it can tolerate a wide range of salinities, and can be found in both fresh and brackish water habitats. It can also tolerate various environmental conditions such as pH, water temperature, and oxygen levels.
348:
Transitions to obligate parthenogenesis have been described. Obligate parthenogens were homozygous for a recessive allele, which caused inability to respond to the chemical signals that normally induce sexual reproduction in this species.
307:
Culture vessel: Brachionus calyciflorus can be cultured in a variety of vessels such as laboratory-grade glassware, plastic containers, and aquariums. The culture vessel should be clean and have a large surface area to promote
325:
Harvesting: Brachionus calyciflorus can be harvested using a fine-mesh filter or by centrifugation. The harvested rotifers can then be used as a live food source for other aquatic organisms or as a sample for
290:
Bioremediation: Brachionus calyciflorus is known to feed on harmful algae and bacteria that can cause water quality issues. As a result, it is considered a potential agent for bioremediation of polluted water
484:
Wang, W., Xu, W., and Yang, L. (2015). Optimization of culture conditions for
Brachionus calyciflorus (Rotifera) and assessment of its potentials as food for larval ornamental fish. Aquaculture Research 46,
254:
Brachionus calyciflorus is a freshwater rotifer species that is widely distributed around the world. It is commonly found in a range of freshwater environments, including ponds, lakes, streams, and rivers.
205:
several species, including B. plicatilis, which is also commonly used in research and aquaculture. Brachionus calyciflorus is distinct from other species in the genus due to its unique calyx-shaped lorica.
330:
In summary, culturing Brachionus calyciflorus requires careful maintenance of optimal temperature, lighting, feeding, water quality, and harvesting to ensure consistent growth and high biomass production.
241:
However, when the food supply remains abundant, the amictic females continue to reproduce asexually, producing new clones of themselves through multiple generations, leading to high population densities.
214:
contains a characteristic ring of cilia, called the corona, which is used for feeding and locomotion. The corona is composed of two types of cilia, the large frontal cilia and smaller ventral cilia.
451:
Spatial patterns of genetic differentiation in Brachionus calyciflorus species complex collected from East China in summer XL Xiang, YL Xi, XL Wen, JY Zhang, Q Ma - Hydrobiologia, 2010 - Springer
429:
Spatial patterns of genetic differentiation in Brachionus calyciflorus species complex collected from East China in summer XL Xiang, YL Xi, XL Wen, JY Zhang, Q Ma - Hydrobiologia, 2010 - Springer
238:
until the environmental conditions become suitable for hatching. In response to suitable environmental conditions, the resting eggs hatch into diploid amictic females, starting a new cycle.
303:
Culturing Brachionus calyciflorus involves growing this species of rotifer in a controlled environment. Here are some important factors to consider when culturing Brachionus calyciflorus:
279:
Food source: Brachionus calyciflorus is an important food source for many aquatic organisms such as fish, amphibians, and invertebrates. It is also used as a live food for aquarium fish.
469:
S. Kang, S. Kim, Y.R. Cho, S. Yi, S.S. Park - Current understanding of bioremediation using Brachionus spp.:a comprehensive review, Environmental Science and Pollution Research (2021).
448:
Brachionus calyciflorus is a species complex: mating behavior and genetic differentiation among four geographically isolated strains JJ Gilbert, EJ Walsh - Rotifera X, 2005 - Springer
420:
Brachionus calyciflorus is a species complex: mating behavior and genetic differentiation among four geographically isolated strains JJ Gilbert, EJ Walsh - Rotifera X, 2005 - Springer
488:
Hagiwara, A. and Sakakura, Y. (2005). Improvement in mass culture of a freshwater rotifer, Brachionus calyciflorus, by the use of a yeast, Candida utilis. Fish Science 71 (1), 87–93.
315:
Light: Brachionus calyciflorus requires a light source with a 12-hour light and dark cycle. Illumination can be artificial or natural, with a light intensity of 2,000 to 4,000 lux.
481:
Dhert, P., Jaspers, E., Avila, A., Henroteaux, M., and Nelis, H. (1990). Laboratory culture and mass production of the rotifer Brachionus plicatilis. Hydrobiologia 197 (1), 59–70.
322:
Water quality: The pH of culture water for Brachionus calyciflorus should be maintained between 6.5 and 7.5, and the salinity level should be between 0.5 and 5 parts per thousand.
225:
Overall, the distinctive morphology of Brachionus calyciflorus plays an important role in its feeding, locomotion, reproduction, and adaptation to its aquatic environment.
454:
Segers, H. (2007). Annotated checklist of the rotifers (Phylum Rotifera), with notes on nomenclature, taxonomy and distribution. Zootaxa, 1564, 1–104.
275:
Brachionus calyciforus is an important zooplankton species that plays a significant role in freshwater ecosystems. Here are some of the reasons why:
445:
C.-P. Stelzer, J. Schmidt, A. Wiedlroither, and S. Riss (2010). Loss of Sexual Reproduction and Dwarfing in a Small Metazoan. PLoS ONE 5(9): e12854.
411:
C.-P. Stelzer, J. Schmidt, A. Wiedlroither, and S. Riss (2010). Loss of Sexual Reproduction and Dwarfing in a Small Metazoan. PLoS ONE 5(9): e12854.
460:
Snell, T. W., & Boyer, G. L. (2010). Rotifers as Model Systems in Ecotoxicology. Environmental Science and Pollution Research, 17(2), 209–213.
669:
721:
442:"Brachionus calyciflorus | Marine Rotifera". rotifera.lifedesks.org. Archived from the original on 23 December 2014. Retrieved 6 June 2022.
643:
682:
826:
687:
604:
382:
622:
757:
726:
635:
708:
295:
In summary, Brachionus calyciflorus has ecological, scientific, and potential biotechnological importance.
457:
Rotifera / Vol. 1, Biology, ecology and systematics / by Thomas Nogrady, Robert L. Wallace, Terry W. Snell
552:
529:
557:
819:
45:
762:
736:
700:
218:
covers the rest of the body. The lorica provides structural support and protection to the rotifer.
800:
850:
674:
534:
497:
845:
812:
466:
R. Wallace, T.W. Snell - Rotifera: vol. 1: Biology, Ecology and Systematics (Springer, 2006).
140:
749:
475:
G.L. Maciocia - The Practice of Chinese Medicine, 2nd edn. (Elsevier Health Sciences, 2008).
578:
478:
Snell, T.W. and Persoone, G. (2013). Rotifers for Aquaculture. John Wiley & Sons, Ltd.
8:
40:
744:
565:
570:
463:
Wallace, R. L., & Snell, T. W. (2010). Rotifera (2 ed.). Backhuys Publishers.
343:
189:
713:
796:
630:
617:
520:
183:
839:
609:
107:
390:
695:
656:
544:
87:
32:
365:
seems also to be a species complex consisting of more than one species.
648:
179:
117:
661:
591:
57:
491:
596:
514:
246:
life cycle of Brachionus calyciflorus can be as short as 2–3 days.
169:
792:
175:
172:
77:
583:
472:
R.M. May - How many species are there on earth?, Science (1988).
97:
67:
784:
837:
383:"Brachionus calyciflorus | Marine Rotifera"
188:Its advantages include the small size and short
186:in toxicology, ecology and evolutionary biology.
820:
249:
827:
813:
31:
838:
496:
495:
779:
737:0c6b7040-8b28-4659-a537-ce4957150879
636:88ffbed6-0383-4148-b159-ddbd250ff128
196:is around 2.2 days at 24 °C).
13:
352:
14:
862:
783:
342:normally reproduces by cyclical
44:
334:
423:
414:
405:
375:
234:produce clones of themselves.
1:
368:
270:
228:
208:
799:. You can help Knowledge by
298:
192:(average generation time of
7:
199:
182:. It is commonly used as a
10:
867:
778:
436:
267:environmental pollutants.
504:
146:
139:
41:Scientific classification
39:
30:
23:
361:cryptic species complex
250:Habitat and Distribution
535:Brachionus_calyciflorus
506:Brachionus calyciflorus
363:Brachionus calyciflorus
340:Brachionus calyciflorus
165:Brachionus calyciflorus
150:Brachionus calyciflorus
25:Brachionus calyciflorus
795:-related article is a
387:rotifera.lifedesks.org
359:Brachionus plicatilis
631:Fauna Europaea (new)
132:B. calyciflorus
393:on 23 December 2014
16:Species of rotifers
808:
807:
773:
772:
745:Open Tree of Life
498:Taxon identifiers
161:
160:
858:
829:
822:
815:
787:
780:
766:
765:
753:
752:
740:
739:
730:
729:
717:
716:
714:NBNSYS0100009701
704:
703:
691:
690:
678:
677:
665:
664:
652:
651:
639:
638:
626:
625:
613:
612:
600:
599:
587:
586:
574:
573:
561:
560:
548:
547:
538:
537:
525:
524:
523:
493:
492:
430:
427:
421:
418:
412:
409:
403:
402:
400:
398:
389:. Archived from
379:
152:
49:
48:
35:
21:
20:
866:
865:
861:
860:
859:
857:
856:
855:
836:
835:
834:
833:
776:
774:
769:
761:
756:
748:
743:
735:
733:
725:
720:
712:
707:
699:
694:
686:
681:
673:
668:
660:
655:
647:
642:
634:
629:
621:
616:
608:
603:
595:
590:
582:
577:
569:
564:
556:
551:
543:
541:
533:
528:
519:
518:
513:
500:
439:
434:
433:
428:
424:
419:
415:
410:
406:
396:
394:
381:
380:
376:
371:
355:
353:Species complex
347:
344:parthenogenesis
337:
301:
273:
252:
231:
211:
202:
194:B. calyciflorus
190:generation time
187:
157:
154:
148:
135:
43:
17:
12:
11:
5:
864:
854:
853:
848:
832:
831:
824:
817:
809:
806:
805:
788:
771:
770:
768:
767:
754:
741:
731:
718:
705:
692:
679:
666:
653:
640:
627:
618:Fauna Europaea
614:
601:
588:
575:
562:
549:
539:
526:
510:
508:
502:
501:
490:
489:
486:
482:
479:
476:
473:
470:
467:
464:
461:
458:
455:
452:
449:
446:
443:
438:
435:
432:
431:
422:
413:
404:
373:
372:
370:
367:
354:
351:
336:
333:
328:
327:
323:
320:
316:
313:
309:
300:
297:
293:
292:
288:
284:
280:
272:
269:
251:
248:
230:
227:
210:
207:
201:
198:
184:model organism
159:
158:
155:
144:
143:
137:
136:
129:
127:
123:
122:
115:
111:
110:
105:
101:
100:
95:
91:
90:
85:
81:
80:
75:
71:
70:
65:
61:
60:
55:
51:
50:
37:
36:
28:
27:
15:
9:
6:
4:
3:
2:
863:
852:
851:Rotifer stubs
849:
847:
844:
843:
841:
830:
825:
823:
818:
816:
811:
810:
804:
802:
798:
794:
789:
786:
782:
781:
777:
764:
759:
755:
751:
746:
742:
738:
732:
728:
723:
719:
715:
710:
706:
702:
697:
693:
689:
684:
680:
676:
671:
667:
663:
658:
654:
650:
645:
641:
637:
632:
628:
624:
619:
615:
611:
606:
602:
598:
593:
589:
585:
580:
576:
572:
567:
563:
559:
554:
550:
546:
540:
536:
531:
527:
522:
516:
512:
511:
509:
507:
503:
499:
494:
487:
483:
480:
477:
474:
471:
468:
465:
462:
459:
456:
453:
450:
447:
444:
441:
440:
426:
417:
408:
392:
388:
384:
378:
374:
366:
364:
360:
350:
345:
341:
332:
324:
321:
317:
314:
310:
306:
305:
304:
296:
289:
285:
281:
278:
277:
276:
268:
264:
260:
256:
247:
243:
239:
235:
226:
223:
219:
215:
206:
197:
195:
191:
185:
181:
178:occurring in
177:
174:
171:
167:
166:
153:
151:
145:
142:
141:Binomial name
138:
134:
133:
128:
125:
124:
121:
120:
116:
113:
112:
109:
106:
103:
102:
99:
96:
93:
92:
89:
86:
83:
82:
79:
76:
73:
72:
69:
66:
63:
62:
59:
56:
53:
52:
47:
42:
38:
34:
29:
26:
22:
19:
846:Brachionidae
801:expanding it
790:
775:
505:
425:
416:
407:
395:. Retrieved
391:the original
386:
377:
362:
358:
356:
339:
338:
335:Reproduction
329:
326:experiments.
302:
294:
287:environment.
274:
265:
261:
257:
253:
244:
240:
236:
232:
224:
220:
216:
212:
203:
193:
164:
163:
162:
156:Pallas, 1766
149:
147:
131:
130:
118:
108:Brachionidae
24:
18:
696:NatureServe
657:iNaturalist
88:Monogononta
840:Categories
369:References
271:Importance
229:Life Cycle
209:Morphology
180:freshwater
170:planktonic
119:Brachionus
701:2.1157767
357:Like the
299:Culturing
126:Species:
64:Kingdom:
58:Eukaryota
675:11423873
542:BioLib:
521:Q2547210
515:Wikidata
485:843–855.
312:biomass.
200:Taxonomy
104:Family:
78:Rotifera
74:Phylum:
68:Animalia
54:Domain:
793:rotifer
649:4984102
584:1062490
437:Sources
308:growth.
291:bodies.
283:change.
263:Japan.
176:species
173:rotifer
114:Genus:
94:Order:
84:Class:
763:134980
750:939320
734:NZOR:
727:104777
662:256162
623:301813
610:312084
597:BRCNCA
397:6 June
98:Ploima
791:This
758:WoRMS
688:58438
670:IRMNG
605:EUNIS
571:5X2DW
558:25428
545:74906
168:is a
797:stub
722:NCBI
683:ITIS
644:GBIF
592:EPPO
553:BOLD
399:2022
709:NBN
579:EoL
566:CoL
530:AFD
319:sp.
842::
760::
747::
724::
711::
698::
685::
672::
659::
646::
633::
620::
607::
594::
581::
568::
555::
532::
517::
385:.
346:.
828:e
821:t
814:v
803:.
401:.
Text is available under the Creative Commons Attribution-ShareAlike License. Additional terms may apply.