27:
126:
may sometimes be performed to prevent buboes from rupturing. Although incision and drainage yields better results in such cases—since usually no further intervention is necessary, whereas repeat aspirations may be
122:. In these conditions, a two-week course of antibiotics is the recommended treatment, and incision and drainage or excision of the swollen lymph nodes is best avoided. However,
521:
441:"Guidelines for the Management of Sexually Transmitted Infections. February 2004: 2. TREATMENT OF STI-ASSOCIATED SYNDROMES: 2.2. Genital ulcer: Inguinal bubo"
79:
bites through the bloodstream to the lymph nodes, where the bacteria replicate, causing the nodes to swell. Plague buboes may turn black and
472:
Lewis, David A (2014). "Epidemiology, clinical features, diagnosis and treatment of
Haemophilus ducreyi – a disappearing pathogen?".
250:
103:
Plague patients whose buboes swell to such a size that they burst tend to survive the disease. Before the discovery of
416:
206:
440:
119:
323:
Nesfield, V.B. (1911). "The treatment of bubonic plague by the immediate incision of the glands".
148:
Drancourt, Michel; Piarroux, Renaud; Bitam, Idir; Mouffok, Nadjet; Raoult, Didier (2013-01-01).
241:
Plague : the mysterious past and terrifying future of the world's most dangerous disease
128:
108:
20:
8:
83:, rotting away the surrounding tissue, or they may rupture, discharging large amounts of
69:
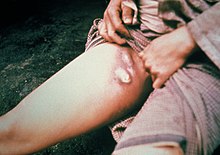
and occur as painful swellings in the thighs, neck, groin or armpits. They are caused by
91:
can spread from buboes around the body, resulting in other forms of the disease such as
384:
351:
123:
336:
497:
489:
422:
412:
389:
371:
305:
297:
256:
246:
239:
212:
202:
179:
171:
481:
407:
Morse, Stephen A.; Holmes, King K.; Moreland, Adele A.; Ballard, Ronald C. (2011).
379:
363:
332:
287:
161:
92:
485:
292:
275:
71:
54:
166:
149:
66:
31:
515:
493:
426:
375:
301:
216:
175:
260:
501:
393:
309:
183:
131:
wounds may heal more slowly, increasing the risk of secondary infection.
367:
104:
50:
115:
88:
80:
46:
26:
352:"Chancroid: clinical manifestations, diagnosis, and management"
147:
76:
406:
84:
111:
buboes with leeches or heated rods to save patients.
114:
Buboes are also symptoms of other diseases, such as
274:Isberg, Ralph R.; Davis, Kimberly M. (2014-09-18).
238:
522:Symptoms and signs: Skin and subcutaneous tissue
513:
201:. New York: Oxford University Press. p. 5.
409:Atlas of sexually transmitted diseases and AIDS
411:(4th ed.). Edinburgh: Saunders/Elsevier.
273:
150:"Plague: History and contemporary analysis"
383:
291:
165:
53:and is an example of reactive infectious
322:
25:
474:Expert Review of Anti-infective Therapy
514:
471:
349:
236:
467:
465:
463:
232:
230:
228:
226:
196:
13:
14:
533:
460:
267:
223:
199:Plague: a very short introduction
60:
356:Sexually Transmitted Infections
16:Inflammation of the lymph nodes
433:
400:
343:
316:
190:
141:
1:
337:10.1016/S0140-6736(01)42126-X
134:
98:
30:Buboes on the leg, caused by
486:10.1586/14787210.2014.892414
293:10.1016/j.immuni.2014.09.003
276:"Plague's Partners in Crime"
7:
350:Lewis, D. A. (2003-02-01).
10:
538:
167:10.1016/j.jinf.2012.09.010
18:
245:. New York: Free Press.
120:lymphogranuloma venereum
75:bacteria spreading from
65:Buboes are a symptom of
49:or inflammation of the
34:
237:Orent, Wendy (2004).
129:incision and drainage
29:
21:Bubo (disambiguation)
197:Paul, Slack (2012).
154:Journal of Infection
19:For other uses, see
368:10.1136/sti.79.1.68
331:(4601): 1262–1264.
35:
529:
506:
505:
469:
458:
457:
455:
454:
445:
437:
431:
430:
404:
398:
397:
387:
347:
341:
340:
320:
314:
313:
295:
271:
265:
264:
244:
234:
221:
220:
194:
188:
187:
169:
145:
107:, doctors often
93:pneumonic plague
537:
536:
532:
531:
530:
528:
527:
526:
512:
511:
510:
509:
470:
461:
452:
450:
443:
439:
438:
434:
419:
405:
401:
348:
344:
321:
317:
272:
268:
253:
235:
224:
209:
195:
191:
146:
142:
137:
101:
72:Yersinia pestis
63:
55:lymphadenopathy
41:(Greek βουβών,
24:
17:
12:
11:
5:
535:
525:
524:
508:
507:
480:(6): 687–696.
459:
432:
417:
399:
342:
315:
286:(3): 347–349.
266:
252:978-0743236850
251:
222:
207:
189:
139:
138:
136:
133:
100:
97:
67:bubonic plague
62:
61:Classification
59:
45:, 'groin') is
32:bubonic plague
15:
9:
6:
4:
3:
2:
534:
523:
520:
519:
517:
503:
499:
495:
491:
487:
483:
479:
475:
468:
466:
464:
449:
442:
436:
428:
424:
420:
418:9780702047640
414:
410:
403:
395:
391:
386:
381:
377:
373:
369:
365:
361:
357:
353:
346:
338:
334:
330:
326:
319:
311:
307:
303:
299:
294:
289:
285:
281:
277:
270:
262:
258:
254:
248:
243:
242:
233:
231:
229:
227:
218:
214:
210:
208:9780199589548
204:
200:
193:
185:
181:
177:
173:
168:
163:
159:
155:
151:
144:
140:
132:
130:
125:
121:
117:
112:
110:
106:
96:
94:
90:
86:
82:
78:
74:
73:
68:
58:
56:
52:
48:
44:
40:
33:
28:
22:
477:
473:
451:. Retrieved
448:apps.who.int
447:
435:
408:
402:
362:(1): 68–71.
359:
355:
345:
328:
324:
318:
283:
279:
269:
240:
198:
192:
160:(1): 18–26.
157:
153:
143:
113:
102:
70:
64:
42:
38:
36:
105:antibiotics
51:lymph nodes
453:2019-02-13
325:The Lancet
135:References
124:aspiration
99:Management
494:1478-7210
427:761212082
376:1368-4973
302:1074-7613
217:749871251
176:0163-4453
127:required—
116:chancroid
89:Infection
516:Category
502:24597521
394:12576620
310:25238090
280:Immunity
261:54034997
184:23041039
81:necrotic
47:adenitis
385:1744597
109:drained
500:
492:
425:
415:
392:
382:
374:
308:
300:
259:
249:
215:
205:
182:
174:
43:boubṓn
444:(PDF)
498:PMID
490:ISSN
423:OCLC
413:ISBN
390:PMID
372:ISSN
306:PMID
298:ISSN
257:OCLC
247:ISBN
213:OCLC
203:ISBN
180:PMID
172:ISSN
118:and
77:flea
39:bubo
482:doi
380:PMC
364:doi
333:doi
329:178
288:doi
162:doi
85:pus
518::
496:.
488:.
478:12
476:.
462:^
446:.
421:.
388:.
378:.
370:.
360:79
358:.
354:.
327:.
304:.
296:.
284:41
282:.
278:.
255:.
225:^
211:.
178:.
170:.
158:66
156:.
152:.
95:.
87:.
57:.
37:A
504:.
484::
456:.
429:.
396:.
366::
339:.
335::
312:.
290::
263:.
219:.
186:.
164::
23:.
Text is available under the Creative Commons Attribution-ShareAlike License. Additional terms may apply.