205:
20:
268:
of tectonic deformation that spans 700 km from the
Aleutian Arc into the interior of Alaska to form. These conditions have allowed for a multitude of major earthquakes to be measured throughout Alaska's history. Most major earthquakes measured in the region tend to be caused by ruptures in the gentle
218:
The
Pacific Plate is continuously converging and moving against the North American Plate at a rate of 48 mm/year eastward and 78 mm/year westward. The oblique direction of convergence in the western and central portions of the area is causing westward transportation of the arc. This movement of the
259:
events to be differentiated. The majority of events have been noted as having a thrusting mechanism, which denotes them as earthquakes occurring from the interface of a plate. Strike-slip and normal faulting does occur in shallow events, where the depth of the event is less than 30 km deep. Events
263:
The constant activity near the
Aleutian Arc has resulted in an area prone to high magnitude earthquakes. One Major earthquake (Mw ≥ 8) occurs every 13 years on average, and strong magnitude earthquakes (Mw 6–7) occur an average of six times per year. The rapid conversion and the gentle subduction
208:
Image showing the
Aleutian Island Arc, along with the trench. The trench is denoted by the dark blue line to the south running parallel with the island arc. The area between the trench and the ridge delineates the blocks of crust that cause much of the seismic activity in the region.
251:) as well as within the subducting and overriding plates themselves accounts for the majority of earthquakes that occur. Some smaller magnitude earthquakes are also caused by the volcanic activity of the Aleutian Arc. The regionality of the earthquakes makes it possible for
183:
in the west. Along the oceanic part of the subduction zone, convergence varies from 6.3 cm (2.5 in) per year to the north-northwest in the east to 7.4 cm (2.9 in) per year towards the northwest in the west. The eastern
Aleutians see an
167:, the north side of which being the area where the most volcanic activity occurs. The Aleutian Ridge is largest near tip of the Alaskan Peninsula (160-225 km wide, 25-35 km thick) and decreases in width (80 km wide near the
260:
with a normal fault mechanism tend to occur where the
Pacific Plate bends as it forms the Aleutian Trench, whereas strike-slip mechanisms are concentrated inland along the axis of the islands themselves.
147:
223:
between the trench and the island arc. The boundaries of the 5 major blocks that have been identified form areas with cohesive movement that are often disrupted by
180:
176:
219:
Pacific Plate relative to the North
American Plate in the central and west Aleutian Arc also causes portions of the forearc to break off and form rotating
618:
723:
235:
are present at the boundaries between the blocks due to the clockwise rotation of each block cutting into the surface of the other crustal blocks.
749:"New kinematic models for Pacific-North America motion from 3 Ma to present, 1: Evidence for steady motion and biases in the NUVEL-1A model"
845:
552:
247:, making the Aleutian islands the most seismically active area in the United States of America. Faulting within the subduction zone (
884:
159:
The
Aleutian Trench, formed by the subduction of the Pacific Plate under the North American Plate, sits south of the island arc. A
196:
direction of convergence relative to the trench. Past Attu Island, the direction of convergence becomes parallel with the trench.
127:
at the southwestern end of the Alaska
Peninsula (~165°W) marks the eastward transition from an intra-oceanic in the west to a
131:
in the east. Volcanic activity on the
Aleutian Ridge extends from the Southwest corner of Alaska to around 175°E, west of
837:
562:
899:
622:
140:
527:
332:
796:
678:
163:
reaching depths of 7km occupies the space between the trench and the island arc and leads up to the
889:
797:"Intra-arc and back-arc volcano-tectonics: Magma pathways at Holocene Alaska-Aleutian volcanoes"
894:
402:
362:
482:
377:
256:
252:
748:
123:
in the east. The arc was formed around 55 million years ago during the early Eocene period.
542:
112:
8:
397:
382:
342:
312:
248:
189:
168:
116:
44:
679:"Review of crustal seismicity in the Aleutian Arc and implications for arc deformation"
193:
48:
816:
694:
307:
812:
724:"Revised age of Aleutian Island Arc formation implies high rate of magma production"
19:
808:
763:
686:
597:
582:
567:
547:
517:
512:
477:
437:
337:
327:
232:
83:
75:
572:
467:
457:
447:
422:
392:
372:
347:
317:
302:
265:
228:
224:
128:
63:
690:
204:
592:
587:
577:
492:
387:
322:
164:
120:
79:
243:
Thousands of earthquakes per year are seen in this region due to the constant
150:
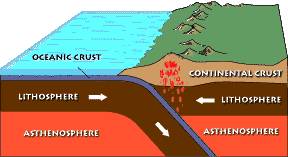
Diagram showing the process of subduction and the formation of volcanic arcs.
878:
860:
847:
820:
698:
537:
522:
507:
427:
417:
412:
352:
282:
185:
108:
172:
532:
502:
472:
442:
432:
407:
367:
297:
287:
87:
32:
677:
Ruppert, Natalia A.; Kozyreva, Natalia P.; Hansen, Roger A. (2012-02-05).
146:
768:
557:
497:
462:
357:
220:
132:
124:
619:"A Policy for Rapid Mobilization of USGS OBS (RMOBS) - Alaska Volcanoes"
264:
angle of the Pacific Plate under the North American Plate also caused a
171:
Islands) as it extends west towards the Kamchatka Peninsula. Due to the
292:
91:
59:
36:
487:
244:
71:
66:. Although taking its name from the Aleutian Islands, this term is a
269:
subduction interface between the subducting and overriding plates.
160:
67:
55:
175:
of the trench, the relative velocity vector changes from almost
62:
of the Pacific Plate beneath the North American Plate along the
136:
40:
621:. Woods Hole Coastal and Marine Science Center. Archived from
452:
192:
relative to the trench, while the more central area sees an
139:
is laterally extended and intact, which is unusual for an
23:
Map showing the volcanoes and islands of the Aleutian Arc.
135:(~173°E). The Aleutian Arc is distinct in that its arc
676:
115:. It extends 3,000 km (1,900 mi) from the
35:of islands extending from the Southwest tip of the
97:
876:
747:DeMets, Charles; Dixon, Timothy (July 1, 1999).
54:It consists of a number of active and dormant
794:
107:The Aleutian Arc reflects subduction of the
94:(magnitude 6-6.7) as well as its volcanism.
86:. The arc makes up a sizable portion of the
746:
74:one. The Aleutian Arc extends through the
795:Tibaldi, A.; Bonali, F. L. (2017-04-01).
767:
740:
611:
203:
145:
18:
877:
672:
670:
668:
666:
664:
662:
660:
16:Volcanic arc in Alaska, United States
790:
788:
786:
718:
716:
714:
712:
710:
708:
658:
656:
654:
652:
650:
648:
646:
644:
642:
640:
272:
213:
154:
58:that have formed as a result of the
277:Volcanoes within this arc include:
199:
90:, and is known for generating many
13:
14:
911:
831:
783:
705:
637:
179:in the Gulf of Alaska to almost
885:Geology of the Aleutian Islands
813:10.1016/j.earscirev.2017.02.004
98:Formation and geologic features
238:
1:
604:
756:Geophysical Research Letters
102:
92:strong magnitude earthquakes
7:
838:Geoprisms.org: Aleutian Arc
691:10.1016/j.tecto.2011.11.024
10:
916:
728:pubs.geoscienceworld.org
70:grouping rather than a
210:
151:
24:
801:Earth-Science Reviews
207:
149:
22:
769:10.1029/1999gl900405
685:. 522–523: 150–157.
543:Semisopochnoi Island
113:North American Plate
88:Pacific Ring of Fire
900:Volcanism of Alaska
857: /
383:Fourpeaked Mountain
249:Aleutian Megathrust
119:in the west to the
117:Kamchatka Peninsula
45:Kamchatka Peninsula
211:
152:
49:Russian Federation
25:
762:(13): 1921–1924.
528:Saint Paul Island
333:Cleveland Volcano
308:Augustine Volcano
273:Volcanic activity
245:tectonic activity
233:Submarine canyons
214:Tectonic activity
155:Geologic features
141:intra-oceanic arc
907:
872:
871:
869:
868:
867:
862:
861:52.28°N 174.15°W
858:
855:
854:
853:
850:
825:
824:
792:
781:
780:
778:
776:
771:
753:
744:
738:
737:
735:
734:
720:
703:
702:
674:
635:
634:
632:
630:
615:
598:Yantarni Volcano
583:Mount Veniaminof
548:Mount Shishaldin
518:Mount Recheshnoi
513:Pogromni Volcano
478:Makushin Volcano
438:Kasatochi Island
338:Cold Bay Volcano
328:Mount Chiginagak
200:Seismic activity
173:arcuate geometry
84:Aleutian Islands
76:Alaska Peninsula
915:
914:
910:
909:
908:
906:
905:
904:
875:
874:
865:
863:
859:
856:
851:
848:
846:
844:
843:
834:
829:
828:
793:
784:
774:
772:
751:
745:
741:
732:
730:
722:
721:
706:
675:
638:
628:
626:
617:
616:
612:
607:
602:
573:Trident Volcano
468:Mount Kupreanof
458:Korovin Volcano
448:Mount Kialagvik
423:Isanotski Peaks
393:Gareloi Volcano
373:Eickelberg Peak
348:Davidof Volcano
318:Bogoslof Island
303:Mount Aniakchak
275:
266:back-arc region
241:
216:
202:
181:trench-parallel
157:
129:continental arc
105:
100:
64:Aleutian Trench
17:
12:
11:
5:
913:
903:
902:
897:
892:
890:Aleutian Range
887:
866:52.28; -174.15
841:
840:
833:
832:External links
830:
827:
826:
782:
739:
704:
683:Tectonophysics
636:
609:
608:
606:
603:
601:
600:
595:
593:Mount Westdahl
590:
588:Mount Vsevidof
585:
580:
578:Ugashik-Peulik
575:
570:
565:
560:
555:
553:Snowy Mountain
550:
545:
540:
535:
530:
525:
520:
515:
510:
505:
500:
495:
493:Nunivak Island
490:
485:
480:
475:
470:
465:
460:
455:
450:
445:
440:
435:
430:
425:
420:
415:
410:
405:
400:
395:
390:
385:
380:
375:
370:
365:
360:
355:
350:
345:
340:
335:
330:
325:
323:Mount Carlisle
320:
315:
310:
305:
300:
295:
290:
285:
279:
274:
271:
240:
237:
221:crustal blocks
215:
212:
201:
198:
165:Aleutian Ridge
156:
153:
121:Gulf of Alaska
104:
101:
99:
96:
80:Aleutian Range
78:following the
15:
9:
6:
4:
3:
2:
912:
901:
898:
896:
895:Volcanic arcs
893:
891:
888:
886:
883:
882:
880:
873:
870:
839:
836:
835:
822:
818:
814:
810:
806:
802:
798:
791:
789:
787:
770:
765:
761:
757:
750:
743:
729:
725:
719:
717:
715:
713:
711:
709:
700:
696:
692:
688:
684:
680:
673:
671:
669:
667:
665:
663:
661:
659:
657:
655:
653:
651:
649:
647:
645:
643:
641:
625:on 2018-09-23
624:
620:
614:
610:
599:
596:
594:
591:
589:
586:
584:
581:
579:
576:
574:
571:
569:
566:
564:
563:Mount Steller
561:
559:
556:
554:
551:
549:
546:
544:
541:
539:
538:Segula Island
536:
534:
531:
529:
526:
524:
523:Mount Redoubt
521:
519:
516:
514:
511:
509:
508:Pavlof Sister
506:
504:
501:
499:
496:
494:
491:
489:
486:
484:
481:
479:
476:
474:
471:
469:
466:
464:
461:
459:
456:
454:
451:
449:
446:
444:
441:
439:
436:
434:
431:
429:
428:Mount Kaguyak
426:
424:
421:
419:
418:Mount Iliamna
416:
414:
413:Hayes Volcano
411:
409:
406:
404:
403:Mount Gilbert
401:
399:
396:
394:
391:
389:
386:
384:
381:
379:
376:
374:
371:
369:
366:
364:
363:Mount Douglas
361:
359:
356:
354:
353:Mount Denison
351:
349:
346:
344:
341:
339:
336:
334:
331:
329:
326:
324:
321:
319:
316:
314:
311:
309:
306:
304:
301:
299:
296:
294:
291:
289:
286:
284:
283:Mount Adagdak
281:
280:
278:
270:
267:
261:
258:
254:
250:
246:
236:
234:
230:
229:normal faults
226:
222:
206:
197:
195:
191:
188:direction of
187:
182:
178:
177:trench-normal
174:
170:
166:
162:
161:forearc basin
148:
144:
142:
138:
134:
130:
126:
122:
118:
114:
110:
109:Pacific Plate
95:
93:
89:
85:
81:
77:
73:
69:
65:
61:
57:
52:
50:
46:
42:
38:
34:
30:
21:
842:
804:
800:
773:. Retrieved
759:
755:
742:
731:. Retrieved
727:
682:
627:. Retrieved
623:the original
613:
533:Mount Seguam
503:Mount Pavlof
483:Mount Martin
473:Mount Mageik
443:Mount Katmai
433:Mount Kanaga
408:Mount Griggs
398:Great Sitkin
388:Mount Frosty
378:Mount Emmons
368:Mount Dutton
298:Mount Amukta
288:Mount Akutan
276:
262:
242:
217:
158:
111:beneath the
106:
82:through the
53:
33:volcanic arc
29:Aleutian Arc
28:
26:
864: /
775:18 November
629:18 November
558:Mount Spurr
498:Mount Okmok
463:Mount Kukak
358:Devils Desk
257:intra-plate
253:inter-plate
239:Earthquakes
225:strike-slip
190:convergence
169:Komandorski
133:Attu Island
125:Unimak Pass
31:is a large
879:Categories
733:2023-11-02
605:References
343:Mount Dana
313:Black Peak
293:Mount Amak
186:orthogonal
72:geographic
60:subduction
37:U.S. state
821:0012-8252
699:0040-1951
488:Novarupta
103:Formation
56:volcanoes
852:174°09′W
807:: 1–26.
68:geologic
849:52°17′N
194:oblique
47:of the
43:to the
819:
697:
568:Tanaga
137:massif
41:Alaska
752:(PDF)
453:Kiska
817:ISSN
777:2018
695:ISSN
631:2018
255:and
227:and
51:.
27:The
809:doi
805:167
764:doi
687:doi
143:.
39:of
881::
815:.
803:.
799:.
785:^
760:26
758:.
754:.
726:.
707:^
693:.
681:.
639:^
231:.
823:.
811::
779:.
766::
736:.
701:.
689::
633:.
Text is available under the Creative Commons Attribution-ShareAlike License. Additional terms may apply.