1361:, to return the water surface to its equilibrium position. Wind waves in the ocean are also known as ocean surface waves. The wind waves interact with both the air and water flows above and below the waves. Therefore, the characteristics of wind waves are determined by the coupling processes between the boundary layers of both the atmosphere and ocean. Wind waves also play an important role themselves in the interaction processes between the ocean and the atmosphere. Wind waves in the ocean can travel thousands of kilometers. A proper description of the physical mechanisms that cause the growth of wind waves and is in accordance with observations has yet to be completed. A necessary condition for wind waves to grow is a minimum wind speed of 0.05 m/s.
172:
163:
1232:. However, the contribution of the wind stress to the forcing of the oceanic general circulation is largest. Ocean waters respond to the wind stress because of their low resistance to shear and the relative consistence with which winds blow over the ocean. The combination of easterly winds near the equator and westerly winds at midlatitudes drives significant circulations in the North and South Atlantic Oceans, the North and South Pacific Oceans and the Indian Ocean with westward currents near the equator and eastward currents at midlatitudes. This results in characteristic
155:
147:
647:. Since the exchange of energy, momentum and moisture is often parametrized using bulk atmospheric formulae, the equation above is the semi-empirical bulk formula for the surface wind stress. The height at which the wind speed is referred to in wind drag formulas is usually 10 meters above the water surface. The formula for the wind stress explains how the stress increases for a denser atmosphere and higher wind speeds.
1212:(southward) currents on the eastern (western) coasts of continents in the Northern Hemisphere and on the western (eastern) coast in the Southern Hemisphere since these generate coastal upwelling which causes biological activity. Examples of such patterns can be observed in figure 2.2 on the East coast of North America and on the West coast of South America.
1207:
stress occur in the
Southern Ocean for the zonal direction with values of about 0.3Pa. Figures 2.3 and 2.4 show that monthly variations in the wind stress patterns are only minor and the general patterns stay the same during the whole year. It can be seen that there are strong easterly winds (i.e. blowing toward the West), called easterlies or
356:
793:
1676:
1886:
is measured and then via a parametrization the wind stress observations are obtained. Still, measurements of the wind stress are important as the value of the drag coefficient is not known for unsteady and non-ideal conditions. Measurements of the wind stress for such conditions can resolve the issue
1206:
The global annual mean wind stress forces the global ocean circulation. Typical values for the wind stress are about 0.1Pa and, in general, the zonal wind stress is stronger than the meridional wind stress as can be seen in figures 2.1 and 2.2. It can also be seen that the largest values of the wind
1079:
Due to the strong temporal variability of the wind, the wind forcing on the ocean surface is also highly variable. This is one of the causes of the internal variability of ocean flows as these changes in the wind forcing cause changes in the wave field and the thereby generated currents. Variability
1338:
Equatorial upwelling occurs due to the trade winds blowing towards the west in both the
Northern Hemisphere and the Southern Hemisphere. However, the Ekman transport that is associated with these trade winds is directed 90° to the right of the winds in the Northern Hemisphere and 90° to the left of
175:
Figure 1.4 A sketch of the boundary layer of an ocean in the
Northern Hemisphere where a zonal wind stress generates a surface Ekman current and other deeper positioned Ekman currents that are turned rightward. At the bottom of the ocean boundary layer the Ekman spiral is depicted. Also, the net
211:
The wind blowing parallel to a water surface deforms that surface as a result of shear action caused by the fast wind blowing over the stagnant water. The wind blowing over the surface applies a shear force on the surface. The wind stress is the component of this force that acts parallel to the
1383:
depends on the past of the wind, the drag coefficient is expressed differently for different time and spatial scales. A general expression for the drag coefficient does not yet exist and the value is unknown for unsteady and non-ideal conditions. In general, the drag coefficient increases with
1211:
near the equator, very strong westerly winds at midlatitudes (between ±30° and ±60°), called westerlies, and weaker easterly winds at polar latitudes. Also, on a large annual scale, the wind-stress field is fairly zonally homogeneous. Important meridional wind stress patterns are northward
1063:
to the wind stress and, again, directed to the right of the wind stress direction in the
Northern Hemisphere and to the left of the wind stress direction in the Southern Hemisphere. Alongshore winds therefore generate transport towards or away from the coast. For small values of
1314:
Coastal upwelling occurs when the wind stress is directed with the coast on its left (right) in the
Northern (Southern) Hemisphere. If so, Ekman transport is directed away from the coast forcing waters from below to move upward. Well known coastal upwelling areas are the
1042:
166:
Figure 1.3 A sketch of an ocean in the
Northern Hemisphere where wind waves and a surface Ekman current have been generated due to shear action of the zonal wind stress. In the Northern Hemisphere, the surface Ekman current is directed 45° to the right of the wind
907:
they are directed with the same angle to the left of the wind stress direction. Flow directions of deeper positioned currents are deflected even more to the right in the
Northern Hemisphere and to the left in the Southern Hemisphere. This phenomenon is called the
1872:
218:
660:
440:(this is the layer of a fluid where the influence of friction is felt). On the other hand, the exerted force on the water surface increases when the vertical eddy viscosity increases. The wind stress can also be described as a downward transfer of
59:. When wind is blowing over a water surface, the wind applies a wind force on the water surface. The wind stress is the component of this wind force that is parallel to the surface per unit area. Also, the wind stress can be described as the
1546:
In global climate models, often a drag coefficient appropriate for a spatial scale of 1° by 1° and a monthly time scale is used. In such a timescale, the wind can strongly fluctuate. The monthly mean shear stress can be expressed as:
1302:
Wind-driven upwelling brings nutrients from deep waters to the surface which leads to biological productivity. Therefore, wind stress impacts biological activity around the globe. Two important forms of wind-driven upwelling are
1553:
1173:
1541:
871:. This balance of forces is known as the Ekman balance. Some important assumptions that underlie the Ekman balance are that there are no boundaries, an infinitely deep water layer, constant vertical eddy viscosity,
1339:
the winds in the
Southern Hemisphere. As a result, to the North of the equator water is transported away from the equator and to the South of the equator water is transported away from the equator. This horizontal
1165:
571:
1251:
which describes the relation between the wind stress and the vertically integrated meridional transport of water. Other significant contributions to the description of large-scale ocean circulation were made by
1887:
of the unknown drag coefficient. Four methods of measuring the drag coefficient are known as the
Reynolds stress method, the dissipation method, the profile method and a method of using radar remote sensing.
192:) around the globe. The different processes described here are depicted in the sketches shown in figures 1.1 till 1.4. Interactions between wind, wind waves and currents are an essential part of the world
930:
665:
223:
2142:
Hersbach, H.; Bell, B.; Berrisford, P.; Biavati, G.; Horányi, A.; Muñoz
Sabater, J.; Nicolas, J.; Peubey, C.; Radu, R.; Rozum, I.; Schepers, D.; Simmons, A.; Soci, C.; Dee, D.; Thépaut, J-N. (2019).
925:
1131:
1440:
1097:
196:. Eventually, the wind waves also influence the wind field leading to a complex interaction between wind and water whereof the research for a correct theoretical description is ongoing. The
351:{\displaystyle {\begin{aligned}F_{x}&={\frac {1}{\rho }}{\frac {\partial \tau _{x}}{\partial z}},\\F_{y}&={\frac {1}{\rho }}{\frac {\partial \tau _{y}}{\partial z}}.\end{aligned}}}
788:{\displaystyle {\begin{aligned}-fv&={\frac {1}{\rho }}{\frac {\partial \tau _{x}}{\partial z}},\\fu&={\frac {1}{\rho }}{\frac {\partial \tau _{y}}{\partial z}},\end{aligned}}}
1764:
1076:
due to the change of sign of the Coriolis parameter in the Northern and Southern Hemisphere and the stable easterly winds that are blowing to the North and South of the equator.
601:
1752:
2278:
Stommel, Henry; Arons, Arnold B. (1959). "On the abyssal circulation of the world ocean—II. An idealized model of the circulation pattern and amplitude in oceanic basins".
645:
1726:
1699:
1470:
500:
469:
407:
383:
1200:
1158:
1124:
1260:
and theories of the abyssal circulation. Long before these theories were formulated, mariners have been aware of the major surface ocean currents. As an example,
842:
901:
865:
1882:
It is not possible to directly measure the wind stress on the ocean surface. To obtain measurements of the wind stress, another easily measurable quantity like
1357:
Wind waves are waves at the water surface that are generated due to the shear action of wind stress on the water surface and the aim of gravity, that acts as a
1168:
Figure 2.3 Animation of the climatology over 1990–2020 of monthly mean zonal wind stress . Positive values imply that wind stress is directed toward the East
1671:{\displaystyle \langle \tau \rangle =\rho \langle C_{D}\rangle \langle U\rangle ^{2}\left(1+{\frac {\langle U'^{2}\rangle }{\langle U\rangle ^{2}}}\right),}
180:
Wind blowing over an ocean at rest first generates small-scale wind waves which extract energy and momentum from the wave field. As a result, the
1478:
2027:
Smith, Stuart D. (1988). "Coefficients for sea surface wind stress, heat flux, and wind profiles as a function of wind speed and temperature".
2251:
Stommel, Henry; Arons, Arnold B. (1959). "On the abyssal circulation of the world ocean—I. Stationary planetary flow patterns on a sphere".
508:
184:(the rate of momentum transfer per unit area and unit time) generates a current. These surface currents are able to transport energy (e.g.
1236:
flows in the Atlantic and Pacific consisting of a subpolar and subtropical gyre. The strong westerlies in the Southern ocean drive the
436:. The equation describes how the force exerted on the water surface decreases for a denser atmosphere or, to be more precise, a denser
2103:
Ekman, Vagn Walfrid (1905). "On the influence of the earth's rotation on ocean-currents". Almqvist \& Wiksells boktryckeri, A.-B.
879:
and a constant Coriolis parameter. The oceanic currents that are generated by this balance are referred to as Ekman currents. In the
1037:{\displaystyle {\begin{aligned}U_{E}&={\frac {\tau _{y}}{f\rho D}},\\V_{E}&=-{\frac {\tau _{x}}{f\rho D}},\end{aligned}}}
2381:
158:
Figure 1.2 A sketch of an ocean that is still at rest but now the wind induced zonal surface stress vector is also depicted.
1080:
of ocean flows also occurs because the changes of the wind forcing are disturbances of the mean ocean flow, which leads to
1240:
which is the dominant current in the Southern Hemisphere whereof no comparable current exists in the Northern Hemisphere.
1390:
1277:
2427:
Komen, Gerbrand J.; Cavaleri, Luigi; Donelan, Mark; Hasselman, Klaus; Hasselman, S; Janssen, P. A. E. M. (1996).
1244:
2159:"Wind-driven currents in a baroclinic ocean; with application to the equatorial currents of the eastern Pacific"
2088:
2063:
1085:
2453:
614:
which is a repository function for all remaining dependencies. An often used value for the drag coefficient is
2313:
Richardson, Philip L (1980). "Benjamin Franklin and Timothy Folger's first printed chart of the Gulf Stream".
1867:{\displaystyle C_{D}=1.3\times 10^{-3}\left(1+{\frac {\langle U'^{2}\rangle }{\langle U\rangle ^{2}}}\right).}
75:
and is therefore an important driver of the large-scale ocean circulation. The wind stress is affected by the
1384:
increasing wind speed and is greater for shallower waters. The geostrophic drag coefficient is expressed as:
1237:
123:
1084:. A well known phenomenon that is caused by changes in surface wind stress over the tropical Pacific is the
1379:
is a dimensionless quantity which quantifies the resistance of the water surface. Due to the fact that the
67:
applied by the wind on the water surface. The wind stress causes a deformation of the water body whereby
1172:
579:
171:
1731:
80:
162:
1285:
815:
212:
surface per unit area. This wind force exerted on the water surface due to shear stress is given by:
2121:
1220:
Wind stress in one of the drivers of the large-scale ocean circulation with other drivers being the
2144:
ERA5 monthly averaged data on single levels from 1979 to present. (Accessed on < 22-06-2021 >
1164:
437:
1288:
can be used which is an object that moves with the currents whereof the velocity can be measured.
1176:
Figure 2.4 Animation of the climatology over 1990–2020 of monthly mean meridional wind stress [N/m
617:
2448:
1895:
The wind can also exert a stress force on land surface which can lead to erosion of the ground.
208:, is stirred by the wind stress. This upper layer of the ocean has a depth on the order of 10m.
2373:
2366:
2108:
430:
119:
20:
1335:. All of these currents support major fisheries due to the increased biological activities.
1269:
2322:
2287:
2225:
2170:
2075:
2036:
1704:
1684:
1448:
478:
454:
414:
392:
368:
84:
1268:
in 1770 and in European discovery of the gulf stream dates back to the 1512 expedition of
1179:
1137:
1103:
8:
1273:
904:
880:
876:
821:
176:
Ekman transport which is directed 90° to the right of the wind stress vector is depicted.
150:
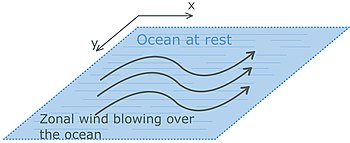
Figure 1.1 A sketch of an ocean at rest with a zonal wind blowing over the ocean surface.
130:. When the deforming force acts parallel to the object's surface, this force is called a
2326:
2291:
2229:
2174:
2079:
2040:
886:
847:
2346:
2193:
2158:
1324:
1224:
pull exerted by the Moon and Sun, differences in atmospheric pressure at sea level and
803:
441:
107:
2377:
2338:
2299:
2264:
2216:
Stommel, Henry (1948). "The westward intensification of wind-driven ocean currents".
2198:
1261:
154:
111:
2350:
2330:
2295:
2260:
2233:
2188:
2178:
2083:
2044:
1380:
1376:
1370:
1328:
1320:
1248:
872:
611:
1130:
146:
2334:
1358:
1056:
916:
1134:
Figure 2.2 Climatology over 1990–2020 of annual mean meridional wind stress [N/m
83:. It is one of the components of the air–sea interaction, with others being the
2163:
Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America
1332:
1316:
868:
651:
386:
197:
193:
24:
122:
of an object. Therefore, stress is defined as the force per unit area and its
2442:
1253:
1096:
1060:
650:
When the wind stress forces, that were given above, are in balance with the
127:
72:
2237:
2048:
16:
The shear stress exerted by the wind on the surface of large bodies of water
2342:
2202:
2183:
1281:
1276:
there are two methods to measure the ocean currents directly. Firstly, the
1100:
Figure 2.1 Climatology over 1990–2020 of annual mean zonal wind stress [N/m
909:
135:
40:
32:
1996:
Introduction to geophysical fluid dynamics: physical and numerical aspects
1536:{\displaystyle U_{g}={\frac {1}{\rho f}}{\frac {\partial p}{\partial y}}.}
1265:
1257:
1229:
1208:
1081:
1052:
205:
131:
1243:
The equations to describe large-scale ocean dynamics were formulated by
1883:
1340:
1233:
1225:
919:
can be obtained from vertically integrating the Ekman balance, giving:
426:
422:
96:
76:
2321:(4431). American Association for the Advancement of Science: 643–645.
1202:]. Positive values imply that wind stress is directed toward the North
1160:]. Positive values imply that wind stress is directed toward the North
1126:]. Positive values imply that wind stress is directed toward the East.
1068:, water can return from or to deeper water layers, resulting in Ekman
1352:
1308:
1304:
1297:
1069:
566:{\displaystyle \tau _{\text{wind}}=\rho _{\text{air}}C_{D}U_{h}^{2}.}
433:
201:
68:
2146:. Copernicus Climate Change Service (C3S) Climate Data Store (CDS).
1280:
velocity can be measured using a current meter along a rope in the
189:
64:
1221:
1073:
471:) is often parametrized as a function of wind speed at a certain
52:
472:
445:
200:
quantifies the correspondence between wind speed and different
88:
883:, Ekman currents at the surface are directed with an angle of
2426:
2141:
2062:
Trenberth, Kevin E; Large, William G; Olson, Jerry G (1990).
115:
44:
1247:
and came to be known as Sverdrup dynamics. Important is the
2089:
10.1175/1520-0485(1990)020<1742:TMACIG>2.0.CO;2
429:
of the wind stress components are also called the vertical
185:
181:
92:
60:
56:
36:
1343:
of mass has to be compensated and hence upwelling occurs.
1072:. Upwelling due to Ekman transport can also happen at the
48:
1364:
903:° to the right of the wind stress direction and in the
1993:
1767:
1734:
1707:
1687:
1556:
1481:
1451:
1393:
1182:
1140:
1106:
928:
889:
850:
824:
663:
620:
582:
511:
481:
457:
395:
371:
221:
2014:
Ocean Currents: Physical Drivers in a Changing World
1994:
Cushman-Roisin, Benoit; Beckers, Jean-Marie (2011).
2064:"The mean annual cycle in global ocean wind stress"
2061:
2365:
1866:
1746:
1720:
1693:
1670:
1535:
1464:
1434:
1194:
1152:
1118:
1036:
895:
859:
836:
787:
639:
595:
565:
494:
463:
401:
377:
350:
2363:
1963:
1435:{\displaystyle C_{g}={\frac {\tau }{U_{g}^{2}}},}
87:on the water surface, as well as the exchange of
2440:
2011:
1256:who formulated the first correct theory for the
1215:
2007:
2005:
409:represents the wind shear stress. Furthermore,
1890:
1091:
204:. Only the top layer of the ocean, called the
1969:
1954:
2368:Pathfinders: A Global History of Exploration
2277:
2250:
2218:Eos, Transactions American Geophysical Union
2002:
1844:
1837:
1832:
1814:
1741:
1735:
1648:
1641:
1636:
1618:
1595:
1588:
1585:
1572:
1563:
1557:
71:are generated. Also, the wind stress drives
2137:
2135:
2133:
2131:
1974:. Vol. 15. Addison-Wesley Reading, MA.
1472:is the geostrophic wind which is given by:
2390:
2312:
1922:
1920:
1918:
1916:
1914:
1912:
1910:
1908:
1758:is the fluctuation from the monthly mean.
867:are respectively the zonal and meridional
2192:
2182:
2087:
2012:Marsh, Robert; van Sebille, Erik (2021).
1970:Young, Hugh D; Freedman, Roger A (1996).
2411:
2156:
2128:
2055:
1926:
1291:
1171:
1163:
1129:
1095:
170:
161:
153:
145:
2416:. Utrecht University - The Netherlands.
2215:
1950:
1948:
1946:
1944:
1942:
1940:
1938:
1905:
1228:resulting from atmospheric cooling and
2441:
2372:. W. W. Norton & Company. p.
1931:. Springer Science and Business Media.
603:is the density of the surface air and
79:, the shape of the wind waves and the
2429:Dynamics and modelling of ocean waves
2396:
2102:
2026:
1989:
1987:
1985:
1983:
1981:
134:and the stress it causes is called a
2224:(2). Wiley Online Library: 202–206.
1935:
1365:Expressions for the drag coefficient
43:of large bodies of water – such as
13:
2364:Fernandez-Armesto, Felipe (2006).
1978:
1521:
1513:
769:
754:
712:
697:
596:{\displaystyle \rho _{\text{air}}}
451:The magnitude of the wind stress (
332:
317:
271:
256:
114:that describes the magnitude of a
14:
2465:
1747:{\displaystyle \langle U\rangle }
2157:Sverdrup, Harald Ulrich (1947).
2068:Journal of Physical Oceanography
1955:Jones, Ian SF; Yoshiaki (2001).
2420:
2405:
2357:
2306:
2271:
2244:
2209:
2150:
1877:
1264:already published a map of the
2096:
2020:
1:
1959:. Cambridge University Press.
1898:
1754:is the monthly mean wind and
1346:
1238:Antarctic Circumpolar Current
1216:Large-scale ocean circulation
816:zonal and meridional currents
102:
2335:10.1126/science.207.4431.643
2300:10.1016/0146-6313(59)90075-9
2265:10.1016/0146-6313(59)90065-6
1086:El Niño-Southern Oscillation
640:{\displaystyle C_{D}=0.0015}
365:represents the shear force,
7:
2414:Ocean waves - lecture notes
1891:Wind stress on land surface
1092:Global wind stress patterns
448:from the air to the water.
141:
10:
2470:
2399:Wind generated ocean waves
1957:Wind stress over the ocean
1368:
1350:
1295:
654:, this can be written as:
438:atmospheric boundary layer
188:) and mass (e.g. water or
95:between the water and the
81:atmospheric stratification
1927:Dijkstra, Henk A (2008).
1728:is the drag coefficient,
2016:. Vol. 1. Elsevier.
1274:hydrographic measurement
610:is a dimensionless wind
425:direction. The vertical
2412:de Swart, H.E. (2019).
2238:10.1029/TR029i002p00202
2049:10.1029/JC093iC12p15467
2184:10.1073/pnas.33.11.318
2116:Cite journal requires
1929:Dynamical oceanography
1868:
1748:
1722:
1695:
1672:
1537:
1466:
1436:
1203:
1196:
1169:
1161:
1154:
1127:
1120:
1038:
897:
861:
838:
789:
641:
597:
567:
496:
465:
403:
379:
352:
177:
168:
159:
151:
2454:Physical oceanography
2397:Young, Ian R (1999).
2286:. Elsevier: 217–233.
2259:. Elsevier: 140–154.
1869:
1749:
1723:
1721:{\displaystyle C_{D}}
1696:
1694:{\displaystyle \rho }
1673:
1538:
1467:
1465:{\displaystyle U_{g}}
1437:
1292:Wind-driven upwelling
1197:
1175:
1167:
1155:
1133:
1121:
1099:
1039:
898:
873:barotropic conditions
862:
839:
814:are respectively the
790:
642:
598:
568:
497:
495:{\displaystyle U_{h}}
466:
464:{\displaystyle \tau }
404:
402:{\displaystyle \tau }
380:
378:{\displaystyle \rho }
353:
174:
165:
157:
149:
21:physical oceanography
1765:
1732:
1705:
1685:
1554:
1479:
1449:
1391:
1309:equatorial upwelling
1195:{\displaystyle ^{2}}
1180:
1153:{\displaystyle ^{2}}
1138:
1119:{\displaystyle ^{2}}
1104:
1051:is the depth of the
926:
887:
848:
822:
661:
618:
580:
509:
479:
455:
393:
369:
219:
85:atmospheric pressure
2327:1980Sci...207..643R
2292:1959DSR.....6..217S
2230:1948TrAGU..29..202S
2175:1947PNAS...33..318S
2080:1990JPO....20.1742T
2041:1988JGR....9315467S
1426:
905:Southern Hemisphere
881:Northern Hemisphere
837:{\displaystyle -fv}
559:
475:above the surface (
421:corresponds to the
413:corresponds to the
1972:University physics
1864:
1744:
1718:
1691:
1668:
1533:
1462:
1432:
1412:
1325:California Current
1284:. And secondly, a
1272:. Apart from such
1270:Juan Ponce de León
1204:
1192:
1170:
1162:
1150:
1128:
1116:
1070:up- or downwelling
1034:
1032:
896:{\displaystyle 45}
893:
860:{\displaystyle fu}
857:
834:
804:Coriolis parameter
785:
783:
637:
593:
563:
545:
492:
461:
399:
375:
348:
346:
178:
169:
160:
152:
118:that is causing a
2383:978-0-393-06259-5
2280:Deep Sea Research
2253:Deep Sea Research
1998:. Academic press.
1854:
1658:
1528:
1508:
1427:
1305:coastal upwelling
1262:Benjamin Franklin
1055:. Depth-averaged
1025:
973:
776:
749:
719:
692:
590:
532:
519:
339:
312:
278:
251:
2461:
2433:
2432:
2424:
2418:
2417:
2409:
2403:
2402:
2394:
2388:
2387:
2371:
2361:
2355:
2354:
2310:
2304:
2303:
2275:
2269:
2268:
2248:
2242:
2241:
2213:
2207:
2206:
2196:
2186:
2154:
2148:
2147:
2139:
2126:
2125:
2119:
2114:
2112:
2104:
2100:
2094:
2093:
2091:
2059:
2053:
2052:
2024:
2018:
2017:
2009:
2000:
1999:
1991:
1976:
1975:
1967:
1961:
1960:
1952:
1933:
1932:
1924:
1873:
1871:
1870:
1865:
1860:
1856:
1855:
1853:
1852:
1851:
1835:
1831:
1830:
1829:
1812:
1799:
1798:
1777:
1776:
1753:
1751:
1750:
1745:
1727:
1725:
1724:
1719:
1717:
1716:
1701:is the density,
1700:
1698:
1697:
1692:
1677:
1675:
1674:
1669:
1664:
1660:
1659:
1657:
1656:
1655:
1639:
1635:
1634:
1633:
1616:
1603:
1602:
1584:
1583:
1542:
1540:
1539:
1534:
1529:
1527:
1519:
1511:
1509:
1507:
1496:
1491:
1490:
1471:
1469:
1468:
1463:
1461:
1460:
1441:
1439:
1438:
1433:
1428:
1425:
1420:
1408:
1403:
1402:
1381:drag coefficient
1377:drag coefficient
1371:Drag coefficient
1329:Humboldt Current
1321:Benguela Current
1249:Sverdrup balance
1201:
1199:
1198:
1193:
1191:
1190:
1159:
1157:
1156:
1151:
1149:
1148:
1125:
1123:
1122:
1117:
1115:
1114:
1043:
1041:
1040:
1035:
1033:
1026:
1024:
1013:
1012:
1003:
991:
990:
974:
972:
961:
960:
951:
942:
941:
902:
900:
899:
894:
877:geostrophic flow
866:
864:
863:
858:
843:
841:
840:
835:
794:
792:
791:
786:
784:
777:
775:
767:
766:
765:
752:
750:
742:
720:
718:
710:
709:
708:
695:
693:
685:
646:
644:
643:
638:
630:
629:
612:drag coefficient
602:
600:
599:
594:
592:
591:
588:
572:
570:
569:
564:
558:
553:
544:
543:
534:
533:
530:
521:
520:
517:
501:
499:
498:
493:
491:
490:
470:
468:
467:
462:
408:
406:
405:
400:
384:
382:
381:
376:
357:
355:
354:
349:
347:
340:
338:
330:
329:
328:
315:
313:
305:
296:
295:
279:
277:
269:
268:
267:
254:
252:
244:
235:
234:
2469:
2468:
2464:
2463:
2462:
2460:
2459:
2458:
2439:
2438:
2437:
2436:
2425:
2421:
2410:
2406:
2395:
2391:
2384:
2362:
2358:
2311:
2307:
2276:
2272:
2249:
2245:
2214:
2210:
2169:(11): 318–326.
2155:
2151:
2140:
2129:
2117:
2115:
2106:
2105:
2101:
2097:
2060:
2056:
2029:J. Geophys. Res
2025:
2021:
2010:
2003:
1992:
1979:
1968:
1964:
1953:
1936:
1925:
1906:
1901:
1893:
1880:
1847:
1843:
1836:
1825:
1821:
1817:
1813:
1811:
1804:
1800:
1791:
1787:
1772:
1768:
1766:
1763:
1762:
1733:
1730:
1729:
1712:
1708:
1706:
1703:
1702:
1686:
1683:
1682:
1651:
1647:
1640:
1629:
1625:
1621:
1617:
1615:
1608:
1604:
1598:
1594:
1579:
1575:
1555:
1552:
1551:
1520:
1512:
1510:
1500:
1495:
1486:
1482:
1480:
1477:
1476:
1456:
1452:
1450:
1447:
1446:
1421:
1416:
1407:
1398:
1394:
1392:
1389:
1388:
1373:
1367:
1359:restoring force
1355:
1349:
1300:
1294:
1245:Harald Sverdrup
1218:
1186:
1183:
1181:
1178:
1177:
1144:
1141:
1139:
1136:
1135:
1110:
1107:
1105:
1102:
1101:
1094:
1057:Ekman transport
1031:
1030:
1014:
1008:
1004:
1002:
992:
986:
982:
979:
978:
962:
956:
952:
950:
943:
937:
933:
929:
927:
924:
923:
917:Ekman transport
888:
885:
884:
869:Coriolis forces
849:
846:
845:
823:
820:
819:
782:
781:
768:
761:
757:
753:
751:
741:
734:
725:
724:
711:
704:
700:
696:
694:
684:
677:
664:
662:
659:
658:
625:
621:
619:
616:
615:
608:
587:
583:
581:
578:
577:
554:
549:
539:
535:
529:
525:
516:
512:
510:
507:
506:
486:
482:
480:
477:
476:
456:
453:
452:
394:
391:
390:
385:represents the
370:
367:
366:
345:
344:
331:
324:
320:
316:
314:
304:
297:
291:
287:
284:
283:
270:
263:
259:
255:
253:
243:
236:
230:
226:
222:
220:
217:
216:
144:
105:
35:exerted by the
17:
12:
11:
5:
2467:
2457:
2456:
2451:
2449:Fluid dynamics
2435:
2434:
2419:
2404:
2389:
2382:
2356:
2305:
2270:
2243:
2208:
2149:
2127:
2118:|journal=
2095:
2054:
2035:(C12): 15467.
2019:
2001:
1977:
1962:
1934:
1903:
1902:
1900:
1897:
1892:
1889:
1879:
1876:
1875:
1874:
1863:
1859:
1850:
1846:
1842:
1839:
1834:
1828:
1824:
1820:
1816:
1810:
1807:
1803:
1797:
1794:
1790:
1786:
1783:
1780:
1775:
1771:
1743:
1740:
1737:
1715:
1711:
1690:
1679:
1678:
1667:
1663:
1654:
1650:
1646:
1643:
1638:
1632:
1628:
1624:
1620:
1614:
1611:
1607:
1601:
1597:
1593:
1590:
1587:
1582:
1578:
1574:
1571:
1568:
1565:
1562:
1559:
1544:
1543:
1532:
1526:
1523:
1518:
1515:
1506:
1503:
1499:
1494:
1489:
1485:
1459:
1455:
1443:
1442:
1431:
1424:
1419:
1415:
1411:
1406:
1401:
1397:
1369:Main article:
1366:
1363:
1351:Main article:
1348:
1345:
1333:Somali Current
1317:Canary Current
1296:Main article:
1293:
1290:
1217:
1214:
1189:
1185:
1147:
1143:
1113:
1109:
1093:
1090:
1045:
1044:
1029:
1023:
1020:
1017:
1011:
1007:
1001:
998:
995:
993:
989:
985:
981:
980:
977:
971:
968:
965:
959:
955:
949:
946:
944:
940:
936:
932:
931:
892:
856:
853:
833:
830:
827:
796:
795:
780:
774:
771:
764:
760:
756:
748:
745:
740:
737:
735:
733:
730:
727:
726:
723:
717:
714:
707:
703:
699:
691:
688:
683:
680:
678:
676:
673:
670:
667:
666:
652:Coriolis force
636:
633:
628:
624:
606:
586:
574:
573:
562:
557:
552:
548:
542:
538:
528:
524:
515:
502:) in the form
489:
485:
460:
417:direction and
398:
374:
359:
358:
343:
337:
334:
327:
323:
319:
311:
308:
303:
300:
298:
294:
290:
286:
285:
282:
276:
273:
266:
262:
258:
250:
247:
242:
239:
237:
233:
229:
225:
224:
198:Beaufort scale
194:ocean dynamics
143:
140:
104:
101:
73:ocean currents
63:of horizontal
25:fluid dynamics
15:
9:
6:
4:
3:
2:
2466:
2455:
2452:
2450:
2447:
2446:
2444:
2430:
2423:
2415:
2408:
2400:
2393:
2385:
2379:
2375:
2370:
2369:
2360:
2352:
2348:
2344:
2340:
2336:
2332:
2328:
2324:
2320:
2316:
2309:
2301:
2297:
2293:
2289:
2285:
2281:
2274:
2266:
2262:
2258:
2254:
2247:
2239:
2235:
2231:
2227:
2223:
2219:
2212:
2204:
2200:
2195:
2190:
2185:
2180:
2176:
2172:
2168:
2164:
2160:
2153:
2145:
2138:
2136:
2134:
2132:
2123:
2110:
2099:
2090:
2085:
2081:
2077:
2073:
2069:
2065:
2058:
2050:
2046:
2042:
2038:
2034:
2030:
2023:
2015:
2008:
2006:
1997:
1990:
1988:
1986:
1984:
1982:
1973:
1966:
1958:
1951:
1949:
1947:
1945:
1943:
1941:
1939:
1930:
1923:
1921:
1919:
1917:
1915:
1913:
1911:
1909:
1904:
1896:
1888:
1885:
1861:
1857:
1848:
1840:
1826:
1822:
1818:
1808:
1805:
1801:
1795:
1792:
1788:
1784:
1781:
1778:
1773:
1769:
1761:
1760:
1759:
1757:
1738:
1713:
1709:
1688:
1665:
1661:
1652:
1644:
1630:
1626:
1622:
1612:
1609:
1605:
1599:
1591:
1580:
1576:
1569:
1566:
1560:
1550:
1549:
1548:
1530:
1524:
1516:
1504:
1501:
1497:
1492:
1487:
1483:
1475:
1474:
1473:
1457:
1453:
1429:
1422:
1417:
1413:
1409:
1404:
1399:
1395:
1387:
1386:
1385:
1382:
1378:
1372:
1362:
1360:
1354:
1344:
1342:
1336:
1334:
1330:
1326:
1322:
1318:
1312:
1310:
1306:
1299:
1289:
1287:
1283:
1279:
1275:
1271:
1267:
1263:
1259:
1255:
1254:Henry Stommel
1250:
1246:
1241:
1239:
1235:
1231:
1227:
1223:
1222:gravitational
1213:
1210:
1187:
1184:
1174:
1166:
1145:
1142:
1132:
1111:
1108:
1098:
1089:
1087:
1083:
1082:instabilities
1077:
1075:
1071:
1067:
1062:
1061:perpendicular
1058:
1054:
1050:
1027:
1021:
1018:
1015:
1009:
1005:
999:
996:
994:
987:
983:
975:
969:
966:
963:
957:
953:
947:
945:
938:
934:
922:
921:
920:
918:
913:
911:
906:
890:
882:
878:
874:
870:
854:
851:
831:
828:
825:
817:
813:
809:
805:
801:
778:
772:
762:
758:
746:
743:
738:
736:
731:
728:
721:
715:
705:
701:
689:
686:
681:
679:
674:
671:
668:
657:
656:
655:
653:
648:
634:
631:
626:
622:
613:
609:
584:
560:
555:
550:
546:
540:
536:
526:
522:
513:
505:
504:
503:
487:
483:
474:
458:
449:
447:
443:
439:
435:
432:
428:
424:
420:
416:
412:
396:
388:
372:
364:
341:
335:
325:
321:
309:
306:
301:
299:
292:
288:
280:
274:
264:
260:
248:
245:
240:
238:
231:
227:
215:
214:
213:
209:
207:
203:
199:
195:
191:
187:
183:
182:momentum flux
173:
164:
156:
148:
139:
137:
133:
129:
125:
121:
117:
113:
109:
100:
98:
94:
90:
86:
82:
78:
74:
70:
66:
62:
58:
54:
50:
46:
42:
38:
34:
30:
26:
22:
2428:
2422:
2413:
2407:
2398:
2392:
2367:
2359:
2318:
2314:
2308:
2283:
2279:
2273:
2256:
2252:
2246:
2221:
2217:
2211:
2166:
2162:
2152:
2143:
2109:cite journal
2098:
2074:(11): 1742.
2071:
2067:
2057:
2032:
2028:
2022:
2013:
1995:
1971:
1965:
1956:
1928:
1894:
1881:
1878:Measurements
1755:
1680:
1545:
1444:
1374:
1356:
1337:
1313:
1301:
1282:water column
1242:
1219:
1205:
1078:
1065:
1059:is directed
1048:
1046:
914:
910:Ekman spiral
811:
807:
799:
797:
649:
604:
575:
450:
418:
410:
362:
360:
210:
179:
136:shear stress
106:
33:shear stress
28:
18:
2401:. Elsevier.
1266:Gulf Stream
1258:Gulf Stream
1230:evaporation
1209:trade winds
1053:Ekman layer
427:derivatives
387:air density
206:mixed layer
132:shear force
120:deformation
29:wind stress
2443:Categories
1899:References
1884:wind speed
1347:Wind waves
1341:divergence
1331:, and the
1226:convection
423:meridional
202:sea states
103:Background
97:atmosphere
77:wind speed
69:wind waves
1845:⟩
1838:⟨
1833:⟩
1815:⟨
1793:−
1785:×
1742:⟩
1736:⟨
1689:ρ
1649:⟩
1642:⟨
1637:⟩
1619:⟨
1596:⟩
1589:⟨
1586:⟩
1573:⟨
1570:ρ
1564:⟩
1561:τ
1558:⟨
1522:∂
1514:∂
1502:ρ
1410:τ
1353:Wind wave
1298:Upwelling
1019:ρ
1006:τ
1000:−
967:ρ
954:τ
826:−
770:∂
759:τ
755:∂
747:ρ
713:∂
702:τ
698:∂
690:ρ
669:−
585:ρ
527:ρ
514:τ
459:τ
434:viscosity
397:τ
373:ρ
333:∂
322:τ
318:∂
310:ρ
272:∂
261:τ
257:∂
249:ρ
190:nutrients
53:estuaries
2351:31388621
2343:17749327
2203:16588757
1823:′
1627:′
1278:Eulerian
1088:(ENSO).
875:with no
442:momentum
142:Dynamics
112:quantity
65:momentum
2323:Bibcode
2315:Science
2288:Bibcode
2226:Bibcode
2194:1079064
2171:Bibcode
2076:Bibcode
2037:Bibcode
1286:drifter
1074:equator
802:is the
167:vector.
126:is the
124:SI unit
110:is the
41:surface
39:on the
31:is the
2380:
2349:
2341:
2201:
2191:
1681:where
1445:where
1327:, the
1323:, the
1319:, the
1047:where
798:where
635:0.0015
576:Here,
473:height
446:energy
361:Here,
128:Pascal
108:Stress
89:energy
45:oceans
27:, the
2347:S2CID
415:zonal
116:force
57:lakes
2378:ISBN
2339:PMID
2199:PMID
2122:help
1375:The
1307:and
1234:gyre
915:The
844:and
818:and
810:and
518:wind
444:and
431:eddy
389:and
186:heat
93:mass
91:and
61:flux
55:and
49:seas
37:wind
23:and
2374:194
2331:doi
2319:207
2296:doi
2261:doi
2234:doi
2189:PMC
2179:doi
2084:doi
2045:doi
1782:1.3
589:air
531:air
19:In
2445::
2376:.
2345:.
2337:.
2329:.
2317:.
2294:.
2282:.
2255:.
2232:.
2222:29
2220:.
2197:.
2187:.
2177:.
2167:33
2165:.
2161:.
2130:^
2113::
2111:}}
2107:{{
2082:.
2072:20
2070:.
2066:.
2043:.
2033:93
2031:.
2004:^
1980:^
1937:^
1907:^
1789:10
1756:U'
1311:.
912:.
891:45
806:,
138:.
99:.
51:,
47:,
2431:.
2386:.
2353:.
2333::
2325::
2302:.
2298::
2290::
2284:6
2267:.
2263::
2257:6
2240:.
2236::
2228::
2205:.
2181::
2173::
2124:)
2120:(
2092:.
2086::
2078::
2051:.
2047::
2039::
1862:.
1858:)
1849:2
1841:U
1827:2
1819:U
1809:+
1806:1
1802:(
1796:3
1779:=
1774:D
1770:C
1739:U
1714:D
1710:C
1666:,
1662:)
1653:2
1645:U
1631:2
1623:U
1613:+
1610:1
1606:(
1600:2
1592:U
1581:D
1577:C
1567:=
1531:.
1525:y
1517:p
1505:f
1498:1
1493:=
1488:g
1484:U
1458:g
1454:U
1430:,
1423:2
1418:g
1414:U
1405:=
1400:g
1396:C
1188:2
1146:2
1112:2
1066:D
1049:D
1028:,
1022:D
1016:f
1010:x
997:=
988:E
984:V
976:,
970:D
964:f
958:y
948:=
939:E
935:U
855:u
852:f
832:v
829:f
812:v
808:u
800:f
779:,
773:z
763:y
744:1
739:=
732:u
729:f
722:,
716:z
706:x
687:1
682:=
675:v
672:f
632:=
627:D
623:C
607:D
605:C
561:.
556:2
551:h
547:U
541:D
537:C
523:=
488:h
484:U
419:y
411:x
363:F
342:.
336:z
326:y
307:1
302:=
293:y
289:F
281:,
275:z
265:x
246:1
241:=
232:x
228:F
Text is available under the Creative Commons Attribution-ShareAlike License. Additional terms may apply.