152:
vehicle's electrical system as possible. The relay(s) modulated the width of a current pulse to regulate the voltage output of the generator by controlling the average field current in the rotating machine which determines strength of the magnetic field produced which determines the unloaded output voltage per rpm. Capacitors are not used to smooth the pulsed voltage as described earlier. The large inductance of the field coil stores the energy delivered to the magnetic field in an iron core so the pulsed field current does not result in as strongly pulsed a field. Both types of rotating machine produce a rotating magnetic field that induces an alternating current in the coils in the stator. A generator uses a mechanical commutator, graphite brushes running on copper segments, to convert the AC produced into DC by switching the external connections at the shaft angle when the voltage would reverse. An alternator accomplishes the same goal using rectifiers that do not wear down and require replacement.
553:
generate output voltages which are higher than the input, or of opposite polarity—something not possible with a linear design. In switched regulators, the pass transistor is used as a "controlled switch" and is operated at either cutoff or saturated state. Hence the power transmitted across the pass device is in discrete pulses rather than a steady current flow. Greater efficiency is achieved since the pass device is operated as a low impedance switch. When the pass device is at cutoff, there is no current and it dissipates no power. Again when the pass device is in saturation, a negligible voltage drop appears across it and thus dissipates only a small amount of average power, providing maximum current to the load. In either case, the power wasted in the pass device is very little and almost all the power is transmitted to the load. Thus the efficiency of a switched-mode power supply is remarkably high-in the range of 70–90%.
179:
solid-state devices. An AVR is a feedback control system that measures the output voltage of the generator, compares that output to a set point, and generates an error signal that is used to adjust the excitation of the generator. As the excitation current in the field winding of the generator increases, its terminal voltage will increase. The AVR will control current by using power electronic devices; generally a small part of the generator's output is used to provide current for the field winding. Where a generator is connected in parallel with other sources such as an electrical transmission grid, changing the excitation has more of an effect on the
583:(SCRs) as the series device. Whenever the output voltage is below the desired value, the SCR is triggered, allowing electricity to flow into the load until the AC mains voltage passes through zero (ending the half cycle). SCR regulators have the advantages of being both very efficient and very simple, but because they can not terminate an ongoing half cycle of conduction, they are not capable of very accurate voltage regulation in response to rapidly changing loads. An alternative is the SCR shunt regulator which uses the regulator output as a trigger. Both series and shunt designs are noisy, but powerful, as the device has a low on resistance.
238:, have also been used to regulate the voltage on AC power distribution lines. These regulators operate by using a servomechanism to select the appropriate tap on an autotransformer with multiple taps, or by moving the wiper on a continuously variable auto transfomer. If the output voltage is not in the acceptable range, the servomechanism switches the tap, changing the turns ratio of the transformer, to move the secondary voltage into the acceptable region. The controls provide a dead band wherein the controller will not act, preventing the controller from constantly adjusting the voltage ("hunting") as it varies by an acceptably small amount.
403:
618:
107:, to produce a higher output voltage–by dropping less of the input voltage (for linear series regulators and buck switching regulators), or to draw input current for longer periods (boost-type switching regulators); if the output voltage is too high, the regulation element will normally be commanded to produce a lower voltage. However, many regulators have over-current protection, so that they will entirely stop sourcing current (or limit the current in some way) if the output current is too high, and some regulators may also shut down if the input voltage is outside a given range (see also:
120:
939:
80:
136:
391:
198:
171:
1084:
manage it for a limited time such as 60 seconds (usually specified in the data sheet). For instance, this situation can occur when a three terminal regulator is incorrectly mounted on a PCB, with the output terminal connected to the unregulated DC input and the input connected to the load. Mirror-image insertion protection is also important when a regulator circuit is used in battery charging circuits, when external power fails or is not turned on and the output terminal remains at battery voltage.
507:. Linear designs have the advantage of very "clean" output with little noise introduced into their DC output, but are most often much less efficient and unable to step-up or invert the input voltage like switched supplies. All linear regulators require a higher input than the output. If the input voltage approaches the desired output voltage, the regulator will "drop out". The input to output voltage differential at which this occurs is known as the regulator's drop-out voltage.
20:
1097:
252:
95:(or series of diodes). Due to the logarithmic shape of diode V-I curves, the voltage across the diode changes only slightly due to changes in current drawn or changes in the input. When precise voltage control and efficiency are not important, this design may be fine. Since the forward voltage of a diode is small, this kind of voltage regulator is only suitable for low voltage regulated output. When higher voltage output is needed, a
1077:) occurs. Some regulators will tend to oscillate or have a slow response time which in some cases might lead to undesired results. This value is different from the regulation parameters, as that is the stable situation definition. The transient response shows the behaviour of the regulator on a change. This data is usually provided in the technical documentation of a regulator and is also dependent on output capacitance.
128:
218:
144:
strengthening the magnetic field produced by the coil and pulling the core towards the field. The magnet is physically connected to a mechanical power switch, which opens as the magnet moves into the field. As voltage decreases, so does the current, releasing spring tension or the weight of the core and causing it to retract. This closes the switch and allows the power to flow once more.
534:
103:
tends to increase regulation accuracy but reduce stability. (Stability is the avoidance of oscillation, or ringing, during step changes.) There will also be a trade-off between stability and the speed of the response to changes. If the output voltage is too low (perhaps due to input voltage reducing or load current increasing), the regulation element is commanded,
455:. Shunt regulators are often (but not always) passive and simple, but always inefficient because they (essentially) dump the excess current which is not available to the load. When more power must be supplied, more sophisticated circuits are used. In general, these active regulators can be divided into several classes:
1024:
automatic voltage regulators may draw and output several times their normal full-load current for a few cycles of the input waveform when first energized or switched on. Power converters also often have inrush currents much higher than their steady state currents, due to the charging current of the input capacitance.
1083:
means that a regulator is designed for use when a voltage, usually not higher than the maximum input voltage of the regulator, is applied to its output pin while its input terminal is at a low voltage, volt-free or grounded. Some regulators can continuously withstand this situation. Others might only
552:
is transferred to the load. This is controlled by a similar feedback mechanism as in a linear regulator. Because the series element is either fully conducting, or switched off, it dissipates almost no power; this is what gives the switching design its efficiency. Switching regulators are also able to
360:
Efficiency at full load is typically in the range of 89% to 93%. However, at low loads, efficiency can drop below 60%. The current-limiting capability also becomes a handicap when a CVT is used in an application with moderate to high inrush current, like motors, transformers or magnets. In this case,
70:
and central power station generator plants, voltage regulators control the output of the plant. In an electric power distribution system, voltage regulators may be installed at a substation or along distribution lines so that all customers receive steady voltage independent of how much power is drawn
1012:
is the minimum difference between input voltage and output voltage for which the regulator can still supply the specified current. The input-output differential at which the voltage regulator will no longer maintain regulation is the dropout voltage. Further reduction in input voltage will result in
596:
generated by the switching regulator. Other designs may use an SCR regulator as the "pre-regulator", followed by another type of regulator. An efficient way of creating a variable-voltage, accurate output power supply is to combine a multi-tapped transformer with an adjustable linear post-regulator.
591:
Many power supplies use more than one regulating method in series. For example, the output from a switching regulator can be further regulated by a linear regulator. The switching regulator accepts a wide range of input voltages and efficiently generates a (somewhat noisy) voltage slightly above the
340:
Older designs of ferroresonant transformers had an output with high harmonic content, leading to a distorted output waveform. Modern devices are used to construct a perfect sine wave. The ferroresonant action is a flux limiter rather than a voltage regulator, but with a fixed supply frequency it can
209:
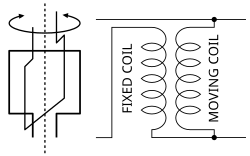
When the movable coil is positioned perpendicular to the fixed coil, the magnetic forces acting on the movable coil balance each other out and voltage output is unchanged. Rotating the coil in one direction or the other away from the center position will increase or decrease voltage in the secondary
183:
produced by the generator than on its terminal voltage, which is mostly set by the connected power system. Where multiple generators are connected in parallel, the AVR system will have circuits to ensure all generators operate at the same power factor. AVRs on grid-connected power station generators
687:
is usually about 0.7 V for a silicon transistor, depending on the load current. If the output voltage drops for any external reason, such as an increase in the current drawn by the load (causing an increase in the collector–emitter voltage to observe KVL), the transistor's base–emitter voltage
410:
Voltage regulators or stabilizers are used to compensate for voltage fluctuations in mains power. Large regulators may be permanently installed on distribution lines. Small portable regulators may be plugged in between sensitive equipment and a wall outlet. Automatic voltage regulators on generator
213:
This type of regulator can be automated via a servo control mechanism to advance the movable coil position in order to provide voltage increase or decrease. A braking mechanism or high-ratio gearing is used to hold the rotating coil in place against the powerful magnetic forces acting on the moving
143:
In electromechanical regulators, voltage regulation is easily accomplished by coiling the sensing wire to make an electromagnet. The magnetic field produced by the current attracts a moving ferrous core held back under spring tension or gravitational pull. As voltage increases, so does the current,
102:
Feedback voltage regulators operate by comparing the actual output voltage to some fixed reference voltage. Any difference is amplified and used to control the regulation element in such a way as to reduce the voltage error. This forms a negative feedback control loop; increasing the open-loop gain
151:
Early automobile generators and alternators had a mechanical voltage regulator using one, two, or three relays and various resistors to stabilize the generator's output at slightly more than 6.7 or 13.4 V to maintain the battery as independently of the engine's rpm or the varying load on the
147:
If the mechanical regulator design is sensitive to small voltage fluctuations, the motion of the solenoid core can be used to move a selector switch across a range of resistances or transformer windings to gradually step the output voltage up or down, or to rotate the position of a moving-coil AC
332:
to produce a nearly constant average output voltage with a varying input current or varying load. The circuit has a primary on one side of a magnet shunt and the tuned circuit coil and secondary on the other side. The regulation is due to magnetic saturation in the section around the secondary.
178:
Generators, as used in power stations, ship electrical power production, or standby power systems, will have automatic voltage regulators (AVR) to stabilize their voltages as the load on the generators changes. The first AVRs for generators were electromechanical systems, but a modern AVR uses
984:
is the degree to which output voltage changes with input (supply) voltage changes—as a ratio of output to input change (for example, "typically 13 mV/V"), or the output voltage change over the entire specified input voltage range (for example, "plus or minus 2% for input voltages between
1023:
usually lasts for half a second, or a few milliseconds, but it is often very high, which makes it dangerous because it can degrade and burn components gradually (over months or years), especially if there is no inrush current protection. Alternating current transformers or electric motors in
336:
The ferroresonant approach is attractive due to its lack of active components, relying on the square loop saturation characteristics of the tank circuit to absorb variations in average input voltage. Saturating transformers provide a simple rugged method to stabilize an AC power supply.
442:
If the stabilizer must provide more power, the shunt output is only used to provide the standard voltage reference for the electronic device, known as the voltage stabilizer. The voltage stabilizer is the electronic device, able to deliver much larger currents on demand.
435:. Each of these devices begins conducting at a specified voltage and will conduct as much current as required to hold its terminal voltage to that specified voltage by diverting excess current from a non-ideal power source to ground, often through a relatively low-value
850:
364:
Minimum maintenance is required, as transformers and capacitors can be very reliable. Some units have included redundant capacitors to allow several capacitors to fail between inspections without any noticeable effect on the device's performance.
411:
sets to maintain a constant voltage for changes in load. The voltage regulator compensates for the change in load. Power distribution voltage regulators normally operate on a range of voltages, for example 150–240 V or 90–280 V.
368:
Output voltage varies about 1.2% for every 1% change in supply frequency. For example, a 2 Hz change in generator frequency, which is very large, results in an output voltage change of only 4%, which has little effect for most loads.
560:
to control the average value of the output voltage. The average value of a repetitive pulse waveform depends on the area under the waveform. If the duty cycle is varied, the average value of the voltage changes proportionally.
205:
This is an older type of regulator used in the 1920s that uses the principle of a fixed-position field coil and a second field coil that can be rotated on an axis in parallel with the fixed coil, similar to a variocoupler.
973:
is the change in output voltage for a given change in load current (for example, "typically 15 mV, maximum 100 mV for load currents between 5 mA and 1.4 A, at some specified temperature and input
1030:
are defined for regulator components, specifying the continuous and peak output currents that may be used (sometimes internally limited), the maximum input voltage, maximum power dissipation at a given temperature,
398:
bank of voltage regulators used to control the voltage on long AC power distribution lines. This bank is mounted on a wooden pole structure. Each regulator weighs about 1200 kg and is rated 576 kVA.
945:
In this case, the operational amplifier drives the transistor with more current if the voltage at its inverting input drops below the output of the voltage reference at the non-inverting input. Using the
514:
Entire linear regulators are available as integrated circuits. These chips come in either fixed or adjustable voltage types. Examples of some integrated circuits are the 723 general purpose regulator and
708:
current for both the Zener diode and the transistor. The current in the diode is minimal when the load current is maximal. The circuit designer must choose a minimum voltage that can be tolerated across
483:
are based on devices that operate in their linear region (in contrast, a switching regulator is based on a device forced to act as an on/off switch). Linear regulators are also classified in two types:
568:
that acts as the energy storage element. The IC regulators combine the reference voltage source, error op-amp, pass transistor with short circuit current limiting and thermal overload protection.
1002:
of a voltage regulator (or simply "the voltage accuracy") reflects the error in output voltage for a fixed regulator without taking into account temperature or aging effects on output accuracy.
1059:
in a regulator circuit is the current drawn internally, not available to the load, normally measured as the input current while no load is connected and hence a source of inefficiency (some
439:
to dissipate the excess energy. The power supply is designed to only supply a maximum amount of current that is within the safe operating capability of the shunt regulating device.
745:
357:
Because it regenerates an output voltage waveform, output distortion, which is typically less than 4%, is independent of any input voltage distortion, including notching.
571:
Switching regulators are more prone to output noise and instability than linear regulators. However, they provide much better power efficiency than linear regulators.
564:
Like linear regulators, nearly complete switching regulators are also available as integrated circuits. Unlike linear regulators, these usually require an
99:
or series of zener diodes may be employed. Zener diode regulators make use of the zener diode's fixed reverse voltage, which can be quite large.
1355:
592:
ultimately desired output. That is followed by a linear regulator that generates exactly the desired voltage and eliminates nearly all the
1019:
or input surge current or switch-on surge is the maximum, instantaneous input current drawn by an electrical device when first turned on.
419:
Many simple DC power supplies regulate the voltage using either series or shunt regulators, but most apply a voltage reference using a
372:
It accepts 100% single-phase switch-mode power-supply loading without any requirement for derating, including all neutral components.
2229:
1870:
1125:
184:
may have additional control features to help stabilize the electrical grid against upsets due to sudden load loss or faults.
1787:
348:(CVTs) or "ferros", are also good surge suppressors, as they provide high isolation and inherent short-circuit protection.
1568:
1348:
511:(LDOs) allow an input voltage that can be much lower (i.e., they waste less energy than conventional linear regulators).
966:
The output voltage can only be held constant within specified limits. The regulation is specified by two measurements:
273:
1551:
1447:
1304:
1188:
299:
281:
1691:
1418:
382:
Drawbacks of CVTs are their larger size, audible humming sound, and the high heat generation caused by saturation.
1203:"Analysis on the Reason of Low Voltage Problem and the Effectiveness of Voltage Regulation in a Distribution Area"
361:
the CVT has to be sized to accommodate the peak current, thus forcing it to run at low loads and poor efficiency.
1739:
1538:
1341:
695:) increases, turning the transistor on further and delivering more current to increase the load voltage again.
277:
159:
technology (transistors) to perform the same function that the relays perform in electromechanical regulators.
1770:
1522:
580:
63:
614:
amplifier is used with the base of the regulating transistor connected directly to the voltage reference:
2393:
1574:
1511:
845:{\displaystyle R_{\text{v}}={\frac {\min V_{R}}{\min I_{\text{D}}+\max I_{\text{L}}/(h_{\text{FE}}+1)}},}
351:
A ferroresonant transformer can operate with an input voltage range ±40% or more of the nominal voltage.
162:
Electromechanical regulators are used for mains voltage stabilisation—see AC voltage stabilizers below.
2403:
2234:
1781:
1115:
996:
of the output voltage is the change with temperature (perhaps averaged over a given temperature range).
528:
402:
1063:
are, surprisingly, more efficient at very low current loads than switch-mode designs because of this).
1988:
1702:
1545:
1430:
716:, bearing in mind that the higher this voltage requirement is, the higher the required input voltage
376:
2398:
1997:
1855:
1707:
1563:
1140:
262:
2008:
1728:
1527:
266:
67:
2177:
1744:
1609:
1585:
928:
659:
by a sufficient margin and that the power handling capacity of the transistor is not exceeded.
557:
432:
2246:
2198:
2019:
1835:
1750:
1681:
1517:
932:
617:
508:
452:
119:
1218:
1159:
451:
Active regulators employ at least one active (amplifying) component such as a transistor or
341:
maintain an almost constant average output voltage even as the input voltage varies widely.
2320:
2064:
1959:
1733:
1626:
1480:
1441:
1372:
1364:
1214:
947:
48:
723:, and hence the lower the efficiency of the regulator. On the other hand, lower values of
324:
is a type of saturating transformer used as a voltage regulator. These transformers use a
8:
2040:
1948:
1840:
1676:
1653:
1227:
1202:
1013:
reduced output voltage. This value is dependent on load current and junction temperature.
730:
lead to higher power dissipation in the diode and to inferior regulator characteristics.
52:
1327:
2345:
2205:
1913:
1880:
1696:
1580:
1558:
1232:
1135:
1130:
1120:
1102:
504:
1069:
is the reaction of a regulator when a (sudden) change of the load current (called the
135:
2340:
2261:
2152:
2104:
1933:
1860:
1300:
1236:
1184:
1110:
938:
201:
Basic design principle and circuit diagram for the rotating-coil AC voltage regulator
108:
44:
40:
2056:
2003:
1830:
1469:
1222:
1060:
1050:
475:
354:
Output power factor remains in the range of 0.96 or higher from half to full load.
79:
1865:
390:
66:
where they stabilize the DC voltages used by the processor and other elements. In
2333:
2266:
2119:
1850:
1760:
1604:
549:
428:
1491:
1049:
noise (mains "hum" or switch-mode "hash" noise) may be given as peak-to-peak or
624:
A simple transistor regulator will provide a relatively constant output voltage
197:
2308:
2089:
2079:
1845:
1648:
1020:
180:
170:
56:
927:
The stability of the output voltage can be significantly increased by using a
499:
were commonly used as the variable resistance. Modern designs use one or more
2387:
2370:
2193:
2109:
1928:
1755:
1723:
2251:
2239:
2127:
2094:
1923:
1908:
1475:
537:
Switching regulator integrated circuit LM2676, 3 A step-down converter
325:
36:
2293:
2035:
1984:
1890:
1875:
1658:
1620:
1252:
Texas
Instruments LM2825 Integrated Power Supply 1 A DC-DC Converter
1038:
663:
611:
496:
424:
395:
96:
19:
1333:
2365:
2355:
2288:
2162:
2132:
2099:
2074:
2069:
2046:
1918:
1898:
1776:
1638:
1615:
1501:
1403:
1398:
1393:
950:(R1, R2 and R3) allows choice of the arbitrary output voltage between U
545:
500:
2328:
2172:
2167:
2157:
2084:
1964:
1798:
1793:
1718:
1643:
379:
even when supplying nonlinear loads with more than 100% current THD.
329:
251:
2350:
2298:
2278:
2256:
2142:
2137:
2025:
2014:
1943:
1713:
1271:
1250:
1096:
565:
436:
88:
51:. Depending on the design, it may be used to regulate one or more
2210:
2147:
1969:
1954:
1808:
1765:
1413:
705:
131:
A voltage stabilizer using electromechanical relays for switching
32:
885:
is the minimum current to be maintained through the Zener diode,
2283:
1974:
1938:
1903:
1463:
1435:
1408:
1383:
123:
Circuit design for a simple electromechanical voltage regulator
2360:
2271:
2030:
1803:
1596:
1458:
1453:
593:
127:
92:
1201:
Guo, Min; Jin, Qingren; Yao, Zhiyang; Chen, Weidong (2020).
1181:
Standard
Handbook for Electrical Engineers Eleventh Edition
217:
2303:
1686:
1632:
1533:
1486:
1424:
1299:. New York and London: John Wiley & Sons. p. 534.
516:
83:
Block scheme for voltage regulator in an electronic circuit
62:
Electronic voltage regulators are found in devices such as
1045:
may be specified as graphs versus frequency, while output
922:
666:
voltage minus the base–emitter voltage of the transistor,
31:
is a system designed to automatically maintain a constant
533:
344:
The ferroresonant transformers, which are also known as
1161:
Voltage
Stabilizer or Automatic Voltage Regulator (AVR)
1207:
87:
A simple voltage/current regulator can be made from a
748:
662:
The output voltage of the stabilizer is equal to the
192:
1294:
1092:
586:
844:
579:Regulators powered from AC power circuits can use
328:composed of a high-voltage resonant winding and a
1323:Linear & Switching Voltage Regulator Handbook
2385:
796:
780:
765:
74:
904:is the forward current gain of the transistor (
868:is the minimum voltage to be maintained across
600:
544:rapidly switch a series device on and off. The
241:
114:
1290:
1288:
375:Input current distortion remains less than 8%
165:
16:System designed to maintain a constant voltage
1349:
1325:; ON Semiconductor; 118 pages; 2002; HB206/D.
1200:
638:of the power source and for changes in load
1285:
280:. Unsourced material may be challenged and
1356:
1342:
985:90 V and 260 V, 50–60 Hz").
961:
1363:
1226:
414:
300:Learn how and when to remove this message
187:
1295:Alley, Charles; Atwood, Kenneth (1973).
532:
401:
389:
216:
196:
169:
134:
126:
118:
78:
18:
1053:voltages, or in terms of their spectra.
923:Regulator with a differential amplifier
605:
522:
139:Graph of voltage output on a time scale
23:An integrated circuit voltage regulator
2386:
1337:
1126:List of LM-series integrated circuits
385:
1788:Three-dimensional integrated circuit
1273:Linear Technology μModule Regulators
469:
446:
278:adding citations to reliable sources
245:
230:Electromechanical regulators called
225:
1569:Programmable unijunction transistor
895:is the maximum design load current,
13:
1470:Multi-gate field-effect transistor
1316:
937:
616:
193:Coil-rotation AC voltage regulator
14:
2415:
1448:Insulated-gate bipolar transistor
1179:Donald G. Fink, H. Wayne Beatty,
1081:Mirror-image insertion protection
574:
556:Switched mode regulators rely on
406:Three phase wye voltage regulator
1692:Heterostructure barrier varactor
1419:Chemical field-effect transistor
1095:
989:Other important parameters are:
587:Combination or hybrid regulators
250:
174:Voltage regulator for generators
1740:Mixed-signal integrated circuit
1073:) or input voltage (called the
1264:
1243:
1228:10.1088/1755-1315/440/3/032128
1194:
1173:
1152:
833:
814:
1:
1146:
931:, possibly implemented as an
581:silicon controlled rectifiers
346:constant-voltage transformers
75:Electronic voltage regulators
1771:Silicon controlled rectifier
1633:Organic light-emitting diode
1523:Diffused junction transistor
601:Example of linear regulators
548:of the switch sets how much
322:constant-voltage transformer
242:Constant-voltage transformer
115:Electromechanical regulators
7:
1575:Static induction transistor
1512:Bipolar junction transistor
1464:MOS field-effect transistor
1436:Fin field-effect transistor
1088:
631:for changes in the voltage
503:instead, perhaps within an
166:Automatic voltage regulator
10:
2422:
1782:Static induction thyristor
1116:Constant current regulator
529:Switched-mode power supply
526:
473:
2319:
2219:
2186:
2118:
2055:
1983:
1951:(Hexode, Heptode, Octode)
1889:
1821:
1703:Hybrid integrated circuit
1667:
1595:
1546:Light-emitting transistor
1500:
1382:
1371:
495:In the past, one or more
429:avalanche breakdown diode
314:ferroresonant transformer
1998:Backward-wave oscillator
1708:Light emitting capacitor
1564:Point-contact transistor
1534:Junction Gate FET (JFET)
1141:Voltage regulator module
1043:output dynamic impedance
1028:Absolute maximum ratings
459:Linear series regulators
221:Magnetic mains regulator
2009:Crossed-field amplifier
1528:Field-effect transistor
1219:2020E&ES..440c2128G
994:Temperature coefficient
962:Regulator specification
610:In the simplest case a
318:ferroresonant regulator
155:Modern designs now use
64:computer power supplies
2178:Voltage-regulator tube
1745:MOS integrated circuit
1610:Constant-current diode
1586:Unijunction transistor
1297:Electronic Engineering
1183:, Mc Graw Hill, 1978,
942:
929:differential amplifier
846:
621:
558:pulse-width modulation
538:
509:Low-dropout regulators
433:voltage regulator tube
415:DC voltage stabilizers
407:
399:
222:
202:
188:AC voltage stabilizers
175:
140:
132:
124:
84:
68:automobile alternators
39:design or may include
35:. It may use a simple
24:
2247:Electrolytic detector
2020:Inductive output tube
1836:Low-dropout regulator
1751:Organic semiconductor
1682:Printed circuit board
1518:Darlington transistor
1365:Electronic components
941:
933:operational amplifier
847:
620:
536:
453:operational amplifier
405:
393:
220:
200:
173:
138:
130:
122:
82:
49:electronic components
22:
2065:Beam deflection tube
1734:Metal oxide varistor
1627:Light-emitting diode
1481:Thin-film transistor
1442:Floating-gate MOSFET
746:
606:Transistor regulator
542:Switching regulators
523:Switching regulators
462:Switching regulators
274:improve this section
2041:Traveling-wave tube
1841:Switching regulator
1677:Printed electronics
1654:Step recovery diode
1431:Depletion-load NMOS
1328:(Free PDF download)
232:voltage stabilizers
2394:Voltage regulation
2346:Crystal oscillator
2206:Variable capacitor
1881:Switched capacitor
1823:Voltage regulators
1697:Integrated circuit
1581:Tetrode transistor
1559:Pentode transistor
1552:Organic LET (OLET)
1539:Organic FET (OFET)
1136:Voltage comparator
1131:Third-brush dynamo
1121:DC-to-DC converter
1103:Electronics portal
1067:Transient response
943:
842:
622:
539:
505:integrated circuit
408:
400:
386:Power distribution
223:
203:
176:
141:
133:
125:
85:
25:
2404:Voltage stability
2381:
2380:
2341:Ceramic resonator
2153:Mercury-arc valve
2105:Video camera tube
2057:Cathode-ray tubes
1817:
1816:
1425:Complementary MOS
1330:
1111:Charge controller
1061:linear regulators
1057:Quiescent current
837:
824:
806:
790:
756:
488:series regulators
481:Linear regulators
470:Linear regulators
447:Active regulators
310:
309:
302:
226:Electromechanical
91:in series with a
45:electromechanical
41:negative feedback
29:voltage regulator
2411:
2235:electrical power
2120:Gas-filled tubes
2004:Cavity magnetron
1831:Linear regulator
1380:
1379:
1358:
1351:
1344:
1335:
1334:
1326:
1311:
1310:
1292:
1283:
1282:
1281:
1280:
1268:
1262:
1261:
1260:
1259:
1247:
1241:
1240:
1230:
1198:
1192:
1177:
1171:
1170:
1169:
1168:
1156:
1105:
1100:
1099:
1010:
1009:
1000:Initial accuracy
982:input regulation
851:
849:
848:
843:
838:
836:
826:
825:
822:
813:
808:
807:
804:
792:
791:
788:
778:
777:
776:
763:
758:
757:
754:
645:, provided that
491:shunt regulators
476:Linear regulator
305:
298:
294:
291:
285:
254:
246:
109:crowbar circuits
43:. It may use an
2421:
2420:
2414:
2413:
2412:
2410:
2409:
2408:
2399:Analog circuits
2384:
2383:
2382:
2377:
2315:
2230:audio and video
2215:
2182:
2114:
2051:
1979:
1960:Photomultiplier
1885:
1813:
1761:Quantum circuit
1669:
1663:
1605:Avalanche diode
1591:
1503:
1496:
1385:
1374:
1367:
1362:
1319:
1317:Further reading
1314:
1307:
1293:
1286:
1278:
1276:
1270:
1269:
1265:
1257:
1255:
1249:
1248:
1244:
1199:
1195:
1178:
1174:
1166:
1164:
1158:
1157:
1153:
1149:
1101:
1094:
1091:
1008:Dropout voltage
1007:
1006:
978:Line regulation
971:Load regulation
964:
957:
953:
948:voltage divider
925:
917:
910:
903:
894:
884:
874:
867:
821:
817:
809:
803:
799:
787:
783:
779:
772:
768:
764:
762:
753:
749:
747:
744:
743:
738:
729:
722:
715:
703:
694:
686:
679:
672:
658:
651:
644:
637:
630:
608:
603:
589:
577:
531:
525:
478:
472:
449:
421:shunt regulator
417:
388:
306:
295:
289:
286:
271:
255:
244:
228:
195:
190:
168:
117:
77:
71:from the line.
17:
12:
11:
5:
2419:
2418:
2407:
2406:
2401:
2396:
2379:
2378:
2376:
2375:
2374:
2373:
2368:
2358:
2353:
2348:
2343:
2338:
2337:
2336:
2325:
2323:
2317:
2316:
2314:
2313:
2312:
2311:
2309:Wollaston wire
2301:
2296:
2291:
2286:
2281:
2276:
2275:
2274:
2269:
2259:
2254:
2249:
2244:
2243:
2242:
2237:
2232:
2223:
2221:
2217:
2216:
2214:
2213:
2208:
2203:
2202:
2201:
2190:
2188:
2184:
2183:
2181:
2180:
2175:
2170:
2165:
2160:
2155:
2150:
2145:
2140:
2135:
2130:
2124:
2122:
2116:
2115:
2113:
2112:
2107:
2102:
2097:
2092:
2090:Selectron tube
2087:
2082:
2080:Magic eye tube
2077:
2072:
2067:
2061:
2059:
2053:
2052:
2050:
2049:
2044:
2038:
2033:
2028:
2023:
2017:
2012:
2006:
2001:
1994:
1992:
1981:
1980:
1978:
1977:
1972:
1967:
1962:
1957:
1952:
1946:
1941:
1936:
1931:
1926:
1921:
1916:
1911:
1906:
1901:
1895:
1893:
1887:
1886:
1884:
1883:
1878:
1873:
1868:
1863:
1858:
1853:
1848:
1843:
1838:
1833:
1827:
1825:
1819:
1818:
1815:
1814:
1812:
1811:
1806:
1801:
1796:
1791:
1785:
1779:
1774:
1768:
1763:
1758:
1753:
1748:
1742:
1737:
1731:
1726:
1721:
1716:
1711:
1705:
1700:
1694:
1689:
1684:
1679:
1673:
1671:
1665:
1664:
1662:
1661:
1656:
1651:
1649:Schottky diode
1646:
1641:
1636:
1630:
1624:
1618:
1613:
1607:
1601:
1599:
1593:
1592:
1590:
1589:
1583:
1578:
1572:
1566:
1561:
1556:
1555:
1554:
1543:
1542:
1541:
1536:
1525:
1520:
1515:
1508:
1506:
1498:
1497:
1495:
1494:
1489:
1484:
1478:
1473:
1467:
1461:
1456:
1451:
1445:
1439:
1433:
1428:
1422:
1416:
1411:
1406:
1401:
1396:
1390:
1388:
1377:
1369:
1368:
1361:
1360:
1353:
1346:
1338:
1332:
1331:
1318:
1315:
1313:
1312:
1305:
1284:
1263:
1242:
1193:
1172:
1150:
1148:
1145:
1144:
1143:
1138:
1133:
1128:
1123:
1118:
1113:
1107:
1106:
1090:
1087:
1086:
1085:
1078:
1075:line transient
1071:load transient
1064:
1054:
1032:
1025:
1021:Inrush current
1017:Inrush current
1014:
1003:
997:
987:
986:
975:
963:
960:
955:
951:
924:
921:
920:
919:
915:
908:
901:
896:
892:
886:
882:
876:
872:
863:
853:
852:
841:
835:
832:
829:
820:
816:
812:
802:
798:
795:
786:
782:
775:
771:
767:
761:
752:
736:
727:
720:
713:
701:
692:
684:
677:
670:
656:
649:
642:
635:
628:
607:
604:
602:
599:
588:
585:
576:
575:SCR regulators
573:
524:
521:
493:
492:
489:
474:Main article:
471:
468:
467:
466:
465:SCR regulators
463:
460:
448:
445:
416:
413:
387:
384:
308:
307:
258:
256:
249:
243:
240:
227:
224:
210:movable coil.
194:
191:
189:
186:
181:reactive power
167:
164:
116:
113:
76:
73:
47:mechanism, or
15:
9:
6:
4:
3:
2:
2417:
2416:
2405:
2402:
2400:
2397:
2395:
2392:
2391:
2389:
2372:
2371:mercury relay
2369:
2367:
2364:
2363:
2362:
2359:
2357:
2354:
2352:
2349:
2347:
2344:
2342:
2339:
2335:
2332:
2331:
2330:
2327:
2326:
2324:
2322:
2318:
2310:
2307:
2306:
2305:
2302:
2300:
2297:
2295:
2292:
2290:
2287:
2285:
2282:
2280:
2277:
2273:
2270:
2268:
2265:
2264:
2263:
2260:
2258:
2255:
2253:
2250:
2248:
2245:
2241:
2238:
2236:
2233:
2231:
2228:
2227:
2225:
2224:
2222:
2218:
2212:
2209:
2207:
2204:
2200:
2197:
2196:
2195:
2194:Potentiometer
2192:
2191:
2189:
2185:
2179:
2176:
2174:
2171:
2169:
2166:
2164:
2161:
2159:
2156:
2154:
2151:
2149:
2146:
2144:
2141:
2139:
2136:
2134:
2131:
2129:
2126:
2125:
2123:
2121:
2117:
2111:
2110:Williams tube
2108:
2106:
2103:
2101:
2098:
2096:
2093:
2091:
2088:
2086:
2083:
2081:
2078:
2076:
2073:
2071:
2068:
2066:
2063:
2062:
2060:
2058:
2054:
2048:
2045:
2042:
2039:
2037:
2034:
2032:
2029:
2027:
2024:
2021:
2018:
2016:
2013:
2010:
2007:
2005:
2002:
1999:
1996:
1995:
1993:
1990:
1986:
1982:
1976:
1973:
1971:
1968:
1966:
1963:
1961:
1958:
1956:
1953:
1950:
1947:
1945:
1942:
1940:
1937:
1935:
1932:
1930:
1929:Fleming valve
1927:
1925:
1922:
1920:
1917:
1915:
1912:
1910:
1907:
1905:
1902:
1900:
1897:
1896:
1894:
1892:
1888:
1882:
1879:
1877:
1874:
1872:
1869:
1867:
1864:
1862:
1859:
1857:
1854:
1852:
1849:
1847:
1844:
1842:
1839:
1837:
1834:
1832:
1829:
1828:
1826:
1824:
1820:
1810:
1807:
1805:
1802:
1800:
1797:
1795:
1792:
1789:
1786:
1783:
1780:
1778:
1775:
1772:
1769:
1767:
1764:
1762:
1759:
1757:
1756:Photodetector
1754:
1752:
1749:
1746:
1743:
1741:
1738:
1735:
1732:
1730:
1727:
1725:
1724:Memtransistor
1722:
1720:
1717:
1715:
1712:
1709:
1706:
1704:
1701:
1698:
1695:
1693:
1690:
1688:
1685:
1683:
1680:
1678:
1675:
1674:
1672:
1666:
1660:
1657:
1655:
1652:
1650:
1647:
1645:
1642:
1640:
1637:
1634:
1631:
1628:
1625:
1622:
1619:
1617:
1614:
1611:
1608:
1606:
1603:
1602:
1600:
1598:
1594:
1587:
1584:
1582:
1579:
1576:
1573:
1570:
1567:
1565:
1562:
1560:
1557:
1553:
1550:
1549:
1547:
1544:
1540:
1537:
1535:
1532:
1531:
1529:
1526:
1524:
1521:
1519:
1516:
1513:
1510:
1509:
1507:
1505:
1499:
1493:
1490:
1488:
1485:
1482:
1479:
1477:
1474:
1471:
1468:
1465:
1462:
1460:
1457:
1455:
1452:
1449:
1446:
1443:
1440:
1437:
1434:
1432:
1429:
1426:
1423:
1420:
1417:
1415:
1412:
1410:
1407:
1405:
1402:
1400:
1397:
1395:
1392:
1391:
1389:
1387:
1381:
1378:
1376:
1373:Semiconductor
1370:
1366:
1359:
1354:
1352:
1347:
1345:
1340:
1339:
1336:
1329:
1324:
1321:
1320:
1308:
1306:0-471-02450-3
1302:
1298:
1291:
1289:
1275:
1274:
1267:
1254:
1253:
1246:
1238:
1234:
1229:
1224:
1220:
1216:
1213:(3): 032128.
1212:
1208:
1204:
1197:
1190:
1189:0-07-020974-X
1186:
1182:
1176:
1163:
1162:
1155:
1151:
1142:
1139:
1137:
1134:
1132:
1129:
1127:
1124:
1122:
1119:
1117:
1114:
1112:
1109:
1108:
1104:
1098:
1093:
1082:
1079:
1076:
1072:
1068:
1065:
1062:
1058:
1055:
1052:
1048:
1044:
1040:
1036:
1033:
1029:
1026:
1022:
1018:
1015:
1011:
1004:
1001:
998:
995:
992:
991:
990:
983:
979:
976:
972:
969:
968:
967:
959:
949:
940:
936:
934:
930:
914:
907:
900:
897:
891:
887:
881:
877:
871:
866:
862:
858:
857:
856:
839:
830:
827:
818:
810:
800:
793:
784:
773:
769:
759:
750:
742:
741:
740:
735:
731:
726:
719:
712:
707:
700:
696:
691:
683:
676:
669:
665:
660:
655:
648:
641:
634:
627:
619:
615:
613:
598:
595:
584:
582:
572:
569:
567:
562:
559:
554:
551:
547:
543:
535:
530:
520:
519:/79xx series
518:
512:
510:
506:
502:
498:
490:
487:
486:
485:
482:
477:
464:
461:
458:
457:
456:
454:
444:
440:
438:
434:
430:
426:
422:
412:
404:
397:
392:
383:
380:
378:
373:
370:
366:
362:
358:
355:
352:
349:
347:
342:
338:
334:
331:
327:
323:
319:
315:
304:
301:
293:
290:November 2020
283:
279:
275:
269:
268:
264:
259:This section
257:
253:
248:
247:
239:
237:
233:
219:
215:
211:
207:
199:
185:
182:
172:
163:
160:
158:
153:
149:
145:
137:
129:
121:
112:
110:
106:
105:up to a point
100:
98:
94:
90:
81:
72:
69:
65:
60:
58:
54:
50:
46:
42:
38:
34:
30:
21:
2128:Cold cathode
2095:Storage tube
1985:Vacuum tubes
1934:Neutron tube
1909:Beam tetrode
1891:Vacuum tubes
1822:
1476:Power MOSFET
1322:
1296:
1277:, retrieved
1272:
1266:
1256:, retrieved
1251:
1245:
1210:
1206:
1196:
1191:, page 7-30
1180:
1175:
1165:, retrieved
1160:
1154:
1080:
1074:
1070:
1066:
1056:
1046:
1042:
1035:Output noise
1034:
1027:
1016:
1005:
999:
993:
988:
981:
977:
970:
965:
944:
926:
912:
905:
898:
889:
879:
869:
864:
860:
854:
739:is given by
733:
732:
724:
717:
710:
698:
697:
689:
681:
674:
667:
661:
653:
646:
639:
632:
625:
623:
609:
590:
578:
570:
563:
555:
541:
540:
513:
497:vacuum tubes
494:
480:
479:
450:
441:
420:
418:
409:
381:
374:
371:
367:
363:
359:
356:
353:
350:
345:
343:
339:
335:
326:tank circuit
321:
317:
313:
311:
296:
287:
272:Please help
260:
236:tap-changers
235:
231:
229:
212:
208:
204:
177:
161:
156:
154:
150:
146:
142:
104:
101:
86:
61:
37:feed-forward
28:
26:
2294:Transformer
2036:Sutton tube
1876:Charge pump
1729:Memory cell
1659:Zener diode
1621:Laser diode
1504:transistors
1386:transistors
1039:white noise
704:provides a
664:Zener diode
612:common base
501:transistors
425:Zener diode
396:three-phase
157:solid state
148:regulator.
97:zener diode
2388:Categories
2366:reed relay
2356:Parametron
2289:Thermistor
2267:resettable
2226:Connector
2187:Adjustable
2163:Nixie tube
2133:Crossatron
2100:Trochotron
2075:Iconoscope
2070:Charactron
2047:X-ray tube
1919:Compactron
1899:Acorn tube
1856:Buck–boost
1777:Solaristor
1639:Photodiode
1616:Gunn diode
1612:(CLD, CRD)
1394:Transistor
1279:2011-03-08
1258:2010-09-19
1167:2024-04-26
1147:References
974:voltage").
546:duty cycle
527:See also:
423:such as a
59:voltages.
2329:Capacitor
2173:Trigatron
2168:Thyratron
2158:Neon lamp
2085:Monoscope
1965:Phototube
1949:Pentagrid
1914:Barretter
1799:Trancitor
1794:Thyristor
1719:Memristor
1644:PIN diode
1421:(ChemFET)
1237:216305194
1037:(thermal
330:capacitor
261:does not
2351:Inductor
2321:Reactive
2299:Varistor
2279:Resistor
2257:Antifuse
2143:Ignitron
2138:Dekatron
2026:Klystron
2015:Gyrotron
1944:Nuvistor
1861:Split-pi
1747:(MOS IC)
1714:Memistor
1472:(MuGFET)
1466:(MOSFET)
1438:(FinFET)
1089:See also
680:, where
652:exceeds
566:inductor
437:resistor
89:resistor
2252:Ferrite
2220:Passive
2211:Varicap
2199:digital
2148:Krytron
1970:Tetrode
1955:Pentode
1809:Varicap
1790:(3D IC)
1766:RF CMOS
1670:devices
1444:(FGMOS)
1375:devices
1215:Bibcode
282:removed
267:sources
33:voltage
2284:Switch
1975:Triode
1939:Nonode
1904:Audion
1784:(SITh)
1668:Other
1635:(OLED)
1597:Diodes
1548:(LET)
1530:(FET)
1502:Other
1450:(IGBT)
1427:(CMOS)
1414:BioFET
1409:BiCMOS
1303:
1235:
1187:
1047:ripple
1041:) and
855:where
550:charge
214:coil.
2361:Relay
2334:types
2272:eFUSE
2043:(TWT)
2031:Maser
2022:(IOT)
2011:(CFA)
2000:(BWO)
1924:Diode
1871:SEPIC
1851:Boost
1804:TRIAC
1773:(SCR)
1736:(MOV)
1710:(LEC)
1629:(LED)
1588:(UJT)
1577:(SIT)
1571:(PUT)
1514:(BJT)
1483:(TFT)
1459:LDMOS
1454:ISFET
1233:S2CID
954:and U
594:noise
431:, or
93:diode
2304:Wire
2262:Fuse
1846:Buck
1699:(IC)
1687:DIAC
1623:(LD)
1492:UMOS
1487:VMOS
1404:PMOS
1399:NMOS
1384:MOS
1301:ISBN
1185:ISBN
1031:etc.
888:max
878:min
859:min
706:bias
517:78xx
312:The
265:any
263:cite
1866:Ćuk
1223:doi
1211:440
1051:RMS
980:or
797:max
781:min
766:min
657:out
629:out
377:THD
320:or
276:by
234:or
111:).
55:or
2390::
2240:RF
1989:RF
1287:^
1231:.
1221:.
1209:.
1205:.
958:.
956:in
935::
918:).
902:FE
823:FE
721:in
693:BE
685:BE
678:BE
673:−
650:in
636:in
427:,
394:A
316:,
57:DC
53:AC
27:A
1991:)
1987:(
1357:e
1350:t
1343:v
1309:.
1239:.
1225::
1217::
952:z
916:B
913:I
911:/
909:C
906:I
899:h
893:L
890:I
883:D
880:I
875:,
873:v
870:R
865:R
861:V
840:,
834:)
831:1
828:+
819:h
815:(
811:/
805:L
801:I
794:+
789:D
785:I
774:R
770:V
760:=
755:v
751:R
737:v
734:R
728:v
725:R
718:U
714:v
711:R
702:v
699:R
690:U
688:(
682:U
675:U
671:Z
668:U
654:U
647:U
643:L
640:R
633:U
626:U
303:)
297:(
292:)
288:(
284:.
270:.
Text is available under the Creative Commons Attribution-ShareAlike License. Additional terms may apply.