520:
502:
146:
220:(also known as dextro-TGA) is a cyanotic heart defect in which the aorta arises from the right ventricle and the pulmonary artery arises from the left ventricle. This switch causes deoxygenated blood from the right heart to be pumped immediately through the aorta and circulated throughout the body and the heart itself, bypassing the lungs altogether. In this same condition, the left heart continuously pumps oxygenated blood back into the lungs through the pulmonary artery, instead of out into the body's circulation as it normally would. In effect, two separate "parallel" circulatory systems are created. It is called a
75:
366:
51:
494:
419:: Catheterization is done if other diagnostic tests do not provide enough information to make a diagnosis, or if a neonate is unstable. During this procedure, a catheter is inserted in the artery or vein in the groin and makes its way up to the heart. Dye is used to visualize the heart’s structures on x-ray. It can also measure the pressures in the heart and lungs.
382:: An electrocardiogram (ECG) records the electrical activity of the heart through the use of electrodes that are placed on the body. The findings through this diagnostic method are not specific to only TGA. If TGA is present, rightward deviation of the QRS complex and right ventricular hypertrophy or biventricular hypertrophy may be noted.
250:
are connected in this condition. Complications can arise from the pressure change due to the fact that the right ventricle, which is adapted for pumping blood into the low-pressure pulmonary circulation, is being tasked with pumping blood at a much higher pressure against the high resistance of the
472:
Lifelong follow-up care with a cardiologist is needed. Most infants who undergo surgery have their symptoms relieved and are able to live a normal life. Potential complications that can occur include coronary artery problems, heart valves problems or irregular heart rhythms (arrhythmias).
447:
can also be performed, usually with a cardiac catheter instead of surgery, to enlarge a natural connection between the heart's upper chambers (atria). This will allow for the oxygen-rich and oxygen-poor blood to mix, resulting in improved oxygen delivery to the baby's body.
442:
open which allows for the mixing of the otherwise isolated pulmonary and systemic circuits. Thus, oxygenated blood that recirculates back to the lungs can mix with blood that circulates throughout the body and can keep the body oxygenated until surgery can be performed.
413:: An echocardiogram is an ultrasound of the heart that accurately assesses the heart’s structure and function, and can show the specific features of TGA, if present. This imaging modality allows for the definitive diagnosis of TGA to be made.
186:
Although "transposed" literally means "swapped", many types of TGV involve vessels that are in abnormal positions, while not actually being swapped with each other. The terms TGV and TGA are most commonly used in reference to
865:
850:
458:
is a surgery where the pulmonary artery and the aorta are moved to their normal positions. This is the most common surgery done to correct dextro-TGA, and is considered the definitive treatment. The
242:
in which the primary arteries are transposed, with the aorta anterior and to the left of the pulmonary artery, and the morphological left and right ventricles with their corresponding
246:
are also transposed. In other words, the right ventricle is on the left side of the heart and the left ventricle is on the right side of the heart. The systemic and the
309:
Symptoms may appear at birth or after birth. The severity of symptoms depends on the type of TGV, and the type and size of other heart defects that may be present (
153:
view showing discordant ventriculoarterial connections together with the presence of parallel, rather than crossing, great arteries arising from the ventricles.
987:
238:
Levo-Transposition of the great arteries (also known as Levo-TGA, congenitally corrected TGA, double discordance, or ventricular inversion) is a rare,
17:
321:). Most babies with TGA have blue skin color (cyanosis) in the first hours or days of their lives, since dextro-TGA is the more common type.
1340:
428:
All infants with TGA will need surgery to correct the defect. Life expectancy is only a few months if corrective surgery is not performed.
1038:
551:
536:
Abbreviations: RA=right atrium, RV=right ventricle, LV=left ventricle, PT=pulmonary trunk, LPA and RPA=left and right pulmonary artery.
217:
212:
188:
1043:
546:
233:
196:
980:
301:
When no other heart defects are present it is called 'simple' TGV; when other defects are present it is called 'complex' TGV.
818:
The morbid anatomy of some of the most important parts of the human body - Digital
Collections - National Library of Medicine
515:
Abbreviations: LV and RV=left and right ventricle, PT=pulmonary trunk, VSD=ventricular septal defect, PS=pulmonary stenosis.
880:
1116:
1075:
195:
in swapped positions; however, both terms are also commonly used, though to a slightly lesser extent, in reference to
1366:
973:
721:
Ferguson EC, Krishnamurthy R, Oldham SA (2007). "Classic imaging signs of congenital cardiovascular abnormalities".
1293:
1298:
1188:
1108:
1183:
1050:
1021:
1013:
462:
operation is an alternative surgical option when the arterial switch is not feasible due to the particular
157:
519:
501:
369:
X-ray showing characteristic finding in a transposition of the great vessels, called the egg on side sign.
145:
203:
are swapped; while other defects in this category are almost never referred to by either of these terms.
1090:
1080:
1026:
506:
455:
310:
279:
183:
depending on the nature and degree of the misplacement, and on which specific vessels are involved.
74:
1210:
1178:
891:
318:
283:
953:
466:
anatomy. This operation creates a tunnel (baffle) between the heart's two upper chambers (atria).
1335:
1205:
996:
416:
243:
95:
165:
1158:
1137:
239:
931:
1345:
1248:
1238:
1057:
247:
221:
1371:
1265:
1243:
1215:
1144:
1067:
314:
275:
271:
252:
137:), which is considered the most common congenital heart lesion that presents in neonates.
8:
1098:
1004:
869:
362:
of a pregnant mother is a risk factor that has been described for the fetus having TGV.
792:
765:
698:
663:
510:
180:
107:
103:
874:
628:
611:
169:
1200:
902:
797:
746:
738:
703:
685:
633:
556:
444:
439:
379:
359:
263:
In many cases, TGV is accompanied by other heart defects, the most common type being
200:
63:
388:: On chest X-ray (CXR), transposition of the great vessels typically shows a cardio-
264:
255:, since it is now in the position of where the left ventricle is typically located.
1330:
1325:
942:
787:
777:
730:
693:
675:
623:
531:
150:
114:
68:
578:
161:
1320:
1260:
1195:
1173:
896:
482:
463:
365:
267:
224:(CHD) because the newborn infant turns blue (cyanotic) from the lack of oxygen.
172:
907:
527:
523:
435:
410:
176:
118:
859:
1360:
1288:
1132:
782:
742:
689:
459:
1310:
1255:
1233:
965:
801:
750:
707:
680:
637:
397:
295:
99:
1303:
926:
734:
530:
giving rise to a vessel that bifurcates, which is thus identified as the
389:
385:
343:
110:
842:
1315:
948:
816:
766:"Surgery for transposition of great arteries: A historical perspective"
579:"Transposition of the great arteries: MedlinePlus Medical Encyclopedia"
92:
526:
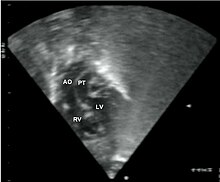
in transposition of the great arteries. This subcostal view shows the
937:
329:
287:
481:
Transposition of the Great
Vessels was first described in 1797 by
401:
336:
885:
854:
404:
126:
50:
291:
206:
122:
720:
227:
129:(pulmonary artery and aorta) belong to a sub-group called
493:
98:
involving an abnormal spatial arrangement of any of the
125:. Congenital heart diseases involving only the primary
832:
505:Echocardiography of a complex transposition with a
407:of the superior mediastinum represents the string.
58:Illustration of transposition of the great vessels
1358:
400:represents an egg on its side and the narrowed,
175:. The effects may range from a slight change in
661:
44:d-TGA, Congenital heart defect - transposition
981:
763:
657:
655:
653:
651:
649:
647:
573:
571:
1341:Anomalous aortic origin of a coronary artery
995:
605:
603:
601:
599:
988:
974:
644:
568:
552:Dextro-Transposition of the great arteries
218:Dextro-Transposition of the great arteries
213:dextro-Transposition of the great arteries
207:Dextro-Transposition of the great arteries
73:
49:
791:
781:
697:
679:
627:
596:
258:
547:Levo-Transposition of the great arteries
518:
500:
492:
364:
234:Levo-Transposition of the great arteries
228:Levo-Transposition of the great arteries
144:
814:
714:
14:
1359:
609:
497:Normal heart anatomy compared to d-TGA
969:
664:"Transposition of the great arteries"
612:"Transposition of the Great Arteries"
304:
199:– in which both the arteries and the
488:
131:transposition of the great arteries
24:
1076:Sinus venosus atrial septal defect
1034:Transposition of the great vessels
954:Transposition of the great vessels
85:Transposition of the great vessels
36:Transposition of the great vessels
25:
1383:
828:
668:Orphanet Journal of Rare Diseases
629:10.1161/circulationaha.105.592352
434:For newborns with transposition,
191:– in which the two main arteries
27:Group of congenital heart defects
222:cyanotic congenital heart defect
353:
1109:Atrioventricular septal defect
821:(The first American ed.).
808:
770:Annals of Pediatric Cardiology
757:
18:Transposition of great vessels
13:
1:
1051:Persistent truncus arteriosus
1022:Double outlet right ventricle
764:Marathe SP, Talwar S (2015).
662:Martins P, Castela E (2008).
562:
1014:Aortopulmonary septal defect
423:
392:silhouette appearing as an "
373:
7:
540:
10:
1388:
476:
231:
210:
1280:
1226:
1166:
1157:
1125:
1107:
1091:Ventricular septal defect
1089:
1066:
1012:
1003:
917:
836:
507:ventricular septal defect
456:arterial switch operation
438:can be given to keep the
311:ventricular septal defect
280:ventricular septal defect
160:vessels can present with
62:
57:
48:
40:
35:
1367:Congenital heart defects
997:Congenital heart defects
783:10.4103/0974-2069.157025
324:Other symptoms include:
319:patent ductus arteriosus
284:patent ductus arteriosus
140:
1336:Coronary artery anomaly
417:Cardiac catheterization
290:, or other defects, of
244:atrioventricular valves
1159:Valvular heart disease
1138:Cyanotic heart disease
1081:Lutembacher's syndrome
681:10.1186/1750-1172-3-27
537:
516:
498:
370:
335:Difficulty breathing (
259:Simple and complex TGV
240:acyanotic heart defect
179:to an interruption in
154:
1346:Ventricular inversion
1058:Aortopulmonary window
1027:Taussig–Bing syndrome
522:
504:
496:
368:
298:may also be present.
248:pulmonary circulation
148:
1145:Eisenmenger syndrome
1068:Atrial septal defect
735:10.1148/rg.275065148
315:atrial septal defect
276:patent foramen ovale
272:atrial septal defect
253:systemic circulation
1099:Tetralogy of Fallot
1005:Heart septal defect
918:External resources
815:Baillie M (1795).
610:Warnes CA (2006).
538:
517:
511:pulmonary stenosis
499:
371:
305:Symptoms and signs
166:ventriculoarterial
155:
1354:
1353:
1276:
1275:
1216:Ebstein's anomaly
1153:
1152:
963:
962:
622:(24): 2699–2709.
557:Mustard Procedure
489:Additional images
445:Atrial septostomy
440:ductus arteriosus
380:Electrocardiogram
360:diabetes mellitus
342:Fast heart rate (
151:echocardiographic
82:
81:
30:Medical condition
16:(Redirected from
1379:
1331:Brugada syndrome
1326:Crisscross heart
1196:tricuspid valves
1174:pulmonary valves
1164:
1163:
1010:
1009:
990:
983:
976:
967:
966:
834:
833:
823:
822:
812:
806:
805:
795:
785:
761:
755:
754:
718:
712:
711:
701:
683:
659:
642:
641:
631:
607:
594:
593:
591:
589:
575:
532:pulmonary artery
396:", in which the
328:Fast breathing (
115:pulmonary artery
91:) is a group of
78:
77:
69:Medical genetics
53:
33:
32:
21:
1387:
1386:
1382:
1381:
1380:
1378:
1377:
1376:
1357:
1356:
1355:
1350:
1321:Cor triatriatum
1287:Underdeveloped
1272:
1222:
1149:
1121:
1103:
1085:
1062:
999:
994:
964:
959:
958:
913:
912:
845:
831:
826:
813:
809:
762:
758:
719:
715:
660:
645:
608:
597:
587:
585:
583:medlineplus.gov
577:
576:
569:
565:
543:
535:
514:
491:
483:Matthew Baillie
479:
464:coronary artery
432:Before surgery:
426:
394:egg on a string
376:
356:
307:
261:
236:
230:
215:
209:
143:
119:pulmonary veins
72:
31:
28:
23:
22:
15:
12:
11:
5:
1385:
1375:
1374:
1369:
1352:
1351:
1349:
1348:
1343:
1338:
1333:
1328:
1323:
1318:
1313:
1308:
1307:
1306:
1301:
1296:
1289:heart chambers
1284:
1282:
1278:
1277:
1274:
1273:
1271:
1270:
1269:
1268:
1263:
1253:
1252:
1251:
1246:
1241:
1230:
1228:
1224:
1223:
1221:
1220:
1219:
1218:
1213:
1208:
1203:
1193:
1192:
1191:
1186:
1181:
1170:
1168:
1161:
1155:
1154:
1151:
1150:
1148:
1147:
1142:
1141:
1140:
1129:
1127:
1123:
1122:
1120:
1119:
1113:
1111:
1105:
1104:
1102:
1101:
1095:
1093:
1087:
1086:
1084:
1083:
1078:
1072:
1070:
1064:
1063:
1061:
1060:
1054:
1053:
1048:
1047:
1046:
1041:
1031:
1030:
1029:
1018:
1016:
1007:
1001:
1000:
993:
992:
985:
978:
970:
961:
960:
957:
956:
945:
934:
922:
921:
919:
915:
914:
911:
910:
899:
888:
877:
862:
846:
841:
840:
838:
837:Classification
830:
829:External links
827:
825:
824:
807:
756:
729:(5): 1323–34.
713:
643:
595:
566:
564:
561:
560:
559:
554:
549:
542:
539:
528:left ventricle
524:Echocardiogram
490:
487:
478:
475:
470:After surgery:
436:prostaglandins
425:
422:
421:
420:
414:
411:Echocardiogram
408:
398:enlarged heart
383:
375:
372:
355:
352:
351:
350:
347:
340:
333:
306:
303:
260:
257:
232:Main article:
229:
226:
211:Main article:
208:
205:
177:blood pressure
142:
139:
80:
79:
66:
60:
59:
55:
54:
46:
45:
42:
38:
37:
29:
26:
9:
6:
4:
3:
2:
1384:
1373:
1370:
1368:
1365:
1364:
1362:
1347:
1344:
1342:
1339:
1337:
1334:
1332:
1329:
1327:
1324:
1322:
1319:
1317:
1314:
1312:
1309:
1305:
1302:
1300:
1297:
1295:
1292:
1291:
1290:
1286:
1285:
1283:
1279:
1267:
1266:regurgitation
1264:
1262:
1259:
1258:
1257:
1256:mitral valves
1254:
1250:
1247:
1245:
1244:insufficiency
1242:
1240:
1237:
1236:
1235:
1234:aortic valves
1232:
1231:
1229:
1225:
1217:
1214:
1212:
1209:
1207:
1206:regurgitation
1204:
1202:
1199:
1198:
1197:
1194:
1190:
1187:
1185:
1184:insufficiency
1182:
1180:
1177:
1176:
1175:
1172:
1171:
1169:
1165:
1162:
1160:
1156:
1146:
1143:
1139:
1136:
1135:
1134:
1133:Cardiac shunt
1131:
1130:
1128:
1124:
1118:
1117:Ostium primum
1115:
1114:
1112:
1110:
1106:
1100:
1097:
1096:
1094:
1092:
1088:
1082:
1079:
1077:
1074:
1073:
1071:
1069:
1065:
1059:
1056:
1055:
1052:
1049:
1045:
1042:
1040:
1037:
1036:
1035:
1032:
1028:
1025:
1024:
1023:
1020:
1019:
1017:
1015:
1011:
1008:
1006:
1002:
998:
991:
986:
984:
979:
977:
972:
971:
968:
955:
951:
950:
946:
944:
940:
939:
935:
933:
929:
928:
924:
923:
920:
916:
909:
905:
904:
900:
898:
894:
893:
889:
887:
883:
882:
878:
876:
872:
871:
867:
863:
861:
857:
856:
852:
848:
847:
844:
839:
835:
820:
819:
811:
803:
799:
794:
789:
784:
779:
775:
771:
767:
760:
752:
748:
744:
740:
736:
732:
728:
724:
723:Radiographics
717:
709:
705:
700:
695:
691:
687:
682:
677:
673:
669:
665:
658:
656:
654:
652:
650:
648:
639:
635:
630:
625:
621:
617:
613:
606:
604:
602:
600:
584:
580:
574:
572:
567:
558:
555:
553:
550:
548:
545:
544:
533:
529:
525:
521:
512:
508:
503:
495:
486:
484:
474:
471:
467:
465:
461:
460:atrial switch
457:
453:
449:
446:
441:
437:
433:
429:
418:
415:
412:
409:
406:
403:
399:
395:
391:
387:
384:
381:
378:
377:
367:
363:
361:
348:
345:
341:
338:
334:
331:
327:
326:
325:
322:
320:
316:
312:
302:
299:
297:
293:
289:
285:
281:
277:
273:
269:
266:
256:
254:
249:
245:
241:
235:
225:
223:
219:
214:
204:
202:
198:
194:
190:
184:
182:
178:
174:
171:
170:arteriovenous
167:
163:
159:
152:
147:
138:
136:
132:
128:
124:
120:
116:
112:
109:
105:
101:
100:great vessels
97:
96:heart defects
94:
90:
86:
76:
70:
67:
65:
61:
56:
52:
47:
43:
39:
34:
19:
1311:Dextrocardia
1126:Consequences
1033:
947:
936:
925:
901:
890:
879:
864:
849:
817:
810:
776:(2): 122–8.
773:
769:
759:
726:
722:
716:
671:
667:
619:
615:
586:. Retrieved
582:
480:
469:
468:
451:
450:
431:
430:
427:
393:
358:Preexisting
357:
354:Risk factors
349:Poor feeding
323:
308:
300:
265:intracardiac
262:
237:
216:
192:
185:
156:
134:
130:
88:
84:
83:
1372:Neonatology
1304:Uhl anomaly
927:MedlinePlus
616:Circulation
390:mediastinal
386:Chest X-ray
344:tachycardia
181:circulation
173:discordance
162:atriovenous
111:venae cavae
41:Other names
1361:Categories
1316:Levocardia
949:Patient UK
903:DiseasesDB
563:References
274:including
201:ventricles
189:dextro-TGA
158:Transposed
149:Subcostal
93:congenital
938:eMedicine
743:0271-5333
690:1750-1172
424:Treatment
374:Diagnosis
330:tachypnea
64:Specialty
1261:stenosis
1249:bicuspid
1239:stenosis
1211:stenosis
1179:stenosis
943:ped/2548
802:26085763
751:17848694
708:18851735
638:17159076
541:See also
452:Surgery:
402:atrophic
288:Stenosis
270:such as
197:levo-TGA
127:arteries
108:inferior
104:superior
1201:atresia
1189:absence
897:D014188
793:4453180
699:2577629
477:History
337:dyspnea
296:vessels
294:and/or
168:and/or
106:and/or
1039:dextro
932:001568
886:608808
800:
790:
749:
741:
706:
696:
688:
674:: 27.
636:
588:28 May
405:thymus
292:valves
282:, and
268:shunts
121:, and
71:
1294:right
1281:Other
1167:Right
908:13259
875:745.1
860:Q20.3
317:, or
141:Types
123:aorta
1299:left
1227:Left
1044:levo
892:MeSH
881:OMIM
870:9-CM
798:PMID
747:PMID
739:ISSN
704:PMID
686:ISSN
634:PMID
590:2019
509:and
454:The
866:ICD
851:ICD
788:PMC
778:doi
731:doi
694:PMC
676:doi
624:doi
620:114
193:are
135:TGA
89:TGV
1363::
952::
941::
930::
906::
895::
884::
873::
858::
855:10
796:.
786:.
772:.
768:.
745:.
737:.
727:27
725:.
702:.
692:.
684:.
670:.
666:.
646:^
632:.
618:.
614:.
598:^
581:.
570:^
485:.
313:,
286:.
278:,
164:,
117:,
113:,
102::
989:e
982:t
975:v
868:-
853:-
843:D
804:.
780::
774:8
753:.
733::
710:.
678::
672:3
640:.
626::
592:.
534:.
513:.
346:)
339:)
332:)
133:(
87:(
20:)
Text is available under the Creative Commons Attribution-ShareAlike License. Additional terms may apply.