17:
443:. For practical purposes, the transmission medium is often chosen to be a fluid—usually water—in which a microscopic object can be immersed. The object, when brought close to the interface, is expected to scatter light proportional to the intensity of the field at its height,
720:
Flicker, Scott G., Jennifer L. Tipa, and Stacy G. Bike. "Quantifying double-layer repulsion between a colloidal sphere and a glass plate using total internal reflection microscopy." Journal of colloid and interface science 158.2 (1993):
441:
463:. Since the penetration depth of the evanescent field is on the order of hundreds of nanometers, this technique is among the most sensitive for tracking displacements in the direction perpendicular to a surface.
480:. Rather than relying on optical scattering, however, often fluorophores are introduced into the sample for more selective visualization in biological applications. This popular imaging technique is known as a
582:
159:
492:
Using a calibrated evanescent wave, the position of a colloidal particle or microscopic probe may be tracked with nanometer precision by monitoring the intensity of light scattered via
340:
730:
Bevan, Michael A., and Dennis C. Prieve. "Hindered diffusion of colloidal particles very near to a wall: Revisited." The
Journal of Chemical Physics 113.3 (2000): 1228-1236.
243:
79:
693:
Prieve, Dennis C., and Nasser A. Frej. "Total internal reflection microscopy: a quantitative tool for the measurement of colloidal forces." Langmuir 6.2 (1990): 396-403.
216:
189:
279:
711:
Walz, John Y. "Measuring particle interactions with total internal reflection microscopy." Current opinion in colloid & interface science 2.6 (1997): 600-606.
348:
630:
606:
461:
636:, one can obtain the potential energy profile of interactions between the particle and a surface. In this manner, sub-picoNewton forces may be detected.
671:
481:
499:
For instance, by collecting the time-independent position probability distribution of a probe particle in thermal equilibrium, and inverting the
493:
639:
On the other hand, diffusive dynamics of a cell or a colloid can be deduced from its position time-series obtained via TIRM or another
609:
509:
496:. Detailed dynamics of the probe or particle can then be obtained, either in thermal equilibrium or non-equilibrium conditions.
702:
Prieve, Dennis C. "Measurement of colloidal forces with TIRM." Advances in
Colloid and Interface Science 82.1 (1999): 93-125.
248:
Under conditions of total internal reflection, the electromagnetic field in the transmission medium takes on the form of an
50:
of light occurs at the interface between materials of differing indices of refraction at incident angles greater than the
87:
500:
51:
27:
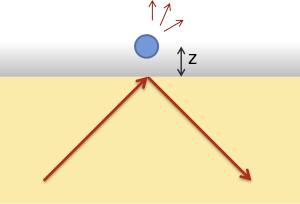
is a specialized optical imaging technique for object tracking and detection utilizing the light scattered from an
476:
The thin excitation region of an evanescent field allows for wide-field imaging of a select sample area with high
287:
666:
47:
640:
221:
57:
656:
477:
36:
436:{\displaystyle \beta ={\frac {4\pi }{\lambda }}{\sqrt {(n_{1}\sin(\theta ))^{2}-n_{2}^{2}}}}
194:
167:
255:
8:
746:
633:
615:
591:
446:
16:
28:
661:
249:
740:
643:
method. Hydrodynamic coupling effects resulting in a particle's reduced
32:
644:
647:
in the vicinity of a solid interface have been studied in this way.
281:
decays exponentially with distance from the interface such that,
577:{\displaystyle p(z)={\frac {1}{Z}}e^{-{\frac {V(z)}{kT}}}}
39:
and a high spatial resolution in the vertical dimension.
20:
Scattering of an evanescent field by a probe particle.
618:
594:
512:
449:
351:
290:
258:
224:
197:
170:
90:
60:
154:{\displaystyle \theta _{c}=\sin ^{-1}(n_{2}/n_{1})}
624:
600:
576:
455:
435:
334:
273:
237:
210:
183:
153:
73:
672:Total internal reflection fluorescence microscopy
482:Total internal reflection fluorescence microscopy
738:
245:is measured from the normal to the interface.
218:the index of the transmission medium and
191:is the index of the incident medium and
15:
739:
335:{\displaystyle I(z)=I_{0}e^{-\beta z}}
35:interface. Its advantages are a high
689:
687:
494:frustrated total internal reflection
487:
25:Total internal reflection microscopy
13:
14:
758:
684:
466:
724:
714:
705:
696:
558:
552:
522:
516:
501:Maxwell–Boltzmann distribution
404:
400:
394:
375:
300:
294:
268:
262:
148:
120:
1:
677:
42:
7:
650:
238:{\displaystyle \theta _{c}}
74:{\displaystyle \theta _{c}}
10:
763:
471:
667:Total internal reflection
48:Total internal reflection
626:
602:
578:
457:
437:
336:
275:
239:
212:
185:
155:
75:
21:
657:Dark-field microscopy
627:
603:
579:
478:signal-to-noise ratio
458:
438:
337:
276:
240:
213:
211:{\displaystyle n_{2}}
186:
184:{\displaystyle n_{1}}
156:
76:
37:signal-to-noise ratio
31:in the vicinity of a
19:
616:
592:
510:
447:
349:
288:
274:{\displaystyle I(z)}
256:
222:
195:
168:
88:
58:
430:
634:Boltzmann constant
622:
610:partition function
598:
574:
453:
433:
416:
332:
271:
252:, whose intensity
235:
208:
181:
151:
71:
22:
641:particle-tracking
625:{\displaystyle k}
601:{\displaystyle Z}
570:
536:
488:Particle Tracking
456:{\displaystyle z}
431:
371:
754:
731:
728:
722:
718:
712:
709:
703:
700:
694:
691:
631:
629:
628:
623:
607:
605:
604:
599:
583:
581:
580:
575:
573:
572:
571:
569:
561:
547:
537:
529:
462:
460:
459:
454:
442:
440:
439:
434:
432:
429:
424:
412:
411:
387:
386:
374:
372:
367:
359:
341:
339:
338:
333:
331:
330:
315:
314:
280:
278:
277:
272:
244:
242:
241:
236:
234:
233:
217:
215:
214:
209:
207:
206:
190:
188:
187:
182:
180:
179:
160:
158:
157:
152:
147:
146:
137:
132:
131:
116:
115:
100:
99:
80:
78:
77:
72:
70:
69:
29:evanescent field
762:
761:
757:
756:
755:
753:
752:
751:
737:
736:
735:
734:
729:
725:
719:
715:
710:
706:
701:
697:
692:
685:
680:
662:Evanescent wave
653:
617:
614:
613:
593:
590:
589:
562:
548:
546:
542:
538:
528:
511:
508:
507:
490:
474:
469:
448:
445:
444:
425:
420:
407:
403:
382:
378:
373:
360:
358:
350:
347:
346:
320:
316:
310:
306:
289:
286:
285:
257:
254:
253:
250:evanescent wave
229:
225:
223:
220:
219:
202:
198:
196:
193:
192:
175:
171:
169:
166:
165:
142:
138:
133:
127:
123:
108:
104:
95:
91:
89:
86:
85:
65:
61:
59:
56:
55:
45:
12:
11:
5:
760:
750:
749:
733:
732:
723:
713:
704:
695:
682:
681:
679:
676:
675:
674:
669:
664:
659:
652:
649:
621:
597:
586:
585:
568:
565:
560:
557:
554:
551:
545:
541:
535:
532:
527:
524:
521:
518:
515:
489:
486:
473:
470:
468:
465:
452:
428:
423:
419:
415:
410:
406:
402:
399:
396:
393:
390:
385:
381:
377:
370:
366:
363:
357:
354:
343:
342:
329:
326:
323:
319:
313:
309:
305:
302:
299:
296:
293:
270:
267:
264:
261:
232:
228:
205:
201:
178:
174:
162:
161:
150:
145:
141:
136:
130:
126:
122:
119:
114:
111:
107:
103:
98:
94:
68:
64:
52:critical angle
44:
41:
9:
6:
4:
3:
2:
759:
748:
745:
744:
742:
727:
717:
708:
699:
690:
688:
683:
673:
670:
668:
665:
663:
660:
658:
655:
654:
648:
646:
642:
637:
635:
619:
611:
595:
566:
563:
555:
549:
543:
539:
533:
530:
525:
519:
513:
506:
505:
504:
502:
497:
495:
485:
483:
479:
464:
450:
426:
421:
417:
413:
408:
397:
391:
388:
383:
379:
368:
364:
361:
355:
352:
327:
324:
321:
317:
311:
307:
303:
297:
291:
284:
283:
282:
265:
259:
251:
246:
230:
226:
203:
199:
176:
172:
143:
139:
134:
128:
124:
117:
112:
109:
105:
101:
96:
92:
84:
83:
82:
66:
62:
53:
49:
40:
38:
34:
30:
26:
18:
726:
716:
707:
698:
638:
587:
498:
491:
475:
467:Applications
344:
247:
163:
46:
24:
23:
747:Microscopy
678:References
43:Background
33:dielectric
645:diffusion
544:−
414:−
398:θ
392:
369:λ
365:π
353:β
325:β
322:−
227:θ
118:
110:−
93:θ
63:θ
741:Category
721:317-325.
651:See also
81:, where
608:is the
472:Imaging
612:, and
588:where
345:with
632:the
164:and
389:sin
106:sin
743::
686:^
503:,
484:.
54:,
620:k
596:Z
584:,
567:T
564:k
559:)
556:z
553:(
550:V
540:e
534:Z
531:1
526:=
523:)
520:z
517:(
514:p
451:z
427:2
422:2
418:n
409:2
405:)
401:)
395:(
384:1
380:n
376:(
362:4
356:=
328:z
318:e
312:0
308:I
304:=
301:)
298:z
295:(
292:I
269:)
266:z
263:(
260:I
231:c
204:2
200:n
177:1
173:n
149:)
144:1
140:n
135:/
129:2
125:n
121:(
113:1
102:=
97:c
67:c
Text is available under the Creative Commons Attribution-ShareAlike License. Additional terms may apply.