1766:
78:
42:
61:
that may be simultaneously accessed by multiple programs with an intent to provide communication among them or avoid redundant copies. Shared memory is an efficient means of passing data between programs. Depending on context, programs may run on a single processor or on multiple separate processors.
138:
A shared memory system is relatively easy to program since all processors share a single view of data and the communication between processors can be as fast as memory accesses to the same location. The issue with shared memory systems is that many CPUs need fast access to memory and will likely
429:
For programming languages with POSIX bindings (say, C/C++), shared memory regions can be created and accessed by calling the functions provided by the operating system. Other programming languages may have their own ways of using these operating facilities for similar effect. For example,
356:
is persistent. It stays in the system until explicitly removed by a process. This has a drawback in that if the process crashes and fails to clean up shared memory it will stay until system shutdown; that limitation is not present in an
Android-specific implementation dubbed
158:
lack of data coherence: whenever one cache is updated with information that may be used by other processors, the change needs to be reflected to the other processors, otherwise the different processors will be working with incoherent data. Such
302:
are generally held in memory once and mapped to multiple processes, and only pages that had to be customized for the individual process (because a symbol resolved differently there) are duplicated, usually with a mechanism known as
163:
protocols can, when they work well, provide extremely high-performance access to shared information between multiple processors. On the other hand, they can sometimes become overloaded and become a bottleneck to
277:). On the other hand, it is less scalable, as for example the communicating processes must be running on the same machine (of other IPC methods, only Internet domain sockets—not Unix domain sockets—can use a
349:. Unix System V provides an API for shared memory as well. This uses shmget from sys/shm.h. BSD systems provide "anonymous mapped memory" which can be used by several processes.
265:
Since both processes can access the shared memory area like regular working memory, this is a very fast way of communication (as opposed to other mechanisms of IPC such as
1092:
769:
249:
a method of conserving memory space by directing accesses to what would ordinarily be copies of a piece of data to a single instance instead, by using
377:, more specifically as a world-writable directory (a directory in which every user of the system can create files) that is stored in memory. Both the
310:
Compared to multiple address space operating systems, memory sharing -- especially of sharing procedures or pointer-based structures -- is simpler in
1182:
604:
The POSIX interprocess communication (IPC) is part of the POSIX:XSI Extension and has its origin in Unix System V interprocess communication.
1034:
281:), and care must be taken to avoid issues if processes sharing memory are running on separate CPUs and the underlying architecture is not
1816:
902:
762:
958:
204:
1163:
591:
525:
311:
1203:
1801:
1430:
755:
292:
on Unix systems, or inside the IStream object returned by CoMarshalInterThreadInterfaceInStream in the COM libraries under
496:
1453:
333:
from sys/mman.h. POSIX interprocess communication (part of the POSIX:XSI Extension) includes the shared-memory functions
738:, Ch. 12 from book by Richard Stevens "UNIX Network Programming, Volume 2, Second Edition: Interprocess Communications".
1342:
1198:
385:
based distributions include it by default. Support for this type of RAM disk is completely optional within the kernel
370:
API for mapping files into memory; a mapping can be shared, allowing the file's contents to be used as shared memory.
1448:
1425:
917:
677:
466:
188:
81:
1027:
307:
that transparently copies the page when a write is attempted, and then lets the write succeed on the private copy.
1420:
1235:
1791:
1527:
1441:
1390:
922:
131:
413:
Some C++ libraries provide a portable and object-oriented access to shared memory functionality. For example,
1806:
1751:
1585:
1436:
1123:
134:(COMA): the local memories for the processors at each node is used as cache instead of as actual main memory.
1811:
1770:
1716:
1176:
1020:
778:
299:
235:
17:
1796:
1695:
1490:
1375:
1337:
1187:
1077:
373:
Linux distributions based on the 2.6 kernel and later offer /dev/shm as shared memory in the form of a
897:
1711:
1690:
1635:
1522:
1512:
1485:
1347:
912:
456:
215:
125:
66:
1665:
1291:
1230:
1143:
689:
615:
561:
147:
access time degradation: when several processors try to access the same memory location it causes
1726:
1721:
1580:
1171:
844:
654:
491:
414:
105:
583:
1465:
1397:
1301:
1193:
1148:
879:
461:
200:
85:
1557:
1517:
1470:
1460:
1255:
1118:
1057:
119:
28:
288:
IPC by shared memory is used for example to transfer images between the application and the
155:. Shared memory computers cannot scale very well. Most of them have ten or fewer processors;
1497:
1385:
1380:
1370:
1357:
1153:
541:
243:
101:
58:
253:
mappings or with explicit support of the program in question. This is most often used for
8:
1660:
1615:
1415:
1281:
973:
735:
239:
148:
1685:
1534:
1507:
1332:
1296:
1286:
1245:
1087:
1067:
1062:
1043:
978:
884:
867:
791:
576:
451:
386:
270:
211:
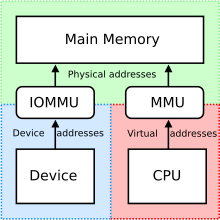
207:(IOMMU) of the GPU have to share certain characteristics, like a common address space.
701:
1731:
1407:
1365:
1260:
587:
521:
293:
628:
238:(IPC), i.e. a way of exchanging data between programs running at the same time. One
1741:
1540:
1475:
1322:
1138:
1133:
1128:
1097:
795:
545:
481:
278:
258:
50:
32:
128:(NUMA): memory access time depends on the memory location relative to a processor;
1605:
1545:
1480:
1327:
1317:
1250:
1240:
1082:
1072:
839:
819:
486:
471:
289:
282:
169:
160:
109:
65:
Using memory for communication inside a single program, e.g. among its multiple
1736:
1552:
1209:
1102:
862:
834:
418:
254:
250:
191:(processor architecture that integrates different types of processors, such as
181:
177:
747:
1785:
1625:
953:
824:
809:
714:
378:
304:
173:
152:
741:
729:
540:
Jeffrey S. Chase; Henry M. Levy; Michael J. Feeley; and Edward D. Lazowska.
1225:
854:
476:
140:
549:
1746:
892:
652:
1001:
927:
829:
658:
405:
functions to map a region of a file into memory in multiple processes.
266:
1620:
1595:
1012:
1670:
1650:
1575:
991:
542:"Sharing and Protection in a Single Address Space Operating System"
374:
1675:
1655:
1630:
1265:
963:
932:
578:
Unix systems programming: communication, concurrency, and threads
77:
41:
1645:
1640:
382:
122:(UMA): all the processors share the physical memory uniformly;
996:
986:
937:
907:
439:
322:
274:
89:
45:
An illustration of a shared memory system of three processors
92:
of the GPU have an identical pageable virtual address space.
1680:
1610:
1600:
948:
943:
814:
787:
366:
38:
Computer memory that can be accessed by multiple processes
1590:
1567:
435:
431:
196:
192:
518:
Advanced
Computer Architecture and Parallel Processing
325:
provides a standardized API for using shared memory,
151:. Trying to access nearby memory locations may cause
515:
84:
defines a special case of memory sharing, where the
653:Christoph Rohland; Hugh Dickins; KOSAKI Motohiro.
575:
1783:
516:El-Rewini, Hesham; Abd-El-Barr, Mostafa (2005).
417:contains the Boost.Interprocess C++ Library and
104:(RAM) that can be accessed by several different
777:
424:
317:
573:
184:can be used to dampen the bottleneck-effects.
1028:
763:
744:, An open source, shared memory hash table.
1035:
1021:
770:
756:
582:(2 ed.). Prentice Hall PTR. p.
574:Robbins, Kay A.; Robbins, Steven (2003).
408:
76:
69:, is also referred to as shared memory.
40:
218:, each having a similar set of issues.
100:refers to a (typically large) block of
14:
1784:
1042:
520:. Wiley-Interscience. pp. 77–80.
312:single address space operating systems
210:The alternatives to shared memory are
1016:
751:
392:
438:to create shared memory, similar to
618:from the Single Unix Specification.
497:Von Neumann Architecture Bottleneck
205:input–output memory management unit
24:
1817:Distributed computing architecture
715:Shared Memory Functions in PHP-API
564:from the Single Unix Specification
421:provides the QSharedMemory class.
25:
1828:
723:
467:Heterogeneous System Architecture
246:which other processes can access;
189:Heterogeneous System Architecture
1765:
1764:
1236:Analysis of parallel algorithms
708:
702:"QSharedMemory Class Reference"
694:
143:, which has two complications:
115:Shared memory systems may use:
690:Boost.Interprocess C++ Library
683:
671:
646:
621:
609:
567:
555:
534:
509:
221:
132:cache-only memory architecture
110:multiprocessor computer system
72:
13:
1:
1183:Simultaneous and heterogenous
502:
352:The shared memory created by
1771:Category: Parallel computing
678:Creating Named Shared Memory
425:Programming language support
318:Support on Unix-like systems
7:
1802:Inter-process communication
779:Inter-process communication
445:
236:inter-process communication
199:, with shared memory), the
10:
1833:
1078:High-performance computing
736:Shared Memory Introduction
26:
1760:
1712:Automatic parallelization
1704:
1566:
1406:
1356:
1348:Application checkpointing
1310:
1274:
1218:
1162:
1111:
1050:
972:
878:
825:Message queue and mailbox
802:
785:
629:"Android Kernel Features"
562:Documentation of shm_open
457:Distributed shared memory
329:. This uses the function
216:distributed shared memory
203:(MMU) of the CPU and the
126:non-uniform memory access
397:On Windows, one can use
364:POSIX also provides the
106:central processing units
27:Not to be confused with
1727:Embarrassingly parallel
1722:Deterministic algorithm
492:Shared snapshot objects
242:will create an area in
1442:Associative processing
1398:Non-blocking algorithm
1204:Clustered multi-thread
616:Shared memory facility
462:Shared graphics memory
409:Cross-platform support
226:In computer software,
201:memory management unit
96:In computer hardware,
93:
46:
1792:Computer architecture
1558:Hardware acceleration
1471:Superscalar processor
1461:Dataflow architecture
1058:Distributed computing
550:10.1145/195792.195795
120:uniform memory access
80:
44:
29:Overlay (programming)
1807:Concurrent computing
1437:Pipelined processing
1386:Explicit parallelism
1381:Implicit parallelism
1371:Dataflow programming
102:random access memory
1661:Parallel Extensions
1466:Pipelined processor
327:POSIX Shared Memory
271:Unix domain sockets
88:of the CPU and the
1812:Parallel computing
1535:Massively parallel
1513:distributed shared
1333:Cache invalidation
1297:Instruction window
1088:Manycore processor
1068:Massively parallel
1063:Parallel computing
1044:Parallel computing
974:Software libraries
815:Memory-mapped file
452:Distributed memory
393:Support on Windows
387:configuration file
212:distributed memory
168:Technologies like
94:
47:
1797:Memory management
1779:
1778:
1732:Parallel slowdown
1366:Stream processing
1256:Karp–Flatt metric
1010:
1009:
940:(various methods)
796:computer programs
730:IPC:Shared Memory
593:978-0-13-042411-2
527:978-0-471-46740-3
399:CreateFileMapping
300:Dynamic libraries
170:crossbar switches
16:(Redirected from
1824:
1768:
1767:
1742:Software lockout
1541:Computer cluster
1476:Vector processor
1431:Array processing
1416:Flynn's taxonomy
1323:Memory coherence
1098:Computer network
1037:
1030:
1023:
1014:
1013:
772:
765:
758:
749:
748:
732:by Dave Marshall
717:
712:
706:
705:
698:
692:
687:
681:
675:
669:
668:
666:
665:
650:
644:
643:
641:
639:
625:
619:
613:
607:
606:
601:
600:
581:
571:
565:
559:
553:
538:
532:
531:
513:
482:Execute in place
404:
400:
369:
360:
355:
348:
344:
340:
336:
332:
279:computer network
259:Execute in place
255:shared libraries
51:computer science
33:Overlapping code
21:
1832:
1831:
1827:
1826:
1825:
1823:
1822:
1821:
1782:
1781:
1780:
1775:
1756:
1700:
1606:Coarray Fortran
1562:
1546:Beowulf cluster
1402:
1352:
1343:Synchronization
1328:Cache coherence
1318:Multiprocessing
1306:
1270:
1251:Cost efficiency
1246:Gustafson's law
1214:
1158:
1107:
1083:Multiprocessing
1073:Cloud computing
1046:
1041:
1011:
1006:
976:
968:
882:
874:
820:Message passing
798:
790:exchange among
781:
776:
726:
721:
720:
713:
709:
700:
699:
695:
688:
684:
676:
672:
663:
661:
651:
647:
637:
635:
627:
626:
622:
614:
610:
598:
596:
594:
572:
568:
560:
556:
539:
535:
528:
514:
510:
505:
487:Shared register
472:Global variable
448:
427:
411:
402:
398:
395:
365:
358:
353:
346:
342:
338:
334:
330:
320:
224:
161:cache coherence
75:
39:
36:
23:
22:
15:
12:
11:
5:
1830:
1820:
1819:
1814:
1809:
1804:
1799:
1794:
1777:
1776:
1774:
1773:
1761:
1758:
1757:
1755:
1754:
1749:
1744:
1739:
1737:Race condition
1734:
1729:
1724:
1719:
1714:
1708:
1706:
1702:
1701:
1699:
1698:
1693:
1688:
1683:
1678:
1673:
1668:
1663:
1658:
1653:
1648:
1643:
1638:
1633:
1628:
1623:
1618:
1613:
1608:
1603:
1598:
1593:
1588:
1583:
1578:
1572:
1570:
1564:
1563:
1561:
1560:
1555:
1550:
1549:
1548:
1538:
1532:
1531:
1530:
1525:
1520:
1515:
1510:
1505:
1495:
1494:
1493:
1488:
1481:Multiprocessor
1478:
1473:
1468:
1463:
1458:
1457:
1456:
1451:
1446:
1445:
1444:
1439:
1434:
1423:
1412:
1410:
1404:
1403:
1401:
1400:
1395:
1394:
1393:
1388:
1383:
1373:
1368:
1362:
1360:
1354:
1353:
1351:
1350:
1345:
1340:
1335:
1330:
1325:
1320:
1314:
1312:
1308:
1307:
1305:
1304:
1299:
1294:
1289:
1284:
1278:
1276:
1272:
1271:
1269:
1268:
1263:
1258:
1253:
1248:
1243:
1238:
1233:
1228:
1222:
1220:
1216:
1215:
1213:
1212:
1210:Hardware scout
1207:
1201:
1196:
1191:
1185:
1180:
1174:
1168:
1166:
1164:Multithreading
1160:
1159:
1157:
1156:
1151:
1146:
1141:
1136:
1131:
1126:
1121:
1115:
1113:
1109:
1108:
1106:
1105:
1103:Systolic array
1100:
1095:
1090:
1085:
1080:
1075:
1070:
1065:
1060:
1054:
1052:
1048:
1047:
1040:
1039:
1032:
1025:
1017:
1008:
1007:
1005:
1004:
999:
994:
989:
983:
981:
970:
969:
967:
966:
961:
956:
951:
946:
941:
935:
930:
925:
920:
915:
910:
905:
900:
895:
889:
887:
876:
875:
873:
872:
871:
870:
865:
857:
852:
847:
842:
837:
835:Anonymous pipe
832:
827:
822:
817:
812:
806:
804:
800:
799:
786:
783:
782:
775:
774:
767:
760:
752:
746:
745:
742:SharedHashFile
739:
733:
725:
724:External links
722:
719:
718:
707:
693:
682:
670:
645:
620:
608:
592:
566:
554:
533:
526:
507:
506:
504:
501:
500:
499:
494:
489:
484:
479:
474:
469:
464:
459:
454:
447:
444:
426:
423:
410:
407:
394:
391:
319:
316:
283:cache coherent
263:
262:
251:virtual memory
247:
223:
220:
182:front-side bus
178:HyperTransport
174:Omega networks
166:
165:
156:
136:
135:
129:
123:
74:
71:
37:
9:
6:
4:
3:
2:
1829:
1818:
1815:
1813:
1810:
1808:
1805:
1803:
1800:
1798:
1795:
1793:
1790:
1789:
1787:
1772:
1763:
1762:
1759:
1753:
1750:
1748:
1745:
1743:
1740:
1738:
1735:
1733:
1730:
1728:
1725:
1723:
1720:
1718:
1715:
1713:
1710:
1709:
1707:
1703:
1697:
1694:
1692:
1689:
1687:
1684:
1682:
1679:
1677:
1674:
1672:
1669:
1667:
1664:
1662:
1659:
1657:
1654:
1652:
1649:
1647:
1644:
1642:
1639:
1637:
1634:
1632:
1629:
1627:
1626:Global Arrays
1624:
1622:
1619:
1617:
1614:
1612:
1609:
1607:
1604:
1602:
1599:
1597:
1594:
1592:
1589:
1587:
1584:
1582:
1579:
1577:
1574:
1573:
1571:
1569:
1565:
1559:
1556:
1554:
1553:Grid computer
1551:
1547:
1544:
1543:
1542:
1539:
1536:
1533:
1529:
1526:
1524:
1521:
1519:
1516:
1514:
1511:
1509:
1506:
1504:
1501:
1500:
1499:
1496:
1492:
1489:
1487:
1484:
1483:
1482:
1479:
1477:
1474:
1472:
1469:
1467:
1464:
1462:
1459:
1455:
1452:
1450:
1447:
1443:
1440:
1438:
1435:
1432:
1429:
1428:
1427:
1424:
1422:
1419:
1418:
1417:
1414:
1413:
1411:
1409:
1405:
1399:
1396:
1392:
1389:
1387:
1384:
1382:
1379:
1378:
1377:
1374:
1372:
1369:
1367:
1364:
1363:
1361:
1359:
1355:
1349:
1346:
1344:
1341:
1339:
1336:
1334:
1331:
1329:
1326:
1324:
1321:
1319:
1316:
1315:
1313:
1309:
1303:
1300:
1298:
1295:
1293:
1290:
1288:
1285:
1283:
1280:
1279:
1277:
1273:
1267:
1264:
1262:
1259:
1257:
1254:
1252:
1249:
1247:
1244:
1242:
1239:
1237:
1234:
1232:
1229:
1227:
1224:
1223:
1221:
1217:
1211:
1208:
1205:
1202:
1200:
1197:
1195:
1192:
1189:
1186:
1184:
1181:
1178:
1175:
1173:
1170:
1169:
1167:
1165:
1161:
1155:
1152:
1150:
1147:
1145:
1142:
1140:
1137:
1135:
1132:
1130:
1127:
1125:
1122:
1120:
1117:
1116:
1114:
1110:
1104:
1101:
1099:
1096:
1094:
1091:
1089:
1086:
1084:
1081:
1079:
1076:
1074:
1071:
1069:
1066:
1064:
1061:
1059:
1056:
1055:
1053:
1049:
1045:
1038:
1033:
1031:
1026:
1024:
1019:
1018:
1015:
1003:
1000:
998:
995:
993:
990:
988:
985:
984:
982:
980:
975:
971:
965:
962:
960:
957:
955:
952:
950:
947:
945:
942:
939:
936:
934:
931:
929:
926:
924:
921:
919:
916:
914:
911:
909:
906:
904:
901:
899:
896:
894:
891:
890:
888:
886:
881:
877:
869:
866:
864:
861:
860:
858:
856:
853:
851:
850:Shared memory
848:
846:
843:
841:
838:
836:
833:
831:
828:
826:
823:
821:
818:
816:
813:
811:
808:
807:
805:
801:
797:
793:
789:
784:
780:
773:
768:
766:
761:
759:
754:
753:
750:
743:
740:
737:
734:
731:
728:
727:
716:
711:
703:
697:
691:
686:
679:
674:
660:
656:
649:
634:
630:
624:
617:
612:
605:
595:
589:
585:
580:
579:
570:
563:
558:
551:
547:
543:
537:
529:
523:
519:
512:
508:
498:
495:
493:
490:
488:
485:
483:
480:
478:
475:
473:
470:
468:
465:
463:
460:
458:
455:
453:
450:
449:
443:
441:
437:
433:
422:
420:
416:
406:
403:MapViewOfFile
390:
388:
384:
380:
376:
371:
368:
362:
350:
328:
324:
315:
313:
308:
306:
305:copy-on-write
301:
297:
295:
291:
286:
284:
280:
276:
272:
268:
260:
256:
252:
248:
245:
241:
237:
233:
232:
231:
229:
228:shared memory
219:
217:
213:
208:
206:
202:
198:
194:
190:
187:In case of a
185:
183:
179:
175:
171:
162:
157:
154:
153:false sharing
150:
146:
145:
144:
142:
133:
130:
127:
124:
121:
118:
117:
116:
113:
111:
107:
103:
99:
98:shared memory
91:
87:
83:
79:
70:
68:
63:
60:
56:
55:shared memory
52:
43:
34:
30:
19:
1502:
1311:Coordination
1241:Amdahl's law
1177:Simultaneous
893:Apple events
849:
710:
696:
685:
673:
662:. Retrieved
648:
636:. Retrieved
632:
623:
611:
603:
597:. Retrieved
577:
569:
557:
536:
517:
511:
477:Nano-threads
434:provides an
428:
412:
396:
372:
363:
351:
326:
321:
309:
298:
287:
264:
234:a method of
227:
225:
209:
186:
167:
164:performance.
141:cache memory
137:
114:
108:(CPUs) in a
97:
95:
64:
54:
48:
1747:Scalability
1508:distributed
1391:Concurrency
1358:Programming
1199:Cooperative
1188:Speculative
1124:Instruction
655:"tmpfs.txt"
442:functions.
267:named pipes
222:In software
73:In hardware
18:Shared code
1786:Categories
1752:Starvation
1491:asymmetric
1226:PRAM model
1194:Preemptive
979:frameworks
928:OpenBinder
830:Named pipe
680:from MSDN.
664:2010-03-16
659:kernel.org
633:elinux.org
599:2011-05-13
552:1993. p. 3
503:References
230:is either
149:contention
1486:symmetric
1231:PEM model
885:standards
880:Protocols
845:Semaphore
1717:Deadlock
1705:Problems
1671:pthreads
1651:OpenHMPP
1576:Ateji PX
1537:computer
1408:Hardware
1275:Elements
1261:Slowdown
1172:Temporal
1154:Pipeline
992:libevent
859:Sockets
446:See also
375:RAM disk
354:shm_open
331:shm_open
290:X server
257:and for
1676:RaftLib
1656:OpenACC
1631:GPUOpen
1621:C++ AMP
1596:Charm++
1338:Barrier
1282:Process
1266:Speedup
1051:General
964:XML-RPC
933:Sun RPC
863:Network
803:Methods
792:threads
294:Windows
240:process
67:threads
1769:
1646:OpenCL
1641:OpenMP
1586:Chapel
1503:shared
1498:Memory
1433:(SIMT)
1376:Models
1287:Thread
1219:Theory
1190:(SpMT)
1144:Memory
1129:Thread
1112:Levels
954:Thrift
855:Signal
638:12 Dec
590:
524:
383:Debian
379:RedHat
359:ashmem
347:shmget
339:shmctl
261:(XIP).
59:memory
1616:Dryad
1581:Boost
1302:Array
1292:Fiber
1206:(CMT)
1179:(SMT)
1093:GPGPU
997:SIMPL
987:D-Bus
938:POSIX
908:D-Bus
903:CORBA
440:POSIX
415:Boost
343:shmdt
335:shmat
323:POSIX
275:CORBA
90:IOMMU
1681:ROCm
1611:CUDA
1601:Cilk
1568:APIs
1528:COMA
1523:NUMA
1454:MIMD
1449:MISD
1426:SIMD
1421:SISD
1149:Loop
1139:Data
1134:Task
1002:LINX
977:and
959:TIPC
949:REST
944:SOAP
898:COM+
883:and
868:Unix
840:Pipe
810:File
788:Data
640:2022
588:ISBN
522:ISBN
401:and
381:and
367:mmap
345:and
214:and
197:GPUs
195:and
193:CPUs
1696:ZPL
1691:TBB
1686:UPC
1666:PVM
1636:MPI
1591:HPX
1518:UMA
1119:Bit
923:ICE
918:DCE
913:DDS
794:in
584:512
546:doi
436:API
432:PHP
273:or
244:RAM
180:or
86:MMU
82:HSA
57:is
49:In
31:or
1788::
657:.
631:.
602:.
586:.
544:.
419:Qt
389:.
361:.
341:,
337:,
314:.
296:.
285:.
269:,
176:,
172:,
112:.
53:,
1036:e
1029:t
1022:v
771:e
764:t
757:v
704:.
667:.
642:.
548::
530:.
35:.
20:)
Text is available under the Creative Commons Attribution-ShareAlike License. Additional terms may apply.