279:
122:
25:
158:
506:
313:
Consumer version of this design typically achieve focus by adjusting the position of the primary mirror rather than a traditional eye-piece. This means that small changes in the position of the mirror are magnified by the focal length of the telescope. As the mirror is not permanently fixed in place,
269:
One very well-corrected type of non-compact design is the concentric (or monocentric) Schmidt–Cassegrain, where all the mirror surfaces and the focal surface are concentric to a single point: the center of curvature of the primary. Optically, non-compact designs give better aberration correction and
254:, or one of each), they can be divided into two principal types: compact and non-compact. In the compact form, the corrector plate is located at or near the focus of the primary mirror. In the non-compact, the corrector plate remains at or near the center of curvature (twice the
314:
it is possible for it to move by a small amount and cause the image to shift. This is otherwise known as "mirror flop". Some
Schmidt-Cassegrain telescopes are equipped with mirror locks to fix the primary mirror in place once focus has been achieved.
261:
Compact designs combine a fast primary mirror and a small, strongly curved secondary. This yields a very short tube length, at the expense of field curvature. Compact designs have a primary mirror with a
227:
located behind the primary. Some designs include additional optical elements (such as field flatteners) near the focal plane. The first large telescope to use the design was the
266:
of around f/2 and a secondary with a focal ratio also around f/2, the separation of the two mirrors determining a typical system focal ratio around f/10.
482:. The Society for Astronomical Sciences 25th Annual Symposium on Telescope Science. Big Bear, Calif.: Society for Astronomical Sciences. p. 191.
42:
89:
61:
510:
68:
441:
75:
242:
is also recognized as the largest
Schmidt-Cassegrain. The telescope is noted for its large field of view, up 60 times a full moon.
57:
286:
The
Schmidt–Cassegrain design is very popular with consumer telescope manufacturers because it combines easy-to-manufacture
185:
manufactured the first one during World War II as part of their research into optical designs for the military. As in the
306:
means they are not a wide-field telescope like their
Schmidt camera predecessor, but they are good for more narrow-field
108:
348:
323:
303:
82:
358:
250:
While there are many variations of the
Schmidt–Cassegrain telescope design (both mirrors spherical, both mirrors
302:. The compact design makes it very portable for its given aperture, which adds to its marketability. Their high
46:
380:
526:
232:
182:
333:
239:
228:
197:
142:
35:
278:
134:
483:
389:
299:
291:
216:
205:
201:
170:
138:
8:
343:
328:
166:
146:
487:
393:
338:
477:
270:
a flatter field than most compact designs, but at the expense of longer tube length.
420:
212:
174:
353:
220:
193:
186:
178:
121:
520:
251:
209:
282:
People demonstrating a
Schmidt–Cassegrain telescope at a sidewalk gathering
255:
464:
290:
optical surfaces to create an instrument with the long focal length of a
263:
224:
409:. Vol. 2, Part 2. Cambridge University Press. 1984. p. 177.
287:
24:
307:
295:
161:
View of the corrector and primary mirror of a
Schmidt–Cassegrain.
157:
505:
190:
421:"The Mount Wilson Optical Shop During the Second World War"
145:
to make a compact astronomical instrument that uses simple
479:
Magnet Loader for
Schmidt-Cassegrain Mirror Flop Reduction
378:
Linfoot, E.H. (1956). "Colloquium on
Schmidt optics".
423:, American Astronomical Society Meeting 205, #02.01;
273:
49:. Unsourced material may be challenged and removed.
442:"A short history of Scotland's largest telescope"
518:
490:– via SAO/NASA Astrophysics Data System.
465:V. Sacek, Telescope-Optics.net page 10.2.2.4.2
475:
425:Bulletin of the American Astronomical Society
377:
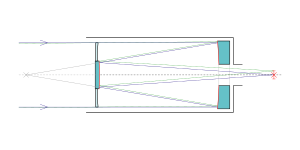
219:and relays the image through the perforated
165:The American astronomer and lens designer
109:Learn how and when to remove this message
277:
156:
120:
439:
152:
519:
435:
433:
245:
47:adding citations to reliable sources
18:
476:Vander Haagen, G.A. (23 May 2006).
13:
430:
125:Light path in a Schmidt–Cassegrain
14:
538:
498:
274:Amateur astronomical applications
504:
407:The General History of Astronomy
23:
440:Dvinsky, Dalcash (2018-04-05).
34:needs additional citations for
469:
458:
413:
399:
371:
58:"Schmidt–Cassegrain telescope"
16:Type of catadioptric telescope
1:
511:Schmidt-Cassegrain telescopes
364:
181:in 1940. The optical shop at
324:Argunov–Cassegrain telescope
7:
359:Schmidt–Newtonian telescope
317:
10:
543:
349:Ritchey–Chrétien telescope
258:) of the primary mirror.
294:with the lower cost per
233:University of St Andrews
183:Mount Wilson Observatory
334:List of telescope types
310:and planetary viewing.
240:James Gregory Telescope
229:James Gregory Telescope
198:Schmidt corrector plate
143:Schmidt corrector plate
141:'s optical path with a
283:
162:
135:catadioptric telescope
126:
281:
189:, this design uses a
160:
124:
513:at Wikimedia Commons
300:reflecting telescope
292:refracting telescope
202:spherical aberration
153:Invention and design
139:Cassegrain reflector
43:improve this article
488:2006SASS...25..191V
427:, Vol. 36, p. 1339.
394:1956Obs....76..170.
344:Newtonian telescope
329:Dobsonian telescope
167:James Gilbert Baker
339:Maksutov telescope
284:
246:Derivative designs
208:configuration the
163:
147:spherical surfaces
131:Schmidt–Cassegrain
127:
509:Media related to
169:first proposed a
119:
118:
111:
93:
534:
508:
492:
491:
473:
467:
462:
456:
455:
453:
452:
437:
428:
417:
411:
410:
403:
397:
396:
375:
238:As of 2021, the
213:secondary mirror
175:Bernhard Schmidt
137:that combines a
114:
107:
103:
100:
94:
92:
51:
27:
19:
542:
541:
537:
536:
535:
533:
532:
531:
527:Telescope types
517:
516:
501:
496:
495:
474:
470:
463:
459:
450:
448:
438:
431:
418:
414:
405:
404:
400:
381:The Observatory
376:
372:
367:
320:
276:
248:
231:of 1962 at the
217:field flattener
200:to correct for
155:
115:
104:
98:
95:
52:
50:
40:
28:
17:
12:
11:
5:
540:
530:
529:
515:
514:
500:
499:External links
497:
494:
493:
468:
457:
429:
419:Abrahams, P.,
412:
398:
369:
368:
366:
363:
362:
361:
356:
354:Schmidt camera
351:
346:
341:
336:
331:
326:
319:
316:
275:
272:
247:
244:
221:primary mirror
194:primary mirror
187:Schmidt camera
179:Schmidt camera
154:
151:
117:
116:
31:
29:
22:
15:
9:
6:
4:
3:
2:
539:
528:
525:
524:
522:
512:
507:
503:
502:
489:
485:
481:
480:
472:
466:
461:
447:
443:
436:
434:
426:
422:
416:
408:
402:
395:
391:
387:
383:
382:
374:
370:
360:
357:
355:
352:
350:
347:
345:
342:
340:
337:
335:
332:
330:
327:
325:
322:
321:
315:
311:
309:
305:
301:
297:
293:
289:
280:
271:
267:
265:
259:
257:
253:
243:
241:
236:
234:
230:
226:
222:
218:
214:
211:
207:
203:
199:
195:
192:
188:
184:
180:
176:
172:
168:
159:
150:
148:
144:
140:
136:
132:
123:
113:
110:
102:
99:November 2023
91:
88:
84:
81:
77:
74:
70:
67:
63:
60: –
59:
55:
54:Find sources:
48:
44:
38:
37:
32:This article
30:
26:
21:
20:
478:
471:
460:
449:. Retrieved
445:
424:
415:
406:
401:
385:
379:
373:
312:
285:
268:
260:
256:focal length
249:
237:
164:
130:
128:
105:
96:
86:
79:
72:
65:
53:
41:Please help
36:verification
33:
388:: 170–177.
264:focal ratio
225:focal plane
223:to a final
173:design for
451:2019-10-27
365:References
252:aspherical
215:acts as a
206:Cassegrain
204:. In this
171:Cassegrain
69:newspapers
288:spherical
191:spherical
521:Category
318:See also
308:deep sky
296:aperture
484:Bibcode
390:Bibcode
304:f-ratio
83:scholar
446:Medium
210:convex
196:and a
85:
78:
71:
64:
56:
298:of a
133:is a
90:JSTOR
76:books
129:The
62:news
177:'s
45:by
523::
444:.
432:^
386:76
384:.
235:.
149:.
486::
454:.
392::
112:)
106:(
101:)
97:(
87:·
80:·
73:·
66:·
39:.
Text is available under the Creative Commons Attribution-ShareAlike License. Additional terms may apply.