700:
764:
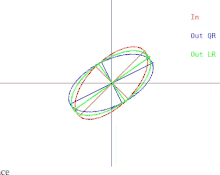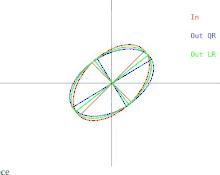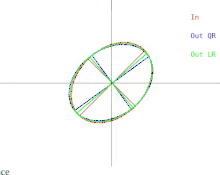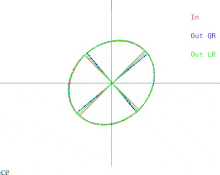
corresponds to a multiple of the identity matrix. A near-circle corresponds to a near-multiple of the identity matrix whose eigenvalues are nearly equal to the diagonal entries of the matrix. Therefore the problem of approximately finding the eigenvalues is shown to be easy in that case. But notice what happens to the semi-axes of the ellipses. An iteration of QR (or LR) tilts the semi-axes less and less as the input ellipse gets closer to being a circle. The eigenvectors can only be known when the semi-axes are parallel to the x-axis and y-axis. The number of iterations needed to achieve near-parallelism increases without bound as the input ellipse becomes more circular.
749:
740:. Observe that one fixed point is stable while the other is unstable. If the ellipse were tilted away from the unstable fixed point by a very small amount, one iteration of QR would cause the ellipse to tilt away from the fixed point instead of towards. Eventually though, the algorithm would converge to a different fixed point, but it would take a long time.
894:. In higher dimensions, shifting like this makes the length of the smallest semi-axis of an ellipsoid small relative to the other semi-axes, which speeds up convergence to the smallest eigenvalue, but does not speed up convergence to the other eigenvalues. This becomes useless when the smallest eigenvalue is fully determined, so the matrix must then be
517:), with a finite sequence of orthogonal similarity transforms, somewhat like a two-sided QR decomposition. (For QR decomposition, the Householder reflectors are multiplied only on the left, but for the Hessenberg case they are multiplied on both left and right.) Determining the QR decomposition of an upper Hessenberg matrix costs
901:
The issue with the unstable fixed point also needs to be addressed. The shifting heuristic is often designed to deal with this problem as well: Practical shifts are often discontinuous and randomised. Wilkinson's shift -- which is well-suited for symmetric matrices like the ones we're visualising --
771:
of an arbitrary symmetric matrix, it is always possible to perturb the matrix by an arbitrarily small amount and compute the eigendecomposition of the resulting matrix. In the case when the matrix is depicted as a near-circle, the matrix can be replaced with one whose depiction is a perfect circle.
763:
We will now discuss how these difficulties manifest in the basic QR algorithm. This is illustrated in Figure 2. Recall that the ellipses represent positive-definite symmetric matrices. As the two eigenvalues of the input matrix approach each other, the input ellipse changes into a circle. A circle
731:
of the ellipse is parallel to the x-axis, one iteration of QR does nothing. Another situation where the algorithm "does nothing" is when the large semi-axis is parallel to the y-axis instead of the x-axis. In that event, the ellipse can be thought of as balancing precariously without being able to
690:
The rate of convergence depends on the separation between eigenvalues, so a practical algorithm will use shifts, either explicit or implicit, to increase separation and accelerate convergence. A typical symmetric QR algorithm isolates each eigenvalue (then reduces the size of the matrix) with only
1428:
times a single vector, normalizing after each iteration. The vector converges to an eigenvector of the largest eigenvalue. Instead, the QR algorithm works with a complete basis of vectors, using QR decomposition to renormalize (and orthogonalize). For a symmetric matrix
388:
566:
arithmetic operations. Moreover, because the
Hessenberg form is already nearly upper-triangular (it has just one nonzero entry below each diagonal), using it as a starting point reduces the number of steps required for convergence of the QR algorithm.
784:
The slowdown when the ellipse gets more circular has a converse: It turns out that when the ellipse gets more stretched - and less circular - then the rotation of the ellipse becomes faster. Such a stretch can be induced when the matrix
723:
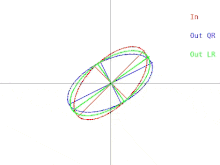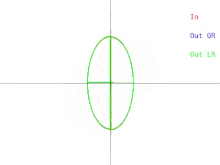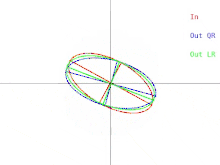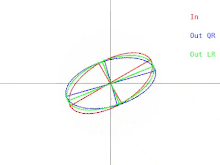
in higher dimensions. The relationship between the input to the algorithm and a single iteration can then be depicted as in Figure 1 (click to see an animation). Note that the LR algorithm is depicted alongside the QR algorithm.
760:). This difficulty exists whenever the multiplicities of a matrix's eigenvalues are not knowable. On the other hand, the same problem does not exist for finding eigenvalues. The eigenvalues of a matrix are always computable.
910:
In modern computational practice, the QR algorithm is performed in an implicit version which makes the use of multiple shifts easier to introduce. The matrix is first brought to upper
Hessenberg form
511:
652:
202:
1192:
1357:, due to the peculiar shape of the non-zero entries of the matrix along the steps of the algorithm. As in the first version, deflation is performed as soon as one of the sub-diagonal entries of
1473:
instead of the QR decomposition. The QR algorithm is more stable, so the LR algorithm is rarely used nowadays. However, it represents an important step in the development of the QR algorithm.
433:. The eigenvalues of a triangular matrix are listed on the diagonal, and the eigenvalue problem is solved. In testing for convergence it is impractical to require exact zeros, but the
956:
564:
1241:
685:
1065:
832:
1267:
1212:
1101:
1019:
852:
892:
1382:
1351:
1294:
983:
1324:
756:
It's worth pointing out that finding even a single eigenvector of a symmetric matrix is not computable (in exact real arithmetic according to the definitions in
1121:
872:
803:
2176:
654:
arithmetic operations using a technique based on
Householder reduction. Determining the QR decomposition of a symmetric tridiagonal matrix costs
732:
fall in either direction. In both situations, the matrix is diagonal. A situation where an iteration of the algorithm "does nothing" is called a
1845:
1942:
Bochkanov Sergey
Anatolyevich. ALGLIB User Guide - General Matrix operations - Singular value decomposition . ALGLIB Project. 2010-12-11. URL:
772:
In that case, the matrix is a multiple of the identity matrix, and its eigendecomposition is immediate. Be aware though that the resulting
2297:
2144:
2322:
2317:
2169:
1878:
451:
1946:
1126:
592:
1627:
implements this iterative method, with some modifications to cover the case where the singular values are very small (
2343:
2276:
2162:
1746:
1538:. After arranging the computation in a suitable shape, he discovered that the qd algorithm is in fact the iteration
2307:
2234:
752:
Figure 2: How the output of a single iteration of QR or LR are affected when two eigenvalues approach each other
699:
383:{\displaystyle A_{k+1}=R_{k}Q_{k}=Q_{k}^{-1}Q_{k}R_{k}Q_{k}=Q_{k}^{-1}A_{k}Q_{k}=Q_{k}^{\mathsf {T}}A_{k}Q_{k},}
768:
728:
440:
In this crude form the iterations are relatively expensive. This can be mitigated by first bringing the matrix
913:
2266:
1640:
36:
1643:. The QR algorithm can also be implemented in infinite dimensions with corresponding convergence results.
520:
727:
A single iteration causes the ellipse to tilt or "fall" towards the x-axis. In the event where the large
2220:
1217:
657:
514:
1453:
is a composite of all the orthogonal similarity transforms required to get there. Thus the columns of
2271:
733:
434:
2185:
2058:
1722:
1024:
703:
Figure 1: How the output of a single iteration of the QR or LR algorithm varies alongside its input
20:
1713:
Vera N. Kublanovskaya, "On some algorithms for the solution of the complete eigenvalue problem,"
808:
2053:
1246:
1197:
1070:
988:
837:
2230:
1396:
are explicitly performed, some authors, for instance
Watkins, suggested changing its name to
985:
is transformed via a small-size
Householder similarity transformation to the first column of
877:
737:
48:
2225:
2091:
2084:
Journal of the
Society for Industrial and Applied Mathematics, Series B: Numerical Analysis
1660:
1607:
algorithm starts with reducing a general matrix into a bidiagonal one. This variant of the
1360:
1329:
1272:
961:
40:
32:
8:
2204:
1947:
https://www.webcitation.org/5utO4iSnR?url=http://www.alglib.net/matrixops/general/svd.php
1405:
1303:
757:
406:
2095:
2107:
2004:
1786:
1669:
1106:
857:
788:
575:
44:
1846:"linear algebra - Why is uncomputability of the spectral decomposition not a problem?"
1976:
1959:
1926:
1874:
1742:
1477:
145:
60:
56:
2135:
1895:
2240:
2099:
2063:
2014:
1971:
1918:
1910:
1825:
1694:
1632:
1527:
1470:
1393:
571:
102:
52:
1943:
2281:
1765:
1631:). Together with a first step using Householder reflections and, if appropriate,
1612:
1421:
445:
2199:
2139:
2019:
1992:
1922:
1636:
1624:
1481:
402:
2337:
2245:
2079:
2075:
2041:
1930:
1717:, vol. 1, no. 3, pages 637–657 (1963, received Feb 1961). Also published in:
1699:
1682:
1401:
2149:
1914:
1830:
1805:
1420:
The QR algorithm can be seen as a more sophisticated variation of the basic
2154:
2125:
2037:
2082:(1965). "Calculating the singular values and pseudo-inverse of a matrix".
874:. In this case, the ratio of the two semi-axes of the ellipse approaches
748:
1591:, applied on a tridiagonal matrix, from which the LR algorithm follows.
2129:
2111:
1485:
773:
426:
77:
be a real matrix of which we want to compute the eigenvalues, and let
2261:
720:
2103:
2067:
958:
as in the explicit version; then, at each step, the first column of
2009:
1896:"From qd to LR, or, how were the qd and LR algorithms discovered?"
743:
1488:. Stiefel suggested that Rutishauser use the sequence of moments
716:
2312:
2302:
1620:
2136:
Notes on orthogonal bases and the workings of the QR algorithm
1123:, is the polynomial that defines the shifting strategy (often
691:
one or two iterations, making it efficient as well as robust.
574:, then the upper Hessenberg matrix is also symmetric and thus
1871:
The Matrix
Eigenvalue Problem: GR and Krylov Subspace Methods
2044:(1990). "Accurate singular values of bidiagonal matrices".
1741:(3rd ed.). Baltimore: Johns Hopkins University Press.
1719:
Zhurnal
Vychislitel'noi Matematiki i Matematicheskoi Fiziki
707:
The basic QR algorithm can be visualized in the case where
405:
and hence they have the same eigenvalues. The algorithm is
63:, multiply the factors in the reverse order, and iterate.
1392:
Since in the modern implicit version of the procedure no
51:, working independently. The basic idea is to perform a
1668:(3), pages 265–271 (1961, received October 1959).
1424:. Recall that the power algorithm repeatedly multiplies
506:{\textstyle {\tfrac {10}{3}}n^{3}+{\mathcal {O}}(n^{2})}
1715:
USSR Computational
Mathematics and Mathematical Physics
1300:). Then successive Householder transformations of size
898:, which simply means removing its last row and column.
711:
is a positive-definite symmetric matrix. In that case,
647:{\textstyle {\tfrac {4}{3}}n^{3}+{\mathcal {O}}(n^{2})}
1187:{\displaystyle p(x)=(x-\lambda )(x-{\bar {\lambda }})}
779:
597:
595:
523:
456:
454:
43:. The QR algorithm was developed in the late 1950s by
1958:
Deift, Percy; Li, Luenchau C.; Tomei, Carlos (1985).
1480:, who worked at that time as a research assistant of
1476:
The LR algorithm was developed in the early 1950s by
1363:
1353:
to upper Hessenberg form. This operation is known as
1332:
1306:
1275:
1249:
1220:
1200:
1129:
1109:
1073:
1027:
991:
964:
916:
880:
860:
840:
811:
791:
660:
205:
2046:
SIAM Journal on Scientific and Statistical Computing
1894:
Parlett, Beresford N.; Gutknecht, Martin H. (2011),
1326:
are performed in order to return the working matrix
1522:are arbitrary vectors) to find the eigenvalues of
1376:
1345:
1318:
1288:
1261:
1235:
1206:
1186:
1115:
1095:
1059:
1013:
977:
950:
886:
866:
846:
826:
797:
679:
646:
558:
505:
382:
1415:
513:arithmetic operations using a technique based on
2335:
1991:Colbrook, Matthew J.; Hansen, Anders C. (2019).
1893:
805:which the ellipse represents gets replaced with
1445:is the diagonal matrix of eigenvalues to which
776:can be quite far from the original eigenbasis.
744:Finding eigenvalues versus finding eigenvectors
1990:
1945:Accessed: 2010-12-11. (Archived by WebCite at
1732:
1730:
2170:
1736:
66:
2184:
1957:
1803:
1785:
1658:J.G.F. Francis, "The QR Transformation, I",
905:
854:is approximately the smallest eigenvalue of
736:. The strategy employed by the algorithm is
169:is an upper triangular matrix. We then form
2036:
1960:"Toda flows with infinitely many variables"
1814:methods for symmetric tridiagonal matrices"
1804:Ortega, James M.; Kaiser, Henry F. (1963).
1781:
1779:
1727:
1628:
2177:
2163:
2074:
1993:"On the infinite-dimensional QR algorithm"
1616:
767:While it may be impossible to compute the
2057:
2018:
2008:
1975:
1829:
1698:
1776:
1760:
1758:
1530:for this task and developed it into the
1243:are the two eigenvalues of the trailing
747:
698:
55:, writing the matrix as a product of an
35:: that is, a procedure to calculate the
2308:Basic Linear Algebra Subprograms (BLAS)
1868:
1680:
951:{\displaystyle A_{0}=QAQ^{\mathsf {T}}}
416:Under certain conditions, the matrices
2336:
1764:
1737:Golub, G. H.; Van Loan, C. F. (1996).
1721:, vol.1, no. 4, pages 555–570 (1961).
942:
351:
2158:
1755:
1465:The QR algorithm was preceded by the
559:{\textstyle 6n^{2}+{\mathcal {O}}(n)}
425:converge to a triangular matrix, the
1387:
1639:routine for the computation of the
1532:quotient–difference algorithm
1526:. Rutishauser took an algorithm of
780:Speeding up: Shifting and deflation
13:
881:
663:
623:
542:
482:
16:Algorithm to calculate eigenvalues
14:
2355:
2119:
1903:IMA Journal of Numerical Analysis
1594:
1236:{\displaystyle {\bar {\lambda }}}
680:{\displaystyle {\mathcal {O}}(n)}
1770:Applied Numerical Linear Algebra
1723:doi:10.1016/0041-5553(63)90168-X
902:is in particular discontinuous.
694:
1984:
1951:
1936:
1887:
738:iteration towards a fixed-point
437:provides a bound on the error.
1964:Journal of Functional Analysis
1862:
1838:
1797:
1707:
1674:
1652:
1416:Interpretation and convergence
1227:
1181:
1175:
1160:
1157:
1145:
1139:
1133:
1090:
1077:
1044:
1031:
1008:
995:
674:
668:
641:
628:
553:
547:
500:
487:
1:
1646:
1060:{\displaystyle p(A_{k})e_{1}}
1977:10.1016/0022-1236(85)90065-5
1641:singular value decomposition
1422:"power" eigenvalue algorithm
37:eigenvalues and eigenvectors
7:
1683:"The QR Transformation, II"
827:{\displaystyle M-\lambda I}
10:
2360:
2221:System of linear equations
2030:
2020:10.1007/s00211-019-01047-5
1873:. Philadelphia, PA: SIAM.
1869:Watkins, David S. (2007).
1681:Francis, J. G. F. (1962).
1670:doi:10.1093/comjnl/4.3.265
1460:
570:If the original matrix is
67:The practical QR algorithm
2290:
2272:Cache-oblivious algorithm
2254:
2213:
2192:
1262:{\displaystyle 2\times 2}
906:The implicit QR algorithm
435:Gershgorin circle theorem
2344:Numerical linear algebra
2323:General purpose software
2186:Numerical linear algebra
2145:Module for the QR Method
1791:Numerical Linear Algebra
1617:Golub & Kahan (1965)
1207:{\displaystyle \lambda }
1096:{\displaystyle p(A_{k})}
1014:{\displaystyle p(A_{k})}
847:{\displaystyle \lambda }
94:-th step (starting with
21:numerical linear algebra
1629:Demmel & Kahan 1990
1615:was first described by
1611:for the computation of
1605:the Golub-Kahan-Reinsch
1384:is sufficiently small.
1269:principal submatrix of
887:{\displaystyle \infty }
589:. This procedure costs
413:similarity transforms.
409:because it proceeds by
1700:10.1093/comjnl/4.4.332
1457:are the eigenvectors.
1378:
1347:
1320:
1290:
1263:
1237:
1208:
1188:
1117:
1097:
1061:
1015:
979:
952:
888:
868:
848:
828:
799:
753:
719:in 2 dimensions or an
715:can be depicted as an
704:
681:
648:
560:
507:
384:
2318:Specialized libraries
2231:Matrix multiplication
2226:Matrix decompositions
1997:Numerische Mathematik
1915:10.1093/imanum/drq003
1831:10.1093/comjnl/6.1.99
1789:; Bau, David (1997).
1449:converged, and where
1379:
1377:{\displaystyle A_{k}}
1348:
1346:{\displaystyle A_{k}}
1321:
1298:implicit double-shift
1291:
1289:{\displaystyle A_{k}}
1264:
1238:
1209:
1189:
1118:
1098:
1062:
1016:
980:
978:{\displaystyle A_{k}}
953:
889:
869:
849:
829:
800:
751:
702:
682:
649:
578:, and so are all the
561:
515:Householder reduction
508:
385:
49:Vera N. Kublanovskaya
1818:The Computer Journal
1687:The Computer Journal
1661:The Computer Journal
1564:(LU decomposition),
1433:, upon convergence,
1361:
1330:
1304:
1273:
1247:
1218:
1198:
1127:
1107:
1071:
1025:
989:
962:
914:
878:
858:
838:
809:
789:
658:
593:
521:
452:
203:
33:eigenvalue algorithm
2205:Numerical stability
2096:1965SJNA....2..205G
1923:20.500.11850/159536
1787:Trefethen, Lloyd N.
1739:Matrix Computations
1599:One variant of the
1319:{\displaystyle r+1}
758:computable analysis
356:
316:
265:
2126:Eigenvalue problem
1374:
1343:
1316:
1286:
1259:
1233:
1204:
1184:
1113:
1093:
1057:
1011:
975:
948:
884:
864:
844:
824:
795:
769:eigendecomposition
754:
705:
677:
644:
606:
556:
503:
465:
407:numerically stable
380:
340:
299:
248:
101:), we compute the
45:John G. F. Francis
2331:
2330:
1880:978-0-89871-641-2
1635:, this forms the
1508:= 0, 1, … (where
1478:Heinz Rutishauser
1469:, which uses the
1398:Francis algorithm
1394:QR decompositions
1388:Renaming proposal
1230:
1178:
1116:{\displaystyle r}
867:{\displaystyle M}
798:{\displaystyle M}
605:
464:
146:orthogonal matrix
61:triangular matrix
57:orthogonal matrix
2351:
2241:Matrix splitting
2179:
2172:
2165:
2156:
2155:
2115:
2071:
2061:
2025:
2024:
2022:
2012:
1988:
1982:
1981:
1979:
1955:
1949:
1940:
1934:
1933:
1900:
1891:
1885:
1884:
1866:
1860:
1859:
1857:
1856:
1842:
1836:
1835:
1833:
1801:
1795:
1794:
1783:
1774:
1773:
1766:Demmel, James W.
1762:
1753:
1752:
1734:
1725:
1711:
1705:
1704:
1702:
1678:
1672:
1656:
1633:QR decomposition
1528:Alexander Aitken
1471:LU decomposition
1383:
1381:
1380:
1375:
1373:
1372:
1352:
1350:
1349:
1344:
1342:
1341:
1325:
1323:
1322:
1317:
1296:, the so-called
1295:
1293:
1292:
1287:
1285:
1284:
1268:
1266:
1265:
1260:
1242:
1240:
1239:
1234:
1232:
1231:
1223:
1213:
1211:
1210:
1205:
1193:
1191:
1190:
1185:
1180:
1179:
1171:
1122:
1120:
1119:
1114:
1102:
1100:
1099:
1094:
1089:
1088:
1066:
1064:
1063:
1058:
1056:
1055:
1043:
1042:
1020:
1018:
1017:
1012:
1007:
1006:
984:
982:
981:
976:
974:
973:
957:
955:
954:
949:
947:
946:
945:
926:
925:
893:
891:
890:
885:
873:
871:
870:
865:
853:
851:
850:
845:
833:
831:
830:
825:
804:
802:
801:
796:
686:
684:
683:
678:
667:
666:
653:
651:
650:
645:
640:
639:
627:
626:
617:
616:
607:
598:
588:
565:
563:
562:
557:
546:
545:
536:
535:
512:
510:
509:
504:
499:
498:
486:
485:
476:
475:
466:
457:
443:
400:
389:
387:
386:
381:
376:
375:
366:
365:
355:
354:
348:
336:
335:
326:
325:
315:
307:
295:
294:
285:
284:
275:
274:
264:
256:
244:
243:
234:
233:
221:
220:
198:
168:
157:
143:
132:
103:QR decomposition
100:
93:
89:
76:
53:QR decomposition
2359:
2358:
2354:
2353:
2352:
2350:
2349:
2348:
2334:
2333:
2332:
2327:
2286:
2282:Multiprocessing
2250:
2246:Sparse problems
2209:
2188:
2183:
2122:
2104:10.1137/0702016
2068:10.1137/0911052
2033:
2028:
1989:
1985:
1956:
1952:
1941:
1937:
1898:
1892:
1888:
1881:
1867:
1863:
1854:
1852:
1844:
1843:
1839:
1802:
1798:
1784:
1777:
1763:
1756:
1749:
1735:
1728:
1712:
1708:
1679:
1675:
1657:
1653:
1649:
1613:singular values
1597:
1590:
1582:
1573:
1563:
1555:
1546:
1521:
1514:
1503:
1494:
1463:
1418:
1410:Francis QR step
1390:
1368:
1364:
1362:
1359:
1358:
1337:
1333:
1331:
1328:
1327:
1305:
1302:
1301:
1280:
1276:
1274:
1271:
1270:
1248:
1245:
1244:
1222:
1221:
1219:
1216:
1215:
1199:
1196:
1195:
1170:
1169:
1128:
1125:
1124:
1108:
1105:
1104:
1084:
1080:
1072:
1069:
1068:
1051:
1047:
1038:
1034:
1026:
1023:
1022:
1002:
998:
990:
987:
986:
969:
965:
963:
960:
959:
941:
940:
936:
921:
917:
915:
912:
911:
908:
879:
876:
875:
859:
856:
855:
839:
836:
835:
810:
807:
806:
790:
787:
786:
782:
746:
697:
662:
661:
659:
656:
655:
635:
631:
622:
621:
612:
608:
596:
594:
591:
590:
587:
579:
541:
540:
531:
527:
522:
519:
518:
494:
490:
481:
480:
471:
467:
455:
453:
450:
449:
446:Hessenberg form
441:
424:
399:
391:
371:
367:
361:
357:
350:
349:
344:
331:
327:
321:
317:
308:
303:
290:
286:
280:
276:
270:
266:
257:
252:
239:
235:
229:
225:
210:
206:
204:
201:
200:
197:
188:
179:
170:
167:
159:
149:
142:
134:
131:
122:
113:
105:
95:
91:
84:
78:
72:
69:
17:
12:
11:
5:
2357:
2347:
2346:
2329:
2328:
2326:
2325:
2320:
2315:
2310:
2305:
2300:
2294:
2292:
2288:
2287:
2285:
2284:
2279:
2274:
2269:
2264:
2258:
2256:
2252:
2251:
2249:
2248:
2243:
2238:
2228:
2223:
2217:
2215:
2211:
2210:
2208:
2207:
2202:
2200:Floating point
2196:
2194:
2190:
2189:
2182:
2181:
2174:
2167:
2159:
2153:
2152:
2147:
2142:
2140:Peter J. Olver
2133:
2121:
2120:External links
2118:
2117:
2116:
2090:(2): 205–224.
2080:Kahan, William
2076:Golub, Gene H.
2072:
2059:10.1.1.48.3740
2052:(5): 873–912.
2042:Kahan, William
2032:
2029:
2027:
2026:
1983:
1970:(3): 358–402.
1950:
1935:
1909:(3): 741–754,
1886:
1879:
1861:
1837:
1796:
1775:
1754:
1747:
1726:
1706:
1693:(4): 332–345.
1673:
1650:
1648:
1645:
1596:
1595:Other variants
1593:
1586:
1578:
1568:
1559:
1551:
1542:
1519:
1512:
1501:
1492:
1482:Eduard Stiefel
1462:
1459:
1417:
1414:
1389:
1386:
1371:
1367:
1340:
1336:
1315:
1312:
1309:
1283:
1279:
1258:
1255:
1252:
1229:
1226:
1203:
1183:
1177:
1174:
1168:
1165:
1162:
1159:
1156:
1153:
1150:
1147:
1144:
1141:
1138:
1135:
1132:
1112:
1092:
1087:
1083:
1079:
1076:
1054:
1050:
1046:
1041:
1037:
1033:
1030:
1010:
1005:
1001:
997:
994:
972:
968:
944:
939:
935:
932:
929:
924:
920:
907:
904:
883:
863:
843:
823:
820:
817:
814:
794:
781:
778:
745:
742:
696:
693:
676:
673:
670:
665:
643:
638:
634:
630:
625:
620:
615:
611:
604:
601:
583:
555:
552:
549:
544:
539:
534:
530:
526:
502:
497:
493:
489:
484:
479:
474:
470:
463:
460:
420:
395:
379:
374:
370:
364:
360:
353:
347:
343:
339:
334:
330:
324:
320:
314:
311:
306:
302:
298:
293:
289:
283:
279:
273:
269:
263:
260:
255:
251:
247:
242:
238:
232:
228:
224:
219:
216:
213:
209:
193:
184:
174:
163:
138:
127:
118:
109:
82:
71:Formally, let
68:
65:
15:
9:
6:
4:
3:
2:
2356:
2345:
2342:
2341:
2339:
2324:
2321:
2319:
2316:
2314:
2311:
2309:
2306:
2304:
2301:
2299:
2296:
2295:
2293:
2289:
2283:
2280:
2278:
2275:
2273:
2270:
2268:
2265:
2263:
2260:
2259:
2257:
2253:
2247:
2244:
2242:
2239:
2236:
2232:
2229:
2227:
2224:
2222:
2219:
2218:
2216:
2212:
2206:
2203:
2201:
2198:
2197:
2195:
2191:
2187:
2180:
2175:
2173:
2168:
2166:
2161:
2160:
2157:
2151:
2148:
2146:
2143:
2141:
2137:
2134:
2131:
2127:
2124:
2123:
2113:
2109:
2105:
2101:
2097:
2093:
2089:
2085:
2081:
2077:
2073:
2069:
2065:
2060:
2055:
2051:
2047:
2043:
2039:
2038:Demmel, James
2035:
2034:
2021:
2016:
2011:
2006:
2002:
1998:
1994:
1987:
1978:
1973:
1969:
1965:
1961:
1954:
1948:
1944:
1939:
1932:
1928:
1924:
1920:
1916:
1912:
1908:
1904:
1897:
1890:
1882:
1876:
1872:
1865:
1851:
1847:
1841:
1832:
1827:
1824:(1): 99–101.
1823:
1819:
1815:
1813:
1809:
1800:
1792:
1788:
1782:
1780:
1771:
1767:
1761:
1759:
1750:
1748:0-8018-5414-8
1744:
1740:
1733:
1731:
1724:
1720:
1716:
1710:
1701:
1696:
1692:
1688:
1684:
1677:
1671:
1667:
1663:
1662:
1655:
1651:
1644:
1642:
1638:
1634:
1630:
1626:
1622:
1618:
1614:
1610:
1606:
1602:
1592:
1589:
1585:
1581:
1577:
1571:
1567:
1562:
1558:
1554:
1550:
1545:
1541:
1537:
1533:
1529:
1525:
1518:
1511:
1507:
1500:
1497:
1491:
1487:
1483:
1479:
1474:
1472:
1468:
1458:
1456:
1452:
1448:
1444:
1440:
1436:
1432:
1427:
1423:
1413:
1411:
1408:use the term
1407:
1403:
1399:
1395:
1385:
1369:
1365:
1356:
1355:bulge chasing
1338:
1334:
1313:
1310:
1307:
1299:
1281:
1277:
1256:
1253:
1250:
1224:
1201:
1172:
1166:
1163:
1154:
1151:
1148:
1142:
1136:
1130:
1110:
1085:
1081:
1074:
1052:
1048:
1039:
1035:
1028:
1003:
999:
992:
970:
966:
937:
933:
930:
927:
922:
918:
903:
899:
897:
861:
841:
821:
818:
815:
812:
792:
777:
775:
770:
765:
761:
759:
750:
741:
739:
735:
730:
725:
722:
718:
714:
710:
701:
695:Visualization
692:
688:
671:
636:
632:
618:
613:
609:
602:
599:
586:
582:
577:
573:
568:
550:
537:
532:
528:
524:
516:
495:
491:
477:
472:
468:
461:
458:
448:(which costs
447:
438:
436:
432:
428:
423:
419:
414:
412:
408:
404:
398:
394:
377:
372:
368:
362:
358:
345:
341:
337:
332:
328:
322:
318:
312:
309:
304:
300:
296:
291:
287:
281:
277:
271:
267:
261:
258:
253:
249:
245:
240:
236:
230:
226:
222:
217:
214:
211:
207:
196:
192:
187:
183:
177:
173:
166:
162:
156:
152:
147:
141:
137:
130:
126:
121:
117:
112:
108:
104:
98:
88:
81:
75:
64:
62:
59:and an upper
58:
54:
50:
46:
42:
38:
34:
30:
26:
22:
2193:Key concepts
2087:
2083:
2049:
2045:
2003:(1): 17–83.
2000:
1996:
1986:
1967:
1963:
1953:
1938:
1906:
1902:
1889:
1870:
1864:
1853:. Retrieved
1850:MathOverflow
1849:
1840:
1821:
1817:
1811:
1807:
1799:
1790:
1769:
1738:
1718:
1714:
1709:
1690:
1686:
1676:
1665:
1659:
1654:
1609:QR algorithm
1608:
1604:
1601:QR algorithm
1600:
1598:
1587:
1583:
1579:
1575:
1569:
1565:
1560:
1556:
1552:
1548:
1543:
1539:
1536:qd algorithm
1535:
1531:
1523:
1516:
1509:
1505:
1498:
1495:
1489:
1475:
1467:LR algorithm
1466:
1464:
1454:
1450:
1446:
1442:
1438:
1434:
1430:
1425:
1419:
1409:
1397:
1391:
1354:
1297:
1103:, of degree
909:
900:
895:
783:
766:
762:
755:
726:
712:
708:
706:
689:
687:operations.
584:
580:
569:
439:
430:
421:
417:
415:
410:
396:
392:
199:. Note that
194:
190:
185:
181:
175:
171:
164:
160:
154:
150:
139:
135:
128:
124:
119:
115:
110:
106:
96:
86:
79:
73:
70:
29:QR iteration
28:
25:QR algorithm
24:
18:
2150:C++ Library
1623:subroutine
734:fixed point
576:tridiagonal
390:so all the
2235:algorithms
2130:PlanetMath
2010:2011.08172
1855:2021-08-09
1647:References
1486:ETH Zurich
774:eigenbasis
427:Schur form
411:orthogonal
2262:CPU cache
2054:CiteSeerX
1931:0272-4979
1254:×
1228:¯
1225:λ
1202:λ
1176:¯
1173:λ
1167:−
1155:λ
1152:−
1067:), where
882:∞
842:λ
819:λ
816:−
729:semi-axis
721:ellipsoid
572:symmetric
444:to upper
310:−
259:−
90:. At the
85: :=
2338:Category
2291:Software
2255:Hardware
2214:Problems
1768:(1997).
1441:, where
1406:Van Loan
1194:, where
896:deflated
2112:2949777
2092:Bibcode
2031:Sources
1793:. SIAM.
1772:. SIAM.
1461:History
1439:QΛ
717:ellipse
403:similar
189:
148:(i.e.,
123:
47:and by
2313:LAPACK
2303:MATLAB
2110:
2056:
1929:
1877:
1745:
1637:DGESVD
1625:DBDSQR
1621:LAPACK
1619:. The
1443:Λ
834:where
158:) and
144:is an
133:where
41:matrix
31:is an
23:, the
2298:ATLAS
2108:JSTOR
2005:arXiv
1899:(PDF)
1806:"The
1402:Golub
39:of a
2277:SIMD
1927:ISSN
1875:ISBN
1810:and
1743:ISBN
1515:and
1404:and
1214:and
1021:(or
401:are
2267:TLB
2138:by
2128:at
2100:doi
2064:doi
2015:doi
2001:143
1972:doi
1919:hdl
1911:doi
1826:doi
1695:doi
1534:or
1484:at
429:of
99:= 0
27:or
19:In
2340::
2106:.
2098:.
2086:.
2078:;
2062:.
2050:11
2048:.
2040:;
2013:.
1999:.
1995:.
1968:64
1966:.
1962:.
1925:,
1917:,
1907:31
1905:,
1901:,
1848:.
1820:.
1816:.
1812:QR
1808:LL
1778:^
1757:^
1729:^
1689:.
1685:.
1664:,
1603:,
1574:=
1572:+1
1547:=
1504:,
1437:=
1435:AQ
1412:.
1400:.
459:10
180:=
178:+1
153:=
114:=
2237:)
2233:(
2178:e
2171:t
2164:v
2132:.
2114:.
2102::
2094::
2088:2
2070:.
2066::
2023:.
2017::
2007::
1980:.
1974::
1921::
1913::
1883:.
1858:.
1834:.
1828::
1822:6
1751:.
1703:.
1697::
1691:4
1666:4
1588:k
1584:L
1580:k
1576:U
1570:k
1566:A
1561:k
1557:U
1553:k
1549:L
1544:k
1540:A
1524:A
1520:0
1517:y
1513:0
1510:x
1506:k
1502:0
1499:x
1496:A
1493:0
1490:y
1455:Q
1451:Q
1447:A
1431:A
1426:A
1370:k
1366:A
1339:k
1335:A
1314:1
1311:+
1308:r
1282:k
1278:A
1257:2
1251:2
1182:)
1164:x
1161:(
1158:)
1149:x
1146:(
1143:=
1140:)
1137:x
1134:(
1131:p
1111:r
1091:)
1086:k
1082:A
1078:(
1075:p
1053:1
1049:e
1045:)
1040:k
1036:A
1032:(
1029:p
1009:)
1004:k
1000:A
996:(
993:p
971:k
967:A
943:T
938:Q
934:A
931:Q
928:=
923:0
919:A
862:M
822:I
813:M
793:M
713:A
709:A
675:)
672:n
669:(
664:O
642:)
637:2
633:n
629:(
624:O
619:+
614:3
610:n
603:3
600:4
585:k
581:A
554:)
551:n
548:(
543:O
538:+
533:2
529:n
525:6
501:)
496:2
492:n
488:(
483:O
478:+
473:3
469:n
462:3
442:A
431:A
422:k
418:A
397:k
393:A
378:,
373:k
369:Q
363:k
359:A
352:T
346:k
342:Q
338:=
333:k
329:Q
323:k
319:A
313:1
305:k
301:Q
297:=
292:k
288:Q
282:k
278:R
272:k
268:Q
262:1
254:k
250:Q
246:=
241:k
237:Q
231:k
227:R
223:=
218:1
215:+
212:k
208:A
195:k
191:Q
186:k
182:R
176:k
172:A
165:k
161:R
155:Q
151:Q
140:k
136:Q
129:k
125:R
120:k
116:Q
111:k
107:A
97:k
92:k
87:A
83:0
80:A
74:A
Text is available under the Creative Commons Attribution-ShareAlike License. Additional terms may apply.