205:
17:
37:
29:
44:
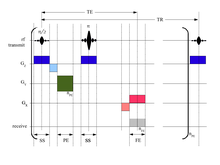
NMR pulse sequence for a heteronuclear experiment. The thin bar denotes a 90° pulse, while the thick bar denotes a 180° pulse. INEPT is a common building block of NMR experiments to improve N signal.
86:
are applied by switching magnetic fields that exhibit a space-dependent gradient which can be used to reconstruct spatially resolved images after applying
Fourier transforms.
107:
82:
270:
49:
32:
Graphical representation of a pulse sequence for a homonuclear NOESY experiment. The three bars represent three 90° pulses.
265:
246:
141:
212:
90:
77:
239:
158:
61:
8:
220:
183:
64:
is related to the characteristic frequencies of the desired signals. After applying a
232:
137:
65:
69:
57:
216:
259:
16:
156:
112:
73:
204:
36:
28:
189:
102:
21:
41:
89:
The outcome of pulse sequences is often analyzed using the
157:
Bernstein, M.A.; King, K.E.; Zhou, X.J.; Fong, W. (2004).
108:
Insensitive nuclei enhanced by polarization transfer
257:
50:Fourier transform NMR spectroscopy and imaging
240:
150:
60:pulses applied to the sample, such that the
247:
233:
131:
35:
27:
15:
68:, the signal can be represented in the
258:
199:
13:
14:
282:
177:
271:Nuclear magnetic resonance stubs
203:
160:Handbook of MRI Pulse Sequences
125:
1:
136:. John Wiley & Sons Ltd.
118:
219:. You can help Knowledge by
7:
96:
10:
287:
266:Nuclear magnetic resonance
213:nuclear magnetic resonance
198:
91:product operator formalism
78:magnetic resonance imaging
20:Timing diagram for an MRI
215:–related article is a
186:in the online textbook
56:describes a series of
45:
33:
25:
39:
31:
19:
62:free induction decay
132:M H Levitt (2008).
192:(by Joseph Hornak)
46:
34:
26:
228:
227:
190:The Basics of NMR
66:Fourier transform
278:
249:
242:
235:
207:
200:
171:
170:
168:
167:
154:
148:
147:
129:
70:frequency domain
286:
285:
281:
280:
279:
277:
276:
275:
256:
255:
254:
253:
196:
184:Pulse sequences
180:
175:
174:
165:
163:
155:
151:
144:
130:
126:
121:
99:
83:gradient pulses
58:radio frequency
24:pulse sequence.
12:
11:
5:
284:
274:
273:
268:
252:
251:
244:
237:
229:
226:
225:
208:
194:
193:
187:
179:
178:External links
176:
173:
172:
149:
143:978-0470511176
142:
123:
122:
120:
117:
116:
115:
110:
105:
98:
95:
54:pulse sequence
9:
6:
4:
3:
2:
283:
272:
269:
267:
264:
263:
261:
250:
245:
243:
238:
236:
231:
230:
224:
222:
218:
214:
209:
206:
202:
201:
197:
191:
188:
185:
182:
181:
162:
161:
153:
145:
139:
135:
134:Spin Dynamics
128:
124:
114:
111:
109:
106:
104:
101:
100:
94:
92:
87:
85:
84:
80:, additional
79:
75:
71:
67:
63:
59:
55:
51:
43:
38:
30:
23:
18:
221:expanding it
210:
195:
164:. Retrieved
159:
152:
133:
127:
113:MRI sequence
88:
81:
74:NMR spectrum
53:
47:
260:Categories
166:2008-04-08
119:References
103:Spin echo
22:spin echo
97:See also
72:as the
140:
211:This
76:. In
42:INEPT
217:stub
138:ISBN
52:, a
48:In
40:An
262::
93:.
248:e
241:t
234:v
223:.
169:.
146:.
Text is available under the Creative Commons Attribution-ShareAlike License. Additional terms may apply.