20:
184:
Gooding C, Roberts GC, Moreau G, Nadal-Ginard B, Smith CW. (1994). Smooth muscle-specific switching of alpha-tropomyosin mutually exclusive exon selection by specific inhibition of the strong default exon.
171:
Gooding C, Roberts GC, Smith CW. (1998). Role of an inhibitory pyrimidine element and polypyrimidine tract binding protein in repression of a regulated alpha-tropomyosin exon.
77:
A number of protein factors bind to or associate with the polypyrimidine tract, including the spliceosome component U2AF and the
79:
91:
silencing, by which a particular exon region normally spliced into the mature mRNA is instead left out, resulting in the
48:
158:
Wagner EJ, Garcia-Blanco MA. (2001). Polypyrimidine tract binding protein antagonizes exon definition.
204:
145:
Lodish H, Berk A, Matsudaira P, Kaiser CA, Krieger M, Scott MP, Zipursky SL, Darnell J. (2004).
209:
84:
8:
126:
express alternate isoforms distinguished by mutually exclusive exon selection in alpha-
23:
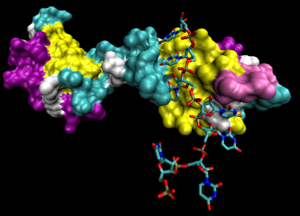
The essential spliceosome component U2AF bound to a short polypyrimidine RNA fragment.
115:
123:
92:
40:
114:
The suppression or selection of exons is critical to the proper expression of
107:, it is thought to suppress the inclusion of "weak" exons with poorly defined
198:
119:
32:
100:
44:
127:
108:
36:
111:. However, PTB binding is not sufficient to suppress "robust" exons.
55:
52:
104:
67:
63:
16:
A pyrimidine-rich sequence involved in pre-messenger RNA maturation
96:
19:
71:
59:
88:
103:. Because PTB is ubiquitously expressed in many higher
196:
66:long, located about 5–40 base pairs before the
35:(mRNA) that promotes the assembly of the
83:(PTB), which plays a regulatory role in
18:
178:
197:
165:
152:
139:
80:polypyrimidine tract-binding protein
13:
99:of the protein for which the mRNA
14:
221:
149:WH Freeman: New York, NY. 5th ed.
118:-specific isoforms. For example,
49:post-transcriptional modification
87:. PTB's primary function is in
1:
133:
43:specialized for carrying out
7:
10:
226:
51:. The region is rich with
147:Molecular Cell Biology.
62:, and is usually 15–20
47:during the process of
24:
22:
85:alternative splicing
29:polypyrimidine tract
25:
162:21(10):3281-3288.
33:pre-messenger RNA
217:
190:
182:
176:
169:
163:
156:
150:
143:
225:
224:
220:
219:
218:
216:
215:
214:
205:Gene expression
195:
194:
193:
189:13(16):3861-72.
183:
179:
170:
166:
157:
153:
144:
140:
136:
124:skeletal muscle
74:to be spliced.
41:protein complex
31:is a region of
17:
12:
11:
5:
223:
213:
212:
207:
192:
191:
177:
164:
151:
137:
135:
132:
15:
9:
6:
4:
3:
2:
222:
211:
208:
206:
203:
202:
200:
188:
181:
174:
168:
161:
160:Mol Cell Biol
155:
148:
142:
138:
131:
129:
125:
121:
120:smooth muscle
117:
112:
110:
106:
102:
98:
94:
90:
86:
82:
81:
75:
73:
69:
65:
61:
58:, especially
57:
54:
50:
46:
42:
38:
34:
30:
21:
186:
180:
172:
167:
159:
154:
146:
141:
113:
109:splice sites
78:
76:
45:RNA splicing
28:
26:
210:Spliceosome
128:tropomyosin
56:nucleotides
37:spliceosome
199:Categories
134:References
105:eukaryotes
93:expression
64:base pairs
53:pyrimidine
175:4:85-100.
97:isoform
70:of the
187:EMBO J
116:tissue
95:of an
72:intron
68:3' end
60:uracil
39:, the
101:codes
122:and
89:exon
27:The
173:RNA
201::
130:.
Text is available under the Creative Commons Attribution-ShareAlike License. Additional terms may apply.