380:
Furthermore, the precision placement machines are capable of handling larger or more irregularly shaped parts such as large package integrated circuits or packaged inductor coils and trimpots. Unlike the rapid placers, precision placers generally do not use turret mounted nozzles and instead rely on a gantry-supported moving head. These precision placers rely upon placement heads with relatively few pickup nozzles. The head sometimes has a laser identifier that scans a reflective marker on the PC board to orient the head to the board. Parts are picked up from tape feeders or trays, scanned by a camera (on some machines), and then placed in the proper position on the board. Some machines also center the parts on the head with two arms that close to center the part; the head then rotates 90 degrees and the arms close again to center the part once more. The margin of error for some components is less than half a millimeter (less than 0.02 inches).
373:, place mainly low-precision, simple package components such as resistors and capacitors. These high-speed P&P machines were built around a single turret design capable of mounting up to two dozen stations. As the turret spins, the stations passing the back of the machine pick up parts from tape feeders mounted on a moving carriage. As the station proceeds around the turret, it passes an optical station that calculates the angle at which the part was picked up, allowing the machine to compensate for drift. Then, as the station reaches the front of the turret, the board is moved into the proper position, the nozzle is spun to put the part in the proper angular orientation, and the part is placed on the board. Typical chip shooters can, under optimal conditions, place up to 53,000 parts per hour, or almost 15 parts per second.
464:
there was a new concept wherein the user could borrow performance during peak periods. There is a big change in the industry approach these days with more focus on software applications for the process. With new applications like POP and wafer placement on substrate the industry is moving beyond conventional component placement. There is a big difference in the needs of SMT users. For many, the high speed machines are not suitable due to cost and speed. With recent changes in the economic climate the requirement for SMT placement becomes focused on the machine's versatility to deal with short runs and fast changeover. This means that lower cost machines with vision systems provide an affordable option for SMT users. There are more users of low end and mid-range machines than the ultra fast placement systems.
278:
539:
to a database for future use. In addition to this, advanced software is available for monitoring the production and interconnect database — of the production floor to that of supply chain — in real-time. ASM provides an optional feature for increasing accuracy while placing LED components on a high end product where in the optical center of the LED is critical rather than the calculated mechanical center based on the component's lead structure. The special camera system measures both physical and optical center and makes the necessary adjustments before placement. It also can acquire the
295:
226:
124:
403:
25:
66:
389:
multi-headed, and multi-gantry machines that could have heads quickly swapped on different modules depending on the product being built to machines with multiple mini turrets capable of placing the whole spectrum of components with theoretical speeds of 136,000 components an hour. The fastest machines can have speeds of up to 200,000 CPH (components per hour).
303:
574:, applied by a glue-dispensing machine that can be incorporated on to the pick and place machine. The glue is added before component placement. It is dispensed by nozzles or by using jet dispensing. Jet dispensing dispenses material by shooting it towards the target, which in this case, is the circuit board.
562:
To minimize the distance the pickup gantry must travel, it is common to have multiple nozzles with separate vertical motion on a single gantry. This can pick up multiple parts with one trip to the feeders. Also, advanced software in the newer generation machines allows different robotic heads to work
463:
Swapping heads onboard placement machines required more inventory of heads and related spare parts for different heads to minimize the downtime. Placement machines have an all-in-one head that can place components ranging from 0.4 mm × 0.2 mm to 50 mm × 40 mm. In addition to this
538:
Some machines have these optical systems on the robot arm and can carry out the optical calculations without losing time, thereby achieving a lower derating factor. The high-end optical systems mounted on the heads can also be used to capture details of the non-standard type components and save them
521:
in the center of the machine. The PCB is clamped, and the nozzles pick up individual components from the feeders/trays, rotate them to the correct orientation and then place them on the appropriate pads on the PCB with high precision. High-end machines can have multiple conveyors to produce multiple
534:
to see if it is damaged or missing (was not picked up), and the inevitable registration errors in pickup are measured and compensated for when the part is placed. For example, if the part was shifted 0.25 mm and rotated 10° when picked up, the pickup head will adjust the placement position to
379:
From the high speed machine, the board transits to a precision placement machine. These pick-and-place machines often use high resolution verification cameras and fine adjustment systems via high precision linear encoders on each axis to place parts more accurately than the high-speed machines.
505:(ICs) are sometimes supplied and arranged in trays which are stacked in a compartment. More commonly used ICs will be provided in tapes rather than trays or sticks. Improvements in feeder technology mean that tape format is becoming the preferred method of presenting parts on an SMT machine.
388:
Due to the huge cost of having two separate machines to place parts, the speed limitations of the chip shooters, and the inflexibility of the machines, the electronic component machine manufacturers abandoned the technique. To overcome these limitations they moved to all-in-one modular,
508:
Early feeder heads were much bulkier, and as a result, it was not designed to be the mobile part of the system. Rather, the PCB itself was mounted on a moving platform that aligned the areas of the board to be populated with the feeder head above.
289:
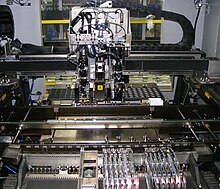
feeders, then the (currently empty) conveyor belt for printed circuit boards, and in back are large parts in a tray. The gantry carries two pickup nozzles, flanking a camera (marked "do not touch" to avoid fingerprints on the
500:
Surface mount components are placed along the front (and often back) faces of the machine. Most components are supplied on paper or plastic tape, in tape reels that are loaded onto feeders mounted to the machine. Larger
530:
The part being carried from the part feeders on either side of the conveyor belt to the PCB, it is photographed from below by using high resolution camera and a lighting system. Its silhouette is
550:
on the PCB to measure its position on the conveyor belt accurately. Two fiducial marks, measured in two dimensions each, usually placed diagonally, let the PCB's orientation and
413:
76:
376:
Because the PCB is moved rather than the turret, only lightweight parts that will not be shaken loose by the violent motion of the PCB can be placed this way.
286:
87:
554:
be measured and compensated for as well. Some machines are also able to measure the PCB shear by measuring a third fiducial mark on the PCB.
734:
492:-like device to allow the cup to be accurately manipulated in three dimensions. Additionally, each nozzle can be rotated independently.
428:
608:
630:
366:
During this time, a typical SMT assembly line employed two different types of pick-and-place (P&P) machines arranged in sequence.
345:, consumer electronics, and industrial, medical, automotive, military and telecommunications equipment. Similar equipment exists for
188:
160:
141:
38:
167:
174:
450:
264:
207:
105:
52:
472:
The placement equipment is part of a larger overall machine that carries out specific programmed steps to create a
156:
432:
329:(PCB). They are used for high speed, high precision placing of a broad range of electronic components (such as
145:
531:
678:
44:
235:
517:
Through the middle of the machine there is a conveyor belt, along which blank PCBs travel, and a PCB
277:
181:
80:
that states a
Knowledge editor's personal feelings or presents an original argument about a topic.
702:
588:
346:
134:
420:
83:
659:
369:
The unpopulated board was fed into a rapid placement machine. These machines, sometimes called
638:
616:
326:
322:
8:
583:
679:"Circuit Assembly Online Magazine - A History of Placement Programming and Optimization"
242:
Please help update this article to reflect recent events or newly available information.
547:
502:
338:
551:
349:
components. This type of equipment is sometimes used to package microchips using the
298:
Tape-and-reel feed mechanism used to load components into a pick-and-place machine
294:
424:
728:
567:
518:
473:
485:
350:
330:
123:
571:
566:
The components may be temporarily adhered to the PCB using the wet
342:
334:
484:
the components onto the PCB. These systems normally use pneumatic
489:
318:
563:
independently of each other to further increase the throughput.
543:
in either single field of view or multiple field of view modes.
540:
281:
Internal details of a two head, gantry style pick-and-place
282:
77:
personal reflection, personal essay, or argumentative essay
311:
Surface-mount technology (SMT) component placement systems
302:
546:
A separate camera on the pick-and-place head photographs
306:
SMD pick-and-place machine (with simulated motion blurs)
522:
same or different kinds of products simultaneously.
431:, and by adding encyclopedic content written from a
148:. Unsourced material may be challenged and removed.
631:"SMT-JUKI, pioneer of "Multi Task Platform JM-20""
238:may be compromised due to out-of-date information
726:
525:
570:itself, or by using small blobs of a separate
704:PICK & PLACE MACHINES: Europlacer 1702 h
53:Learn how and when to remove these messages
341:) onto the PCBs which are in turn used in
451:Learn how and when to remove this message
265:Learn how and when to remove this message
208:Learn how and when to remove this message
106:Learn how and when to remove this message
535:place the part in the correct location.
301:
293:
276:
476:. Several sub-systems work together to
727:
412:contains content that is written like
396:
285:SMT machine. In the foreground are
219:
146:adding citations to reliable sources
117:
59:
18:
735:Printed circuit board manufacturing
13:
495:
361:
14:
746:
321:machines which are used to place
34:This article has multiple issues.
710:, InterElectronic, February 2017
676:
512:
401:
224:
122:
64:
23:
392:
133:needs additional citations for
42:or discuss these issues on the
695:
670:
652:
623:
601:
1:
594:
557:
526:Inspection and visual system
467:
7:
577:
10:
751:
356:
383:
157:"Pick-and-place machine"
589:Insertion mount machine
315:pick-and-place machines
609:"PCB Assembly Example"
307:
299:
291:
86:by rewriting it in an
664:Yamaha Motor Co., Ltd
433:neutral point of view
327:printed circuit board
323:surface-mount devices
305:
297:
280:
683:circuitsassembly.com
142:improve this article
584:Component placement
503:integrated circuits
425:promotional content
339:integrated circuits
427:and inappropriate
313:, commonly called
308:
300:
292:
88:encyclopedic style
75:is written like a
619:on April 1, 2018.
552:thermal expansion
461:
460:
453:
317:or P&Ps, are
275:
274:
267:
257:
256:
218:
217:
210:
192:
116:
115:
108:
57:
742:
719:
718:
717:
715:
709:
699:
693:
692:
690:
689:
674:
668:
667:
656:
650:
649:
647:
646:
637:. Archived from
627:
621:
620:
615:. Archived from
605:
488:, attached to a
456:
449:
445:
442:
436:
414:an advertisement
405:
404:
397:
270:
263:
252:
249:
243:
236:factual accuracy
228:
227:
220:
213:
206:
202:
199:
193:
191:
150:
126:
118:
111:
104:
100:
97:
91:
68:
67:
60:
49:
27:
26:
19:
750:
749:
745:
744:
743:
741:
740:
739:
725:
724:
723:
722:
713:
711:
707:
701:
700:
696:
687:
685:
677:Ford, Michael.
675:
671:
658:
657:
653:
644:
642:
629:
628:
624:
607:
606:
602:
597:
580:
560:
528:
515:
498:
496:Component feeds
470:
457:
446:
440:
437:
418:
406:
402:
395:
386:
364:
362:1980s and 1990s
359:
271:
260:
259:
258:
253:
247:
244:
241:
233:This article's
229:
225:
214:
203:
197:
194:
151:
149:
139:
127:
112:
101:
95:
92:
84:help improve it
81:
69:
65:
28:
24:
17:
16:Robotic machine
12:
11:
5:
748:
738:
737:
721:
720:
694:
669:
651:
635:www.juki.co.jp
622:
599:
598:
596:
593:
592:
591:
586:
579:
576:
559:
556:
548:fiducial marks
527:
524:
514:
511:
497:
494:
480:and correctly
469:
466:
459:
458:
429:external links
409:
407:
400:
394:
391:
385:
382:
363:
360:
358:
355:
325:(SMDs) onto a
273:
272:
255:
254:
232:
230:
223:
216:
215:
130:
128:
121:
114:
113:
72:
70:
63:
58:
32:
31:
29:
22:
15:
9:
6:
4:
3:
2:
747:
736:
733:
732:
730:
706:
705:
698:
684:
680:
673:
665:
661:
655:
641:on 2019-12-08
640:
636:
632:
626:
618:
614:
610:
604:
600:
590:
587:
585:
582:
581:
575:
573:
569:
564:
555:
553:
549:
544:
542:
536:
533:
523:
520:
513:Conveyor belt
510:
506:
504:
493:
491:
487:
483:
479:
475:
465:
455:
452:
444:
434:
430:
426:
422:
416:
415:
410:This section
408:
399:
398:
390:
381:
377:
374:
372:
371:chip shooters
367:
354:
352:
348:
344:
340:
336:
332:
328:
324:
320:
316:
312:
304:
296:
288:
287:tape and reel
284:
279:
269:
266:
251:
248:February 2010
239:
237:
231:
222:
221:
212:
209:
201:
190:
187:
183:
180:
176:
173:
169:
166:
162:
159: –
158:
154:
153:Find sources:
147:
143:
137:
136:
131:This article
129:
125:
120:
119:
110:
107:
99:
96:December 2011
89:
85:
79:
78:
73:This article
71:
62:
61:
56:
54:
47:
46:
41:
40:
35:
30:
21:
20:
712:, retrieved
703:
697:
686:. Retrieved
682:
672:
663:
654:
643:. Retrieved
639:the original
634:
625:
617:the original
612:
603:
568:solder paste
565:
561:
545:
537:
529:
516:
507:
499:
486:suction cups
481:
477:
474:PCB assembly
471:
462:
447:
438:
423:by removing
419:Please help
411:
393:2010 onwards
387:
378:
375:
370:
368:
365:
347:through-hole
314:
310:
309:
261:
245:
234:
204:
195:
185:
178:
171:
164:
152:
140:Please help
135:verification
132:
102:
93:
74:
50:
43:
37:
36:Please help
33:
714:January 27,
688:2016-05-10
645:2019-06-01
595:References
558:Variations
421:improve it
331:capacitors
198:March 2015
168:newspapers
39:improve it
532:inspected
468:Operation
441:June 2016
351:flip chip
343:computers
335:resistors
45:talk page
729:Category
660:"Z:TA-R"
578:See also
572:adhesive
353:method.
490:plotter
478:pick up
357:History
319:robotic
182:scholar
82:Please
541:images
337:, and
290:lens).
184:
177:
170:
163:
155:
708:(PDF)
519:clamp
482:place
384:2000s
189:JSTOR
175:books
716:2023
613:Fuji
283:JUKI
161:news
144:by
731::
681:.
662:.
633:.
611:.
333:,
48:.
691:.
666:.
648:.
454:)
448:(
443:)
439:(
435:.
417:.
268:)
262:(
250:)
246:(
240:.
211:)
205:(
200:)
196:(
186:·
179:·
172:·
165:·
138:.
109:)
103:(
98:)
94:(
90:.
55:)
51:(
Text is available under the Creative Commons Attribution-ShareAlike License. Additional terms may apply.