123:
298:
1941:
597:
two ecologically defined groups of species) but that mimic evolution along the relevant phylogenetic tree. If such data sets (typically 1,000 or more) are analyzed with the same statistical procedure that is used to analyze a real data set, then results for the simulated data sets can be used to create phylogenetically correct (or "PC") null distributions of the test statistic (e.g., a correlation coefficient, t, F). Such simulation approaches can also be combined with such methods as phylogenetically independent contrasts or PGLS (see above).
588:
601:
84:
4773:
3474:
4783:
4809:
3151:
3486:
40:. However, the fact that closely related lineages share many traits and trait combinations as a result of the process of descent with modification means that lineages are not independent. This realization inspired the development of explicitly phylogenetic comparative methods. Initially, these methods were primarily developed to control for phylogenetic history when testing for
76:
evolutionary events. Such an approach is particularly useful when there is little or no variation within species. And because they can be used to explicitly model evolutionary processes occurring over very long time periods, they can provide insight into macroevolutionary questions, once the exclusive domain of
596:
Martins and
Garland proposed in 1991 that one way to account for phylogenetic relations when conducting statistical analyses was to use computer simulations to create many data sets that are consistent with the null hypothesis under test (e.g., no correlation between two traits, no difference between
1501:
Ackerly, D. D. 1999. Comparative plant ecology and the role of phylogenetic information. Pages 391–413 in M. C. Press, J. D. Scholes, and M. G. Braker, eds. Physiological plant ecology. The 39th symposium of the
British Ecological Society held at the University of York 7–9 September 1998. Blackwell
363:
have occurred) or as a phylogenetically weighted estimate of the mean for the entire set of tip species (terminal taxa). The value at the root is equivalent to that obtained from the "squared-change parsimony" algorithm and is also the maximum likelihood estimate under
Brownian motion. The
75:
Phylogenetic comparative approaches can complement other ways of studying adaptation, such as studying natural populations, experimental studies, and mathematical models. Interspecific comparisons allow researchers to assess the generality of evolutionary phenomena by considering independent
380:
Probably the most commonly used PCM is phylogenetic generalized least squares (PGLS). This approach is used to test whether there is a relationship between two (or more) variables while accounting for the fact that lineage are not independent. The method is a special case of
2493:
Rezende, E. L., and
Garland, T. Jr. 2003. Comparaciones interespecíficas y métodos estadísticos filogenéticos. Pages 79–98 in F. Bozinovic, ed. Fisiología Ecológica & Evolutiva. Teoría y casos de estudios en animales. Ediciones Universidad Católica de Chile, Santiago.
44:; however, in recent years the use of the term has broadened to include any use of phylogenies in statistical tests. Although most studies that employ PCMs focus on extant organisms, many methods can also be applied to extinct taxa and can incorporate information from the
568:, and Pagel's λ model. (When a Brownian motion model is used, PGLS is identical to the independent contrasts estimator.). In PGLS, the parameters of the evolutionary model are typically co-estimated with the regression parameters.
481:
591:
Data for a continuous-valued trait can be simulated in such a way that taxa at the tips of a hypothetical phylogenetic tree will exhibit phylogenetic signal, i.e., closely related species will tend to resemble each
543:
552:
is a matrix of expected variance and covariance of the residuals given an evolutionary model and a phylogenetic tree. Therefore, it is the structure of residuals and not the variables themselves that show
1070:
Martins, Emilia P.; Hansen, Thomas F. (April 1997). "Phylogenies and the
Comparative Method: A General Approach to Incorporating Phylogenetic Information into the Analysis of Interspecific Data".
1594:
Cheverud, J. M.; Dow, M. M.; Leutenegger, W. (1985). "The quantitative assessment of phylogenetic constraints in comparative analyses: sexual dimorphism in body weight among primates".
137:
and mating system. Larger-bodied species tend to have larger testes, but at any given body size species in which females tend to mate with multiple males have males with larger testes.
2100:
Martins, E. P.; Hansen, T. F. (1997). "Phylogenies and the comparative method: a general approach to incorporating phylogenetic information into the analysis of interspecific data".
859:
Pennell, Matthew W.; Harmon, Luke J. (June 2013). "An integrative view of phylogenetic comparative methods: connections to population genetics, community ecology, and paleobiology".
2057:
Maddison, W. P. (1990). "A method for testing the correlated evolution of two binary characters: Are gains or losses concentrated on certain branches of a phylogenetic tree?".
359:
by themselves. An exception occurs for the basal (root) node, which can be interpreted as an estimate of the ancestral value for the entire tree (assuming that no directional
4505:
259:
Does a trait exhibit significant phylogenetic signal in a particular group of organisms? Do certain types of traits tend to "follow phylogeny" more than others?
63:), though there are some approaches that do both simultaneously. Typically the tree that is used in conjunction with PCMs has been estimated independently (see
1506:
Berenbrink, M.; Koldkjær, P.; Kepp, O.; Cossins, A. R. (2005). "Evolution of oxygen secretion in fishes and the emergence of a complex physiological system".
360:
2093:
Maddison, W. P., and D. R. Maddison. 1992. MacClade. Analysis of phylogeny and character evolution. Version 3. Sinauer
Associates, Sunderland, Mass. 398 pp.
1590:
Brooks, D. R., and D. A. McLennan. 1991. Phylogeny, ecology, and behavior: a research program in comparative biology. Univ. Chicago Press, Chicago. 434 pp.
1837:"General quantitative genetic methods for comparative biology: phylogenies, taxonomies and multi-trait models for continuous and categorical characters"
1408:"General quantitative genetic methods for comparative biology: phylogenies, taxonomies and multi-trait models for continuous and categorical characters"
2828:
2823:
2813:
1991:
1455:
Martins, Emilia P.; Garland, Theodore (May 1991). "Phylogenetic
Analyses of the Correlated Evolution of Continuous Characters: A Simulation Study".
2243:
Organ, C. L.; Shedlock, A. M.; Meade, A.; Pagel, M.; Edwards, S. V. (2007). "Origin of avian genome size and structure in non-avian dinosaurs".
415:
320:
proposed the first general statistical method in 1985 for incorporating phylogenetic information, i.e., the first that could use any arbitrary
2684:
Smith, R. J.; Cheverud, J. M. (2002). "Scaling of sexual size dimorphism in body mass: a phylogenetic analysis of Rensch's rule in primates".
1630:
Eggleton, P., and R. I. Vane-Wright, eds. 1994. Phylogenetics and ecology. Linnean
Society Symposium Series Number 17. Academic Press, London.
3006:
2036:
Maddison, D. R. (1994). "Phylogenetic methods for inferring the evolutionary history and process of change in discretely valued characters".
4254:
989:
Garland, T.; Dickerman, A. W.; Janis, C. M.; Jones, J. A. (1 September 1993). "Phylogenetic
Analysis of Covariance by Computer Simulation".
492:
3554:
1236:
Freckleton, R. P.; Harvey, P. H.; Pagel, M. (December 2002). "Phylogenetic
Analysis and Comparative Data: A Test and Review of Evidence".
134:
95:
2880:
2951:
951:
Weber, Marjorie G.; Agrawal, Anurag A. (July 2012). "Phylogeny, ecology, and the coupling of comparative and experimental approaches".
2762:
Adaptation and the comparative method online lecture, with worked example of phylogenetically independent contrasts and mastery quiz
557:. This has long been a source of confusion in the scientific literature. A number of models have been proposed for the structure of
4758:
4213:
3089:
2536:
Ridley, M. 1983. The explanation of organic diversity: The comparative method and adaptations for mating. Clarendon, Oxford, U.K.
1640:
Freckleton, R. P.; Harvey, P. H.; Pagel, M. (2002). "Phylogenetic analysis and comparative data: a test and review of evidence".
2833:
3564:
2981:
3021:
4521:
4281:
2741:
Vanhooydonck, B.; Van Damme, R. (1999). "Evolutionary relationships between body shape and habitat use in lacertid lizards".
2096:
Martins, E. P., ed. 1996. Phylogenies and the comparative method in animal behavior. Oxford University Press, Oxford. 415 pp.
3031:
3878:
3284:
1682:"Using the past to predict the present: Confidence intervals for regression equations in phylogenetic comparative methods"
340:
like model of trait evolution) to transform the original tip data (mean values for a set of species) into values that are
4604:
3524:
2294:
Pagel, M. D. (1993). "Seeking the evolutionary regression coefficient: an analysis of what comparative methods measure".
51:
PCMs can generally be divided into two types of approaches: those that infer the evolutionary history of some character (
2761:
4266:
3926:
2931:
575:
is continuously distributed; however, the phylogenetic tree can also be incorporated into the residual distribution of
67:) such that both the relationships between lineages and the length of branches separating them is assumed to be known.
3244:
813:
4333:
4338:
3936:
2167:"Comparative methods for the analysis of gene-expression evolution: an example using yeast functional genomic data"
2647:
Schluter, D.; Price, T.; Mooers, A. O.; Ludwig, D. (1997). "Likelihood of ancestor states in adaptive radiation".
2502:
4583:
4573:
4497:
3772:
3329:
3262:
1806:
Gittleman, J. L.; Kot, M. (1990). "Adaptation: statistics and a null model for estimating phylogenetic effects".
2379:
1575:
4711:
4578:
4358:
4102:
3900:
3804:
3693:
3490:
3339:
3269:
2803:
565:
118:). Whether this difference is considered statistically significant depends on what type of analysis is applied
2818:
2638:
2621:
30:) to test evolutionary hypotheses. The comparative method has a long history in evolutionary biology; indeed,
4776:
4363:
4107:
3846:
4308:
1363:
Housworth, Elizabeth A.; Martins, Emília P.; Lynch, Michael (January 2004). "The Phylogenetic Mixed Model".
4716:
4218:
2166:
2290:, ed. 2003. Tangled trees: phylogeny, cospeciation, and coevolution. University of Chicago Press, Chicago.
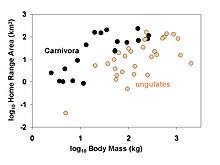
98:. Larger-bodied species tend to have larger home ranges, but at any given body size members of the order
4813:
4786:
4380:
3249:
3156:
3112:
3082:
1994:
2018. Mixed and phylogenetic models: a conceptual introduction to correlated data. leanpub.com, 125 pp.,
721:
655:
409:
are assumed to be independent and identically distributed random variables that are assumed to be normal
301:
The standardized contrasts are used in conventional statistical procedures, with the constraint that all
64:
3061:
2946:
1725:
4799:
4482:
3656:
2495:
1878:
Herrada, E. A.; Tessone, C. J.; Klemm, K.; Eguiluz, V. M.; Hernandez-Garcia, E.; Duarte, C. M. (2008).
1320:
Lynch, Michael (August 1991). "Methods for the Analysis of Comparative Data in Evolutionary Biology".
4276:
4073:
3883:
3651:
3544:
3439:
3365:
680:
670:
576:
382:
341:
329:
4405:
1940:
829:
O'Meara, Brian C. (December 2012). "Evolutionary Inferences from Phylogenies: A Review of Methods".
579:, making it possible to generalize the approach to a broader set of distributions for the response.
4699:
4563:
4535:
4510:
4467:
4370:
4303:
4178:
4051:
4019:
3992:
3982:
686:
160:
4183:
2423:
4704:
4634:
4543:
4271:
4153:
3921:
3517:
3319:
3117:
675:
398:
394:
345:
2875:
2766:
2209:"Testing for different rates of continuous trait evolution in different groups using likelihood"
4829:
4743:
4392:
4261:
4223:
4124:
4095:
4068:
4063:
3661:
3478:
3202:
3075:
650:
402:
310:
4249:
1772:"Procedures for the analysis of comparative data using phylogenetically independent contrasts"
1189:"The relationship between sexual size dimorphism and habitat use in Greater Antillean lizards"
16:
Use of information on the historical relationships of lineages to test evolutionary hypotheses
4684:
4558:
4477:
4472:
4457:
4442:
4432:
4348:
4323:
4158:
4114:
4078:
4046:
3987:
3965:
3946:
3809:
3762:
3713:
3708:
3666:
3454:
3132:
2459:
1771:
1681:
1556:
324:(branching order) and a specified set of branch lengths. The method is now recognized as an
266:
60:
36:
2991:
2913:
2503:"Phylogenetic analyses: comparing species to infer adaptations and physiological mechanisms"
122:
4658:
4553:
4487:
4288:
4203:
4119:
4031:
4014:
3941:
3931:
3641:
3549:
3533:
3291:
3197:
2971:
2332:
2252:
2208:
1901:
1677:
1552:
1515:
1034:
868:
746:
660:
390:
386:
297:
4293:
4163:
2898:
842:
8:
4721:
4679:
4629:
4548:
4396:
4388:
4318:
4298:
4244:
4088:
3841:
3784:
3646:
3629:
3607:
3334:
3216:
2542:"Comparative methods for the analysis of continuous variables: geometric interpretations"
1107:"Comparative methods for the analysis of continuous variables: geometric interpretations"
639:
554:
369:
302:
275:
3999:
3046:
2336:
2256:
1905:
1557:"Testing for phylogenetic signal in comparative data: behavioral traits are more labile"
1519:
1038:
872:
59:) across a phylogeny and those that infer the process of evolutionary branching itself (
4694:
4646:
4639:
4236:
4148:
4009:
3970:
3794:
3738:
3728:
3688:
3602:
3597:
3592:
3510:
3257:
3211:
3127:
2701:
2664:
2608:
2571:
2558:
2541:
2482:
2410:
2366:
2276:
2231:
2153:
2117:
2074:
1980:
1924:
1891:
1879:
1866:
1823:
1794:
1758:
1712:
1665:
1611:
1539:
1472:
1437:
1388:
1337:
1261:
1218:
1205:
1188:
1136:
1123:
1106:
1087:
892:
786:
701:
644:
619:
572:
317:
2883:
2733:
587:
4782:
4736:
4462:
4410:
4188:
4004:
3905:
3868:
3863:
3819:
3814:
3767:
3733:
3185:
2961:
2956:
2714:
2672:
2612:
2600:
2563:
2525:
2446:
2414:
2402:
2370:
2358:
2311:
2287:
2268:
2191:
2082:
2024:
1972:
1929:
1858:
1853:
1836:
1750:
1704:
1657:
1619:
1579:
1531:
1480:
1429:
1424:
1407:
1380:
1345:
1302:
1253:
1210:
1172:
1155:
1128:
1052:
968:
933:
884:
809:
726:
706:
2705:
2575:
2235:
2157:
2121:
2003:"Within-species variation and measurement error in phylogenetic comparative methods"
1984:
1870:
1762:
1669:
1543:
1441:
1392:
1265:
1140:
1091:
4328:
3895:
3873:
3681:
3274:
3228:
2888:
2729:
2693:
2656:
2633:
2592:
2553:
2517:
2474:
2438:
2394:
2348:
2340:
2303:
2280:
2260:
2223:
2181:
2143:
2109:
2066:
2045:
2014:
1964:
1919:
1909:
1848:
1815:
1786:
1740:
1716:
1696:
1649:
1603:
1571:
1523:
1464:
1419:
1372:
1329:
1292:
1245:
1222:
1200:
1167:
1118:
1079:
1042:
998:
960:
923:
896:
876:
838:
790:
778:
731:
227:
204:
34:
used differences and similarities between species as a major source of evidence in
4173:
2860:
2808:
2049:
4689:
4313:
4140:
4129:
4083:
4026:
3975:
3755:
3559:
3375:
2908:
2838:
2204:
1914:
1633:
691:
600:
562:
337:
285:
3026:
2865:
1279:
Blomberg, S. P.; Lefevre, J. G.; Wells, J. A.; Waterhouse, M. (3 January 2012).
1187:
Butler, Marguerite A.; Schoener, Thomas W.; Losos, Jonathan B. (February 2000).
4529:
4401:
4343:
3703:
3698:
3636:
3614:
3349:
1949:
1636:
2004. Inferring phylogenies. Sinauer Associates, Sunderland, Mass. xx + 664 pp.
964:
711:
629:
365:
31:
2697:
2323:
Pagel, M (1999). "Inferring the historical patterns of biological evolution".
2019:
2002:
1002:
928:
911:
769:
Felsenstein, Joseph (January 1985). "Phylogenies and the Comparative Method".
4823:
4731:
4609:
4568:
4414:
4168:
3836:
3831:
3344:
3314:
3221:
3098:
3016:
716:
665:
582:
352:
200:
45:
3036:
3001:
2870:
2186:
1527:
1297:
1280:
141:
Phylogenetic comparative methods are commonly applied to such questions as:
4726:
4674:
4619:
4452:
4447:
4041:
3799:
3449:
3395:
3390:
3385:
3370:
3178:
3173:
2676:
2604:
2567:
2529:
2450:
2442:
2406:
2362:
2307:
2272:
2195:
2086:
2028:
1976:
1933:
1862:
1754:
1708:
1661:
1623:
1583:
1535:
1484:
1433:
1384:
1349:
1306:
1257:
1214:
1132:
1047:
1022:
972:
937:
888:
624:
306:
77:
2903:
2353:
2315:
1056:
476:{\displaystyle \varepsilon \mid X\sim {\mathcal {N}}(0,\sigma ^{2}I_{n}).}
83:
4753:
4624:
4353:
3888:
3718:
3624:
3582:
3444:
3137:
3011:
2976:
2936:
2521:
741:
27:
4193:
2264:
4614:
4515:
4437:
4424:
4058:
3858:
3745:
3723:
3676:
3671:
3619:
3587:
3502:
3122:
3056:
2926:
2798:
2668:
2486:
2078:
1827:
1798:
1615:
1476:
1341:
880:
736:
696:
634:
356:
251:
237:
214:
196:
173:
150:
115:
103:
87:
52:
41:
2771:
2148:
2131:
1745:
1027:
Philosophical Transactions of the Royal Society B: Biological Sciences
538:{\displaystyle \varepsilon \mid X\sim {\mathcal {N}}(0,\mathbf {V} ).}
4748:
4599:
4208:
3826:
3574:
3459:
3423:
3418:
3413:
3308:
3190:
2596:
2424:"Analysis of comparative data using generalized estimating equations"
2227:
2165:
Oakley, T. H.; Gu, Z.; Abouheif, E.; Patel, N. H.; Li, W.-H. (2005).
1995:
1281:"Independent Contrasts and PGLS Regression Estimators Are Equivalent"
912:"Estimating a Binary Character's Effect on Speciation and Extinction"
614:
325:
223:
111:
107:
99:
2660:
2478:
2070:
1819:
1790:
1607:
1468:
1333:
4651:
3853:
2941:
2398:
2132:"Comparative methods for studying primate adaptation and allometry"
2113:
1968:
1700:
1653:
1376:
1249:
1083:
782:
321:
247:
130:
56:
2986:
2344:
1896:
4036:
3750:
2966:
2893:
2202:
336:
of the method is to use phylogenetic information (and an assumed
187:
183:
91:
3067:
3041:
375:
4808:
3150:
2781:
2620:
Sanford, G. M.; Lutterschmidt, W. I.; Hutchison, V. H. (2002).
328:
that implements a special case of what are termed phylogenetic
169:
126:
26:) use information on the historical relationships of lineages (
2715:"Comparative quantitative genetics: evolution of the G matrix"
1278:
3957:
3279:
3207:
2996:
2855:
2619:
2583:
Rohlf, F. J. (2006). "A comment on phylogenetic correction".
2460:"Polytomies in comparative analyses of continuous characters"
2380:"Statistical analysis of diversification with species traits"
1505:
910:
Maddison, Wayne; Midford, Peter; Otto, Sarah (October 2007).
355:
as an intermediate step, but they are generally not used for
333:
146:
3051:
2776:
486:
whereas in PGLS the errors are assumed to be distributed as
364:
independent contrasts algebra can also be used to compute a
2834:
Philosophical Transactions of the Royal Society of London B
1576:
10.1554/0014-3820(2003)057[0717:tfpsic]2.0.co;2
1156:"Phylogenetic signal and linear regression on species data"
2786:
1877:
988:
583:
Phylogenetically informed Monte Carlo computer simulations
2646:
2639:
10.1641/0006-3568(2002)052[0830:tcmr]2.0.co;2
292:
1880:"Universal Scaling in the Branching of the Tree of Life"
1724:
Garland, T. Jr.; Bennett, A. F.; Rezende, E. L. (2005).
2843:
2242:
2849:
1593:
4797:
2740:
2164:
2001:
Ives, A. R.; Midford, P. E.; Garland, T. Jr. (2007).
1947:
1723:
1639:
1362:
1235:
495:
418:
3146:
2712:
1948:
Housworth, E. A.; Martins, E. P.; Lynch, M. (2004).
1770:
Garland, T. Jr.; Harvey, P. H.; Ives, A. R. (1992).
831:
Annual Review of Ecology, Evolution, and Systematics
2894:
ouch: Ornstein-Uhlenbeck for Comparative Hypotheses
2713:Steppan, S. J.; Phillips, P. C.; Houle, D. (2002).
1726:"Phylogenetic approaches in comparative physiology"
1550:
1186:
909:
284:Example: why do small-bodied species have shorter
278:
trade-off, as in the so-called fast-slow continuum?
2500:
2000:
537:
475:
1769:
4821:
1834:
1405:
808:. Oxford: Oxford University Press. p. 248.
571:PGLS can only be applied to questions where the
401:. In many statistical situations where GLS (or,
2207:; Sanderson, M. J.; Wainwright, P. C. (2006).
1454:
1229:
806:The Comparative Method in Evolutionary Biology
3518:
3083:
2866:Comparative Analysis by Independent Contrasts
2683:
2457:
2421:
2099:
1069:
984:
982:
858:
854:
852:
385:(GLS) and as such the PGLS estimator is also
376:Phylogenetic generalized least squares (PGLS)
2899:PDAP: Phenotypic Diversity Analysis Programs
1805:
1406:Hadfield, J. D.; Nakagawa, S. (March 2010).
1272:
1016:
1014:
1012:
950:
1676:
1448:
903:
828:
803:
768:
351:The algorithm involves computing values at
3525:
3511:
3090:
3076:
2777:Phylogenetic Tools for Comparative Biology
2501:Rezende, E.L.; Diniz-Filho, J.A.F (2012).
2129:
1180:
1147:
1063:
979:
861:Annals of the New York Academy of Sciences
849:
240:evolve in the lineage that led to mammals?
2637:
2557:
2352:
2185:
2147:
2018:
1923:
1913:
1895:
1852:
1744:
1423:
1296:
1204:
1171:
1122:
1098:
1046:
1009:
927:
822:
797:
172:of organisms differ with respect to some
4759:Transgenerational epigenetic inheritance
3532:
2056:
2035:
944:
804:Harvey, Paul H.; Pagel, Mark D. (1991).
599:
586:
296:
161:brain mass vary in relation to body mass
121:
82:
2856:Analyses of Phylogenetics and Evolution
2377:
110:) tend to have larger home ranges than
4822:
1153:
1020:
293:Phylogenetically independent contrasts
4522:Dialogues Concerning Natural Religion
3506:
3071:
2839:Physiological and Biochemical Zoology
2582:
2539:
2322:
2293:
1835:Hadfield, J. D; Nakagawa, S. (2010).
1319:
1104:
843:10.1146/annurev-ecolsys-110411-160331
764:
762:
313:, etc., must pass through the origin.
3485:
2686:International Journal of Primatology
2458:Purvis, A.; Garland, T. Jr. (1993).
213:Example: do carnivores have larger
2850:Software packages (incomplete list)
2130:Nunn, C. L.; Barton, R. A. (2001).
246:Example: where, when, and why did
13:
3927:Evolutionary developmental biology
2622:"The comparative method revisited"
2559:10.1111/j.0014-3820.2001.tb00731.x
1996:https://leanpub.com/correlateddata
1494:
1206:10.1111/j.0014-3820.2000.tb00026.x
1124:10.1111/j.0014-3820.2001.tb00731.x
759:
510:
433:
195:Do groups of species that share a
14:
4841:
3097:
2755:
1154:Revell, Liam J. (December 2010).
1105:Rohlf, F. James (November 2001).
953:Trends in Ecology & Evolution
4807:
4781:
4772:
4771:
3484:
3473:
3472:
3325:Phylogenetic comparative methods
3149:
2422:Paradis, E.; Claude, J. (2002).
1939:
1854:10.1111/j.1420-9101.2009.01915.x
1425:10.1111/j.1420-9101.2009.01915.x
1173:10.1111/j.2041-210x.2010.00044.x
1160:Methods in Ecology and Evolution
525:
265:Example: are behavioral traits
20:Phylogenetic comparative methods
4584:Extended evolutionary synthesis
3773:Gene-centered view of evolution
3330:Phylogenetic niche conservatism
2919:
2829:Journal of Evolutionary Biology
2722:Trends in Ecology and Evolution
2174:Molecular Biology and Evolution
1841:Journal of Evolutionary Biology
1733:Journal of Experimental Biology
1412:Journal of Evolutionary Biology
1399:
1356:
1313:
1021:Grafen, A. (21 December 1989).
70:
4712:Hologenome theory of evolution
4579:History of molecular evolution
3805:Evolutionarily stable strategy
3694:Last universal common ancestor
2431:Journal of Theoretical Biology
2296:Journal of Theoretical Biology
1950:"The phylogenetic mixed model"
529:
515:
467:
438:
207:) differ in average phenotype?
1:
4506:Renaissance and Enlightenment
2819:Evolutionary Ecology Research
2743:Evolutionary Ecology Research
2734:10.1016/s0169-5347(02)02505-3
2050:10.1146/annurev.ento.39.1.267
1023:"The Phylogenetic Regression"
753:
199:or ecological feature (e.g.,
4717:Missing heritability problem
4344:Gamete differentiation/sexes
1915:10.1371/journal.pone.0002757
288:than their larger relatives?
7:
3250:Phylogenetic reconciliation
3157:Evolutionary biology portal
3113:Computational phylogenetics
2792:
2038:Annual Review of Entomology
722:Phylogenetic reconciliation
656:Computational phylogenetics
607:
129:mass of various species of
65:computational phylogenetics
10:
4846:
4349:Life cycles/nuclear phases
3901:Trivers–Willard hypothesis
2782:Phylogeny of Sleep website
2767:List of phylogeny programs
965:10.1016/j.tree.2012.04.010
405:) is used residual errors
274:Do species differences in
4767:
4667:
4592:
4496:
4423:
4379:
4234:
4138:
3955:
3914:
3847:Parent–offspring conflict
3783:
3652:Earliest known life forms
3573:
3540:
3468:
3440:Phylogenetic nomenclature
3432:
3406:
3358:
3300:
3237:
3166:
3144:
3105:
2136:Evolutionary Anthropology
2126:Erratum Am. Nat. 153:448.
2020:10.1080/10635150701313830
929:10.1080/10635150701607033
681:Generalized least squares
671:Evolutionary neurobiology
577:generalized linear models
383:generalized least squares
342:statistically independent
330:generalized least-squares
4700:Cultural group selection
4564:The eclipse of Darwinism
4536:On the Origin of Species
4511:Transmutation of species
2884:PDAP:PDTree for Mesquite
2510:Comprehensive Physiology
687:Generalized linear model
186:have larger hearts than
4705:Dual inheritance theory
4544:History of paleontology
3320:Molecular phylogenetics
3270:Distance-matrix methods
3118:Molecular phylogenetics
2909:Phylogenetic Regression
2698:10.1023/A:1019654100876
1528:10.1126/science.1107793
1365:The American Naturalist
1238:The American Naturalist
1072:The American Naturalist
1003:10.1093/sysbio/42.3.265
771:The American Naturalist
676:Evolutionary physiology
346:identically distributed
90:areas of 49 species of
4393:Punctuated equilibrium
3714:Non-adaptive radiation
3662:Evolutionary arms race
3340:Phylogenetics software
3254:Probabilistic methods
3203:Long branch attraction
2443:10.1006/jtbi.2002.3066
2308:10.1006/jtbi.1993.1148
1680:; Ives, A. R. (2000).
1555:; Ives, A. R. (2003).
1048:10.1098/rstb.1989.0106
651:Comparative physiology
604:
593:
539:
477:
403:ordinary least squares
314:
311:analysis of covariance
138:
119:
4685:Evolutionary medicine
4559:Mendelian inheritance
4267:Biological complexity
4255:Programmed cell death
3947:Phenotypic plasticity
3667:Evolutionary pressure
3657:Evidence of evolution
3555:Timeline of evolution
3133:Evolutionary taxonomy
2540:Rohlf, F. J. (2001).
2187:10.1093/molbev/msh257
1502:Science, Oxford, U.K.
1298:10.1093/sysbio/syr118
603:
590:
540:
478:
399:asymptotically normal
300:
153:scaling relationship?
133:in relation to their
125:
94:in relation to their
86:
61:diversification rates
37:The Origin of Species
4814:Evolutionary biology
4659:Teleology in biology
4554:Blending inheritance
3932:Genetic assimilation
3795:Artificial selection
3534:Evolutionary biology
3292:Three-taxon analysis
3198:Phylogenetic network
2522:10.1002/cphy.c100079
747:Theodore Garland Jr.
661:Disk-covering method
493:
416:
236:Example: where did
4722:Molecular evolution
4680:Ecological genetics
4549:Transitional fossil
4339:Sexual reproduction
4179:endomembrane system
4108:pollinator-mediated
4064:dolphins and whales
3842:Parental investment
3335:Phylogenetic signal
2799:American Naturalist
2378:Paradis, E (2005).
2337:1999Natur.401..877P
2265:10.1038/nature05621
2257:2007Natur.446..180O
2102:American Naturalist
1957:American Naturalist
1906:2008PLoSO...3.2757H
1689:American Naturalist
1642:American Naturalist
1520:2005Sci...307.1752B
1514:(5716): 1752–1757.
1039:1989RSPTB.326..119G
873:2013NYASA1289...90P
640:Comparative anatomy
555:phylogenetic signal
370:confidence interval
361:evolutionary trends
276:life history traits
159:Example: how does
4695:Cultural evolution
3810:Fisher's principle
3739:Handicap principle
3729:Parallel evolution
3593:Adaptive radiation
3263:Bayesian inference
3258:Maximum likelihood
2876:Felsenstein's List
2844:Systematic Biology
2824:Functional Ecology
2804:Behavioral Ecology
2467:Systematic Biology
2007:Systematic Biology
1808:Systematic Zoology
1779:Systematic Biology
1285:Systematic Biology
991:Systematic Biology
916:Systematic Biology
881:10.1111/nyas.12157
702:Maximum likelihood
645:Comparative method
620:Behavioral ecology
605:
594:
573:dependent variable
566:Ornstein-Uhlenbeck
535:
473:
315:
139:
120:
114:(all of which are
4795:
4794:
4411:Uniformitarianism
4364:Sex-determination
3869:Sexual dimorphism
3864:Natural selection
3768:Unit of selection
3734:Signalling theory
3500:
3499:
3245:Maximum parsimony
3238:Inference methods
3186:Phylogenetic tree
2552:(11): 2143–2160.
2331:(6756): 877–884.
2251:(7132): 180–184.
2149:10.1002/evan.1019
1746:10.1242/jeb.01745
1739:(16): 3015–3035.
1551:Blomberg, S. P.;
1117:(11): 2143–2160.
1033:(1233): 119–157.
727:Roderic D.M. Page
707:Maximum parsimony
269:during evolution?
4837:
4812:
4811:
4803:
4785:
4775:
4774:
4574:Modern synthesis
4334:Multicellularity
4329:Mosaic evolution
4214:auditory ossicle
3896:Social selection
3879:Flowering plants
3874:Sexual selection
3527:
3520:
3513:
3504:
3503:
3488:
3487:
3476:
3475:
3275:Neighbor-joining
3229:Ghost population
3159:
3154:
3153:
3092:
3085:
3078:
3069:
3068:
2750:
2737:
2719:
2709:
2692:(5): 1095–1135.
2680:
2655:(6): 1699–1711.
2643:
2641:
2616:
2597:10.1554/05-550.1
2591:(7): 1509–1515.
2579:
2561:
2533:
2507:
2490:
2464:
2454:
2428:
2418:
2384:
2374:
2356:
2319:
2284:
2239:
2228:10.1554/05-130.1
2213:
2203:O'Meara, B. C.;
2199:
2189:
2171:
2161:
2151:
2125:
2090:
2053:
2032:
2022:
1988:
1954:
1944:
1943:
1937:
1927:
1917:
1899:
1874:
1856:
1831:
1802:
1776:
1766:
1748:
1730:
1720:
1686:
1673:
1627:
1602:(6): 1335–1351.
1587:
1561:
1547:
1489:
1488:
1452:
1446:
1445:
1427:
1403:
1397:
1396:
1360:
1354:
1353:
1328:(5): 1065–1080.
1317:
1311:
1310:
1300:
1276:
1270:
1269:
1233:
1227:
1226:
1208:
1184:
1178:
1177:
1175:
1151:
1145:
1144:
1126:
1102:
1096:
1095:
1067:
1061:
1060:
1050:
1018:
1007:
1006:
986:
977:
976:
948:
942:
941:
931:
907:
901:
900:
856:
847:
846:
826:
820:
819:
801:
795:
794:
766:
732:Sexual selection
544:
542:
541:
536:
528:
514:
513:
482:
480:
479:
474:
466:
465:
456:
455:
437:
436:
217:than herbivores?
4845:
4844:
4840:
4839:
4838:
4836:
4835:
4834:
4820:
4819:
4818:
4806:
4798:
4796:
4791:
4763:
4690:Group selection
4663:
4588:
4492:
4419:
4381:Tempo and modes
4375:
4230:
4134:
3951:
3910:
3786:
3779:
3756:Species complex
3569:
3560:History of life
3536:
3531:
3501:
3496:
3464:
3428:
3402:
3376:Symplesiomorphy
3354:
3296:
3233:
3162:
3155:
3148:
3142:
3106:Relevant fields
3101:
3096:
3066:
2922:
2852:
2795:
2758:
2753:
2717:
2661:10.2307/2410994
2505:
2479:10.2307/2992489
2462:
2426:
2382:
2211:
2169:
2071:10.2307/2409434
1952:
1938:
1820:10.2307/2992183
1791:10.2307/2992503
1774:
1728:
1684:
1678:Garland, T. Jr.
1634:Felsenstein, J.
1608:10.2307/2408790
1559:
1553:Garland, T. Jr.
1497:
1495:Further reading
1492:
1469:10.2307/2409910
1453:
1449:
1404:
1400:
1361:
1357:
1334:10.2307/2409716
1318:
1314:
1277:
1273:
1234:
1230:
1185:
1181:
1152:
1148:
1103:
1099:
1068:
1064:
1019:
1010:
987:
980:
949:
945:
908:
904:
857:
850:
827:
823:
816:
802:
798:
767:
760:
756:
751:
692:Joe Felsenstein
610:
585:
563:Brownian motion
524:
509:
508:
494:
491:
490:
461:
457:
451:
447:
432:
431:
417:
414:
413:
378:
338:Brownian motion
295:
73:
17:
12:
11:
5:
4843:
4833:
4832:
4817:
4816:
4793:
4792:
4790:
4789:
4779:
4768:
4765:
4764:
4762:
4761:
4756:
4751:
4746:
4741:
4740:
4739:
4729:
4724:
4719:
4714:
4709:
4708:
4707:
4702:
4697:
4687:
4682:
4677:
4671:
4669:
4665:
4664:
4662:
4661:
4656:
4655:
4654:
4649:
4644:
4643:
4642:
4632:
4627:
4622:
4617:
4612:
4602:
4596:
4594:
4590:
4589:
4587:
4586:
4581:
4576:
4571:
4566:
4561:
4556:
4551:
4546:
4541:
4540:
4539:
4530:Charles Darwin
4527:
4526:
4525:
4513:
4508:
4502:
4500:
4494:
4493:
4491:
4490:
4485:
4480:
4475:
4470:
4468:Non-ecological
4465:
4460:
4455:
4450:
4445:
4440:
4435:
4429:
4427:
4421:
4420:
4418:
4417:
4408:
4399:
4385:
4383:
4377:
4376:
4374:
4373:
4368:
4367:
4366:
4361:
4356:
4351:
4346:
4336:
4331:
4326:
4321:
4316:
4311:
4306:
4301:
4296:
4291:
4286:
4285:
4284:
4274:
4269:
4264:
4259:
4258:
4257:
4252:
4241:
4239:
4232:
4231:
4229:
4228:
4227:
4226:
4221:
4219:nervous system
4216:
4211:
4206:
4198:
4197:
4196:
4191:
4186:
4181:
4176:
4171:
4161:
4156:
4151:
4145:
4143:
4136:
4135:
4133:
4132:
4127:
4122:
4117:
4112:
4111:
4110:
4100:
4099:
4098:
4093:
4092:
4091:
4086:
4076:
4071:
4066:
4061:
4056:
4055:
4054:
4049:
4039:
4029:
4024:
4023:
4022:
4012:
4007:
4002:
3997:
3996:
3995:
3985:
3980:
3979:
3978:
3968:
3962:
3960:
3953:
3952:
3950:
3949:
3944:
3939:
3934:
3929:
3924:
3918:
3916:
3912:
3911:
3909:
3908:
3903:
3898:
3893:
3892:
3891:
3886:
3881:
3871:
3866:
3861:
3856:
3851:
3850:
3849:
3844:
3834:
3829:
3824:
3823:
3822:
3812:
3807:
3802:
3797:
3791:
3789:
3781:
3780:
3778:
3777:
3776:
3775:
3765:
3760:
3759:
3758:
3753:
3743:
3742:
3741:
3731:
3726:
3721:
3719:Origin of life
3716:
3711:
3706:
3704:Microevolution
3701:
3699:Macroevolution
3696:
3691:
3686:
3685:
3684:
3674:
3669:
3664:
3659:
3654:
3649:
3644:
3639:
3637:Common descent
3634:
3633:
3632:
3622:
3617:
3615:Baldwin effect
3612:
3611:
3610:
3605:
3595:
3590:
3585:
3579:
3577:
3571:
3570:
3568:
3567:
3562:
3557:
3552:
3547:
3541:
3538:
3537:
3530:
3529:
3522:
3515:
3507:
3498:
3497:
3495:
3494:
3482:
3469:
3466:
3465:
3463:
3462:
3457:
3452:
3447:
3442:
3436:
3434:
3430:
3429:
3427:
3426:
3421:
3416:
3410:
3408:
3404:
3403:
3401:
3400:
3399:
3398:
3393:
3388:
3380:
3379:
3378:
3373:
3362:
3360:
3356:
3355:
3353:
3352:
3350:Phylogeography
3347:
3342:
3337:
3332:
3327:
3322:
3317:
3312:
3304:
3302:
3301:Current topics
3298:
3297:
3295:
3294:
3289:
3288:
3287:
3282:
3277:
3267:
3266:
3265:
3260:
3252:
3247:
3241:
3239:
3235:
3234:
3232:
3231:
3226:
3225:
3224:
3214:
3205:
3200:
3195:
3194:
3193:
3183:
3182:
3181:
3170:
3168:
3167:Basic concepts
3164:
3163:
3161:
3160:
3145:
3143:
3141:
3140:
3135:
3130:
3125:
3120:
3115:
3109:
3107:
3103:
3102:
3095:
3094:
3087:
3080:
3072:
3065:
3064:
3059:
3054:
3049:
3044:
3039:
3034:
3029:
3024:
3019:
3014:
3009:
3004:
2999:
2994:
2989:
2984:
2979:
2974:
2969:
2964:
2959:
2954:
2949:
2944:
2939:
2934:
2932:Bininda-Emonds
2929:
2923:
2921:
2918:
2917:
2916:
2911:
2906:
2901:
2896:
2891:
2886:
2878:
2873:
2868:
2863:
2858:
2851:
2848:
2847:
2846:
2841:
2836:
2831:
2826:
2821:
2816:
2811:
2806:
2801:
2794:
2791:
2790:
2789:
2784:
2779:
2774:
2769:
2764:
2757:
2756:External links
2754:
2752:
2751:
2738:
2728:(7): 320–327.
2710:
2681:
2644:
2632:(9): 830–836.
2617:
2580:
2537:
2534:
2516:(1): 639–674.
2498:
2491:
2473:(4): 569–575.
2455:
2437:(2): 175–185.
2419:
2399:10.1554/04-231
2375:
2354:2027.42/148253
2320:
2302:(2): 191–205.
2291:
2288:Page, R. D. M.
2285:
2240:
2200:
2162:
2127:
2114:10.1086/286013
2108:(4): 646–667.
2097:
2094:
2091:
2065:(3): 539–557.
2054:
2033:
2013:(2): 252–270.
1998:
1989:
1969:10.1086/380570
1945:
1875:
1847:(3): 494–508.
1832:
1814:(3): 227–241.
1803:
1767:
1721:
1701:10.1086/303327
1695:(3): 346–364.
1674:
1654:10.1086/343873
1648:(6): 712–726.
1637:
1631:
1628:
1591:
1588:
1570:(4): 717–745.
1548:
1503:
1498:
1496:
1493:
1491:
1490:
1463:(3): 534–557.
1447:
1418:(3): 494–508.
1398:
1377:10.1086/380570
1355:
1312:
1291:(3): 382–391.
1271:
1250:10.1086/343873
1244:(6): 712–726.
1228:
1199:(1): 259–272.
1179:
1166:(4): 319–329.
1146:
1097:
1084:10.1086/286013
1078:(4): 646–667.
1062:
1008:
997:(3): 265–292.
978:
959:(7): 394–403.
943:
922:(5): 701–710.
902:
848:
837:(1): 267–285.
821:
814:
796:
783:10.1086/284325
757:
755:
752:
750:
749:
744:
739:
734:
729:
724:
719:
714:
712:Paul H. Harvey
709:
704:
699:
694:
689:
684:
678:
673:
668:
663:
658:
653:
648:
647:in linguistics
642:
637:
632:
630:Bioinformatics
627:
622:
617:
611:
609:
606:
584:
581:
546:
545:
534:
531:
527:
523:
520:
517:
512:
507:
504:
501:
498:
484:
483:
472:
469:
464:
460:
454:
450:
446:
443:
440:
435:
430:
427:
424:
421:
377:
374:
366:standard error
353:internal nodes
294:
291:
280:
279:
261:
260:
232:
231:
209:
208:
178:
177:
155:
154:
72:
69:
32:Charles Darwin
15:
9:
6:
4:
3:
2:
4842:
4831:
4830:Phylogenetics
4828:
4827:
4825:
4815:
4810:
4805:
4804:
4801:
4788:
4784:
4780:
4778:
4770:
4769:
4766:
4760:
4757:
4755:
4752:
4750:
4747:
4745:
4742:
4738:
4735:
4734:
4733:
4732:Phylogenetics
4730:
4728:
4725:
4723:
4720:
4718:
4715:
4713:
4710:
4706:
4703:
4701:
4698:
4696:
4693:
4692:
4691:
4688:
4686:
4683:
4681:
4678:
4676:
4673:
4672:
4670:
4666:
4660:
4657:
4653:
4650:
4648:
4645:
4641:
4638:
4637:
4636:
4635:Structuralism
4633:
4631:
4628:
4626:
4623:
4621:
4618:
4616:
4613:
4611:
4610:Catastrophism
4608:
4607:
4606:
4603:
4601:
4598:
4597:
4595:
4591:
4585:
4582:
4580:
4577:
4575:
4572:
4570:
4569:Neo-Darwinism
4567:
4565:
4562:
4560:
4557:
4555:
4552:
4550:
4547:
4545:
4542:
4538:
4537:
4533:
4532:
4531:
4528:
4524:
4523:
4519:
4518:
4517:
4514:
4512:
4509:
4507:
4504:
4503:
4501:
4499:
4495:
4489:
4486:
4484:
4483:Reinforcement
4481:
4479:
4476:
4474:
4471:
4469:
4466:
4464:
4461:
4459:
4456:
4454:
4451:
4449:
4446:
4444:
4441:
4439:
4436:
4434:
4431:
4430:
4428:
4426:
4422:
4416:
4415:Catastrophism
4412:
4409:
4407:
4406:Macromutation
4403:
4402:Micromutation
4400:
4398:
4394:
4390:
4387:
4386:
4384:
4382:
4378:
4372:
4369:
4365:
4362:
4360:
4357:
4355:
4352:
4350:
4347:
4345:
4342:
4341:
4340:
4337:
4335:
4332:
4330:
4327:
4325:
4322:
4320:
4317:
4315:
4312:
4310:
4309:Immune system
4307:
4305:
4302:
4300:
4297:
4295:
4292:
4290:
4287:
4283:
4280:
4279:
4278:
4275:
4273:
4270:
4268:
4265:
4263:
4260:
4256:
4253:
4251:
4248:
4247:
4246:
4243:
4242:
4240:
4238:
4233:
4225:
4222:
4220:
4217:
4215:
4212:
4210:
4207:
4205:
4202:
4201:
4199:
4195:
4192:
4190:
4187:
4185:
4182:
4180:
4177:
4175:
4172:
4170:
4169:symbiogenesis
4167:
4166:
4165:
4162:
4160:
4157:
4155:
4152:
4150:
4147:
4146:
4144:
4142:
4137:
4131:
4128:
4126:
4123:
4121:
4118:
4116:
4113:
4109:
4106:
4105:
4104:
4101:
4097:
4094:
4090:
4087:
4085:
4082:
4081:
4080:
4077:
4075:
4072:
4070:
4067:
4065:
4062:
4060:
4057:
4053:
4050:
4048:
4045:
4044:
4043:
4040:
4038:
4035:
4034:
4033:
4030:
4028:
4025:
4021:
4018:
4017:
4016:
4013:
4011:
4008:
4006:
4003:
4001:
3998:
3994:
3991:
3990:
3989:
3986:
3984:
3981:
3977:
3974:
3973:
3972:
3969:
3967:
3964:
3963:
3961:
3959:
3954:
3948:
3945:
3943:
3940:
3938:
3935:
3933:
3930:
3928:
3925:
3923:
3920:
3919:
3917:
3913:
3907:
3904:
3902:
3899:
3897:
3894:
3890:
3887:
3885:
3882:
3880:
3877:
3876:
3875:
3872:
3870:
3867:
3865:
3862:
3860:
3857:
3855:
3852:
3848:
3845:
3843:
3840:
3839:
3838:
3837:Kin selection
3835:
3833:
3832:Genetic drift
3830:
3828:
3825:
3821:
3818:
3817:
3816:
3813:
3811:
3808:
3806:
3803:
3801:
3798:
3796:
3793:
3792:
3790:
3788:
3782:
3774:
3771:
3770:
3769:
3766:
3764:
3761:
3757:
3754:
3752:
3749:
3748:
3747:
3744:
3740:
3737:
3736:
3735:
3732:
3730:
3727:
3725:
3722:
3720:
3717:
3715:
3712:
3710:
3707:
3705:
3702:
3700:
3697:
3695:
3692:
3690:
3687:
3683:
3680:
3679:
3678:
3675:
3673:
3670:
3668:
3665:
3663:
3660:
3658:
3655:
3653:
3650:
3648:
3645:
3643:
3640:
3638:
3635:
3631:
3628:
3627:
3626:
3623:
3621:
3618:
3616:
3613:
3609:
3606:
3604:
3601:
3600:
3599:
3596:
3594:
3591:
3589:
3586:
3584:
3581:
3580:
3578:
3576:
3572:
3566:
3563:
3561:
3558:
3556:
3553:
3551:
3548:
3546:
3543:
3542:
3539:
3535:
3528:
3523:
3521:
3516:
3514:
3509:
3508:
3505:
3493:
3492:
3483:
3481:
3480:
3471:
3470:
3467:
3461:
3458:
3456:
3453:
3451:
3448:
3446:
3443:
3441:
3438:
3437:
3435:
3431:
3425:
3422:
3420:
3417:
3415:
3412:
3411:
3409:
3405:
3397:
3394:
3392:
3389:
3387:
3384:
3383:
3381:
3377:
3374:
3372:
3369:
3368:
3367:
3364:
3363:
3361:
3357:
3351:
3348:
3346:
3345:Phylogenomics
3343:
3341:
3338:
3336:
3333:
3331:
3328:
3326:
3323:
3321:
3318:
3316:
3315:DNA barcoding
3313:
3311:
3310:
3306:
3305:
3303:
3299:
3293:
3290:
3286:
3285:Least squares
3283:
3281:
3278:
3276:
3273:
3272:
3271:
3268:
3264:
3261:
3259:
3256:
3255:
3253:
3251:
3248:
3246:
3243:
3242:
3240:
3236:
3230:
3227:
3223:
3222:Ghost lineage
3220:
3219:
3218:
3215:
3213:
3209:
3206:
3204:
3201:
3199:
3196:
3192:
3189:
3188:
3187:
3184:
3180:
3177:
3176:
3175:
3172:
3171:
3169:
3165:
3158:
3152:
3147:
3139:
3136:
3134:
3131:
3129:
3126:
3124:
3121:
3119:
3116:
3114:
3111:
3110:
3108:
3104:
3100:
3099:Phylogenetics
3093:
3088:
3086:
3081:
3079:
3074:
3073:
3070:
3063:
3060:
3058:
3055:
3053:
3050:
3048:
3045:
3043:
3040:
3038:
3035:
3033:
3030:
3028:
3025:
3023:
3020:
3018:
3015:
3013:
3010:
3008:
3005:
3003:
3000:
2998:
2995:
2993:
2990:
2988:
2985:
2983:
2980:
2978:
2975:
2973:
2970:
2968:
2965:
2963:
2960:
2958:
2955:
2953:
2950:
2948:
2945:
2943:
2940:
2938:
2935:
2933:
2930:
2928:
2925:
2924:
2915:
2912:
2910:
2907:
2905:
2902:
2900:
2897:
2895:
2892:
2890:
2887:
2885:
2882:
2879:
2877:
2874:
2872:
2869:
2867:
2864:
2862:
2859:
2857:
2854:
2853:
2845:
2842:
2840:
2837:
2835:
2832:
2830:
2827:
2825:
2822:
2820:
2817:
2815:
2812:
2810:
2807:
2805:
2802:
2800:
2797:
2796:
2788:
2785:
2783:
2780:
2778:
2775:
2773:
2770:
2768:
2765:
2763:
2760:
2759:
2748:
2744:
2739:
2735:
2731:
2727:
2723:
2716:
2711:
2707:
2703:
2699:
2695:
2691:
2687:
2682:
2678:
2674:
2670:
2666:
2662:
2658:
2654:
2650:
2645:
2640:
2635:
2631:
2627:
2623:
2618:
2614:
2610:
2606:
2602:
2598:
2594:
2590:
2586:
2581:
2577:
2573:
2569:
2565:
2560:
2555:
2551:
2547:
2543:
2538:
2535:
2531:
2527:
2523:
2519:
2515:
2511:
2504:
2499:
2497:
2492:
2488:
2484:
2480:
2476:
2472:
2468:
2461:
2456:
2452:
2448:
2444:
2440:
2436:
2432:
2425:
2420:
2416:
2412:
2408:
2404:
2400:
2396:
2392:
2388:
2381:
2376:
2372:
2368:
2364:
2360:
2355:
2350:
2346:
2345:10.1038/44766
2342:
2338:
2334:
2330:
2326:
2321:
2317:
2313:
2309:
2305:
2301:
2297:
2292:
2289:
2286:
2282:
2278:
2274:
2270:
2266:
2262:
2258:
2254:
2250:
2246:
2241:
2237:
2233:
2229:
2225:
2221:
2217:
2210:
2206:
2201:
2197:
2193:
2188:
2183:
2179:
2175:
2168:
2163:
2159:
2155:
2150:
2145:
2141:
2137:
2133:
2128:
2123:
2119:
2115:
2111:
2107:
2103:
2098:
2095:
2092:
2088:
2084:
2080:
2076:
2072:
2068:
2064:
2060:
2055:
2051:
2047:
2043:
2039:
2034:
2030:
2026:
2021:
2016:
2012:
2008:
2004:
1999:
1997:
1993:
1990:
1986:
1982:
1978:
1974:
1970:
1966:
1962:
1958:
1951:
1946:
1942:
1935:
1931:
1926:
1921:
1916:
1911:
1907:
1903:
1898:
1893:
1889:
1885:
1881:
1876:
1872:
1868:
1864:
1860:
1855:
1850:
1846:
1842:
1838:
1833:
1829:
1825:
1821:
1817:
1813:
1809:
1804:
1800:
1796:
1792:
1788:
1784:
1780:
1773:
1768:
1764:
1760:
1756:
1752:
1747:
1742:
1738:
1734:
1727:
1722:
1718:
1714:
1710:
1706:
1702:
1698:
1694:
1690:
1683:
1679:
1675:
1671:
1667:
1663:
1659:
1655:
1651:
1647:
1643:
1638:
1635:
1632:
1629:
1625:
1621:
1617:
1613:
1609:
1605:
1601:
1597:
1592:
1589:
1585:
1581:
1577:
1573:
1569:
1565:
1558:
1554:
1549:
1545:
1541:
1537:
1533:
1529:
1525:
1521:
1517:
1513:
1509:
1504:
1500:
1499:
1486:
1482:
1478:
1474:
1470:
1466:
1462:
1458:
1451:
1443:
1439:
1435:
1431:
1426:
1421:
1417:
1413:
1409:
1402:
1394:
1390:
1386:
1382:
1378:
1374:
1370:
1366:
1359:
1351:
1347:
1343:
1339:
1335:
1331:
1327:
1323:
1316:
1308:
1304:
1299:
1294:
1290:
1286:
1282:
1275:
1267:
1263:
1259:
1255:
1251:
1247:
1243:
1239:
1232:
1224:
1220:
1216:
1212:
1207:
1202:
1198:
1194:
1190:
1183:
1174:
1169:
1165:
1161:
1157:
1150:
1142:
1138:
1134:
1130:
1125:
1120:
1116:
1112:
1108:
1101:
1093:
1089:
1085:
1081:
1077:
1073:
1066:
1058:
1054:
1049:
1044:
1040:
1036:
1032:
1028:
1024:
1017:
1015:
1013:
1004:
1000:
996:
992:
985:
983:
974:
970:
966:
962:
958:
954:
947:
939:
935:
930:
925:
921:
917:
913:
906:
898:
894:
890:
886:
882:
878:
874:
870:
867:(1): 90–105.
866:
862:
855:
853:
844:
840:
836:
832:
825:
817:
815:9780198546405
811:
807:
800:
792:
788:
784:
780:
776:
772:
765:
763:
758:
748:
745:
743:
740:
738:
735:
733:
730:
728:
725:
723:
720:
718:
717:Phylogenetics
715:
713:
710:
708:
705:
703:
700:
698:
695:
693:
690:
688:
685:
682:
679:
677:
674:
672:
669:
667:
666:Ecophysiology
664:
662:
659:
657:
654:
652:
649:
646:
643:
641:
638:
636:
633:
631:
628:
626:
623:
621:
618:
616:
613:
612:
602:
598:
589:
580:
578:
574:
569:
567:
564:
560:
556:
551:
532:
521:
518:
505:
502:
499:
496:
489:
488:
487:
470:
462:
458:
452:
448:
444:
441:
428:
425:
422:
419:
412:
411:
410:
408:
404:
400:
396:
392:
388:
384:
373:
371:
367:
362:
358:
354:
349:
347:
343:
339:
335:
331:
327:
323:
319:
312:
308:
304:
299:
290:
289:
287:
277:
273:
272:
271:
270:
268:
258:
257:
256:
255:
253:
249:
242:
241:
239:
229:
225:
222:What was the
221:
220:
219:
218:
216:
206:
202:
201:social system
198:
194:
193:
192:
191:
189:
185:
182:Example: do
175:
171:
168:Do different
167:
166:
165:
164:
162:
152:
148:
144:
143:
142:
136:
132:
128:
124:
117:
113:
109:
105:
101:
97:
93:
89:
85:
81:
79:
68:
66:
62:
58:
54:
49:
47:
46:fossil record
43:
39:
38:
33:
29:
25:
21:
4744:Polymorphism
4727:Astrobiology
4675:Biogeography
4630:Saltationism
4620:Orthogenesis
4605:Alternatives
4534:
4520:
4453:Cospeciation
4448:Cladogenesis
4397:Saltationism
4354:Mating types
4277:Color vision
4262:Avian flight
4184:mitochondria
3922:Canalisation
3800:Biodiversity
3545:Introduction
3489:
3477:
3450:Sister group
3433:Nomenclature
3396:Autapomorphy
3391:Synapomorphy
3371:Plesiomorphy
3359:Group traits
3324:
3307:
3179:Cladogenesis
3174:Phylogenesis
2920:Laboratories
2787:Tree of Life
2746:
2742:
2725:
2721:
2689:
2685:
2652:
2648:
2629:
2625:
2588:
2584:
2549:
2545:
2513:
2509:
2470:
2466:
2434:
2430:
2390:
2386:
2328:
2324:
2299:
2295:
2248:
2244:
2219:
2215:
2177:
2173:
2142:(3): 81–98.
2139:
2135:
2105:
2101:
2062:
2058:
2041:
2037:
2010:
2006:
1963:(1): 84–96.
1960:
1956:
1890:(7): e2757.
1887:
1883:
1844:
1840:
1811:
1807:
1785:(1): 18–32.
1782:
1778:
1736:
1732:
1692:
1688:
1645:
1641:
1599:
1595:
1567:
1563:
1511:
1507:
1460:
1456:
1450:
1415:
1411:
1401:
1371:(1): 84–96.
1368:
1364:
1358:
1325:
1321:
1315:
1288:
1284:
1274:
1241:
1237:
1231:
1196:
1192:
1182:
1163:
1159:
1149:
1114:
1110:
1100:
1075:
1071:
1065:
1030:
1026:
994:
990:
956:
952:
946:
919:
915:
905:
864:
860:
834:
830:
824:
805:
799:
774:
770:
625:Biodiversity
595:
570:
558:
549:
547:
485:
406:
379:
350:
332:models. The
316:
307:correlations
283:
281:
264:
262:
245:
243:
235:
233:
212:
210:
181:
179:
158:
156:
145:What is the
140:
78:paleontology
74:
71:Applications
50:
35:
23:
19:
18:
4754:Systematics
4625:Mutationism
4443:Catagenesis
4371:Snake venom
4304:Eusociality
4282:in primates
4272:Cooperation
4200:In animals
4020:butterflies
3993:Cephalopods
3983:Brachiopods
3915:Development
3889:Mate choice
3642:Convergence
3625:Coevolution
3583:Abiogenesis
3445:Crown group
3407:Group types
3138:Systematics
2947:Felsenstein
2861:BayesTraits
2393:(1): 1–12.
2222:: 922–933.
2044:: 267–292.
1992:Ives, A. R.
777:(1): 1–15.
742:Systematics
318:Felsenstein
303:regressions
267:more labile
226:state of a
215:home ranges
28:phylogenies
4615:Lamarckism
4593:Philosophy
4516:David Hume
4478:Peripatric
4473:Parapatric
4458:Ecological
4438:Anagenesis
4433:Allopatric
4425:Speciation
4389:Gradualism
4314:Metabolism
4174:chromosome
4164:Eukaryotes
3942:Modularity
3859:Population
3785:Population
3746:Speciation
3724:Panspermia
3677:Extinction
3672:Exaptation
3647:Divergence
3620:Cladistics
3608:Reciprocal
3588:Adaptation
3123:Cladistics
2952:Freckleton
2749:: 785–805.
2626:BioScience
754:References
737:Statistics
697:Mark Pagel
635:Cladistics
391:consistent
357:inferences
286:life spans
252:viviparity
238:endothermy
197:behavioral
174:phenotypic
151:allometric
116:herbivores
104:carnivores
88:Home range
53:phenotypic
42:adaptation
4749:Protocell
4600:Darwinism
4488:Sympatric
4237:processes
4125:Tetrapods
4074:Kangaroos
4000:Dinosaurs
3937:Inversion
3906:Variation
3827:Gene flow
3820:Inclusive
3630:Mutualism
3575:Evolution
3460:Supertree
3424:Polyphyly
3419:Paraphyly
3414:Monophyly
3386:Apomorphy
3366:Primitive
3309:PhyloCode
3191:Cladogram
3062:Sanderson
2987:Housworth
2962:Gittleman
2814:Evolution
2772:Phylocomm
2649:Evolution
2613:198156300
2585:Evolution
2546:Evolution
2415:196612333
2387:Evolution
2371:205034365
2216:Evolution
2180:: 40–50.
2059:Evolution
1897:0807.4042
1596:Evolution
1564:Evolution
1457:Evolution
1322:Evolution
1193:Evolution
1111:Evolution
615:Allometry
506:∼
500:∣
497:ε
449:σ
429:∼
423:∣
420:ε
395:efficient
326:algorithm
248:placentas
224:ancestral
135:body size
112:ungulates
108:omnivores
100:Carnivora
96:body size
4824:Category
4777:Category
4652:Vitalism
4647:Theistic
4640:Spandrel
4324:Morality
4319:Monogamy
4194:plastids
4159:Flagella
4115:Reptiles
4096:sea cows
4079:primates
3988:Molluscs
3966:Bacteria
3854:Mutation
3787:genetics
3763:Taxonomy
3709:Mismatch
3689:Homology
3603:Cheating
3598:Altruism
3479:Category
3382:Derived
3128:Taxonomy
2992:Irschick
2937:Blomberg
2904:Phylocom
2881:Mesquite
2793:Journals
2706:42439809
2677:28565128
2605:16929667
2576:23200090
2568:11794776
2530:23728983
2451:12381290
2407:15792222
2363:10553904
2273:17344851
2236:13796463
2196:15356281
2158:16959643
2122:29362369
2087:28567979
2029:17464881
1985:10568814
1977:14767838
1934:18648500
1884:PLOS ONE
1871:27706318
1863:20070460
1763:14871059
1755:16081601
1709:10718731
1670:19796539
1662:18707460
1624:28564267
1584:12778543
1544:36391252
1536:15774753
1485:28568838
1442:27706318
1434:20070460
1393:10568814
1385:14767838
1350:28564168
1307:22215720
1266:19796539
1258:18707460
1215:10937202
1141:23200090
1133:11794776
1092:29362369
973:22658878
938:17849325
889:23773094
608:See also
561:such as
387:unbiased
322:topology
131:Primates
4668:Related
4498:History
4359:Meiosis
4294:Empathy
4289:Emotion
4189:nucleus
4130:Viruses
4120:Spiders
4032:Mammals
4015:Insects
3815:Fitness
3751:Species
3550:Outline
3491:Commons
3217:Lineage
3052:Rambaut
3042:Paradis
3007:Martins
2957:Garland
2927:Ackerly
2889:mvMorph
2871:COMPARE
2809:Ecology
2669:2410994
2487:2992489
2333:Bibcode
2316:8246516
2281:3031794
2253:Bibcode
2205:Ané, C.
2079:2409434
1925:2447175
1902:Bibcode
1828:2992183
1799:2992503
1717:4384701
1616:2408790
1516:Bibcode
1508:Science
1477:2409910
1342:2409716
1223:7887284
1057:2575770
1035:Bibcode
897:8384900
869:Bibcode
791:9731499
254:evolve?
92:mammals
57:genetic
4800:Portal
4787:Portal
4463:Hybrid
4299:Ethics
4141:organs
4103:Plants
4089:lemurs
4084:humans
4069:horses
4059:hyenas
4047:wolves
4042:canids
3976:origin
3047:Purvis
3027:Oakley
3012:Mooers
2982:Harvey
2977:Harmon
2972:Hansen
2967:Grafen
2942:Butler
2914:PHYSIG
2704:
2675:
2667:
2611:
2603:
2574:
2566:
2528:
2485:
2449:
2413:
2405:
2369:
2361:
2325:Nature
2314:
2279:
2271:
2245:Nature
2234:
2194:
2156:
2120:
2085:
2077:
2027:
1983:
1975:
1932:
1922:
1869:
1861:
1826:
1797:
1761:
1753:
1715:
1707:
1668:
1660:
1622:
1614:
1582:
1542:
1534:
1483:
1475:
1440:
1432:
1391:
1383:
1348:
1340:
1305:
1264:
1256:
1221:
1213:
1139:
1131:
1090:
1055:
971:
936:
895:
887:
812:
789:
592:other.
548:where
397:, and
188:felids
184:canids
176:trait?
170:clades
149:of an
127:Testes
4250:Death
4245:Aging
4224:brain
4010:Fungi
3971:Birds
3884:Fungi
3682:Event
3565:Index
3455:Basal
3280:UPGMA
3212:Grade
3208:Clade
3057:Rohlf
3037:Pagel
3002:Losos
2718:(PDF)
2702:S2CID
2665:JSTOR
2609:S2CID
2572:S2CID
2506:(PDF)
2483:JSTOR
2463:(PDF)
2427:(PDF)
2411:S2CID
2383:(PDF)
2367:S2CID
2277:S2CID
2232:S2CID
2212:(PDF)
2170:(PDF)
2154:S2CID
2118:S2CID
2075:JSTOR
1981:S2CID
1953:(PDF)
1892:arXiv
1867:S2CID
1824:JSTOR
1795:JSTOR
1775:(PDF)
1759:S2CID
1729:(PDF)
1713:S2CID
1685:(PDF)
1666:S2CID
1612:JSTOR
1560:(PDF)
1540:S2CID
1473:JSTOR
1438:S2CID
1389:S2CID
1338:JSTOR
1262:S2CID
1219:S2CID
1137:S2CID
1088:S2CID
893:S2CID
787:S2CID
683:(GLS)
334:logic
228:trait
147:slope
4737:Tree
4209:hair
4149:Cell
4052:dogs
4037:cats
4027:Life
4005:Fish
3958:taxa
3032:Page
3022:Nunn
3017:Mort
2997:Ives
2673:PMID
2601:PMID
2564:PMID
2526:PMID
2447:PMID
2403:PMID
2359:PMID
2312:PMID
2269:PMID
2192:PMID
2083:PMID
2025:PMID
1973:PMID
1930:PMID
1859:PMID
1751:PMID
1705:PMID
1658:PMID
1620:PMID
1580:PMID
1532:PMID
1481:PMID
1430:PMID
1381:PMID
1346:PMID
1303:PMID
1254:PMID
1211:PMID
1129:PMID
1053:PMID
969:PMID
934:PMID
885:PMID
865:1289
810:ISBN
344:and
250:and
205:diet
106:and
24:PCMs
4235:Of
4204:eye
4154:DNA
4139:Of
3956:Of
3210:vs
2730:doi
2694:doi
2657:doi
2634:doi
2593:doi
2554:doi
2518:doi
2496:PDF
2475:doi
2439:doi
2435:218
2395:doi
2349:hdl
2341:doi
2329:401
2304:doi
2300:164
2261:doi
2249:446
2224:doi
2182:doi
2144:doi
2110:doi
2106:149
2067:doi
2046:doi
2015:doi
1965:doi
1961:163
1920:PMC
1910:doi
1849:doi
1816:doi
1787:doi
1741:doi
1737:208
1697:doi
1693:155
1650:doi
1646:160
1604:doi
1572:doi
1524:doi
1512:307
1465:doi
1420:doi
1373:doi
1369:163
1330:doi
1293:doi
1246:doi
1242:160
1201:doi
1168:doi
1119:doi
1080:doi
1076:149
1043:doi
1031:326
999:doi
961:doi
924:doi
877:doi
839:doi
779:doi
775:125
368:or
55:or
4826::
2745:.
2726:17
2724:.
2720:.
2700:.
2690:23
2688:.
2671:.
2663:.
2653:51
2651:.
2630:52
2628:.
2624:.
2607:.
2599:.
2589:60
2587:.
2570:.
2562:.
2550:55
2548:.
2544:.
2524:.
2512:.
2508:.
2481:.
2471:42
2469:.
2465:.
2445:.
2433:.
2429:.
2409:.
2401:.
2391:59
2389:.
2385:.
2365:.
2357:.
2347:.
2339:.
2327:.
2310:.
2298:.
2275:.
2267:.
2259:.
2247:.
2230:.
2220:60
2218:.
2214:.
2190:.
2178:22
2176:.
2172:.
2152:.
2140:10
2138:.
2134:.
2116:.
2104:.
2081:.
2073:.
2063:44
2061:.
2042:39
2040:.
2023:.
2011:56
2009:.
2005:.
1979:.
1971:.
1959:.
1955:.
1928:.
1918:.
1908:.
1900:.
1886:.
1882:.
1865:.
1857:.
1845:23
1843:.
1839:.
1822:.
1812:39
1810:.
1793:.
1783:41
1781:.
1777:.
1757:.
1749:.
1735:.
1731:.
1711:.
1703:.
1691:.
1687:.
1664:.
1656:.
1644:.
1618:.
1610:.
1600:39
1598:.
1578:.
1568:57
1566:.
1562:.
1538:.
1530:.
1522:.
1510:.
1479:.
1471:.
1461:45
1459:.
1436:.
1428:.
1416:23
1414:.
1410:.
1387:.
1379:.
1367:.
1344:.
1336:.
1326:45
1324:.
1301:.
1289:61
1287:.
1283:.
1260:.
1252:.
1240:.
1217:.
1209:.
1197:54
1195:.
1191:.
1162:.
1158:.
1135:.
1127:.
1115:55
1113:.
1109:.
1086:.
1074:.
1051:.
1041:.
1029:.
1025:.
1011:^
995:42
993:.
981:^
967:.
957:27
955:.
932:.
920:56
918:.
914:.
891:.
883:.
875:.
863:.
851:^
835:43
833:.
785:.
773:.
761:^
393:,
389:,
372:.
348:.
309:,
305:,
282:→
263:→
244:→
234:→
211:→
203:,
180:→
157:→
80:.
48:.
4802::
4413:/
4404:/
4395:/
4391:/
3526:e
3519:t
3512:v
3091:e
3084:t
3077:v
2747:1
2736:.
2732::
2708:.
2696::
2679:.
2659::
2642:.
2636::
2615:.
2595::
2578:.
2556::
2532:.
2520::
2514:2
2489:.
2477::
2453:.
2441::
2417:.
2397::
2373:.
2351::
2343::
2335::
2318:.
2306::
2283:.
2263::
2255::
2238:.
2226::
2198:.
2184::
2160:.
2146::
2124:.
2112::
2089:.
2069::
2052:.
2048::
2031:.
2017::
1987:.
1967::
1936:.
1912::
1904::
1894::
1888:3
1873:.
1851::
1830:.
1818::
1801:.
1789::
1765:.
1743::
1719:.
1699::
1672:.
1652::
1626:.
1606::
1586:.
1574::
1546:.
1526::
1518::
1487:.
1467::
1444:.
1422::
1395:.
1375::
1352:.
1332::
1309:.
1295::
1268:.
1248::
1225:.
1203::
1176:.
1170::
1164:1
1143:.
1121::
1094:.
1082::
1059:.
1045::
1037::
1005:.
1001::
975:.
963::
940:.
926::
899:.
879::
871::
845:.
841::
818:.
793:.
781::
559:V
550:V
533:.
530:)
526:V
522:,
519:0
516:(
511:N
503:X
471:.
468:)
463:n
459:I
453:2
445:,
442:0
439:(
434:N
426:X
407:ε
230:?
190:?
163:?
102:(
22:(
Text is available under the Creative Commons Attribution-ShareAlike License. Additional terms may apply.