566:
634:
736:
624:
57:
31:
787:
The image of the ascending and descending orbital nodes as the head and tail of a dragon, 180 degrees apart in the sky, goes back to the
Chaldeans; it was used by the Zoroastrians, and then by Arabic astronomers and astrologers. In Middle Persian, its head and tail were respectively called
589:) is where it moves south through the plane. In the case of objects outside the Solar System, the ascending node is the node where the orbiting secondary passes away from the observer, and the descending node is the node where it moves towards the observer.
573:
If a reference direction from one side of the plane of reference to the other is defined, the two nodes can be distinguished. For geocentric and heliocentric orbits, the
946:
1284:
Livingston, John W. (1971). "Ibn Qayyim al-Jawziyyah: A Fourteenth
Century Defense against Astrological Divination and Alchemical Transmutation".
613:
is the straight line resulting from the intersection of the object's orbital plane with the plane of reference; it passes through the two nodes.
1043:
1218:
644:
In medieval and early modern times, the ascending and descending nodes of the Moon in the ecliptic plane were called the "dragon's head" (
1324:
452:
224:
293:
1185:
879:
473:
857:
599:
1178:
Webster's third new international dictionary of the
English language unabridged: with seven language dictionary
114:
17:
445:
378:
1334:
889:
1040:
1271:
658:
373:
288:
1230:
973:
921:
244:
1197:
819:
438:
161:
1226:
992:, R. G. Aitken, New York: Semi-Centennial Publications of the University of California, 1918.
884:
603:
346:
181:
89:
219:
176:
166:
94:
8:
547:
261:
99:
713:
were also used for the ascending and descending nodes, giving rise to the
English terms
1301:
1159:
1120:
1081:
1023:
752:
524:
497:
481:
477:
334:
209:
1181:
760:
744:
249:
186:
65:
949:
1293:
1151:
1112:
1073:
1015:
776:
594:
581:) is where the orbiting object moves north through the plane of reference, and the
552:
532:
513:
505:
419:
368:
133:
77:
35:
1329:
1047:
653:
565:
424:
329:
239:
214:
663:
645:
396:
312:
306:
229:
154:
148:
143:
1318:
675:
401:
234:
191:
1252:
852:
735:
592:
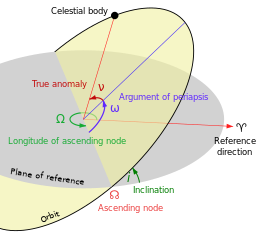
The position of the node may be used as one of a set of parameters, called
543:
119:
104:
893:
1050:, Ephraim Chambers, London: Printed for J. and J. Knapton , 1728, vol. 1.
698:
633:
550:
perpendicular to a line through the observer and the primary (called the
485:
283:
27:
Point where an orbit crosses a plane of reference to which it is inclined
623:
1163:
1139:
1027:
1003:
772:
730:
670:), respectively. These terms originally referred to the times when the
363:
319:
278:
56:
1305:
1124:
1100:
1085:
1061:
569:
Animation about nodes of two elliptic trajectories. (Click on image.)
1155:
1019:
1297:
1140:"Lexicographical Gleanings from the Philobiblon of Richard de Bury"
1116:
1077:
756:
528:
1144:
Transactions of the
American Philological Association (1869-1896)
847:
764:
638:
628:
1219:"Introduction: Coordinates, Seasons, Eclipses (lecture notes)"
1062:"Planetary Latitudes, the Theorica Gerardi, and Regiomontanus"
694:
were used in the medieval West to denote either of the nodes.
748:
708:
702:
509:
470:
84:
1041:
Cyclopædia, or, An universal dictionary of arts and sciences
978:
The
Encyclopedia of Astrobiology, Astronomy, and Spaceflight
926:
The
Encyclopedia of Astrobiology, Astronomy, and Spaceflight
671:
598:, which describe the orbit. This is done by specifying the
779:
westward, completing a cycle in approximately 18.6 years.
1101:"Prophatius Judaeus and the Medieval Astronomical Tables"
768:
674:
crossed the apparent path of the sun in the sky (as in a
30:
1198:
New thoughts on the genesis of the mysteries of
Mithras
631:: U+260A, ☊), and the symbol of the descending node is
795:
789:
1008:Transactions of the American Philosophical Society
818:. Among the arguments against astrologers made by
1316:
980:, David Darling, on line, accessed May 17, 2007.
678:). Also, corruptions of the Arabic term such as
826:"Why is it that you have given an influence to
535:. In this case, non-inclined orbits are called
516:. In this case, non-inclined orbits are called
1259:. February 17, 2012. Vol. XI, Fasc. 2, p. 184
446:
915:
913:
911:
833:
827:
813:
807:
801:
616:
1283:
1277:
1180:, Chicago: Encyclopædia Britannica, 1986.
453:
439:
1004:"A Survey of Islamic Astronomical Tables"
967:
908:
1286:Journal of the American Oriental Society
1257:Encyclopædia Iranica (iranicaonline.org)
1216:
734:
564:
29:
1001:
812:— or in the case of the Moon, ___
14:
1317:
1098:
491:
488:in the reference plane, has no nodes.
874:
872:
469:is either of the two points where an
34:The ascending node is one of several
1137:
1059:
838:, which are two imaginary points ?"
621:The symbol of the ascending node is
919:
782:
657:
560:
24:
869:
25:
1346:
945:
225:Kepler's laws of planetary motion
632:
622:
55:
1245:
1210:
1191:
1170:
1131:
858:Longitude of the ascending node
600:longitude of the ascending node
1325:Technical factors of astrology
1092:
1053:
1034:
995:
983:
939:
724:
13:
1:
1207:, #1 (2001), pp. 59–76.
863:
7:
1099:Harper, Richard I. (1971).
841:
480:to which it is inclined. A
379:Tsiolkovsky rocket equation
10:
1351:
888:(6th ed.). New York:
728:
709:
703:
348:Engineering and efficiency
167:Bi-elliptic transfer orbit
890:Columbia University Press
542:For an orbit outside the
1272:Gochihr (Zoroastrianism)
1138:West, Andrew F. (1891).
617:Symbols and nomenclature
546:, the plane through the
374:Propellant mass fraction
273:Gravitational influences
1002:Kennedy, E. S. (1956).
796:
790:
662:) and "dragon's tail" (
500:include the following:
245:Specific orbital energy
1060:Kren, Claudia (1977).
892:. 2004. Archived from
834:
828:
824:Miftah Dar al-SaCadah:
820:Ibn Qayyim al-Jawziyya
814:
808:
802:
740:
667:
649:
570:
162:Hohmann transfer orbit
39:
1227:University of Arizona
1176:anabibazon, entry in
885:Columbia Encyclopedia
771:upon the Moon causes
738:
604:longitude of the node
568:
358:Preflight engineering
90:Argument of periapsis
33:
822:(1292–1350), in his
809:al-dhanab al-jawzihr
602:(or, sometimes, the
414:Propulsive maneuvers
954:Celestial Mechanics
755:is taken to be the
498:planes of reference
492:Planes of reference
391:Efficiency measures
294:Sphere of influence
263:Celestial mechanics
45:Part of a series on
1233:on August 26, 2016
1046:2008-12-02 at the
803:al-ra's al-jawzihr
741:
571:
525:heliocentric orbit
482:non-inclined orbit
478:plane of reference
210:Dynamical friction
40:
797:gōzihr dumb
745:orbit of the Moon
739:Nodes of the Moon
463:
462:
313:Lagrangian points
250:Vis-viva equation
220:Kepler's equation
67:Orbital mechanics
16:(Redirected from
1342:
1335:Point (geometry)
1310:
1309:
1281:
1275:
1268:
1266:
1264:
1249:
1243:
1242:
1240:
1238:
1229:. Archived from
1214:
1208:
1195:
1189:
1174:
1168:
1167:
1135:
1129:
1128:
1096:
1090:
1089:
1057:
1051:
1038:
1032:
1031:
999:
993:
990:The Binary Stars
987:
981:
971:
965:
964:
962:
960:
947:Tatum, Jeremy B.
943:
937:
936:
934:
932:
920:Darling, David.
917:
906:
905:
903:
901:
896:on March 9, 2007
876:
837:
831:
817:
811:
805:
799:
793:
791:gōzihr sar
783:Use in astrology
761:equatorial plane
712:
711:
706:
705:
661:
636:
626:
595:orbital elements
561:Node distinction
553:plane of the sky
533:invariable plane
514:equatorial plane
506:geocentric orbit
455:
448:
441:
420:Orbital maneuver
369:Payload fraction
349:
330:Lissajous orbits
264:
235:Orbital velocity
182:Hyperbolic orbit
78:Orbital elements
68:
59:
42:
41:
36:orbital elements
21:
1350:
1349:
1345:
1344:
1343:
1341:
1340:
1339:
1315:
1314:
1313:
1282:
1278:
1269:
1262:
1260:
1251:
1250:
1246:
1236:
1234:
1215:
1211:
1196:
1192:
1175:
1171:
1156:10.2307/2935702
1136:
1132:
1097:
1093:
1058:
1054:
1048:Wayback Machine
1039:
1035:
1020:10.2307/1005726
1000:
996:
988:
984:
972:
968:
958:
956:
944:
940:
930:
928:
922:"line of nodes"
918:
909:
899:
897:
878:
877:
870:
866:
844:
785:
733:
727:
619:
583:descending node
563:
494:
459:
430:
429:
425:Orbit insertion
415:
407:
406:
392:
384:
383:
359:
351:
347:
340:
339:
335:Lyapunov orbits
326:
325:
309:
299:
298:
274:
266:
262:
255:
254:
240:Surface gravity
215:Escape velocity
205:
197:
196:
177:Parabolic orbit
173:
172:
139:
137:
134:two-body orbits
125:
124:
115:Semi-major axis
80:
70:
66:
28:
23:
22:
15:
12:
11:
5:
1348:
1338:
1337:
1332:
1327:
1312:
1311:
1298:10.2307/600445
1276:
1244:
1217:Marcia Rieke.
1209:
1200:, Roger Beck,
1190:
1169:
1130:
1117:10.1086/350708
1091:
1078:10.1086/351767
1072:(2): 194–205.
1052:
1033:
1014:(2): 123–177.
994:
982:
974:ascending node
966:
938:
907:
867:
865:
862:
861:
860:
855:
850:
843:
840:
784:
781:
729:Main article:
726:
723:
668:cauda draconis
650:caput draconis
641:: U+260B, ☋).
618:
615:
575:ascending node
562:
559:
558:
557:
540:
521:
493:
490:
461:
460:
458:
457:
450:
443:
435:
432:
431:
428:
427:
422:
416:
413:
412:
409:
408:
405:
404:
399:
397:Gravity assist
393:
390:
389:
386:
385:
382:
381:
376:
371:
366:
360:
357:
356:
353:
352:
345:
342:
341:
338:
337:
332:
324:
323:
315:
311:
310:
305:
304:
301:
300:
297:
296:
291:
286:
281:
275:
272:
271:
268:
267:
260:
257:
256:
253:
252:
247:
242:
237:
232:
230:Orbital period
227:
222:
217:
212:
206:
203:
202:
199:
198:
195:
194:
192:Decaying orbit
189:
184:
179:
171:
170:
164:
157:
155:Transfer orbit
153:
152:
151:
149:Elliptic orbit
146:
144:Circular orbit
140:
131:
130:
127:
126:
123:
122:
117:
112:
107:
102:
97:
92:
87:
81:
76:
75:
72:
71:
64:
61:
60:
52:
51:
47:
46:
26:
9:
6:
4:
3:
2:
1347:
1336:
1333:
1331:
1328:
1326:
1323:
1322:
1320:
1307:
1303:
1299:
1295:
1292:(1): 96–103.
1291:
1287:
1280:
1273:
1258:
1254:
1248:
1232:
1228:
1224:
1223:Astronomy 250
1220:
1213:
1206:
1203:
1199:
1194:
1187:
1186:0-85229-503-0
1183:
1179:
1173:
1165:
1161:
1157:
1153:
1149:
1145:
1141:
1134:
1126:
1122:
1118:
1114:
1110:
1106:
1102:
1095:
1087:
1083:
1079:
1075:
1071:
1067:
1063:
1056:
1049:
1045:
1042:
1037:
1029:
1025:
1021:
1017:
1013:
1009:
1005:
998:
991:
986:
979:
975:
970:
955:
951:
948:
942:
927:
923:
916:
914:
912:
895:
891:
887:
886:
881:
875:
873:
868:
859:
856:
854:
851:
849:
846:
845:
839:
836:
830:
825:
821:
816:
810:
804:
800:; in Arabic,
798:
792:
780:
778:
775:to gradually
774:
770:
766:
765:gravitational
762:
758:
754:
750:
746:
737:
732:
722:
720:
716:
700:
695:
693:
689:
685:
681:
677:
676:solar eclipse
673:
669:
665:
660:
655:
651:
647:
642:
640:
635:
630:
625:
614:
612:
611:line of nodes
607:
605:
601:
597:
596:
590:
588:
584:
580:
576:
567:
555:
554:
549:
545:
541:
538:
534:
530:
526:
522:
519:
515:
511:
507:
503:
502:
501:
499:
489:
487:
483:
479:
475:
472:
468:
456:
451:
449:
444:
442:
437:
436:
434:
433:
426:
423:
421:
418:
417:
411:
410:
403:
402:Oberth effect
400:
398:
395:
394:
388:
387:
380:
377:
375:
372:
370:
367:
365:
362:
361:
355:
354:
350:
344:
343:
336:
333:
331:
328:
327:
321:
317:
316:
314:
308:
307:N-body orbits
303:
302:
295:
292:
290:
289:Perturbations
287:
285:
282:
280:
277:
276:
270:
269:
265:
259:
258:
251:
248:
246:
243:
241:
238:
236:
233:
231:
228:
226:
223:
221:
218:
216:
213:
211:
208:
207:
201:
200:
193:
190:
188:
185:
183:
180:
178:
175:
174:
168:
165:
163:
159:
158:
156:
150:
147:
145:
142:
141:
135:
129:
128:
121:
118:
116:
113:
111:
110:Orbital nodes
108:
106:
103:
101:
98:
96:
93:
91:
88:
86:
83:
82:
79:
74:
73:
69:
63:
62:
58:
54:
53:
50:Astrodynamics
49:
48:
44:
43:
37:
32:
19:
18:Orbital nodes
1289:
1285:
1279:
1261:. Retrieved
1256:
1247:
1235:. Retrieved
1231:the original
1222:
1212:
1204:
1201:
1193:
1177:
1172:
1147:
1143:
1133:
1111:(1): 61–68.
1108:
1104:
1094:
1069:
1065:
1055:
1036:
1011:
1007:
997:
989:
985:
977:
969:
957:. Retrieved
953:
950:"Chapter 17"
941:
929:. Retrieved
925:
898:. Retrieved
894:the original
883:
853:Euler angles
823:
786:
767:pull of the
742:
718:
714:
696:
691:
687:
683:
679:
643:
620:
610:
608:
593:
591:
586:
582:
578:
574:
572:
551:
544:Solar System
536:
517:
495:
467:orbital node
466:
464:
187:Radial orbit
138:eccentricity
120:True anomaly
109:
105:Mean anomaly
95:Eccentricity
976:, entry in
725:Lunar nodes
719:catabibazon
710:καταβιβάζων
699:Koine Greek
659:رأس الجوزهر
484:, which is
320:Halo orbits
284:Hill sphere
100:Inclination
1319:Categories
1150:: 93–104.
864:References
759:, not the
731:Lunar node
715:anabibazon
704:αναβιβάζων
587:south node
579:north node
518:equatorial
474:intersects
364:Mass ratio
279:Barycenter
1263:March 28,
835:al-Dhanab
815:al-tennin
773:its nodes
486:contained
204:Equations
132:Types of
1253:"Gōzihr"
1044:Archived
842:See also
757:ecliptic
743:For the
692:zeuzahar
684:genzahar
537:ecliptic
529:ecliptic
1237:May 17,
1164:2935702
1028:1005726
959:May 17,
931:May 17,
900:May 17,
848:Eclipse
829:al-Ra's
777:precess
747:around
688:geuzaar
680:ganzaar
639:Unicode
629:Unicode
548:primary
496:Common
1330:Orbits
1306:600445
1304:
1184:
1162:
1125:229000
1123:
1086:230070
1084:
1026:
880:"node"
763:. The
751:, the
701:terms
654:Arabic
527:, the
523:For a
504:For a
1302:JSTOR
1202:Topoi
1160:JSTOR
1121:JSTOR
1082:JSTOR
1024:JSTOR
753:plane
749:Earth
664:Latin
646:Latin
510:Earth
471:orbit
85:Apsis
1270:Cf.
1265:2023
1239:2007
1182:ISBN
1105:Isis
1066:Isis
961:2007
933:2007
902:2007
832:and
806:and
794:and
717:and
707:and
697:The
690:and
672:Moon
609:The
585:(or
577:(or
1294:doi
1152:doi
1113:doi
1074:doi
1016:doi
769:Sun
606:.)
531:or
512:'s
465:An
136:by
1321::
1300:.
1290:91
1288:.
1255:.
1225:.
1221:.
1205:11
1158:.
1148:22
1146:.
1142:.
1119:.
1109:62
1107:.
1103:.
1080:.
1070:68
1068:.
1064:.
1022:.
1012:46
1010:.
1006:.
952:.
924:.
910:^
882:.
871:^
721:.
686:,
682:,
666::
656::
652:,
648::
556:).
508:,
476:a
1308:.
1296::
1274:.
1267:.
1241:.
1188:.
1166:.
1154::
1127:.
1115::
1088:.
1076::
1030:.
1018::
963:.
935:.
904:.
637:(
627:(
539:.
520:.
454:e
447:t
440:v
322:)
318:(
169:)
160:(
38:.
20:)
Text is available under the Creative Commons Attribution-ShareAlike License. Additional terms may apply.