2023:, using the rate of change of quantities at the instant J2000. The J2000 rate of change equals the coefficient of the first-degree term of VSOP polynomials. In the original VSOP87 elements, the units are arcseconds(”) and Julian centuries. There are 1,296,000” in a circle, 36525 days in a Julian century. The sidereal month is the time of a revolution of longitude λ with respect to the fixed J2000 equinox. VSOP87 gives 1732559343.7306” or 1336.8513455 revolutions in 36525 days–27.321661547 days per revolution. The tropical month is similar, but the longitude for the equinox of date is used. For the anomalistic year, the mean anomaly (λ−ω) is used (equinox does not matter). For the draconic month, (λ−Ω) is used. For the synodic month, the sidereal period of the mean Sun (or Earth) and the Moon. The period would be 1/(1/m−1/e). VSOP elements from
45:
610:
599:
1357:, meaning that it keeps the same face toward Earth at all times. This synchronous rotation is only true on average because the Moon's orbit has a definite eccentricity. As a result, the angular velocity of the Moon varies as it orbits Earth and hence is not always equal to the Moon's rotational velocity which is more constant. When the Moon is at its perigee, its orbital motion is faster than its rotation. At that time the Moon is a bit ahead in its orbit with respect to its rotation about its axis, and this creates a perspective effect which allows us to see up to eight degrees of longitude of its eastern (right)
1442:, its centre of gravity is within Earth, about 4,671 km (2,902 mi) or 73.3% of the Earth's radius from the centre of the Earth. This centre of gravity remains on the line between the centres of the Earth and Moon as the Earth completes its diurnal rotation. The path of the Earth–Moon system in its solar orbit is defined as the movement of this mutual centre of gravity around the Sun. Consequently, Earth's centre veers inside and outside the solar orbital path during each synodic month as the Moon moves in its orbit around the common centre of gravity.
1342:
1323:, in which the Moon will orbit Earth in about 47 days (currently 27 days), and both the Moon and Earth would rotate around their axes in the same time, always facing each other with the same side. This has already happened to the Moon—the same side always faces Earth—and is also slowly happening to the Earth. However, the slowdown of Earth's rotation is not occurring fast enough for the rotation to lengthen to a month before other effects change the situation: approximately 2.3 billion years from now, the increase of the Sun's
529:
1431:, it is common to draw the trajectory of Earth from the point of view of the Sun, and the trajectory of the Moon from the point of view of Earth. This could give the impression that the Moon orbits Earth in such a way that sometimes it goes backwards when viewed from the Sun's perspective. However, because the orbital velocity of the Moon around Earth (1 km/s) is small compared to the orbital velocity of Earth about the Sun (30 km/s), this never happens. There are no rearward loops in the Moon's solar orbit.
737:. Therefore, the angle between the ecliptic and the lunar equator is always 1.543°, even though the rotational axis of the Moon is not fixed with respect to the stars. It also means that when the Moon is farthest north of the ecliptic, the centre of the part seen from Earth is about 6.7° south of the lunar equator and the south pole is visible, whereas when the Moon is farthest south of the ecliptic the centre of the visible part is 6.7° north of the equator and the north pole is visible. This is called
583:
923:
4801:
455:
3672:
3933:
3921:
1397:
651:
372:
4739:
4777:
2537:
4789:
441:
691:
946:
786:
between lunar night and lunar day. At the lunar poles, instead of usual lunar days and nights of about 15 Earth days, the Sun will be "up" for 173 days as it will be "down"; polar sunrise and sunset takes 18 days each year. "Up" here means that the centre of the Sun is above the horizon. Lunar polar sunrises and sunsets occur around the time of eclipses (solar or lunar). For example, at the
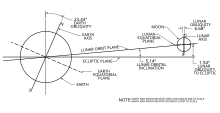
589:—The major axis of Moon's elliptical orbit rotates by one complete revolution once every 8.85 years in the same direction as the Moon's rotation itself. This image looks upwards depicting Earth's geographic south pole and the elliptical shape of the Moon's orbit (vastly exaggerated from its almost circular shape to make the precession evident) is rotating from white to greyer orbits.
4765:
1210:
1282:
Although the ocean's response is the more complex of the two, it is possible to split the ocean tides into a small ellipsoid term which affects the Moon plus a second term which has no effect. The ocean's ellipsoid term also slows the Earth and accelerates the Moon, but because the ocean dissipates
1373:, which allows one to see almost 7° of latitude beyond the pole on the far side. Finally, because the Moon is only about 60 Earth radii away from Earth's centre of mass, an observer at the equator who observes the Moon throughout the night moves laterally by one Earth diameter. This gives rise to a
1314:
between natural ocean frequencies and tidal frequencies. Another explanation is that in the past the Earth rotated much faster, a day possibly lasting only 9 hours on the early Earth. The resulting tidal waves in the ocean would have then been much shorter and it would have been more difficult for
1262:
in both the ocean and the solid Earth; the Sun has a smaller tidal influence. The solid Earth responds quickly to any change in the tidal forcing, the distortion taking the form of an ellipsoid with the high points roughly beneath the Moon and on the opposite side of Earth. This is a result of the
1306:
from 620 million years ago show that, over hundreds of millions of years, the Moon receded at an average rate of 22 mm (0.87 in) per year (2200 km or 0.56% or the Earth-moon distance per hundred million years) and the day lengthened at an average rate of 12 microseconds per year (or
713:
is 5.145°. Theoretical considerations show that the present inclination relative to the ecliptic plane arose by tidal evolution from an earlier near-Earth orbit with a fairly constant inclination relative to Earth's equator. It would require an inclination of this earlier orbit of about 10° to the
1445:
The Sun's gravitational effect on the Moon is more than twice that of Earth's on the Moon; consequently, the Moon's trajectory is always convex (as seen when looking
Sunward at the entire Sun–Earth–Moon system from a great distance outside Earth–Moon solar orbit), and is nowhere concave (from the
1278:
In the case of the ocean tides, the speed of tidal waves in the ocean is far slower than the speed of the Moon's tidal forcing. As a result, the ocean is never in near equilibrium with the tidal forcing. Instead, the forcing generates the long ocean waves which propagate around the ocean basins
1274:
is not infinite and, together with the effect of energy loss within the Earth, this causes a slight delay between the passage of the maximum forcing due to the Moon across and the maximum Earth tide. As the Earth rotates faster than the Moon travels around its orbit, this small angle produces a
785:
or eclipse year. The "seasons" on the Moon fit into this period. For about half of this draconic year, the Sun is north of the lunar equator (but at most 1.543°), and for the other half, it is south of the lunar equator. The effect of these seasons, however, is minor compared to the difference
857:
every day from latitudes less than 70°43' (90° − 18°20' – 57' parallax) north or south. When the inclination is at its maximum of 28°36', the centre of the Moon's disk will be above the horizon every day only from latitudes less than 60°27' (90° − 28°36' – 57' parallax) north or south.
507:" occurs when the full Moon is closest to Earth (perigee). The largest possible apparent diameter of the Moon is the same 12% larger (as perigee versus apogee distances) than the smallest; the apparent area is 25% more and so is the amount of light it reflects toward Earth.
1423:
can be used to indicate the direction of the angular velocity. If the thumb of the right hand points to the north celestial pole, its fingers curl in the direction that the Moon orbits Earth, Earth orbits the Sun, and the Moon and Earth rotate on their own axes.
769:: for an observer on Earth, it rotates westward along the ecliptic with a period of 18.6 years or 19.3549° per year. When viewed from the celestial north, the nodes move clockwise around Earth, opposite to Earth's own spin and its revolution around the Sun. An
674:, respectively – makes one complete revolution every 8.85 Earth years, or 3,232.6054 days, as it rotates slowly in the same direction as the Moon itself (direct motion) – meaning precesses eastward by 360°. The Moon's apsidal precession is distinct from the
790:, the Moon was near its descending node, and the Sun was near the point in the sky where the equator of the Moon crosses the ecliptic. When the Sun reaches that point, the centre of the Sun sets at the lunar north pole and rises at the lunar south pole.
773:
of the Moon or Sun can occur when the nodes align with the Sun, roughly every 173.3 days. Lunar orbit inclination also determines eclipses; shadows cross when nodes coincide with full and new moon when the Sun, Earth, and Moon align in three dimensions.
797:, the Moon was near its ascending node, and the Sun was near the point in the sky where the equator of the Moon crosses the ecliptic. When the Sun reaches that point, the centre of the Sun rises at the lunar north pole and sets at the lunar south pole.
922:
528:
1286:
Because of the tidal torque, caused by the ellipsoids, some of Earth's angular (or rotational) momentum is gradually being transferred to the rotation of the Earth–Moon pair around their mutual centre of mass, called the barycentre. See
986:
in human history. However, the
Babylonians seem to have lacked any geometric or physical interpretation of their data, and they could not predict future lunar eclipses (though "warnings" were issued before likely eclipse times).
1318:
The Moon is gradually receding from Earth into a higher orbit, and calculations suggest that this would continue for about 50 billion years. By that time, Earth and the Moon would be in a mutual spin–orbit resonance or
2055:(Richmond, VA: Willmann-Bell, 1998) p 354. From 1900–2100, the shortest time from one new moon to the next is 29 days, 6 hours, and 35 min, and the longest 29 days, 19 hours, and 55 min.
3648:
969:
writing recording the times and dates of moonrises and moonsets, the stars that the Moon passed close by, and the time differences between rising and setting of both the Sun and the Moon around the time of a
1368:
The Moon's axis of rotation is inclined by in total 6.7° relative to the normal to the plane of the ecliptic. This leads to a similar perspective effect in the north–south direction that is referred to as
714:
equator to produce a present inclination of 5° to the ecliptic. It is thought that originally the inclination to the equator was near zero, but it could have been increased to 10° through the influence of
865:, there will be a period of at least one day each month when the Moon does not rise, but there will also be a period of at least one day each month when the Moon does not set. This is similar to the
2025:
Simon, J.L.; Bretagnon, P.; Chapront, J.; Chapront-Touzé, M.; Francou, G.; Laskar, J. (February 1994). "Numerical expressions for precession formulae and mean elements for the Moon and planets".
721:
The rotational axis of the Moon is not perpendicular to its orbital plane, so the lunar equator is not in the plane of its orbit, but is inclined to it by a constant value of 6.688° (this is the
1176:. This varies notably throughout the year, but averages around 29.53 days. The synodic period is longer than the sidereal period because the Earth–Moon system moves in its orbit around the
1361:. Conversely, when the Moon reaches its apogee, its orbital motion is slower than its rotation, revealing eight degrees of longitude of its western (left) far side. This is referred to as
982:
to build lunar calendars that extended well into the future. This use of detailed, systematic observations to make predictions based on experimental data may be classified as the first
965:
were the first human civilization known to have kept a consistent record of lunar observations. Clay tablets from that period, which have been found in Iraq, are inscribed with
3595:
911:
in the Arctic when the Sun is below the horizon for months and must have been helpful to the animals that lived in Arctic and
Antarctic regions when the climate was warmer.
718:
passing near the Moon while falling to the Earth. If this had not happened, the Moon would now lie much closer to the ecliptic and eclipses would be much more frequent.
314:
around the barycentre between the Earth and the Moon, of 1.022 km/s (0.635 miles/s, 2,286 miles/h), the Moon covers a distance approximately its diameter, or about
838:
will vary from −28°36′ to +28°36′. Conversely, 9.3 years later, the angle between the Moon's orbit and Earth's equator reaches its minimum of 18°20′. This is called a
3553:
935:
of the Earth–Moon system (respecting sizes and distances), utilizing the mean radii of both bodies and mean distance of the orbit. Scroll right to find the Moon.
842:. The last lunar standstill was a minor standstill in October 2015. At that time the descending node was lined up with the equinox (the point in the sky having
538:
Minimum, mean and maximum distances of the Moon from Earth with its angular diameter as seen from Earth's surface, to scale. Scroll to right to see the Moon.
888:
for almost two weeks every month, even though the Sun is below the horizon for six months at a time. The period from moonrise to moonrise at the poles is a
949:
The apparent trajectory of the Moon in the sky seen from Earth each night is like a wide ellipse, although the path depends on the time of the year and
2000:
1384:
Besides these "optical librations" caused by the change in perspective for an observer on Earth, there are also "physical librations" which are actual
3588:
1298:
means that Earth's axial rotation is gradually slowing, and because of this its day lengthens by approximately 24 microseconds every year (excluding
1206:(a twelfth of a year) is about 30.4 days. This is not a lunar period, though the calendar month is historically related to the visible lunar phase.
869:
behaviour of the Sun, but with a period of 27.2 days instead of 365 days. Note that a point on the Moon can actually be visible when it is about 34
2306:
The reference by H. L. Vacher (2001) (details separately cited in this list) describes this as 'convex outward', whereas older references such as "
1951:
1485:
755:
The nodes are points at which the Moon's orbit crosses the ecliptic. The Moon crosses the same node every 27.2122 days, an interval called the
503:
Since nearer objects appear larger, the Moon's apparent size changes as it moves toward and away from an observer on Earth. An event called a "
3709:
1839:
853:
When the inclination of the Moon's orbit to the Earth's equator is at its minimum of 18°20′, the centre of the Moon's disk will be above the
49:
Diagram of the Moon's orbit with respect to the Earth. Angles are correct and relative sizes are to scale, but distances are not to scale.
1184:
is the time between perigees and is about 27.55 days. The Earth–Moon separation determines the strength of the lunar tide raising force.
3581:
3228:
2363:
484:
about Earth (the semimajor and semiminor axes are 384,400 km and 383,800 km, respectively: a difference of only 0.16%). The
1294:
This slightly greater orbital angular momentum causes the Earth–Moon distance to increase at approximately 38 millimetres per year.
3162:
662:
and is the rotation of the Moon's orbit within the orbital plane, i.e. the axes of the ellipse change direction. The lunar orbit's
1377:, which allows one to view an additional one degree's worth of lunar longitude. For the same reason, observers at both of Earth's
1180:
during each sidereal month, hence a longer period is required to achieve a similar alignment of Earth, the Sun, and the Moon. The
307:
is about 385,000 km (239,000 mi) from Earth's centre, which corresponds to about 60 Earth radii or 1.282 light-seconds.
3567:
4616:
3560:
1889:
Kaveh
Pahlevan & Alessandro Morbidelli (Nov 26, 2015). "Collisionless encounters and the origin of the lunar inclination".
3905:
3895:
553:
535:
424:
The properties of the orbit described in this section are approximations. The Moon's orbit around Earth has many variations (
4676:
2288:
1168:
is the time it takes to make one complete orbit around Earth with respect to the fixed stars. It is about 27.32 days. The
3779:
880:
Because of the inclination of the Moon's orbit with respect to the Earth's equator, the Moon is above the horizon at the
564:, that is, the Sun, Moon and Earth are nearly aligned. When elongation is either 90° or 270°, the Moon is said to be in
2430:
794:
389:
1646:
M. Chapront-Touzé; J. Chapront (1988). "ELP2000-85: a semi-analytical lunar ephemeris adequate for historical times".
850:
zero). The nodes are moving west by about 19° per year. The Sun crosses a given node about 20 days earlier each year.
3702:
2343:
2270:
2078:
1711:
1687:
1279:
until eventually losing their energy through turbulence, either in the deep ocean or on shallow continental shelves.
729:
in 1722, the rotational axis of the Moon precesses with the same rate as its orbital plane, but is 180° out of phase
411:
1283:
so much tidal energy, the present ocean tides have an order of magnitude greater effect than the solid Earth tides.
4671:
4551:
3970:
3626:
3611:
1295:
17:
4636:
4390:
3033:
3019:
4709:
4348:
4339:
4076:
3185:
3178:
3155:
2465:
2070:
1490:
787:
510:
The variance in the Moon's orbital distance corresponds with changes in its tangential and angular speeds, per
500:
distances of 362,600 km (225,300 mi) and 405,400 km (251,900 mi) respectively (a difference of 12%).
393:
256:
2846:
2651:
1538:
1521:
1475:
1990:
Calculated from arcsin(0.25°/1.543°)/90° times 173 days, since the angular radius of the Sun is about 0.25°.
658:
The orientation of the orbit is not fixed in space but rotates over time. This orbital precession is called
4656:
4126:
3695:
3214:
1595:
km, "equatorial horizontal parallax at mean distance" 3422.608″, and "equatorial radius for Earth" 6,378.14
929:
552:
is its angular distance east of the Sun at any time. At new moon, it is zero and the Moon is said to be in
296:
295:), which lies about 4,670 km (2,900 mi) from Earth's centre (about 73% of its radius), forming a
44:
4601:
3357:
2927:
2920:
2906:
2862:
901:
609:
2311:, Turner, A. B. Journal of the Royal Astronomical Society of Canada, Vol. 6, p. 117, 1912JRASC...6..117T
1327:
will have caused Earth's oceans to evaporate, removing the bulk of the tidal friction and acceleration.
4821:
4755:
4581:
4408:
3026:
2674:
2568:
2554:
2502:
1416:
and Earth orbits the Sun anticlockwise, and the Moon and Earth rotate on their own axes anticlockwise.
1195:
to ascending node. The time between two successive passes of the same ecliptic longitude is called the
892:, about 27.3 days, quite close to the sidereal period. When the Sun is the furthest below the horizon (
304:
2869:
234:
4719:
3879:
2837:
1345:
Animation of the Moon as it cycles through its phases. The apparent wobbling of the Moon is known as
343:
598:
224:
4704:
4229:
3744:
3251:
3111:
1852:
1299:
870:
425:
4714:
4022:
3574:
3205:
3079:
2819:
2509:
2486:
705:. At such times, the Earth's north pole is toward the Moon and the Moon is north of the ecliptic.
382:
4576:
4178:
4098:
4086:
3855:
3118:
2749:
2523:
2479:
2423:
1741:
897:
874:
862:
565:
557:
549:
511:
1726:
1446:
same perspective) or looped. That is, the region enclosed by the Moon's orbit of the Sun is a
514:. The mean angular movement relative to an imaginary observer at the Earth–Moon barycentre is
4699:
4641:
4611:
4399:
4276:
4244:
4214:
4173:
4158:
4037:
3804:
3655:
3171:
3141:
2853:
2784:
2314:
1812:
1435:
738:
710:
2367:
2151:"Geological constraints on the Precambrian history of Earth's rotation and the Moon's orbit"
2038:
1659:
1632:
4724:
4546:
4330:
4219:
4188:
4116:
4091:
4066:
4027:
4008:
3963:
3871:
3484:
3470:
3288:
3237:
2791:
2211:
2162:
2107:
2034:
1908:
1861:
1821:
1784:
1655:
1628:
1460:
1358:
1354:
975:
489:
140:
8:
4793:
4586:
4381:
4121:
3818:
3267:
3104:
2448:
1495:
1388:
of the direction of the pole of rotation of the Moon in space: but these are very small.
1341:
1016:
820:
694:
347:
335:
2215:
2166:
2111:
1912:
1865:
1825:
1788:
4781:
4259:
4148:
4046:
3900:
3798:
3452:
3304:
3072:
2973:
2720:
2658:
2616:
2224:
2199:
2180:
2131:
1932:
1898:
1288:
1245:
994:
659:
586:
561:
2387:
350:
by about 5.1° with respect to the ecliptic plane, whereas Earth's equatorial plane is
4626:
4524:
4454:
4209:
4081:
3932:
3920:
3718:
3634:
3394:
3093:
3058:
3051:
2416:
2339:
2307:
2266:
2254:
2135:
2123:
2095:
2074:
1924:
1772:
1707:
1683:
1378:
1307:
20 minutes per hundred million years), both about half of their current values.
1181:
1109:
983:
958:
766:
732:
2184:
4606:
4538:
4302:
4264:
4138:
4108:
4061:
3924:
3530:
3194:
2996:
2812:
2805:
2765:
2607:
2561:
2536:
2219:
2170:
2115:
2020:
1936:
1916:
1869:
1829:
1792:
1525:
1500:
1209:
830:
806:
679:
675:
577:
339:
319:
315:
2913:
2405:
Good diagrams of Moon, Earth, tilts of orbits and axes, courtesy of U. of
Arkansas
1275:
gravitational torque which slows the Earth and accelerates the Moon in its orbit.
666:– the longest diameter of the orbit, joining its nearest and farthest points, the
428:) due to the gravitational attraction of the Sun and planets, the study of which (
4646:
4239:
4143:
4133:
4032:
3956:
3537:
3274:
3127:
2890:
2292:
1249:
1082:
with respect to the Sun (phases of the Moon, 12.36874634 passes per solar orbit)
893:
843:
726:
55:
2285:
1302:). Both figures are valid only for the current configuration of the continents.
4805:
4742:
4694:
4686:
4681:
4566:
4561:
4492:
4472:
4463:
4056:
4042:
4018:
4013:
3988:
3297:
3221:
3086:
3003:
2980:
1573:
is traditionally the Moon's mean distance from Earth (center to center), where
1470:
1420:
1405:
1196:
1188:
1165:
1138:
1087:
1051:
990:
889:
765:. The line of nodes, the intersection between the two respective planes, has a
757:
292:
276:
272:
260:
201:
2119:
1796:
896:), the Moon will be full when it is at its highest point. When the Moon is in
4815:
4596:
4591:
4510:
4153:
4071:
3675:
3641:
3523:
3417:
3350:
2959:
2899:
2736:
2713:
2681:
2667:
2644:
2127:
2005:
1465:
1439:
1413:
1381:
would be able to see one additional degree's worth of libration in latitude.
1320:
1264:
1169:
1069:
979:
782:
778:
311:
284:
264:
213:
1833:
1541:
expressions for the distance, which is the mean distance averaged over time.
4769:
4661:
4571:
4445:
4428:
4286:
4183:
4051:
3936:
3751:
3737:
3509:
3325:
3244:
3065:
2943:
2758:
2598:
2472:
2262:
1928:
1591:
1976 Astronomical
Constants were "mean distance of Moon from Earth" 384,400
1428:
1192:
1101:
1012:
715:
429:
323:
2883:
1888:
582:
493:
485:
4666:
4501:
4271:
4251:
4168:
3863:
3847:
3792:
3786:
3618:
3602:
3544:
3516:
3502:
3477:
3368:
3318:
2989:
2727:
2706:
2493:
2175:
2150:
1843:
1255:
1218:
1173:
1164:
There are several different periods associated with the lunar orbit. The
1028:
1019:. The observations of the lunar motion were the main test of his theory.
932:
908:
847:
835:
268:
169:
31:
1920:
1315:
the long wavelength tidal forcing to excite the short wavelength tides.
497:
4234:
3948:
3887:
3811:
3758:
3431:
3010:
2936:
2876:
2830:
2772:
2591:
1619:
M. Chapront-Touzé; J. Chapront (1983). "The lunar ephemeris ELP-2000".
1447:
1303:
1064:
with respect to the distant stars (13.36874634 passes per solar orbit)
885:
881:
816:
750:
663:
454:
396: in this section. Unsourced material may be challenged and removed.
351:
288:
158:
4800:
4651:
4003:
3772:
3765:
3438:
3424:
3410:
3387:
3336:
2966:
2690:
2630:
2584:
2516:
1480:
1346:
1336:
1324:
1311:
1228:
1199:. The latter periods are slightly different from the sidereal month.
971:
966:
722:
702:
650:
504:
3687:
2024:
371:
3825:
3445:
3403:
3380:
3258:
2623:
1903:
1874:
1847:
1396:
1385:
1224:
1006:
1002:
950:
824:
698:
355:
331:
177:
2402:
2286:
Caltech
Scientists Predict Greater Longevity for Planets with Life
1969:
1001:
described lunar motion by using a well-defined geometric model of
900:
it will be above the horizon at the North Pole, and when it is in
800:
4556:
2637:
2001:"Moonlight helps plankton escape predators during Arctic winters"
1524:) which is the semimajor axis of the Moon's elliptical orbit via
1409:
998:
962:
854:
812:
811:
Every 18.6 years, the angle between the Moon's orbit and Earth's
770:
667:
519:
481:
461:
81:
978:
discovered the three main periods of the Moon's motion and used
1271:
866:
671:
556:. At full moon, the elongation is 180° and it is said to be in
465:
327:
110:
4361:
3980:
3730:
3311:
3134:
2952:
2575:
1952:"Flying gold knocked the moon off course and ruined eclipses"
1838:
1214:
1203:
1123:
1032:
945:
690:
639:
252:
249:
1645:
1618:
3343:
2699:
2439:
1745:
1259:
1241:
940:
625:
440:
246:
4764:
1810:
Peter
Goldreich (Nov 1966). "History of the Lunar Orbit".
1400:
Section of Earth's and Moon's trajectories around the Sun
701:. This shows the specific configuration at major northern
2096:"Secular tidal changes in lunar orbit and Earth rotation"
1775:(1998). "Moon-Earth-Sun: The oldest three-body problem".
1588:
1258:
attraction that the Moon exerts on Earth is the cause of
1177:
280:
781:" on the Moon is only 347 days long. This is called the
2408:
2238:
1172:
is the time it takes the Moon to reach the same visual
1682:, Richmond, VA: Willmann-Bell, pp. 11–12, 22–23,
1015:
was the first to develop a complete theory of motion,
4753:
2204:
Geophysical
Journal of the Royal Astronomical Society
1408:(that is, from the approximate direction of the star
1771:
1391:
993:
astronomers were the first to introduce and analyze
2336:Explanatory Supplement to the Astronomical Almanac
2200:"Tides and the evolution of the Earth-Moon system"
1704:Explanatory Supplement to the Astronomical Almanac
446:Moon's orbit and sizes of Earth and Moon to scale.
2364:"The Orbit of the Moon around the Sun is Convex!"
1151:with respect to the ascending node (precesses in
4813:
815:reaches a maximum of 28°36′, the sum of Earth's
460:Comparison of the Moon's apparent size at lunar
30:For the orbit of an object around the Moon, see
1809:
1706:, University Science Books, pp. 696, 701,
1486:Jet Propulsion Laboratory Development Ephemeris
801:Inclination to the equator and lunar standstill
709:The mean inclination of the lunar orbit to the
697:—the Moon's orbit is inclined by 5.14° to the
3964:
3703:
2424:
2093:
1520:The geometric mean distance in the orbit (of
795:solar eclipse of September 1 of the same year
2327:
2100:Celestial Mechanics and Dynamical Astronomy
2094:Williams, James G.; Boggs, Dale H. (2016).
2064:
1673:
1671:
1669:
1639:
1583:is the Moon's parallax between the ends of
480:The orbit of the Moon is a nearly circular
4738:
3971:
3957:
3710:
3696:
2431:
2417:
2333:
2320:" describe the same geometry by the words
2302:
2300:
2243:. Cambridge University Press. p. 184.
1949:
1701:
43:
2358:
2356:
2354:
2338:, University Science Books, p. 701,
2253:
2223:
2174:
1902:
1873:
1695:
1310:The present high rate may be due to near
412:Learn how and when to remove this message
3978:
2148:
1666:
1395:
1340:
1208:
944:
941:History of observations and measurements
689:
649:
644:Top: polar view; bottom: equatorial view
581:
322:, each hour. The Moon differs from most
287:). Earth and the Moon orbit about their
3834:) may be read as "within" or "part of".
2317:Elementary Treatise on the Lunar Theory
2297:
1728:The Cambridge Guide to the Solar System
1719:
1612:
86:363,228.9 km (225,700.0 mi),
14:
4814:
4617:Transposition, docking, and extraction
2351:
1731:, 2nd ed., Cambridge University Press.
3952:
3896:History of the center of the Universe
3717:
3691:
2412:
1767:
1765:
1763:
1761:
1677:
997:of the motion of objects in the sky.
279:) and one revolution relative to the
2388:The Moon Always Veers Toward the Sun
2334:Seidelmann, P. Kenneth, ed. (1992),
2197:
1848:"Evolution of the Earth-Moon system"
1702:Seidelmann, P. Kenneth, ed. (1992),
618:Animation of Moon orbit around Earth
394:adding citations to reliable sources
365:
330:in that its orbit is closer to the
115:405,400 km (251,900 mi),
24:
2239:C.D. Murray; S.F. Dermott (1999).
2225:10.1111/j.1365-246X.1982.tb06404.x
2045:
1758:
1577:is Earth's equatorial radius, and
1235:
25:
4833:
4677:Kepler's laws of planetary motion
3906:Pisces–Cetus Supercluster Complex
3649:Lilith (hypothetical second moon)
2396:
1392:Path of Earth and Moon around Sun
1291:for a more detailed description.
904:it will be up at the South Pole.
654:Earth's lunar orbit perturbations
475:
354:by about 23° with respect to the
76:384,400 km (238,900 mi)
68:385,000 km (239,000 mi)
60:384,748 km (239,071 mi)
4799:
4787:
4775:
4763:
4737:
4672:Interplanetary Transport Network
4552:Collision avoidance (spacecraft)
3931:
3919:
3671:
3670:
3612:Moon landing conspiracy theories
2535:
2019:The periods are calculated from
1296:Conservation of angular momentum
1022:
921:
777:In effect, this means that the "
608:
597:
560:. In both cases, the Moon is in
527:
453:
439:
370:
4637:Astronomical coordinate systems
4391:Longitude of the ascending node
3034:Selenographic coordinate system
2381:
2309:The Moon's Orbit Around the Sun
2279:
2247:
2232:
2191:
2142:
2087:
2058:
2013:
1993:
1984:
1972:. U. of Arkansas at Little Rock
1962:
1943:
1882:
1803:
834:. Around this time, the Moon's
381:needs additional citations for
27:The Moon's circuit around Earth
4710:Retrograde and prograde motion
3561:Artificial objects on the Moon
2071:Johns Hopkins University Press
1734:
1680:Mathematical Astronomy Morsels
1544:
1531:
1514:
1491:Lunar Laser Ranging experiment
1363:optical libration in longitude
914:
788:Solar eclipse of March 9, 2016
685:
13:
1:
2652:Total penumbral lunar eclipse
2259:From the Big Bang to Planet X
1606:
1371:optical libration in latitude
1104:(precesses in ~26,000 years)
571:
543:
361:
235:precession of line of apsides
4657:Equatorial coordinate system
3627:Moon is made of green cheese
2921:Permanently shadowed craters
2149:Williams, George E. (2000).
1648:Astronomy & Astrophysics
1621:Astronomy & Astrophysics
1330:
907:The Moon's light is used by
259:direction and completes one
187:of lunar equator to ecliptic
7:
1950:Jacob Aron (Nov 28, 2015).
1453:
1404:When viewed from the north
1250:Axial tilt § Long term
338:'s (in this case, Earth's)
10:
4838:
4409:Longitude of the periapsis
3554:Craters named after people
3027:Transient lunar phenomenon
2675:Solar eclipses on the Moon
2067:The Science of Ocean Waves
2027:Astronomy and Astrophysics
1550:The inverse sine parallax
1427:In representations of the
1334:
1239:
1227:, 0.25—first quarter, 0.5—
1026:
873:below the horizon, due to
804:
748:
575:
29:
4733:
4720:Specific angular momentum
4625:
4537:
4481:
4417:
4370:
4310:
4301:
4197:
4107:
3996:
3987:
3914:
3840:
3725:
3665:
3494:
3462:
3367:
3284:
3204:
3043:
2746:
2544:
2533:
2455:
2446:
2120:10.1007/s10569-016-9702-3
1797:10.1103/RevModPhys.70.589
1777:Reviews of Modern Physics
1725:Lang, Kenneth R. (2011),
1213:The Moon's distance from
678:of its orbital plane and
233:
223:
211:
199:
194:
186:
175:
167:
156:
138:
109:
80:
72:
64:
54:
42:
3745:Local Interstellar Cloud
2438:
2261:. Camden East, Ontario:
1853:The Astronomical Journal
1507:
1412:) the Moon orbits Earth
1267:within the solid Earth.
1202:The average length of a
819:(23°27′) and the Moon's
744:
725:). As was discovered by
4715:Specific orbital energy
3575:Moon in science fiction
3080:Giant-impact hypothesis
2928:South Pole–Aitken basin
2198:Webb, David J. (1982).
2053:Astronomical Algorithms
2039:1994A&A...282..663S
1834:10.1029/RG004i004p00411
1660:1988A&A...190..342C
1633:1983A&A...124...50C
1133:days = 8.850578 years)
518:° per day to the east (
486:equation of the ellipse
283:in about 29.53 days (a
271:in about 27.32 days (a
4127:Geostationary transfer
3857:To the Moon and Beyond
3596:futuristic exploration
3119:Late Heavy Bombardment
1401:
1350:
1232:
1158:days = 18.5996 years)
954:
875:atmospheric refraction
840:minor lunar standstill
706:
655:
590:
432:) has a long history.
4700:Orbital state vectors
4642:Characteristic energy
4612:Trans-lunar injection
4400:Argument of periapsis
4077:Prograde / Retrograde
4038:Hyperbolic trajectory
3875:(1968 and 1977 films)
3805:Laniakea Supercluster
3656:Splitting of the Moon
3568:Memorials on the Moon
3172:Lunar sample displays
2854:Peak of eternal light
2241:Solar System Dynamics
2155:Reviews of Geophysics
1813:Reviews of Geophysics
1399:
1344:
1270:However the speed of
1212:
948:
739:libration in latitude
693:
653:
585:
334:plane instead of its
73:Inverse sine parallax
4547:Bi-elliptic transfer
4067:Parabolic trajectory
2176:10.1029/1999RG900016
2065:J.B. Zirkir (2013).
1773:Martin C. Gutzwiller
1678:Meeus, Jean (1997),
1537:The constant in the
1461:Ernest William Brown
1355:synchronous rotation
1122:with respect to the
1100:with respect to the
976:Babylonian astronomy
682:of the moon itself.
390:improve this article
305:distance to the Moon
212:orbit around Earth (
200:orbit around Earth (
4587:Low-energy transfer
3819:Observable universe
3156:Lunar laser ranging
2216:1982GeoJ...70..261W
2167:2000RvGeo..38...37W
2112:2016CeMDA.126...89W
1921:10.1038/nature16137
1913:2015Natur.527..492P
1866:1994AJ....108.1943T
1826:1966RvGSP...4..411G
1789:1998RvMP...70..589G
1496:Milankovitch cycles
1231:, 0.75—last quarter
1223:Moon phases: 0 (1)—
1017:Newtonian mechanics
995:mathematical models
821:orbital inclination
695:Orbital inclination
512:Kepler's second law
225:precession of nodes
39:
4582:Inclination change
4230:Distant retrograde
3901:Order of magnitude
3883:(1996 documentary)
3799:Virgo Supercluster
3780:Milky Way subgroup
3305:Lunisolar calendar
2974:Lunar basalt 70017
2721:Tidal acceleration
2576:Perigee and apogee
2466:Internal structure
2322:concave to the sun
2291:2012-03-30 at the
2265:. pp. 79–81.
2255:Dickinson, Terence
1970:"View of the Moon"
1402:
1379:geographical poles
1351:
1289:tidal acceleration
1246:Tidal acceleration
1233:
955:
707:
660:apsidal precession
656:
591:
587:Apsidal precession
324:regular satellites
303:. On average, the
229:18.5996 years
37:
4822:Orbit of the Moon
4751:
4750:
4725:Two-line elements
4533:
4532:
4455:Eccentric anomaly
4297:
4296:
4164:Orbit of the Moon
4023:Highly elliptical
3946:
3945:
3719:Location of Earth
3685:
3684:
3635:Natural satellite
3094:Lunar magma ocean
2870:Volcanic features
1897:(7579): 492–494.
1742:"Moon Fact Sheet"
1436:Earth–Moon system
1375:diurnal libration
1191:is the time from
1182:anomalistic month
1162:
1161:
1110:Anomalistic month
827:. This is called
767:retrograde motion
422:
421:
414:
301:Earth–Moon system
243:
242:
239:8.8504 years
182:5.15° (4.99–5.30)
38:Orbit of the Moon
18:Moon's orbit
16:(Redirected from
4829:
4804:
4803:
4792:
4791:
4790:
4780:
4779:
4778:
4768:
4767:
4759:
4741:
4740:
4682:Lagrangian point
4577:Hohmann transfer
4522:
4508:
4499:
4490:
4470:
4461:
4452:
4443:
4439:
4435:
4426:
4406:
4397:
4388:
4379:
4359:
4355:
4346:
4337:
4328:
4308:
4307:
4277:Heliosynchronous
4226:Lagrange points
4179:Transatmospheric
3994:
3993:
3973:
3966:
3959:
3950:
3949:
3935:
3925:Astronomy portal
3923:
3835:
3833:
3824:
3817:
3810:
3803:
3797:
3791:
3785:
3778:
3771:
3764:
3757:
3750:
3743:
3736:
3712:
3705:
3698:
3689:
3688:
3678:
3674:
3673:
3658:
3651:
3644:
3637:
3630:
3621:
3614:
3605:
3598:
3591:
3584:
3577:
3570:
3563:
3556:
3547:
3540:
3533:
3526:
3519:
3512:
3505:
3487:
3480:
3478:Meridian passage
3473:
3455:
3448:
3441:
3434:
3427:
3420:
3413:
3406:
3397:
3390:
3383:
3360:
3353:
3346:
3339:
3328:
3321:
3314:
3307:
3300:
3277:
3270:
3261:
3254:
3247:
3240:
3231:
3224:
3217:
3197:
3195:Lunar seismology
3188:
3181:
3174:
3165:
3158:
3151:
3144:
3137:
3130:
3128:Lunar meteorites
3121:
3114:
3107:
3096:
3089:
3082:
3075:
3068:
3061:
3054:
3036:
3029:
3022:
3013:
3006:
2999:
2997:Space weathering
2992:
2983:
2976:
2969:
2962:
2955:
2946:
2939:
2930:
2923:
2916:
2909:
2902:
2893:
2886:
2879:
2872:
2865:
2856:
2849:
2840:
2833:
2822:
2815:
2808:
2801:
2794:
2787:
2780:
2775:
2768:
2761:
2739:
2730:
2723:
2716:
2709:
2702:
2693:
2684:
2677:
2670:
2661:
2654:
2647:
2640:
2633:
2626:
2619:
2610:
2601:
2594:
2587:
2578:
2571:
2564:
2562:Orbital elements
2557:
2539:
2526:
2519:
2512:
2505:
2496:
2489:
2482:
2475:
2468:
2433:
2426:
2419:
2410:
2409:
2403:View of the Moon
2391:
2385:
2379:
2378:
2376:
2375:
2370:on 31 March 2004
2366:. Archived from
2360:
2349:
2348:
2331:
2325:
2304:
2295:
2283:
2277:
2276:
2251:
2245:
2244:
2236:
2230:
2229:
2227:
2195:
2189:
2188:
2178:
2146:
2140:
2139:
2091:
2085:
2084:
2062:
2056:
2049:
2043:
2042:
2021:orbital elements
2017:
2011:
2010:
1997:
1991:
1988:
1982:
1981:
1979:
1977:
1966:
1960:
1959:
1947:
1941:
1940:
1906:
1886:
1880:
1879:
1877:
1837:
1807:
1801:
1800:
1769:
1756:
1755:
1753:
1752:
1738:
1732:
1723:
1717:
1716:
1699:
1693:
1692:
1675:
1664:
1663:
1643:
1637:
1636:
1616:
1600:
1598:
1594:
1581:
1572:
1570:
1569:
1567:
1561:
1558:
1548:
1542:
1535:
1529:
1518:
1501:Orbital elements
1434:Considering the
1304:Tidal rhythmites
1157:
1156:
1148:
1147:
1132:
1131:
1119:
1118:
1097:
1096:
1079:
1078:
1061:
1060:
1037:
1036:
984:scientific study
925:
863:higher latitudes
831:lunar standstill
807:Lunar standstill
763:draconitic month
680:axial precession
676:nodal precession
642:
637:
628:
623:
612:
601:
578:Lunar precession
531:
517:
457:
443:
417:
410:
406:
403:
397:
374:
366:
340:equatorial plane
320:celestial sphere
312:orbital velocity
297:satellite system
263:relative to the
150:
149:
133:
132:
126:
125:
118:
104:
103:
97:
96:
89:
47:
40:
36:
21:
4837:
4836:
4832:
4831:
4830:
4828:
4827:
4826:
4812:
4811:
4810:
4798:
4788:
4786:
4776:
4774:
4762:
4754:
4752:
4747:
4729:
4647:Escape velocity
4628:
4621:
4602:Rocket equation
4529:
4521:
4515:
4506:
4497:
4488:
4477:
4468:
4459:
4450:
4441:
4437:
4433:
4424:
4413:
4404:
4395:
4386:
4377:
4366:
4357:
4353:
4349:Semi-minor axis
4344:
4340:Semi-major axis
4335:
4326:
4320:
4293:
4215:Areosynchronous
4199:
4193:
4174:Sun-synchronous
4159:Near-equatorial
4103:
3983:
3977:
3947:
3942:
3910:
3836:
3831:
3829:
3828:
3822:
3815:
3808:
3801:
3795:
3789:
3783:
3776:
3769:
3762:
3755:
3748:
3741:
3734:
3721:
3716:
3686:
3681:
3669:
3661:
3654:
3647:
3640:
3633:
3624:
3617:
3610:
3601:
3594:
3587:
3580:
3573:
3566:
3559:
3552:
3543:
3538:Man in the Moon
3536:
3529:
3522:
3515:
3508:
3501:
3490:
3483:
3476:
3469:
3463:Daily phenomena
3458:
3451:
3444:
3437:
3430:
3423:
3416:
3411:Super and micro
3409:
3402:
3393:
3386:
3379:
3372:
3363:
3356:
3349:
3342:
3335:
3324:
3317:
3310:
3303:
3296:
3286:
3280:
3275:Lunar resources
3273:
3266:
3257:
3250:
3243:
3236:
3227:
3220:
3213:
3200:
3193:
3184:
3177:
3170:
3161:
3154:
3149:
3140:
3133:
3126:
3117:
3110:
3103:
3092:
3085:
3078:
3071:
3064:
3057:
3050:
3039:
3032:
3025:
3018:
3009:
3002:
2995:
2988:
2979:
2972:
2965:
2958:
2951:
2942:
2935:
2926:
2919:
2912:
2905:
2898:
2889:
2882:
2875:
2868:
2861:
2852:
2845:
2836:
2829:
2818:
2811:
2804:
2799:
2790:
2783:
2778:
2771:
2764:
2757:
2748:
2742:
2735:
2726:
2719:
2712:
2705:
2698:
2689:
2680:
2673:
2666:
2657:
2650:
2643:
2636:
2629:
2622:
2615:
2606:
2597:
2590:
2583:
2574:
2567:
2560:
2553:
2540:
2531:
2522:
2515:
2508:
2501:
2492:
2485:
2478:
2471:
2464:
2457:
2451:
2442:
2437:
2399:
2394:
2386:
2382:
2373:
2371:
2362:
2361:
2352:
2346:
2332:
2328:
2305:
2298:
2293:Wayback Machine
2284:
2280:
2273:
2252:
2248:
2237:
2233:
2196:
2192:
2147:
2143:
2092:
2088:
2081:
2073:. p. 264.
2063:
2059:
2050:
2046:
2018:
2014:
2009:. Jan 16, 2016.
1999:
1998:
1994:
1989:
1985:
1975:
1973:
1968:
1967:
1963:
1948:
1944:
1887:
1883:
1808:
1804:
1770:
1759:
1750:
1748:
1740:
1739:
1735:
1724:
1720:
1714:
1700:
1696:
1690:
1676:
1667:
1644:
1640:
1617:
1613:
1609:
1604:
1603:
1596:
1592:
1587:. Three of the
1579:
1565:
1562:
1559:
1554:
1553:
1551:
1549:
1545:
1536:
1532:
1519:
1515:
1510:
1505:
1456:
1421:right-hand rule
1394:
1353:The Moon is in
1339:
1333:
1300:glacial rebound
1252:
1238:
1236:Tidal evolution
1222:
1154:
1152:
1145:
1143:
1129:
1127:
1116:
1114:
1094:
1092:
1076:
1074:
1058:
1056:
1035:
1025:
943:
938:
937:
936:
931:
926:
917:
894:winter solstice
844:right ascension
823:(5°09′) to the
817:equatorial tilt
809:
803:
753:
747:
727:Jacques Cassini
688:
648:
647:
646:
645:
643:
635:
634:
621:
620:
619:
615:
614:
613:
604:
603:
602:
580:
574:
546:
541:
540:
539:
537:
532:
515:
478:
473:
472:
471:
470:
469:
458:
449:
448:
447:
444:
418:
407:
401:
398:
387:
375:
364:
151:
147:
145:
130:
128:
123:
121:
119:
116:
101:
99:
94:
92:
90:
87:
56:Semi-major axis
50:
35:
28:
23:
22:
15:
12:
11:
5:
4835:
4825:
4824:
4809:
4808:
4796:
4784:
4772:
4749:
4748:
4746:
4745:
4743:List of orbits
4734:
4731:
4730:
4728:
4727:
4722:
4717:
4712:
4707:
4702:
4697:
4695:Orbit equation
4692:
4684:
4679:
4674:
4669:
4664:
4659:
4654:
4649:
4644:
4639:
4633:
4631:
4623:
4622:
4620:
4619:
4614:
4609:
4604:
4599:
4594:
4589:
4584:
4579:
4574:
4569:
4567:Gravity assist
4564:
4562:Delta-v budget
4559:
4554:
4549:
4543:
4541:
4535:
4534:
4531:
4530:
4528:
4527:
4519:
4513:
4504:
4495:
4493:Orbital period
4485:
4483:
4479:
4478:
4476:
4475:
4473:True longitude
4466:
4464:Mean longitude
4457:
4448:
4431:
4421:
4419:
4415:
4414:
4412:
4411:
4402:
4393:
4384:
4374:
4372:
4368:
4367:
4365:
4364:
4351:
4342:
4333:
4323:
4321:
4319:
4318:
4315:
4311:
4305:
4299:
4298:
4295:
4294:
4292:
4291:
4290:
4289:
4281:
4280:
4279:
4274:
4269:
4268:
4267:
4254:
4249:
4248:
4247:
4242:
4237:
4232:
4224:
4223:
4222:
4220:Areostationary
4217:
4212:
4203:
4201:
4195:
4194:
4192:
4191:
4189:Very low Earth
4186:
4181:
4176:
4171:
4166:
4161:
4156:
4151:
4146:
4141:
4136:
4131:
4130:
4129:
4124:
4117:Geosynchronous
4113:
4111:
4105:
4104:
4102:
4101:
4099:Transfer orbit
4096:
4095:
4094:
4089:
4079:
4074:
4069:
4064:
4059:
4057:Lagrange point
4054:
4049:
4040:
4035:
4030:
4025:
4016:
4011:
4006:
4000:
3998:
3991:
3985:
3984:
3979:Gravitational
3976:
3975:
3968:
3961:
3953:
3944:
3943:
3941:
3940:
3928:
3915:
3912:
3911:
3909:
3908:
3903:
3898:
3893:
3885:
3877:
3869:
3861:
3853:
3844:
3842:
3838:
3837:
3729:
3727:
3723:
3722:
3715:
3714:
3707:
3700:
3692:
3683:
3682:
3680:
3679:
3666:
3663:
3662:
3660:
3659:
3652:
3645:
3638:
3631:
3622:
3615:
3608:
3607:
3606:
3599:
3592:
3585:
3571:
3564:
3557:
3550:
3549:
3548:
3541:
3527:
3520:
3513:
3506:
3498:
3496:
3492:
3491:
3489:
3488:
3481:
3474:
3466:
3464:
3460:
3459:
3457:
3456:
3449:
3442:
3435:
3428:
3421:
3414:
3407:
3400:
3399:
3398:
3384:
3376:
3374:
3365:
3364:
3362:
3361:
3358:Lunar distance
3354:
3347:
3340:
3333:
3332:
3331:
3330:
3329:
3308:
3301:
3298:Lunar calendar
3293:
3291:
3282:
3281:
3279:
3278:
3271:
3264:
3263:
3262:
3248:
3241:
3234:
3233:
3232:
3225:
3222:Apollo program
3210:
3208:
3202:
3201:
3199:
3198:
3191:
3190:
3189:
3182:
3168:
3167:
3166:
3159:
3147:
3146:
3145:
3138:
3131:
3124:
3123:
3122:
3101:
3100:
3099:
3098:
3097:
3090:
3069:
3062:
3055:
3047:
3045:
3041:
3040:
3038:
3037:
3030:
3023:
3016:
3015:
3014:
3007:
3004:Micrometeorite
2993:
2986:
2985:
2984:
2981:Changesite-(Y)
2977:
2963:
2960:Wrinkle ridges
2956:
2949:
2948:
2947:
2933:
2932:
2931:
2924:
2917:
2910:
2896:
2895:
2894:
2887:
2880:
2866:
2859:
2858:
2857:
2843:
2842:
2841:
2827:
2826:
2825:
2824:
2823:
2809:
2797:
2796:
2795:
2788:
2776:
2769:
2762:
2754:
2752:
2744:
2743:
2741:
2740:
2733:
2732:
2731:
2724:
2717:
2710:
2696:
2695:
2694:
2687:
2686:
2685:
2678:
2671:
2664:
2663:
2662:
2655:
2634:
2627:
2613:
2612:
2611:
2604:
2603:
2602:
2588:
2581:
2580:
2579:
2558:
2555:Lunar distance
2550:
2548:
2542:
2541:
2534:
2532:
2530:
2529:
2528:
2527:
2513:
2506:
2503:Magnetic field
2499:
2498:
2497:
2483:
2476:
2469:
2461:
2459:
2453:
2452:
2447:
2444:
2443:
2436:
2435:
2428:
2421:
2413:
2407:
2406:
2398:
2397:External links
2395:
2393:
2392:
2380:
2350:
2344:
2326:
2296:
2278:
2271:
2246:
2231:
2210:(1): 261–271.
2190:
2141:
2086:
2079:
2057:
2044:
2012:
1992:
1983:
1961:
1942:
1881:
1875:10.1086/117209
1802:
1783:(2): 589–639.
1757:
1733:
1718:
1712:
1694:
1688:
1665:
1638:
1610:
1608:
1605:
1602:
1601:
1543:
1530:
1512:
1511:
1509:
1506:
1504:
1503:
1498:
1493:
1488:
1483:
1478:
1473:
1471:List of orbits
1468:
1463:
1457:
1455:
1452:
1406:celestial pole
1393:
1390:
1335:Main article:
1332:
1329:
1263:high speed of
1237:
1234:
1204:calendar month
1197:tropical month
1193:ascending node
1189:draconic month
1166:sidereal month
1160:
1159:
1149:
1141:
1139:Draconic month
1135:
1134:
1126:(precesses in
1120:
1112:
1106:
1105:
1098:
1090:
1088:Tropical month
1084:
1083:
1080:
1072:
1066:
1065:
1062:
1054:
1052:Sidereal month
1048:
1047:
1044:
1041:
1024:
1021:
942:
939:
928:
927:
920:
919:
918:
916:
913:
890:tropical month
805:Main article:
802:
799:
758:draconic month
749:Main article:
746:
743:
733:Cassini's Laws
711:ecliptic plane
687:
684:
617:
616:
607:
606:
605:
596:
595:
594:
593:
592:
576:Main article:
573:
570:
545:
542:
534:
533:
526:
525:
524:
492:of 0.0549 and
477:
476:Elliptic shape
474:
459:
452:
451:
450:
445:
438:
437:
436:
435:
434:
420:
419:
402:September 2024
378:
376:
369:
363:
360:
356:ecliptic plane
293:centre of mass
277:sidereal month
273:tropical month
265:Vernal Equinox
241:
240:
237:
231:
230:
227:
221:
220:
217:
209:
208:
205:
197:
196:
192:
191:
188:
184:
183:
180:
173:
172:
165:
164:
161:
154:
153:
143:
136:
135:
113:
107:
106:
84:
78:
77:
74:
70:
69:
66:
62:
61:
58:
52:
51:
48:
26:
9:
6:
4:
3:
2:
4834:
4823:
4820:
4819:
4817:
4807:
4802:
4797:
4795:
4785:
4783:
4773:
4771:
4766:
4761:
4760:
4757:
4744:
4736:
4735:
4732:
4726:
4723:
4721:
4718:
4716:
4713:
4711:
4708:
4706:
4703:
4701:
4698:
4696:
4693:
4691:
4690:-body problem
4689:
4685:
4683:
4680:
4678:
4675:
4673:
4670:
4668:
4665:
4663:
4660:
4658:
4655:
4653:
4650:
4648:
4645:
4643:
4640:
4638:
4635:
4634:
4632:
4630:
4624:
4618:
4615:
4613:
4610:
4608:
4605:
4603:
4600:
4598:
4595:
4593:
4592:Oberth effect
4590:
4588:
4585:
4583:
4580:
4578:
4575:
4573:
4570:
4568:
4565:
4563:
4560:
4558:
4555:
4553:
4550:
4548:
4545:
4544:
4542:
4540:
4536:
4526:
4518:
4514:
4512:
4511:Orbital speed
4505:
4503:
4496:
4494:
4487:
4486:
4484:
4480:
4474:
4467:
4465:
4458:
4456:
4449:
4447:
4432:
4430:
4423:
4422:
4420:
4416:
4410:
4403:
4401:
4394:
4392:
4385:
4383:
4376:
4375:
4373:
4369:
4363:
4352:
4350:
4343:
4341:
4334:
4332:
4325:
4324:
4322:
4316:
4313:
4312:
4309:
4306:
4304:
4300:
4288:
4285:
4284:
4282:
4278:
4275:
4273:
4270:
4266:
4265:Earth's orbit
4263:
4262:
4261:
4258:
4257:
4255:
4253:
4250:
4246:
4243:
4241:
4238:
4236:
4233:
4231:
4228:
4227:
4225:
4221:
4218:
4216:
4213:
4211:
4208:
4207:
4205:
4204:
4202:
4196:
4190:
4187:
4185:
4182:
4180:
4177:
4175:
4172:
4170:
4167:
4165:
4162:
4160:
4157:
4155:
4152:
4150:
4147:
4145:
4142:
4140:
4137:
4135:
4132:
4128:
4125:
4123:
4122:Geostationary
4120:
4119:
4118:
4115:
4114:
4112:
4110:
4106:
4100:
4097:
4093:
4090:
4088:
4085:
4084:
4083:
4080:
4078:
4075:
4073:
4070:
4068:
4065:
4063:
4060:
4058:
4055:
4053:
4050:
4048:
4044:
4041:
4039:
4036:
4034:
4031:
4029:
4026:
4024:
4020:
4017:
4015:
4012:
4010:
4007:
4005:
4002:
4001:
3999:
3995:
3992:
3990:
3986:
3982:
3974:
3969:
3967:
3962:
3960:
3955:
3954:
3951:
3939:
3938:
3934:
3929:
3927:
3926:
3922:
3917:
3916:
3913:
3907:
3904:
3902:
3899:
3897:
3894:
3892:
3890:
3886:
3884:
3882:
3881:Cosmic Voyage
3878:
3876:
3874:
3873:Powers of Ten
3870:
3868:
3866:
3862:
3860:
3858:
3854:
3852:
3850:
3846:
3845:
3843:
3839:
3827:
3820:
3813:
3806:
3800:
3794:
3788:
3781:
3774:
3767:
3760:
3753:
3746:
3739:
3732:
3728:
3724:
3720:
3713:
3708:
3706:
3701:
3699:
3694:
3693:
3690:
3677:
3668:
3667:
3664:
3657:
3653:
3650:
3646:
3643:
3642:Double planet
3639:
3636:
3632:
3628:
3623:
3620:
3616:
3613:
3609:
3604:
3600:
3597:
3593:
3590:
3586:
3583:
3579:
3578:
3576:
3572:
3569:
3565:
3562:
3558:
3555:
3551:
3546:
3542:
3539:
3535:
3534:
3532:
3528:
3525:
3524:Moon illusion
3521:
3518:
3514:
3511:
3507:
3504:
3503:Lunar deities
3500:
3499:
3497:
3493:
3486:
3482:
3479:
3475:
3472:
3468:
3467:
3465:
3461:
3454:
3450:
3447:
3443:
3440:
3436:
3433:
3429:
3426:
3422:
3419:
3415:
3412:
3408:
3405:
3401:
3396:
3392:
3391:
3389:
3385:
3382:
3378:
3377:
3375:
3370:
3366:
3359:
3355:
3352:
3351:Lunar station
3348:
3345:
3341:
3338:
3334:
3327:
3323:
3322:
3320:
3316:
3315:
3313:
3309:
3306:
3302:
3299:
3295:
3294:
3292:
3290:
3285:Time-telling
3283:
3276:
3272:
3269:
3265:
3260:
3256:
3255:
3253:
3249:
3246:
3242:
3239:
3235:
3230:
3226:
3223:
3219:
3218:
3216:
3212:
3211:
3209:
3207:
3203:
3196:
3192:
3187:
3183:
3180:
3176:
3175:
3173:
3169:
3164:
3160:
3157:
3153:
3152:
3148:
3143:
3139:
3136:
3132:
3129:
3125:
3120:
3116:
3115:
3113:
3109:
3108:
3106:
3102:
3095:
3091:
3088:
3084:
3083:
3081:
3077:
3076:
3074:
3070:
3067:
3063:
3060:
3056:
3053:
3049:
3048:
3046:
3042:
3035:
3031:
3028:
3024:
3021:
3017:
3012:
3008:
3005:
3001:
3000:
2998:
2994:
2991:
2987:
2982:
2978:
2975:
2971:
2970:
2968:
2964:
2961:
2957:
2954:
2950:
2945:
2941:
2940:
2938:
2934:
2929:
2925:
2922:
2918:
2915:
2911:
2908:
2904:
2903:
2901:
2897:
2892:
2888:
2885:
2881:
2878:
2874:
2873:
2871:
2867:
2864:
2860:
2855:
2851:
2850:
2848:
2844:
2839:
2835:
2834:
2832:
2828:
2821:
2817:
2816:
2814:
2810:
2807:
2803:
2802:
2798:
2793:
2789:
2786:
2782:
2781:
2777:
2774:
2770:
2767:
2763:
2760:
2756:
2755:
2753:
2751:
2745:
2738:
2737:Lunar station
2734:
2729:
2725:
2722:
2718:
2715:
2714:Tidal locking
2711:
2708:
2704:
2703:
2701:
2697:
2692:
2688:
2683:
2682:Eclipse cycle
2679:
2676:
2672:
2669:
2668:Solar eclipse
2665:
2660:
2656:
2653:
2649:
2648:
2646:
2645:Lunar eclipse
2642:
2641:
2639:
2635:
2632:
2628:
2625:
2621:
2620:
2618:
2614:
2609:
2605:
2600:
2596:
2595:
2593:
2589:
2586:
2582:
2577:
2573:
2572:
2570:
2566:
2565:
2563:
2559:
2556:
2552:
2551:
2549:
2547:
2543:
2538:
2525:
2521:
2520:
2518:
2514:
2511:
2507:
2504:
2500:
2495:
2491:
2490:
2488:
2487:Gravity field
2484:
2481:
2477:
2474:
2470:
2467:
2463:
2462:
2460:
2454:
2450:
2445:
2441:
2434:
2429:
2427:
2422:
2420:
2415:
2414:
2411:
2404:
2401:
2400:
2389:
2384:
2369:
2365:
2359:
2357:
2355:
2347:
2345:0-935702-68-7
2341:
2337:
2330:
2323:
2319:
2318:
2312:
2310:
2303:
2301:
2294:
2290:
2287:
2282:
2274:
2272:0-921820-71-2
2268:
2264:
2260:
2256:
2250:
2242:
2235:
2226:
2221:
2217:
2213:
2209:
2205:
2201:
2194:
2186:
2182:
2177:
2172:
2168:
2164:
2160:
2156:
2152:
2145:
2137:
2133:
2129:
2125:
2121:
2117:
2113:
2109:
2106:(1): 89–129.
2105:
2101:
2097:
2090:
2082:
2080:9781421410784
2076:
2072:
2068:
2061:
2054:
2048:
2040:
2036:
2032:
2028:
2022:
2016:
2008:
2007:
2006:New Scientist
2002:
1996:
1987:
1971:
1965:
1957:
1956:New Scientist
1953:
1946:
1938:
1934:
1930:
1926:
1922:
1918:
1914:
1910:
1905:
1900:
1896:
1892:
1885:
1876:
1871:
1867:
1863:
1859:
1855:
1854:
1849:
1845:
1841:
1835:
1831:
1827:
1823:
1819:
1815:
1814:
1806:
1798:
1794:
1790:
1786:
1782:
1778:
1774:
1768:
1766:
1764:
1762:
1747:
1743:
1737:
1730:
1729:
1722:
1715:
1713:0-935702-68-7
1709:
1705:
1698:
1691:
1689:0-943396-51-4
1685:
1681:
1674:
1672:
1670:
1661:
1657:
1653:
1649:
1642:
1634:
1630:
1626:
1622:
1615:
1611:
1590:
1586:
1582:
1576:
1568:
1557:
1547:
1540:
1534:
1527:
1526:Kepler's laws
1523:
1517:
1513:
1502:
1499:
1497:
1494:
1492:
1489:
1487:
1484:
1482:
1479:
1477:
1474:
1472:
1469:
1467:
1466:Double planet
1464:
1462:
1459:
1458:
1451:
1449:
1443:
1441:
1440:binary planet
1437:
1432:
1430:
1425:
1422:
1417:
1415:
1414:anticlockwise
1411:
1407:
1398:
1389:
1387:
1382:
1380:
1376:
1372:
1366:
1364:
1360:
1356:
1348:
1343:
1338:
1328:
1326:
1322:
1321:tidal locking
1316:
1313:
1308:
1305:
1301:
1297:
1292:
1290:
1284:
1280:
1276:
1273:
1272:seismic waves
1268:
1266:
1265:seismic waves
1261:
1257:
1256:gravitational
1251:
1247:
1243:
1230:
1226:
1220:
1216:
1211:
1207:
1205:
1200:
1198:
1194:
1190:
1185:
1183:
1179:
1175:
1171:
1170:synodic month
1167:
1150:
1142:
1140:
1137:
1136:
1125:
1121:
1113:
1111:
1108:
1107:
1103:
1099:
1091:
1089:
1086:
1085:
1081:
1073:
1071:
1070:Synodic month
1068:
1067:
1063:
1055:
1053:
1050:
1049:
1045:
1043:Value (days)
1042:
1039:
1038:
1034:
1030:
1023:Lunar periods
1020:
1018:
1014:
1010:
1008:
1004:
1000:
996:
992:
991:Ancient Greek
988:
985:
981:
980:data analysis
977:
973:
968:
964:
960:
952:
947:
934:
930:
924:
912:
910:
905:
903:
899:
895:
891:
887:
883:
878:
876:
872:
868:
864:
859:
856:
851:
849:
845:
841:
837:
833:
832:
826:
822:
818:
814:
808:
798:
796:
791:
789:
784:
783:draconic year
780:
779:tropical year
775:
772:
768:
764:
760:
759:
752:
742:
740:
736:
734:
728:
724:
719:
717:
716:planetesimals
712:
704:
700:
696:
692:
683:
681:
677:
673:
669:
665:
661:
652:
641:
632:
627:
611:
600:
588:
584:
579:
569:
567:
563:
559:
555:
551:
536:
530:
523:
521:
513:
508:
506:
501:
499:
495:
491:
487:
483:
467:
463:
456:
442:
433:
431:
427:
426:perturbations
416:
413:
405:
395:
391:
385:
384:
379:This section
377:
373:
368:
367:
359:
357:
353:
349:
345:
344:orbital plane
342:. The Moon's
341:
337:
333:
329:
325:
321:
317:
316:half a degree
313:
308:
306:
302:
298:
294:
290:
286:
285:synodic month
282:
278:
274:
270:
266:
262:
258:
254:
251:
248:
238:
236:
232:
228:
226:
222:
218:
215:
210:
206:
203:
198:
193:
189:
185:
181:
179:
174:
171:
166:
162:
160:
155:
152:(0.026–0.077)
144:
142:
137:
114:
112:
108:
85:
83:
79:
75:
71:
67:
65:Mean distance
63:
59:
57:
53:
46:
41:
33:
19:
4794:Solar System
4705:Perturbation
4687:
4662:Ground track
4572:Gravity turn
4523:
4516:
4509:
4500:
4491:
4471:
4462:
4453:
4446:True anomaly
4444:
4429:Mean anomaly
4427:
4407:
4398:
4389:
4380:
4360:
4347:
4338:
4331:Eccentricity
4329:
4287:Lunar cycler
4260:Heliocentric
4200:other points
4163:
4149:Medium Earth
4047:Non-inclined
3937:Space portal
3930:
3918:
3888:
3880:
3872:
3864:
3856:
3848:
3830:Each arrow (
3752:Local Bubble
3738:Solar System
3510:Lunar effect
3326:Nodal period
3252:Colonization
3066:Lunar theory
2759:Selenography
2599:Nodal period
2545:
2390:at MathPages
2383:
2372:. Retrieved
2368:the original
2335:
2329:
2321:
2316:
2308:
2281:
2263:Camden House
2258:
2249:
2240:
2234:
2207:
2203:
2193:
2161:(1): 37–60.
2158:
2154:
2144:
2103:
2099:
2089:
2066:
2060:
2052:
2051:Jean Meeus,
2047:
2030:
2026:
2015:
2004:
1995:
1986:
1974:. Retrieved
1964:
1955:
1945:
1894:
1890:
1884:
1857:
1851:
1846:(Nov 1994).
1817:
1811:
1805:
1780:
1776:
1749:. Retrieved
1736:
1727:
1721:
1703:
1697:
1679:
1651:
1647:
1641:
1624:
1620:
1614:
1584:
1578:
1574:
1564:
1555:
1546:
1533:
1516:
1444:
1433:
1429:Solar System
1426:
1418:
1403:
1383:
1374:
1370:
1367:
1362:
1352:
1317:
1309:
1293:
1285:
1281:
1277:
1269:
1253:
1201:
1186:
1163:
1102:vernal point
1013:Isaac Newton
1011:
989:
956:
906:
879:
860:
852:
839:
828:
810:
792:
776:
762:
756:
754:
730:
720:
708:
657:
630:
547:
509:
502:
490:eccentricity
479:
430:lunar theory
423:
408:
399:
388:Please help
383:verification
380:
310:With a mean
309:
300:
244:
176:of orbit to
141:eccentricity
4782:Spaceflight
4667:Hill sphere
4502:Mean motion
4382:Inclination
4371:Orientation
4272:Mars cycler
4210:Areocentric
4082:Synchronous
3867:(1968 film)
3865:Cosmic Zoom
3859:(1964 film)
3851:(1957 book)
3849:Cosmic View
3793:Local Sheet
3787:Local Group
3619:Moon Treaty
3603:Hollow Moon
3545:Moon rabbit
3517:Earth phase
3319:Lunar month
3206:Exploration
3150:Experiments
3052:Observation
2914:Ray systems
2779:Hemispheres
2747:Surface and
2728:Tidal range
2707:Tidal force
2510:Sodium tail
2494:Hill sphere
2315:H Godfray,
1844:Jack Wisdom
1840:Jihad Touma
1219:Moon phases
1046:Definition
1029:Lunar month
963:Babylonians
933:Scale model
915:Scale model
909:zooplankton
902:Sagittarius
871:arc minutes
848:declination
836:declination
686:Inclination
554:conjunction
548:The Moon's
299:called the
219:29.530 days
207:27.322 days
170:inclination
32:Lunar orbit
4607:Rendezvous
4303:Parameters
4139:High Earth
4109:Geocentric
4062:Osculating
4019:Elliptical
3889:Cosmic Eye
3812:Local Hole
3759:Gould Belt
3589:Apollo era
3531:Pareidolia
3289:navigation
3011:Sputtering
2891:Lava tubes
2813:South pole
2806:North pole
2766:Terminator
2608:Precession
2524:Earthshine
2480:Atmosphere
2473:Topography
2458:properties
2374:2022-04-14
2033:(2): 669.
1904:1603.06515
1820:(4): 411.
1751:2014-01-08
1607:References
1448:convex set
1240:See also:
1027:See also:
886:South Pole
751:Lunar node
664:major axis
572:Precession
566:quadrature
558:opposition
550:elongation
544:Elongation
488:yields an
362:Properties
289:barycentre
261:revolution
4652:Ephemeris
4629:mechanics
4539:Maneuvers
4482:Variation
4245:Libration
4240:Lissajous
4144:Low Earth
4134:Graveyard
4033:Horseshoe
3773:Milky Way
3766:Orion Arm
3337:Fortnight
3229:Explorers
3186:Apollo 17
3179:Apollo 11
3142:Volcanism
3112:Timescale
3059:Libration
2847:Mountains
2785:Near side
2691:Supermoon
2631:Full moon
2585:Libration
2517:Moonlight
2136:124256137
2128:0923-2958
1481:Ephemeris
1386:nutations
1347:libration
1337:Libration
1331:Libration
1325:radiation
1312:resonance
1229:full moon
1003:epicycles
972:full moon
967:cuneiform
846:zero and
723:obliquity
703:lunistice
505:supermoon
326:of other
195:Period of
159:obliquity
134: km)
105: km)
4816:Category
4418:Position
4043:Inclined
4014:Circular
3826:Universe
3726:Included
3676:Category
3471:Moonrise
3404:Crescent
3344:Sennight
3259:Moonbase
3215:Missions
2884:Calderas
2792:Far side
2750:features
2638:Eclipses
2624:New moon
2569:Distance
2456:Physical
2313:"; and "
2289:Archived
2257:(1993).
2185:51948507
1929:26607544
1860:: 1943.
1454:See also
1359:far side
1225:new moon
1221:in 2014.
1155:793.4765
1130:232.6054
1007:evection
951:latitude
867:seasonal
825:ecliptic
699:ecliptic
522:epoch).
348:inclined
332:ecliptic
291:(common
267:and the
257:prograde
202:sidereal
178:ecliptic
4806:Science
4756:Portals
4627:Orbital
4597:Phasing
4557:Delta-v
4362:Apsides
4356:,
4154:Molniya
4072:Parking
4009:Capture
3997:General
3841:Related
3495:Related
3485:Moonset
3268:Tourism
3245:Landing
3105:Geology
3044:Science
2900:Craters
2863:Valleys
2449:Outline
2212:Bibcode
2163:Bibcode
2108:Bibcode
2035:Bibcode
1937:4456736
1909:Bibcode
1862:Bibcode
1822:Bibcode
1785:Bibcode
1656:Bibcode
1654:: 351.
1629:Bibcode
1571:
1552:
1476:ELP2000
1410:Polaris
1124:perigee
999:Ptolemy
959:1000 BC
855:horizon
813:equator
771:Eclipse
668:perigee
520:J2000.0
494:perigee
482:ellipse
462:perigee
336:primary
328:planets
318:on the
255:in the
214:synodic
82:Perigee
4283:Other
4184:Tundra
4052:Kepler
4028:Escape
3981:orbits
3891:(2012)
3821:
3814:
3807:
3782:
3775:
3768:
3761:
3754:
3747:
3740:
3733:
3453:Tetrad
3369:Phases
3238:Probes
3073:Origin
3020:Quakes
2953:Rilles
2944:swirls
2659:Tetrad
2617:Syzygy
2342:
2269:
2183:
2134:
2126:
2077:
1976:May 9,
1935:
1927:
1891:Nature
1842:&
1710:
1686:
1627:: 54.
1597:
1593:
1248:, and
1144:27.212
1115:27.554
1093:27.321
1075:29.530
1057:27.321
961:, the
957:About
898:Gemini
829:major
672:apogee
638:
636:
631:·
629:
624:
622:
562:syzygy
516:13.176
498:apogee
466:apogee
352:tilted
250:orbits
190:1.543°
163:6.687°
111:Apogee
4770:Stars
4525:Epoch
4314:Shape
4252:Lunar
4206:Mars
4198:About
4169:Polar
3989:Types
3731:Earth
3432:Black
3418:Blood
3395:Names
3373:names
3312:Month
3163:ALSEP
3135:KREEP
3087:Theia
2990:Water
2967:Rocks
2877:Domes
2831:Maria
2800:Poles
2592:Nodes
2546:Orbit
2181:S2CID
2132:S2CID
1933:S2CID
1899:arXiv
1508:Notes
1438:as a
1260:tides
1215:Earth
1174:phase
1040:Name
1033:Month
882:North
745:Nodes
731:(see
640:Earth
633:
269:stars
253:Earth
168:Mean
157:Mean
146:0.054
139:Mean
4317:Size
4256:Sun
4235:Halo
4087:semi
3582:list
3439:Dark
3425:Blue
3388:Full
3287:and
2937:Soil
2907:List
2838:List
2820:Face
2773:Limb
2700:Tide
2440:Moon
2340:ISBN
2267:ISBN
2124:ISSN
2075:ISBN
1978:2016
1925:PMID
1746:NASA
1708:ISBN
1684:ISBN
1563:sin
1419:The
1254:The
1242:Tide
1217:and
1187:The
1031:and
1005:and
884:and
793:The
670:and
626:Moon
496:and
275:and
247:Moon
245:The
148:9006
117:avg.
88:avg.
4092:sub
4004:Box
3446:Wet
3381:New
3371:and
2220:doi
2171:doi
2116:doi
2104:126
2031:282
1917:doi
1895:527
1870:doi
1858:108
1830:doi
1793:doi
1652:190
1625:124
1599:km.
1589:IAU
1539:ELP
1522:ELP
1178:Sun
1146:221
1117:550
1095:582
1077:589
1059:662
861:At
761:or
392:by
346:is
281:Sun
131:700
129:406
124:000
122:404
102:400
100:370
95:400
93:356
4818::
4440:,
4436:,
4045:/
4021:/
2353:^
2299:^
2218:.
2208:70
2206:.
2202:.
2179:.
2169:.
2159:38
2157:.
2153:.
2130:.
2122:.
2114:.
2102:.
2098:.
2069:.
2029:.
2003:.
1954:.
1931:.
1923:.
1915:.
1907:.
1893:.
1868:.
1856:.
1850:.
1828:.
1816:.
1791:.
1781:70
1779:.
1760:^
1744:.
1668:^
1650:.
1623:.
1450:.
1365:.
1244:,
1009:.
974:.
877:.
741:.
568:.
358:.
4758::
4688:n
4520:0
4517:t
4507:v
4498:n
4489:T
4469:l
4460:L
4451:E
4442:f
4438:θ
4434:ν
4425:M
4405:ϖ
4396:ω
4387:Ω
4378:i
4358:q
4354:Q
4345:b
4336:a
4327:e
3972:e
3965:t
3958:v
3832:→
3823:→
3816:→
3809:→
3802:→
3796:→
3790:→
3784:→
3777:→
3770:→
3763:→
3756:→
3749:→
3742:→
3735:→
3711:e
3704:t
3697:v
3629:"
3625:"
2432:e
2425:t
2418:v
2377:.
2324:.
2275:.
2228:.
2222::
2214::
2187:.
2173::
2165::
2138:.
2118::
2110::
2083:.
2041:.
2037::
1980:.
1958:.
1939:.
1919::
1911::
1901::
1878:.
1872::
1864::
1836:.
1832::
1824::
1818:4
1799:.
1795::
1787::
1754:.
1662:.
1658::
1635:.
1631::
1585:ɑ
1580:π
1575:ɑ
1566:π
1560:/
1556:ɑ
1528:.
1349:.
1153:6
1128:3
953:.
735:)
468:.
464:–
415:)
409:(
404:)
400:(
386:.
216:)
204:)
127:–
120:(
98:–
91:(
34:.
20:)
Text is available under the Creative Commons Attribution-ShareAlike License. Additional terms may apply.